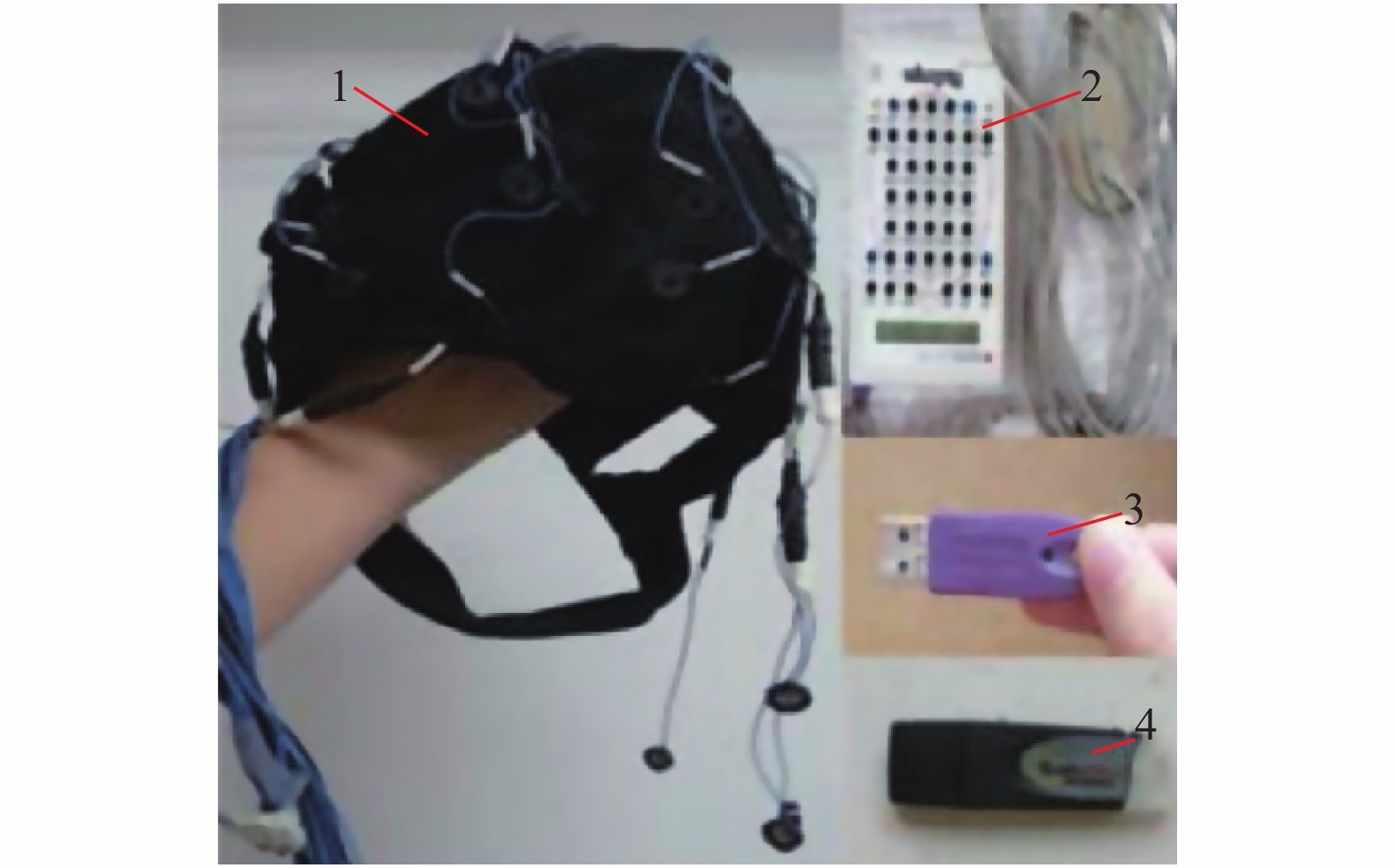
Influence Mechanism of Bridge Sign Complexity on Cognitive Characteristics of Drivers’ Electroencephalogram
-
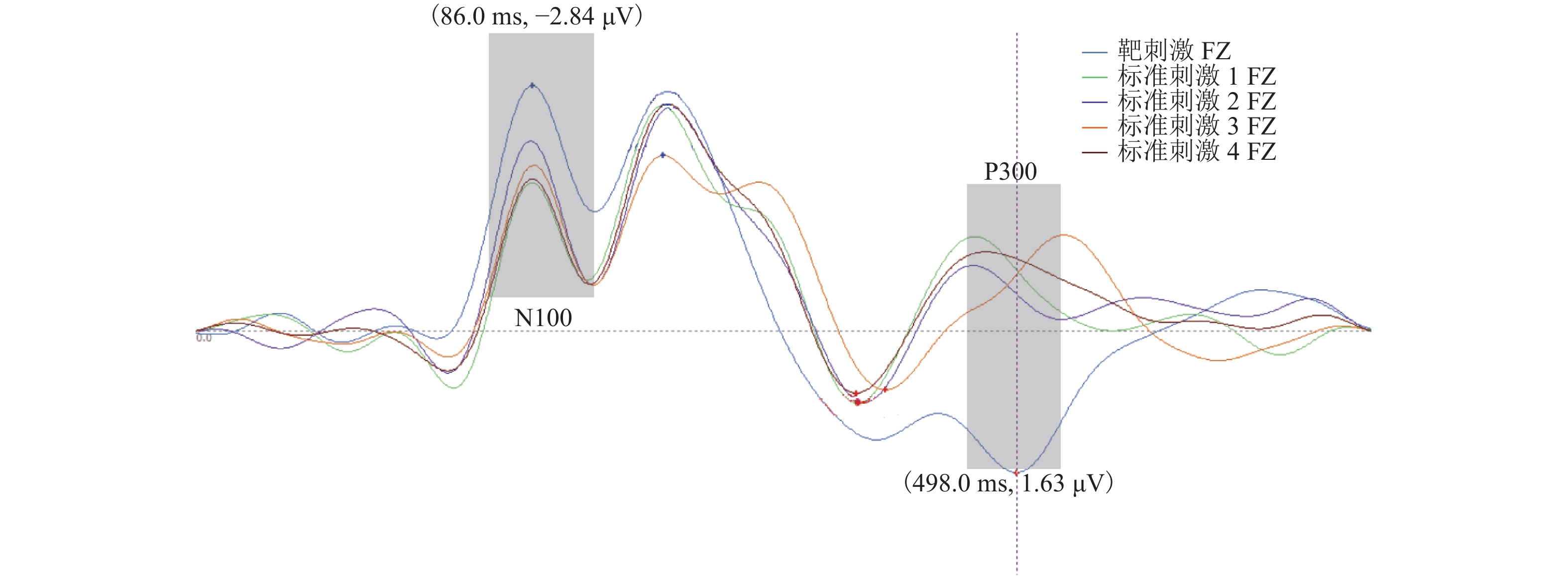
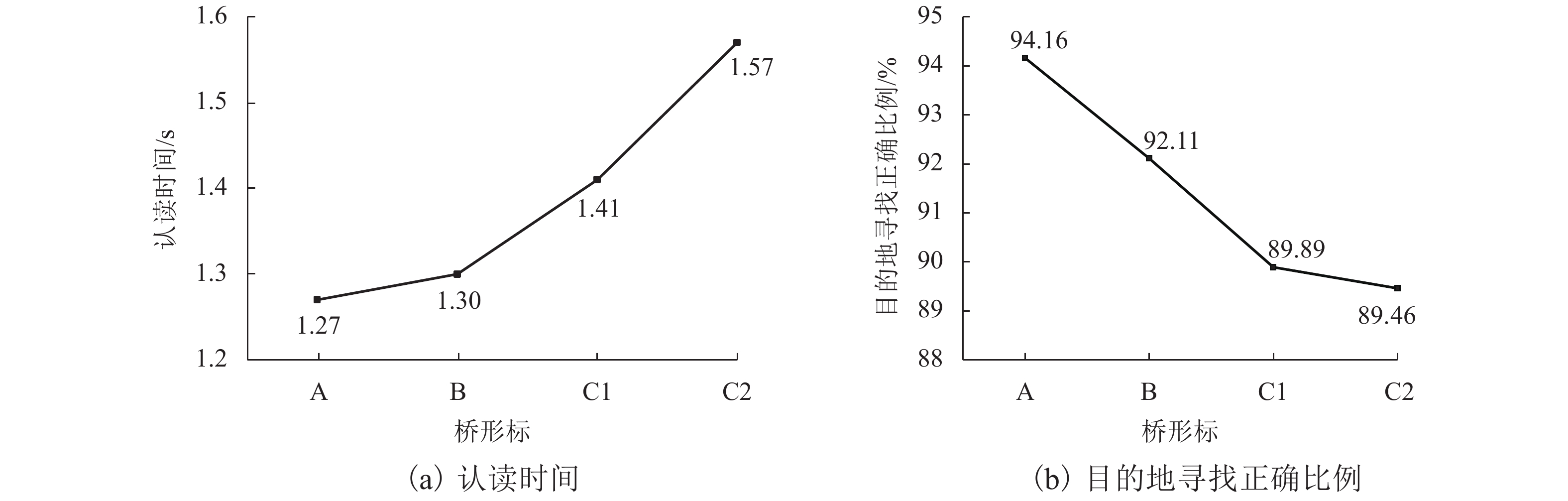
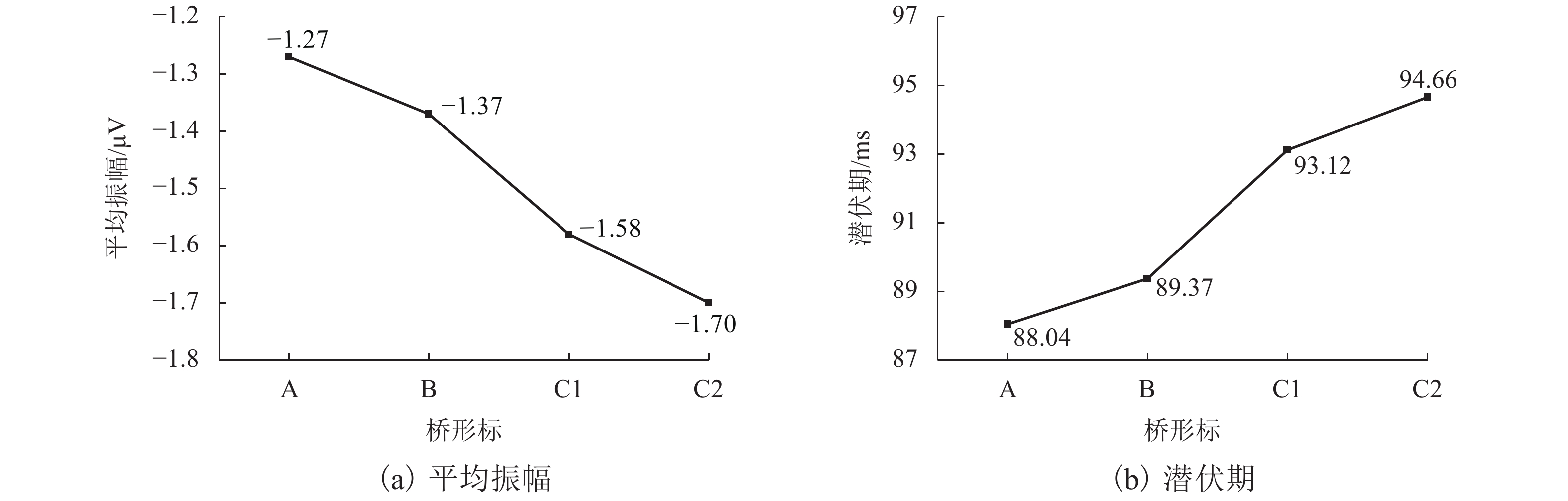
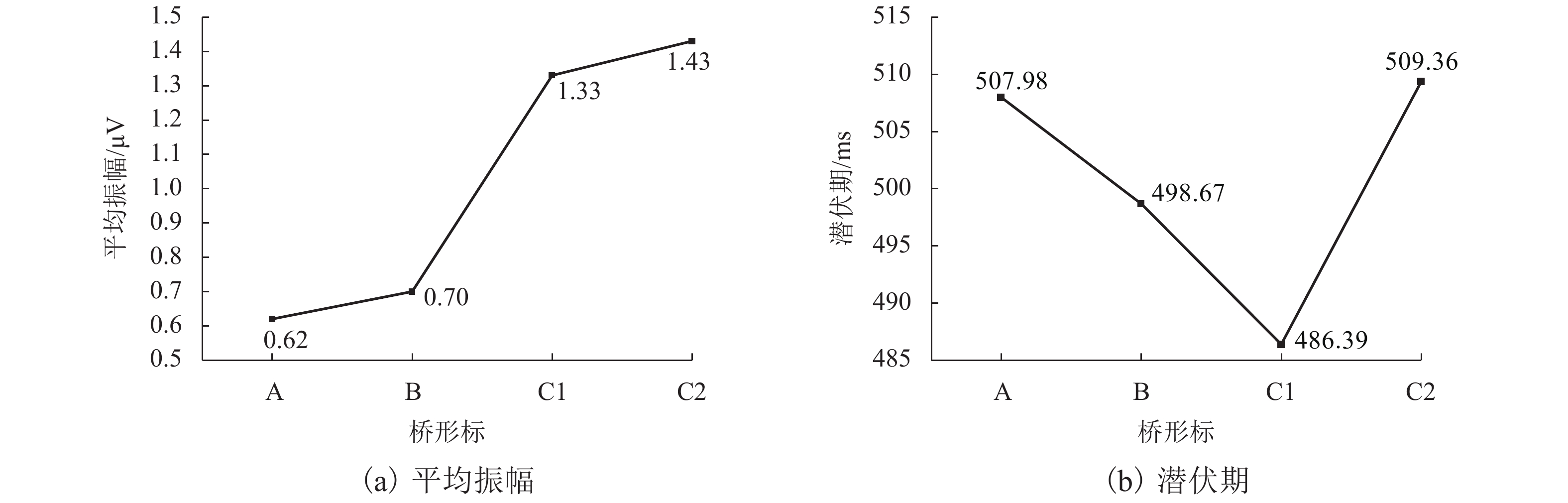
摘要: 桥形标设计应用缺乏规范性,复杂桥形标影响驾驶人认读,进而影响通行效率及交通安全. 为明确桥形标复杂度对驾驶人认知加工的影响规律,借助Oddball范式针对不同复杂度桥形标开展脑电认知实验;综合考虑驾驶人的认读行为及脑电特性,提取认读时间、目的地寻找正确比例、脑电事件相关电位(event-related potential,ERP)中早期注意电位N100及认知电位P300 4个主要分析指标;采用重复测量方差分析量化桥形标复杂度对驾驶人认知过程及脑电特性的影响. 结果表明:随着桥形标复杂度的增加,驾驶人认读时间增长,目的地寻找正确比例降低;同时,诱发N100平均振幅、峰值更多地呈现负向偏移,P300平均振幅正向偏移增大,即驾驶人早期注意分配增加,早期注意时间滞后,认知难度增加;靶刺激与标准刺激的相对差异性越大,P300潜伏期越短,越容易与标准刺激低等复杂度桥形标辨别.Abstract: Normative documents about design and application of bridge signs are unavailable, while the complex bridge signs affect drivers’ recognition, which further impairs traffic efficiency and traffic safety. In order to clarify the influence of bridge sign complexity on the cognitive processing of drivers, Oddball paradigm is adopted in cognitive electroencephalogram experiments for bridge signs with different complexities. Taking into account the reading behavior and electroencephalogram characteristics of drivers, four main analysis indexes are extracted: the reading time, proportion of seeking correct destination, early attention potential N100 and cognitive potential P300 in event-related potential (ERP). Analysis of variance with repeated measurements is used to quantify the effect of bridge signs complexity on cognitive process and electroencephalogram characteristics of drivers. The results show that with an increase in bridge sign complexity, the drivers’ reading time increases, and the proportion of seeking correct destination decreases. Meanwhile, the migration of N100 average amplitude and peak value shows more negative shift, while the average amplitude of P300 increases positively; that is, to drivers, the early attention distribution increases, the early attention time lags behind, and the cognitive difficulty increases. In addition, the greater the relative difference between the target stimulus and standard stimulus, the shorter the latency of P300, and the easier to distinguish it from the standard stimulus with a low complexity.
-
Key words:
- bridge sign /
- cognitive process /
- electroencephalogram (EEG) /
- event-related potential (EPR) /
- N100 /
- P300
-
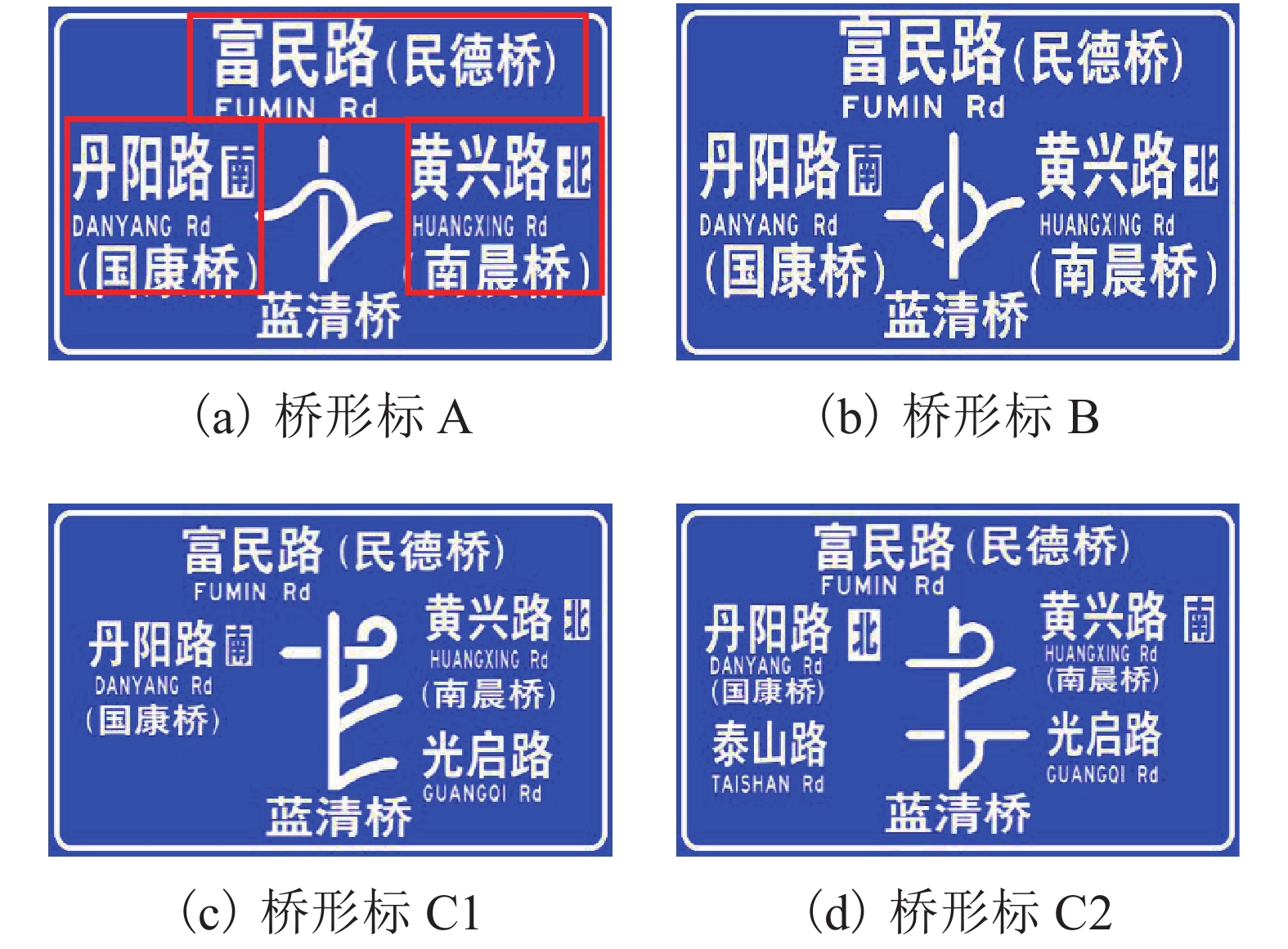
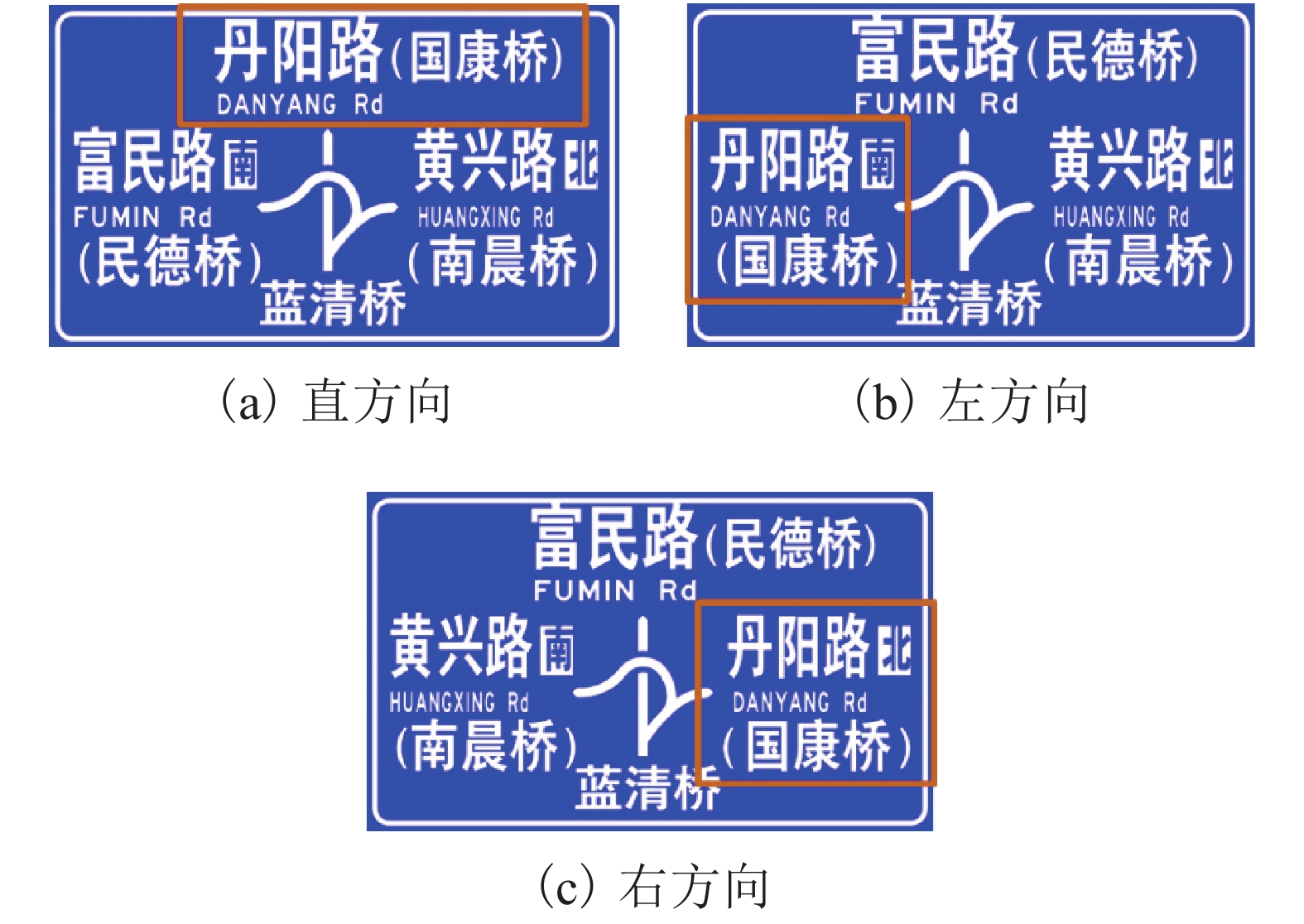
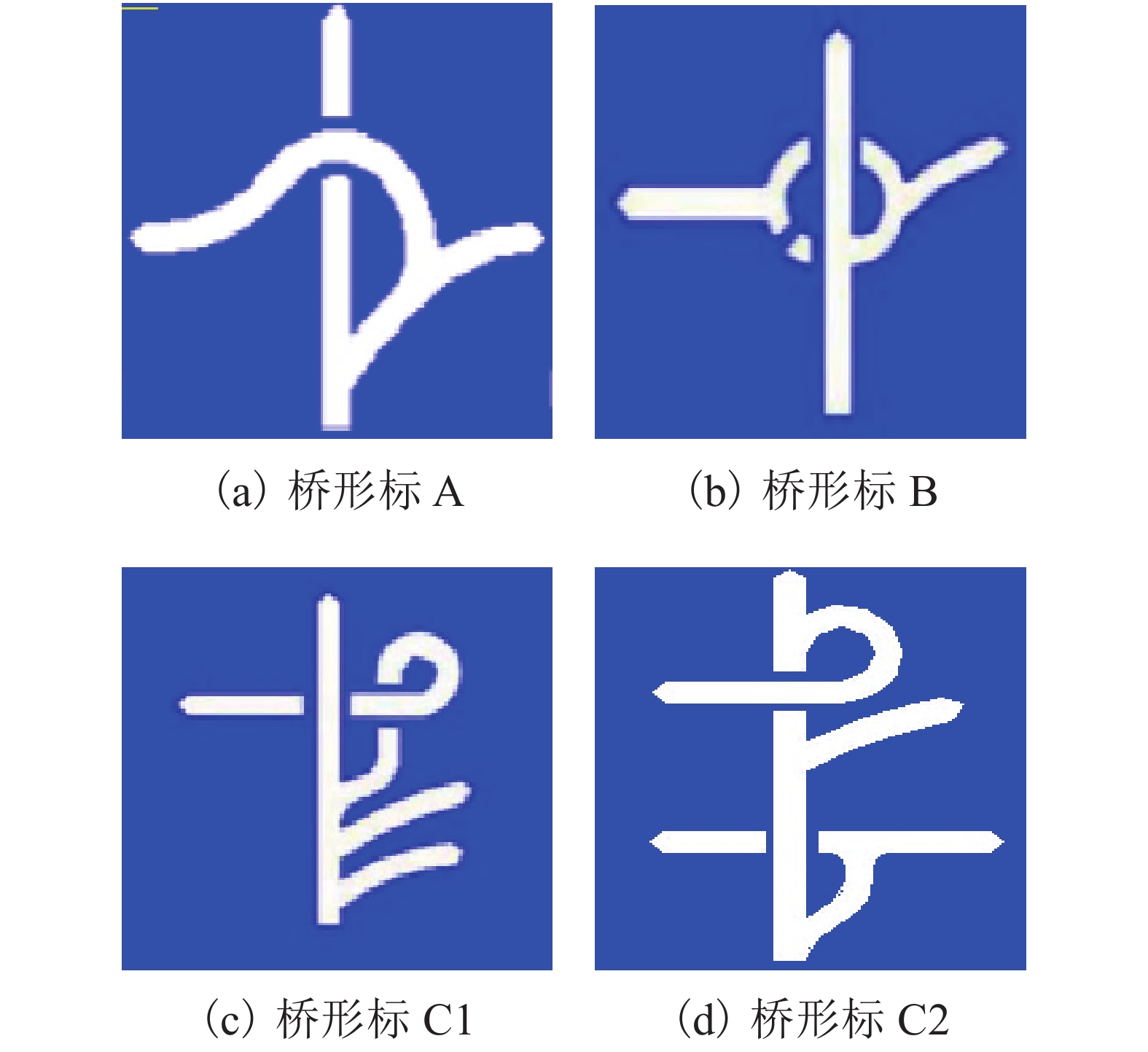
表 1 37种桥形标图形分类结果
Table 1. Classification results of 37 bridge sign diagrams
复杂度 桥形标 低等 
中等 
高等 
表 2 两种脑电成分代表电极及分析时间窗
Table 2. Electrode and time window of two electroencephalogram compositions
成分 电极 时间窗口/ms N100 F3、FZ、F4、FC3、FCZ、FC4 60~130 P300 C3、CZ、C4、CP3、CPZ、CP4、
P3、PZ、P4400~600 -
赵晓华. 城市快速路指路标志系统效用评估及优化设置方法研究[R]. 北京: 北京市交通委员会, 2016. 赫尔曼•哈肯. 大脑工作原理: 脑活动、行为和认知的协同学研究[M]. 郭治安, 吕翎, 译. 上海: 上海科技教育出版社, 2000. BYRNE M D, KIRLIK A. Integrated modeling of cognition and the information environment: a closed-loop, ACT-R approach to modeling approach and landing with and without synthetic vision systems (SVS) technology (technical report)[R]. Houston: Rice University, 2004. 杜志刚,潘晓东,郭雪斌. 高速公路隧道出口交通标志安全距离研究[J]. 公路工程,2008,33(1): 55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0610.2008.01.015DU Zhigang, PAN Xiaodong, GUO Xuebin. Traffic sign’s safe distance from freeway tunnel’s exit[J]. Highway Engineering, 2008, 33(1): 55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0610.2008.01.015 NEWELL A, SIMON H A. Human problem solving[M]. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, 1972. ANDERSON J R. The architecture of cognition[M]. New York: Psychology Press, 2013. SALVUCCI D D. Modeling driver behavior in a cognitive architecture[J]. Human Factors:The Journal of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society, 2006, 48(2): 362-380. doi: 10.1518/001872006777724417 NEISSER U. Cognitive psychology[M]. Classic edition. New York: Psychology Press, 2014. BROOKS R A. Intelligence without representation[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 1991, 47(1/2/3): 139-159. 付辉建. 基于脑电信号分析的风险感知研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016. LIU B L, WANG Z N, SONG G J, et al. Cognitive processing of traffic signs in immersive virtual reality environment:an ERP study[J]. Neuroscience Letters, 2010, 485(1): 43-48. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.08.059 GIRAUDET L, IMBERT J P, BÉRENGER M, et al. The neuroergonomic evaluation of human machine interface design in air traffic control using behavioral and EEG/ERP measures[J]. Behavioural Brain Research, 2015, 294: 246-253. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.07.041 李洋,赵晓华,何庆,等. 立交桥图形指路标志视认复杂程度综合评价方法[J]. 北京工业大学学报,2019,45(4): 64-72.LI Yang, ZHAO Xiaohua, HE Qing, et al. Comprehensive evaluation method of recognition complexity of interchange diagrammatic guide signs[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2019, 45(4): 64-72. CHRYSLER S T, WILLIAMS A A, FUNKHOUSER D S, et al. Driver comprehension of diagrammatic freeway guide signs[R]. Austin: Texas Transportation Institute. 2007. ZWAHLEN H T, RUSS A, ROTH J, et al. Evaluation of the effectiveness of ground mounted diagrammatic advance guide signs for freeway entrance ramps[J]. Transportation Research Record:Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2003, 1843: 70-80. doi: 10.3141/1843-09 LYU N C, XIE L, WU C Z, et al. Driver’s cognitive workload and driving performance under traffic sign information exposure in complex environments:a case study of the highways in China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017, 14(2): 14020203.1-14020203.25. 关伟. 驾驶员对交通标志的视觉信息认知过程实验研究[D]. 北京: 北京工业大学, 2014. 何文强. 高速公路互通区指路标志对驾驶员情境意识的影响研究[D]. 福州: 福州大学, 2018. 赵仑. ERPs实验教程[M]. 修订版. 南京: 东南大学出版社, 2010. LI Y, ZHAO X, HE Q, et al. Comprehensive evaluation and classification of interchange diagrammatic guide signs’ complexity[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2018, 2018: 9865305.1-9865305.11. 张锴铎. 基于脑电的视觉信息加工机制研究[D]. 泉州: 华侨大学, 2017. TSOLAKI A C, KOSMIDOU V, KOMPATSIARIS I Y, et al. Brain source localization of MMN and P300 ERPs in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer ’s disease:a high-density EEG approach[J]. Neurobiology of Aging, 2017, 55: 190-201. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.03.025 -




 下载:
下载: