Vibration Serviceability Evaluation Under Typical Local Deformations of Pavement
-
摘要:
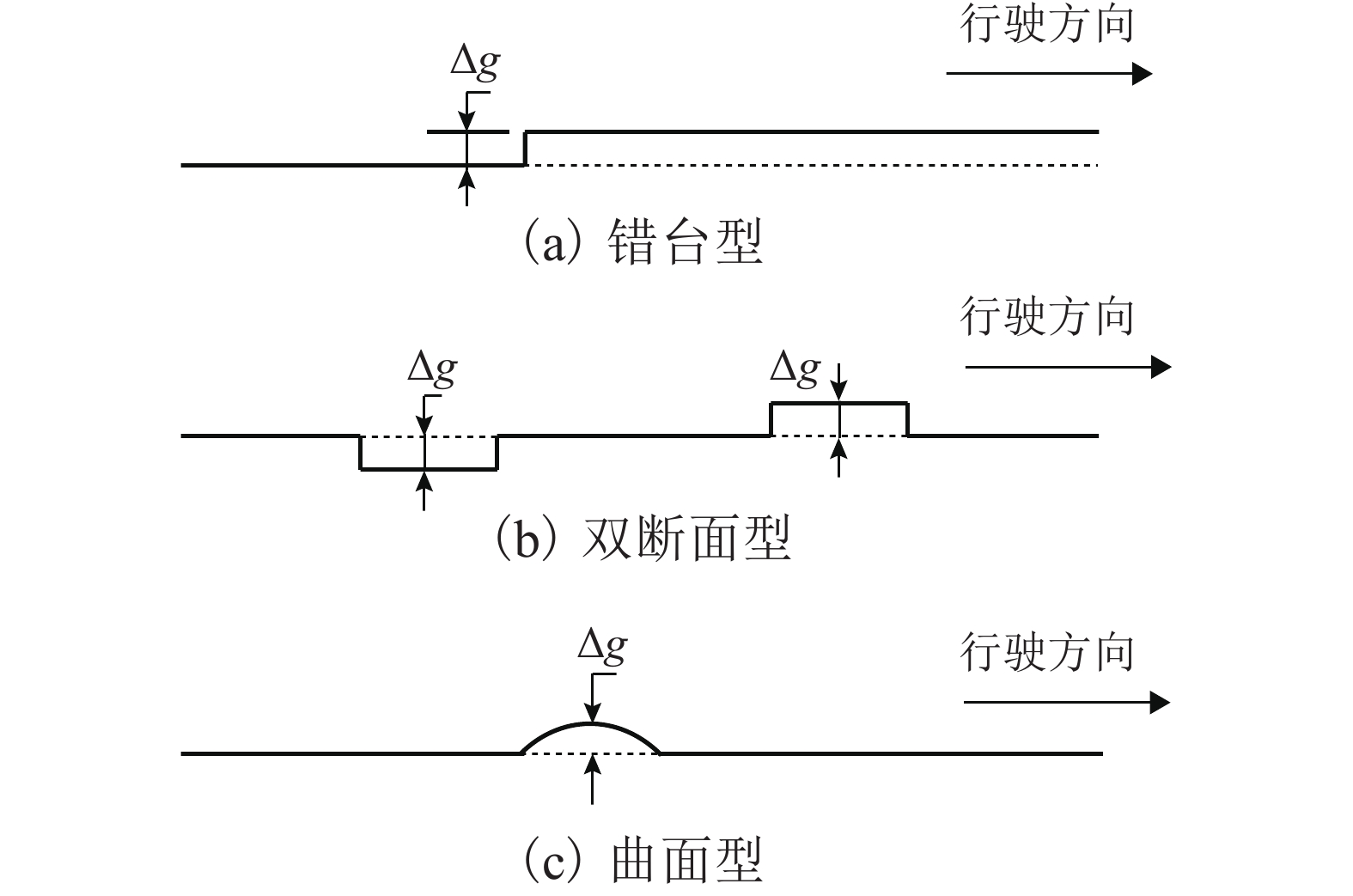
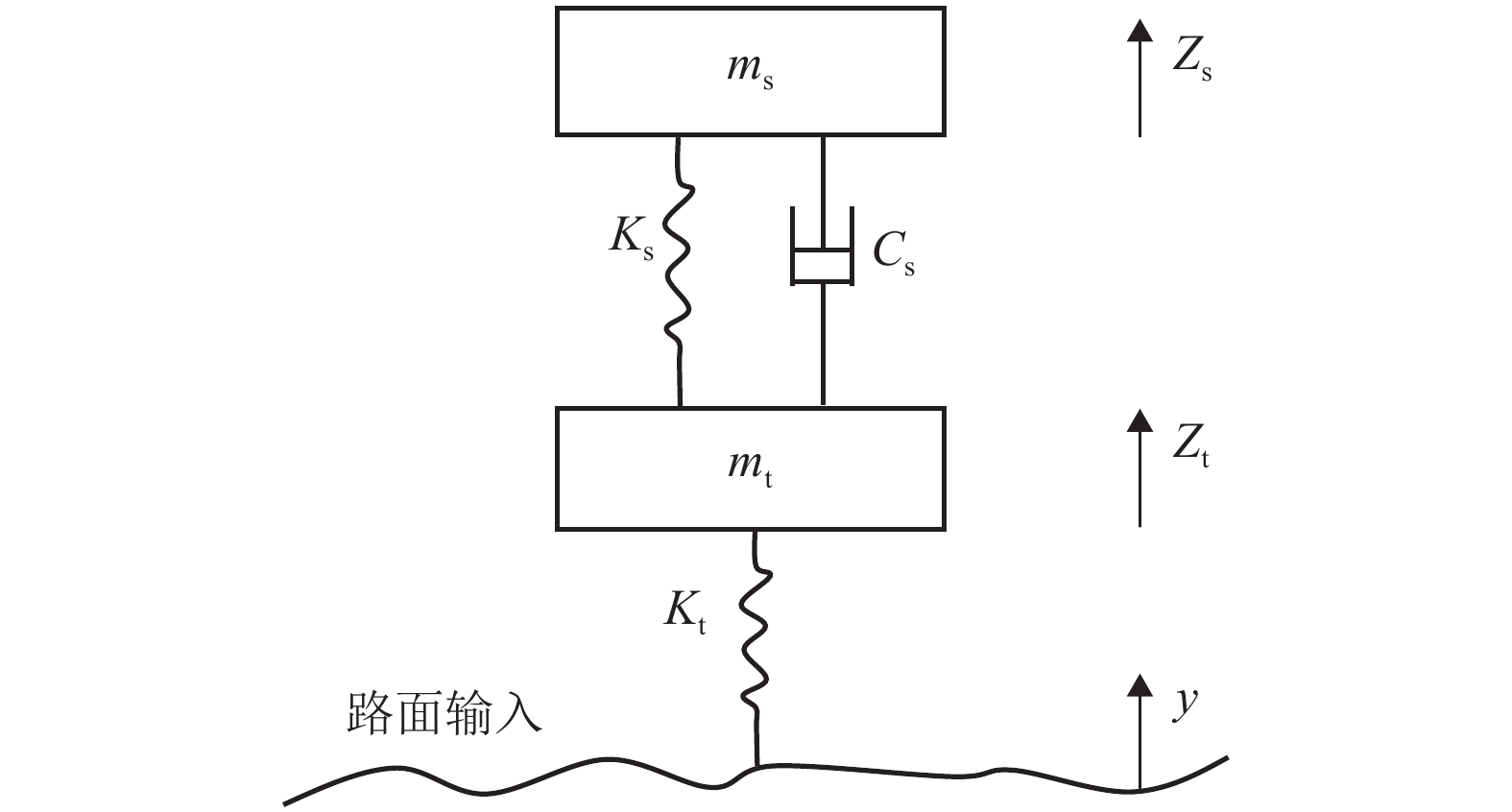
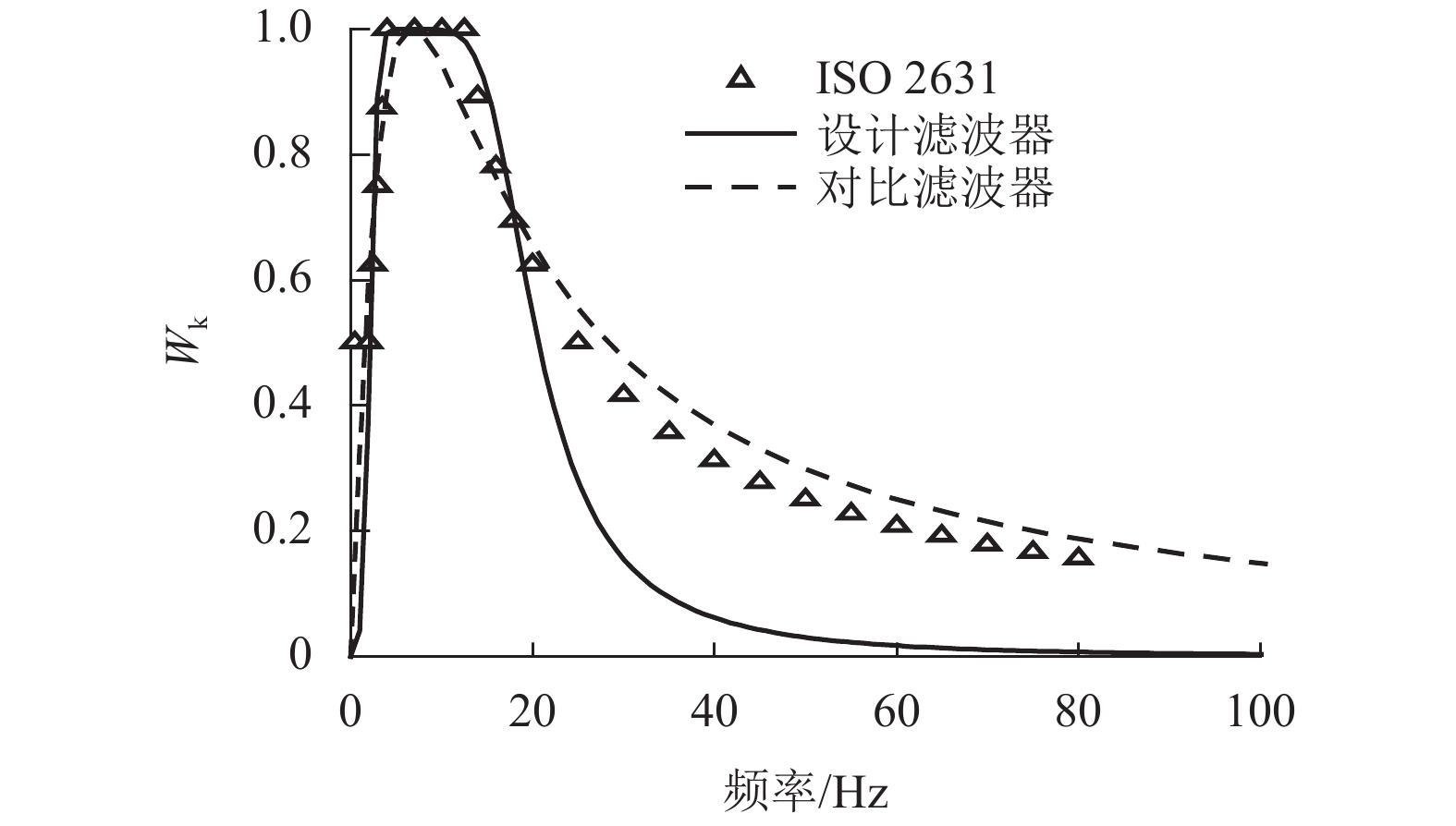
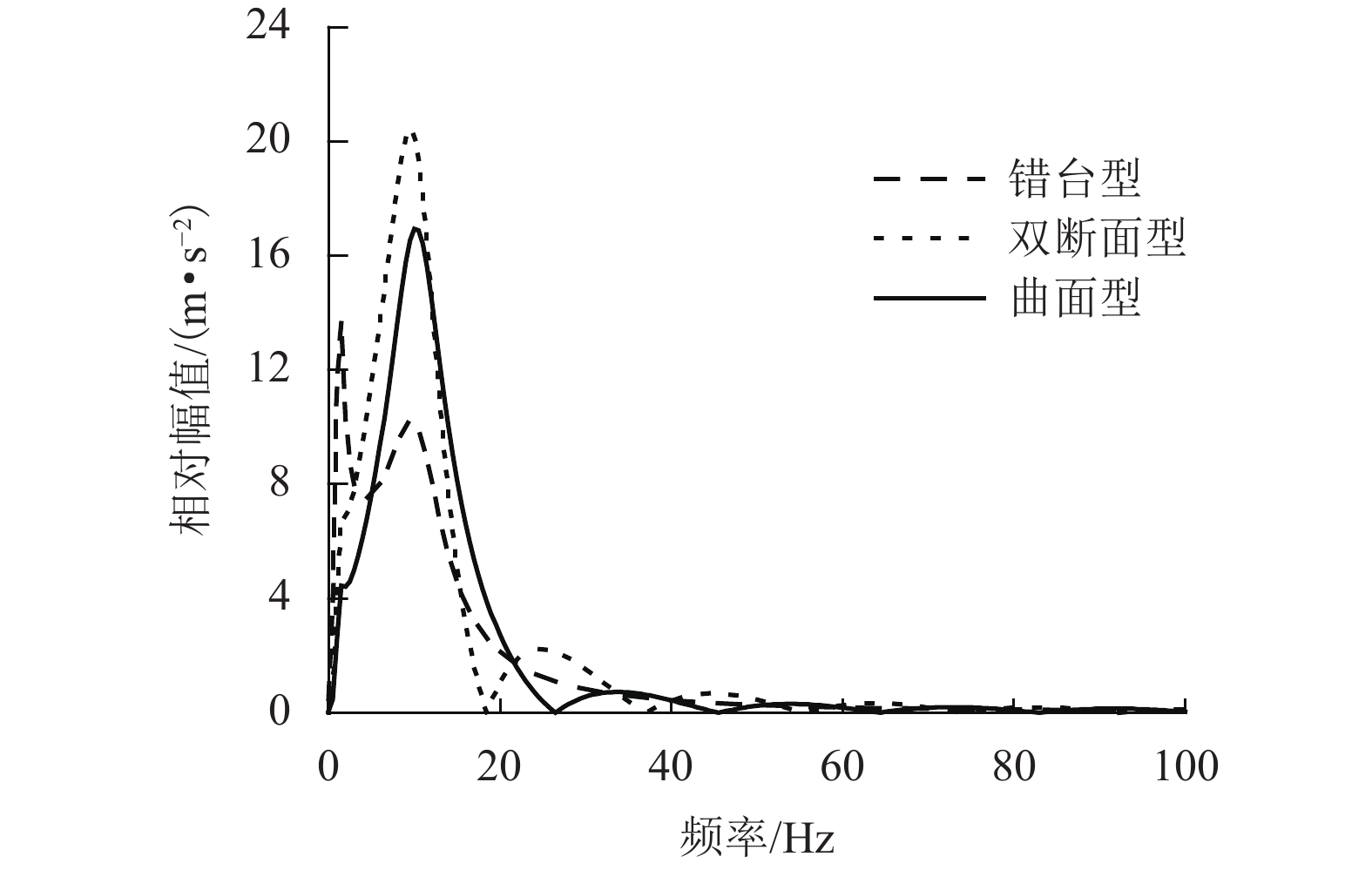
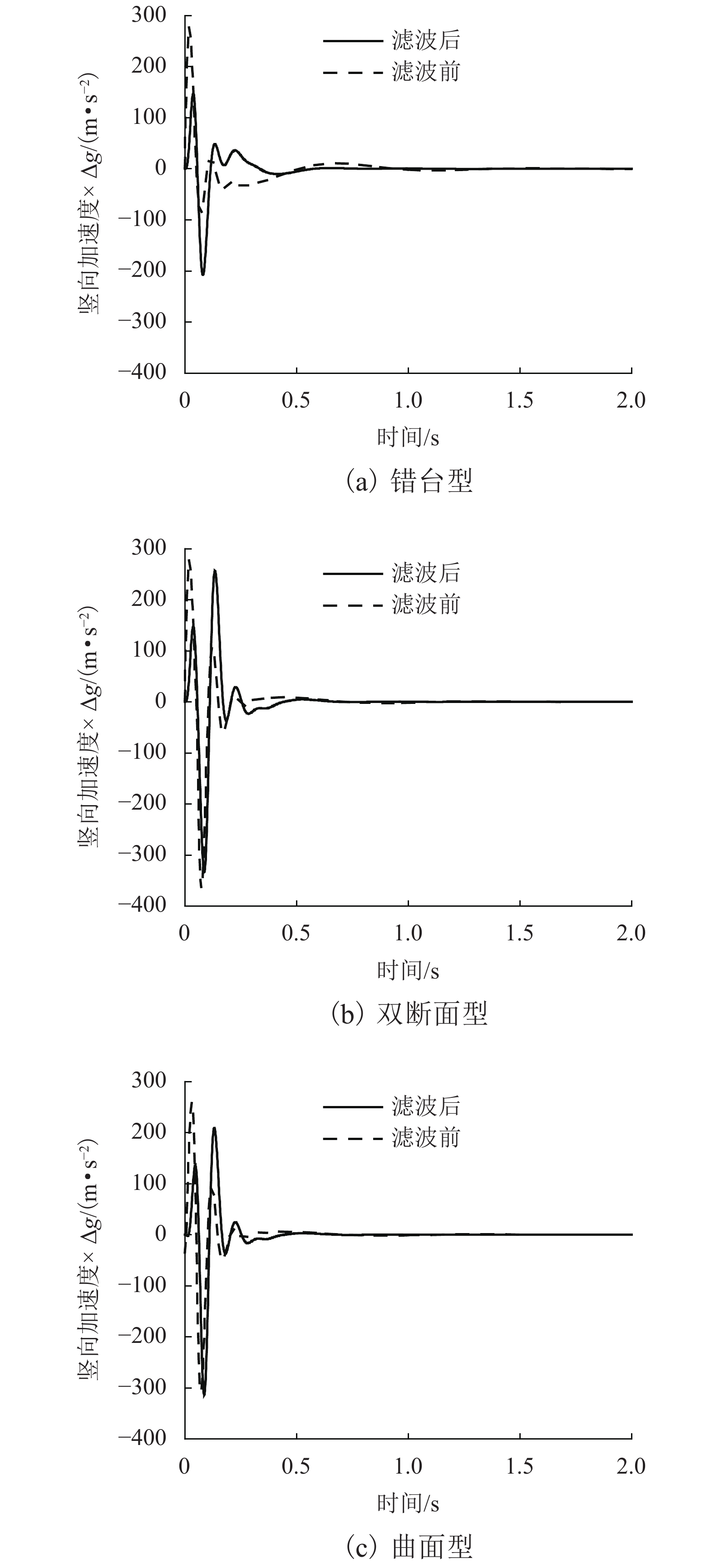
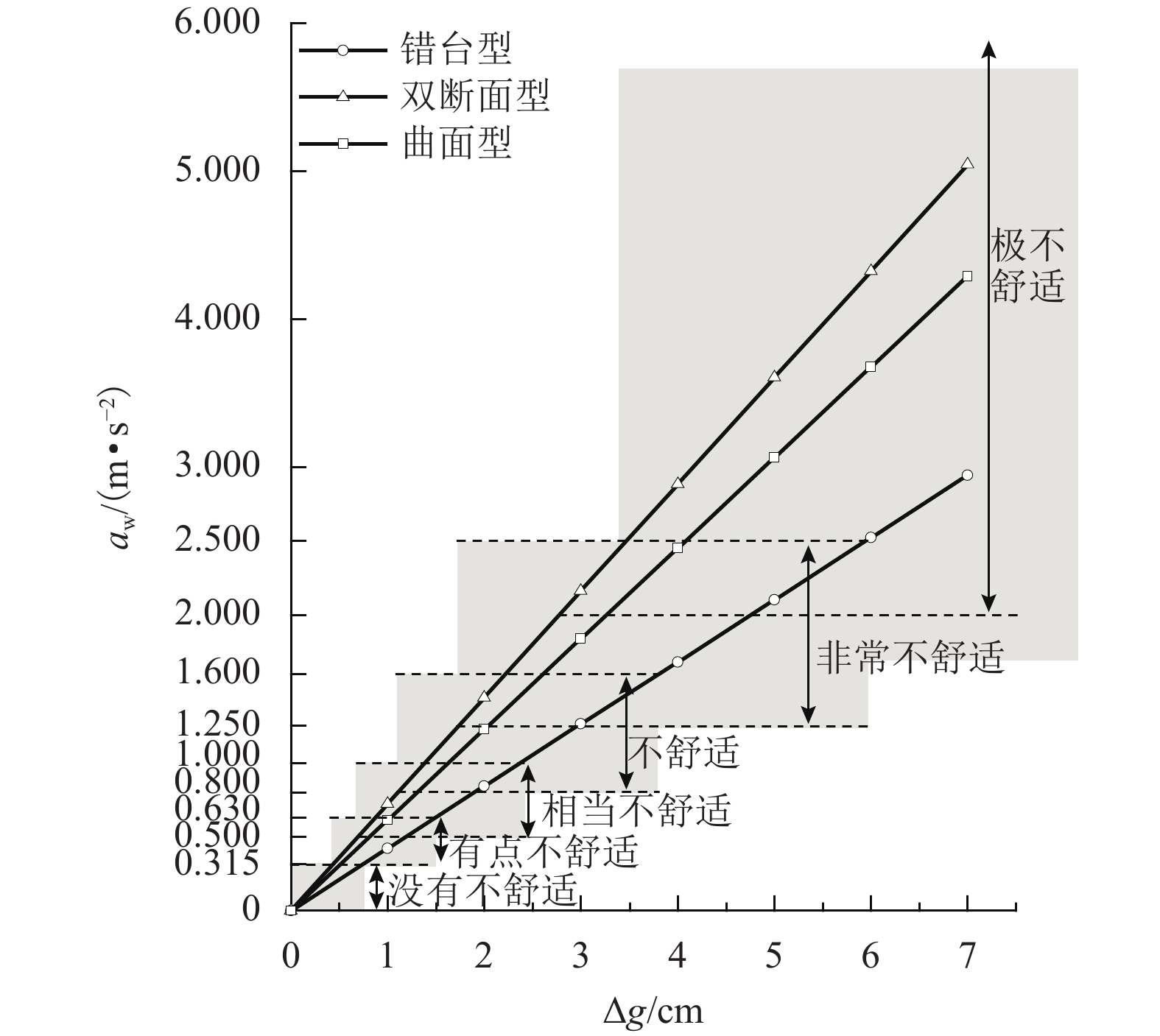
为研究沥青路面局部变形对行驶质量的影响,对路面养护管理中常见的错台型、双断面型和曲面型3类局部变形激励下的振动舒适性进行了评价. 首先,建立了局部变形的纵断面简化模型,并基于1/4车理论推导出路面局部变形激励下的人体竖向加速度时域表达式;其次,设计频率加权滤波器对竖向加速度进行滤波,得到瞬时频率加权加速度,从而求解出不同工况下均方根加速度,实现了振动舒适性的时域加权评价;最后,提出了局部变形的评价标准. 分析结果表明:均方根加速度与局部变形高差呈正比关系;同等变形程度下,双断面型变形的行驶感受最差;当错台型、双断面型及曲面型3类局部变形分别达到4.76、2.78、3.26 cm时,行驶质量均达到极不舒适状态.
Abstract:To study the influence of local deformation of asphalt pavement on riding quality, the vibration serviceability under three types of local deformation, joint faulting type, double-section type and curved surface type, which are common in pavement maintenance management, was evaluated. Firstly, simplified profile model of local deformations are established, and vertical vibration accelerations of human body with the excitation of local deformations are derived, based on the quarter car model. Then, the vertical accelerations are filtered with designed frequency-weighted filter, and instantaneous frequency-weighted accelerations are hence obtained, root-mean-square accelerations under different working conditions are calculated, and weighted vibration serviceability evaluation in time-domain is achieved. Finally, evaluation criteria of local deformations are proposed. The results show that, root-mean-square acceleration is directly proportional to height difference of local deformation. Under the same deformation degree, the driving experience of double-section deformation is the worst. When local deformation height difference of joint faulting, double-section and curved surface reaches 4.76, 2.78 and 3.26 cm, respectively, riding quality reaches extremely uncomfortable states.
-
表 1 局部变形高差评价标准
Table 1. Evaluation criteria for height difference of local deformation
均方根加速度/
(m • s−2)振动感受 △g 范围/cm 错台型 双断面型 曲面型 < 0.315 没有不
舒适< 0.75 < 0.45 < 0.51 0.315~0.630 有些不
舒适0.75~
1.500.45~
0.870.51~
1.030.500~1.000 比较不
舒适1.19~
2.380.69~
1.390.82~
1.630.800~1.600 不舒适 1.90~
3.811.11~
2.221.31~
2.611.250~2.500 很不舒适 2.97~ 5.95 1.73~ 3.47 2.04~ 4.08 > 2.000 极不舒适 > 4.76 > 2.78 > 3.26 -
[1] 孙立军. 道路与机场设施管理学[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2009. [2] 刘婷. 城市道路平整度评价方法研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2013. [3] CANTISANI G, LOPRENCIPE G. Road roughness and whole body vibration:evaluation tools and comfort limits[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2010, 136(9): 818-826. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)TE.1943-5436.0000143 [4] 王锋,张金喜. 基于驾乘舒适性的沥青混凝土路面评价[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(4): 687-692. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.04.020WANG Feng, ZAHNG Jinxi. Evaluation of asphalt concrete pavement based on passenger ride comfort level[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(4): 687-692. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.04.020 [5] AHN S J. Discomfort of vertical whole-body shock-type vibration in the frequency range of 0.5 to 16 Hz[J]. International Journal of Automotive Technology, 2010, 11(6): 909-916. doi: 10.1007/s12239-010-0108-z [6] HUSTON D R, ZHAO X, JOHNSON C C. Whole-body shock and viabration:frequency and amplitude dependence of comfort[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2000, 230(4): 964-970. [7] 陶向华. 路桥过渡段差异沉降控制标准与人车相互作用[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2005. [8] JAME H L, SCOTT M O, TIMOTHY D S. Differential movement at emankment bridge structure interface in Illinois[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1998, 1633: 53-60. doi: 10.3141/1633-07 [9] 何智龙. 上海道路窨井病害调研及机理分析[J]. 城市道桥与防洪,2010(8): 51-53,57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7716.2010.08.016HE Zhilong. Investigation and mechanism analysis of damage of road basket well in Shanghai[J]. Urban Roads Bridges & Flood Control, 2010(8): 51-53,57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7716.2010.08.016 [10] 王雪如. 基于乘车舒适性的高速公路路面平整度评价方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京工业大学, 2014. [11] International Organization for Standardization. Mechanical vibration and shock—evaluation of human exposure to whole-body vibration—part 1, general requirements: ISO 2631-1[S]. Geneva: [s.n.], 1997. [12] 黄舫. 考虑路面局部不平整的城市道路行驶质量评价方法研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2015. [13] SAYERS M W, GILLESPIE T D, PATERSON W. Guidelines for conducting and calibrating road roughness measurements[M]. Washington D C: International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, 1986. [14] 靳晓雄, 张立军, 江浩. 汽车振动分析[M]. 上海: 同济大学出版社, 2002. [15] 李惠彬. 振动理论与工程应用[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2006. [16] 彭华. 交通资产管理系统优化框架的研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2010. [17] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 城市道路工程技术规范: GB 51286—2018[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2018. [18] 余志生. 汽车理论[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2004. -




 下载:
下载: