Automatic Traffic State Recognition from Road Videos Based on 3D Convolution Neural Network
-
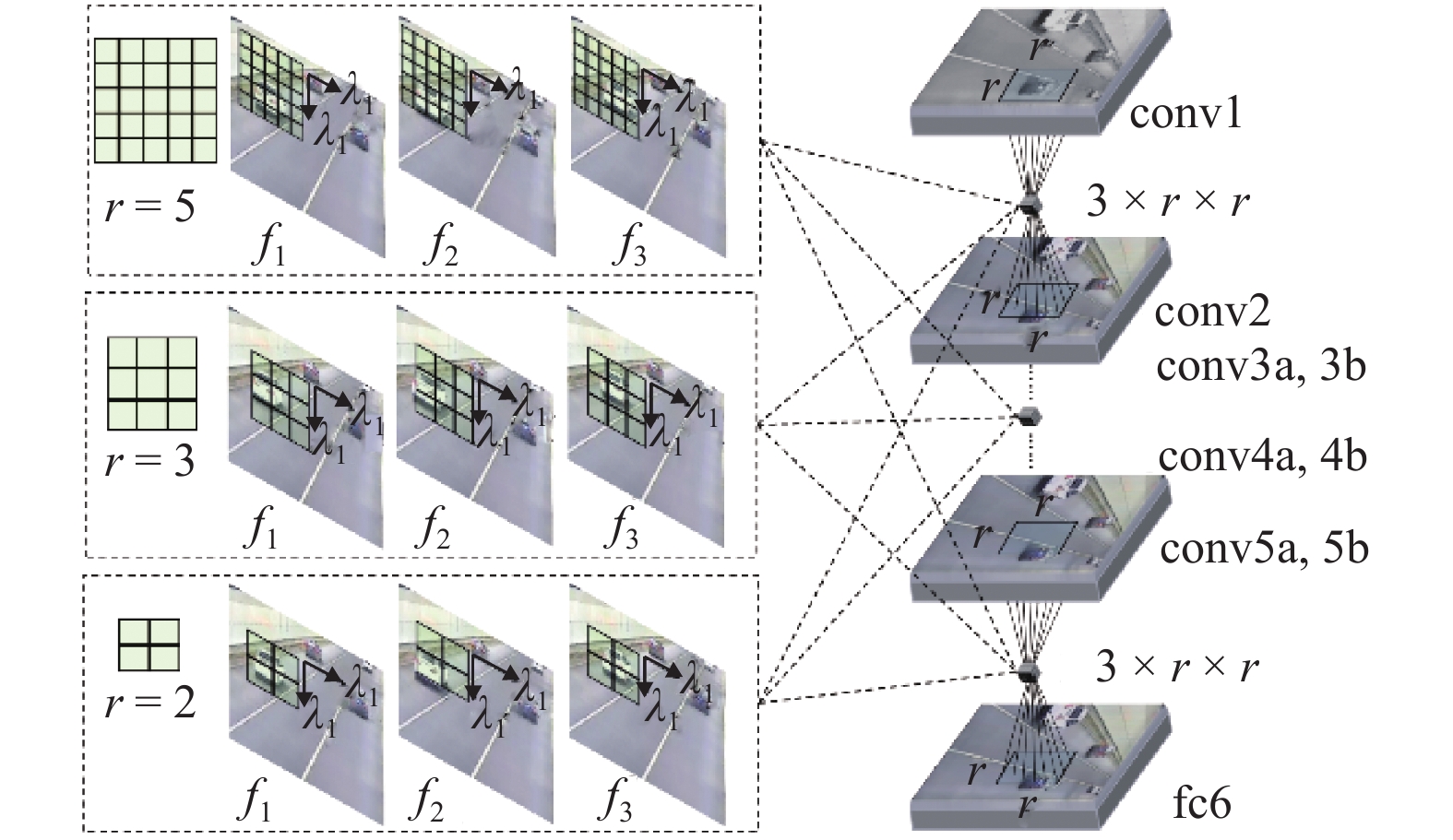
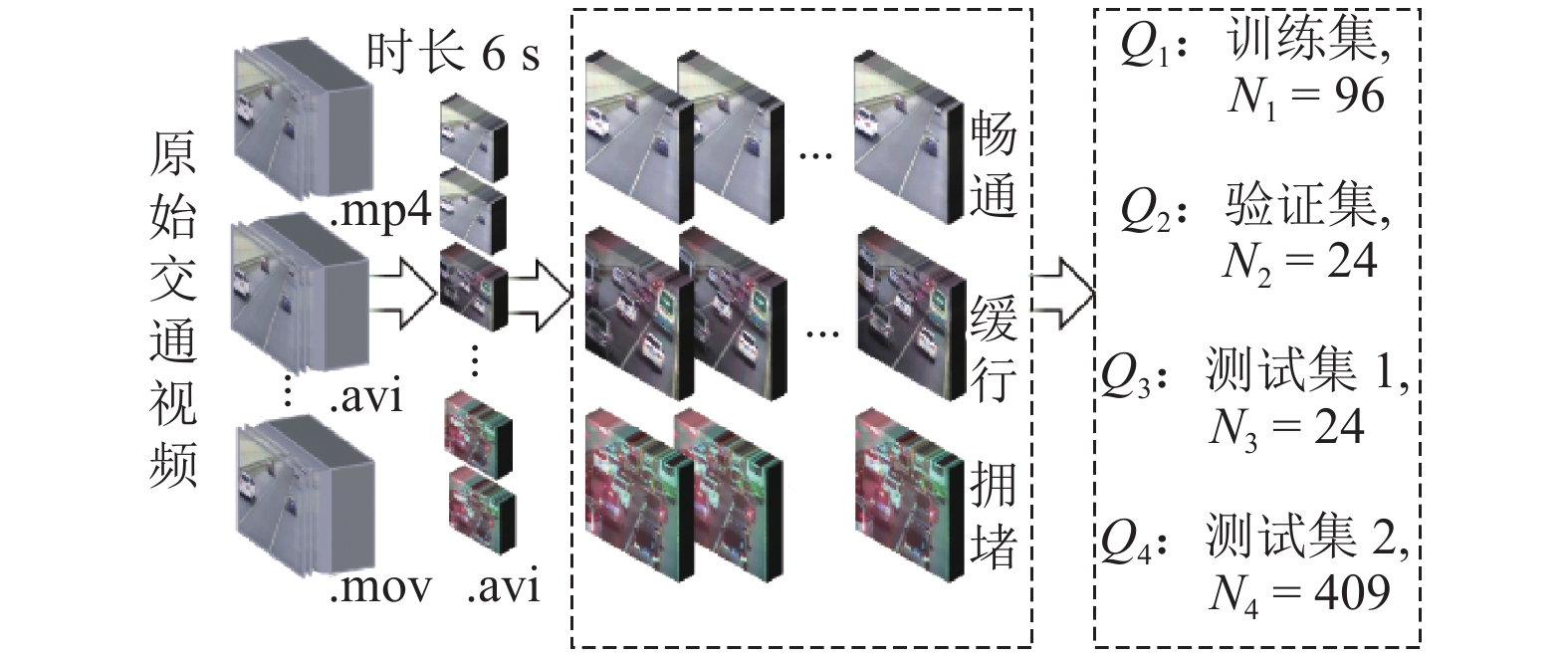
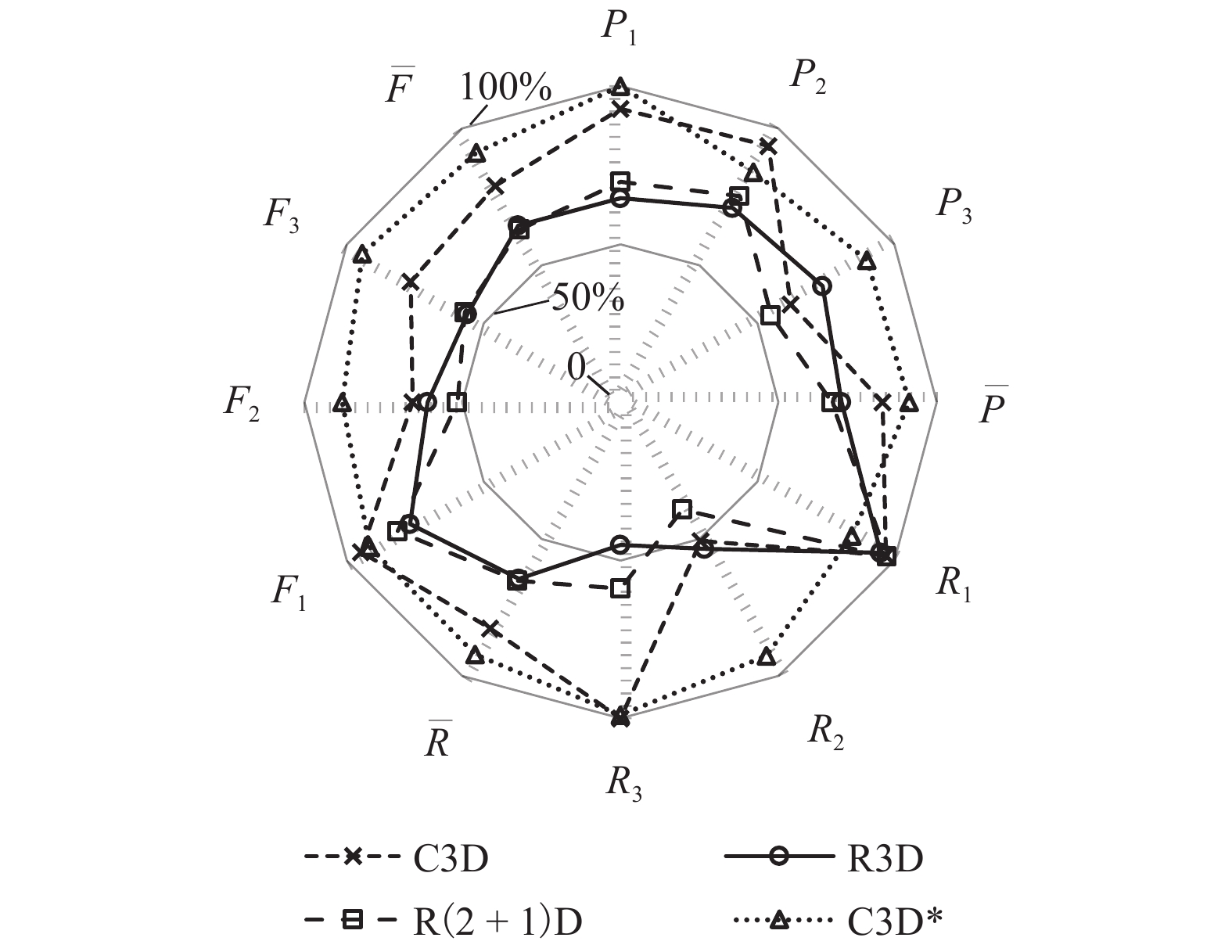
摘要: 为了从视频直接有效地提取交通信息,提出了基于三维卷积神经网络 (3D convolutional neural networks,3D CNN)的交通状态识别方法.首先,以C3D (convolutional 3D)深度卷积网络为3D CNN原型,对卷积层数量与位置、平面卷积尺寸及三维卷积深度进行优化调整,形成了37个备选模型;其次,建立了视频数据集,对备选模型进行系统的训练测试,提出了交通状态识别模型C3D*;然后,对C3D* 和现有三维卷积网络模型进行视频交通状态识别测试分析;最后,对比测试了C3D* 及常用二维卷积网络的交通状态识别效果. 对比结果显示:针对视频交通状态识别,C3D* 的F均值为91.32%,比C3D、R3D (region convolutional 3D network)、R (2+1) D (resnets adopting 2D spatial convolution and a 1D temporal convolution)分别高12.24%、26.72%、28.02%;与LeNet、AlexNet、GoogleNet、VGG16的图像识别结果相比,C3D* 的F均值分别高32.61%、69.91%、50.11%、69.17%.Abstract: In order to directlyextract effective traffic information from videos, a traffic state recognition method based on 3D CNN (3D convolutional neural networks)was put forward. Firstly, with the deep convolutional network C3D (convolutional 3D) as 3D CNN prototype, the number and position of convolutional layers, convolutional kernelsize and 3D convolutional depth were optimized and adjusted; thus 37 candidate models were built. Secondly, video datasets were established to systematically train and test candidate models, and a traffic state recognition model C3D* was proposed. Then, tests and analysis were conducted on traffic state recognition results of C3D* and existing 3D convolutional models. At last, traffic recognition results were compared between C3D* and commonly used 2D convolutional networks. The results show that for video traffic state recognition, the average F value of C3D* reaches 91.32%, which is 12.24%, 26.72% and 28.02% higher than that of C3D, R3D (region convolutional 3D network) and R(2+1)D (resnets adopting 2D spatial convolution and a 1D temporal convolution), respectively, demonstrating that the proposed model C3D* is more accurate and effective. Compared with image recognition results from LeNet, AlexNet, GoogleNet and VGG16, the average C3D* is 32.61%, 69.91%, 50.11% and 69.17% higher respectively, proving that 3D video convolution F value of outperforms 2D image convolution in terms of traffic status recognition.
-
Key words:
- intelligent transportation /
- traffic state recognition /
- 3D convolution /
- road videos /
- deep learning
-
表 1 既有三维卷积模型测试指标
Table 1. Test indexes of existing 3D convolutional models
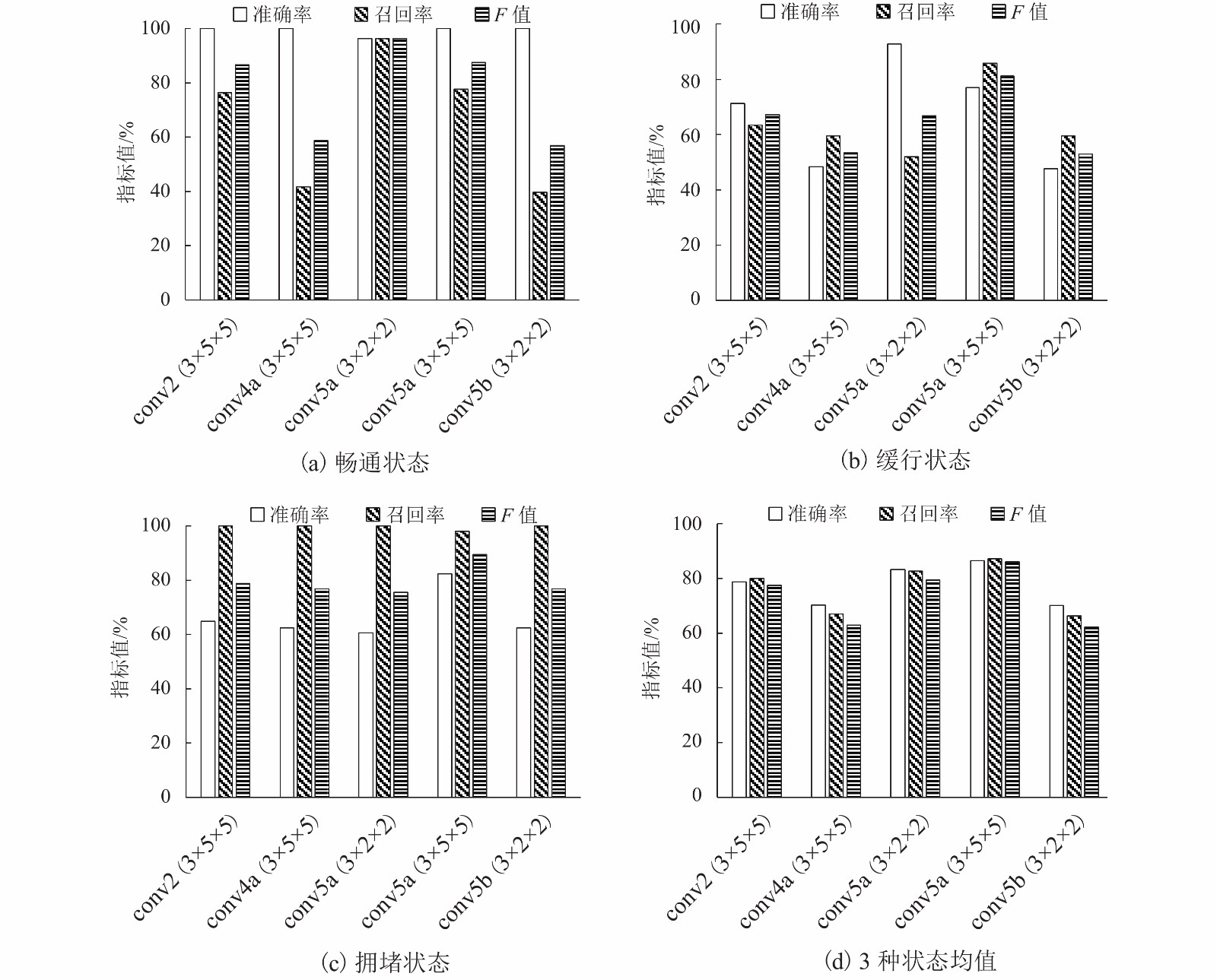
% 交通状态 C3D R3D R (2+1) D 准确率 召回率 $F$ 值 准确率 召回率 $F$ 值 准确率 召回率 $F$ 值 畅通 92.86 96.89 94.83 64.56 95.03 76.88 69.78 97.52 81.35 缓行 93.75 50.68 65.79 71.17 53.38 61.00 75.32 39.19 51.56 拥堵 62.11 100.00 76.63 73.77 45.00 55.90 55.14 59.00 57.00 均值 82.91 82.52 79.08 69.83 64.47 64.60 66.75 65.23 63.30 表 2 C3D删减conv4b或conv5b后识别结果
Table 2. C3D recognition results without conv4b or conv5b
% 交通状态 C3D 删减 conv4b 后 C3D 删减 conv5b 后 准确率 召回率 F 值 准确率 召回率 F 值 畅通 98.73 96.89 97.81 100.00 59.01 74.22 缓行 94.74 60.81 74.07 64.74 83.11 72.78 拥堵 64.10 100.00 78.13 79.84 99.00 88.39 均值 85.86 85.90 83.33 81.53 80.37 78.46 表 3 视频检测样例
Table 3. Samples of video detection results
模型 


C3D 畅通,Pr=0.57 拥堵,Pr=1.00 拥堵,Pr=1.00 R3D 缓行,Pr=0.45 拥堵,Pr=0.41 拥堵,Pr=0.64 R(2+1)D 缓行,Pr=0.49 缓行,Pr=0.46 拥堵,Pr=0.97 C3D* 畅通,Pr=0.99 缓行,Pr=0.97 拥堵,Pr=1.00 真实状态 畅通 缓行 拥堵 表 4 C3D*指标提升(相对于C3D)
Table 4. Index increase of C3D* compared to C3D
% 交通状态 准确率 召回率 F 值 畅通 7.14 −12.42 −3.25 缓行 −9.70 41.89 22.31 拥堵 27.89 −1.00 17.66 均值 8.44 9.49 12.24 表 5 C3D*与二维卷积模型对比
Table 5. Comparison between C3D* and 2-d convolutional models
% 交通状态 Lenet Alxnet Googlenet VGG16 C3D* 准确率 召回率 F 值 准确率 召回率 F 值 准确率 召回率 F 值 准确率 召回率 F 值 准确率 召回率 F 值 畅通 88.13 32.61 47.61 0 0 0 90.01 36.94 52.38 35.02 100.00 51.87 98.31 76.15 85.82 缓行 76.64 38.74 51.47 33.01 100.00 49.64 35.69 85.06 50.28 0 0 0 76.36 87.83 81.70 拥堵 45.44 100.00 62.49 0 0 0 17.79 3.88 6.37 0 0 0 86.06 98.49 91.86 均值 70.07 57.12 53.85 11.00 33.33 16.55 47.83 41.96 36.35 11.67 33.33 17.29 86.91 87.49 86.46 对比 C3D*
下降值16.84 30.37 32.61 75.91 54.16 69.91 39.08 45.53 50.11 75.24 54.16 69.17 -
WEI L, HONG Y D. Real-time road congestion detection based on image texture analysis[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2016, 137: 196-201. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2016.01.250 SHI X, SHAN Z, ZHAO N. Learning for an aesthetic model for estimating the traffic state in the traffic video[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 181: 29-37. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.08.099 崔华,袁超,魏泽发,等. 利用FCM对静态图像进行交通状态识别[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报,2017,44(6): 85-90.CUI Hua, YUAN Chao, WEI Zefa, et al. Traffic state recognition using state images and FCM[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2017, 44(6): 85-90. LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]//3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego: [s.n.], 2015: 1-14. JI S, XU W, YANG M, et al. 3D Convolutional neural networks for human action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 221-231. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59 TRAN D, BOURDEV L, FERGUS R, et al. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago: IEEE, 2015: 4489-4497. XU H, DAS A, SAENKO K. R-C3D: region convolutional 3D network for temporal activity detection[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice: IEEE, 2017: 5794-5803. TRAN D, WANG H, TORRESANI L, et al. A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 6450-6459. -





 下载:
下载: