Effects of Strength Degradation of Sliding Mass on Movement of Vajont Landslide Numerical Simulation Based on Discontinuous Deformation Analysis
-
摘要:
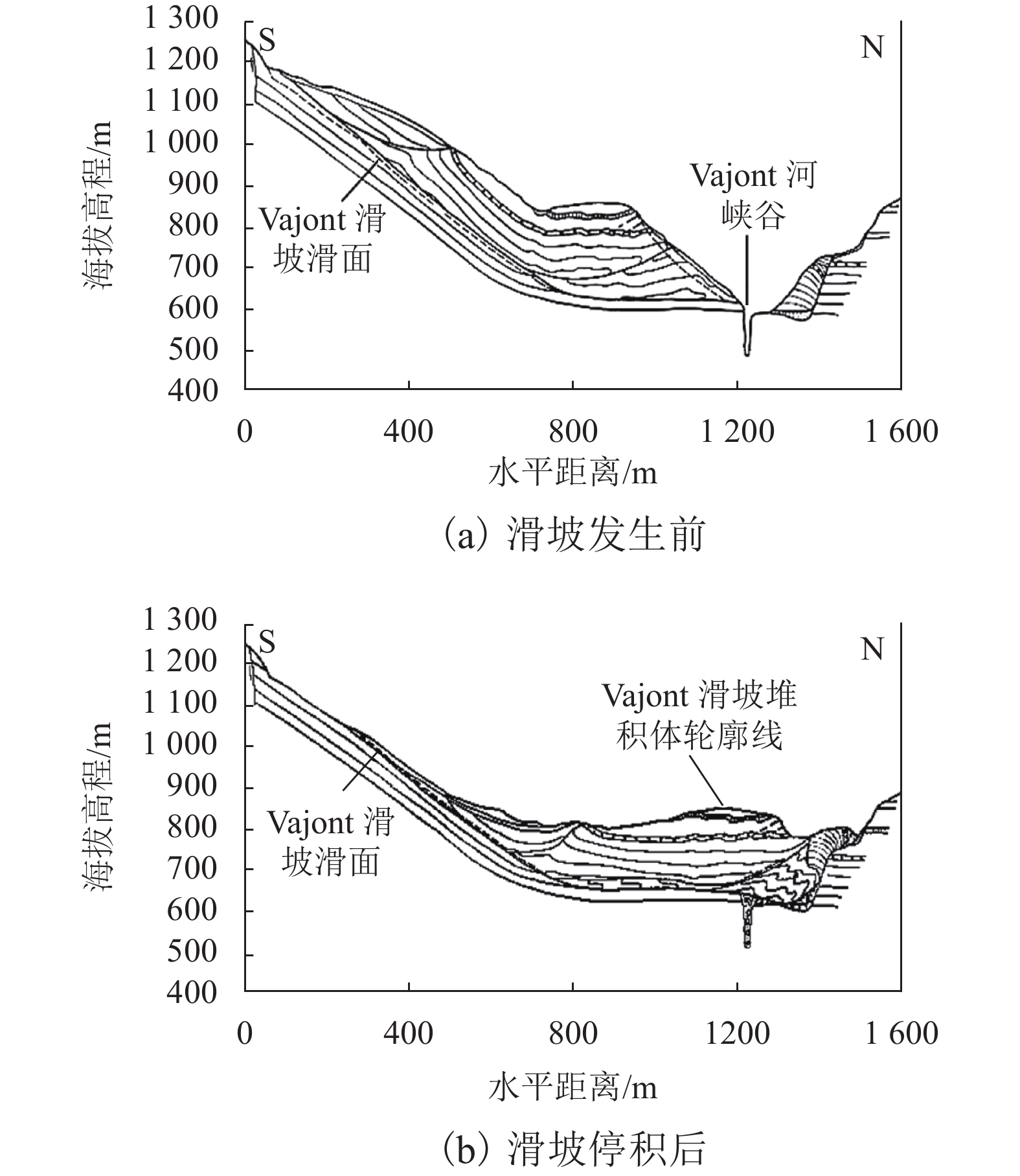
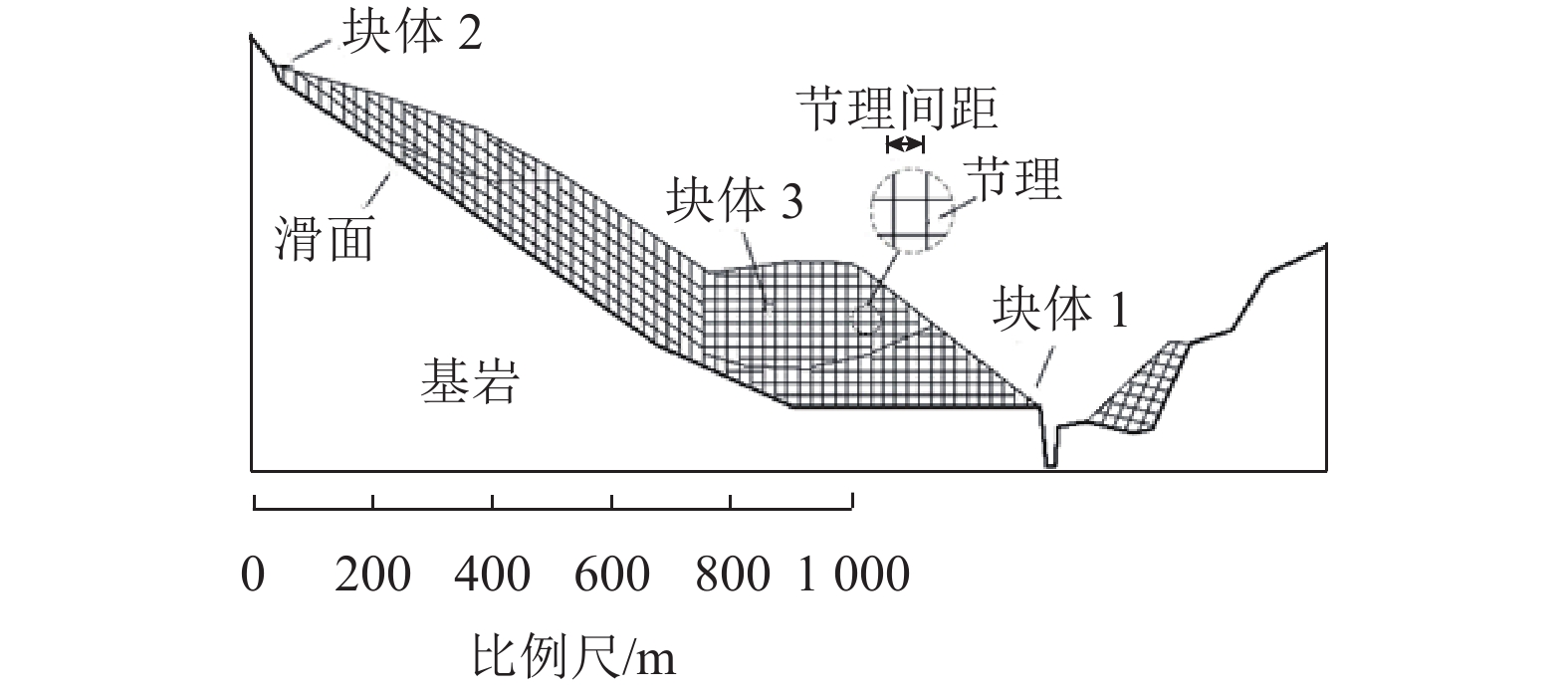
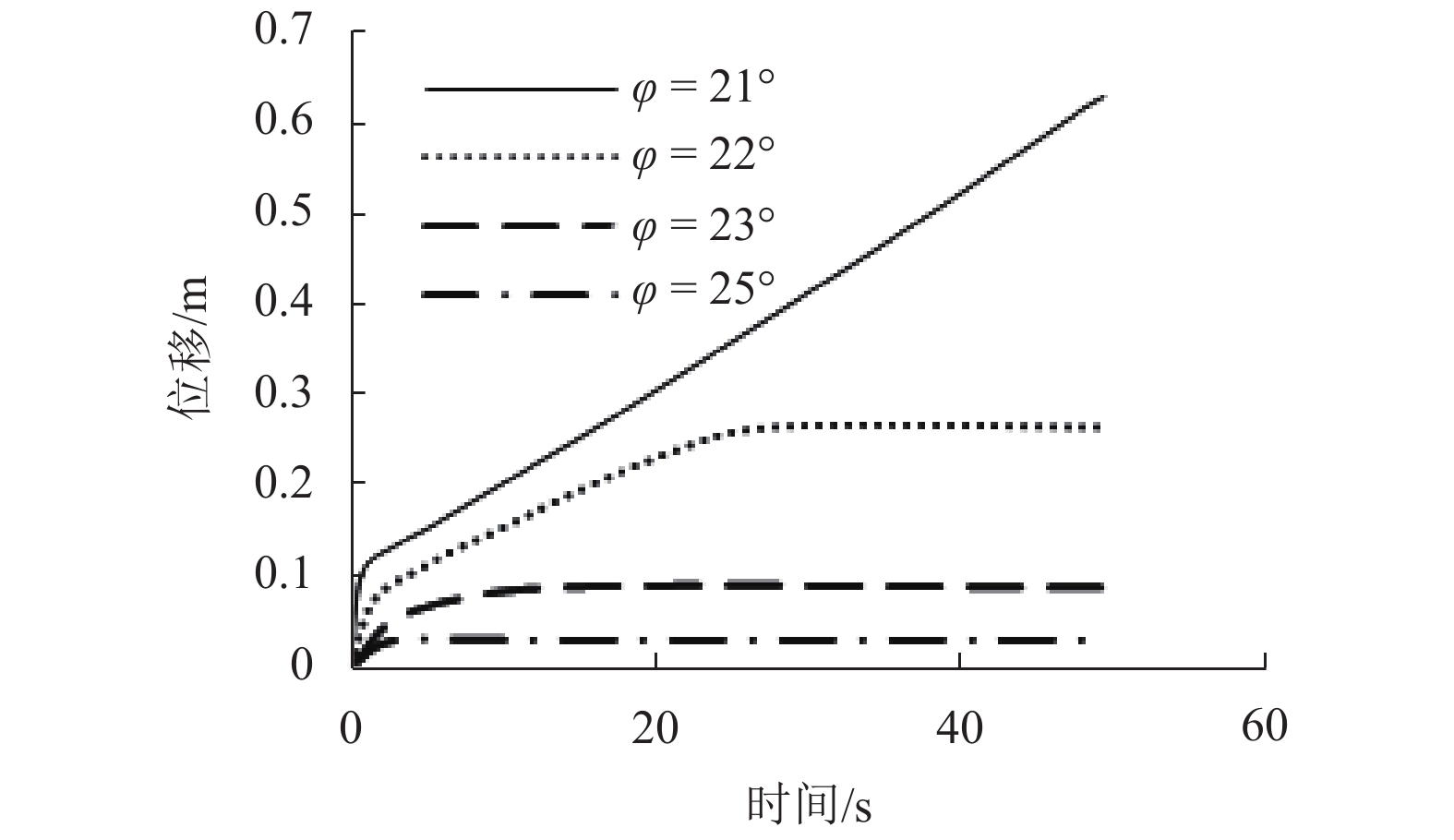
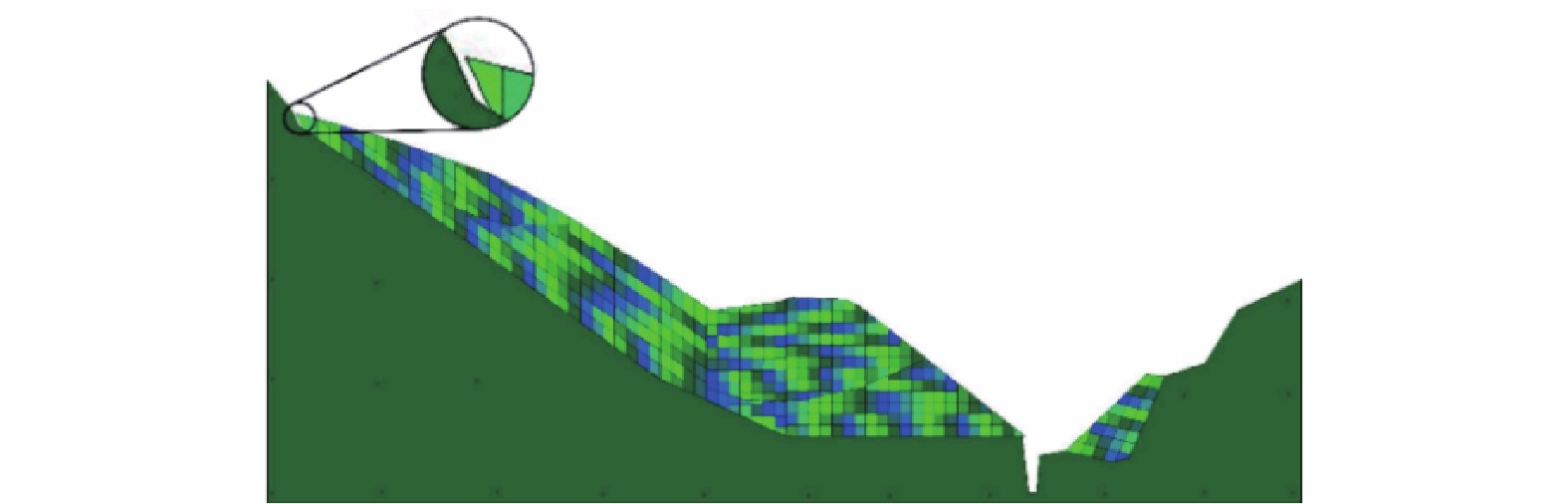
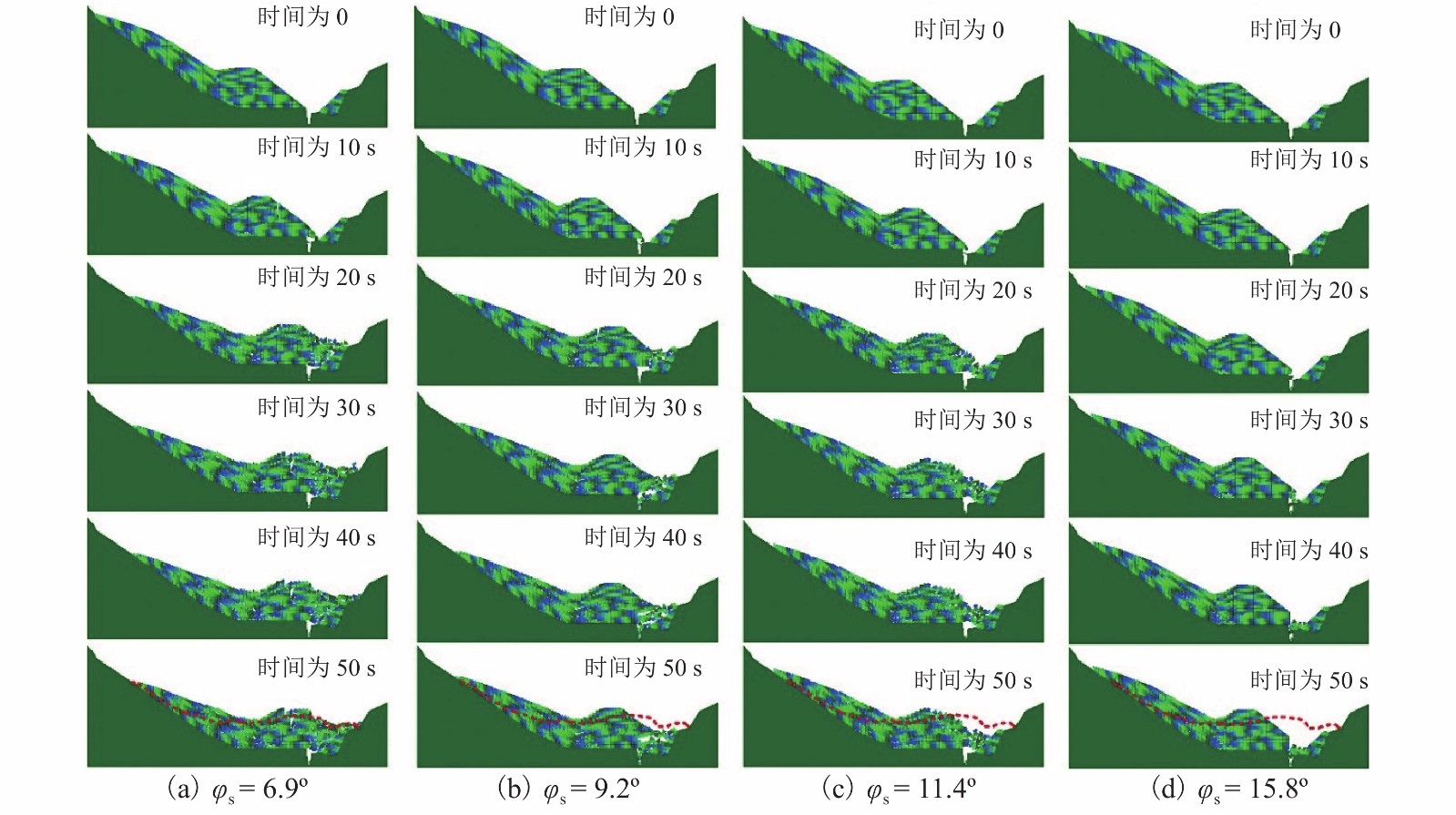
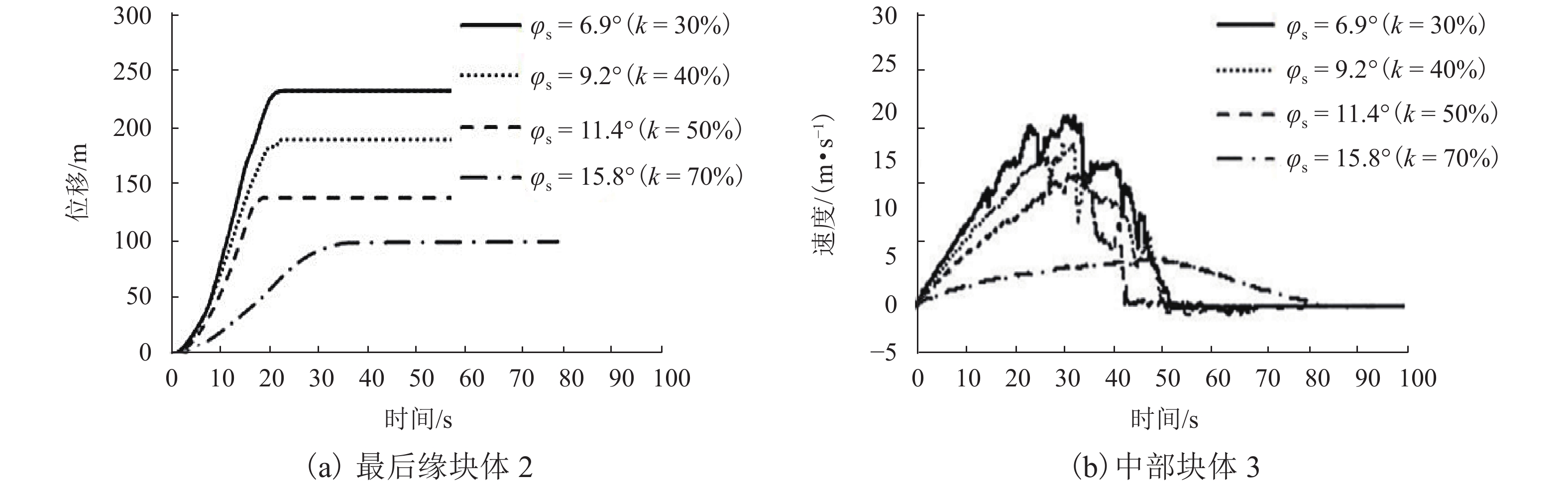
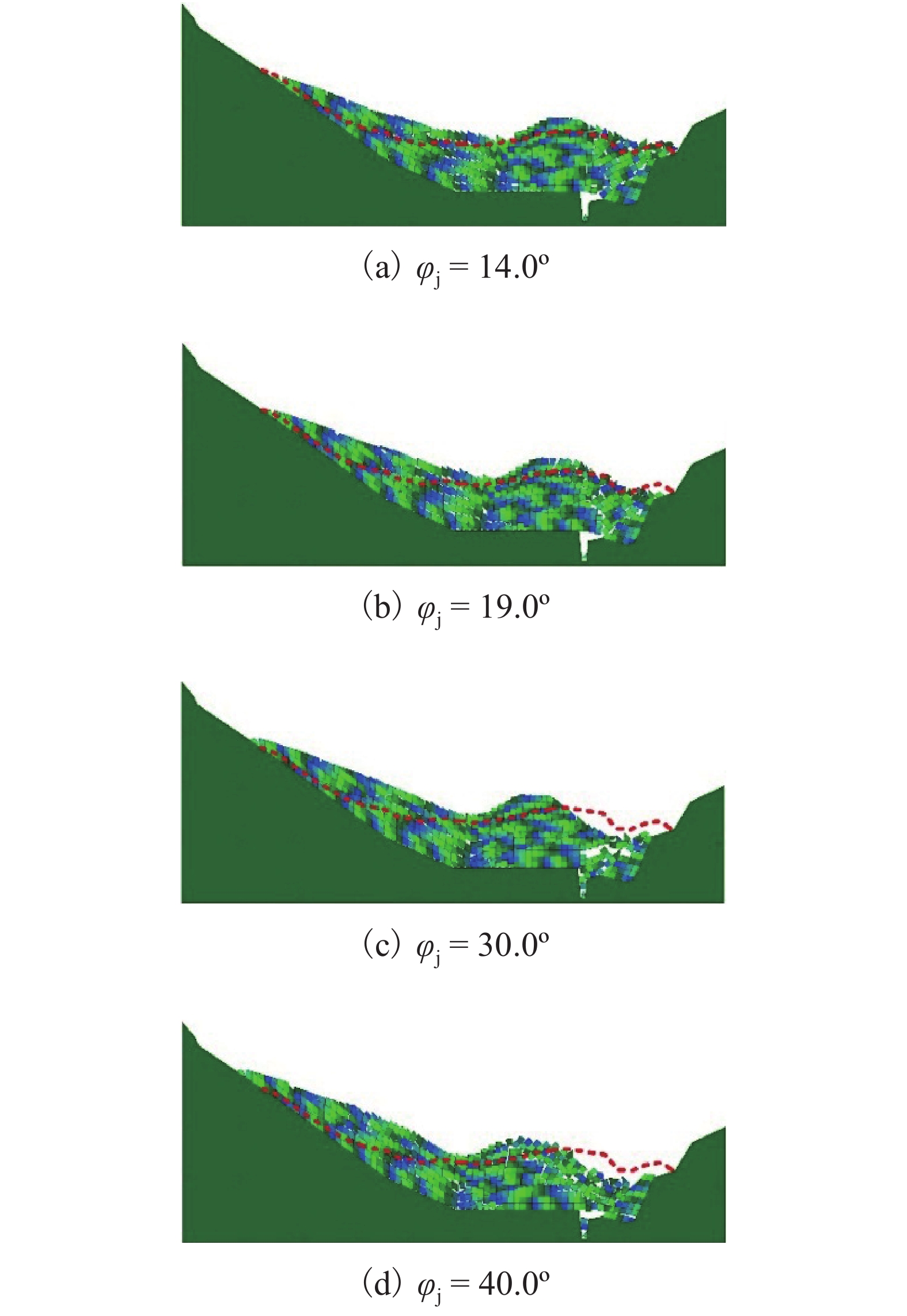
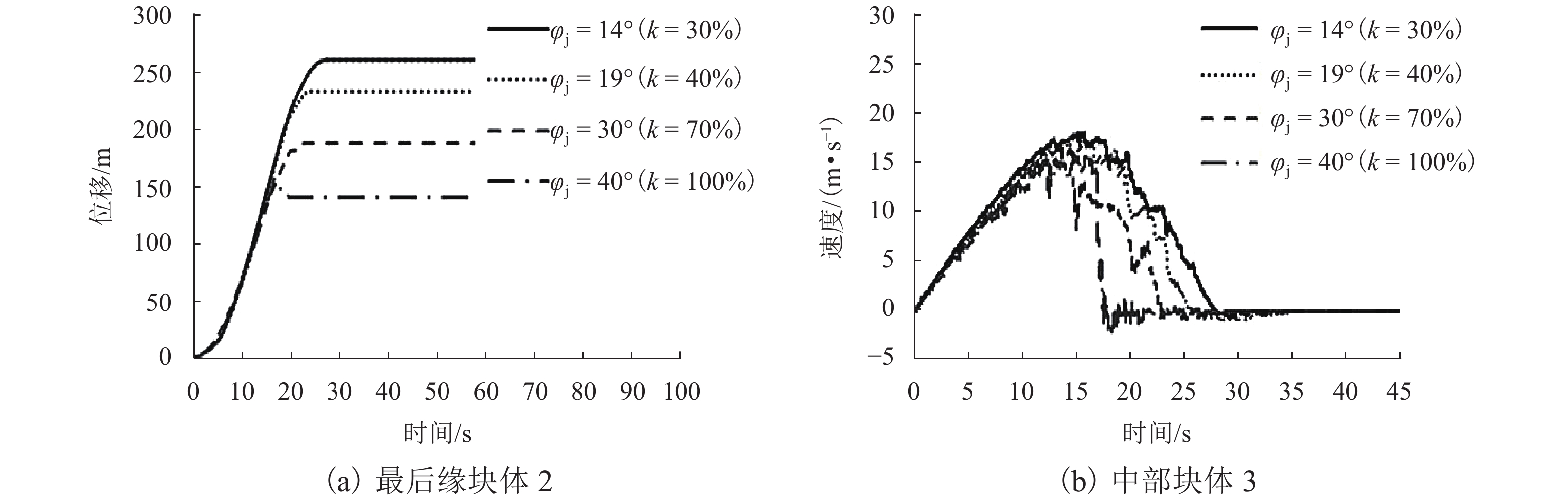
强度衰减是滑坡高速远程运动的重要原因,为了探明滑体强度衰减对滑坡运动能力的影响,以意大利Vajont高速滑坡为例,结合现场调查以及滑坡历史资料,基于岩土体剪切强度衰减理论,利用非连续变形分析(DDA)方法,探讨滑带强度衰减、滑体强度衰减及其共同作用对Vajont滑坡独特运动堆积特征的影响. 研究结果表明:滑带和滑体强度衰减的共同作用造成了Vajont滑坡显著高速运动和独特堆积特征,滑带强度衰减对滑坡运动速度起主导作用,当滑带强度衰减为15.8° 时,监测块体最大速度为5 m/s,当滑带强度衰减为6.9° 时,监测块体的最大速度为19 m/s;滑体强度衰减则对其高速持时具有显著影响,进而大幅提高滑坡运动的远程能力,当滑体强度为40.0° 时,监测块体水平最大位移为140 m,当滑体强度衰减为14.0° 时,监测块体水平最大位移为260 m;数值模拟过程中滑坡呈现出“一体化”运动特征,此特征可用来解释在实际滑坡堆积体高速远程运动过程中保持良好层序的原因.
Abstract:The strength degradation is an important reason for the high-speed and long-distance movement of landslides. In order to explore the influence of landslide strength attenuation on landslide movement ability, taking a high-speed Vajont landslide in Italy as an example, combined with field investigation and landslide history data and based on the shear strength attenuation theory of rock and soil mass, the discontinuous deformation analysis (DDA) method is used to study the influence of sliding band strength attenuation, sliding mass strength attenuation, and their joint action on the unique movement accumulation characteristics of the Vajont landslide. The results show that the remarkable high-speed movement and unique accumulation characteristics of the Vajont landslide are the consequences of strength degradation in both the sliding band and the sliding mass. Among them, the strength attenuation of sliding band play a dominant role in the movement velocity of the landslide. When the strength of sliding band is 15.8° and 6.9°, the maximum velocity of the monitored block is 5 m/s and 19 m/s, respectively. Meanwhile, the strength degradation of sliding mass has a significant effect on its high-speed duration and greatly improves the long-distance ability of landslide movement. When the strength of sliding mass is 40.0° and 14.0°, the maximum horizontal displacement of the monitored block is 140m and 260m, respectively. The ‘en masse’ motion character in the sliding mode can explain well the good strata sequence in the slide deposit after the landslide is fully started.
-
Key words:
- high-speed slide /
- Vajont landslide /
- DDA /
- strength degradation /
- numerical simulation
-
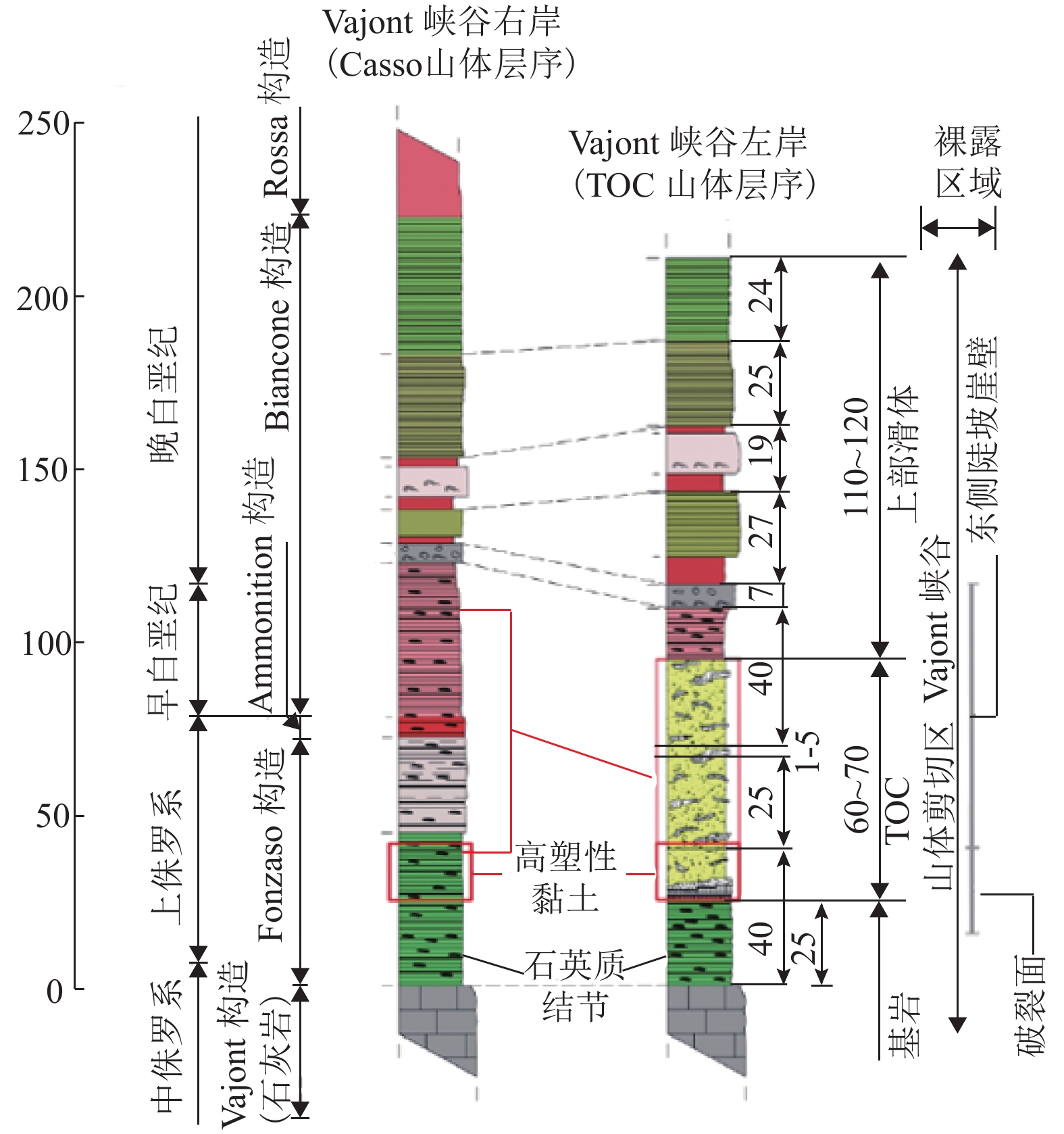
表 1 Vajont滑坡的物理参数
Table 1. Physical parameters of the Vajont landslide
项目 密度 ρ/
( kg•m−3)重度 wy/
( kN•m−3)杨氏模量 E/
GPa泊松比 μ 基岩 2 700 26.46 19 0.35 滑体 2 700 26.46 15 0.31 表 2 节理参数
Table 2. Joint parameters
位置 黏聚力
c /MPa内摩擦角
φj /(°)抗拉强度/Pa 岩体内部节理 2.5 40(稳定时)
30(破坏后)0 表 3 模型控制参数
Table 3. Model control parameters
项目 数值 动力系数 1.0 单步允许最大位移率 0.001 时间步/s 0.005 弹簧刚度/( × 1011 N•mm−1) 1 超松弛系数 1.3 表 4 滑带内摩擦角不同时滑坡的最大速度
Table 4. Maximum velocities of the landslide with different friction angles of sliding band
φs/(°) 最大速度/(m•s−1) 6.9 19.47 9.2 16.74 11.4 13.60 15.8 5.05 -
[1] MÜLLER-SALZBURG L. The rock slide in the Vajont valley[M]. Springer-Verlag, 1964: 148-212. [2] MÜLLER-SALZBURG L. The Vajont catastrophe-A personal review[J]. Engineering Geology, 1987, 24(1/2/3/4): 423-444. [3] HENDRON A J, PATTON F D. The Vaiont slide: a geotechnical analysis based on new geological observations of the failure surface: US army engineer waterways experiment station[R]. Washington D. C.: Department of the Army US Army Corps of Engineers, 1985. [4] SUPERCHI L, FLORIS M, GHIROTTI M, et al. Implementation of a geodatabase of published and unpublished data on the catastrophic Vaiont landslide[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2010, 10(4): 865-873. [5] ALONSO E E, PINYOL N M. Criteria for rapid sliding I: a review of Vaiont case[J]. Engineering Geology, 2010, 114(3/4): 198-210. [6] PARONUZZI P, BOLLA A. The prehistoric Vajont rockslide:an updated geological model[J]. Geomorphology, 2012, 169(10): 165-191. [7] CECINATO F, ZERVOS A, VEVEAKIS E. A thermo-mechanical model for the catastrophic collapse of large landslides[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2010, 35(14): 1507-1535. [8] HABIB P. Production of gaseous pore pressure during rock slides[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 1975, 7(4): 193-197. [9] NONVEILLER E. The Vajont reservoir slope failure[J]. Engineering Geology, 1987, 24(87): 493-512. [10] VOIGHT B, FAUST C. Frictional heat and strength loss in some rapid landslides[J]. Geotechnique, 1982, 32(1): 43-54. doi: 10.1680/geot.1982.32.1.43 [11] ARDOULAKIS I. Dynamic thermo-poro-mechanical analysis of catastrophic landslides[J]. Geotechnique, 2002, 52(3): 157-171. [12] PINYOL N M, ALONSO E E. Criteria for rapid sliding Ⅱ.: thermo-hydro-mechanical and scale effects in Vaiont case[J]. Engineering Geology, 2010, 114(3/4): 211-227. [13] HU W, HUANG R Q, MCSAVENEY M, et al. Superheated steam,hot CO2 and dynamic recrystallization from frictional heat jointly lubricated a giant landslide:field and experimental evidence[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2019, 510: 85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2019.01.005 [14] TIKA T E, HUTCHINSON J N. Ring shear tests on soil from the Vaiont landslide slip surface[J]. Geotechnique, 1999, 49(1): 59-74. doi: 10.1680/geot.1999.49.1.59 [15] FERRI F, DI TORO G, HIROSE T, et al. Low-to high-velocity frictional properties of the clay-rich gouges from the slipping zone of the 1963 Vaiont slide,northern Italy[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2011, 116(B9): 1-17. [16] 崔圣华,裴向军,黄润秋,等. 大光包滑坡不连续地质特征及其工程地质意义[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2019,54(1): 65-76.CUI Shenghua, PEI Xiangjun, HUANG Runqiu, et al. Discontinuities and engineering geological significances of strong earthquake-induced daguangbao landslide[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(1): 65-76. [17] ZHANG Y B, CHEN G Q, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of near-fault seismic loadings on run-out of large-scale landslide:a case study[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, 166(11): 216-236. [18] ZHANG Y B, WANG J M, XU Q, et al. DDA validation of the mobility of earthquake-induced landslides[J]. Engineering Geology, 2015, 194: 38-51. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.08.024 [19] ZHANG Y B, XU Q, CHEN G Q, et al. Extension of discontinuous deformation analysis and application in cohesive-frictional slope analysis[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2014, 70(10): 533-545. [20] 邬爱清,丁秀丽,李会中,等. 非连续变形分析方法模拟千将坪滑坡启动与滑坡全过程[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2006,25(7): 1297-1303. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.07.001WU Aiqing, DING Xiuli, LI Huizhong, et al. Numerical simulation of startup and whole failure process of Qianjiangping landslide using discontinuous deformation analysis method[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(7): 1297-1303. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.07.001 [21] 赵兴权,张迎宾,陈光齐,等. 非连续变形分析方法及其在灾害防治研究中的应用[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(2): 300-312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.010ZHAO Xingquan, ZHANG Yingbin, CHEN Guangqi, et al. Discontinuous deformation analysis method and its applications to disaster prevention[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 300-312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.010 [22] 刘军,李仲奎. 非连续变形分析(DDA)方法研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(5): 839-845. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.05.024LIU Jun, LI Zhongkui. Current situation and development of DDA method[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2004, 23(5): 839-845. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.05.024 [23] 姜清辉,周创兵. 岩土工程不连续变形分析计算中的若干问题[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(10): 2014-2026. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.10.009JIANG Qinghui, ZHOU Chuangbing. Some issues in discontinuous deformation analysis for geotechnical engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(10): 2014-2026. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.10.009 [24] 陈岩岩. Vajont滑坡稳定性及高速运动特征的DDA模拟研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. [25] SEMENZA E. Sintesi degli studi geologici sulla frana del Vajont dal 1959 al 1964[J]. Museo Tridentino di Scienze Naturali, 1965, 16: 1-52. [26] SEMENZA E, GHIROTTI M. History of the 1963 Vaiont slide:the importance of geological factors[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2000, 59(2): 87-97. [27] 张迎宾,余鹏程,赵兴权. 类梯形山体的地震动力响应分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(3): 435-441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.03.008ZHANG Yingbin, YU Pengcheng, ZHAO Xingquan. Analytical solutions of earthquake dynamic responses of trapezoid-like mountain[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(3): 435-441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.03.008 [28] TROLLOPE D H. The Vajont slope failure[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 1980, 13(2): 71-88. [29] BOON C W, HOULSBY G T, UTILI S. New insights into the 1963 Vajont slide using 2D and 3D distinct-element method analyses[J]. Geotechnique, 2014, 64(10): 800-816. doi: 10.1680/geot.14.P.041 [30] SUPERCHI L. The Vajont rockslide: new techniques and traditional methods to re-evaluate the catastrophic event[D]. Padova: Padova University, 2012. [31] 郑颖人,赵尚毅,孔位学,等. 极限分析有限元法讲座——I岩土工程极限分析有限元法[J]. 岩土力学,2005,26(1): 163-168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2005.01.035ZHENG Yingren, ZHAO Shangyi, KONG Weixue, et al. Geotechnical engineering limit analysis using finite element method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2005, 26(1): 163-168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2005.01.035 [32] 郑颖人,赵尚毅. 有限元强度折减法在土坡与岩坡中的应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(19): 3381-3388. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.19.029ZHENG Yingren, ZHAO Shangyi. Application of strength reduction fem in soil and rock slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(19): 3381-3388. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.19.029 [33] MACLAUGHLIN M M. Discontinuous deformation analysis of the kinematics of landslides[D]. Berkeley: University of California, 1997. [34] MACLAUGHLIN M, SITAR N, DOOLIN D, et al. Investigation of slope-stability kinematics using discontinuous deformation analysis[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2001, 38(5): 753-762. [35] GHIROTTI M. Edoardo semenza: the importance of geological and geomorphological factors in the identification of the ancient Vaiont landslide[M]. Netherlands: Springer, 2006: 395-406. [36] BARTON N. The shear strength of rock and rock joints[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Science & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1976, 13(9): 255-279. -




 下载:
下载: