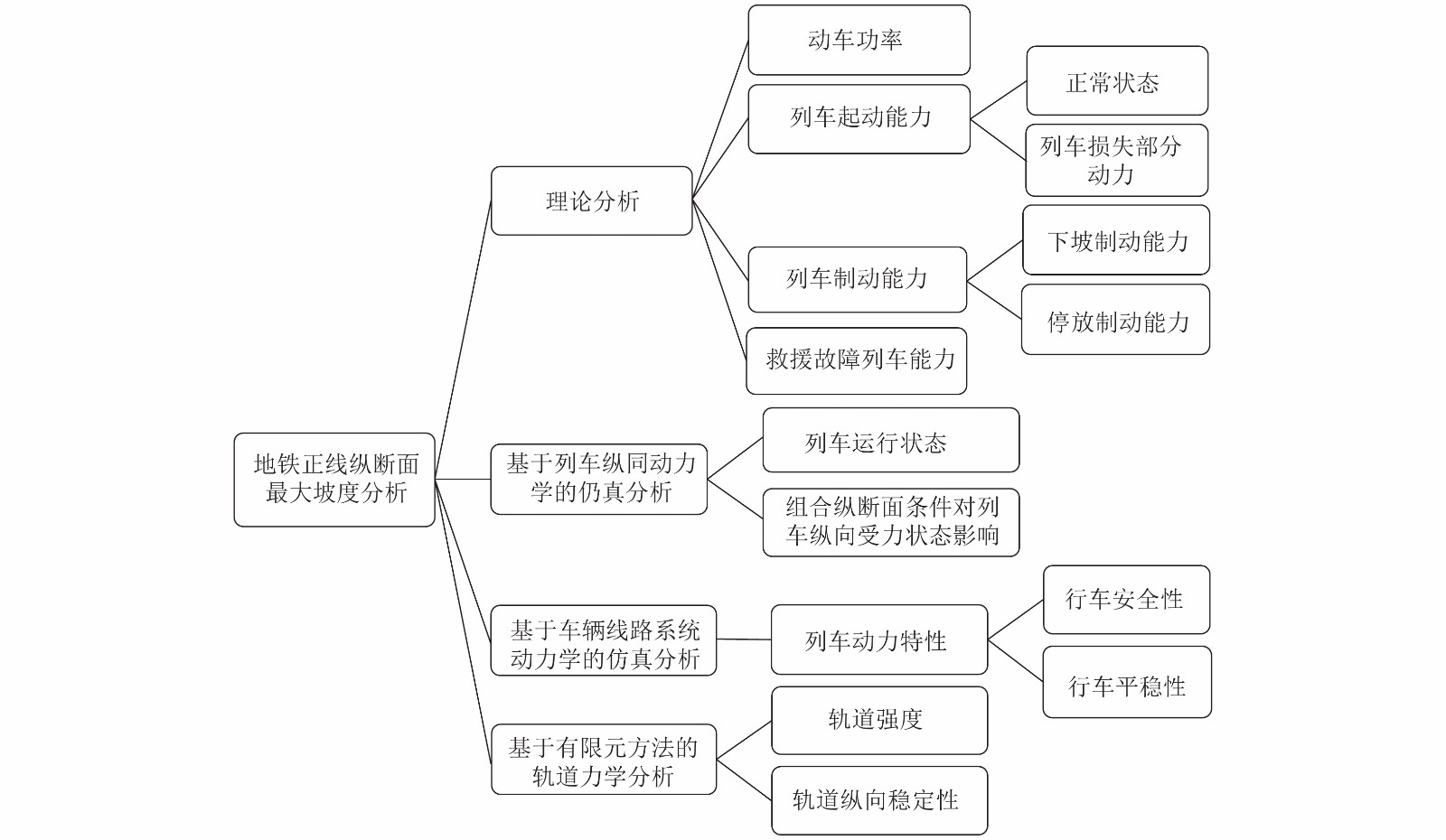
Influence of 40.0‰ Maximum Gradient of Metro Main Line on Running Characteristics of Trains
-
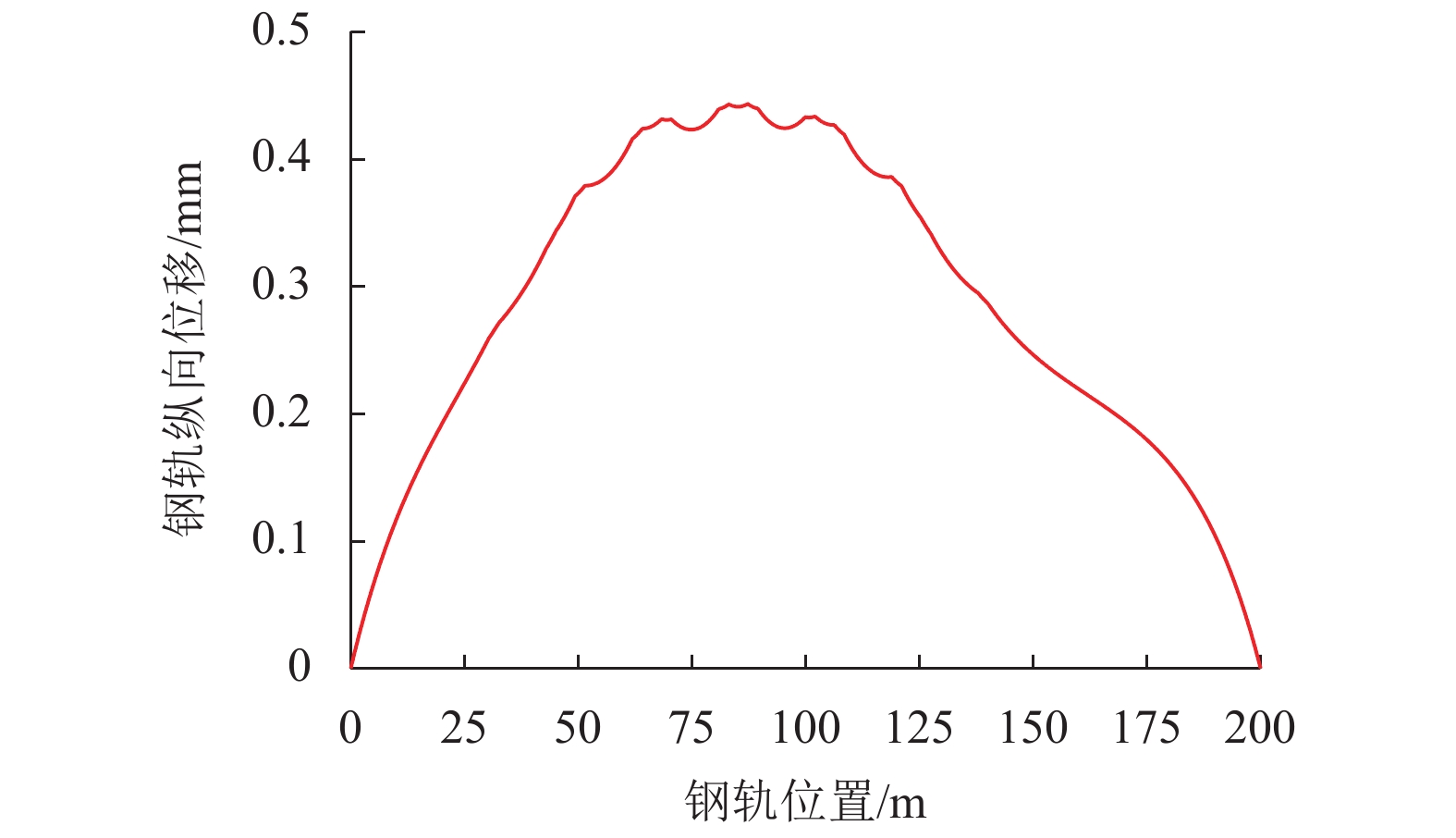
摘要: 地铁线路穿越山岭或跨江渡河时,适当提高正线最大坡度标准有利于减少建设成本、降低设计和施工难度. 为了研究地铁正线40.0‰ 最大坡度取值的可行性,结合苏州市轨道交通8号线车线系统特点,采用理论分析、列车纵向动力学、车辆-线路系统动力学以及有限元等方法,从动车功率、列车起动与制动能力、故障列车救援、列车运行状态与动力特性、轨道力学特性等方面分析了地铁正线40.0‰ 最大坡度对行车特性的影响. 研究结果表明:当采用4动2拖B2型车时,地铁正线最大坡度值可采用40.0‰;列车通过40.0‰ 大坡道地段时,行车安全性、平稳性、列车起动制动以及故障救援能力均能满足要求;钢轨所受最大应力仅为容许应力的37%,纵向最大位移值仅为0.443 mm.Abstract: When metro lines cross mountains or rivers, properly increasing the maximum slope standard of the metro main lines will help reduce costs and difficulties of design and construction. In order to study the feasibility of applying the maximum gradient value of 40.0‰ on the metro main line, combined with the vehicle-track system properties of Suzhou Rail Transit Line 8, the influence of the 40.0‰ maximum gradient value on the running characteristics of trains was analyzed from the power of motor car, starting and braking capacity of trains, rescue of failed trains, train running status and dynamic characteristics, and track mechanical characteristics, by using theoretical analysis, train longitudinal dynamics, vehicle-track system dynamics, and finite element method. Results show that the maximum gradient of a metro main line can be 40.0‰ when the B2 type vehicle with 4 motors and 2 trailers is used; when the train passes through the 40.0‰ ramp section, the running safety, stability, starting-braking and fault rescue ability of the train meet the requirements; the maximum stress of the rail is only 37% of the allowable stress, and the maximum longitudinal displacement is only 0.443 mm.
-
Key words:
- metro /
- main line /
- maximum gradient /
- safety /
- stability /
- running characteristics
-
表 1 B2型车技术参数
Table 1. Technical parameters of B2 type vehicle
项目 技术参数 最高运行速度/
(km•h−1)80 车辆自重/t 动车:35;拖车:32 车辆载荷/t 动车:19.5;拖车:17.4 列车总重/t 空车:204.0;定员:291.2;超员:316.8 列车起动牵引力/kN 空车:254;定员:356;超员:384 表 2 动车功率确定的最大坡度
Table 2. Maximum gradients determined by the power of motor vehicles
工况 列车载
客状态列车通过坡段
最大速度/(km•h−1)最大坡
度/‰1 超员 80.0 37.6 2 超员 79.0 39.1 3 超员 78.0 41.6 4 定员 80.0 42.0 表 3 起动能力允许的最大坡度
Table 3. Maximum allowable gradients determined by starting capacity
工况 起动牵引力/kN 黏着牵引力/kN 最大坡度/‰ 动力正常 384 382.66 106.0 动力损失1/4 288 287.82 76.0 动力损失1/2 192 192.24 45.0 表 4 空车救援故障列车能力允许的最大坡度
Table 4. Maximum allowable gradients determined by empty train rescue capability
救援方法 起动牵引力/kN 黏着牵引力/kN 最大坡度/‰ 1 254 247.06 33.0 2 254 287.82 34.0 3 254 246.91 47.0 4 384 384.27 59.0 表 5 列车动力正常时的制动能力
Table 5. Train braking capacity under normal power
速度/
(km•h−1)电制动
力/kN列车运行
阻力/kN加速
力/kN电制动减
速度/(m•s−2)10 352 7.540 124.312 0.675 20 352 8.994 124.312 0.679 30 352 11.418 124.312 0.686 40 352 14.812 124.312 0.696 50 352 19.175 124.312 0.708 60 352 24.508 124.312 0.724 70 352 30.811 124.312 0.742 80 352 38.083 124.312 0.763 表 6 故障列车停放制动能力
Table 6. Braking capacity of fault train on parking
kN 载客
状态考虑安全余量后所
需停放制动力故障列车可提
供制动力超员 235.016 290.88 定员 223.464 290.88 空车 184.114 290.88 表 7 大坡度地段平竖曲线叠加时车辆平稳性指标
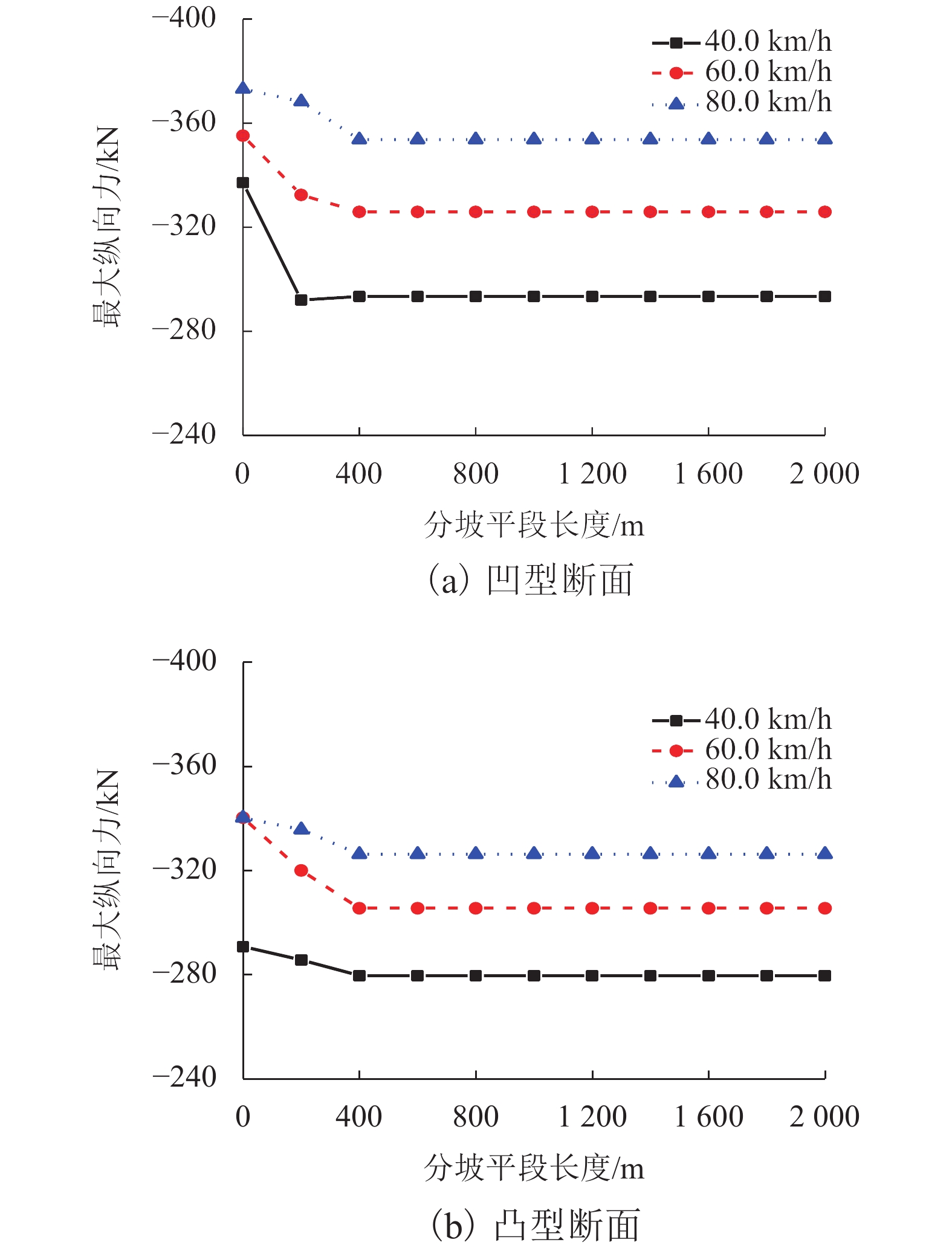
Table 7. Stability index of vehicles in large gradient section with overlayed horizontal and vertical curves
曲线半径/m 横向平稳性 垂向平稳性 空车 重车 空车 重车 250 1.357 1.351 0.831 0.819 500 1.371 1.304 0.938 0.923 1 000 1.335 1.282 0.932 0.921 2 000 1.288 1.257 0.918 0.919 4 000 1.128 1.181 0.908 0.904 -
殷继兴,王进勇. 我国山区铁路最大限制坡度选择的研究[J]. 铁道运输与经济,2007(9): 80-83,86. 张明. 阿富汗铁路复杂山区最大坡度与牵引质量的研究[J]. 铁道标准设计,2013(6): 28-32.ZHANG Ming. Study on maximum gradient and traction weight of Afghanistan railway in complex mountain area[J]. China Academic Journal Electronic Publishing House, 2013(6): 28-32. 陈亮. 贵阳至广州线线路最大坡度方案比选[J]. 铁道工程学报,2008,25(8): 18-22.CHEN Liang. Scheme alternative of maximum route gradienton Guiyang—Guangzhou railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2008, 25(8): 18-22. 陈学贤. 基于综合优化方法的困难艰险山区铁路最大坡度决策研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016. 苏梅. 客货共线铁路隧道内最大坡度设计浅析[J]. 铁道工程学报,2009,26(8): 73-76.SU Mei. Analysis on the design of the maximum slope in the railway tunnel on the passenger and freight line[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2009,26(8): 73-76. 王小红. 新建西安至十堰高速铁路最大坡度研究[J]. 铁道标准设计,2019,63(4): 47-51,57.WANG Xiaohong. Study on maximum grade of the newly-built Xi’an—Shiyan high-speed railway[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2019, 63(4): 47-51,57. 后宗彪. 京沪高速铁路最大坡度研究[J]. 铁道标准设计,2008(6): 5-7. 杨勃. 西安至成都客运专线翻越秦岭地段最大坡度研究分析[J]. 铁道标准设计,2010(增刊1): 46-48. 汪莹. 基于动力分析的重载铁路纵断面最大坡度的研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2014. 池君惠. 大轴重重载铁路最大坡度研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. 陈聪. 基于动力分析的中低速磁悬浮线路最大坡度研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2015. 吴跃成. 基于动力学分析的中速磁浮线路纵断面技术参数研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2018. 黄义桐. 城轨磁悬浮交通线路纵断面技术条件研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2008. 梁广深,包童,黄隆飞. 地铁B型车爬坡能力及提高地下正线坡度可行性探讨[J]. 都市快轨交通,2013,26(4): 68-77,81.LIANG Guangshen, BAO Tong, HUANG Longfei. On gradeability of metro B-type trains and the feasibility to increase the gradient of main line slopes[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit, 2013, 26(4): 68-77,81. 梁广深,唐健. 对地铁线路长大陡坡和连续提升高度限制的不同看法[J]. 都市快轨交通,2015,28(1): 67-71.LIANG Guangshen, Tang Jian. Different perspectives on limitation of urban rail lines with long distance,big gradient and continuous hoisting height[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit, 2015, 28(1): 67-71. 郑翔. 西安地铁四号线长大坡度设计研究[J]. 铁道建筑,2014(9): 44-46. -




 下载:
下载: