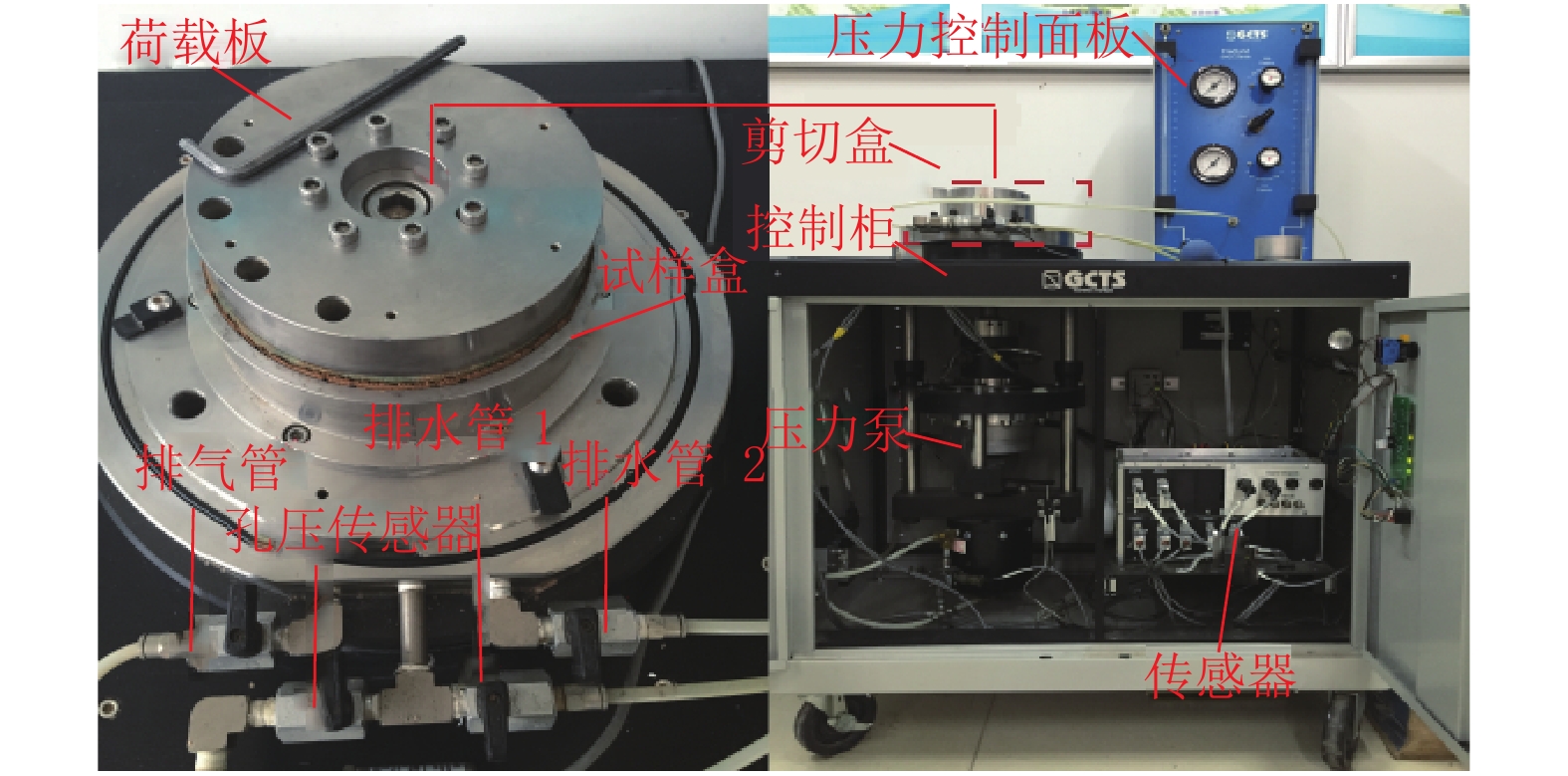
Shear Properties of Paleosol Containing Calcareous ConcretionsBased on Ring Shear Tests
-
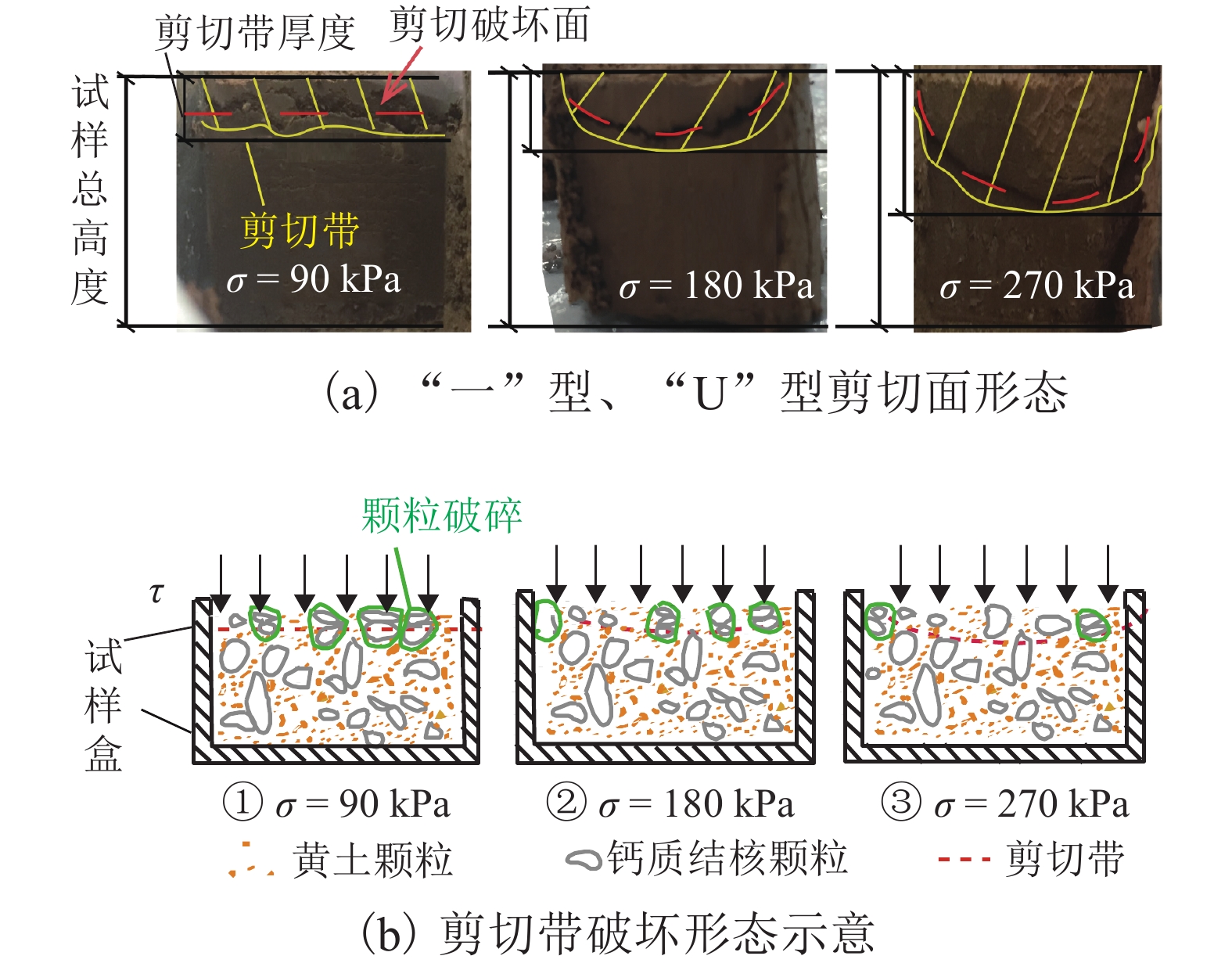
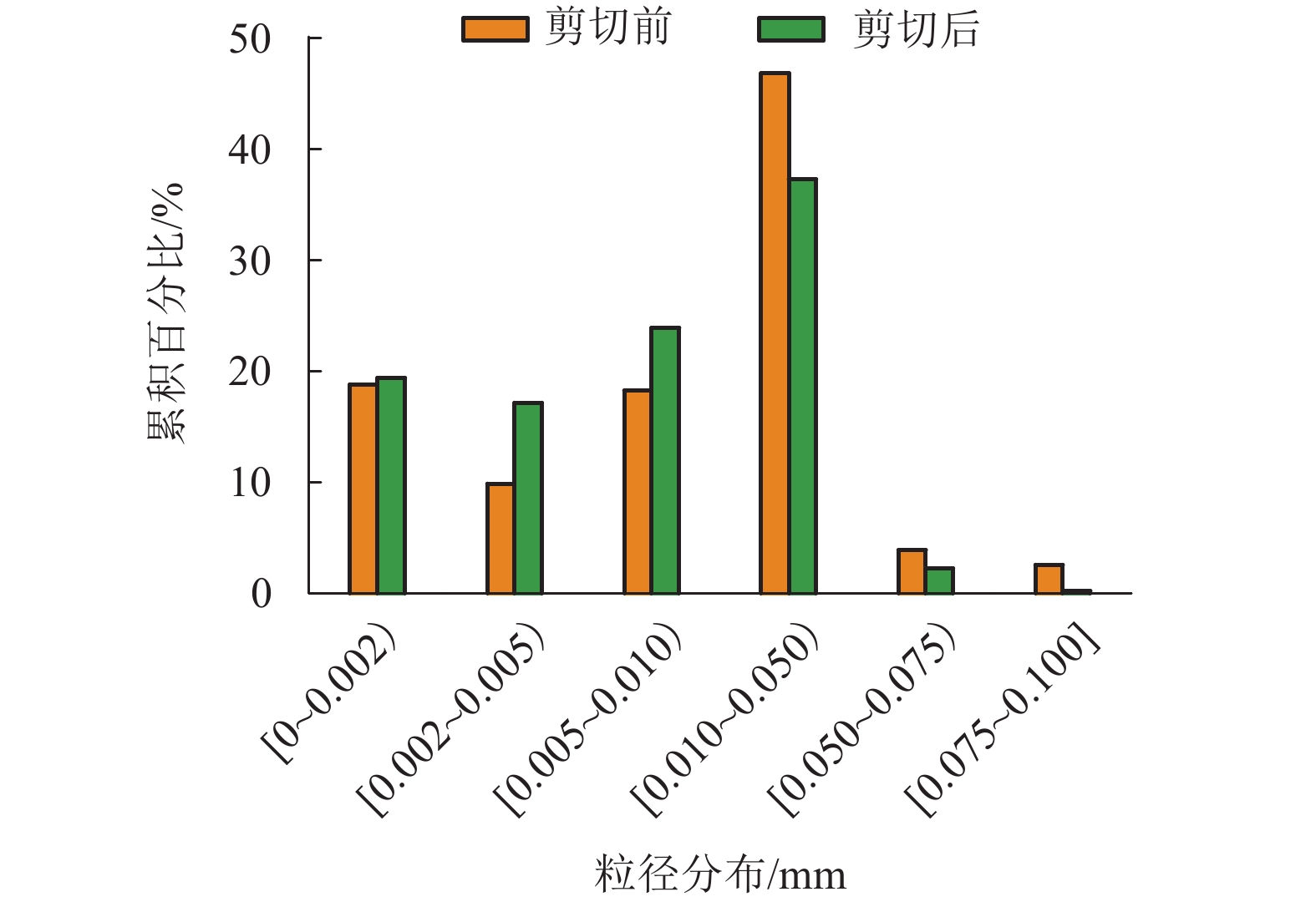
摘要: 含钙质结核古土壤在黄土滑坡的剪切带中广泛分布,影响滑坡的剪切特性. 通过固结排水环剪试验,改变轴应力大小,研究不同钙质结核含量下古土壤的剪切力学特性;基于对剪切破坏面的宏观结构分析,总结并提出剪切破坏面的“一”型和“U”型两种破坏形态及平稳、过渡、波动3种破坏模式. 研究结果表明:在低轴应力下,应力-位移曲线均为软化型,具有明显的残余强度特性,随钙质结核含量增大,应变软化特性变弱;在高轴应力下,则表现为硬化型;钙质结核颗粒能增大土的剪切强度、摩擦角,减小黏聚力;剪切带厚度与钙质结核含量正相关,与 D50 负相关;在大位移剪切作用下,颗粒会发生破碎,通过对剪切前后粒径分析,确定了钙质结核主要破碎区间为3~5 mm,破碎率为19.5%~55.5%;古土壤由 0.01~0.05 mm颗粒破碎为 0.002~0.010 mm的较小颗粒.Abstract: Paleosol containing calcareous concretion is widely distributed in the shear zone of loess landslides and affects the shear failure characteristics of landslides. Based on ring shear tests, the shear characteristics of paleosol with different contents of calcareous concretions under different normal stresses were discussed, and the test results were analyzed from macro-and micro-aspects. The results indicate that under low axial (normal) stress, the stress-displacement curves are of softening type and have obvious residual strength characteristics. With the increase of calcium nodule content, the strain softening characteristics become weak. Under high axial (normal) stress, the stress-displacement curves show strain hardening. Calcareous nodule particles can increase the shear strength and peak friction angle of soil and reduce the cohesion. The thickness of shear band is positively correlated with the content of calcareous concretions and negatively correlated with D50. Particle crushing occurred under the larger deformation. According to the particle size distribution analysis before and after shearing, the breakage of calcareous concretions mainly occurred to particles in the size range of 3−5 mm, with a breakage percentage of 19.5%−55.5%, and the paleosol was broken from 0.01−0.05 mm into smaller particles of 0.002−0.010 mm. Based on macroscopic observation and mechanical analysis of shear failure surfaces, all samples can be divided into two groups with “—” and “U” failure surface patterns, respectively, and three failure modes, including sliding shear mode, turbulent and transitional shear mode.
-
表 1 土样物性参数表
Table 1. Basic physical properties of soil specimen
参数 含水率/% 密度/(g•cm−3) 干密度/(g•cm−3) 液限 w 塑限 wp 塑性指数 Ip 土粒比重 Gs 取值 21.27 1.67 1.44 28.1 19.3 8.8 2.71 表 2 S2古土壤粒径分布
Table 2. Particle size distribution of S2 paleosol
% 粒组 黏粒组/mm 粉粒组/mm 砂粒组/mm 细(胶粒)(< 0.002) 粗[0.002~0.005) 细[0.005~0.010) 粗[0.010~0.050) 级细[0.050~0.075) 细[0.075~0.100] 取值 18.78 9.83 18.22 46.78 3.86 0.36 表 3 试验方案与分组表
Table 3. Test plan and group table
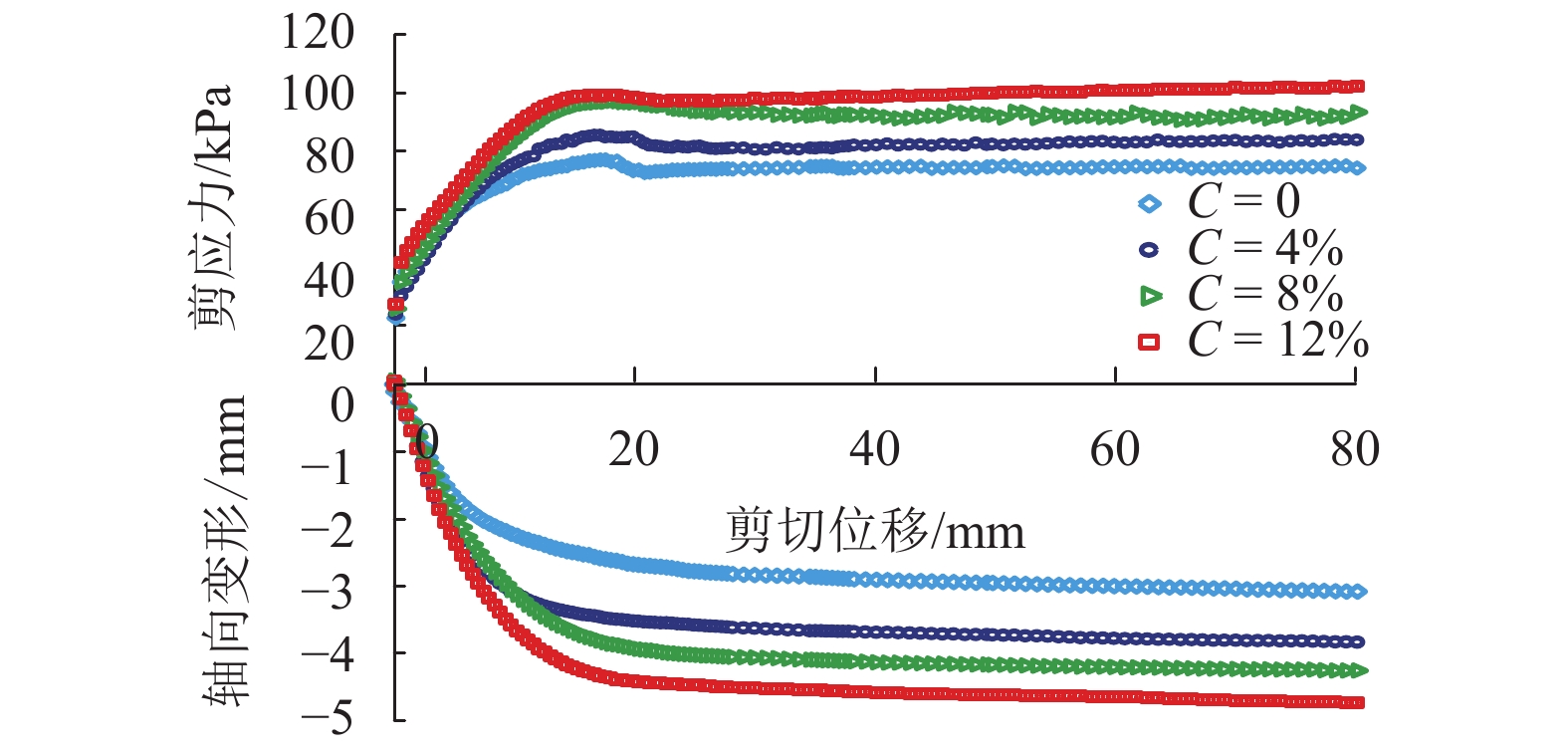
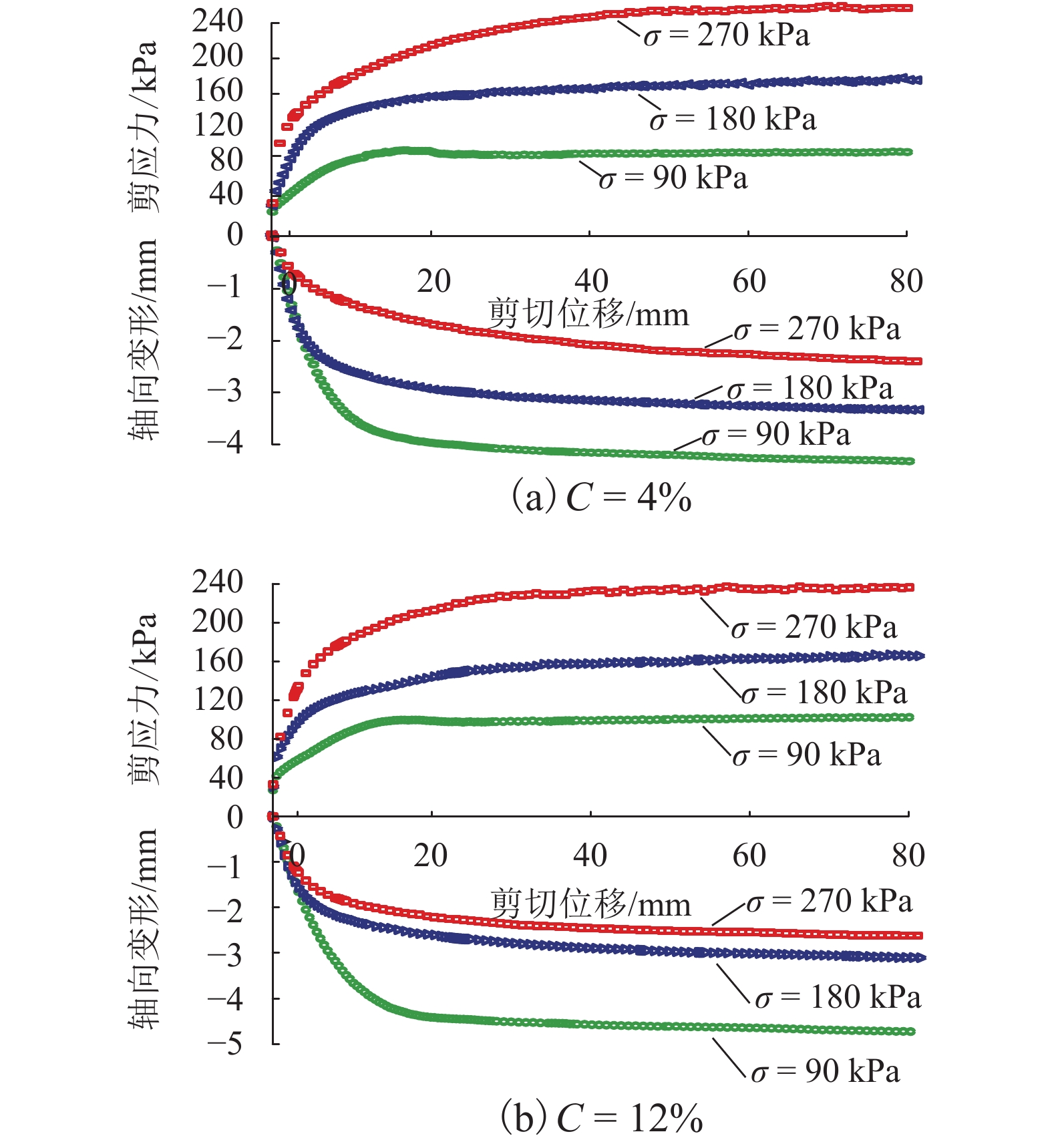
试验编号 轴应力/kPa C/% 1-1、1-2、1-3 90 0、4、8、12 2-1、2-2、2-3 180 3-1、3-2、3-3 270 表 4
$\sigma = 90 \;{\rm{kPa}}$ 时试样的强度与剪切位移的关系Table 4. Relationship between strength and shear displacement at
$\sigma = 90 \;{\rm{kPa}} $ C/% Rs/kPa Rs 差/kPa 至 Rt 所需
位移/mm至 Rs 所需
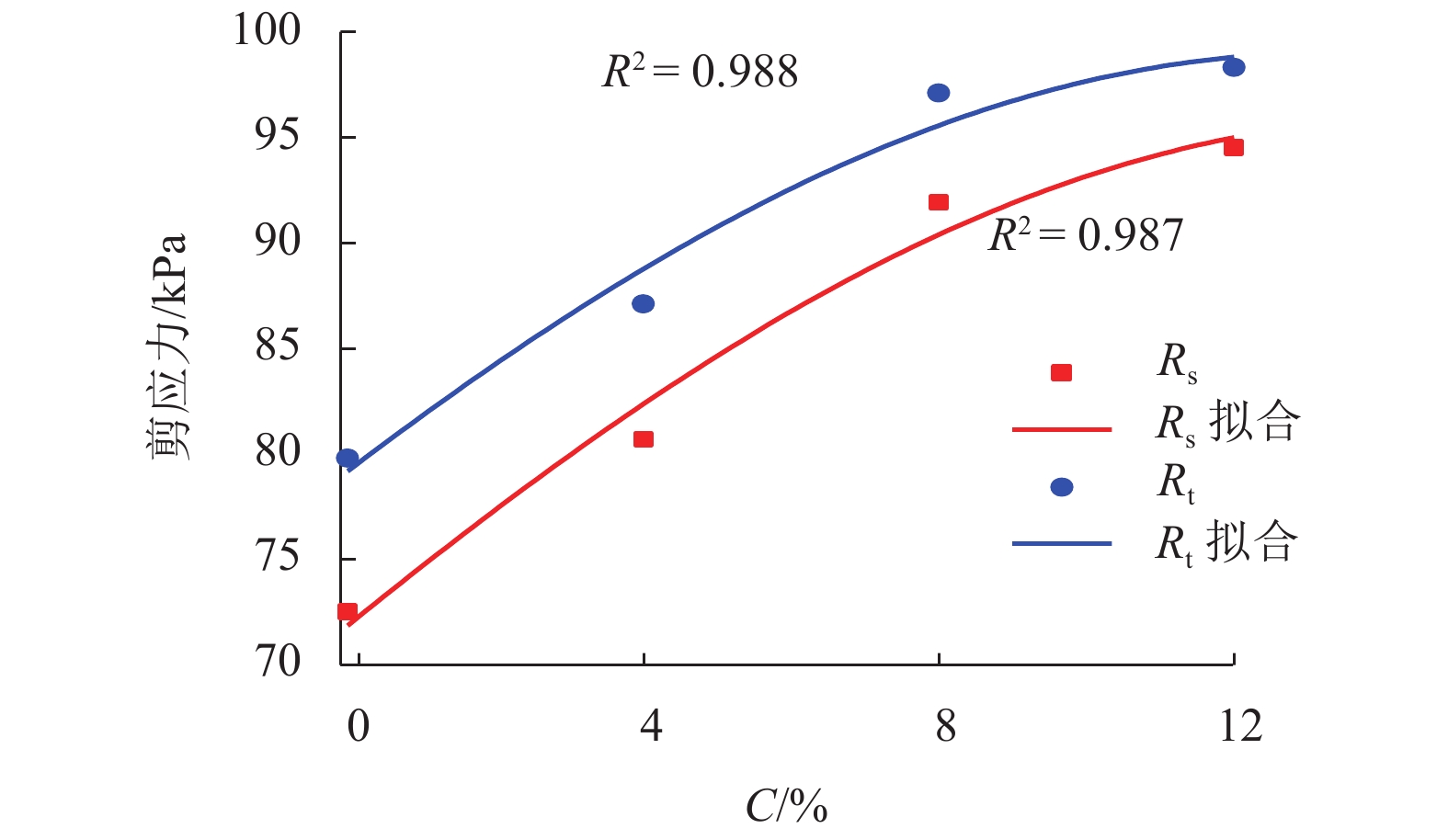
位移/mm0 72.5 7.0~7.2 16.1~17.1 21.4~21.7 4 80.7 6.2~6.6 17.6~18.1 23.0~23.6 8 91.9 5.1~5.9 18.8~20.1 36.8~37.9 1 94.5 2.2~1.8 21.3~21.9 41.9~42.1 表 5 不同钙质结核含量下试样的软化系数
Table 5. Softness factor of samples tested with different contents of calcareous concretions
C/% Rc/kPa Rs/kPa 软化系数 0 79.8 65.5 0.180 4 87.1 80.7 0.073 8 97.1 91.9 0.053 12 98.3 94.5 0.039 表 6 抗剪强度指标
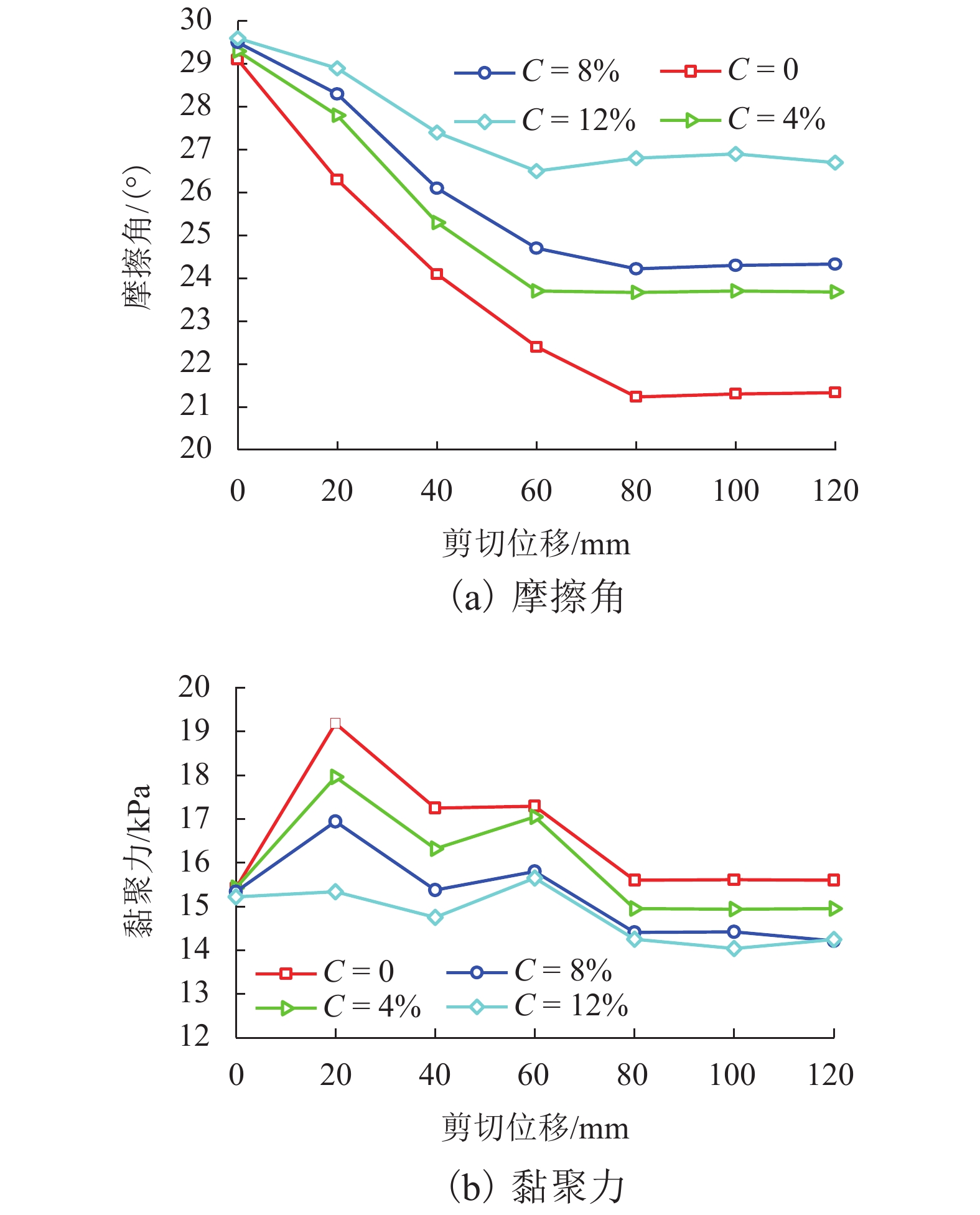
Table 6. Shear strength indexes
参数 C /% 0 4 8 12 φ/(°) 21.23 23.67 24.22 26.80 c/kPa 14.50 14.51 14.43 14.28 表 7 样品的矿物成分
Table 7. Mineral proportions of samples
% 矿物成分 古土壤 钙质结核 石英+长石 71.0 27.9 方解石 13.2 65.6 黏土矿物 13.5 6.5 其它 2.3 0 表 8 剪切前后钙质结核粒径分布
Table 8. Size distribution of particles before and after shearing of samples
% 状态 轴应
力/kPa粒组(粗)/mm 砾粒组(细)/mm < 1 [1~2) [2~3) [3~4) [4~5] 剪切前 0 5.20 18.50 41.34 15.15 19.81 90 5.80 18.40 40.76 14.90 20.14 180 5.60 18.70 41.26 16.79 17.65 270 5.50 18.40 41.78 15.99 18.33 剪切后 0 5.80 18.40 41.67 15.74 18.39 90 6.70 19.80 42.83 16.90 13.77 180 7.90 23.70 43.26 13.79 11.35 270 8.50 29.40 47.78 10.36 3.96 -
刘祖典, 黄土力学与工程[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 1997: 1-4. LI Y R. A review of shear and tensile strengths of the Malan Loess in China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 236: 4-10. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.02.023 孙建中. 黄土学(上篇)[M]. 香港: 香港考古学会出版社, 2005: 206-208. 黄宏翔,陈育民,王建平,等. 钙质砂抗剪强度特性的环剪试验[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(6): 2082-2088.HUANG Hongxiang, CHEN Yumin, WANG Jianping, et al. Ring shear tests on shear strength of calcareous sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(6): 2082-2088. 张彦君,年廷凯,王亮,等. 岩质边坡物理模型试验相似材料研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2019,54(1): 59-64,76.ZHANG Yanjun, NIAN Tingkai, WANG Liang, et al. Research on similar materials for physical model tests of rock slopes[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(1): 59-64,76. 崔圣华,裴向军,黄润秋,等. 大光包滑坡不连续地质特征及其工程地质意义[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2019,54(1): 65-76.CUI Shenghua, PEI Xiangjun, HUANG Runqiu, et al. Discontinuities and engineering geological significances of strong earthquake-induced daguangbao landslide[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(1): 65-76. 洪勇,孙涛,栾茂田,等. 土工环剪仪的开发及其应用研究现状[J]. 岩土力学,2009,30(3): 628-634. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.03.037HONG Yong, SUN Tao, LUAN Maotian, et al. Development and application of geotechnical ring shear apparatus:an overview[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(3): 628-634. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.03.037 丁树云,毕庆涛,蔡正银,等. 环剪仪的试验方法研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,35(增刊2): 197-201.DING Shuyun, BI Qingtao, CAI Zhengyin, et al. Test procedures for ring shear apparatus[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(S2): 197-201. HOYOS L R, VELOSA C L, PUPPALA A J. Residual shear strength of unsaturated soils via suction-controlled ring shear testing[J]. Engineering Geology, 2014, 172(5): 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.01.001 YUAN W N, FAN W, JIANG C C, et al. Experimental study on the shear behavior of loess and paleosol based on ring shear tests[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 250: 11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.01.007 MA C, ZHAN H B, ZHANG T, et al. Investigation on shear behavior of soft interlayers by ring shear tests[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 254: 34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.04.002 滕志宏,刘荣谟,陈苓,等. 中国黄土地层中的钙质结核研究[J]. 科学通报,1990,35(13): 1008-1011. doi: 10.1360/csb1990-35-13-1008TENG Zhihong, LIU Rongmo, CHEN Ling, et al. Study on calcareous nodules in loess plateau of China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1990, 35(13): 1008-1011. doi: 10.1360/csb1990-35-13-1008 曹亚娟. 安徽淮北平原钙质结核土的分布及成因研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2009. 蓝天鹏,吴道祥,杨远杰,等. 钙质结核土及其大型直剪试验研究[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版),2012,35(2): 257-261.LAN Tianpeng, WU Daoxiang, YANG Yuanjie, et al. Research on cohesive soil containing calcareous nodule and its large direct shear test[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2012, 35(2): 257-261. 胡雪婷. 钙质结核土细观结构要素与抗剪强度关系的研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2017. LIU X Y, LIU E L, ZHANG D, et al. Study on effect of coarse-grained content on the mechanical properties of frozen mixed soils[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2019, 158: 237-251. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2018.09.001 屈智炯, 刘恩龙. 土的塑性力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 57-59. 崔凯,苏磊. 粗颗粒含量对川西混合土抗剪强度的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2019,54(4): 778-785.CUI Kai, SU Lei. Effect of coarse grain content on shear strength of mixed soil in Western Sichuan[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(4): 778-785. 王炜. 重塑黄土残余强度的环剪试验研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2014. LI Y R, AYDIN A. Shear zone structures and stress fluctuations in large ring shear tests[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, 167: 6-13. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.10.001 SKEMPTON A W. Residual strength of clays in landslides,folded strata and the laboratory[J]. Geotechnique, 1985, 35(1): 3-18. doi: 10.1680/geot.1985.35.1.3 SADREKARIMI A, OLSON S M. Shear band formation observed in ring shear tests on sandy soils[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2010, 136(2): 366-375. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000220 何建乔,魏厚振,孟庆山,等. 大位移剪切下钙质砂破碎演化特性[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(1): 165-172.HE Jianqiao, WEI Houzhen, MENG Qingshan, et al. Evolution of particle breakage of calcareous sand under large displacement shearing[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(1): 165-172. -




 下载:
下载: