Experimental Study on Effect of Geogrid on Direct Shear Behavior of Contaminated Ballast
-
摘要:
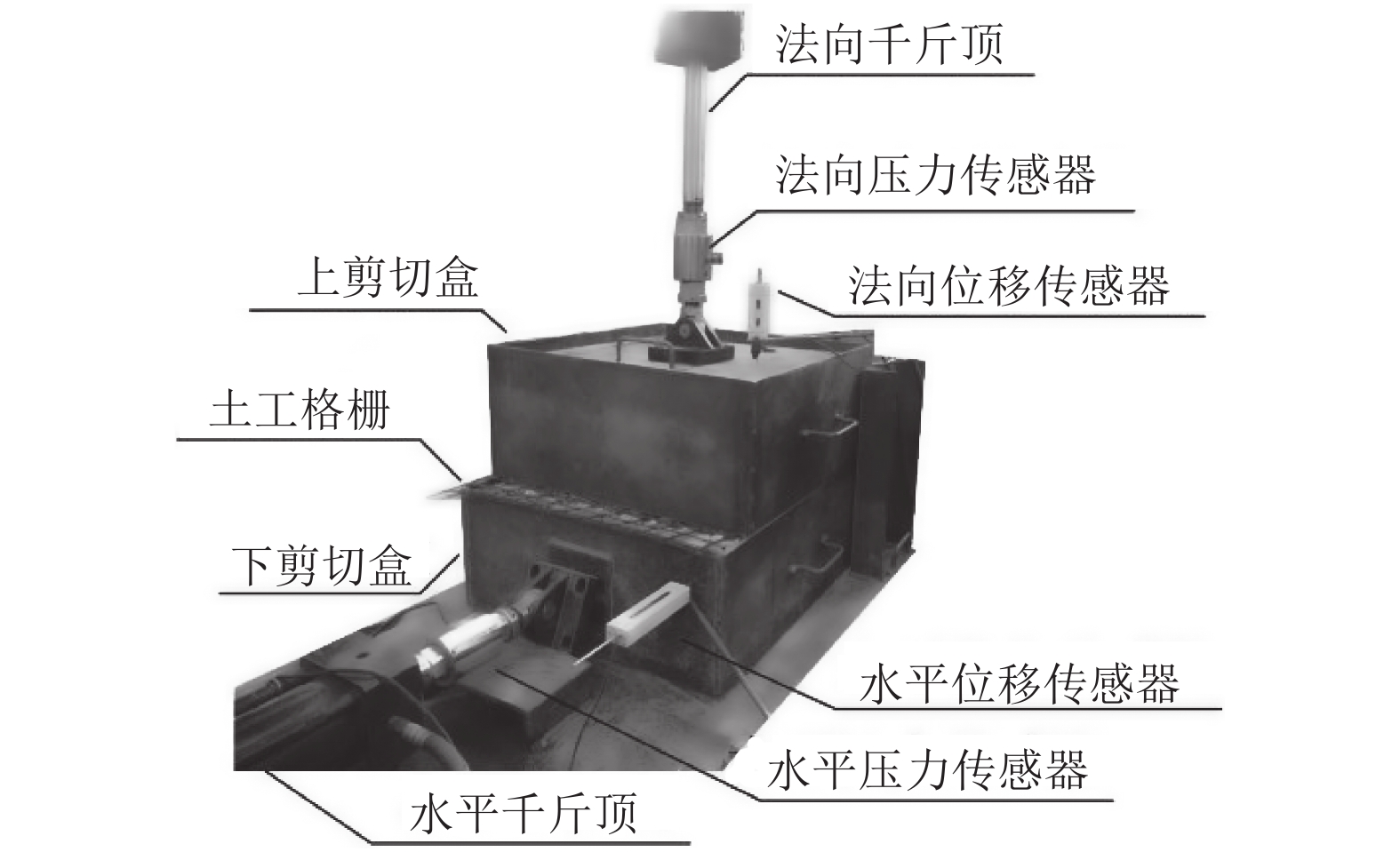
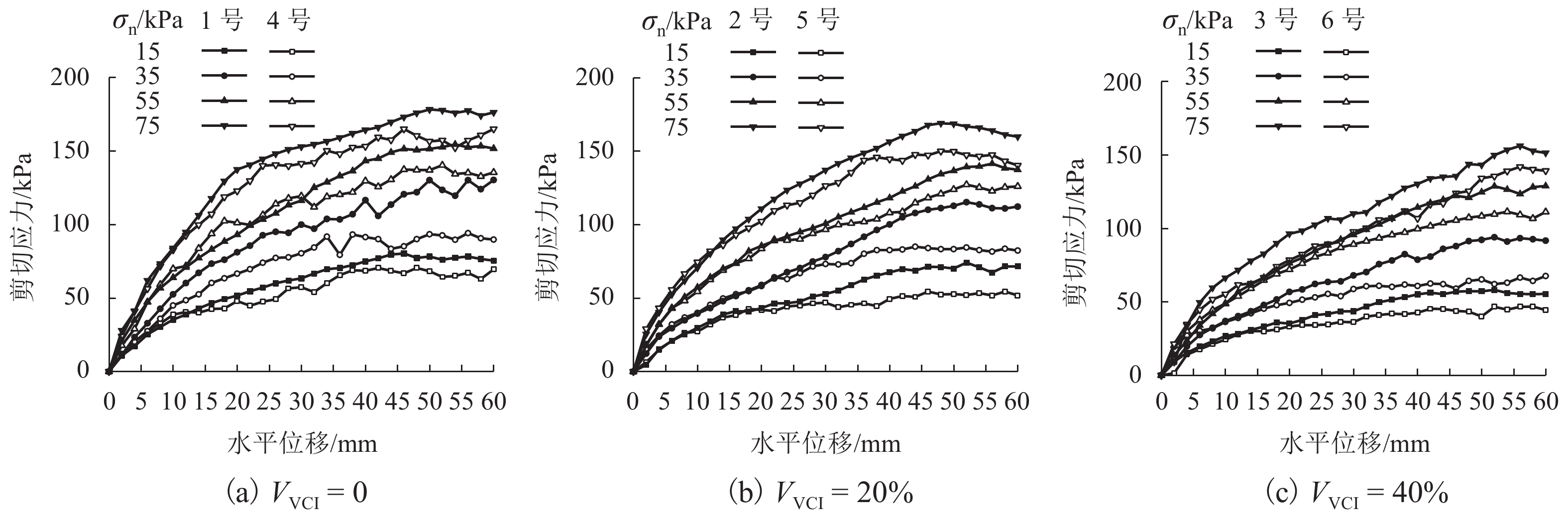
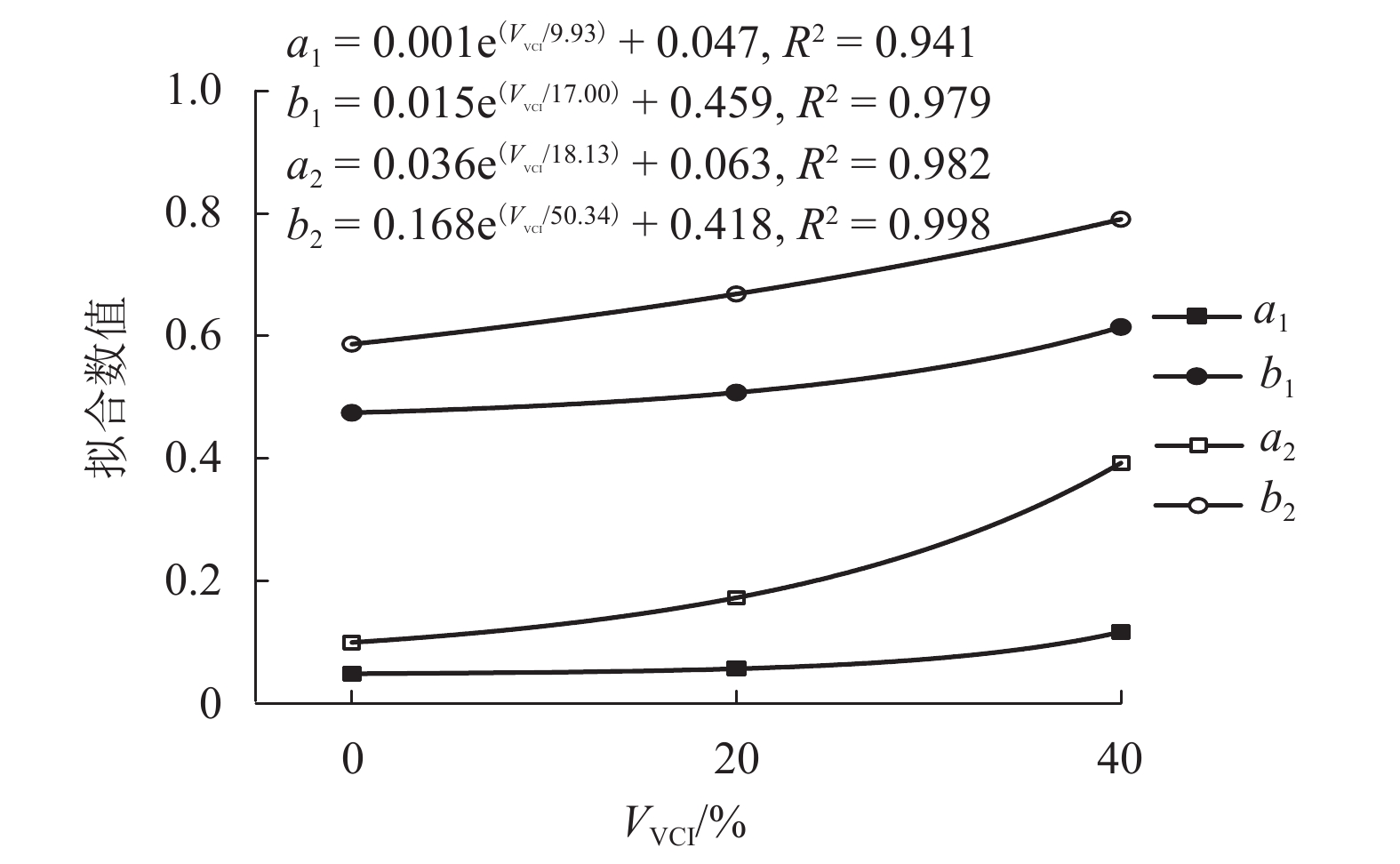
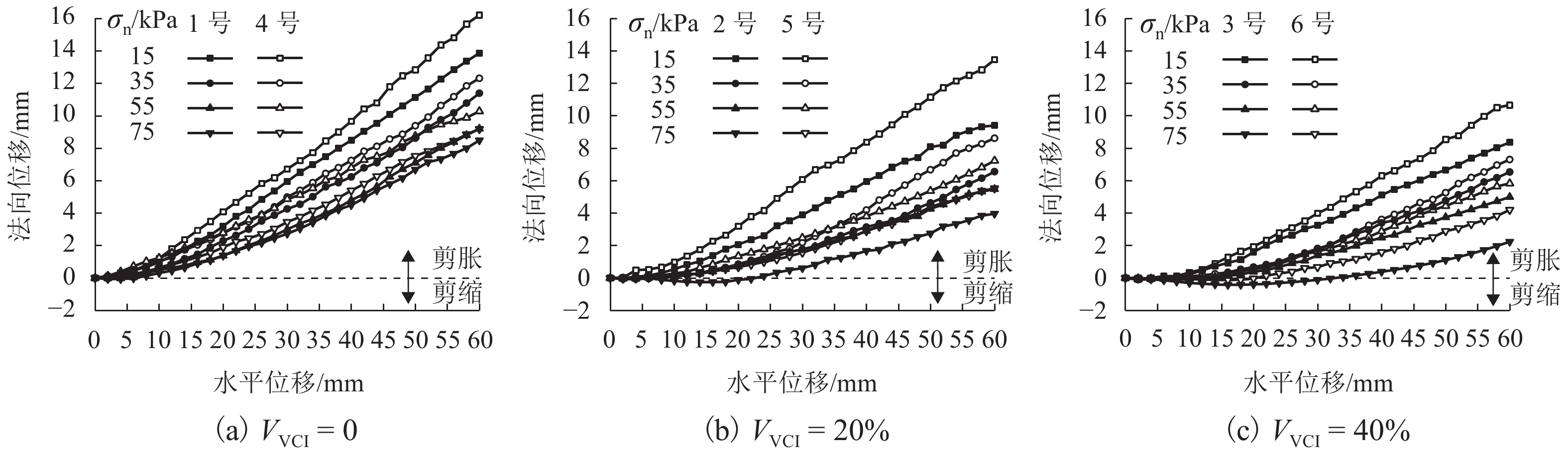
为探究土工格栅对受黏土污染道砟力学特性的影响,通过对4种法向压力、3种黏土污染程度下土工格栅加固的道砟试样进行一系列直剪试验,对比分析土工格栅对道砟试样剪切强度和剪切变形的影响,研究了考虑黏土污染情况下土工格栅对道砟的加固效果. 研究结果表明:土工格栅增大了洁净及受黏土污染道砟试样的剪切强度,当污染指标VCI (void contamination index)为20%时提升峰值剪切强度最大达到24%;道砟剪切强度表现出典型的非线性特征,非线性强度准则拟合参数与道砟污染程度利用指数函数拟合,拟合结果可作为实际工程受污染道砟强度估计的依据;土工格栅可减小试样的最大剪胀量,同时可减小约0.7°~3.7° 的峰值剪胀角,并且在VCI为20%时土工格栅加固的效果最为明显.
Abstract:In order to investigate the effect of geogrid on the mechanical properties of clay-contaminated ballast, a series of direct shear tests were carried out on geogrid-reinforced ballast specimens under four normal pressures and three degrees of clay pollution. The effects of geogrid on the shear strength and shear deformation of ballast specimens were compared and analyzed. The reinforcement effect of geogrid on ballast with consideration of clay pollution was studied. The results show that the geogrid can increase the shear strength of clean and clay-contaminated ballast samples, and the peak shear strength reaches 24% when the void contamination index (VCI) is 20%. Ballast shear strength exhibits typical non-linear characteristics, and the relationship between fitting parameters of non-linear strength criterion and pollution degrees can be fitted by an exponential function. The fitting results can be used as the basis for strength estimation of contaminated-ballast in practical engineering. Meanwhile, geogrid can reduce the maximum dilatancy of the sample; it can also reduce the peak dilatancy angle by about 0.7°~3.7°, and achieve its maximum reinforcement effect at the VCI of 20%.
-
Key words:
- geogrid reinforcement /
- clay fouling /
- direct shear test /
- shear properties /
- ballast
-
表 1 试验材料参数表
Table 1. Physical properties of test materials
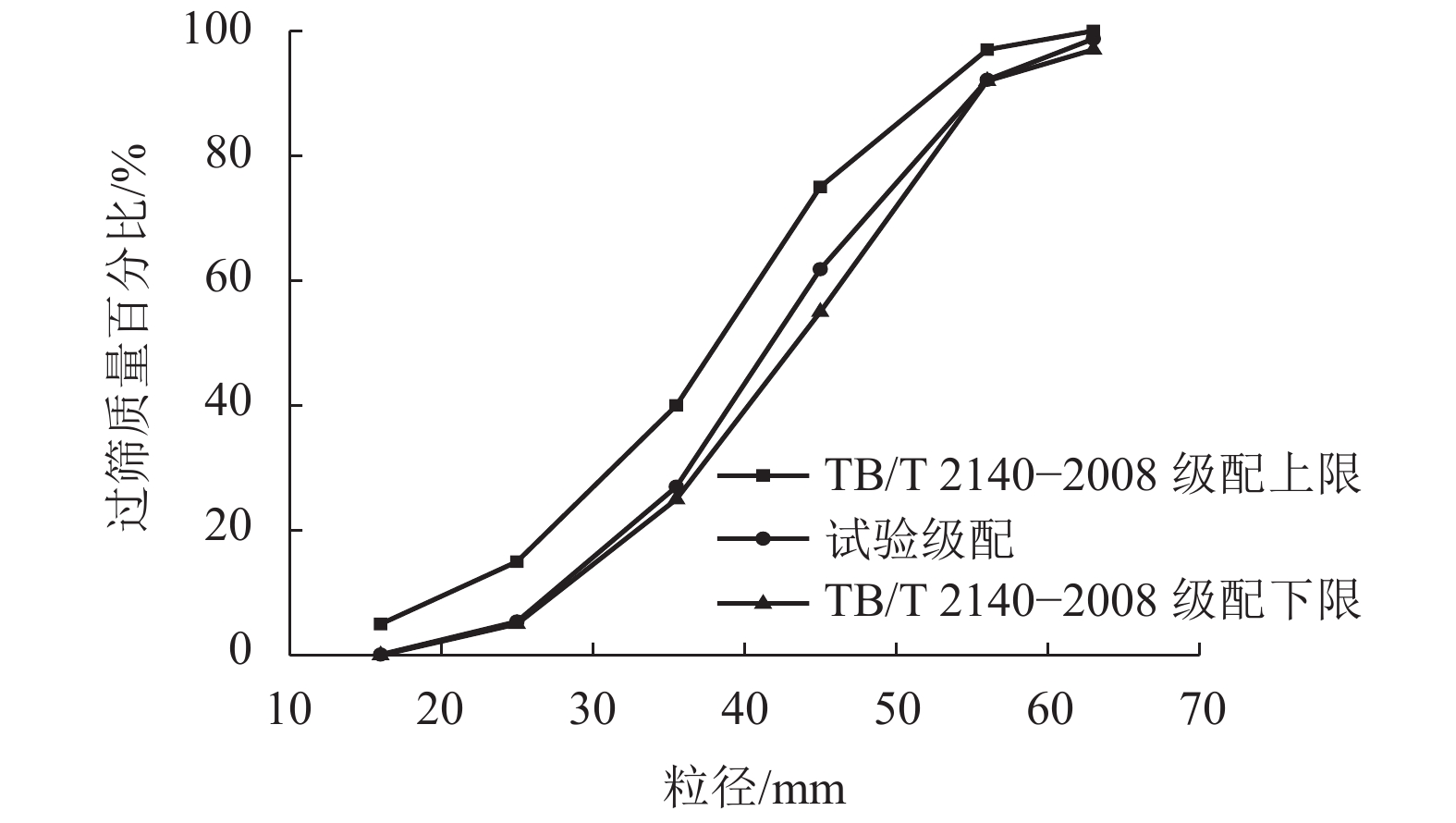
材料 堆积密度ρ/(kg•m−3) 比重 d 孔隙比 e 含水率ω/% 液限/% 塑限/% 道砟 1432 2.66 0.858 黏土 1178 2.70 1.292 22.2 42.1 22.4 表 2 土工格栅参数表
Table 2. Physical and technical properties of geogrid
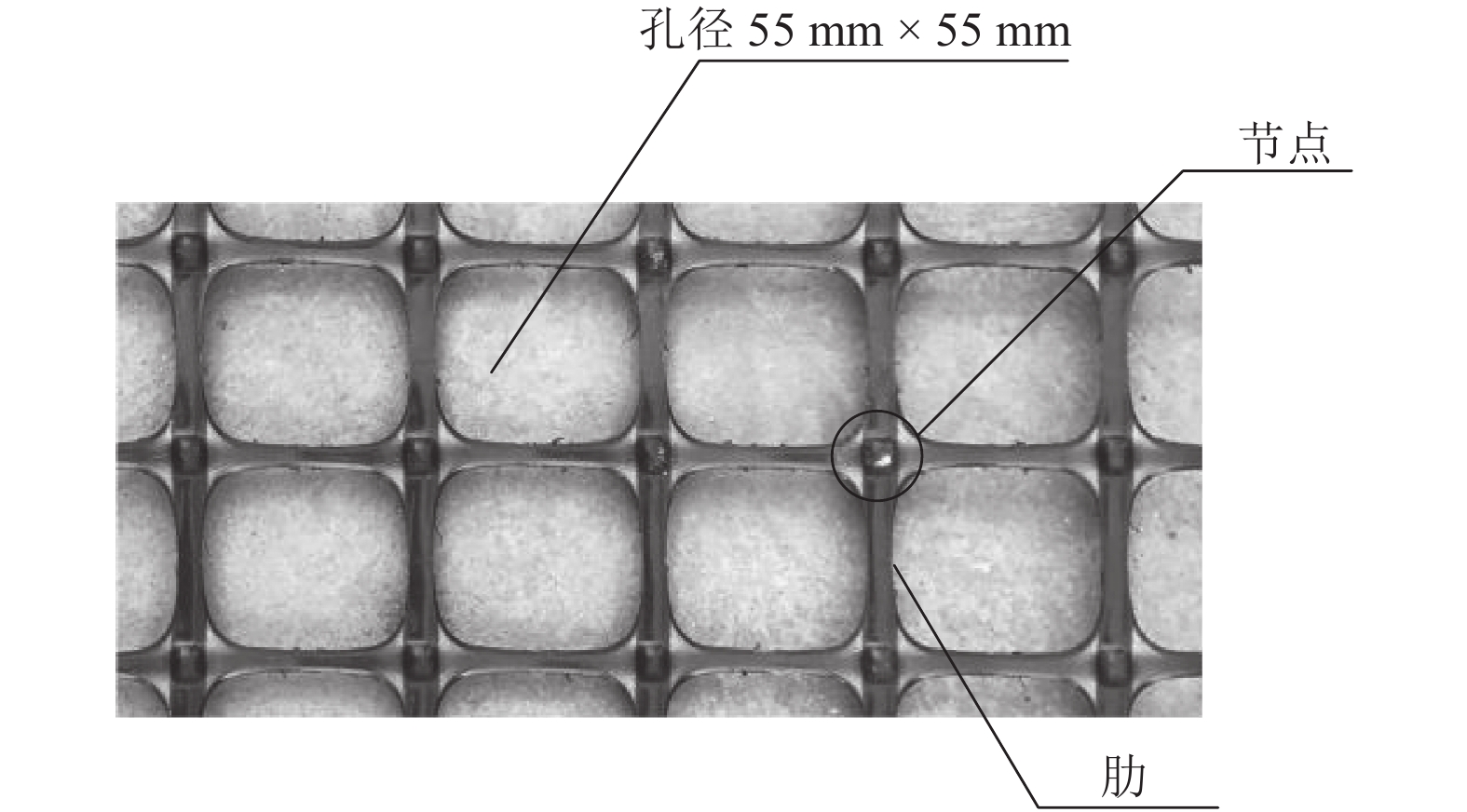
材料 类型 孔径/mm 空隙率/% 极限抗拉强度/(kN•m−1) 聚丙烯 双向方形格栅 55 × 55 81 30 表 3 试验方案
Table 3. Experiment schemes
试验组别 试样编号 VCI/% 法向压力/kPa 有格栅 1 号 0 15、35、55、75 2 号 20 3 号 40 无格栅 4 号 0 15、35、55、75 5 号 20 6 号 40 表 4 峰值剪切强度数据
Table 4. Results of peak shear stress
试样编号 σn=15 kPa σn=35 kPa σn=55 kPa σn=75 kPa 1 号 80.28 130.28 155.44 178.19 2 号 74.17 115.28 141.53 169.03 3 号 58.19 94.03 128.89 153.47 4 号 70.42 94.10 140.28 164.93 5 号 54.44 84.44 136.04 149.72 6 号 46.81 67.64 111.39 141.94 -
[1] HUDSON A, WATSSN G, PEN L L, et al. Remediation of mud pumping on a ballast railway track[C]//The 3rd International Conference on Transportation Geotechnics. Guimarães: Procedia Engineering, 2016, 143: 1043-1050. [2] SELIG E T, WATERS J M. Track geotechnology and substructure management[M]. London: Thomas Telford, 1994: 8-9. [3] SWETA K, HUSSAINI S K K. Behavior evaluation of geogrid-reinforced ballast-subballast interface under shear condition[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2019, 47(1): 23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2018.09.002 [4] AKBAR D, MASSOUD P, ASGHAR M A. Effect of sand and clay fouling on the shear strength of railway ballast for different ballast gradations[J]. Granular Matter, 2018, 20(51): 1-14. [5] KASHANI H F, HO C L, HYSLIP J P. Fouling and water content influence on the ballast deformation properties[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 190: 881-895. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.09.058 [6] 徐旸,高亮,井国庆,等. 脏污对道床剪切性能影响及评估指标的离散元分析[J]. 工程力学,2015,32(8): 96-102. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.01.0051XU Yang, GAO Liang, JING Guoqing, et al. Shear behavior analysis of fouling railroad ballast by DEM and its evaluation index[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2015, 32(8): 96-102. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.01.0051 [7] 高亮,徐旸,殷浩. 脏污材质对散体道床剪切力学性能影响的试验研究[J]. 北京交通大学学报,2017,41(1): 1-6. doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291.2017.01.001GAO Liang, XU Yang, YIN Hao. Experiment research of shear behavior of railway ballast influenced by different fouling materials[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2017, 41(1): 1-6. doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291.2017.01.001 [8] HUSSAINI S K K, INDRARATNA B, VINOD J S. A laboratory investigation to assess the functioning of railway ballast with and without geogrids[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2016, 6: 45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2016.02.001 [9] FERNANDES G, PALMEIRA E M, GOMES R C. Performance of geosynthetic-reinforced alternative sub-ballast material in a railway track[J]. Geosynthetics International, 2008, 15(5): 311-321. doi: 10.1680/gein.2008.15.5.311 [10] CHEN C, MCDOWELL G R, THOM N H. Discrete element modelling of cyclic loads of geogrid-reinforced ballast under confined and unconfined conditions[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2012, 35: 76-86. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2012.07.004 [11] BROWN S F, KWAN J, THOM N H. Identifying the key parameters that influence geogrid reinforcement of railway ballast[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2007, 25(6): 326-335. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2007.06.003 [12] SWETA K, HUSSAINI S K K. Effect of shearing rate on the behavior of geogrid-reinforced railroad ballast under direct shear conditions[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2018, 46(3): 251-256. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2017.12.001 [13] 井国庆,黄红梅,常锦秀,等. 清洗后的劣化道砟直剪力学特性分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(6): 1055-1060. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.06.003JING Guoqing, HUANG Hongmei, CHANG Jinxiu, et al. Analysis of mechanical characteristics of degradation railway ballast by direct shear test[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(6): 1055-1060. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.06.003 [14] 王军, 胡惠丽, 刘飞禹, 等. 粒孔比对筋土界面直剪特性的影响[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(增刊2): 115-122.WANG Jun, HU Huili, LIU Feiyu, et al. Effects of direct shear characteristics of sand-geogrid interface under different aperture ratios[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(S2): 115-122. [15] 井国庆,强伟乐,常锦秀,等. 针片状指数对道砟直剪力学特性的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(4): 688-694.JING Guoqing, QIANG Weile, CHANG Jinxiu, et al. Effect of flakiness-elongation index on shear behavior of railway ballast[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(4): 688-694. [16] INDRARATNA B, WIJEWARDENA L S S, BALASUBRAMANIAM A S. Large-scale triaxial testing of greywacke rockfill[J]. Geotechnique, 1993, 43(1): 37-51. doi: 10.1680/geot.1993.43.1.37 [17] INDRARATNA B, NIMBALKAR S S, TENNAKOON N. The behaviour of ballasted track foundations: track drainage and geosynthetic reinforcement[C]//GeoFlorida 2010: Advances in Analysis, Modeling & Design (GSP 199). West Palm Beach: ASCE, 2010: 2378-2387. [18] INDRARATNA B, NGO N T, RUJIKIATKAMJORN C. Behavior of geogrid-reinforced ballast under various levels of fouling[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2011, 29: 313-322. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2011.01.015 [19] INDRARATNA B, IONESCU D, CHRISTIE H D. Shear behavior of railway ballast based on large-scale triaxial tests[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 1998, 124(5): 439-449. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1998)124:5(439) [20] 朱学敏,崔晓燕. 桩承式加筋路堤中土工格栅加筋效应的室内试验研究[J]. 河北工程大学学报(自然科学版),2020,37(1): 35-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9469.2020.01.007ZHU Xueming, CUI xiaoyan. Experimental study on the effect of geogrid reinforcement in pile-supported embankment[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Engineering (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 37(1): 35-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9469.2020.01.007 [21] 苗晨曦. 格栅加筋粗粒料界面细观特性及性能优化研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2016. [22] 周跃峰,谭国焕,甄伟文. 原状黄土剪缩性测试与理论分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(6): 166-173.ZHOU Yuefeng, THAM L G, YAN W M. Testing and theoretical analysis on contractive behavior of undisturbed loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(6): 166-173. -




 下载:
下载: