Steel Corrosion Monitoring Based on Partial Modulus of Magnetic Gradient Tensor
-
摘要:
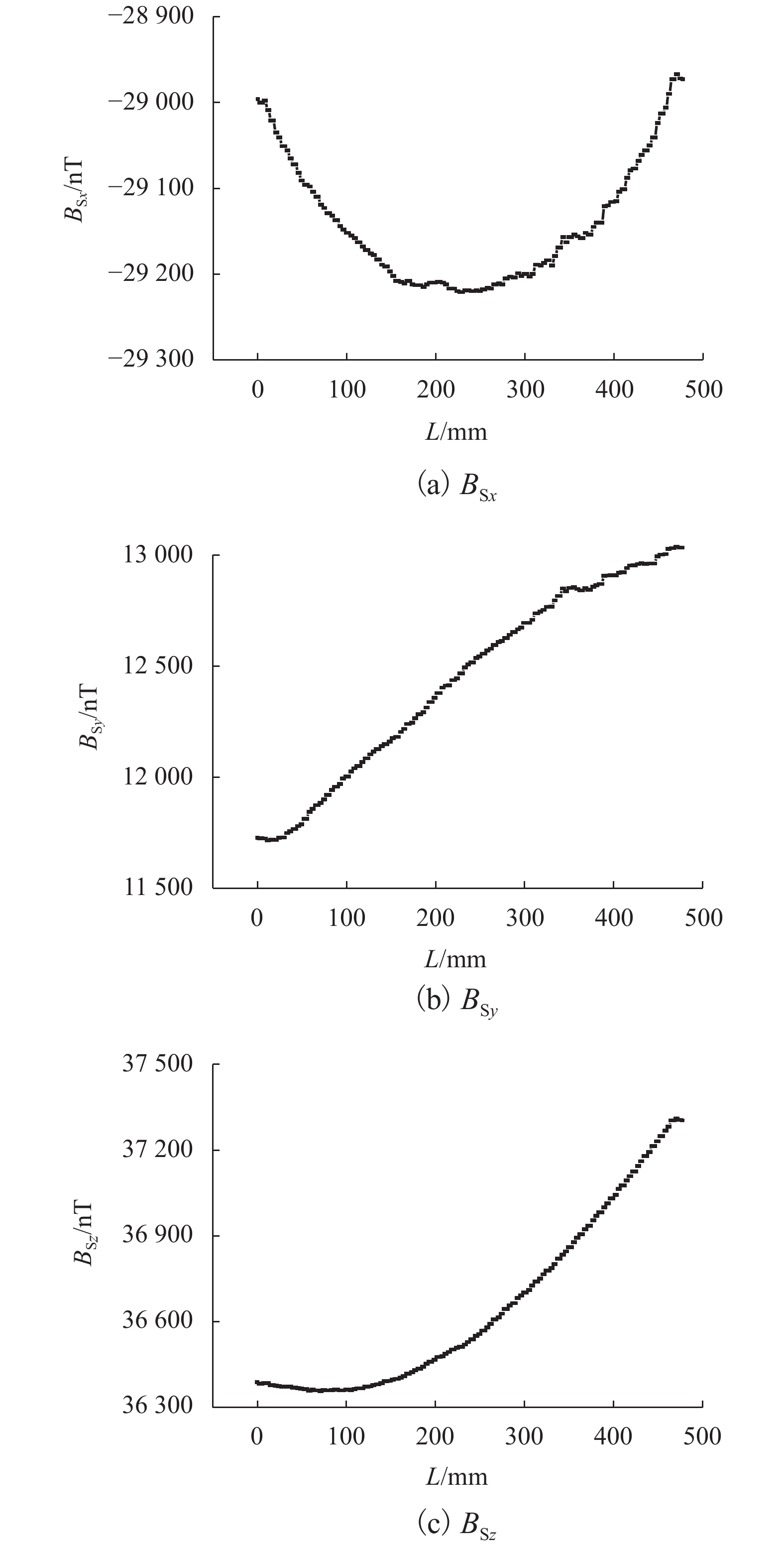
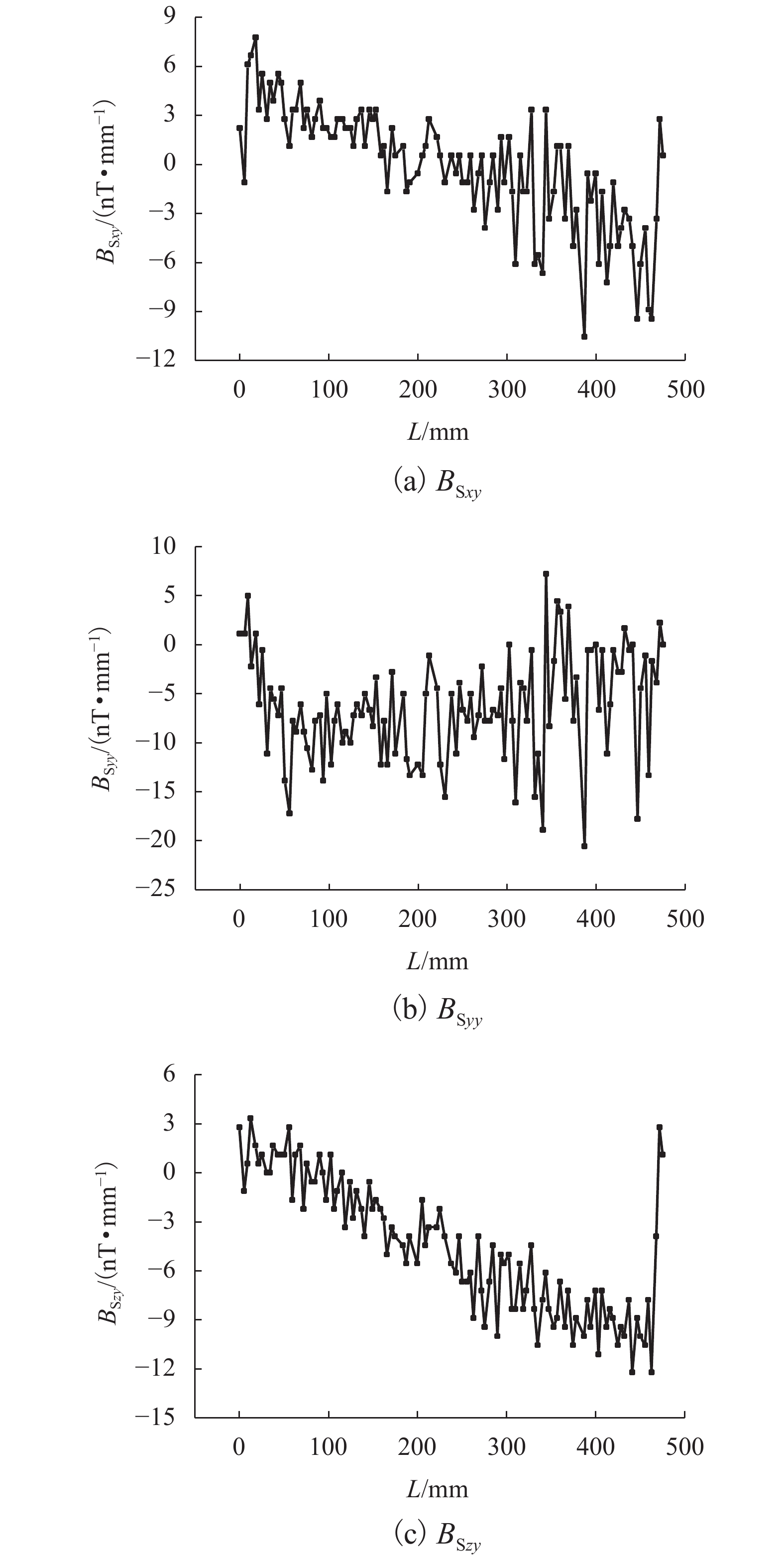
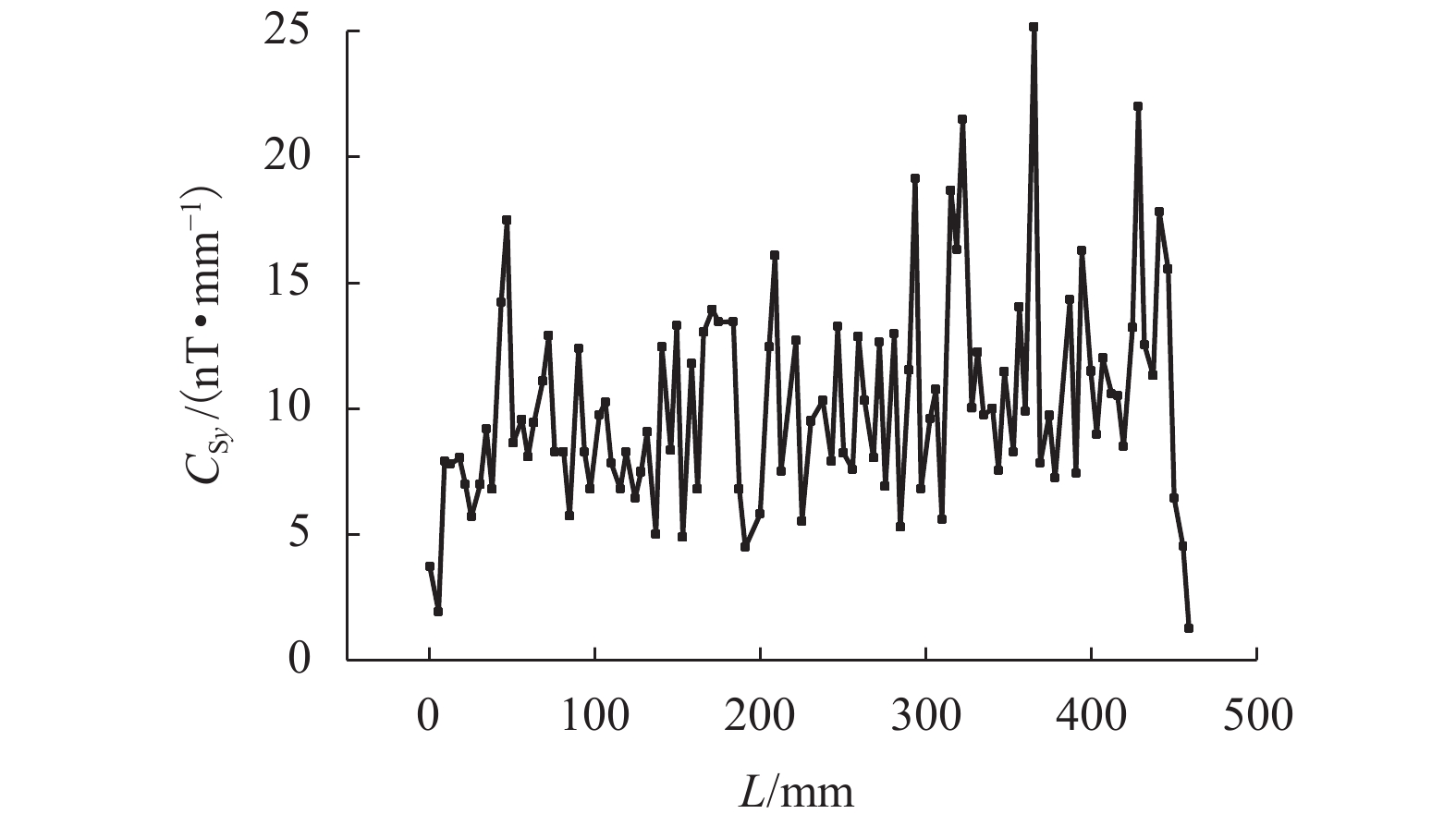
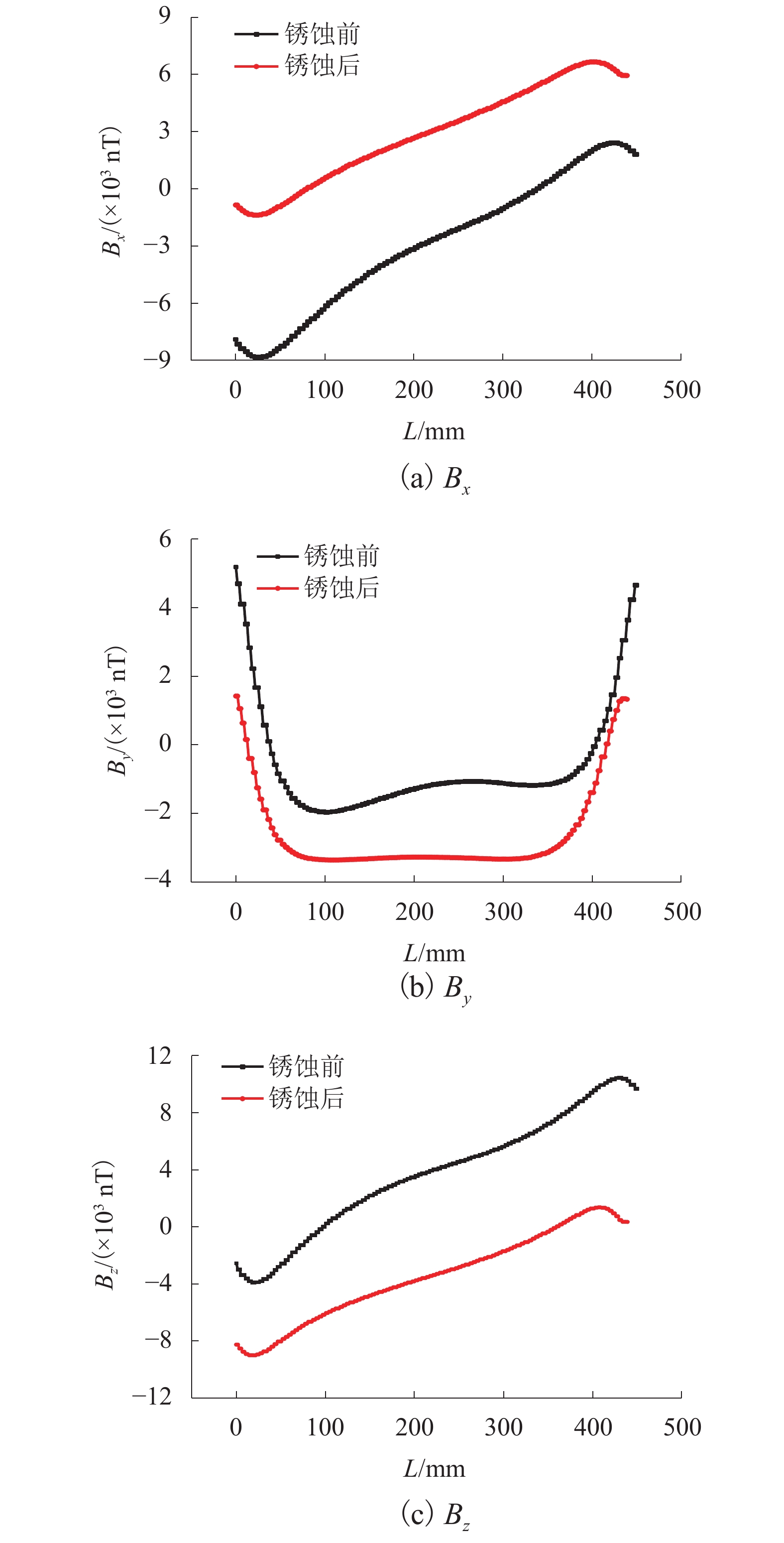
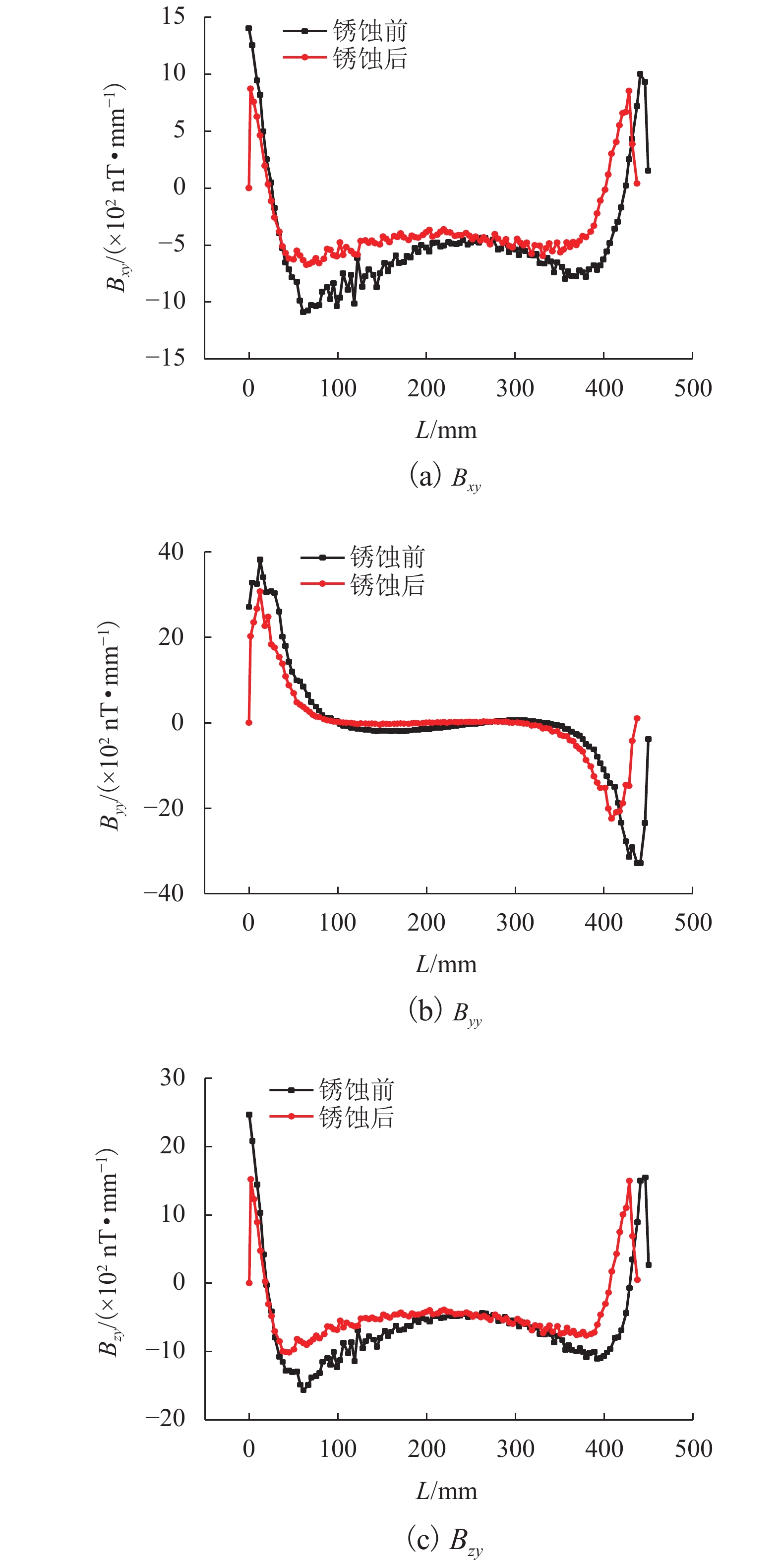
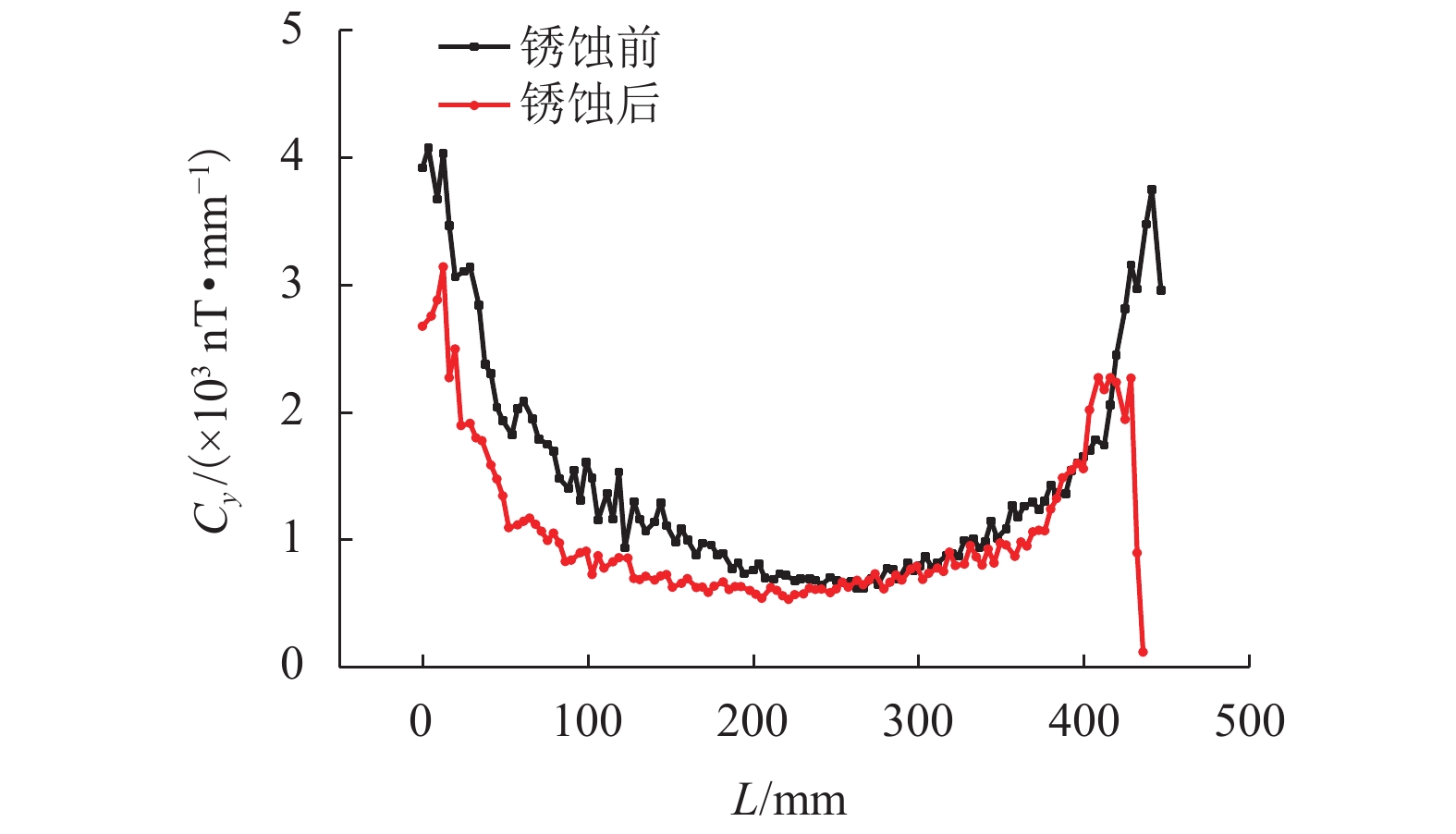
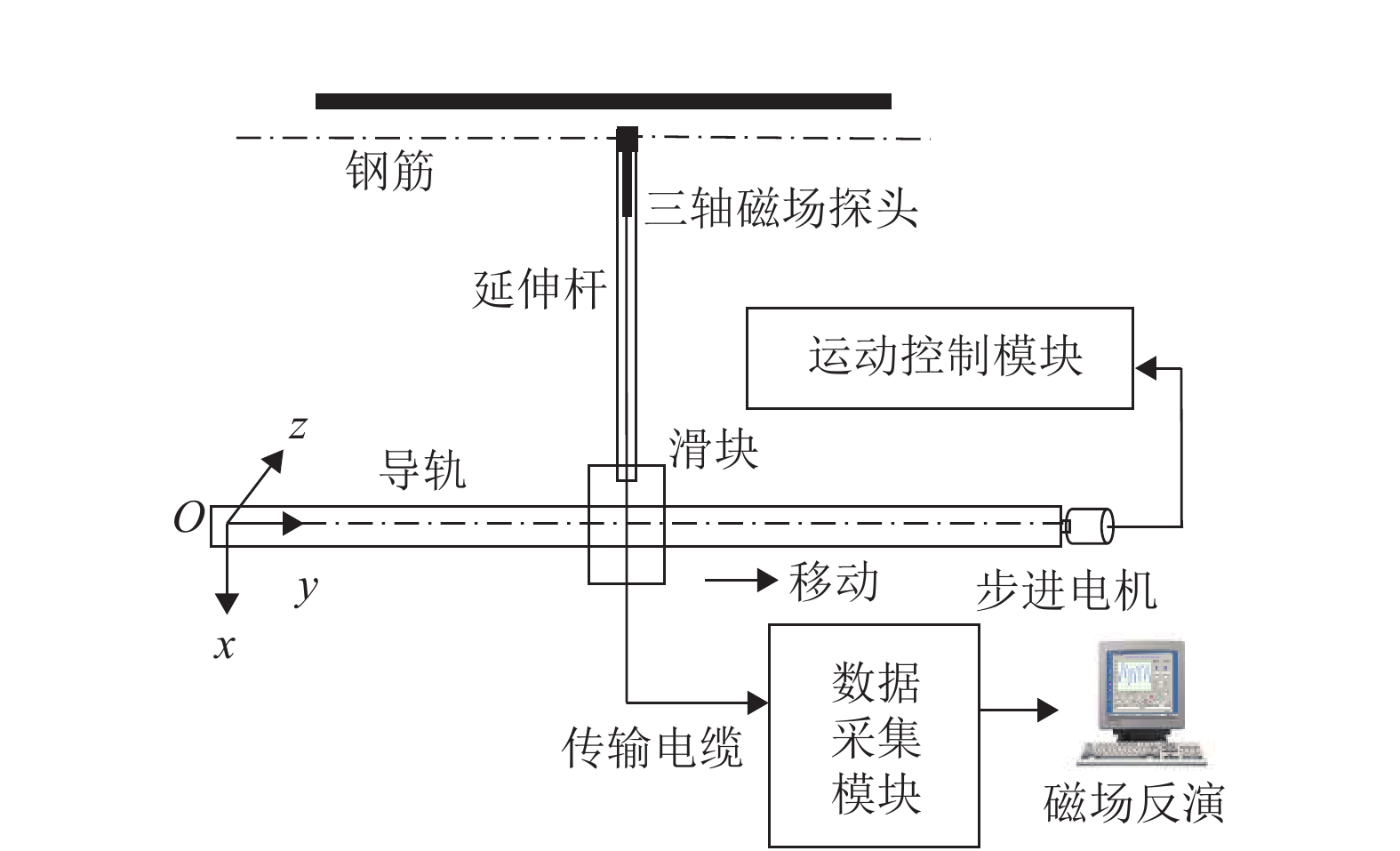
为研究钢筋混凝土中钢筋锈蚀的无损及定量监测方法,分析地球背景磁场和环境干扰磁场的影响,探讨钢筋的锈蚀率与磁场梯度张量局部模量的理论公式. 通过8根钢筋进行通电加速锈蚀试验模拟钢筋不同程度的锈蚀. 研制钢筋锈蚀监测系统,测量锈蚀前后钢筋的磁感应强度,采用磁场梯度张量局部模量反演钢筋的锈蚀率. 试验结果表明:在钢筋锈蚀后测试的磁感应强度曲线发生非等距离的偏移,磁感应强度绝对值相比锈蚀前有增大也有降低,没有一致性的规律;在锈蚀后钢筋磁场梯度绝对值及局部模量的平均值减小;在钢筋锈蚀的磁场监测中,钢筋自身的磁场梯度及局部模量远远大于环境磁场,环境磁场的梯度及其局部模量可忽略不计;8根试件的计算锈蚀率与试验中实际失重率的最小误差为0.22%,最大误差为9.40%,误差的平均值为3.92%,误差的标准差为3.32%.
Abstract:In order to find a nondestructive and quantitative monitoring method for steel corrosion in reinforced concrete, theoretical formulas of the partial modulus and corrosion rate of rebar are derived with consideration of the influence of the Earth’s background magnetic field and environmental interference magnetic field. Accelerated corrosion tests were performed on 8 steel bars through electrification to obtain specimens with different degrees of corrosion. A rebar corrosion monitoring system was then developed to measure the magnetic field intensity of rebar before and after corrosion. Finally, the partial modulus of the magnetic gradient tensor is used to calculate the corrosion rate of the rebar. Results show that the magnetic field intensity curve of the rebar is generally shifted after corrosion, but the absolute value after corrosion may increase or decrease compared with that before corrosion, without consistency. The absolute value of the magnetic gradient and the average value of the partial modulus of the steel bar after corrosion are less than their counterparts before corrosion. In the magnetic monitoring of rebar corrosion, the magnetic gradient and partial modulus of the rebar are much larger than those of the environmental magnetic field, and therefore the gradient of the environmental magnetic field and its partial modulus are negligible. The minimum error between calculated and measured corrosion rates of the 8 specimens is 0.22%, while the maximum error is 9.40%, and the average error is 3.92%, with a standard deviation of 3.32%.
-
Key words:
- reinforced concrete /
- rebar /
- corrosion monitoring /
- magnetic gradient /
- partial modulus
-
表 1 试件设计
Table 1. Specimen design
编号 D0/mm l0/m m0/g t/d 1 9.54 503 278.74 4 2 9.43 481 261.81 4 3 9.43 484 265.83 4 4 9.39 485 266.93 4 5 9.48 504 275.56 4 6 9.44 495 272.38 4 7 9.72 500 277.48 5 8 9.60 496 274.91 5 表 2 钢筋锈蚀前后对比
Table 2. Comparison before and after corrosion
编号 D0/mm Dc/mm l0/mm lc/mm m0/g mc/g ζ/% 1 9.54 7.90 503 498 278.74 201.70 27.64 2 9.43 8.82 481 478 261.81 237.87 9.14 3 9.43 7.99 484 480 265.83 181.57 31.70 4 9.39 9.19 485 481 266.93 244.68 8.34 5 9.48 8.85 504 502 275.56 231.47 16.00 6 9.44 9.08 495 492 272.38 249.73 8.32 7 9.72 8.88 500 499 277.48 237.56 14.39 8 9.60 9.08 496 491 274.91 249.26 9.33 表 3 环境磁场参数绝对值的平均值
Table 3. Average absolute values of environmental magnetic
$E\left( {\left| { {B_{{\rm{S} }x} } } \right|} \right)$/nT $E\left( {| { {B_{{\rm{S} }y} } } |} \right)$/nT $E\left( {\left| { {B_{{\rm{S} }{\textit{z}}} } } \right|} \right)$/nT $E\left( {| { {B_{{\rm{S} }xy} } } |} \right)$/(nT•mm−1) $E\left( {| { {B_{{\rm{S}}yy} } }|} \right)$/(nT•mm−1) $E\left( {| { {B_{{\rm{S}}{\textit{z}}y} } } |} \right)$/(nT•mm−1) $E\left( { { {C_{{\rm{S} }y}} } } \right)$/(nT•mm−1) 29142 12439 36654 2.92 6.88 5.01 10.14 表 4 1号钢筋锈蚀前后磁场参数的平均值对比
Table 4. Comparison of average values of magnetic parameters before and after corrosion of specimen No. 1
项目 E(|Bx|)/nT E(|By|)/nT E(|Bz|)/nT E(|Bxy|)/(nT•mm−1) E(|Byy|)/(nT•mm−1) E(|Bzy|)/(nT•mm−1) E(Cy)/(nT•mm−1) 锈蚀前 36684.76 14767.02 47463.04 647.70 709.75 832.91 1464.17 锈蚀后 32380.07 27619.37 38090.48 468.86 489.32 615.00 1062.76 锈蚀后/
锈蚀前0.882 7 1.870 3 0.822 5 0.723 9 0.689 4 0.738 4 0.725 8 Table 5. Comparison of calculated and measured corrosion rates
试件编号 η/% ζ/% 误差/% 1 27.42 27.64 0.22 2 12.46 9.14 3.32 3 41.10 31.70 9.40 4 16.00 8.34 7.66 5 18.75 16.00 2.75 6 9.02 8.32 0.70 7 8.83 14.39 5.56 8 11.11 9.33 1.78 -
[1] 苏成光,刘丹,赵坪锐,等. 道床板钢筋锈蚀的细观力学影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(2): 273-281, 289.SU Chengguang, LIU Dan, ZHAO Pingrui, et al. Meso-mechanical effect of track slab rebar corrosion[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(2): 273-281, 289. [2] DOUBOV A A. Screening of weld quality using the magnetic metal memory effect[J]. Weld World, 1998, 41(3): 196-199. [3] DOUBOV A A. The express technique of welded joints examination with use of metal magnetic memory[J]. NDT & E International, 2000, 33(6): 351-362. [4] FERNANDES B, TITUS M, NIMS D K, et al. Field test of magnetic methods for corrosion detection in prestressing strands in adjacent box-beam bridges[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2012, 17(6): 984-988. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000379 [5] 陈海龙,王长龙,朱红运. 基于磁梯度张量的金属磁记忆检测方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2016,37(3): 602-609. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2016.03.017CHEN Hailong, WANG Changlong, ZHU Hongyun. Metal magnetic memory test method based on magnetic gradient tensor[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2016, 37(3): 602-609. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2016.03.017 [6] 马惠香,周建庭,赵瑞强,等. 基于金属磁记忆技术的钢筋应力无损检测试验[J]. 江苏大学学报(自然科学版),2018,39(3): 106-111.MA Huixiang, ZHOU Jianting, ZHAO Ruiqiang, et al. Non-destructive testing of steel bar stress based on metal magnetic memory technology[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 39(3): 106-111. [7] WIEGERT R, OESCHGER J. Generalized magnetic gradient contraction based method for detection, localization and discrimination of underwater mines and unexploded ordnance[C]//Proceedings of Oceans 2005 MTS/IEEE. Washington D. C.: IEEE, 2005: 1-8 [8] WIEGERT R F, PURPURA J W. Magnetic scalar triangulation and ranging system for autonomous underwater vehicle based detection, localization and classification of magnetic mines[C]//Oceans. Kobe: IEEE, 2005: 890-896. [9] LIU R, WANG H. Detection and localization of improvised explosive devices based on 3-axis magnetic sensor array system[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2010, 7: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2010.11.001 [10] SCHMIDT P W, CLARK D A. The magnetic gradient tensor:its properties and uses in source characterization[J]. Leading Edge, 2006, 25(1): 75-78. doi: 10.1190/1.2164759 [11] WIEGERT R, LEE K, OESCHGER J. Improved magnetic STAR methods for real-time, point-by-point localization of unexploded ordnance and buried mines[C]//Oceans. Quebec City: IEEE, 2008: 1-7. [12] WIEGERT R F. Magnetic STAR technology for real-time localization and classification of unexploded ordnance and buried mines[C]//Detection and Sensing of Mines, Explosive Objects, and Obscured Targets XIV. Orlando: [s.n.], 2009: 73031U.1-73031U.19. [13] 江胜华,申宇,褚玉程. 基于磁偶极子的磁场梯度张量缩并的试验验证及相关参数确定[J]. 中国惯性技术学报,2015,23(1): 103-106,114.JIANG Shenghua, SHEN Yu, CHU Yucheng. Experimental verification and related parameter’s determination for magnetic gradient tensor contraction using magnetic dipole[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2015, 23(1): 103-106,114. [14] 江胜华,侯建国,何英明. 基于磁偶极子的磁场梯度张量局部缩并及试验验证[J]. 中国惯性技术学报,2017,25(4): 473-477.JIANG Shenghua, HOU Jianguo, HE Yingming, et al. Theoretical study and experimental verification of magnetic gradient tensor partial contraction using magnetic dipole[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2017, 25(4): 473-477. [15] 江胜华,武立群,侯建国,等. 基于磁性标签石块的桥墩局部冲刷监测方法[J]. 重庆大学学报,2016,39(1): 88-97.JIANG Shenghua, WU Liqun, HOU Jianguo, et al. Bridge local scour monitoring using magnetic label rock[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2016, 39(1): 88-97. [16] 江胜华,周智,欧进萍. 基于磁测的边坡深部大变形监测方法[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(10): 3033-3038.JIANG Shenghua, ZHOU Zhi, OU Jinping. Slope internal large deformation monitoring using magnetic survey[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(10): 3033-3038. [17] 江胜华,周智,欧进萍. 基于磁场梯度定位的边坡变形监测原理[J]. 岩土工程学报,2012,34(10): 1944-1949.JIANG Shenghua, ZHOU Zhi, OU Jinping. Slope deformation monitoring principle based on magnetic gradient tensor[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(10): 1944-1949. [18] 干伟忠,金伟良,高明赞. 混凝土中钢筋加速锈蚀试验适用性研究[J]. 建筑结构学报,2011,32(2): 41-47.GAN Weizhong, JIN Weiliang, GAO Mingzan. Applicability study on accelerated corrosion methods of Steel bars in concrete structure[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2011, 32(2): 41-47. [19] 张伟平, 王晓刚, 顾祥林等. 加速锈蚀与自然锈蚀钢筋混凝土梁受力性能比较分析[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 36(增刊Ⅱ): 139-144.ZHANG Weiping, WANG Xiaogang, GU Xianglin, et al. Comparative study on structural performance of reinforced concrete beams subjected to natural corrosion and accelerated corrosion[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 36(SⅡ): 139-144. -




 下载:
下载: