Text-Mining Based Risk Source Identification Model for Transportation Safety
-
摘要: 为了解决当前道路运输安全风险源辨识工作中数据短缺和人员工作量较大的问题,从文本挖掘的角度出发,提出一种能够自动辨识道路运输过程中安全风险源的模型. 该模型首先对道路运输文本进行因果句提取,并对因果句进行分词操作,实现安全风险源特征的增强;其次,进行适应卷积神经网络(convolutional neural networks,CNN)输入的、包含词信息和位置信息的特征构造;然后,将特征构造的结果输入到CNN实现安全风险源的辨识;最后,利用道路交通事故报告进行实验. 实验结果表明:提出的辨识模型能辨识大部分的道路运输安全风险源因素,准确率约为77.321%.Abstract: In order to solve data deficiency and excessive staff workload in the risk-source identification of road transportation safety, an automatic identification model is proposed from the angle of text mining. Firstly, the model performs feature enhancement preprocessing operation through the causality sentence extraction and extracted sentence segmentation. Secondly, the feature construction adapted to the convolutional neural network (CNN) is conducted, which contains word information and position information. Thirdly, the results of feature construction feed into the CNN to realize the identification of risk sources. Finally, experiments are conducted with the data sets of traffic accidents, demonstrating that the proposed model can identify most of risk sources for road transportation safety with the accuracy of about 77.321%.
-
表 1 因果提示词清单列举
Table 1. Causality cue words
事故报告 现代汉语语料库 致使、导致、造成、是、加剧了、与、致、继、后、再次、接着、以致、发生 导致、产生、造成、造就、酿成、引发、引起、引来、引致、诱发、致使、滋生、归于、带来、触发、致死、致残、波及、关系到、牵动、渗入、渗透、影响、推动、推进、出于、出自、引导、引入、诱导、指引、诱惑、使得、······ 表 2 因果句子结构列举
Table 2. Causality sentence structures
由因到果 由果到因 分开式 [因] <提示词> [果] [果] <提示词> [因] <提示词> [因],<提示词> [果] [因][因] …… <提示词> [果] [果][果] <提示词> [因] <提示词> [果],<提示词> [因] [因] <提示词> [果][果]…… [果] <提示词> [因][因] …… …… 表 3 因果句子标注列举
Table 3. Causality sentence annotations
句子 风险源辨识因果词汇标注 事故车辆驾驶人王某行经事故地点时超速行驶、 疲劳驾驶,致使车辆向道路右侧偏离,正面冲撞秦岭1号隧道洞口端墙 超速行驶:1; 疲劳驾驶:2; 车辆向道路右侧偏离:11; 冲撞隧道洞口端墙:12 驾驶人曾某疲劳驾车上路、超载、超速,因疲劳过度车辆失去控制,与对向摩托车相撞 疲劳驾车:1; 超载:2; 超速:3; 车辆失去控制:11; 与对向摩托车相撞:12 表 4 参数设置
Table 4. Parameters setting
参数名称 值 参数名称 值 词向量维度 144 卷积层数/层 2 卷积核大小 3 × 3 下采样层/层 2 过滤器数量/个 32 Word2vec词向量维度 129 初始学习率 0.001 Softmax输出维度 13 批处理大小/个 500 数据迭代数/次 96 丢弃率/% 0.5 表 5 准确率、召回率以及准确率和召回率的调和平均值
Table 5. Tested results of precision,recall,and their F-score values
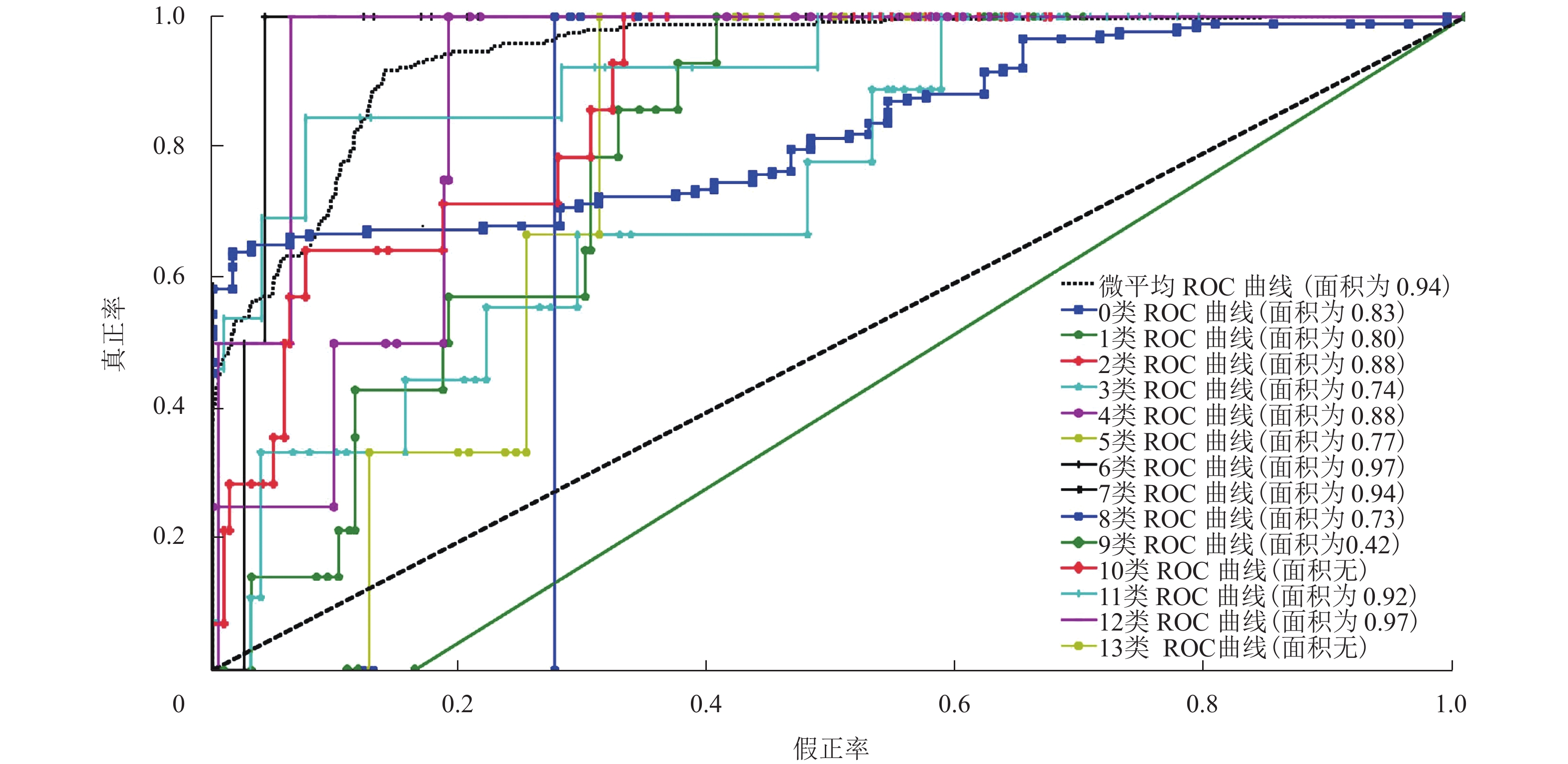
% 类别 P R F 0 71.921 89.115 79.6001 1 68.714 81.181 74.4291 2 67.571 77.391 72.1484 3 70.333 75.077 72.6276 4 80.025 84.668 82.2811 5 52.354 65.422 58.1630 6 70.564 82.325 75.9921 7 78.558 84.456 81.4003 8 70.556 71.544 71.0466 9 38.248 52.555 44.2744 11 76.154 98.000 81.6496 12 75.440 85.470 80.1424 -
丁辉. 风险、风险源、危险源的关系探讨[J]. 安全,2019,40(4): 1-4.DING Hui. Discussion on the relationship among risk,risk source and hazard[J]. Safety & Security, 2019, 40(4): 1-4. LI J, WANG J, XU N, et al. Importance degree research of safety risk management processes of urban rail transit based on text mining method[J]. Information, 2018, 9(2): 9-26. SHI D, GUAN J, ZURADA J, et al. A data-mining approach to identification of risk factors in safety management systems[J]. Journal of Management Information Systems, 2017, 34(4): 1054-1081. doi: 10.1080/07421222.2017.1394056 WILLIAMS T, BETAK J. A comparison of LSA and LDA for the analysis of railroad accident text[J]. Journal of Ubiquitous System & Pervasive Networks, 2019, 11(1): 11-15. ANDRZEJCZAK C, KARWOWSKI W, MIKUSINSKI P. Application of diffusion maps to identify human factors of self-reported anomalies in aviation[J]. Work, 2012, 41(S1): 188-197. TANGUY L, TULECHKI N, URIELI A, et al. Natural language processing for aviation safety reports:from classification to interactive analysis[J]. Computers in Industry, 2016, 78: 80-95. doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2015.09.005 ZHANG X, MAHADEVAN S. Ensemble machine learning models for aviation incident risk prediction[J]. Decision Support Systems, 2019, 116: 48-63. doi: 10.1016/j.dss.2018.10.009 AN N, XIAO Y B, YUAN J, et al. Extracting causal relations from the literature with word vector mapping[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2019, 115: 103524.1-103524.8. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.103524 ZENG D, LIU K, LAI S, et al. Relation classification via convolutional deep neural network[C]//Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Computational Linguistics. New York: Curran Associates, 2014: 2335-2344. 袁飞,赵绪言,王一戈,等. 基于轻量级卷积神经网络的烟雾识别算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(5): 1111-1116,1132.YUAN Fei, ZHAo Xuyan, WANG Yige, et al. Smoke recognition algorithm based on lightweight convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(5): 1111-1116,1132. 裘江南. 汉语文本中突发事件因果关系抽取方法研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2012. HE B, GUAN Y, DAI R. Classifying medical relations in clinical text via convolutional neural networks[J]. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2019, 93: 43-49. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2018.05.001 -




 下载:
下载: