Visual Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Algorithm Based on Convolutional Neural Network to Optimize Loop Detection
-
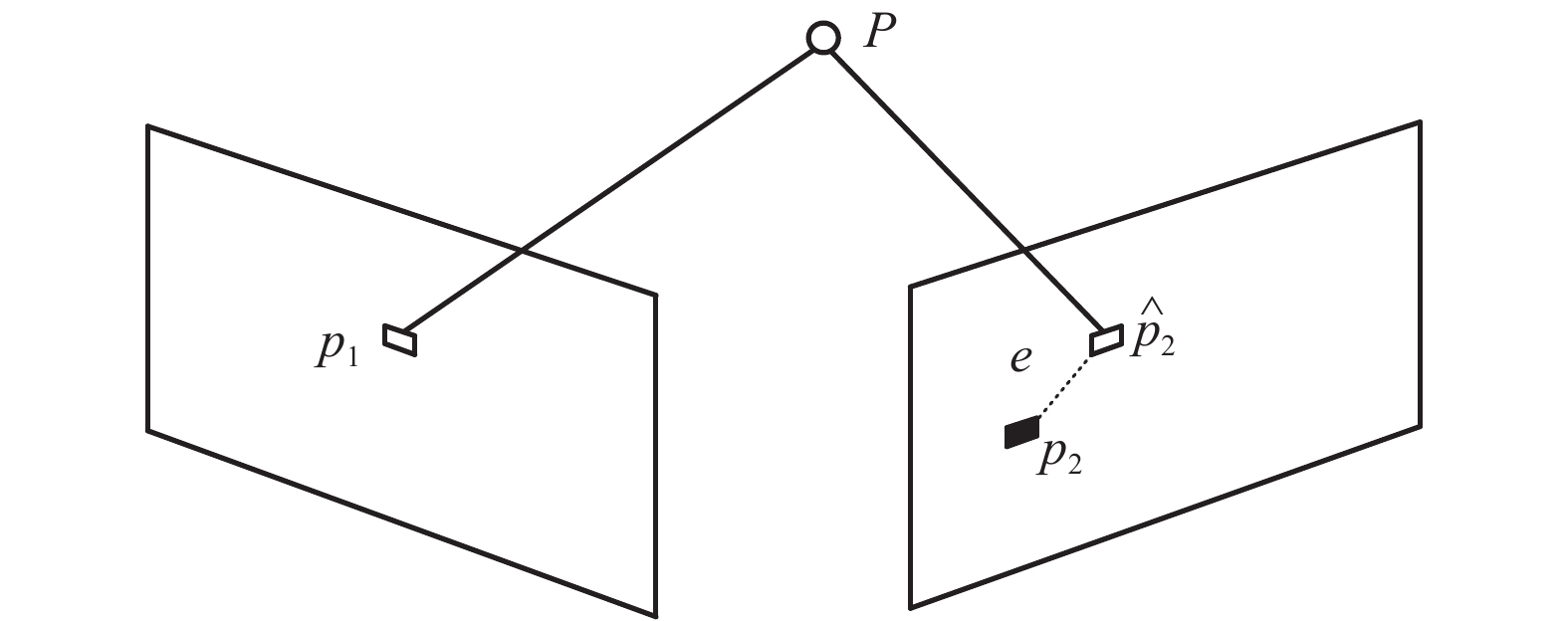
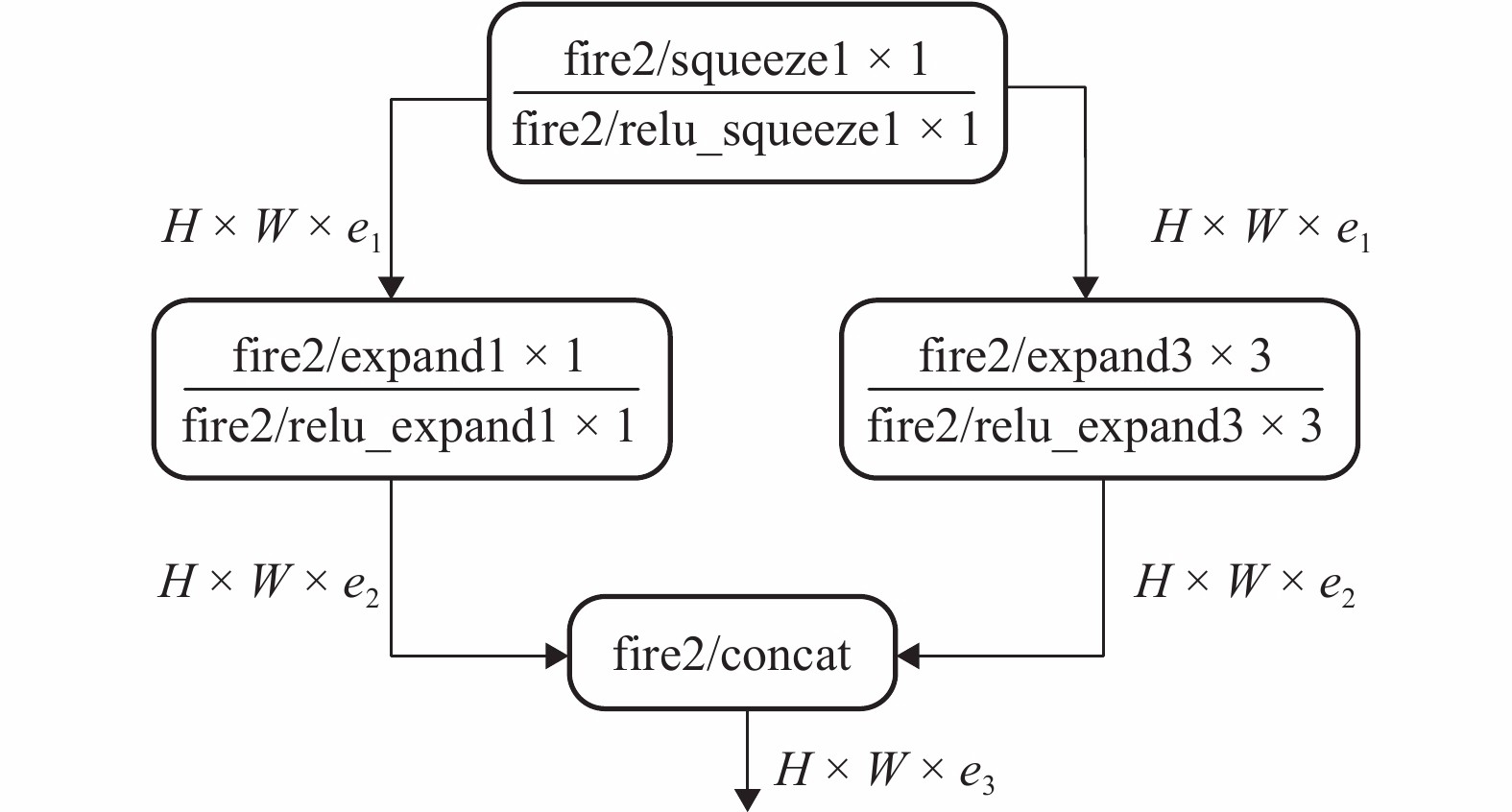
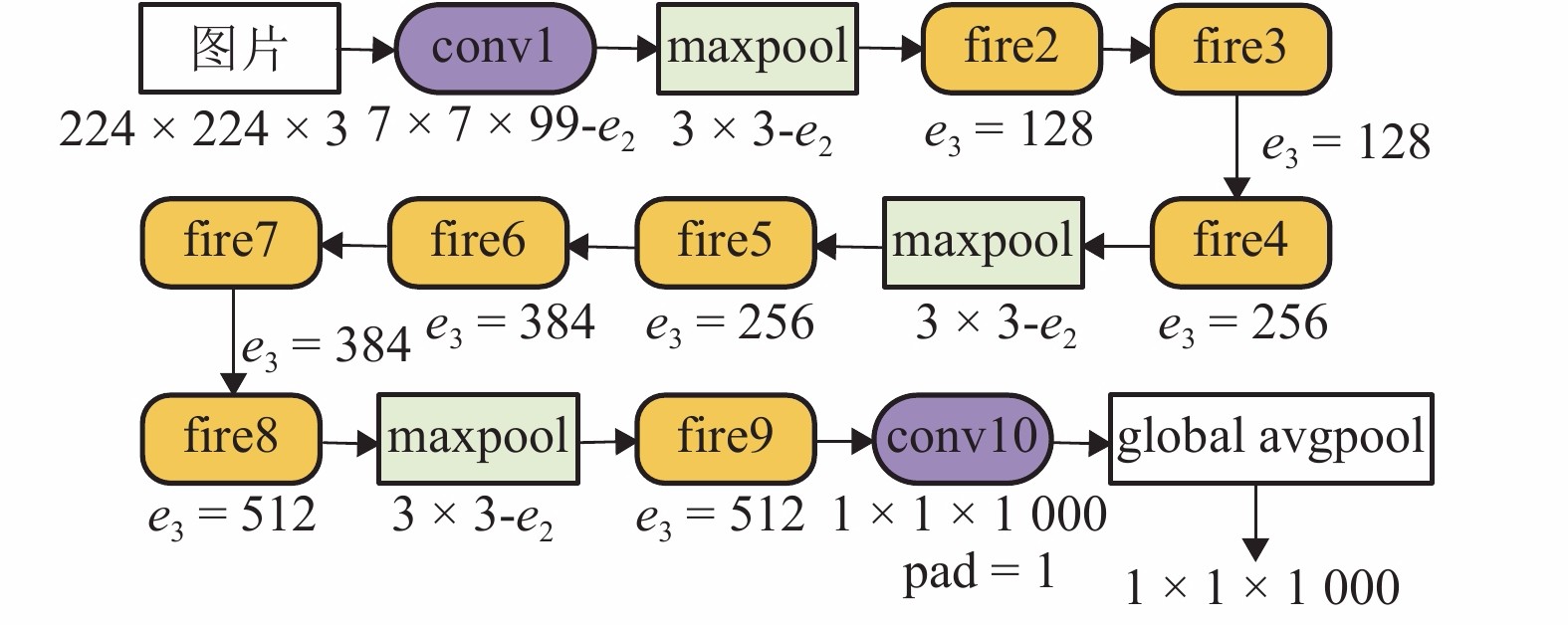
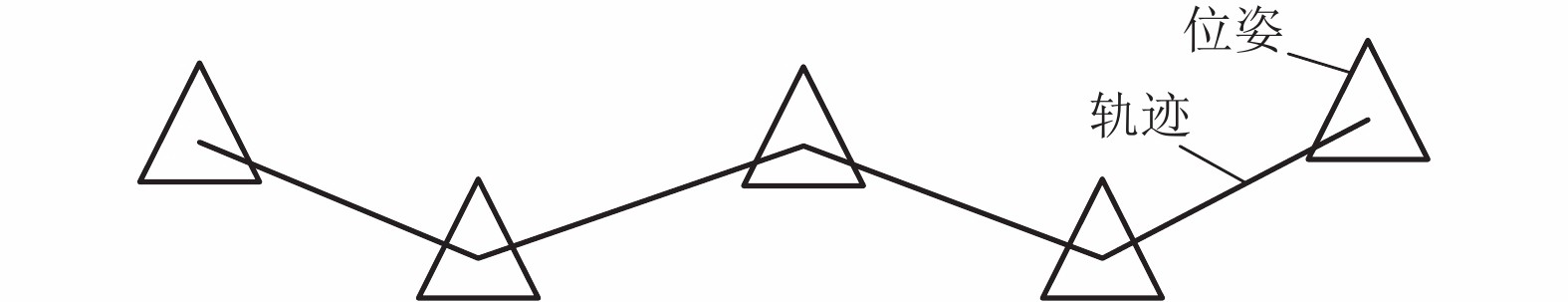
摘要: 传统视觉即时定位与建图(SLAM)算法若无回环检测可能会存在累积误差无法消除的现象,即使有回环检测,也因准确率和效率比较低而无法应用于轻量级设备上,为此,研究一种回环检测优化的视觉SLAM算法. 前端估计时,对相邻帧图像进行ORB (oriented fast and rotated brief)特征提取与匹配,对匹配成功的特征点进行PnP (perspective-n-point)求解,获得相机运动估计并筛选出关键帧图像;后端优化时,利用SqueezeNet卷积神经网络 (CNN)提取图像的特征向量,计算余弦相似度判断是否出现回环,若出现回环则在位姿图中增加相应约束,利用图优化理论对全局位姿进行整体优化;最后利用项目组制作的数据集和TUM (technical university of munich)公开数据集进行测试与对比. 研究结果表明:相比于无回环检测算法,本文方法可以成功检测到回环并为全局轨迹优化增添约束;相比于传统词袋法,在回环检测准确率相同的情况下,本文方法召回率可提高21%且计算耗时减少74%;与RGB-D (red green blue-depth) SLAM算法相比,本文方法建图误差可降低29%.Abstract: Traditional visual SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) without loop detection may lead to error accumulation. Even if there exits loop detection, it is unable to be applied to the lightweight applications because of its low accuracy and efficiency. Thus, a visual SLAM with loop detection optimization is studied. In the front-end estimation, ORB (oriented fast and rotated brief) feature points were abstracted and matched. PnP (perspective-n-point) was solved for the successful matched point to estimate the camera motion and screen out the key frame images. In the back-end optimization, SqueezeNet convolution neural network (CNN) was used to extract the feature vectors. The cosine similarities were calculated to determine whether there were loops or not. If there was a loop, the corresponding constraint was added to the posture graph. Then the global posture was optimized by using the graph optimization theory. Finally, tests and comparisons were conducted on the data sets produced by our research group and the public data sets of TUM. The results show that the proposed algorithm can detect loops successfully and add constraints to global trajectory optimization compared with the non-loop detection algorithm. Compared with the traditional word bag method, the recall rate of this method can be increased by 21% and the calculation time can be reduced by 74% under the same loop detection accuracy. Compared with RGB-D SLAM algorithm, the error of this method can be reduced by 29%.
-
表 1 实验采用的数据集
Table 1. Data sets for testing
序号 数据集 数量/帧 1 nyuv2 782 2 TUM fr3_stf 938 3 Turtlebot2采集 968 4 TUM fr1_xyz 902 表 2 回环检测可能出现的结果
Table 2. Possible results for loop detection
检测结果 事实上存在回环 事实上不存在回环 是回环 真阳性 假阳性 不是回环 假阴性 真阴性 表 3 本文算法与词袋法对比
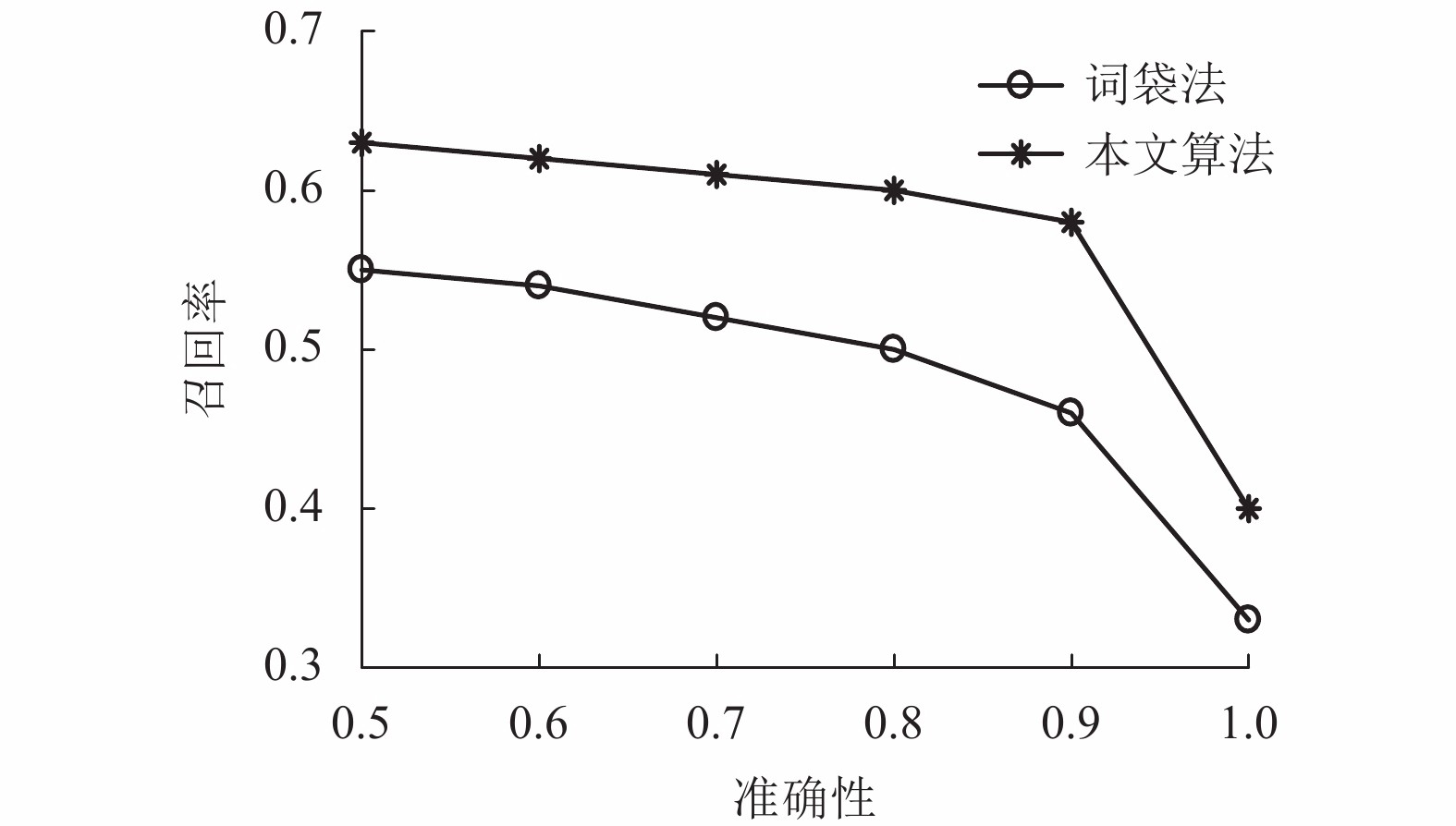
Table 3. Comparison between algorithm and word bag method in this paper
算法 准确率为 1 时的
召回率对两张图片进行相似度
计算所花时间/s词袋法 0.33 0.50 本文算法 0.40 0.13 两者差值 0.07 0.37 百分比/% 21 74 表 4 建图误差对比
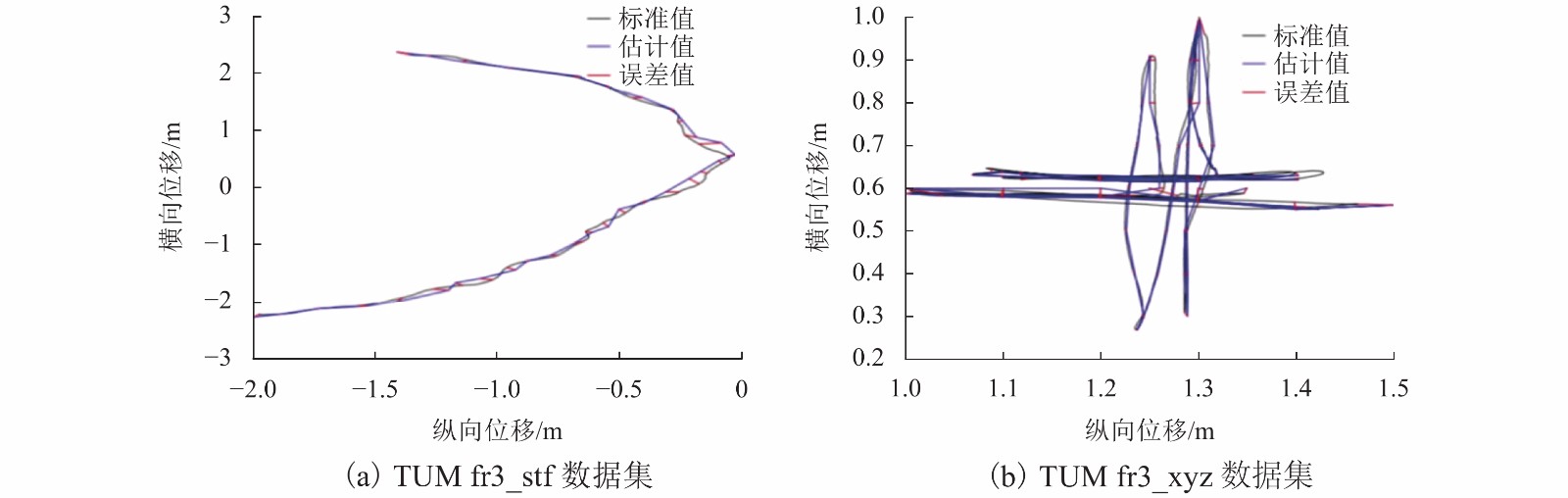
Table 4. Comparison of mapping errors
数据集 本文算法
误差/m文献[19]算法
误差/m两者差值/% TUM fr3_stf 0.050 0 0.049 0 2 TUM fr3_xyz 0.010 4 0.013 5 29 -
高翔, 张涛. 视觉SLAM十四讲[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2017: 9-32. 蔡军,陈科宇,张毅. 基于Kinect的改进移动机器人视觉SLAM[J]. 智能系统学报,2018,13(5): 734-740.CAI Jun, CHEN Keyu, ZHANG Yi. Improved V-SLAM for mobile robots based on Kinect[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2018, 13(5): 734-740. 吕宪伟. 基于RGB-D数据的SLAM算法研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2016. DAVISON A J, REID I D, MOLTON N D, et al. MonoSLAM:real-time single camera SLAM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(6): 1052-1067. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1049 KLEIN G, MURRAY D. Parallel tracking and mapping for small AR workspaces[C]//6th IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality. Piscataway: IEEE, 2007: 225-234. MUR-ARTAL R, MONTIEL J M M, TARDOS J D. ORB-SLAM: a versatile and accurate monocular SLAM system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2015, 31(5): 1147-1163. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2015.2463671 徐晓苏,代维,杨博,等. 室内环境下基于图优化的视觉惯性SLAM方法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报,2017,25(3): 313-319.XU Xiaosu, DAI Wei, YANG Bo, et al. Visual-aid inertial SLAM method based on graph optimization in indoor[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2017, 25(3): 313-319. 余杰. 基于ORB关键帧闭环检测算法的SLAM方法研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2016. RUBLEE E, RABAUG V, KONOLIGE K, et al. ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF[C]// International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2011: 2564-2571. SCARAMUZZA D, FRAUNDORFER F. Visual odometry[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Magazine, 2011, 18(4): 80-92. doi: 10.1109/MRA.2011.943233 LOWE D G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features[C]//International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 1999: 1150-1157 席志红,李爽,甘兴利. PnP算法在室内定位中的应用[J]. 无线电工程,2017,47(10): 39-44.XI Zhihong, LI Shuang, GAN Xingli. PnP solution applied in indoor location[J]. Radio Engineering, 2017, 47(10): 39-44. 刘国忠,胡钊政. 基于SURF和ORB全局特征的快速闭环检测[J]. 机器人,2017,39(1): 36-45.LIU Guozhong, HU Zhaozheng. Fast loop closure detection based on holistic features from SURF and ORB[J]. Robot, 2017, 39(1): 36-45. GAO X, ZHANG T. Loop closure detection for visual slam systems using deep neural networks[C]//Chinese Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE, 2015: 5851-5856. SHANG W, SOHN K, ALMEIDA D, et al. Understanding and improving convolutional neural networks via concatenated rectified linear units[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning. Princeton: IMLS, 2016: 3276-3284. KUMMERLE R, GRISETTI G, STRASDAT H, et al. G2o: a general framework for graph optimization[C]// IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE, 2011: 3607-3613. JIA Y Q, SHELHAMER E, JEFF D. Caffe: convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding[C]//ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2014: 675-678. STURM J, ENGELHARD N, ENDRES F, et al. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems[C]//International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE, 2012: 573-580. ENDRES F, HESS J, STURM J, et al. 3-D mapping with an RGB-D camera[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2014, 30(1): 177-187. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2013.2279412 -




 下载:
下载: