Cab Signal Denoising Process Based on Fully Convolutional Networks
-
摘要: 机车信号从钢轨提取轨道电路信号作为行车凭证,其译码输出性能对列控系统的可靠性和安全性有直接影响. 但列车运行过程中,机车信号不可避免地混入大量噪声和干扰,译码前需要降噪以提高准确性. 为此,提出一种基于全卷积神经网络(fully convolutionalnetworks, FCN)的机车信号降噪方法,该方法利用基于原始波形“端到端”处理方式的FCN,直接从时域对机车信号进行降噪处理,以提高信噪比(signal-to-noise ratio,SNR);并利用仿真和实测数据对本方法进行了实验. 结果表明:相较于传统基于频谱的滤波方法,本方法对带内干扰有更显著的效果,采用FCN能使机车信号信噪比提高8~14 dB,可有效降低带内噪声.Abstract: Since cab signals extract information from track circuits as the running token, its decoding performance has a direct impact on the reliability and security of train operation control system. However, as it is inevitable that a lot of noise and interference will mix into the cab signal during operation, it is necessary to denoise before decoding in order to improve demodulation accuracy. To this end, a raw waveform-based fully convolutional network (FCN) for denoising is proposed in an end-to-end manner, which denoises the cab signal in time domain directly and improves the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). This proposed network is validated through simulation and measured data. The experimental results show that compared with the traditional spectrum-based denoising methods, this method has a more significant effect on in-band interference; FCN can improve the SNR of cab signals by 8~14 dB and effectively reduce the in-band interference.
-
Key words:
- railway signal /
- train operation control system /
- cab signal /
- signal processing /
- neural networks
-
表 1 信息特征参数
Table 1. Information characteristic parameters
Hz 参数 指标 ${f_{\rm{c}}}$ 上行 1998.7,2001.4,2598.7,2601.4 下行 1698.7,1701.4,2298.7,2301.4 ${f_{\rm{d}}}$ ${\rm{10} }{\rm{.3 + 1} }{\rm{.1} } n{\simfont\text{,} }n = 0{\simfont\text{~} } 17$ $\Delta f$ $ \pm 11$ 表 2 样本的噪声特性
Table 2. Noise characteristics of samples
噪声类型 相关参数 样本/个 样本长
度/点频率/Hz 幅度/V 单频噪声 1650~2650 0~2 25000 2048 谐波干扰 1650、1700、···、2650 0~1 25000 2048 带内干扰 ${f_{\rm{c}}} - {f_{\rm{d}}}{\simfont\text{~} } {f_{\rm{c}}} + {f_{\rm{d}}}$ 0~2 25000 2048 白噪声 0~10 25000 2048 表 3 本文算法RMSE结果与其他算法对比
Table 3. RMSE comparison with various algorithms
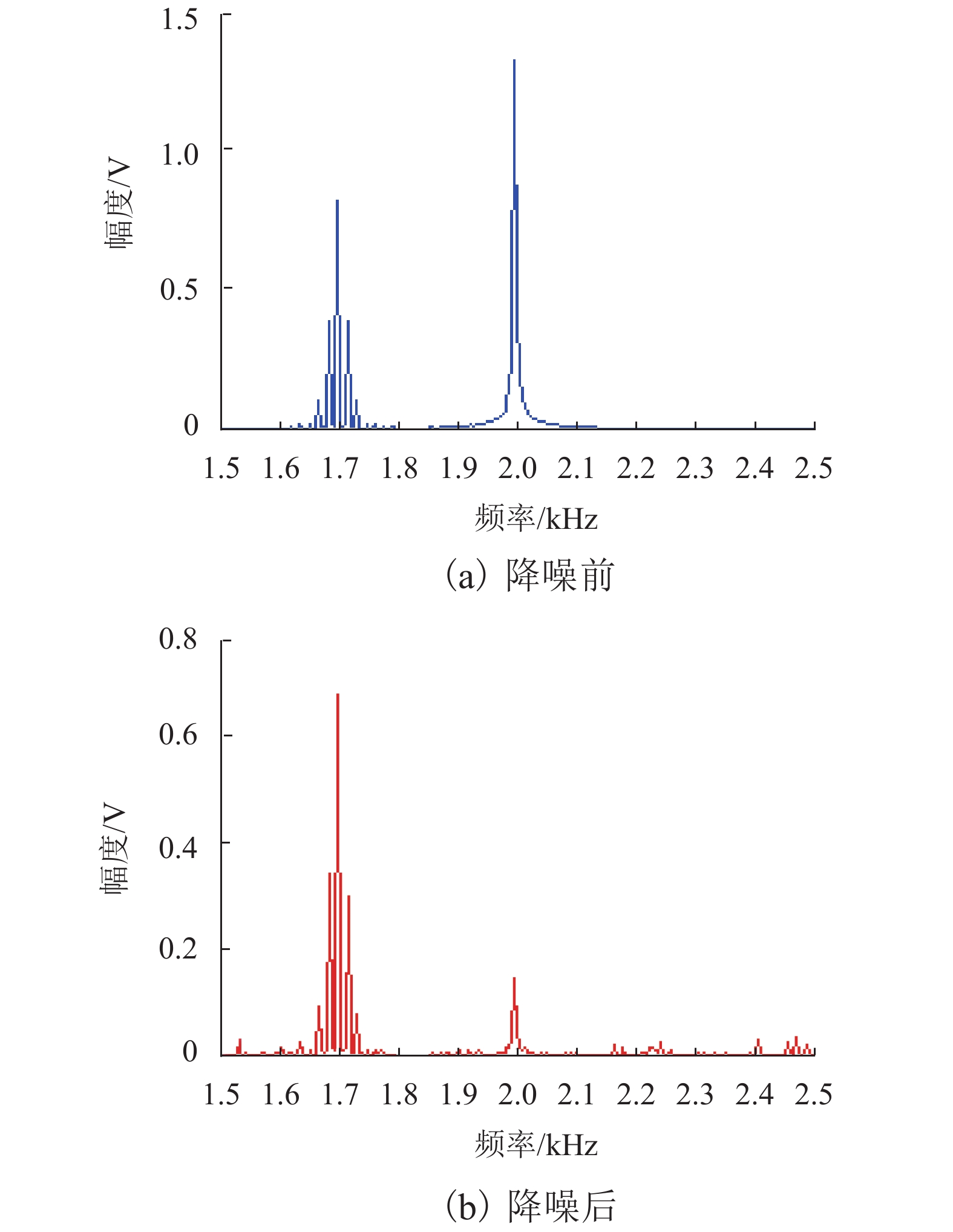
V 噪声类型 去噪前 FCN CNN 带通滤波 EMD 稀疏分解 单频噪声 0.593 0.244 0.430 0.493 0.386 0.317 谐波干扰 1.287 0.118 0.384 0.547 0.498 0.409 白噪声 1.199 0.264 0.321 0.654 0.332 0.300 带内干扰 0.859 0.236 0.287 0.719 0.603 0.580 全体噪声 0.945 0.169 0.198 0.686 0.554 0.526 表 4 本文算法SNR结果与其他算法对比
Table 4. SNR comparison with various algorithms
dB 噪声类型 去噪前 FCN CNN 带通滤波 EMD 稀疏分解 单频噪声 3.197 8.874 4.394 3.338 5.496 6.009 谐波干扰 −2.756 14.214 5.331 2.235 4.477 4.848 白噪声 −2.930 9.734 9.172 0.832 8.672 9.037 带内干扰 0.203 11.943 11.218 2.493 5.492 5.984 全体噪声 0.030 13.012 12.164 3.138 4.360 4.896 -
邱宽民. JT1-CZ2000型机车信号车载系统[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2010: 1-12. ZHAO Linhai, LI Zhankui, LIU Weining. The compensation capacitors fault detection method of jointless track circuit based on DBWT and WR[C]//IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Computing & Intelligent Systems. Shanghai: IEEE, 2009: 875-879. 剌博. 基于EMD降噪的轨道移频信号检测算法研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2014. 轩春霞,王小敏,杨扬,等. 基于稀疏分解的轨道移频信号降噪算法研究[J]. 计算机测量与控制,2014,22(9): 2870-2874. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4598.2014.09.048XUAN Chunxia, WANG Xiaomin, YANG Yang, et al. Denoising algorithm for track circuit frequency:shift signal based on sparse decomposition[J]. Computer Measurement & Control, 2014, 22(9): 2870-2874. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4598.2014.09.048 NAIK D C, MURTHY A S, NUTHAKKI R. Modified magnitude spectral subtraction methods for speech enhancement[C]//2017 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computer, and Optimization Techniques(ICEECCOT). Mysuru: [s.n.], 2017: 274-279. EPHRAIM Y, MALAH D. Speech enhancement using a minimum-mean square error short-time spectral amplitude estimator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1984, 32(6): 1109-1121. SCALART P, FILHO J V. Speech enhancement based on a priori signal to noise estimation[C]//IEEE International Conference on Acoustics. Atlanta: IEEE, 1996: 629-632. IBARROLA F J, DI PERSIA L, SPIES R D. A Bayesian approach to convolutive nonnegative matrix factorization for blind speech dereverberation[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 151(4): 89-98. HOU J C, WANG S S, LAI Y H, et al. Audio-visual speech enhancement using multimodal deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2018, 2(2): 117-128. PALAZ D, COLLOBERT R, DOSS M M. Estimating phoneme class conditional probabilities from raw speech signal using convolutional neural networks[C]//14th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association. Lyon: Interspeech, 2013: 1765-1769. OORD A V D, DIELEMAN S, ZEN H, et al. WaveNet: a generative model for raw audio[J]. Computer Science, 2016, 1: 1-15. FU S W, WANG T W, TSAO Y, et al. End-to-end waveform utterance enhancement for direct evaluation metrics optimization by fully convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio Speech & Language Processing, 2018, 26(9): 1570-1584. 赵自信. ZPW—2000A无绝缘移频自动闭塞系统的技术综述[J]. 铁路通信信号工程技术, 2003, 2003(增刊1): 12-19.ZHAO Zixin. A review of ZPW-2000 automatic block with jointless frequency-shift system[J]. Railway Signalling & Communication Engineering, 2003, 2003(S1): 12-19. 中华人民共和国铁道部. ZPW-2000轨道电路技术条件: TB/T 3206—2008[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2008 LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine, 2015, 39(4): 640-651. THAKKAR V, TEWARY S, CHAKRABORTY C.Batch normalization in convolutional neural networks: a comparative study with CIFAR-10 data[C]//2018 Fifth International Conference on Emerging Applications of Information Technology (EAIT). Kolkata: [s.n.], 2018: 1-5. ZHANG Yudong, PAN Chichun, SUN Junding, et al. Multiple sclerosis identification by convolutional neural network with dropout and parametric ReLU[J]. Journal of Computational Science, 2018, 28(9): 1-10. -





 下载:
下载: