Calculation of Urban Rail AC/DC Power Supply with Traction Substation in Multi-Operation Modes
-
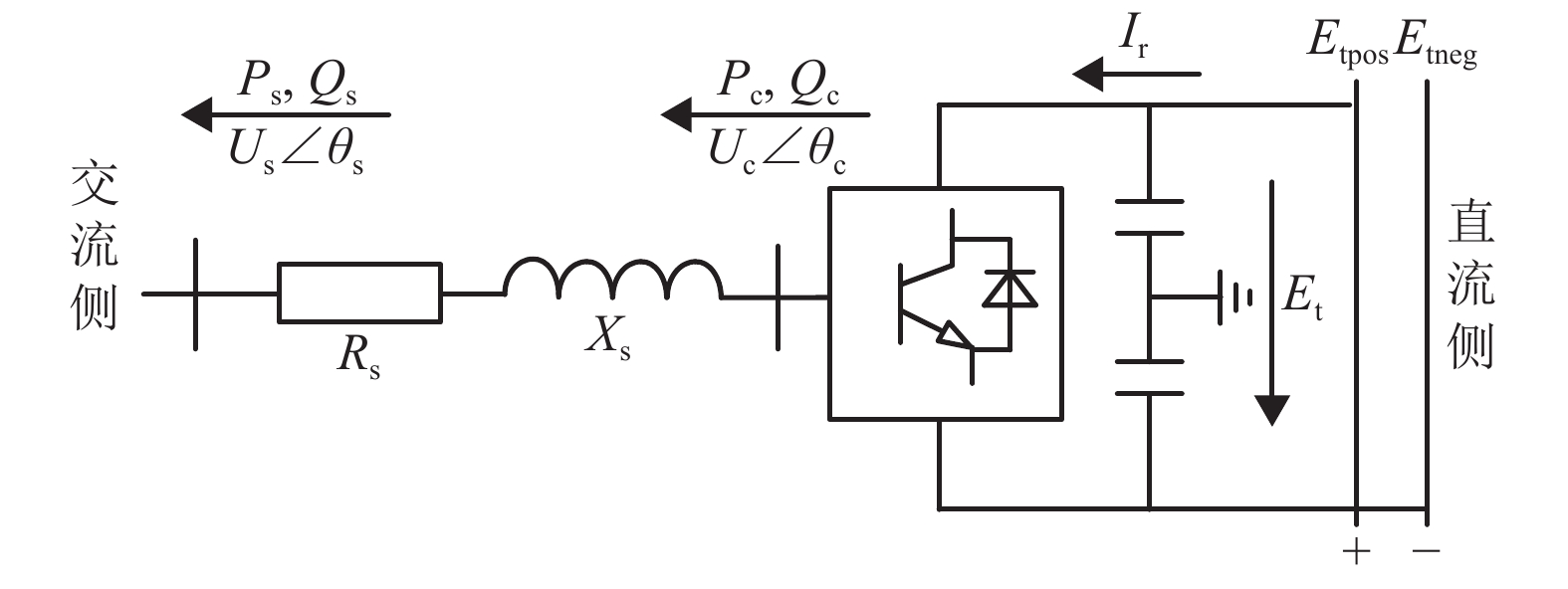
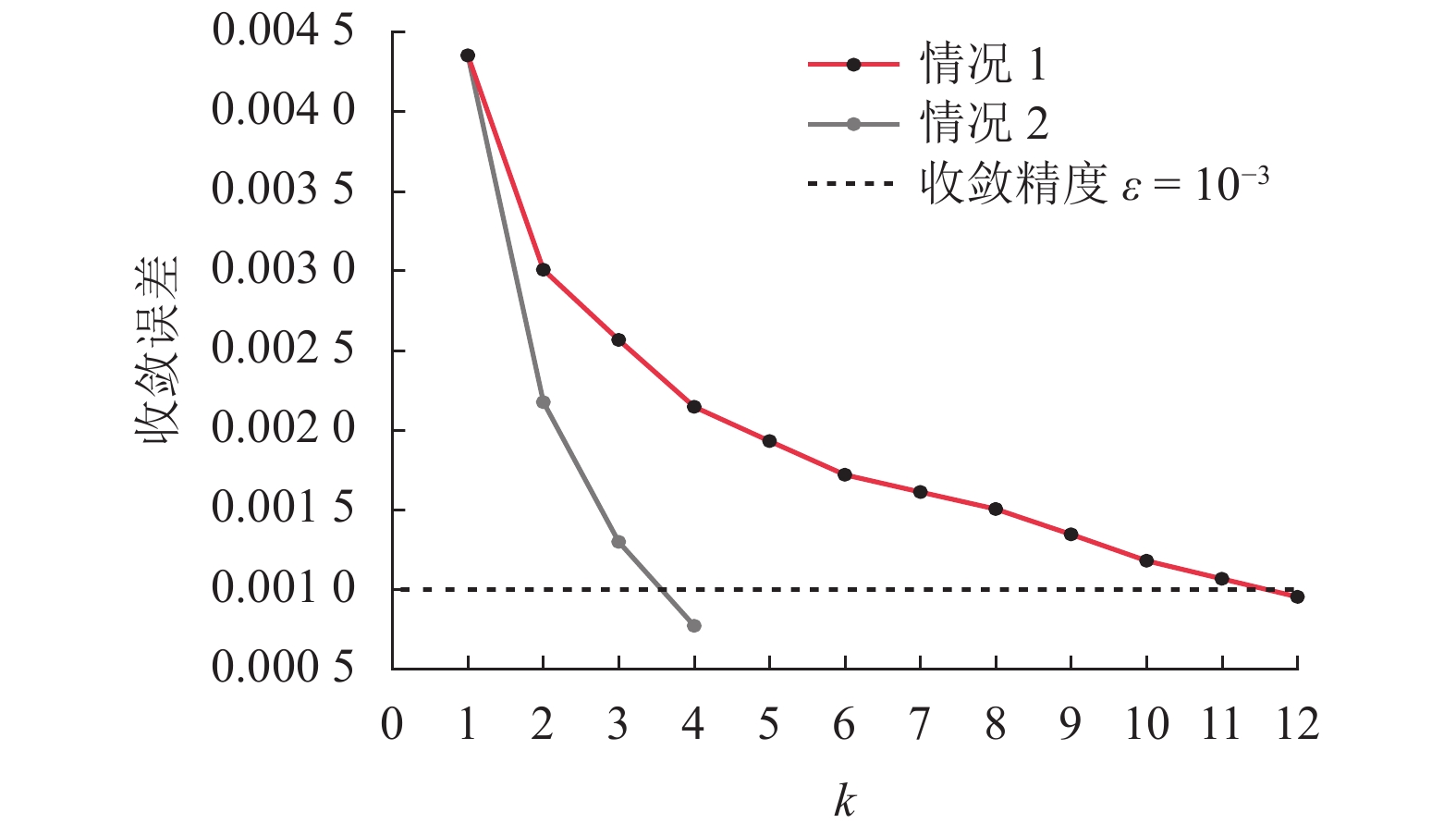
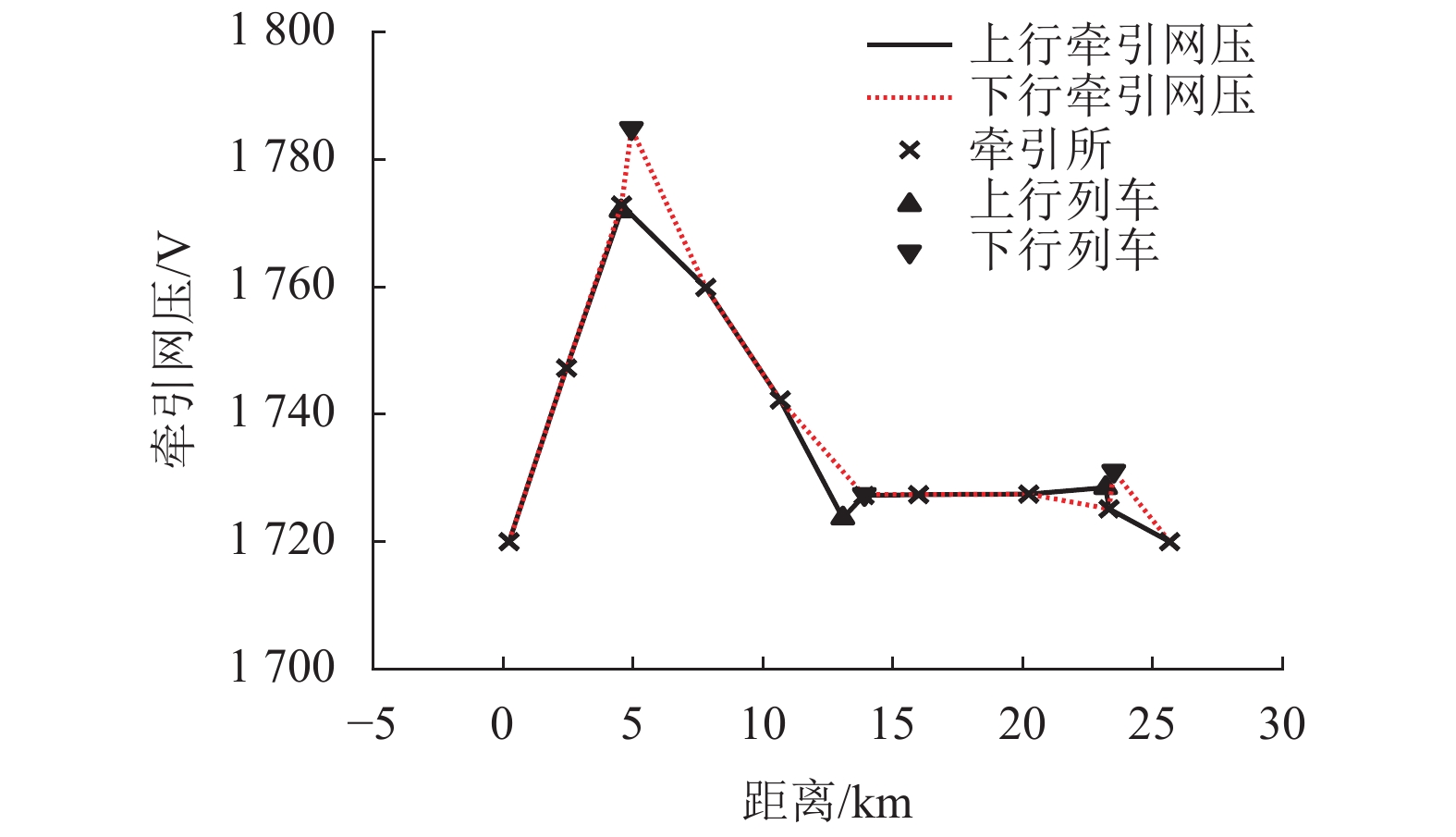
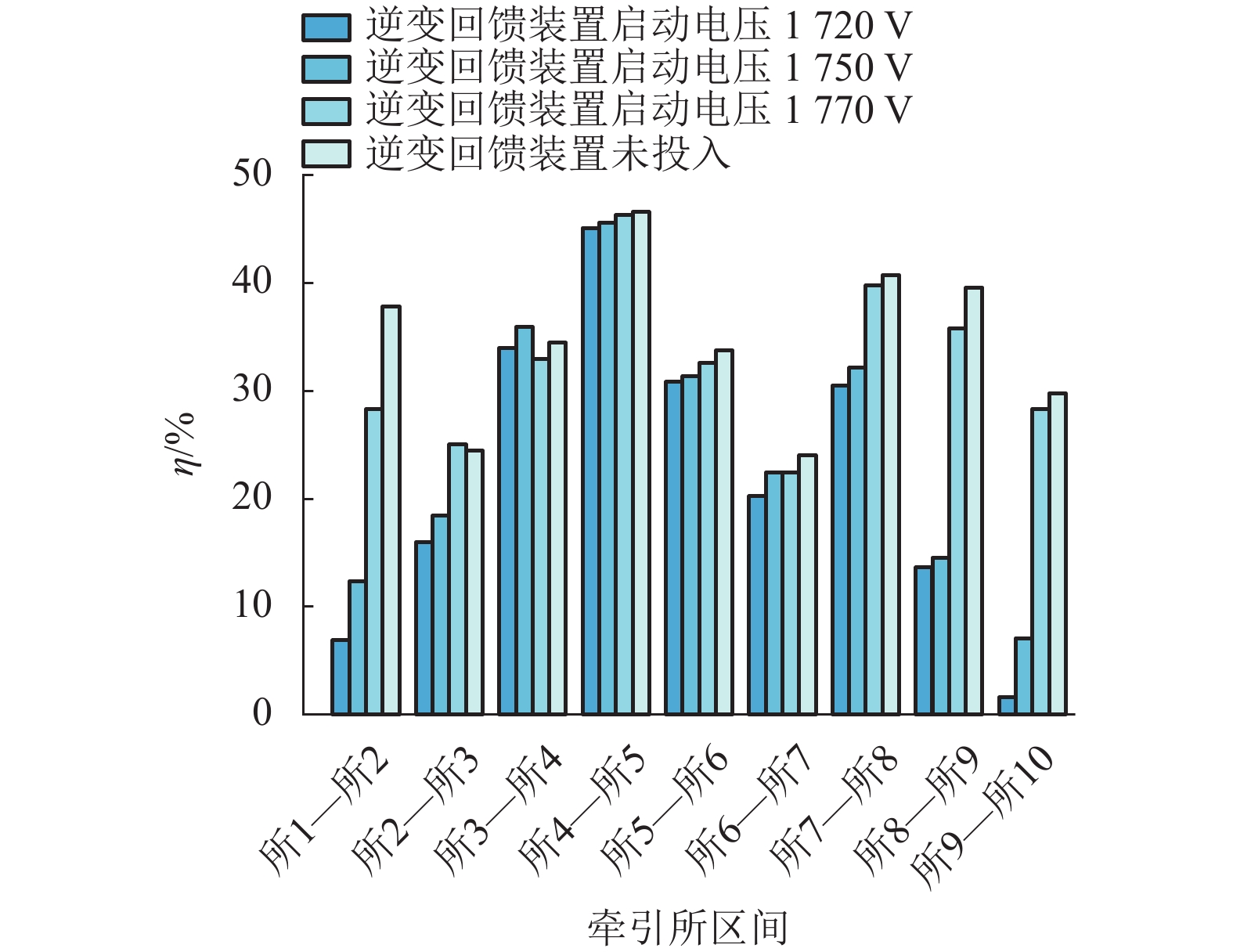
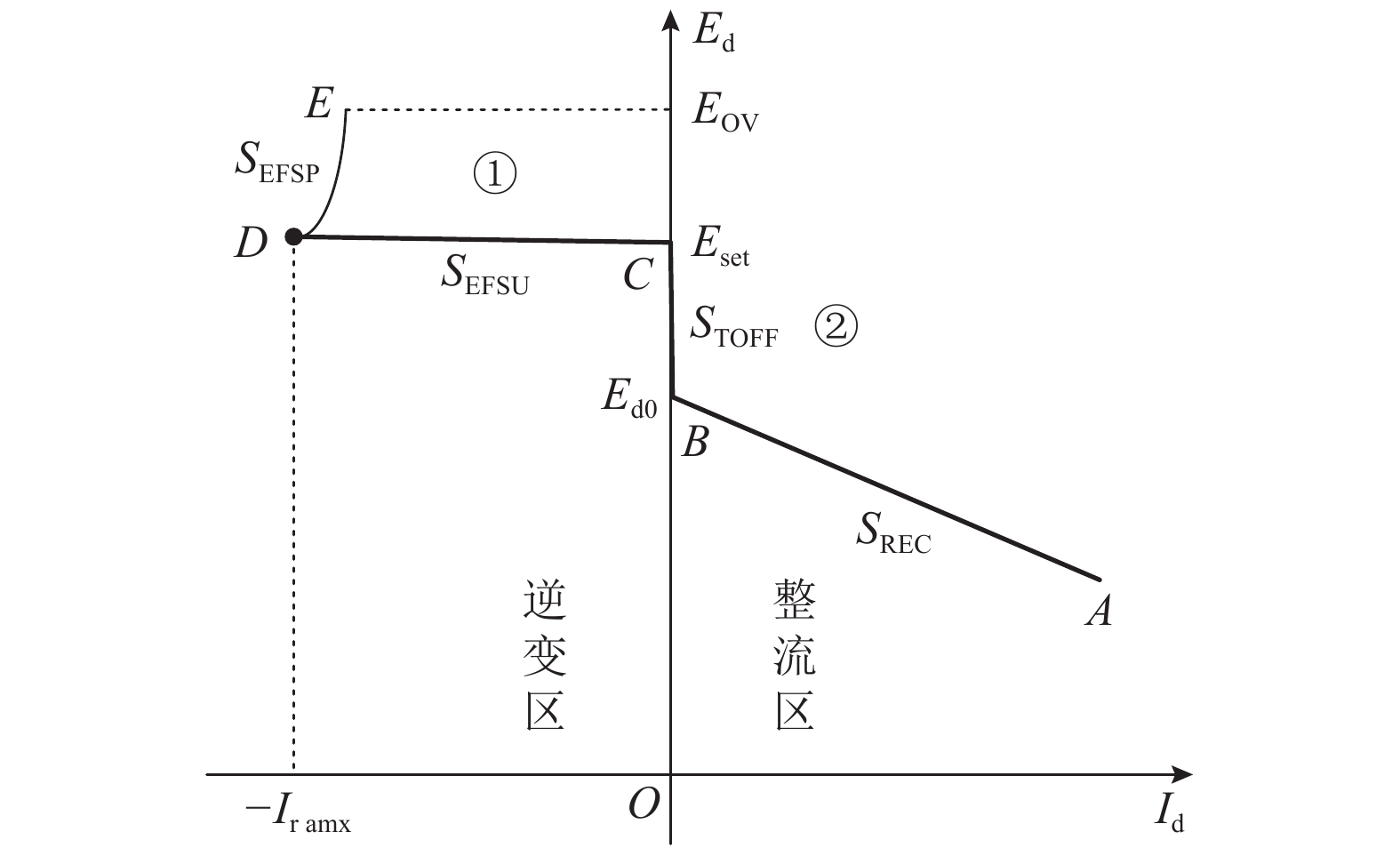
摘要: 城市轨道牵引变电所存在多种运行状态:整流状态、整流机组关断状态、逆变回馈装置恒定电压运行状态、逆变回馈装置最大功率运行状态. 针对潮流计算中牵引变电所状态的不确定而影响计算收敛性的问题,提出一种考虑牵引变电所多运行状态的城轨交直流供电计算算法. 该算法对逆变回馈装置和车载制动电阻建模,根据迭代过程中牵引变电所网压、电流,采用滞环比较策略确定牵引变电所状态,通过交直流交替迭代方法求解潮流. 对某地铁工程进行仿真分析和实测验证,结果表明:仿真与实测的牵引变电所负荷过程曲线Pearson相关系数为0.76~0.92;逆变回馈装置节能率的仿真结果与实测误差不超过1.7%;在全线整流机组空载电压较高的场合,当逆变回馈装置的启动电压设置在1750 V以上时,消耗在车载制动电阻上的能量显著增大.Abstract: Traction substations operate in such modes as the rectification, rectifier turn-off, constant voltage operation of inverting-feedback devices, and maximum-power operation of inverting-feedback device. To achieve convergence in power flow calculation when the states of traction substations are uncertain, a calculation algorithm for urban rail AC/DC power supply is proposed while it considers the multi-operation states of traction substation. As for this algorithm, the inverting-feedback devices and onboard resistors on trains are modeled. According to the network voltage of the traction substation in the iterative process, the state of traction substation is determined by hysteretic comparison strategy, and the power flow is solved by AC/DC alternating iteration method. The simulation and field tests of a subway project show that the Pearson correlation coefficient between the simulated and measured load process falls between 0.76 and 0.92; and the errors between the simulation and measured energy-saving rate of the inverting-feedback devices are not more than 1.7%. In the case of high no-load voltage of substations in DC traction power supply system, when the starting voltage of the inverting feedback device is set above 1750 V, the energy consumed by the on-board braking resistor is significantly increased.
-
Key words:
- urban rail transit /
- inverting feedback devices /
- flow calculation /
- hysteresis loop /
- energy-savings
-
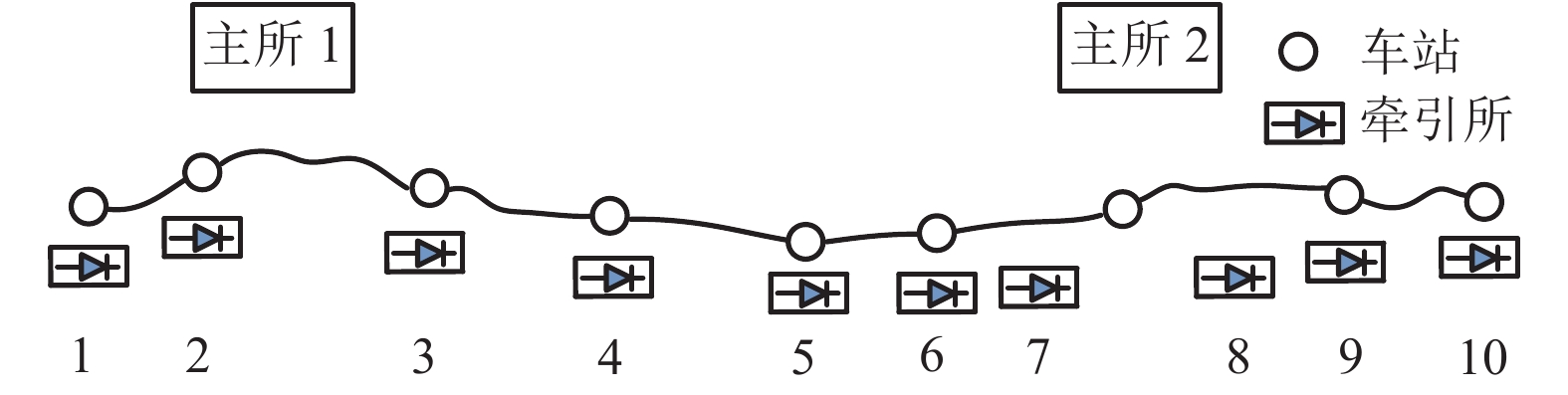
表 1 某地铁工程牵引所位置分布
Table 1. Position distribution of traction station in subway project
牵引所编号 位置/km 牵引所编号 位置/km 1 0.243 6 13.900 2 2.456 7 15.995 3 4.568 8 20.235 4 7.804 9 23.322 5 10.670 10 25.650 表 2 仿真主要参数设置
Table 2. Main parameters in simulation
参数 数值 主变压器容量/(MV•A) 2 × 25 整流机组额定功率/kW 2 × 2500 车载制动电阻启动电压/V 1790 降压所负载率 0.25 接触网电阻/(Ω•(km)−1) 0.0172 钢轨纵向电阻/(Ω•(km)−1) 0.02 钢轨对地过渡电阻/(Ω•km) 15 表 3 系统列车功率分布
Table 3. System train power distribution
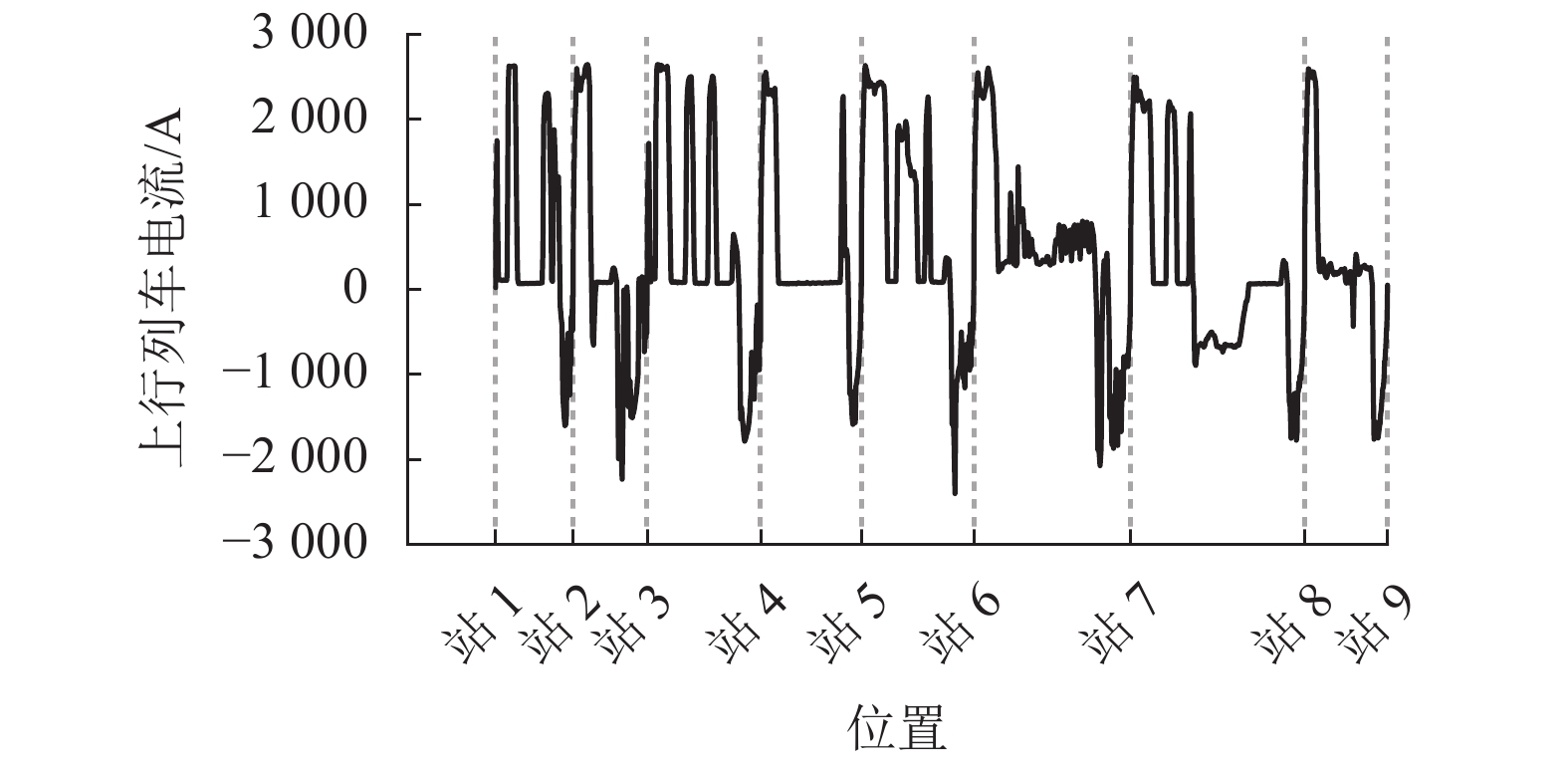
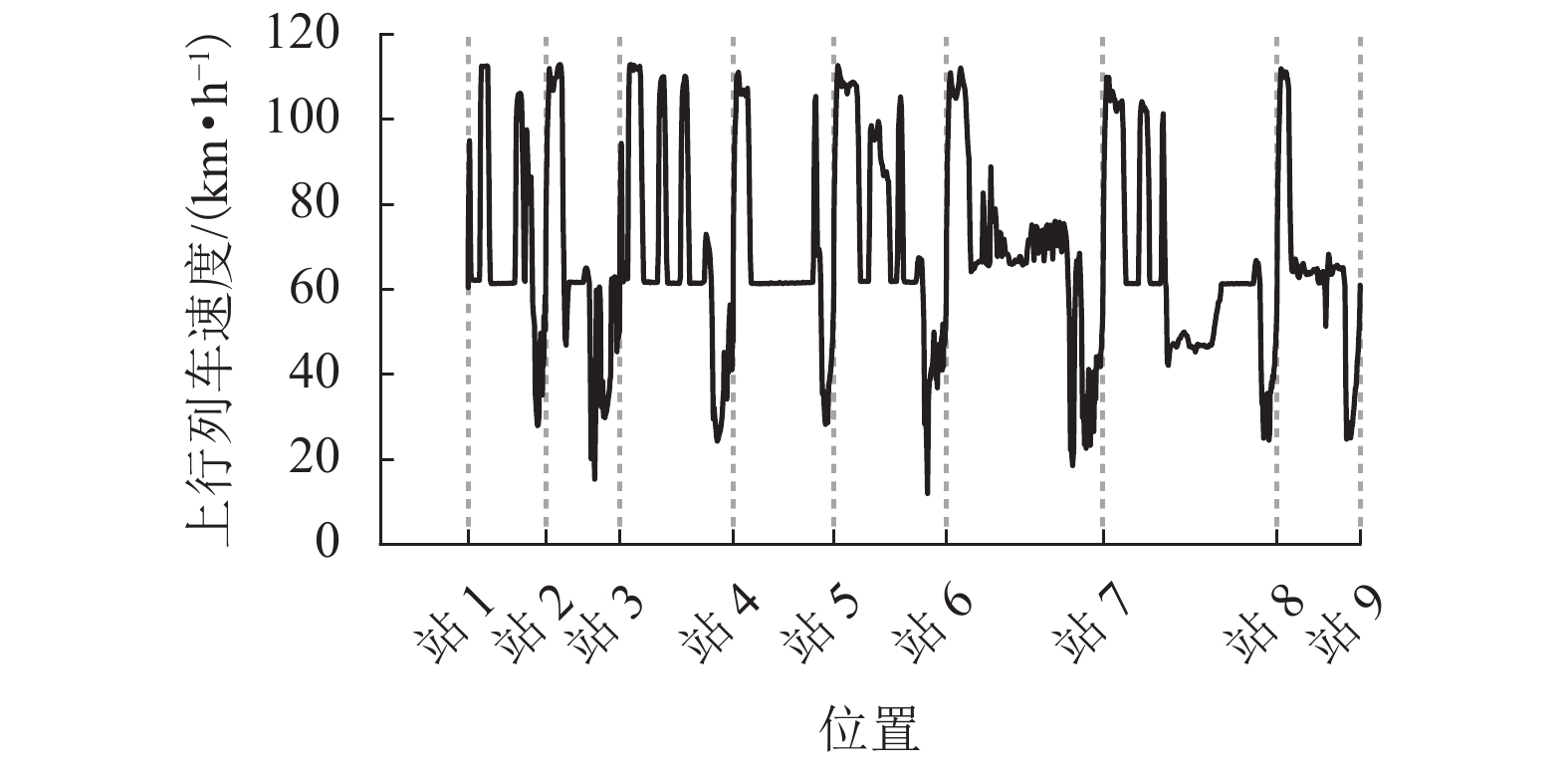
上行列车 下行列车 位置/km 功率/kW 位置/km 功率/kW 4.553 57.000 4.958 −1432.606 13.078 547.800 13.916 32.550 23.190 −924.885 23.508 −1833.192 表 4 牵引所9负荷过程的仿真与实测比较
Table 4. Comparison of simulation and actual load process in traction station 9
逆变回馈装置启动电压/V 每小时牵引能
耗/(kW•h)每小时反馈能
量/(kW•h)整流机组工作电流峰值/A 逆变回馈装置工作电流峰值/A 占空比/% 节能率/% 1720 实测 461.6 117.2 1571.7 1191.7 18.2 25.4 仿真 439.4 110.8 1670.3 944.0 22.8 25.2 1750 实测 577.7 78.3 1753.8 652.0 14.8 13.6 仿真 604.4 71.9 1693.8 813.1 18.2 11.9 1770 实测 683.3 23.1 1832.7 209.6 10.8 3.4 仿真 678.7 28.8 1701.2 541.3 11.4 4.2 -
魏文婧,胡海涛,王科,等. 基于铁路功率调节器的高速铁路牵引供电系统储能方案及控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报,2019,34(6): 1290-1299.WEI Wenjing, HU Haitao, WANG Ke, et al. Energy storage scheme and control strategies of high-speed railway based on railway power conditioner[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34(6): 1290-1299. 刘学军,于松伟,刘学. 轨道交通牵引供电仿真模型与算法的研究[J]. 计算机仿真,2004,21(12): 213-218.LIU Xuejun, YU Songwei, LIU Xue. Model and algorithm for traction power system simulation of urban rail-line[J]. Computer Simulation, 2004, 21(12): 213-218. 刘炜,李群湛,唐兵,等. 基于蒙特卡洛模拟的城市轨道概率潮流分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2010,45(4): 561-567.LIU Wei, LI Qunzhan, TANG Bing, et al. Probabilistic load flow for urban rail traction power supply based on Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010, 45(4): 561-567. PABLO A. DC railway simulation including controllable power electronic and energy storage devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33(5): 5319-5329. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2018.2801023 胡海涛,王江峰,何正友,等. 地铁牵引供电系统交-直流潮流算法研究[J]. 铁道学报,2012,34(11): 22-28.HU Haitao, WANG Jiangfeng, HE Zhengyou, et al. Study on power flow algorithm for metro traction supply system[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2012, 34(11): 22-28. TZENG Y S, WU Ruannan, CHEN Nanming, et al. Electric network solutions of DC transit systems with inverting substations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 1998, 47(4): 1405-1412. doi: 10.1109/25.728537 TYLAVSKY D J. The Newton raphson load flow applied to AC/DC systems with commutation impedance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 1983, IA-19(6): 940-948. doi: 10.1109/TIA.1983.4504318 BEERTEN J, COLE S, BELMANS R. Generalized steady-state VSC MTDC model for sequential AC/DC power flow algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2012, 27(2): 821-829. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2011.2177867 徐殿国,刘瑜超,武健. 多端直流输电系统控制研究综述[J]. 电工技术学报,2015,30(17): 1-12.XU Dianguo, LIU Yuchao, WU Jian. Review on control strategies of multi-terminal direct current transmission system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2015, 30(17): 1-12. 王家融,艾欣,王坤宇,等. 基于增广雅可比矩阵的交直流解耦潮流新算法[J]. 电工技术学报,2018,33(6): 1382-1389.WANG Jiarong, AI Xin, WANG Kunyu, et al. A Novel AC-DC decoupled power flow calculation method based on the augmented Jacobian matrix[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2018, 33(6): 1382-1389. 刘志刚,郝峰杰,陈杰,等. 城轨牵引供电系统车-地配合参数优化方法[J]. 北京交通大学学报,2019,43(1): 79-87.LIU Zhigang, HAO Fengjie, CHEN Jie, et al. Optimization method of train-ground coordination parameters for urban traction power supply system[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019, 43(1): 79-87. 刘斌. 城市轨道交通供电系统中压能馈装置应用分析[J]. 电气技术,2016,35(3): 148-151.LIU Bin. Analysis of application of medium voltage power feeder in urban rail transit power supply system[J]. Electrical Engineering, 2016, 35(3): 148-151. 刘炜,李群湛,陈民武. 城市轨道交通交直流统一的牵引供电计算[J]. 电力系统保护与控制,2010,38(8): 128-133.LIU Wei, LI Qunzhan, CHEN Minwu. Study of unified AC/DC power flow in DC traction power supply system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2010, 38(8): 128-133. VAHEDI H, LABBE P A, AI-HADDAD K. Balancing three-level neutral point clamped inverter DC bus using closed-loop space vector modulation:Real-time implementation and investigation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2016, 9(10): 2076-2084. doi: 10.1049/iet-pel.2015.0226 任敬国,赵建国,于大洋,等. VSC-HVDC输电系统模式切换控制策略[J]. 电力系统自动化,2012,36(6): 69-73.REN Jingguo, ZHAO Jianguo, YU Dayang, et al. Mode switching control strategy for VSC-HVDC transmission system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2012, 36(6): 69-73. 邓旗,张英敏,李志晗. 不同调度模式下VSC-MTDC系统的协调控制策略[J]. 电力建设,2017,38(8): 67-72.DENG Qi, ZANG Yingmin, LI Zhihan. Coordinated control strategy of VSC-MTDC system under different power dispatching modes[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2017, 38(8): 67-72. -




 下载:
下载: