Multi-objective Optimization of Yaw Damper Parameters for High-Speed Train
-
摘要:
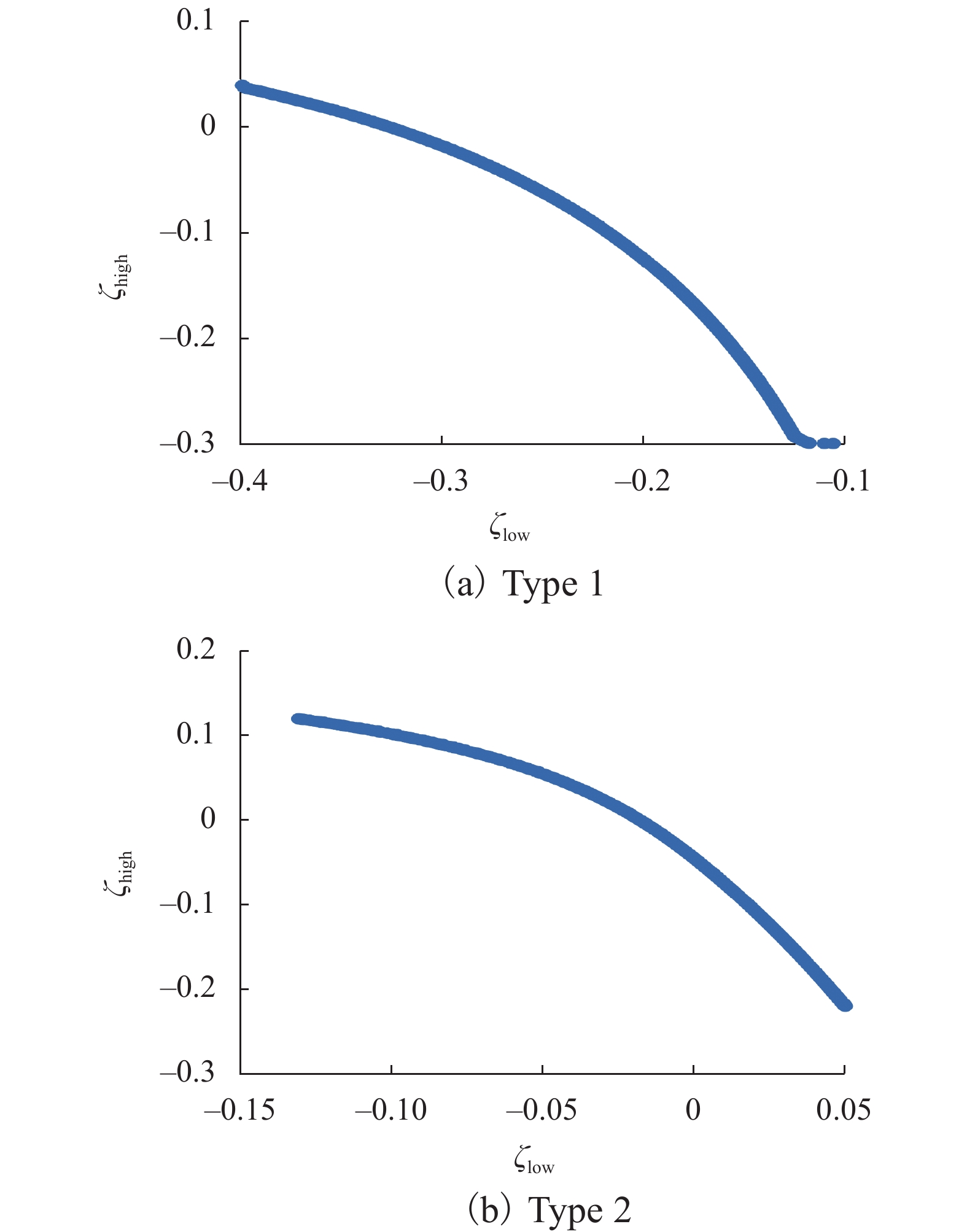
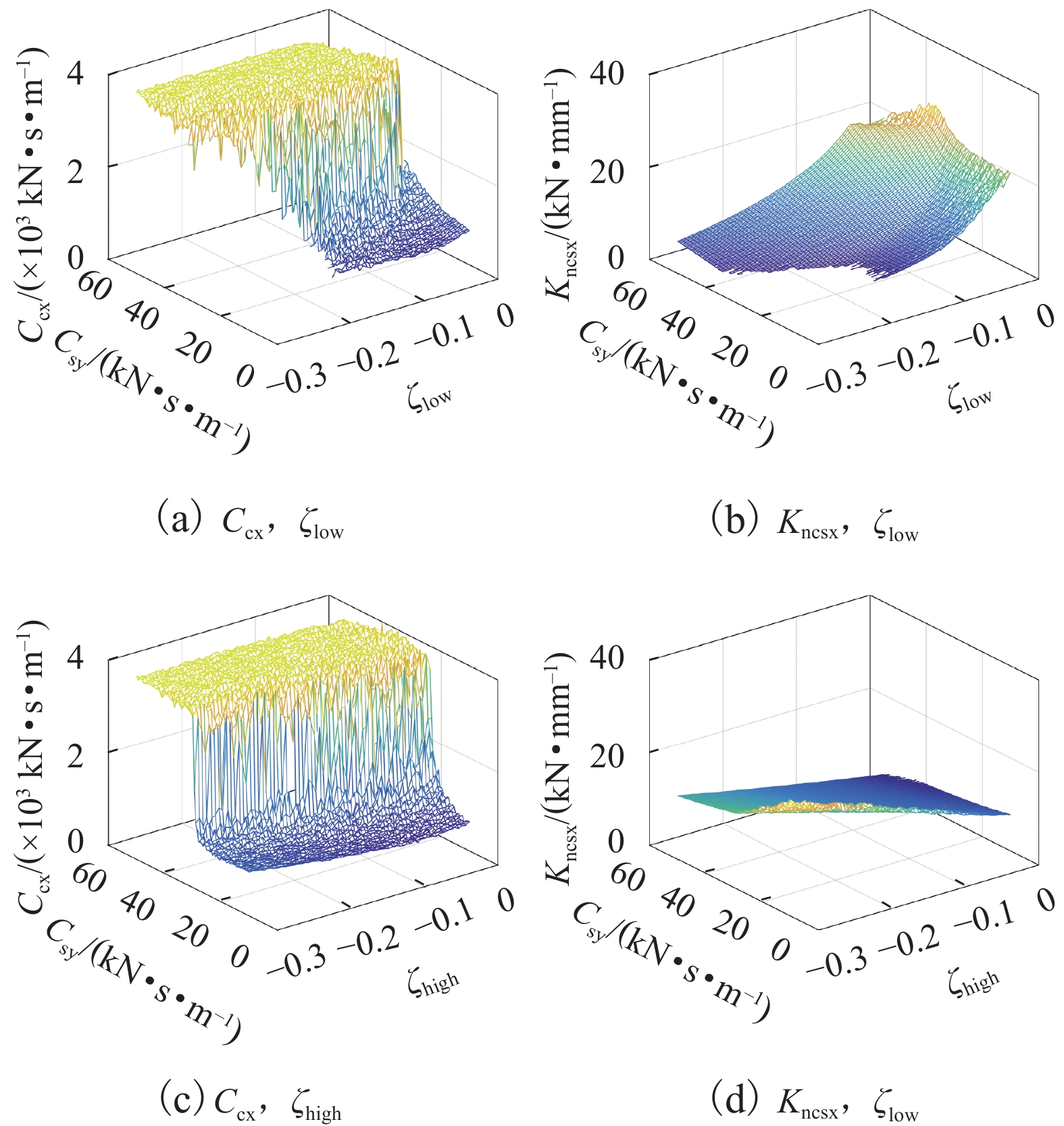
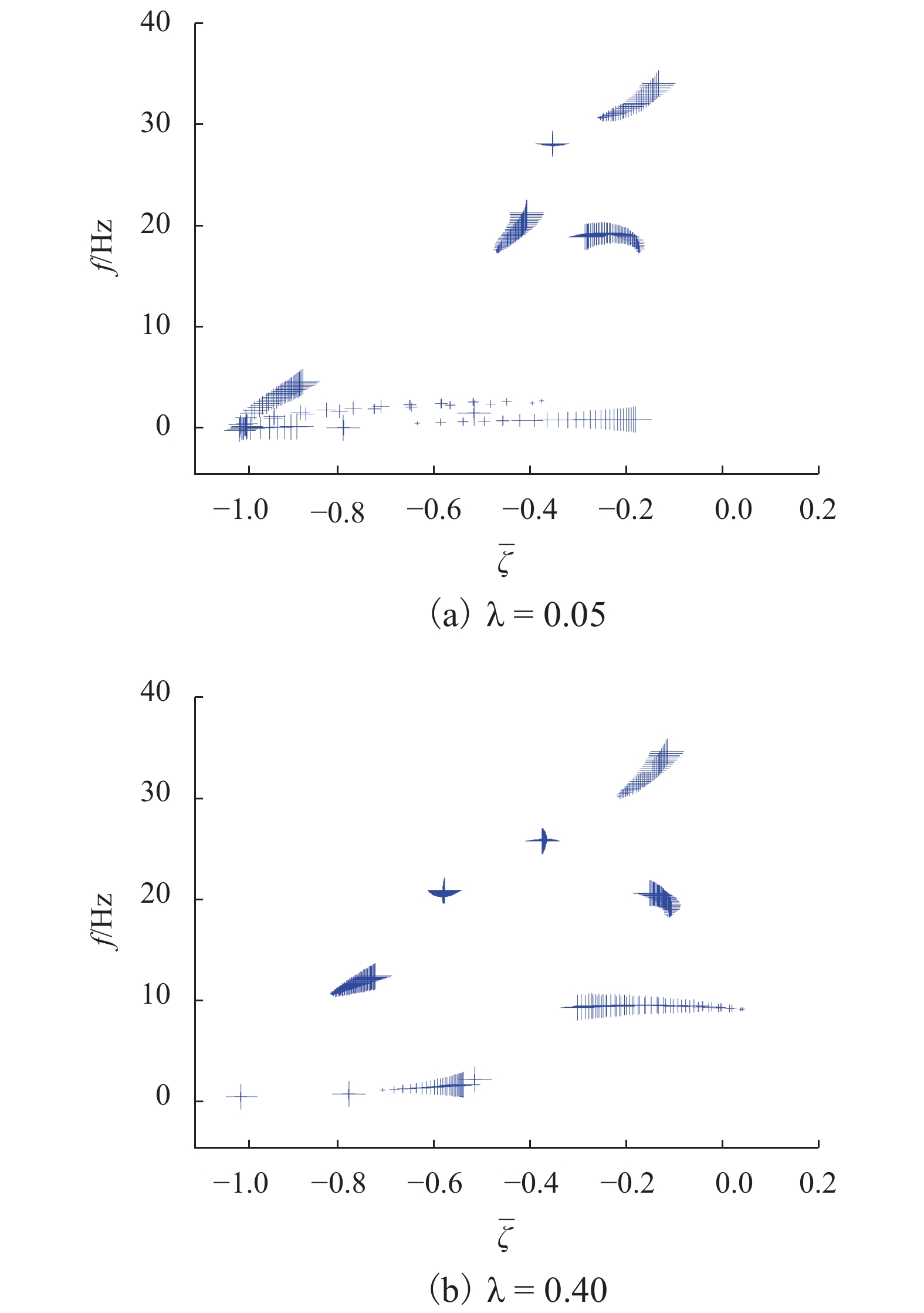
为了研究抗蛇行减振器参数匹配规律以兼顾不同轮轨接触状态下高速列车横向稳定性,针对国内运行典型结构参数的高速列车,建立车辆横向动力学简化模型,分别考虑到高、低锥度两种轮轨接触状态下车辆的横向稳定性,采用多目标优化方法对抗蛇行减振器刚度和阻尼值进行多参数优化,并分析最优抗蛇行减振器参数的影响因素. 结果表明:优化的抗蛇行减振器阻尼值主要取决于车辆二系横向阻尼,得出了两类阻尼值的抗蛇行减振器选配类型,即当二系横向阻尼较小时,转向架单侧需匹配较小阻尼值600~1000 kN•s•m−1,或当二系横向阻尼较大时,匹配大于4 000 kN•s•m−1的抗蛇行减振器;抗蛇行减振器刚度显著影响不同轮轨接触状态下的车辆稳定性,减小抗蛇行减振器刚度有利于低锥度状态车辆稳定性,反之亦然.
Abstract:In order to study the parameter matching law of yaw damper for the lateral stability of high-speed trains under different wheel-rail contact conditions, a simplified model of vehicle lateral dynamics was established aiming at the typical parameters of high-speed trains operating in China. Considering the lateral stability of vehicles under the high or low wheel-rail contact conicity states respectively, the multi-objective optimization method was used to optimize the stiffness and damping parameters of yaw damper, and the influencing factors of the optimal parameters of yaw damper were analyzed as well. The results show that the optimal damping value of yaw damper mainly depends on the lateral damping of the secondary suspension, and two types of damping value selection for yaw damper are obtained. That is, when the secondary lateral damping is small, a small damping value of 600−1 000 kN•s•m−1 in one side of bogie should be selected. On the contrary, the yaw damper greater than 4 000 kN•s•m−1 should match the vehicle adopting a large secondary lateral damping. The stiffness of yaw damper significantly affects the stability of vehicles in different wheel-rail contact states. A smaller stiffness is conductive to the lateral stability of vehicles in low conicity wheel-rail contact state, and vice versa.
-
Key words:
- high-speed train /
- lateral stability /
- yaw damper /
- multi-objective optimization /
- parameter matching
-
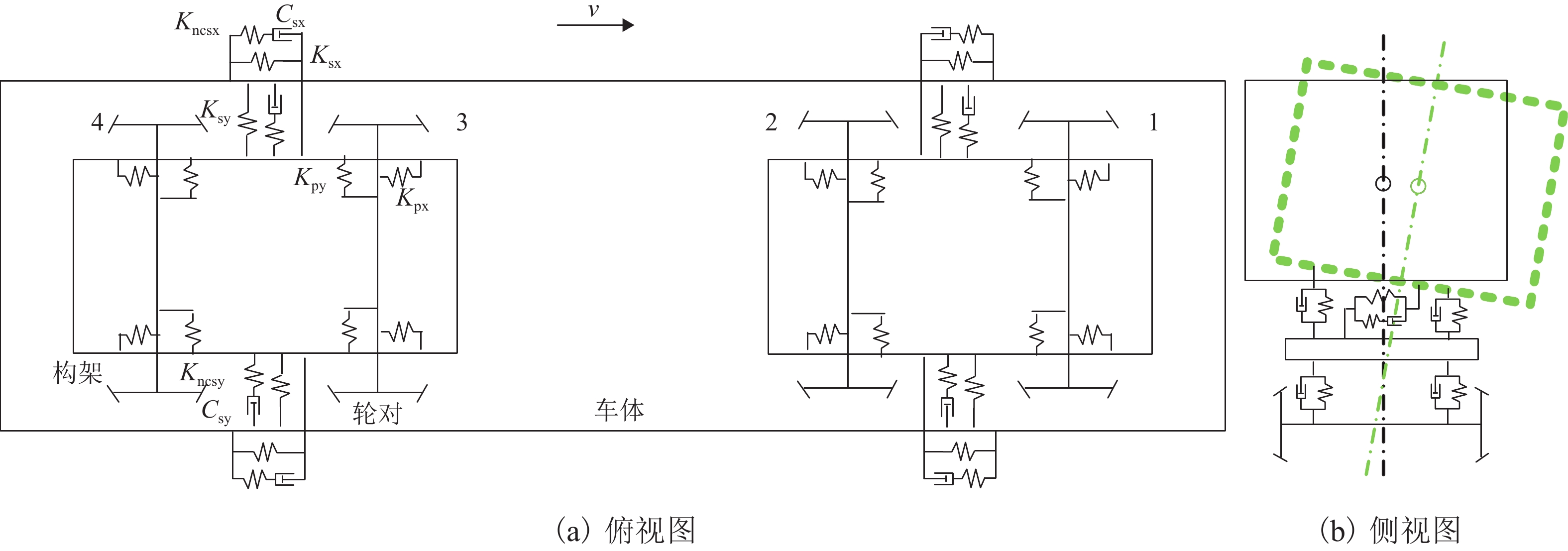
表 1 两类高速列车悬挂参数
Table 1. Suspension parameters of two types of high-speed trains
类型 Kpx/(kN•mm−1) Kpy/(kN•mm−1) Csy/(kN•s•m−1) Type 1 13.7 5.49 40 Type 2 120.0 12.50 15 -
[1] 曾京,邬平波. 减振器橡胶节点刚度对铁道客车系统临界速度的影响[J]. 中国铁道科学,2008,29(2): 94-98. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2008.02.018ZENG Jing, WU Pingbo. Influence of the damper rubber joint stiffness on the critical speed of railway passenger car system[J]. China Railway Science, 2008, 29(2): 94-98. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2008.02.018 [2] 张卫华,李艳,宋冬利. 高速列车运动稳定性设计方法研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2013,48(1): 1-9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2006.04.002ZHANG Weihua, LI Yan, SONG Dongli. Design methods for motion stability of high-speed trains[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013, 48(1): 1-9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2006.04.002 [3] 孙建锋,池茂儒,吴兴文,等. 抗蛇行减振器参数对车辆稳定性的影响分析[J]. 振动、测试与诊断,2018,38(6): 1155-1160.SUN Jianfeng, CHI Maoru, WU Xingwen, et al. Analysis of the influence of the yaw damper parameters on the vehicle stability[J]. Journal of Vibration,Measurement & Diagnosis, 2018, 38(6): 1155-1160. [4] 于曰伟,周长城,赵雷雷. 高速客车抗蛇行减振器阻尼匹配的解析研究[J]. 机械工程学报,2018,54(2): 159-168. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.02.159YU Yuewei, ZHOU Changcheng, ZHAO Leilei. Analytical research of yaw damper damping matching for high-speed train[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(2): 159-168. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.02.159 [5] BRAGHIN F, BRUNI S, RESTA F. Active yaw damper for the improvement of railway vehicle stability and curving performances:simulations and experimental results[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2006, 44(11): 857-869. doi: 10.1080/00423110600733972 [6] HE Y P, MCPHEE J. Multidisciplinary optimization of multibody systems with application to the design of rail vehicles[J]. Multibody System Dynamics, 2005, 14(2): 111-135. doi: 10.1007/s11044-005-4310-0 [7] 李奇,孟翔,陈维荣,等. 燃料电池混合动力系统参数匹配与多目标优化[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2019,54(5): 1079-1086.LI Qi, MENG Xiang, CHEN Weirong, et al. Parameter matching and multi-objective optimization of fuel cell hybrid system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(5): 1079-1086. [8] 解欢,杨岳,童林军,等. 基于混合代理模型的高速轨道车辆悬挂参数多目标优化[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2016,13(10): 2056-2063. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2016.10.025XIE Huan, YANG Yue, TONG Linjun, et al. Multi-objective optimization of the suspension parameters for high speed rail vehicle based on a hybrid surrogate model[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2016, 13(10): 2056-2063. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2016.10.025 [9] JOHNSSON A, BERBYUK V, ENELUND M. Pareto optimisation of railway bogie suspension damping to enhance safety and comfort[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2012, 50(9): 1379-1407. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2012.659846 [10] BIDELEH S M, BERBYUK V, PERSSON R. Wear/comfort pareto optimisation of bogie suspension[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2016, 54(8): 1053-1076. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2016.1180405 [11] ALONSO A, GIMÉNEZ J G, GOMEZ E. Yaw damper modelling and its influence on the railway dynamic stability[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2011, 49(8): 1367-1387. [12] YAO Y, YAN Y P, HU Z K, et al. The motor active flexible suspension and its dynamic effect on the high-speed train bogie[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems,Measurement and Control, 2017, 140(6): 064501.1-064501.7. [13] YAO Y, ZHANG XX, LIU X. The active control of the lateral movement of a motor suspended under a high-speed locomotive[J]. Rail and Rapid Transit, 2016, 230(6): 1509-1520. doi: 10.1177/0954409715605138 [14] YAO Y, LI G, WU G S, et al. Suspension parameters optimum of high-speed train bogie for hunting stability robustness[J]. International Journal of Rail Transportation, 2020, 8(3): 195-214. doi: 10.1080/23248378.2019.1625824 [15] AGRAWAL R B, DEB K, AGRAWAL R B. Simulated binary crossover for continuous search space[J]. Complex Systems, 2000, 9(3): 115-148. [16] 董浩. 铁道车辆运动稳定性及分岔类型研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2014. -




 下载:
下载: