Two-Stage Optimization Method of Train Energy-Efficient Operation Based on Dynamic Programming
-
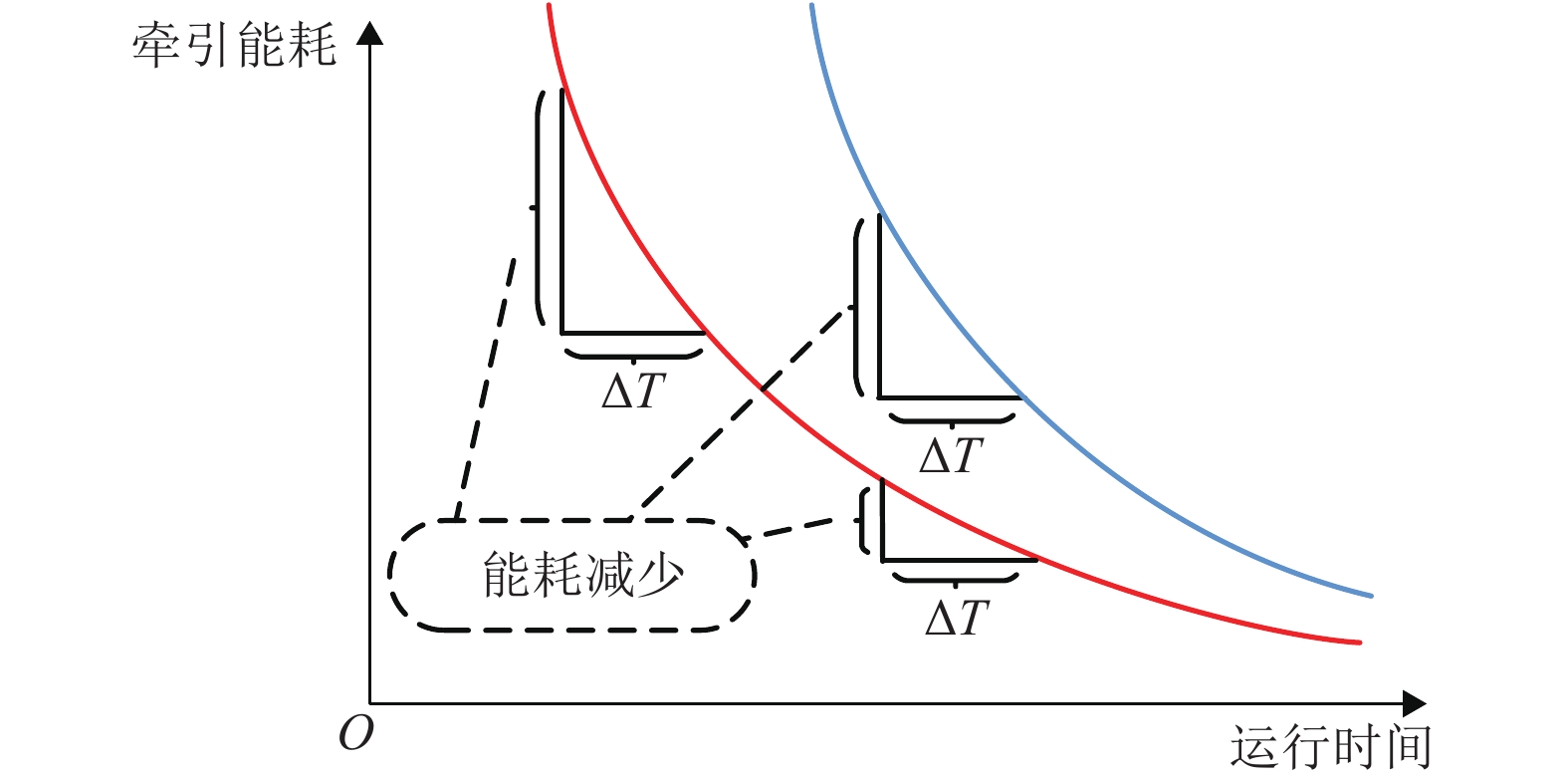
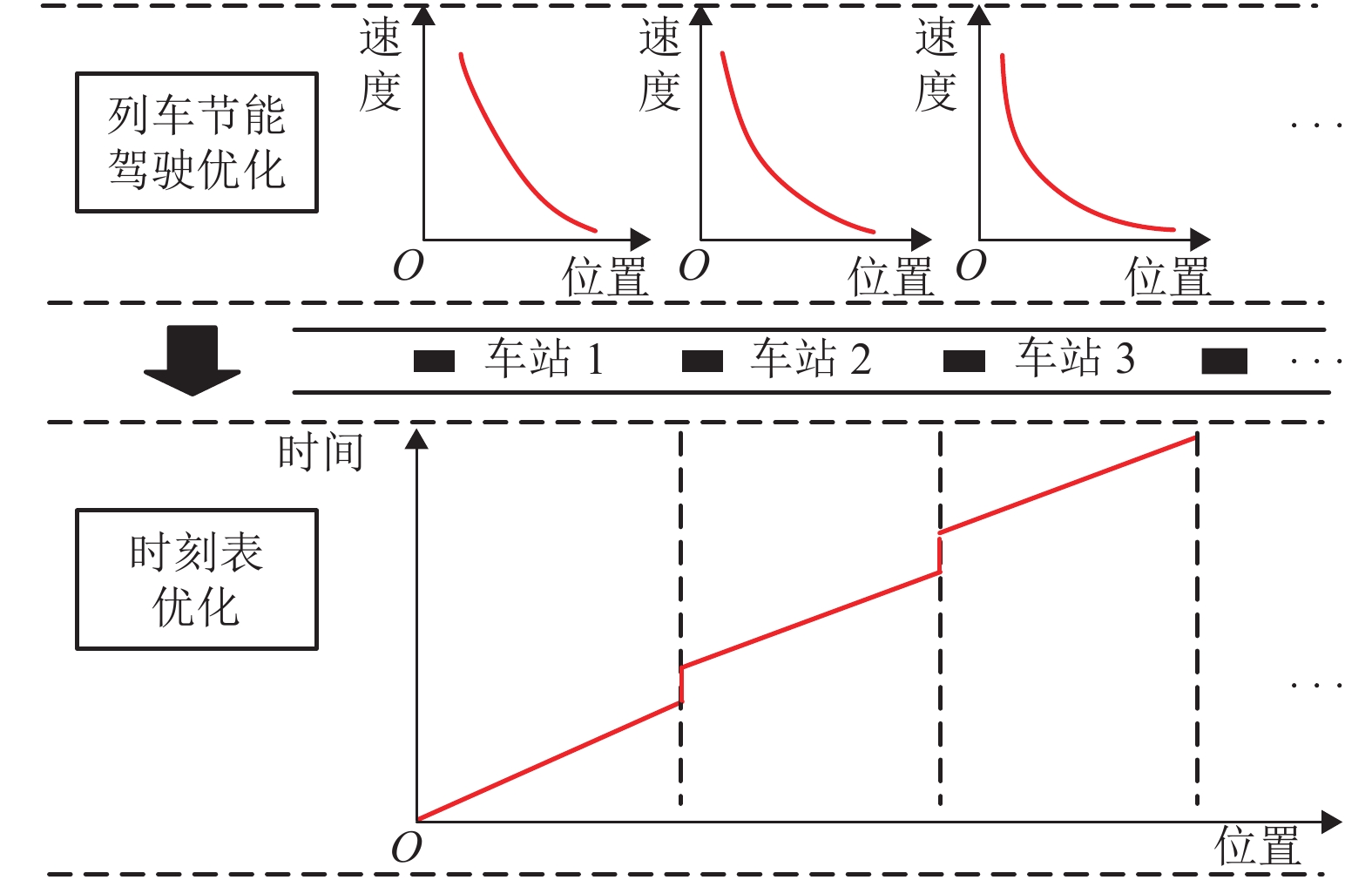
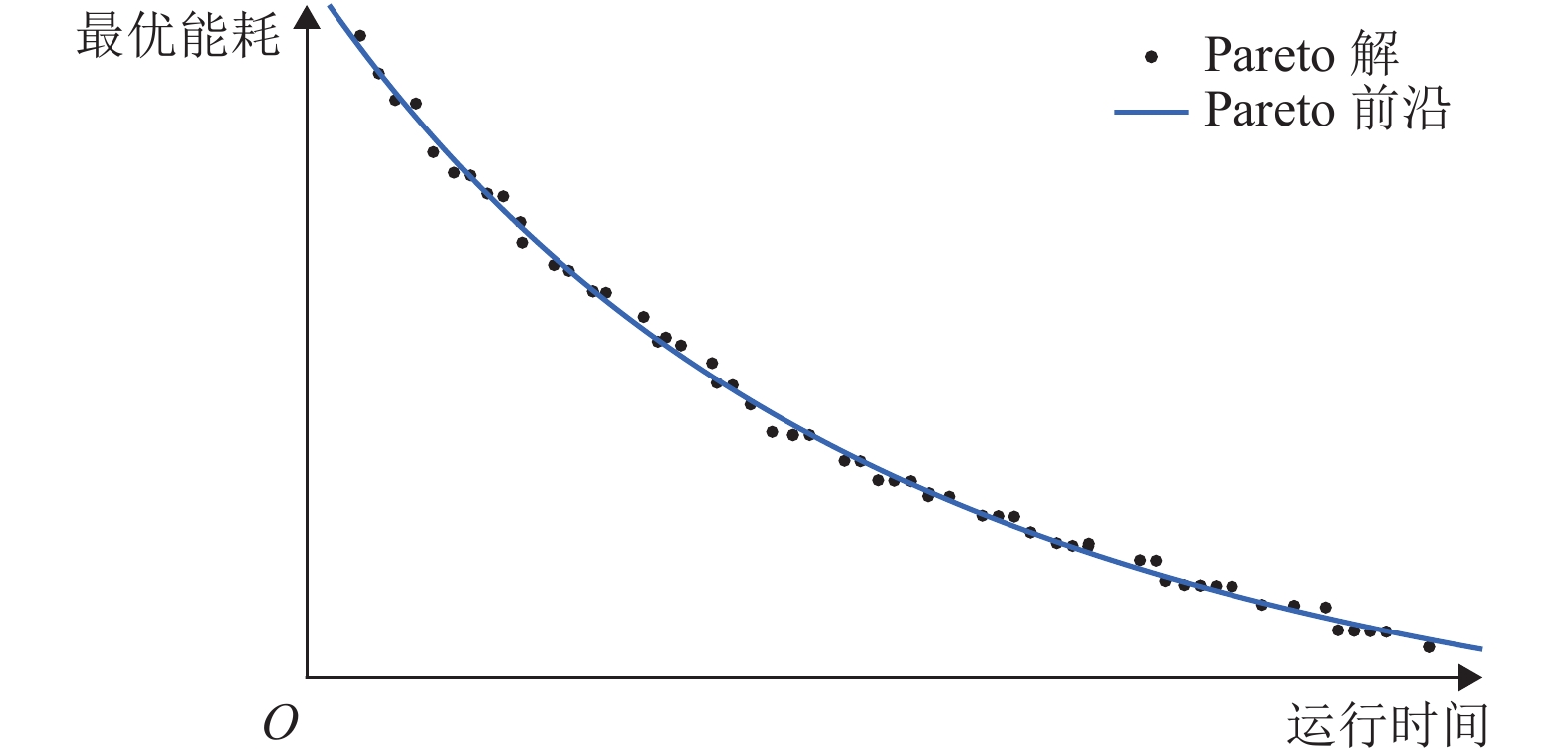
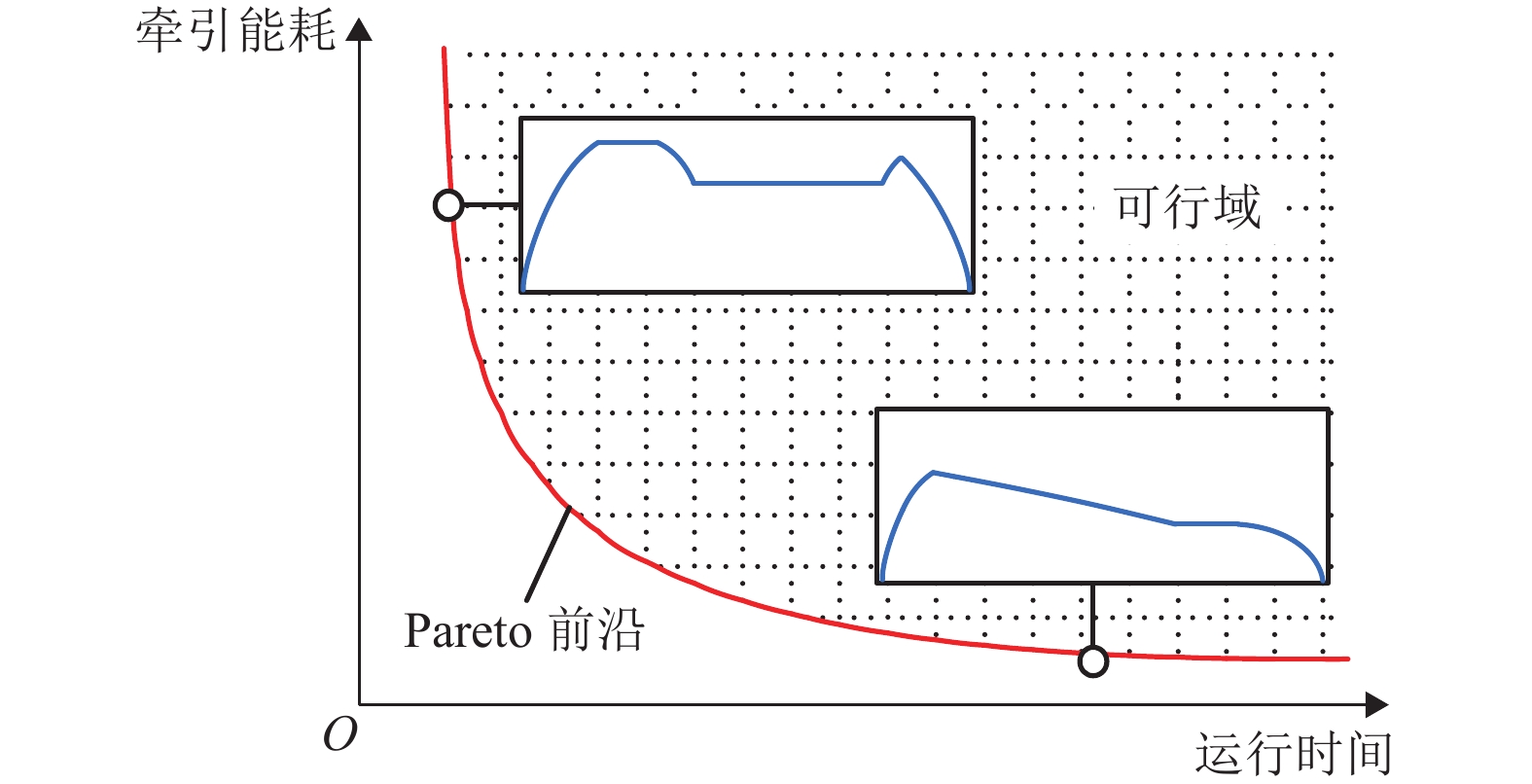
摘要: 针对地铁列车多站间节能运行优化问题,提出将列车节能驾驶优化过程和时刻表优化过程结合的两阶段优化方法,分别求解两优化过程的全局最优解,从而获取列车在多站间运行的最优操纵策略. 首先考虑节能和节时两个目标,构建列车节能驾驶多目标优化模型,结合动态规划多阶段寻优思路,建立一系列包含多个过程指标及约束的子阶段求解模型,逆序求解后获取列车站间运行最优操纵策略的Pareto前沿;其次建立时刻表优化模型,基于动态规划方法,调用各站间Pareto前沿,搜索站间运行时间最优分配方案;最后以北京地铁亦庄线为例,验证两阶段优化方法的有效性和高效性. 试验结果表明,与最速操纵策略相比,经过两个阶段优化后的列车牵引能耗分别降低了53.87%和54.69%,两阶段优化过程分别用时258.90 s和0.08 s.Abstract: Focusing on the problem of train energy-efficient operation between multi-sections in urban rail transit, a two-stage optimization method was proposed by integrating the processes of energy-efficient driving optimization and timetable optimization. To obtain the optimum train driving strategy between multi-sections, each process was solved with global optimum solutions, respectively. First, to realize energy saving and time saving, a multi-objective energy-efficient driving model was constructed. Utilizing the multistage-based dynamic programming searching approach, a series of sub-stage models that contain multiple objects and constrains were constructed. The Pareto front of the optimum driving strategy was generated by inverse order method. Then, a timetable optimization model was constructed, in which the Pareto front of sections was applied, and the optimum running time allocation of multi-sections was searched by dynamic programming approach. A case study of Yizhuang urban rail line in Beijing was conducted to verify the effectiveness and efficiency of the two-stage optimization method. Compared with the flat-out running strategy, the optimization of two stages resulted in 53.87% and 54.69% energy saving improvement respectively; the calculation time of two process was 258.90 s and 0.08 s respectively.
-
Key words:
- subways /
- energy efficiency /
- optimization /
- train operation /
- dynamic programming
-
表 1 符号定义
Table 1. Symbol definition
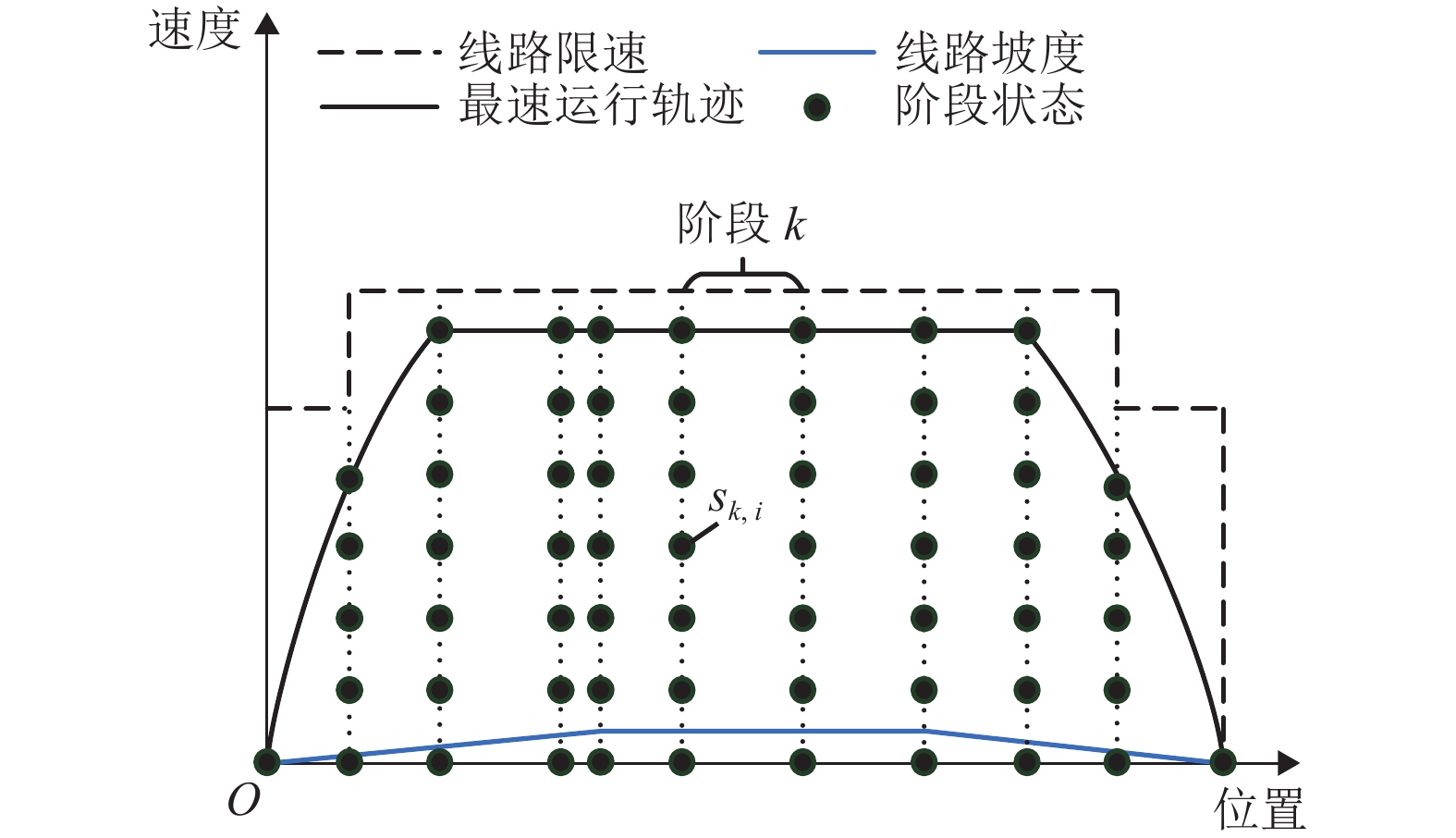
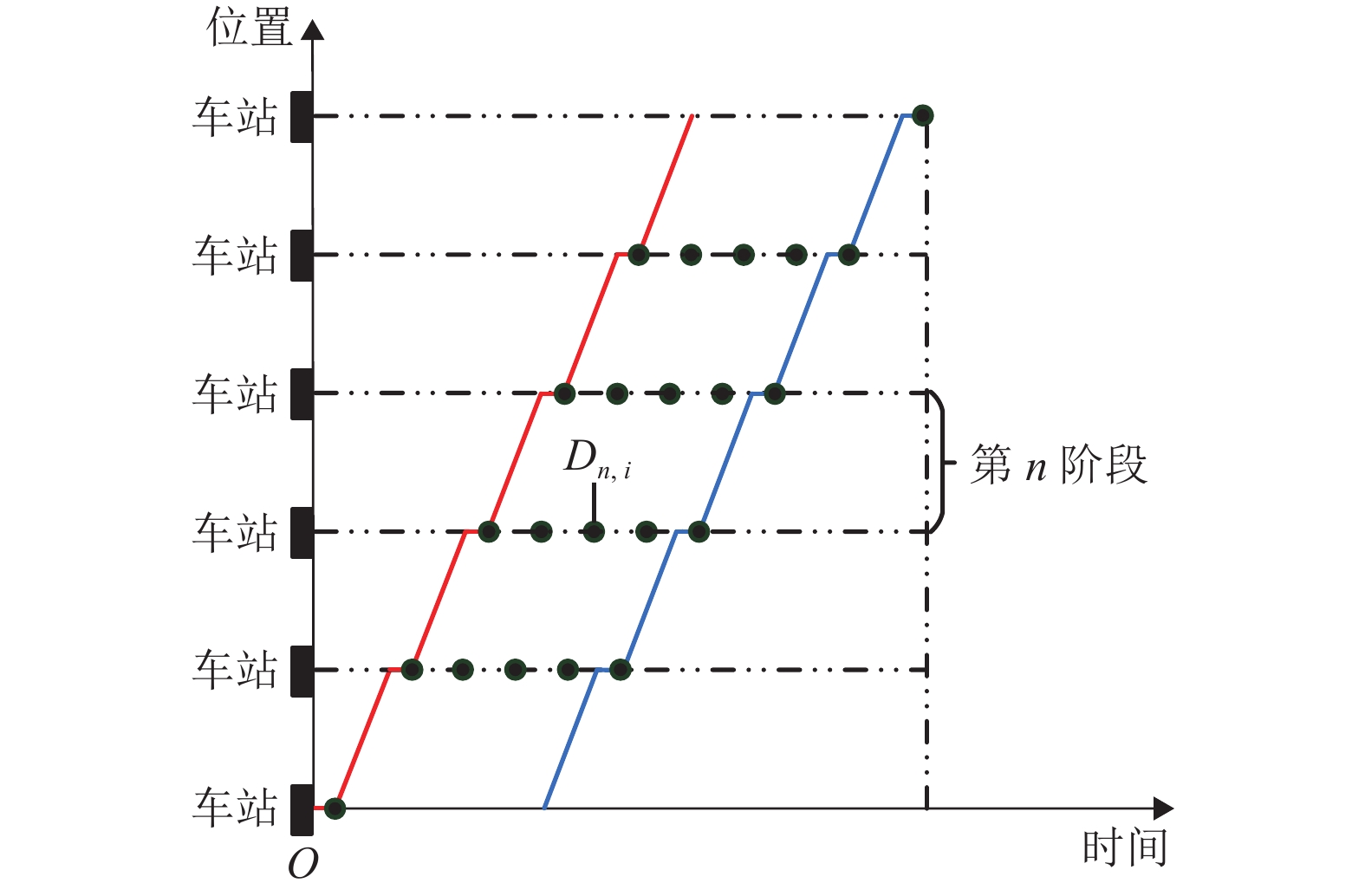
符号 定义 符号 定义 $x$ 列车运行位置 $P$ 列车最大牵引力 $v$ 列车运行速度 $Q$ 列车最大制动力 $t$ 列车运行时间 $\Delta v$ 速度离散间隔 $M$ 列车总质量 $\overline V \left( {{x_k}} \right)$ 位置${x_k}$处的列车最大运行速度 $\alpha $ 列车回转质量系数 $e\left( {{s_{k,i}},{u_k}} \right)$ ${s_{k,i}}$ 处施加 ${u_k}$后的列车牵引能耗 $r$ 列车运行阻力 $t\left( {{s_{k,i}},{u_k}} \right)$ ${s_{k,i}}$ 处施加${u_k}$ 后的列车运行时间 $a,b,c$ 戴维斯方程系数 $F\left( {{s_{k,i}},{u_k}} \right)$ ${s_{k,i}} $ 处施加${u_k}$ 后的列车状态转移方程 ${T_{{\rm{run }},n}}$ 第$n$站间的运行时间 $N$ 全线站间个数 $g$ 重力加速度 ${T_{{\rm{dwell }},n}}$ 第 n 站的停站时间 $\theta $ 线路坡度 ${T_{\min,n}}$ 第$n$站间的最小运行时间 $X$ 站间距离 ${E_{{\rm{total}}}}$ 列车全线总牵引能耗 ${V_{\rm{limit}}}$ 线路限速 ${T_{{\rm{total}}}}$ 列车全线总运行时间 $K$ 站间子阶段划分个数 $\Delta t$ 时间离散间隔 $U$ 列车运行操纵策略 $E_n^*\left( {{T_{{\rm{run }},n}}} \right)$ 第$n$站间条件${T_{{\rm{run }},n}}$下的最小牵引能耗 ${U^{\rm{*}}}$ 列车运行 Pareto 最优操纵策略 ${A_n}$、${B_n}$、${C_n}$ 第$n$站间 Pareto 前沿函数拟合参数 ${s_{k,i}}$ 节能驾驶优化第$k$子阶段第 $i$开始状态 $L$ 全线运行时间分配策略 $U\left( {{s_{k,i}}} \right)$ $ {s_{k,i}} $ 处的操纵子策略 ${L^{\rm{*}}}$ 全线运行时间最优分配策略 $U_w^*\left( {{s_{k,i}}} \right)$ $ {s_{k,i}} $ 处的第$w$个 Pareto 最优子策略 $E\left( L \right)$ 时间分配策略$L$的牵引能耗 $W\left( {{s_{k,i}}} \right)$ $ {s_{k,i}}$ 处的 Pareto 最优子策略个数 ${D_{n,i}}$ 时刻表优化第$n$子阶段第 $i$开始状态 $E\left( U \right)$ 操纵策略 $U$的牵引能耗 $F\left( {{D_{n,i}},{T_{{\rm{run }},n}}} \right)$ ${D_{n,i}}$ 运行${T_{{\rm{run }},n}}$时间后的状态转移方程 $T\left( U \right)$ 操纵策略 $U$的运行时间 $L\left( {{D_{n,i}}} \right)$ ${D_{n,i}}$处的时间分配子策略 ${u_k}$ 第$k$子阶段的控制工况 ${L^*}\left( {{D_{n,i}}} \right)$ ${D_{n,i}}$ 处的最优时间分配子策略 ${x_k}$ 第$k$子阶段的开始位置 $q\left( {{u_k}} \right)$ 工况${u_k}$下的列车制动力 $p\left( {{u_k}} \right)$ 工况 uk下的列车牵引力 表 2 不同控制工况下的牵引制动力输出
Table 2. Tractive and braking force under different control commands
控制工况 输出 最大牵引 $p\left( {{u_k}} \right) = P,\;\;q\left( {{u_k}} \right) = 0,$ 巡航 $p\left( {{u_k}} \right) = r,\;\;q\left( {{u_k}} \right) = 0,$ 惰行 $p\left( {{u_k}} \right) = 0,\;\;q\left( {{u_k}} \right) = 0,$ 最大制动 $p\left( {{u_k}} \right) = 0,\;\;q\left( {{u_k}} \right) = Q.$ 表 3 最优驾驶Pareto曲线拟合结果
Table 3. Fitting results of each Pareto front
区间 站间距离/m ${A_n}$ ${B_n}$ ${C_n}$ 最优操纵策略解数/个 求解时间/s 亦庄站—次渠站 1 334 2.68 × 1014 6.83 3.28 116 8.92 次渠站—次渠南 1 286 2.88 × 1013 6.54 12.13 113 8.19 次渠南—经海路 2 086 2.49 × 1014 6.49 21.97 214 23.24 经海路—同济南 2 265 2.57 × 1011 4.93 8.33 247 44.83 同济南—荣昌东 2 338 2.75 × 1010 4.38 7.00 256 35.69 荣昌东—荣京东 1 354 4.90 × 109 4.43 3.85 106 10.20 荣京东—万源街 1 280 3.55 × 1010 4.94 3.92 109 7.01 万源街—文化园 1 538 1.84 × 1011 5.15 6.44 141 11.11 文化园—亦庄桥 993 3.90 × 1012 6.33 5.22 98 4.25 亦庄桥—旧宫站 1 982 3.56 × 107 3.07 2.22 167 16.56 旧宫站—小红门 2 366 3.79 × 109 3.96 1.95 165 47.60 小红门—肖村站 1 275 2.20 × 1011 5.36 6.23 126 4.71 肖村站—宋家庄 2 631 1.72 × 1014 6.06 10.28 195 36.59 总计 258.90 表 4 列车节能运行两阶段优化结果
Table 4. Results of two-stage optimization method
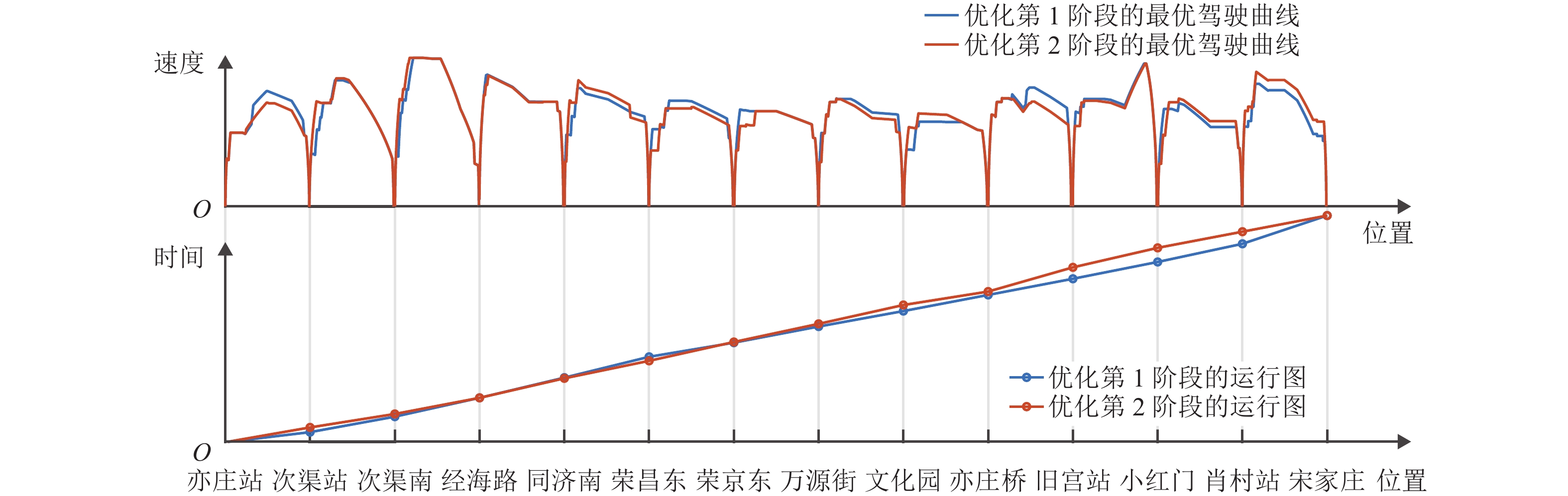
区间 优化第 1 阶段 优化第 2 阶段 最速牵引能耗/(kW•h) 时刻表运行时间/s 牵引能耗/
(kW•h)节能率/% 优化后运行时间/s 牵引能耗/
(kW•h)节能率/% 节能效果
对比/%亦庄站—次渠站 18.60 105 7.59 59.21 112 6.05 67.46 8.25 次渠站—次渠南 29.42 102 14.23 51.65 99 14.68 50.11 −1.54 次渠南—经海路 38.07 140 24.92 34.55 136 25.53 32.95 −1.60 经海路—同济南 22.79 150 13.17 42.20 149 13.33 41.49 −0.71 同济南—荣昌东 28.51 164 12.36 56.63 159 13.14 53.90 −2.73 荣昌东—荣京东 22.63 104 9.50 58.03 111 8.08 64.29 6.26 荣京东—万源街 21.59 103 7.98 63.02 106 7.45 65.51 2.49 万源街—文化园 24.22 114 11.26 53.52 119 10.30 57.46 3.94 文化园—亦庄桥 21.35 90 6.86 67.86 86 7.41 65.28 −2.57 亦庄桥—旧宫站 25.95 135 12.68 51.15 147 10.27 60.41 9.26 旧宫站—小红门 21.64 157 9.54 55.90 161 8.82 59.23 3.33 小红门—肖村站 23.35 108 9.07 61.17 105 9.53 59.19 −1.98 肖村站—宋家庄 32.07 190 12.93 59.67 172 15.13 52.82 −6.85 总计 330.19 1662 152.05 53.87 1662 149.76 54.69 0.82 -
中国轨道交通协会. 城市轨道交通2019年度统计和分析报告[EB/OL]. (2020-05-18)[2020-07-22]. http://www.camet.org.cn/tjxx/5133. GONZALEZ-GIL, PALACIN R, BATTY P, et al. A systems approach to reduce urban rail energy consumption[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2014, 80: 509-524. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2014.01.060 ICHIKAWA K. Application of optimization theory for bounded state variable problems to the operation of train[J]. Bulletin of JSME, 1968, 11(47): 857-865. doi: 10.1299/jsme1958.11.857 HOWLETT P G, PUDNEY P J, VU X. Local energy minimization in optimal train control[J]. Automatica, 2009, 45(11): 2692-2698. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.07.028 LIU R, GOLOVITCHER I M. Energy-efficient operation of rail vehicles[J]. Transportation Research Part A:Policy and Practice, 2003, 37(10): 917-932. doi: 10.1016/j.tra.2003.07.001 KHMELNITSKY E. On an optimal control problem of train operation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2000, 45(7): 1257-1266. doi: 10.1109/9.867018 CHANG C S, SIM S S. Optimising train movements through coast control using genetic algorithms[J]. IEE Proceedings-Electric Power Applications, 1997, 144(1): 65-73. doi: 10.1049/ip-epa:19970797 卢启衡,冯晓云,王青元. 基于遗传算法的追踪列车节能优化[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2012,47(2): 265-270.LU Qiheng, FENG Xiaoyun, WANG Qingyuan. Energy-saving optimal control of following trains based on genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2012, 47(2): 265-270. 李诚,王小敏. 基于粒子群优化的ATO控制策略[J]. 铁道学报,2017,39(3): 53-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2017.03.010LI Cheng, WANG Xiaomin. An ATO control strategy based on particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2017, 39(3): 53-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2017.03.010 余进,何正友,钱清泉. 基于微粒群算法的多目标列车运行过程优化[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2010,45(1): 70-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2010.01.012YU Jin, HE Zhengyou, QIAN Qingquan. Multi-objective train operation optimization based on particle swarm algorithm[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010, 45(1): 70-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2010.01.012 MIYATAKE M, KO H. Optimization of train speed profile for minimum energy consumption[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 2010, 5(3): 263-269. doi: 10.1002/tee.20528 LU Shaofeng, HILLMANSEN S, HO T K, et al. Single-train trajectory optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2013, 14(2): 743-750. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2012.2234118 刘炜,王栋,李群湛,等. 基于时间逼近搜索算法的城轨列车运行节能优化研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(5): 918-924. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.014LIU Wei, WANG Dong, LI Qunzhan, et al. A novel time-approaching search algorithm for energy-saving optimization of urban rail train[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5): 918-924. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.014 唐海川,朱金陵,王青元,等. 一种可在线调整的列车正点运行节能操纵控制算法[J]. 中国铁道科学,2013,34(4): 89-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2013.04.15TANG Haichuan, ZHU Jinling, WANG Qingyuan, et al. An on-line adjustable control algorithm for on-time and energy saving operations of trains[J]. China Railway Science, 2013, 34(4): 89-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2013.04.15 ALBRECHT T, OETTICH S. A new integrated approach to dynamic schedule synchronization and energy-saving train control[C]//Computers in Railways. Southampton: WIT Press, 2002: 847-856. 丁勇,刘海东,栢赟,等. 地铁列车节能运行的两阶段优化模型算法研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,2011,11(1): 96-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2011.01.016DING Yong, LIU Haidong, BAI Yun, et al. A two-level optimization model and algorithm for energy-efficient urban train operation[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2011, 11(1): 96-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2011.01.016 SU Shuai, LI Xiang, TANG Tao, et al. A subway train timetable optimization approach based on energy-efficient operation strategy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2013, 14(2): 883-893. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2013.2244885 张惠茹,贾利民,王莉,等. 面向列车节能控制的时刻表优化[J]. 铁道学报,2019,41(2): 8-15.ZHANG Huiru, JIA Limin, WANG Li, et al. Study of timetable optimization based on train energy saving control[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2019, 41(2): 8-15. SICRE C, CUCALAAP, FERNANDEZ A, et al. A method to optimise train energy consumption combining manual energy efficient driving and scheduling[J]. WIT Transactions on the Built Environment, 2010, 114: 549-560. CUCALA A P, FERNANDEZ A, SICRE C, et al. Fuzzy optimal schedule of high speed train operation to minimize energy consumption with uncertain delays and driver's behavioral response[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2012, 25(8): 1548-1557. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2012.02.006 黄友能,宫少丰,曹源,等. 基于粒子群算法的城轨列车节能驾驶优化模型[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2016,16(2): 118-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2016.02.014HUANG Youneng, GONG Shaofeng, CAO Yuan, et al. Optimization model of energy-efficient driving for train in urban rail transit based on particle swarm algorithm[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2016, 16(2): 118-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2016.02.014 陈荣武,诸昌钤,刘莉. 基于CBTC的城市轨道交通列车能耗算法及仿真[J]. 计算机应用研究,2011,28(6): 2126-2129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2011.06.034CHEN Rongwu, ZHU Changqian, LIU Li. CBTC based urban rail transit train energy consumption algorithm and simulation[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2011, 28(6): 2126-2129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2011.06.034 杨欣. 面向节能的城市轨道交通列车运行图优化研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2016. HUANG Youneng, YANG Chen, GONG Shaofeng. Energy optimization for train operation based on an improved ant colony optimization methodology[J]. Energies, 2016, 9(8): 626. doi: 10.3390/en9080626 -




 下载:
下载: