Method of Motor Starting Current Control Based on Hydraulic Pump/Motor Reverse Drive
-
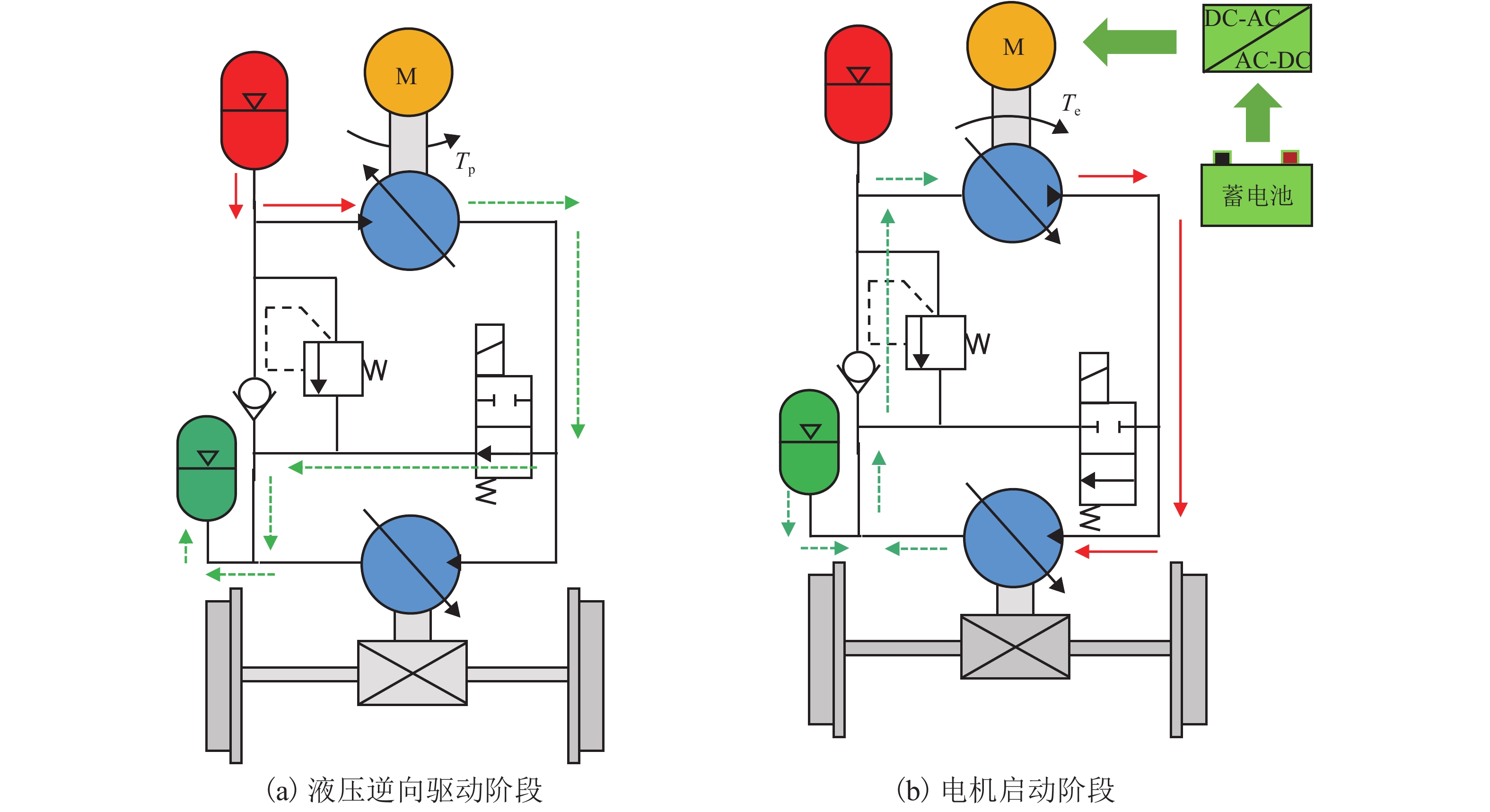
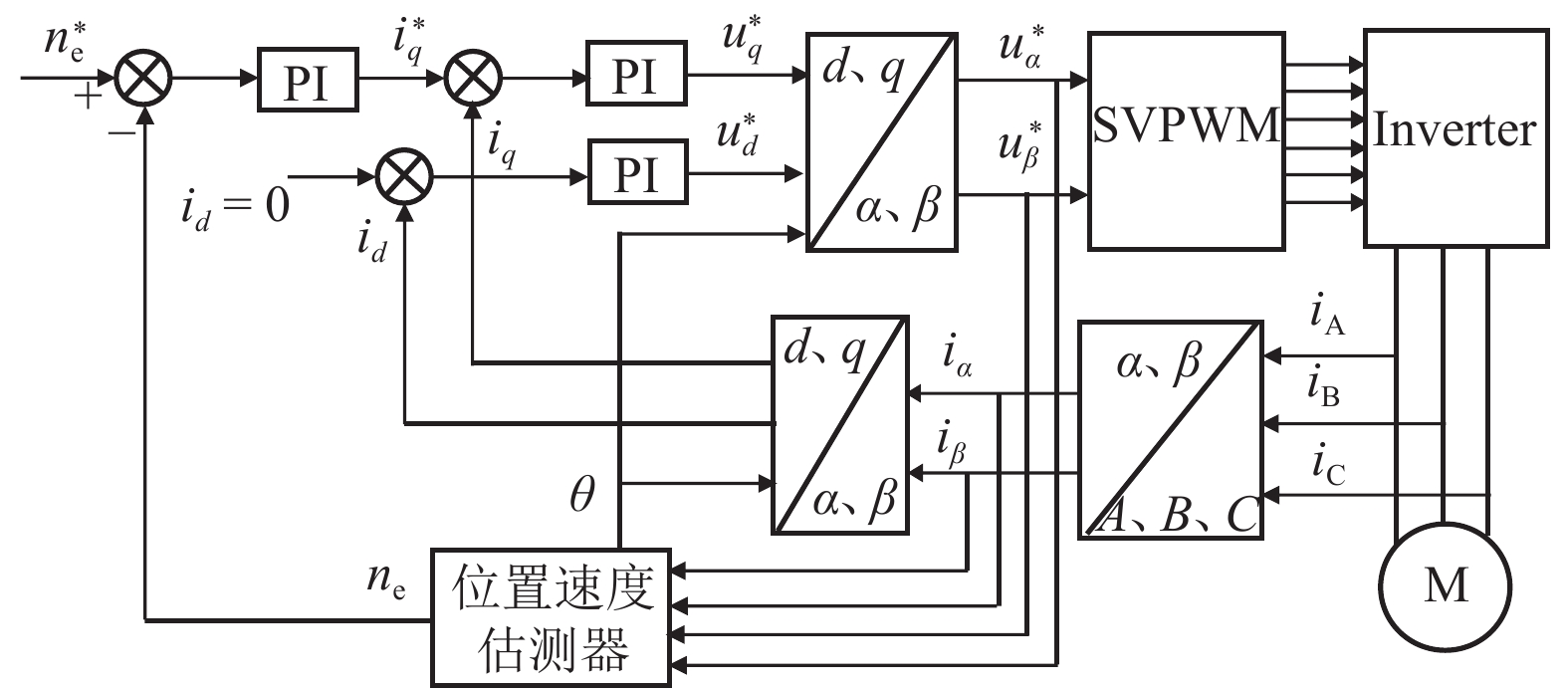
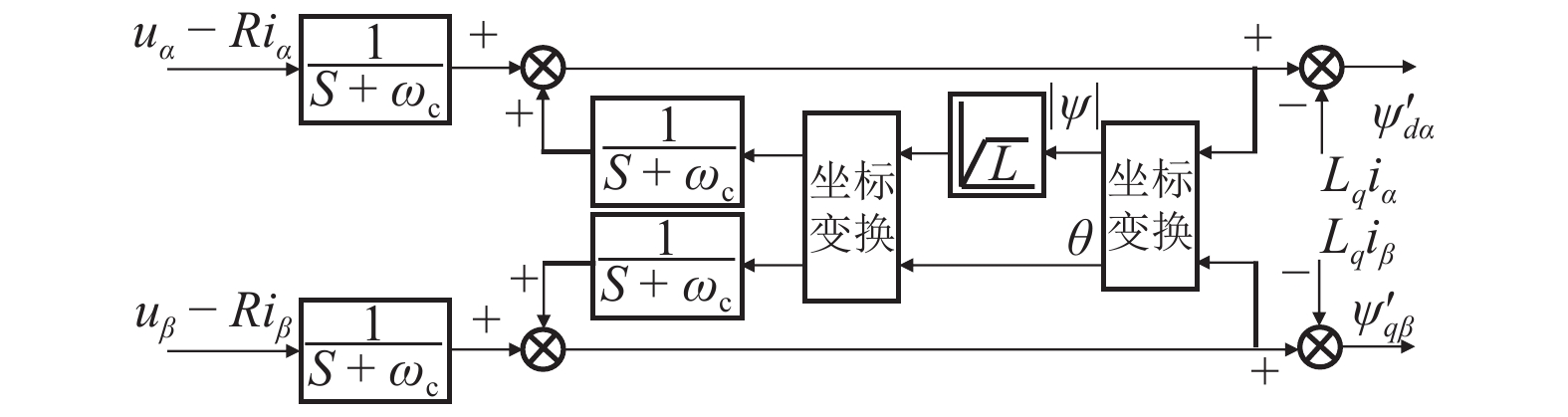
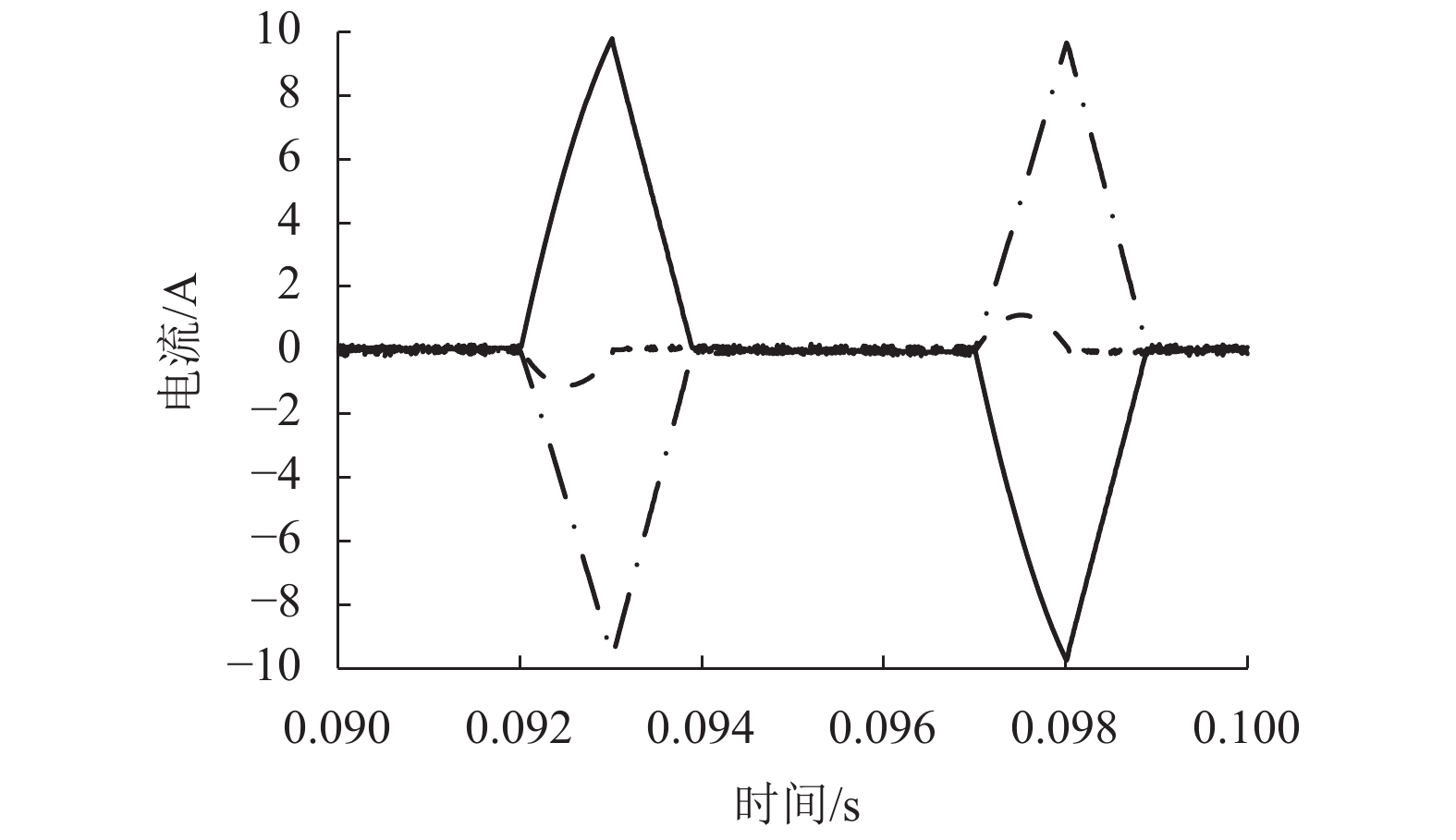
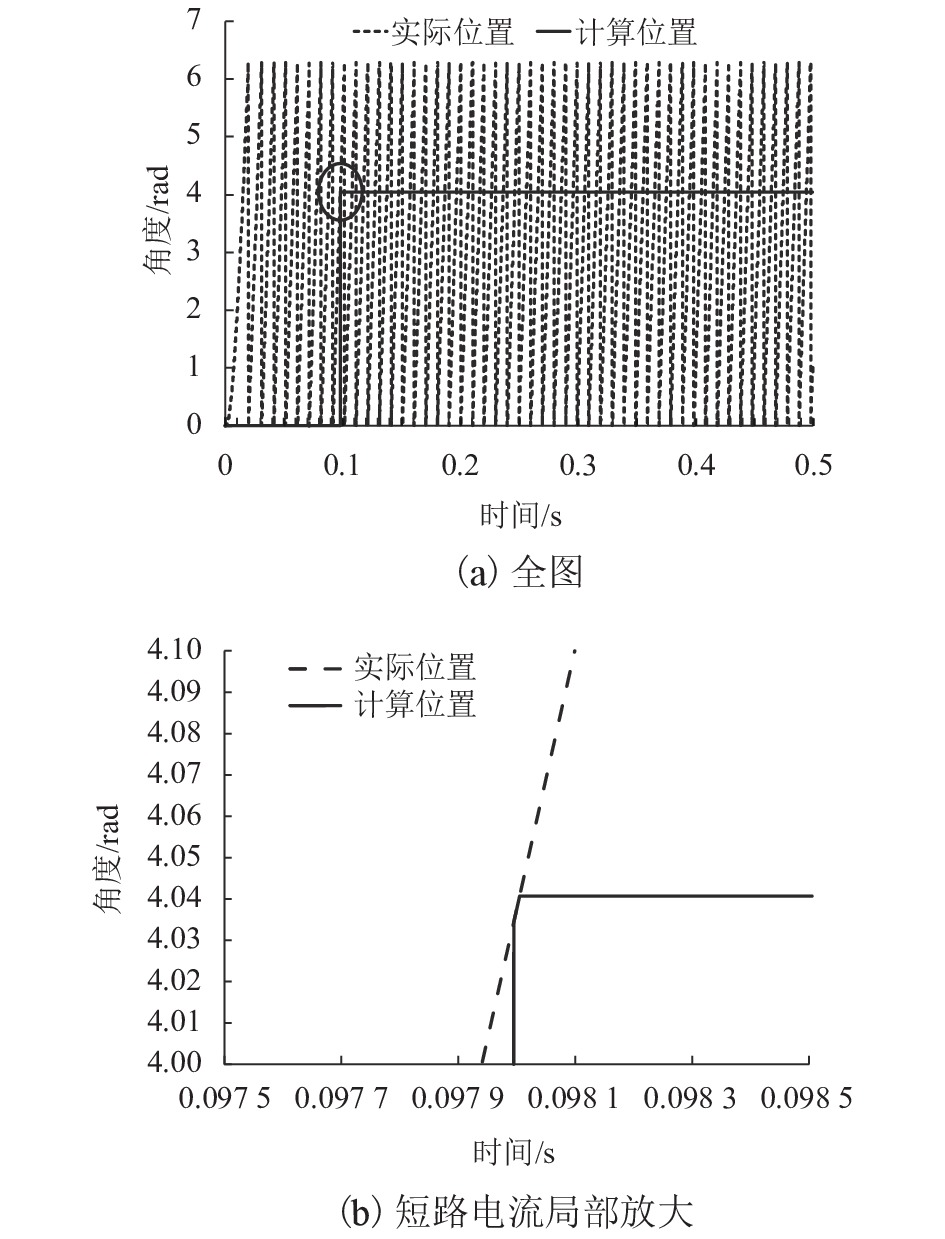
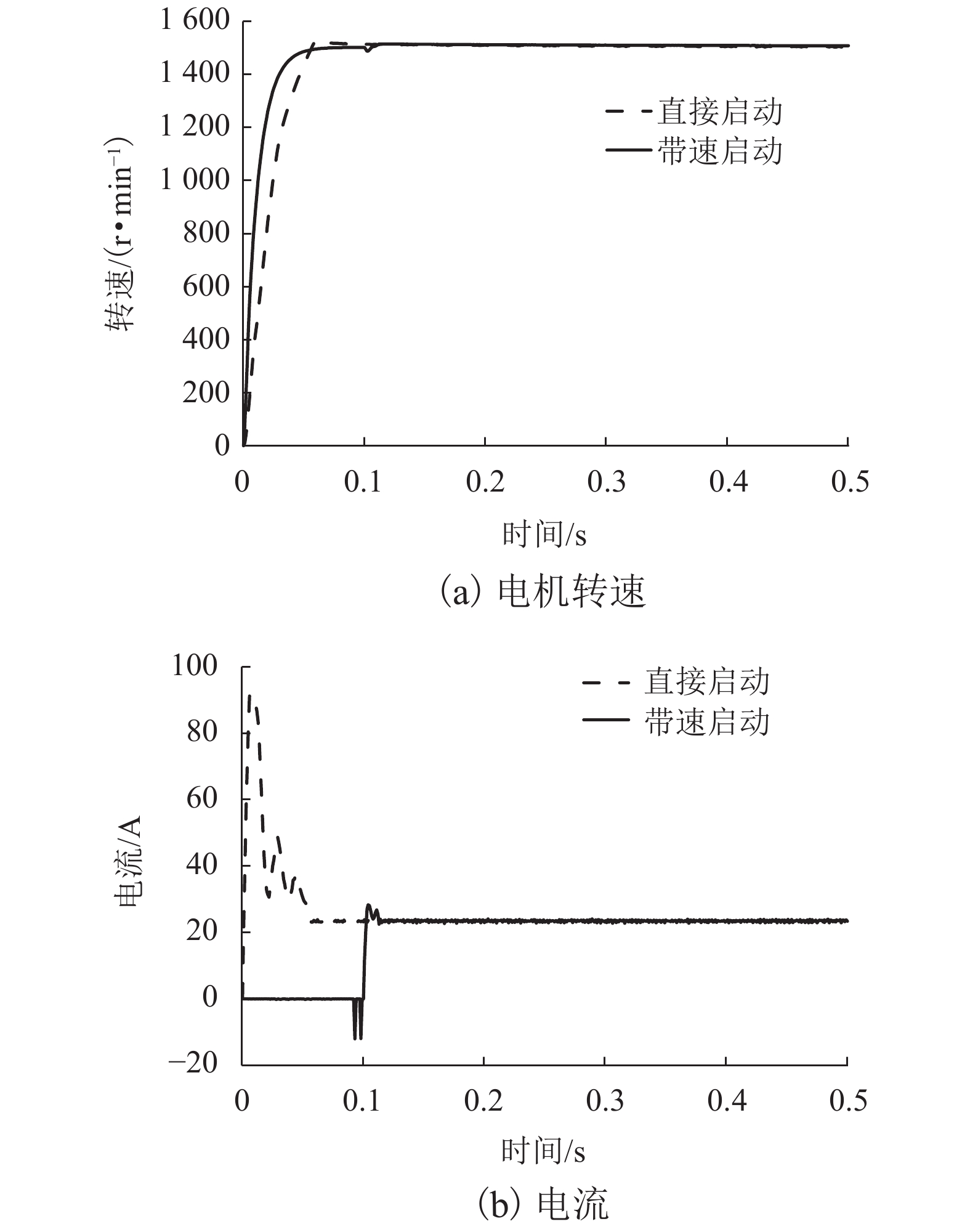
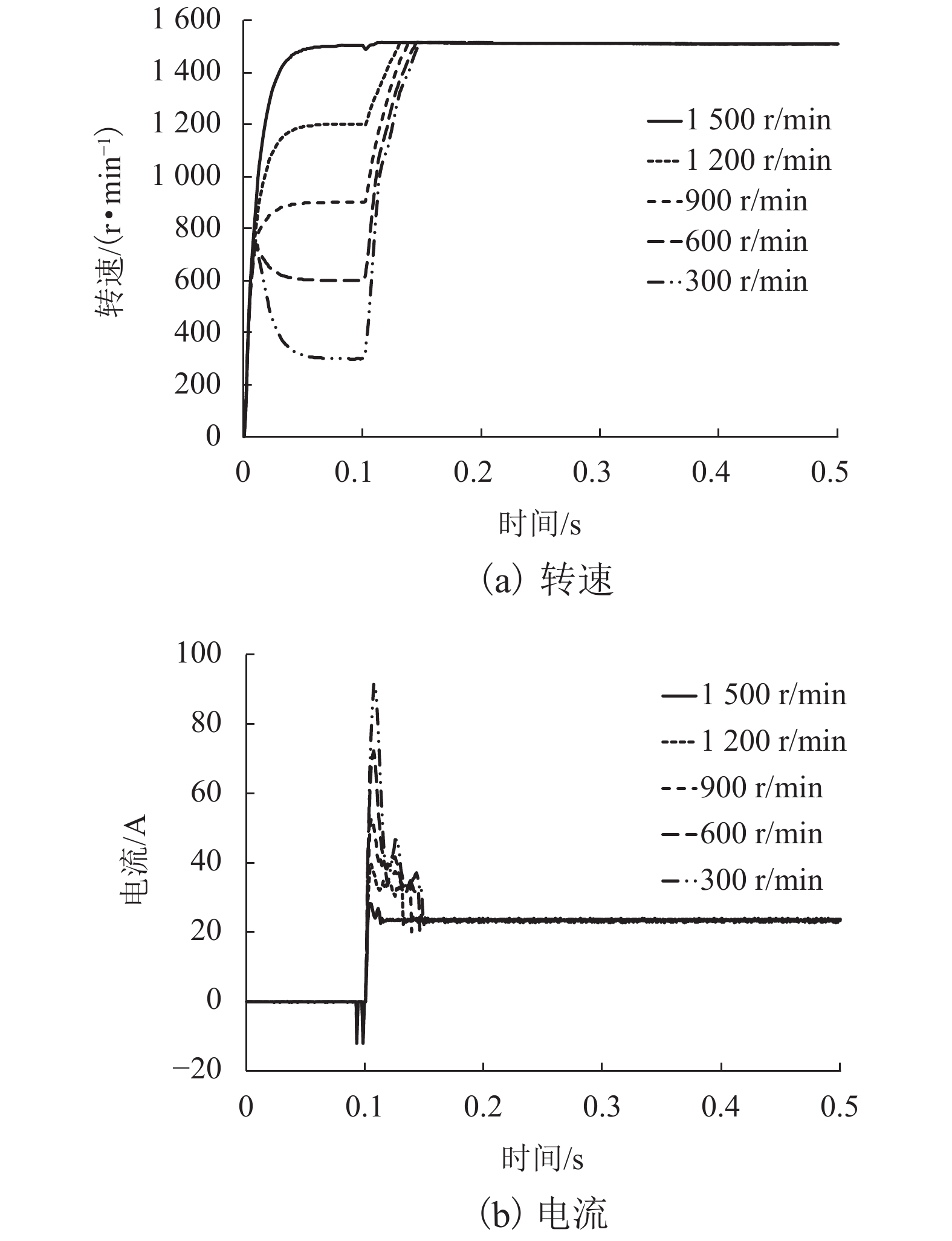
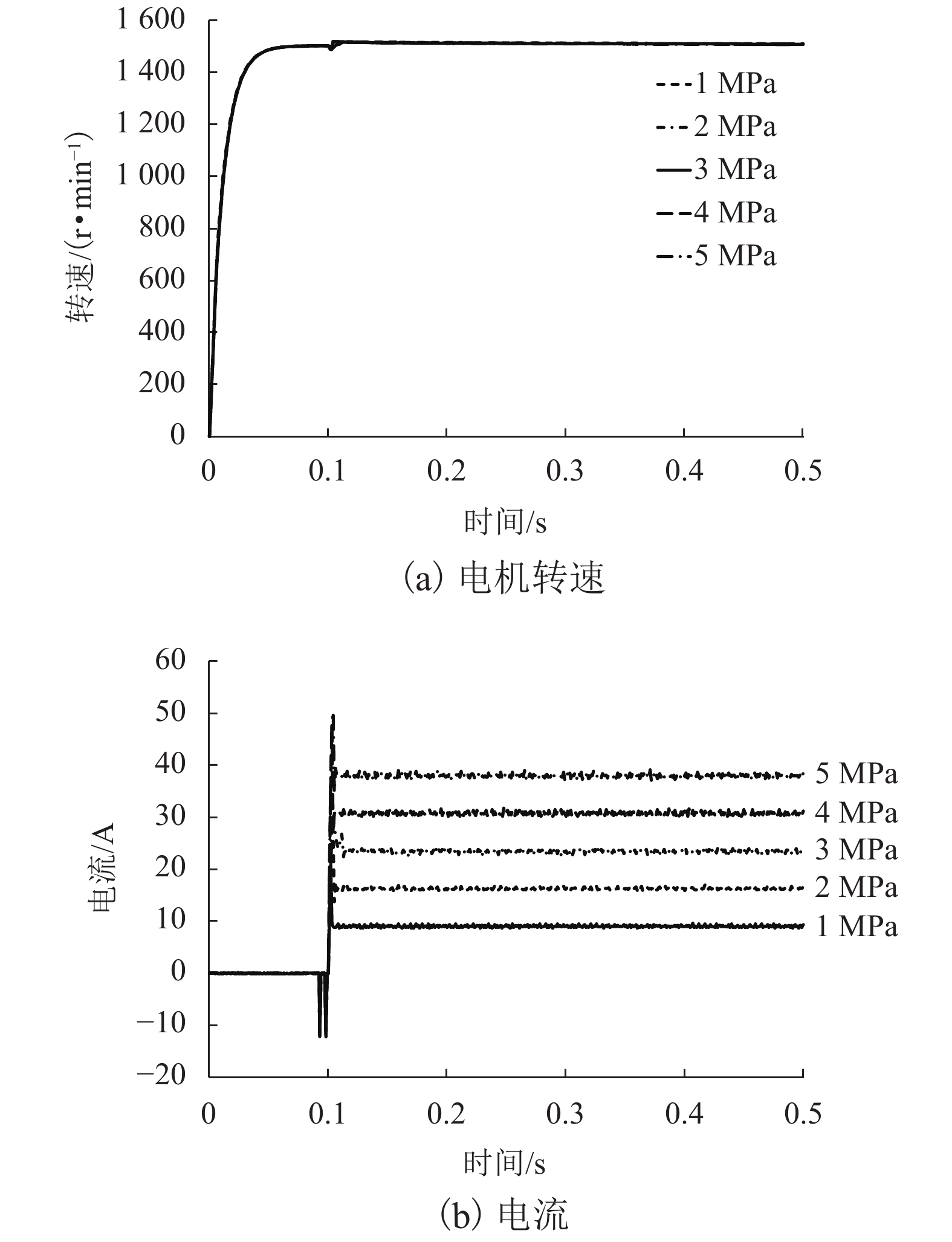
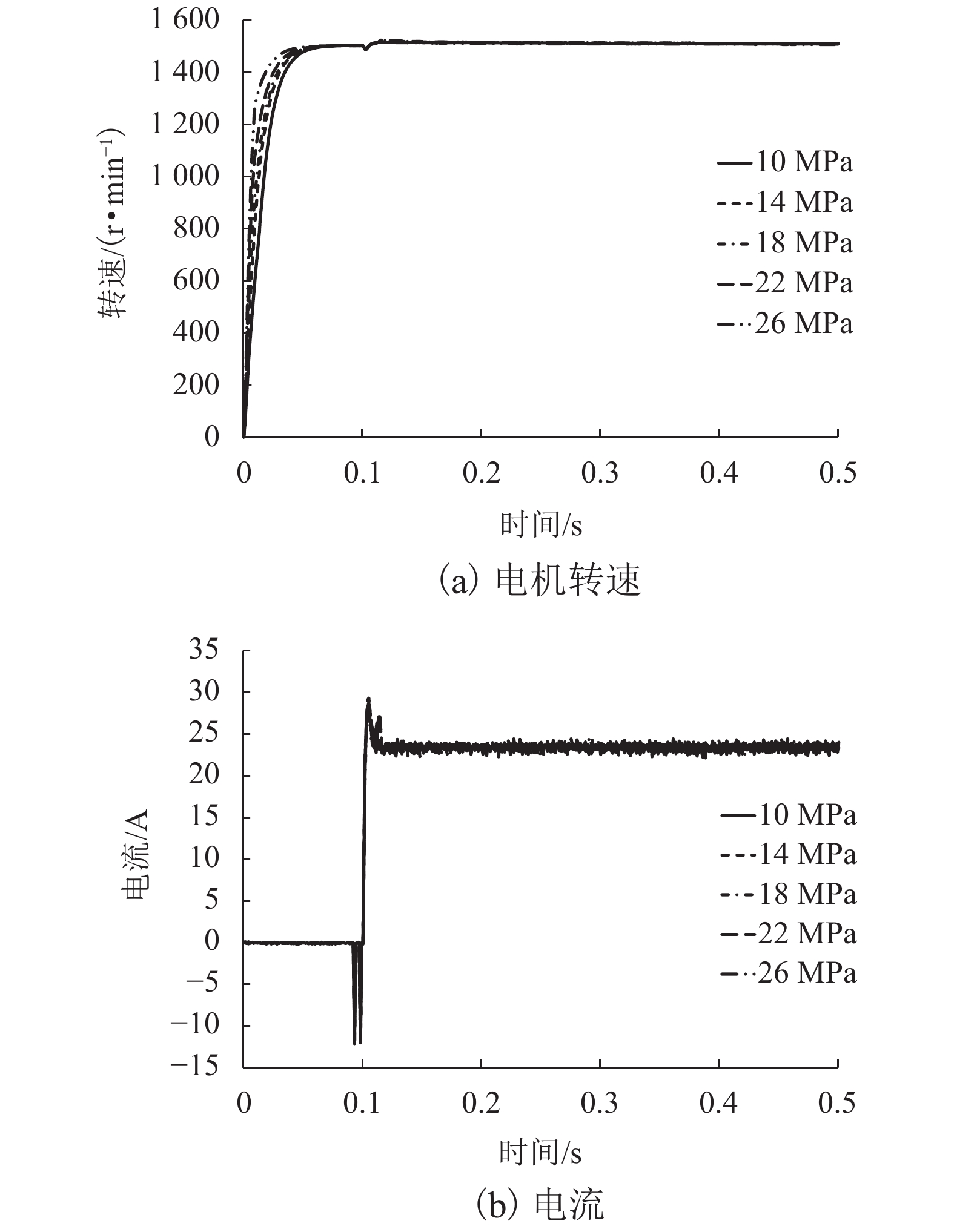
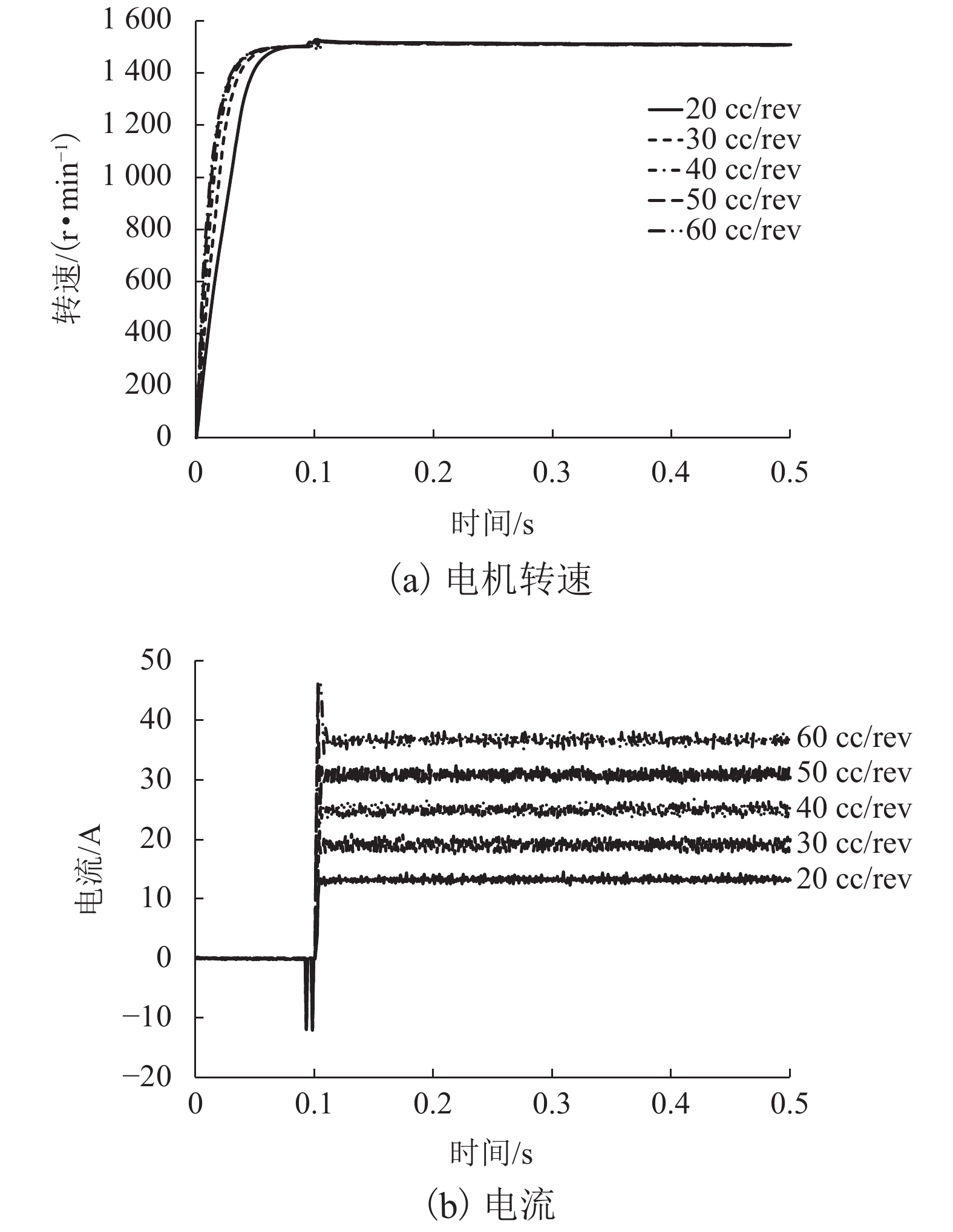
摘要: 针对蓄电池轨道工程车续航里程短、永磁同步牵引电机启动电流大等问题,基于液压泵/马达能量逆向传递特性,提出了利用液压泵/马达逆向驱动的电机启动电流控制新方法. 通过使液压泵/马达工作在马达模式将电机驱动至一定初始转速后接通电源实现电机带速启动,抑制或削弱电机启动电流;永磁同步电机带速启动采用无位置矢量控制方式,结合短路电流矢量法对电机启动时刻的转子转速和位置进行计算,并通过AMESim与MATLAB/Simulink进行联合仿真. 研究结果表明:所提出的电机启动电流控制新方法能让电机的启动峰值电流最大降低70%左右;启动电流与电机接通电源启动时的初始转速有关,且初始转速越接近需求转速则启动电流越小;电机转速稳定后电流大小仅与电机负载有关;液压泵/马达工作排量或蓄能器充液压力越大,电机被逆向驱动时的转速响应越快.Abstract: Aiming at the short cruising range of the battery rail engineering vehicles (BREVs) and the large starting current of the permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM), a new method of controlling the starting current of the PMSM driven by the hydraulic pump/motor was proposed based on the characteristics of the reverse transmission of the energy of the hydraulic pump/motor. By making the hydraulic pump/motor work in the motor mode, the PMSM was driven to a certain initial speed and then the power was turned on to realize the start of the PMSM with initial speed, which can suppress or weaken the starting current of PMSM. The PMSM was started at initial speed by adopting the positionless vector control method, combined with the short-circuit current vector method, the rotor speed and position at the starting time of the motor were calculated, and the joint simulation was carried out by AMESim and MATLAB/Simulink.The results show that the proposed new method of starting current control of PMSM can reduce the starting peak current of the PMSM by about 70%. The starting current is related to the initial speed when the PMSM is switched on and starting. The closer the initial speed of PMSM is to the required speed, the smaller the starting current is. After the speed of PMSM is stable, the current is only related to the PMSM load. The greater the working displacement of the hydraulic pump/motor or the charging pressure of the accumulator, the faster the speed response of motor during reverse drive.
-
表 1 仿真参数设置
Table 1. Simulation parameters
参数名 数值 定子电阻/Ω 0.875 d 轴电感/mH 8.5 q 轴电感/mH 8.5 主磁极磁通/Wb 0.175 极对数 4 转动惯量 J/(kg•m2) 0.01 泵/马达排量/(cc•rev−1) 50 溢流阀调定压力/MPa 4 囊式蓄能器充气压力/MPa 17 囊式蓄能器标称体积/V 40 囊式蓄能器最大压力/MPa 32 -
郭四洲,张奕黄,言海燕,等. 抑制异步牵引电机启动峰值电流的控制策略研究[J]. 机车电传动,2008(5): 23-26.GUO Sizhou, ZHANG Yihuang, YAN Haiyan, et al. Research on control strategy for suppressing starting peat current of asynchronous traction motor[J]. Electric Drive for Locomotives, 2008(5): 23-26. 陶鑫,庄哲民,JOSEPHRAJ A N,等. 基于改进的三段式永磁同步电机启动方法[J]. 测试技术学报,2018,32(3): 79-85.TAO Xin, ZHUANG Zhemin, JOSEPHRAJ A N, et al. An improved 3-step start-up method for PMSM[J]. Journal of Test and Measurement Technology, 2018, 32(3): 79-85. 杨淑霞,冯茜. 基于软启动的电机控制系统设计[J]. 移动电源与车辆,2019(2): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4250.2019.02.003YANG Shuxia, FENG Qian. Designed soft starting of motor control system based on DSP[J]. Movable Power Station and Vehicle, 2019(2): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4250.2019.02.003 周勇,米彦昭,汪嘉瑶,等. 无位置传感器无刷直流电机位置检测与启动控制研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报,2017,35(2): 208-212. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2017.02.006ZHOU Yong, MI Yanzhao, WANG Jiayao, et al. Research on the position detection and start control for sensorless brushless DC motor[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2017, 35(2): 208-212. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2017.02.006 许文学,刘桓龙,柯坚,等. 泵马达辅助启动电机的启动特性分析[J]. 液压气动与密封,2016,36(10): 27-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0813.2016.10.008XU Wenxue, LIU Huanlong, KE Jian, et al. Analysis on starting characteristics of electric motor with hydraulic pump motor auxiliary starting[J]. Hydraulics Pneumatics and Seals, 2016, 36(10): 27-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0813.2016.10.008 冯磊,刘桓龙. 轨道车的电液混合功率迁移与耦合特性[J]. 液压与气动,2018(6): 88-93. doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2018.06.017FENG Lei, LIU Huanlong. Electro-hydraulic hybrid power transfer and coupling characteristics of rail vehicle[J]. Chinese Hydraulics and Pneumatics, 2018(6): 88-93. doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2018.06.017 蒋越. 蓄电池液压混合动力轨道工程车的再生和复合制动特性[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2019. 陈思溢,皮佑国. 基于滑模观测器与滑模控制器的永磁同步电机无位置传感器控制[J]. 电工技术学报,2016,31(12): 108-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2016.12.013CHEN Siyi, PI Youguo. Position sensorless control for permanent magnet synchronous motor based on sliding mode observer and sliding mode controller[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2016, 31(12): 108-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2016.12.013 毛永乐,杨家强,赵寿华,等. 带负载转矩估算的非线性观测器内嵌式永磁同步电机无位置传感器控制策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2016,36(8): 2252-2259.MAO Yongle, YANG Jiaqiang, ZHAO Shouhua, et al. Nonlinear observer with load-torque estimation for sensorless control strategy of interior permanent magnet synchronous motor[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(8): 2252-2259. 钟臻峰,金孟加,沈建新. 基于分段PI调节器的模型参考自适应永磁同步电动机全转速范围无传感器控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2018,38(4): 1203-1209.ZHONG Zhenfeng, JIN Mengjia, SHEN Jianxin. Full speed range sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous motor with phased PI regulator-based model reference adaptive system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(4): 1203-1209. SMIDL V, PEROUTKA Z. Advantages of square-root extended Kalman filter for sensorless control of AC drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(11): 4189-4196. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2011.2180273 郭希铮, 刘帅, 宋玉美. 永磁同步电机无位置传感器带速重投研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2016, 31(增刊2): 255-261.GUO Xizheng, LIU Shuai, SONG Yumei. Research on restart at coasting condition for rotation sensorless permanent magnet synchronous machines[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2016, 31(S2): 255-261. TANIGUCHI S, MOCHIDUKI S, YAMAKAWA T, et al. Starting procedure of rotational sensorless PMSM in the rotating condition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2009, 45(1): 194-202. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2008.2009496 袁倩. 牵引永磁同步电机无传感器控制的带速重投的研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2012. 王逸之. 永磁同步牵引电机全速域无位置传感器控制研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2019. -





 下载:
下载: