Analysis on Extreme Distance of Power Supply for Urban Rail AC Power Supply System
-
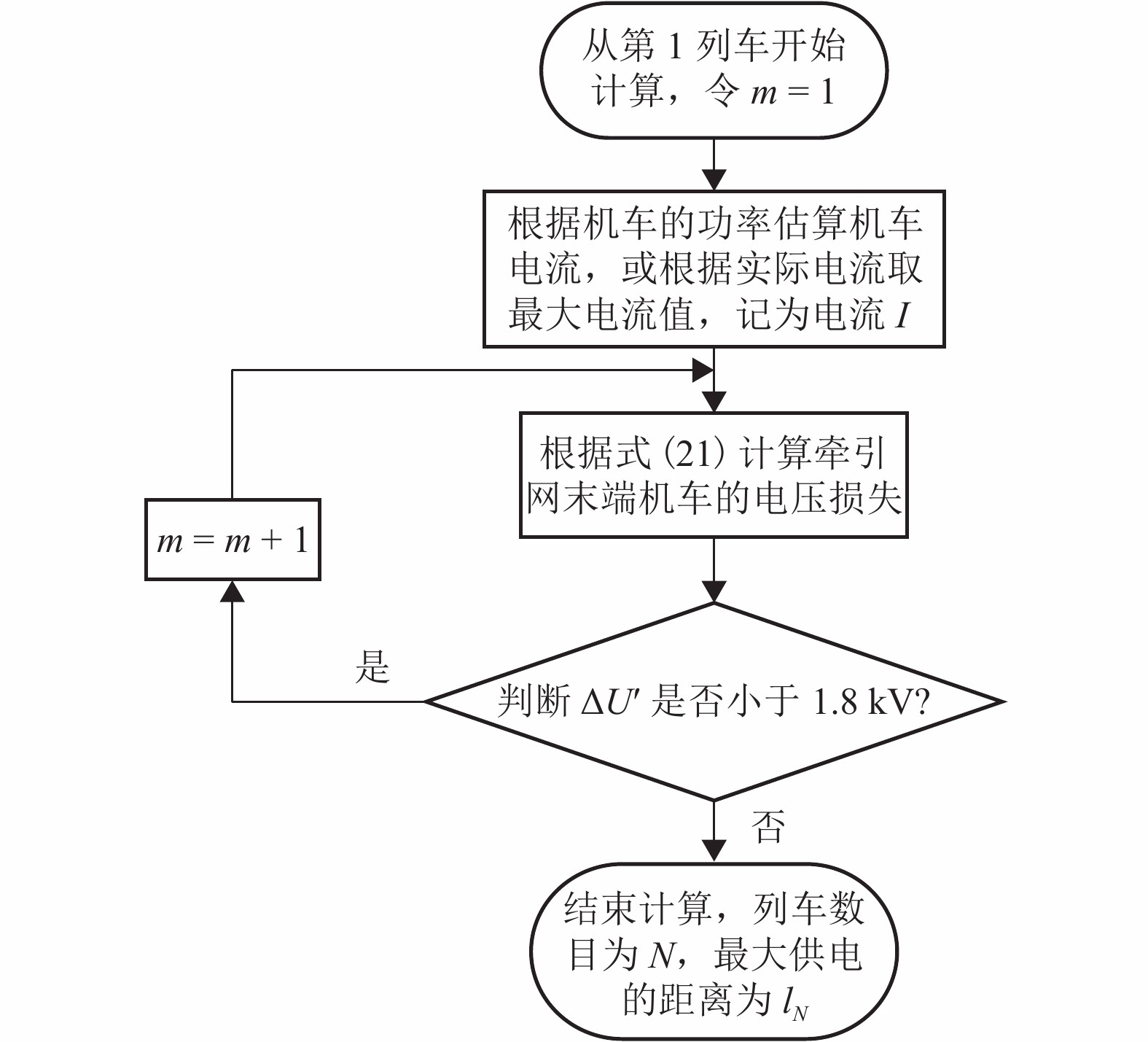
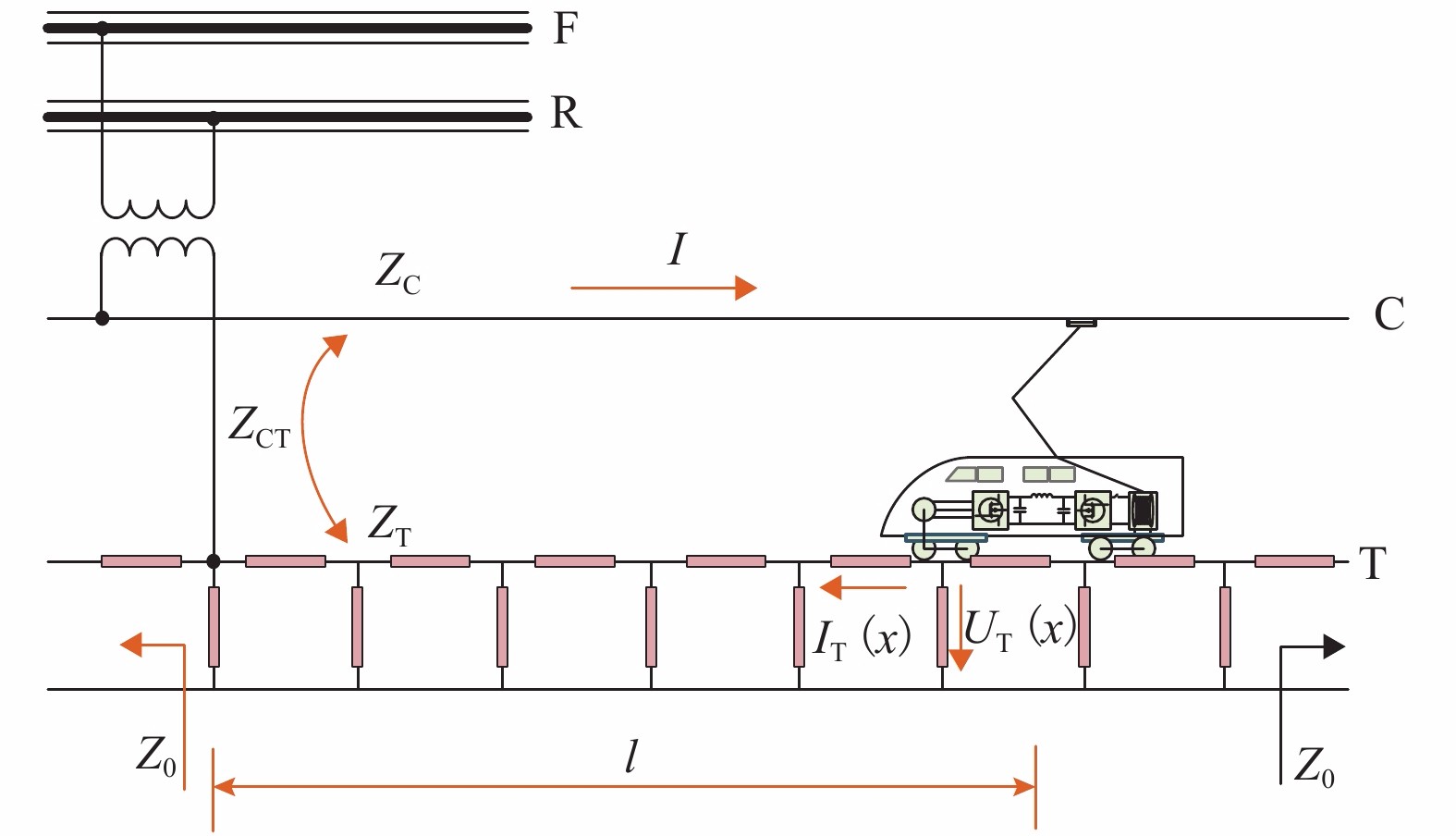
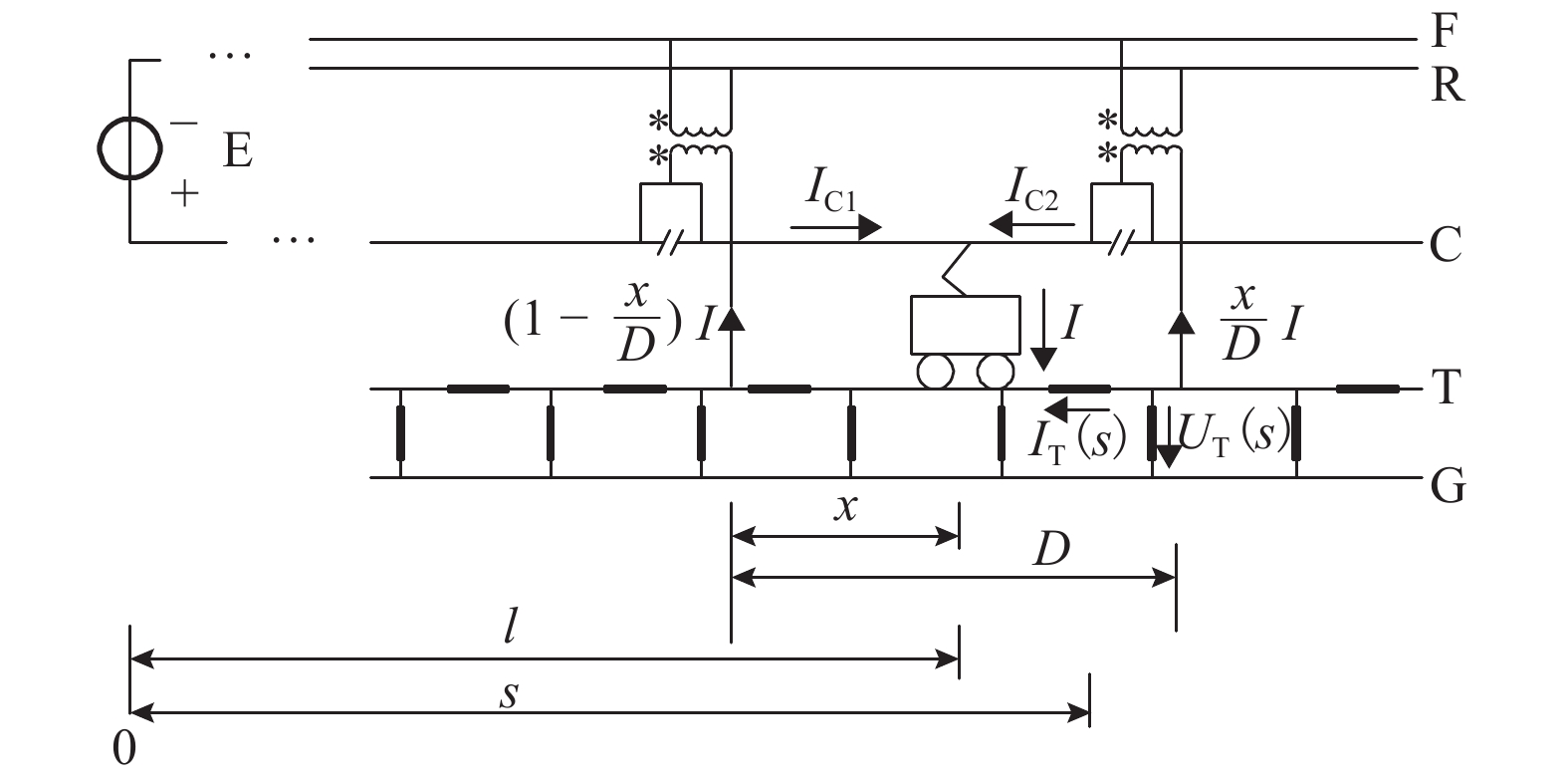
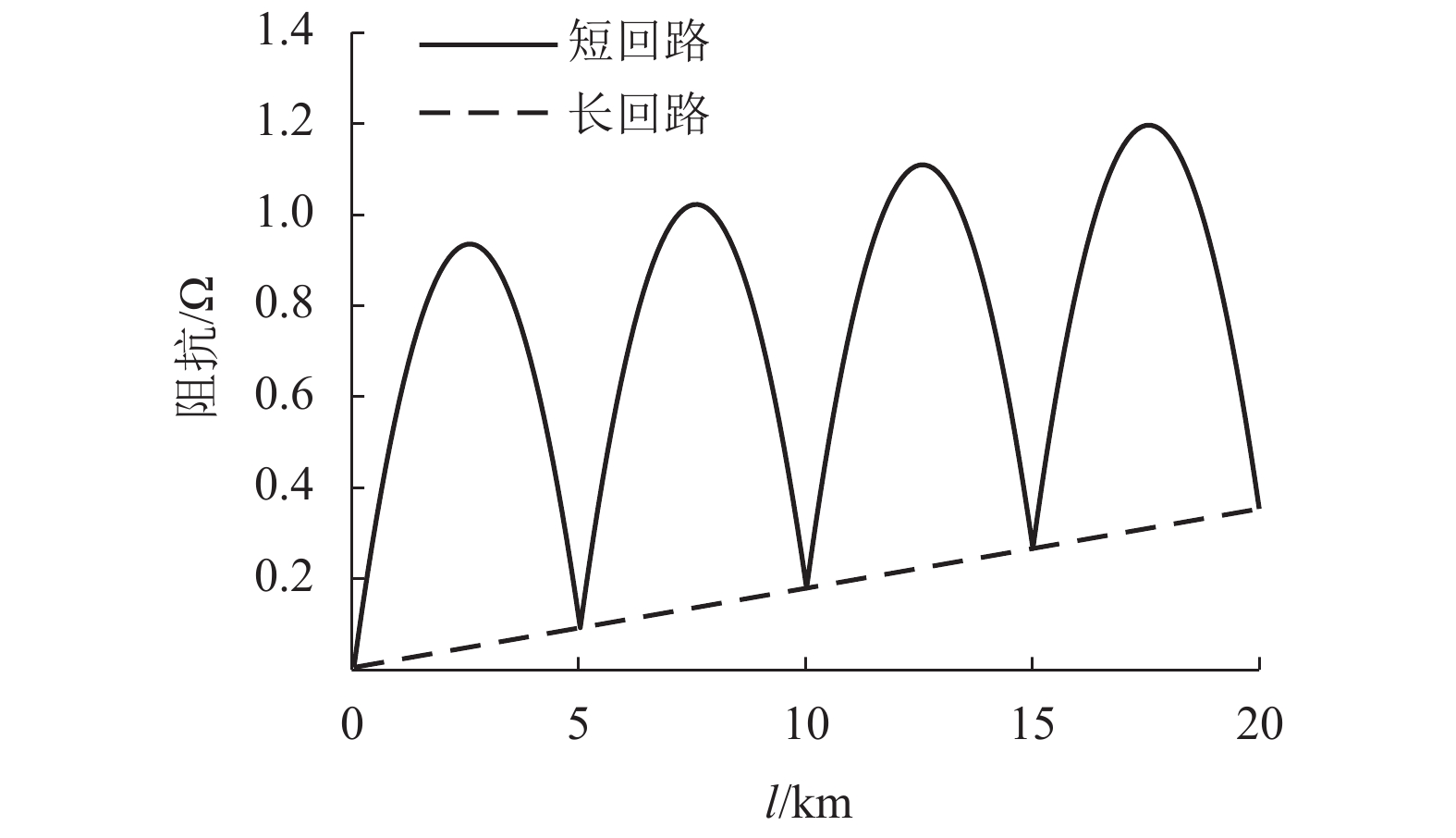
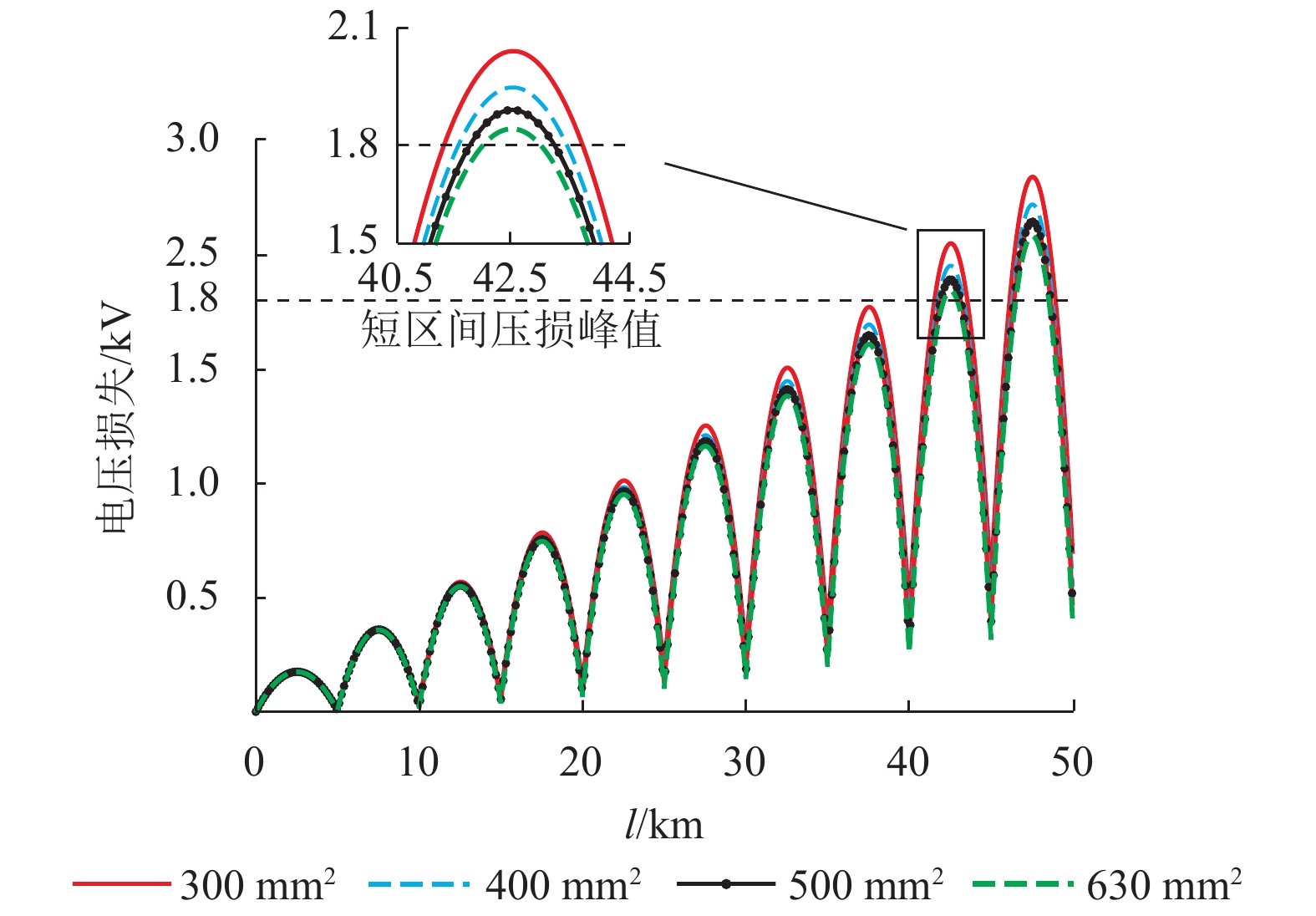
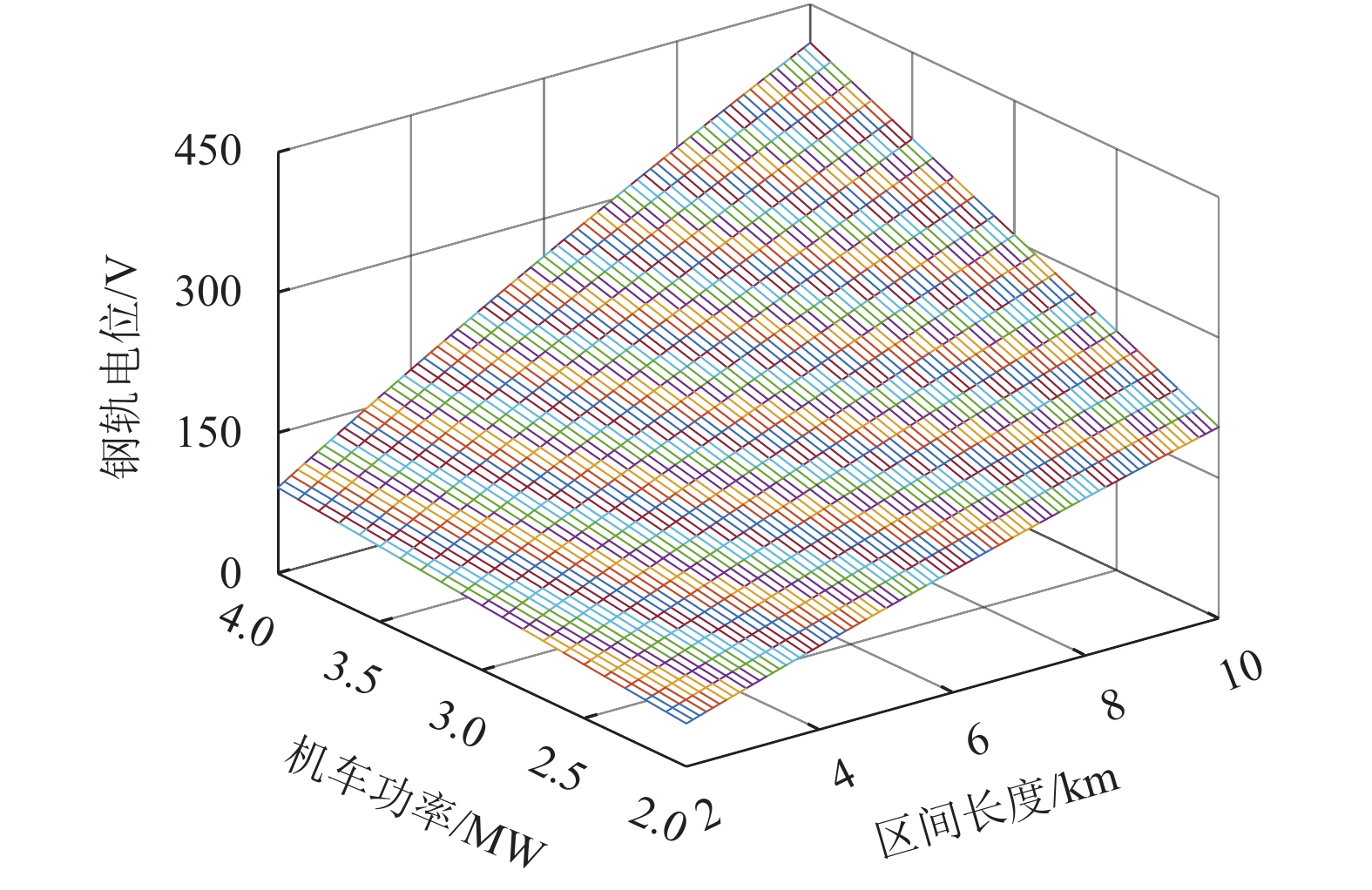
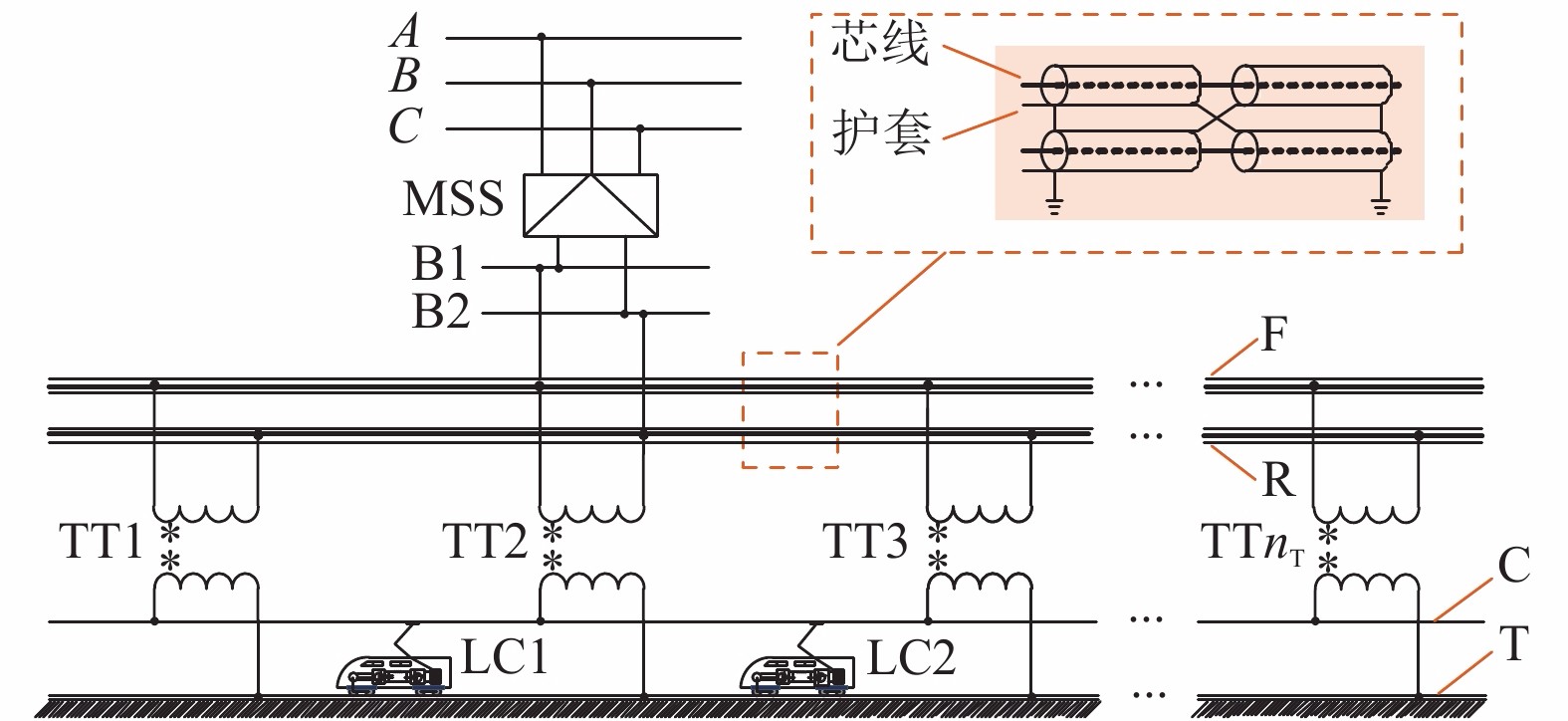
摘要: 供电距离是衡量一个牵引系统供电能力的重要指标,对系统的稳定、经济运行具有现实影响. 城轨交流供电系统采用电缆结构的牵引网,具有稳定、大容量输电的突出特点,因此量化研究该系统供电距离具有重要意义,本文从理论推导的角度对系统极限供电距离进行分析,根据系统的电路拓扑特点,理论推导系统牵引网阻抗、单车多车时牵引网电压损失、钢轨电位. 首先从牵引网采用架空线与电缆时的自然功率对比,推算采用不同截面积电缆时系统的极限供电距离;其次以系统高峰工况时的电压损失作为限制条件,分析系统极限供电距离;最后以既有电气化铁路标准对钢轨电位规定的限值作为限制条件,分析系统最大短回路区间长度. 系统仿真结果表明:城轨交流供电系统最大单区间供电长度可达9.31 km,主变电所位于线路中间位置时,系统极限供电距离可达84.22 km.Abstract: The power supply distance is an important indicator to measure the power supply capacity of a traction system, and has a practical impact on the stability and economic operation of the system. The urban rail AC power supply system uses the cable structure of the traction network, which has the outstanding characteristics of stable and large-capacity transmission. Therefore, it is of great significance to quantitatively study the power supply distance of the system. In this work, the extreme distance of power supply is analyzed theoretically. According to the circuit topology characteristics of the system, the traction network impedance as well as traction network voltage loss and rail potential are deduced for a single vehicle and multiple vehicles. First, by the natural power comparison between the overhead line and the cable in the traction network, the extreme distance of power supply is calculated in the cases of different cable cross-sectional areas. Secondly, the extreme distance of power supply is analyzed with the constraint of the voltage loss at the peak operating of the system. Finally the rail potential values prescribed in existing electrified railway standards are used as constraints to analyze the maximum short loop length of the system. In simulation, the maximum single-section power supply length of the urban rail AC power supply system can reach 9.31 km. When the main substation is located in the middle of the line, the extreme power-supply distance can reach 84.22 km.
-
Key words:
- AC subway /
- traction cable /
- power supply distance /
- natural power /
- rail potential
-
表 1 电缆参数
Table 1. Cable parameters
截面/mm2 电容/(× 10−7 F•km−1) 电感/(mH•km−1) 300 2.07 2.28 400 2.29 2.25 500 2.53 2.22 630 2.76 2.21 表 2 与电缆对应架空线参数
Table 2. Corresponding overhead line parameters
截面/mm2 电容/(mF•km−1) 电感/(mH•km−1) 300 7.93 2.29 400 811 2.26 500 8.25 2.24 630 8.40 2.22 表 3 电缆与对应架空线波阻抗对比
Table 3. Wave impedance comparison between cable and corresponding overhead line
Ω 截面积/mm2 电缆 裸导线 300 105.5 537.4 400 100.2 527.9 500 93.3 521.1 630 89.3 515.0 表 4 系统牵引网阻抗与互阻抗参数
Table 4. Traction network impedance andmutual impedance parameters
类型 阻抗/(Ω•km−1) ZF = ZR 0.108 + i0.717 ZFR 0.049 + i0.563 ZC 0.196 + i0.764 ZT 0.117 + i0.555 ZCT 0.049 + i0.313 表 5 电缆截面积变化时系统单边极限供电距离
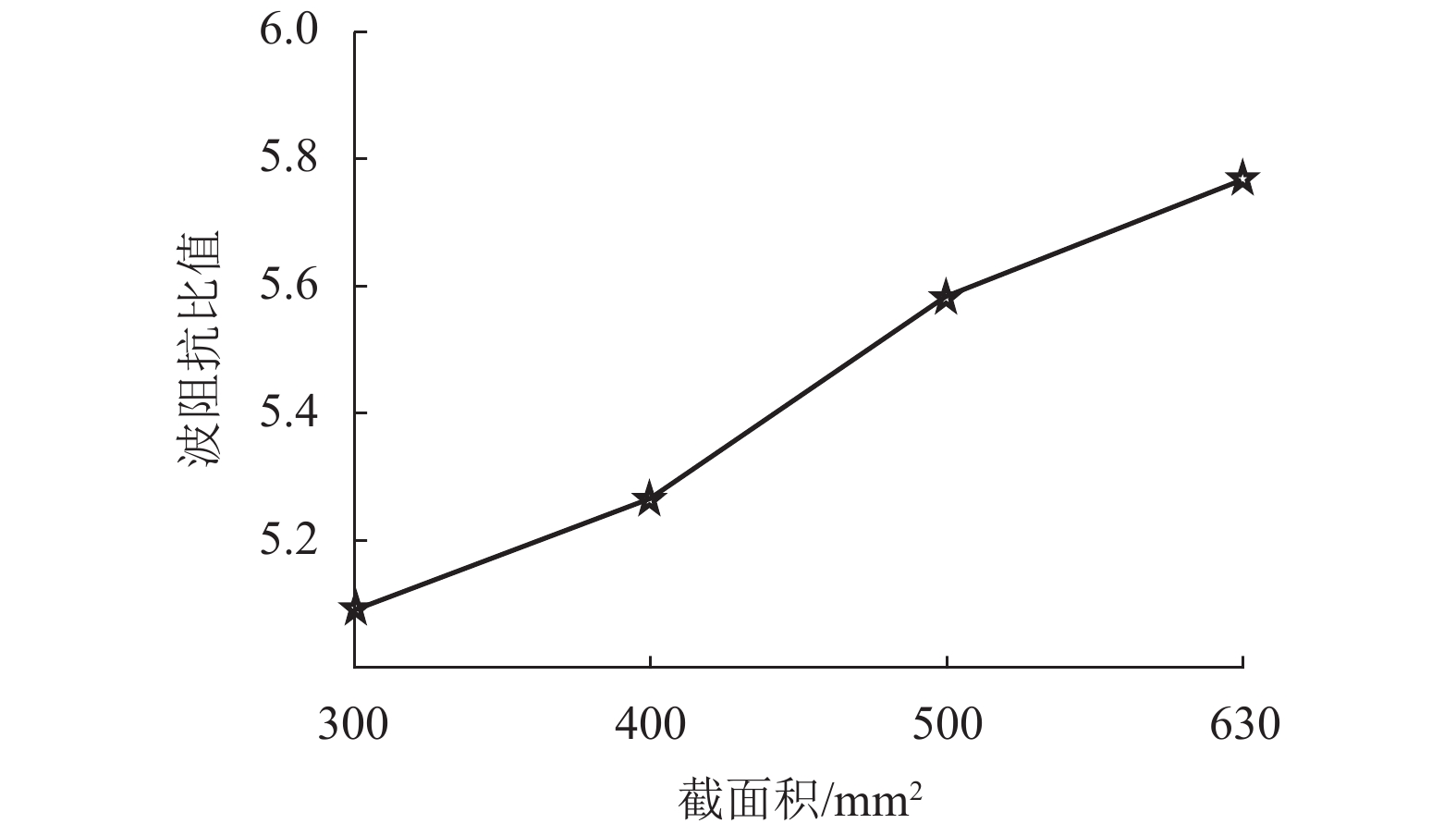
Table 5. System power supply distance when cable cross-sectional area changes
电缆截面/mm2 300 400 500 630 供电距离/km 41.53 41.75 41.91 42.11 -
李群湛. 城市轨道交通交流牵引供电系统及其关键技术[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(2): 199-207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.02.001LI Qunzhan. Industrial frequency single-phase AC traction power supply system and its key technologies for urban rail transit[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(2): 199-207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.02.001 刘政. 城市轨道交流牵引供电系统供电技术研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2018. 李玉光. 城市轨道交通交流供电方案探讨[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. 王延青. 城市轨道牵引与电力混合式主变电所方案研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2018. 岳新华. 城市轨道交通交流供电系统钢轨电位研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2018. 康·古·马克瓦尔特. 电气化铁路供电[M]. 袁则富, 何其光, 译. 峨眉山: 西南交通大学出版社, 1989. 于松伟, 杨兴山, 韩连祥, 等. 城市轨道交通供电系统设计原理与应用[M]. 成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 2008. 李群湛, 贺建闽. 牵引供电系统分析[M]. 2版. 成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 2010. 黄德胜. 地下铁道供电[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2010. 张友鹏,张耀,范小楷,等. 干旱地区电气化铁路的钢轨电位限制方案[J]. 电网技术,2013,37(2): 533-538.ZHANG Youpeng, ZHANG Yao, FAN Xiaokai, et al. Measures to restrict steel rail potential of electrified railway in arid regions[J]. Power System Technology, 2013, 37(2): 533-538. 雷栋. 高速电气化铁路牵引回流及钢轨电位特性研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2010. 米泽辉. AT供电系统轨地电位与降低措施研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2013. 邢晓乾. 带加强线的全并联直接供电技术的研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2011. 熊骜寒. 高速铁路不同路段综合接地系统钢轨电位与地表电位分析[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. 魏巍. 含综合地线的牵引供电系统建模与仿真[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. 《中国电力百科全书》编辑委员会. 中国电力百科全书: 公用电网卷[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 1995: 309-310. 邱关源. 电路: 下册[M]. 3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1989: 185-198. 郭鑫鑫. 电气化铁路电缆牵引网研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016. 李群湛,易东,贺建闽. 交流电气化铁路牵引电缆供电分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2013,48(1): 81-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.01.013LI Qunzhan, YI Dong, HE Jianmin. Power supply capacity of traction cable for AC electrified railway[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013, 48(1): 81-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.01.013 李群湛. 论新一代牵引供电系统及其关键技术[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(4): 559-568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.04.001LI Qunzhan. On new generation traction power supply system and its key technologies for electrification railway[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(4): 559-568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.04.001 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 66 kV及以下架空电力线路设计规范: GB 50061—2010[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2010. -




 下载:
下载: