Evaluation of Activity Location Recognition Using Cellular Signaling Data
-
摘要: 为了研究利用手机信令数据识别个体出行端点的应用效果,开展实地采集手机信令数据的出行试验,且同步采集相应的GPS轨迹数据和出行日志作为算法评估的真实数据,提出出行端点识别的3阶段处理算法. 首先,提出等时距补点算法平衡各信令定位点的时间权重;然后,利用凝聚层次聚类算法将定位点聚类成不同的类簇;最后,针对已有研究中缺乏关注的类簇震荡现象,提出新的震荡修正算法对聚类结果做进一步优化. 案例结果表明:本文提出的方法对出行端点识别的精度、距离误差和时间误差上均有较好的效果,出行端点识别个数的精度在84%以上,端点位置识别距离平均误差在220 m以内,出行端点的离开和到达时间的平均误差分别为7.7 min 和5.3 min;在不同的出行目的的比较中,以工作为目的的端点识别效果最好,以娱乐购物为目的的端点识别效果相对较差.Abstract: In order to investigate the recognition results of individuals’ activity locations using cellular signaling data, the field experiment for collecting cellular signaling data was carried out. The GPS trajectory data and the travel logs were collected synchronously as the real data for reference. A three-step method for recognizing activity locations is proposed. Firstly, an equal time interval interpolation method is used to balance the time weight of each trace. Secondly, an agglomerative hierarchical clustering algorithm is applied to merge the traces into different clusters. Finally, a new method of correcting location oscillation is proposed, to solve the problem that clusters in the same activity location oscillate. Results show that the proposed method performs well in term of the accuracy of identifying activity locations, distance error and time error. The average recognition accuracy and distance error is over 84% and within 220 m, respectively. The average errors of departure and arrival time are 7.7 min and 5.3 min, respectively. In the comparison of different travel purposes, the activity locations for work receive the best recognition results, and the results of the locations for shopping is relatively inferior.
-
表 1 手机信令数据样例数据
Table 1. Example records of cellular signaling dataset
全球标识 手机号码 设备标识 位置区 基站小区 460****71 130***4926 869***664 34051 167939598 460****72 130***4927 869***665 34050 168004374 460****73 130***4928 869***666 34051 167936011 通信事件 开始时间/
(时:分:秒)结束时间/
(时:分:秒)经度/(°) 纬度/(°) 105 12:54:18 12:54:18 106.71 26.60 105 12:54:20 12:54:20 106.74 26.59 104 12:54:21 12:54:21 106.72 26.61 表 2 出行端点识别统计结果
Table 2. Recognition results of activity locations
出行
目的端点
数/个识别比例/% 平均时间
误差/min平均距离误差/m 正确率 多识
别率到达
时间离开
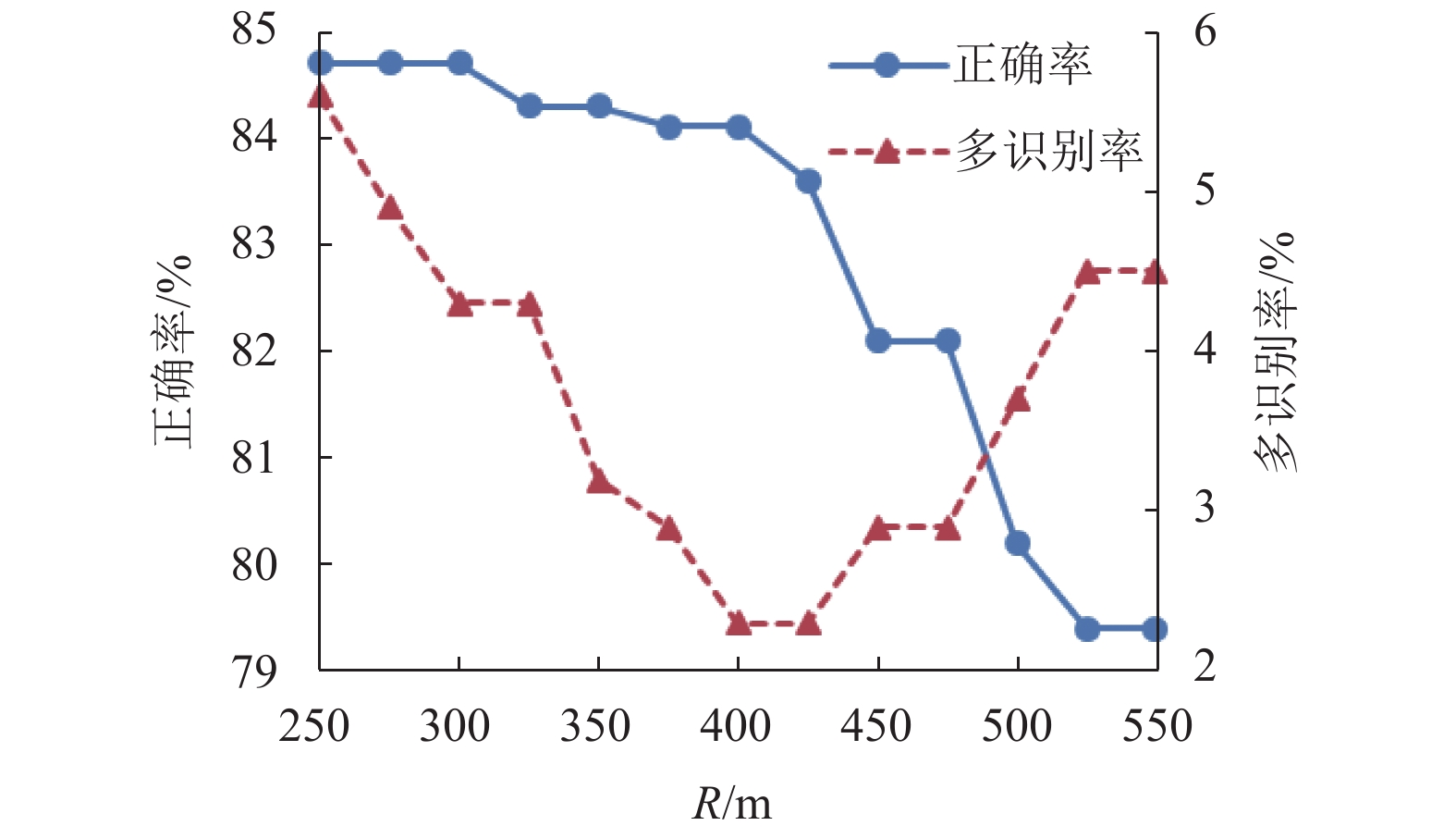
时间工作 141 86.2 1.3 5.4 7.5 173.4 居家 187 84.7 1.7 4.7 7.6 195.7 娱/购 85 79.4 5.2 6.5 8.4 348.4 总计 413 84.1 2.3 5.3 7.7 219.6 -
AHAS R, SILM S, JÄRV O, et al. Using mobile positioning data to model locations meaningful to users of mobile phones[J]. Journal of Urban Technology, 2010, 17(1): 3-27. doi: 10.1080/10630731003597306 ISAACMAN S, BECKER R, CÁCERES R, et al. Identifying important places in people’s lives from cellular network data[C]//International Conference on Pervasive Computing. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2011: 133-151. WANG P, HUNTER T, BAYEN A M, et al. Understanding road usage patterns in urban areas[J]. Scientific Reports, 2012, 2: 1-6. JÄRV O, AHAS R, WITLOX F. Understanding monthly variability in human activity spaces:a twelve-month study using mobile phone call detail records[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2014, 38: 122-135. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2013.11.003 XU Y, SHAW S L, ZHAO Z, et al. Another tale of two cities:understanding human activity space using actively tracked cellphone location data[J]. Annals of the American Association of Geographers, 2016, 106(2): 489-502. WANG Z, HE S Y, LEUNG Y. Applying mobile phone data to travel behaviour research:a literature review[J]. Travel Behaviour and Society, 2018, 11: 141-155. doi: 10.1016/j.tbs.2017.02.005 CALABRESE F, COLONNA M, LOVISOLO P, et al. Real-time urban monitoring using cell phones:a case study in Rome[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2011, 12(1): 141-151. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2010.2074196 CALABRESE F, DIAO M, DI LORENZO G, et al. Understanding individual mobility patterns from urban sensing data:a mobile phone trace example[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2013, 26: 301-313. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2012.09.009 JIANG S, FIORE G A, YANG Y, et al. A review of urban computing for mobile phone traces: Current methods, challenges and opportunities[C]//Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: Association for Computing Machinery, 2013: 1-9. WANG F, CHEN C. On data processing required to derive mobility patterns from passively-generated mobile phone data[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2018, 87: 58-74. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2017.12.003 HARIHARAN R, TOYAMA K. Project lachesis: parsing and modeling location histories[C]//Interna- tional Conference on Geographic Information Science. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2004: 106-124. ALEXANDER L, JIANG S, MURGA M, et al. Origin-destination trips by purpose and time of day inferred from mobile phone data[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2015, 58: 240-250. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2015.02.018 WIDHALM P, YANG Y, ULM M, et al. Discovering urban activity patterns in cell phone data[J]. Transportation, 2015, 42(4): 597-623. doi: 10.1007/s11116-015-9598-x WANG M, CHEN C, MA J. Time-of-day dependence of location variability: application of passively-generated mobile phone dataset[C]//The 94th Annual Meeting of Transportation Research Board. Washington D. C.: [s.n.], 2015: 11-15. LEE J K, HOU J C. Modeling steady-state and transient behaviors of user mobility: formulation, analysis, and application[C]//Proceedings of the 7th ACM International Symposium on Mobile ad Hoc Networking and Computing (MobiHoc). New York: Association for Computing Machinery, 2006: 85-96. BAYIR M A, DEMIRBAS M, EAGLE N. Mobility profiler:a framework for discovering mobility profiles of cell phone users[J]. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 2010, 6(4): 435-454. doi: 10.1016/j.pmcj.2010.01.003 SHAD S A, CHEN E. Cell oscillation resolution in mobility profile building[J]. International Journal of Computer Science Issues (IJCSI), 2012, 9(3): 205-213. QI L, QIAO Y, ABDESSLEM F B, et al. Oscillation resolution for massive cell phone traffic data[C]// Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Mobile Data. New York: Association for Computing Machinery, 2016: 25-30. IOVAN C, OLTEANU-RAIMOND A M, COURONNÉ T, et al. Moving and calling: mobile phone data quality measurements and spatiotemporal uncertainty in human mobility studies[J]. Lecture Notes in Geoinformation and Cartography, 2013: 247-265. DEMISSIE M G, DE ALMEIDA CORREIA G H, BENTO C. Intelligent road traffic status detection system through cellular networks handover information:an exploratory study[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2013, 32: 76-88. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2013.03.010 WU W, WANG Y, GOMES J B, et al. Oscillation resolution for mobile phone cellular tower data to enable mobility modelling[C]// Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 15th International Conference on Mobile Data Management. Washington D. C.: IEEE Computer Society, 2014, 1: 317-324. CHEN C, MA J, SUSILO Y, et al. The promises of big data and small data for travel behavior (aka human mobility) analysis[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2016, 68: 285-299. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2016.04.005 CHEN C, BIAN L, MA J. From traces to trajectories:How well can we guess activity locations from mobile phone traces?[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2014, 46: 326-337. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2014.07.001 -





 下载:
下载: