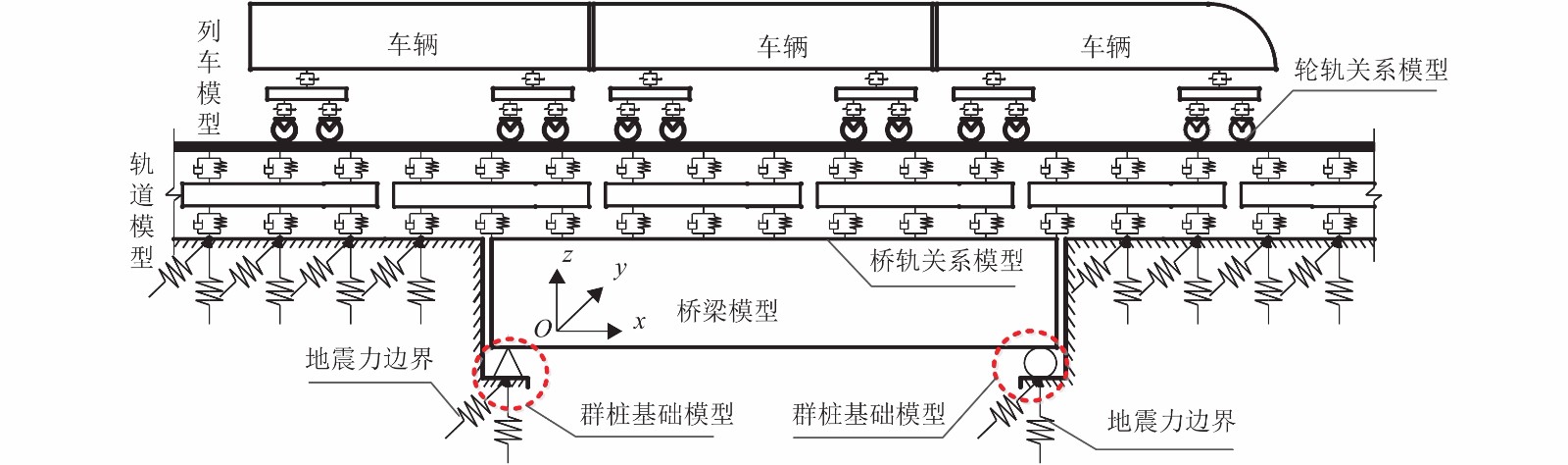
Seismic Responses Analysis of Train-Track-Bridge System Considering Pile-Soil Interaction
-
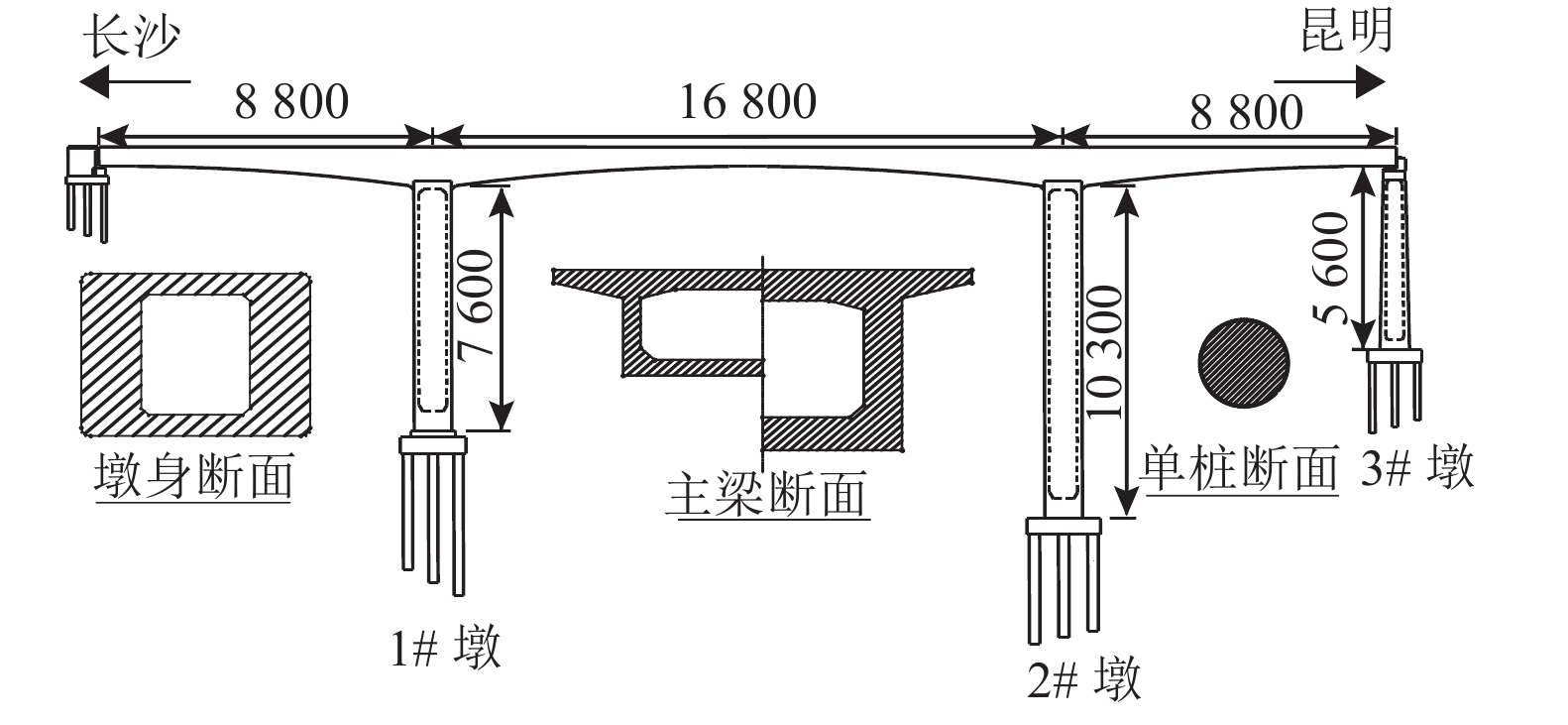
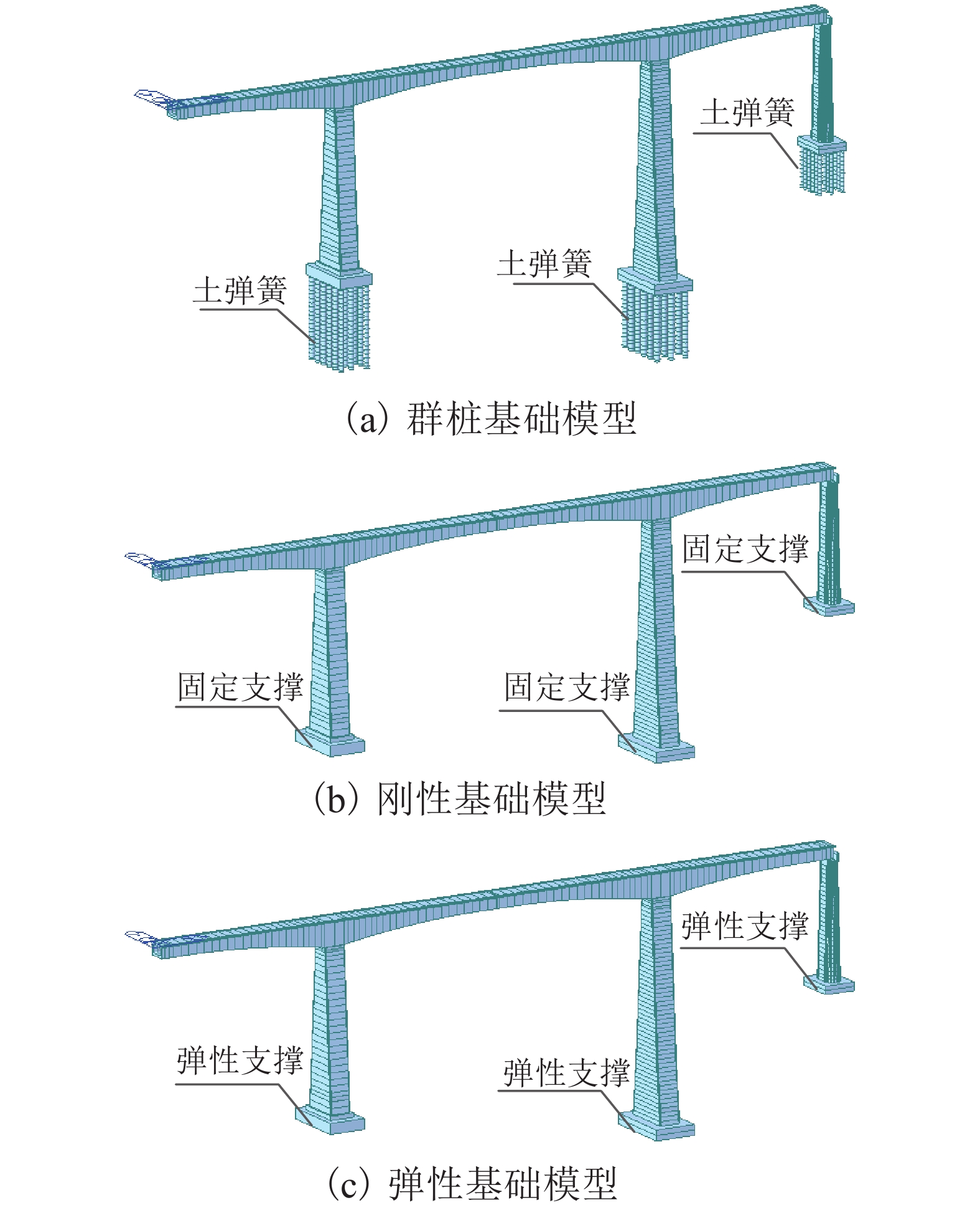
摘要: 弄清桩土相互作用对车桥系统地震响应的影响对于研究地震引起的高速铁路桥上列车行车安全问题十分必要. 基于列车-轨道-桥梁耦合振动理论,采用Winkler地基梁模拟群桩基础并通过m法计算弹簧参数,建立了地震作用下的列车-轨道-桥梁-群桩耦合振动模型,并编制了仿真分析程序. 以某(88 + 168 + 88)m预应力混凝土连续刚构桥为例,分别建立了考虑桩土相互作用的群桩基础模型以及作为对比的刚性基础模型和弹性基础模型,通过输入3条典型地震波,计算对比了3种模型的耦合振动响应,研究了桩土相互作用的影响. 结果表明:地震作用下桩土相互作用对桥梁、轨道和列车子系统动力响应的影响横向大于竖向,且对桥梁、轨道子系统动力响应的影响大于列车子系统;对于本文的计算条件,不考虑桩土相互作用会使桥梁、轨道和列车子系统的动力响应偏小,其中列车的脱轨系数、轮重减载率和轮轴横向力平均值分别偏小5.8%、8.6%和9.0%;桩土相互作用对列车行车安全性指标的影响不会随车速的变化而变化. 本文的研究成果可为震区高速铁路桥梁的抗震设计提供参考.Abstract: Understanding the influence of pile-soil interaction on seismic responses of a train-bridge system is necessary for studying the safety of trains running over high-speed railway bridges under earthquake. Based on the train-track-bridge coupled vibration theory, the Winkler foundation beam is used to simulate the pile group foundation and spring parameters are calculated by m method. A complete train-track-bridge-pile group coupled vibration model with seismic excitations is established, and a simulation analysis program is developed. Taking a (88 + 168 + 88) m prestressed concrete continuous rigid frame bridge as an example, a pile group foundation model considering pile-soil interaction, a rigid foundation model and an elastic foundation model are established respectively, and the last two models are used for comparison with the first one. By inputting three typical seismic waves, the coupled vibration responses of the three models are calculated and compared, and the pile-soil interaction is studied. The results show that the influence of pile-soil interaction on the lateral dynamic responses of the bridge, track and train subsystems under earthquake is greater than that on the vertical one, and the influence on the dynamic responses of the bridge and track subsystems is greater than that of the train subsystem. For the calculation conditions of this paper, the dynamic responses of bridge, track and train subsystems will be smaller if pile-soil interaction is not considered; specifically, the derailment coefficient, wheel load reduction rate and wheel-axle lateral force of the train are 5.8%, 8.6% and 9.0% smaller, respectively. Besides, the influence of pile-soil interaction on the safety index of the train will not change with the train speed. The obtained results can provide reference for the seismic design of high-speed railway bridges in earthquake areas.
-
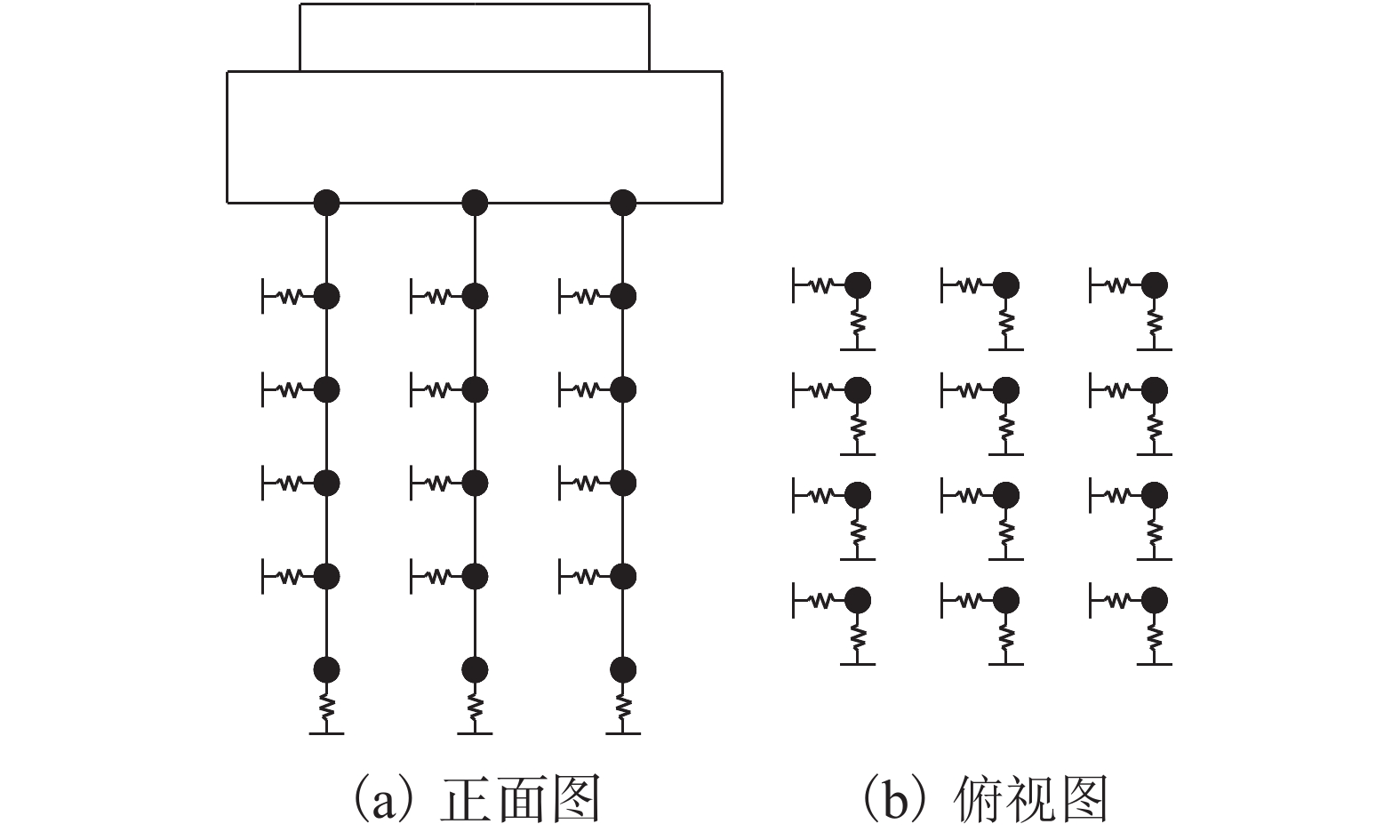
表 1 承台底等效基础刚度
Table 1. Equivalent foundation stiffness of the cap bottom
墩号 Dx /(× 1010 N•m−1) Dy /(× 1010 N•m−1) Dz/(× 1010 N•m−1) Rx /(× 1013 N•m/rad−1) Ry /(× 1012 N•m•rad−1) 1# 4.36 3.93 1.28 1.040 4.590 2# 5.86 5.22 2.04 2.140 8.470 3# 1.85 1.47 8.28 0.288 2.080 表 2 桥梁频率及振型特征
Table 2. Frequency and vibration features of the bridge
Hz 阶数 桥梁频率 振型特征 群桩基础
模型刚性基础
模型弹性基础
模型1 0.537 0.657 0.587 刚构墩纵向
弯曲2 0.642 0.751 0.690 主梁正对称
横弯4 0.917 1.097 0.990 主梁反对称
横弯5 1.351 1.420 1.381 主梁正对称
竖弯表 3 选用地震波信息
Table 3. Information for the selected ground motions
名称 事件 台站 分量 PGA/(×g) Tg/s RSN15 Kern County (1952-7-21) Taft Lincoln School Up 0.111 0.349 RSN51 San Fernando (1971-2-9) 2516 Via Tejon PV 65° 0.026 0.641 RSN78 San Fernando (1971-2-9) Palmdale Fire Station 120° 0.112 0.842 表 4 不同工况下桥梁位移、加速度和钢轨位移幅值对比
Table 4. Bridge displacement,bridge acceleration and rail displacement amplitudes comparison under different conditions
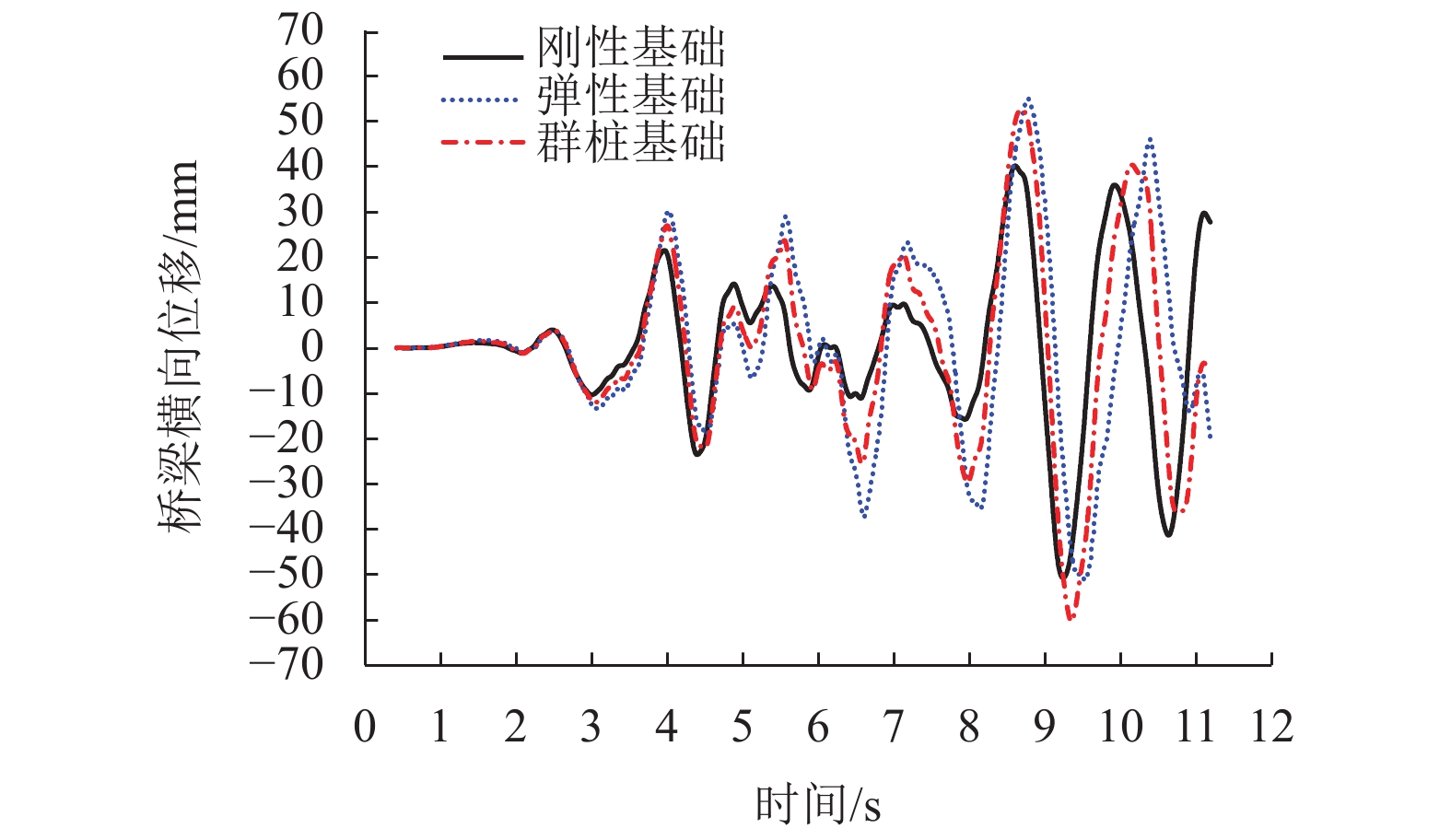
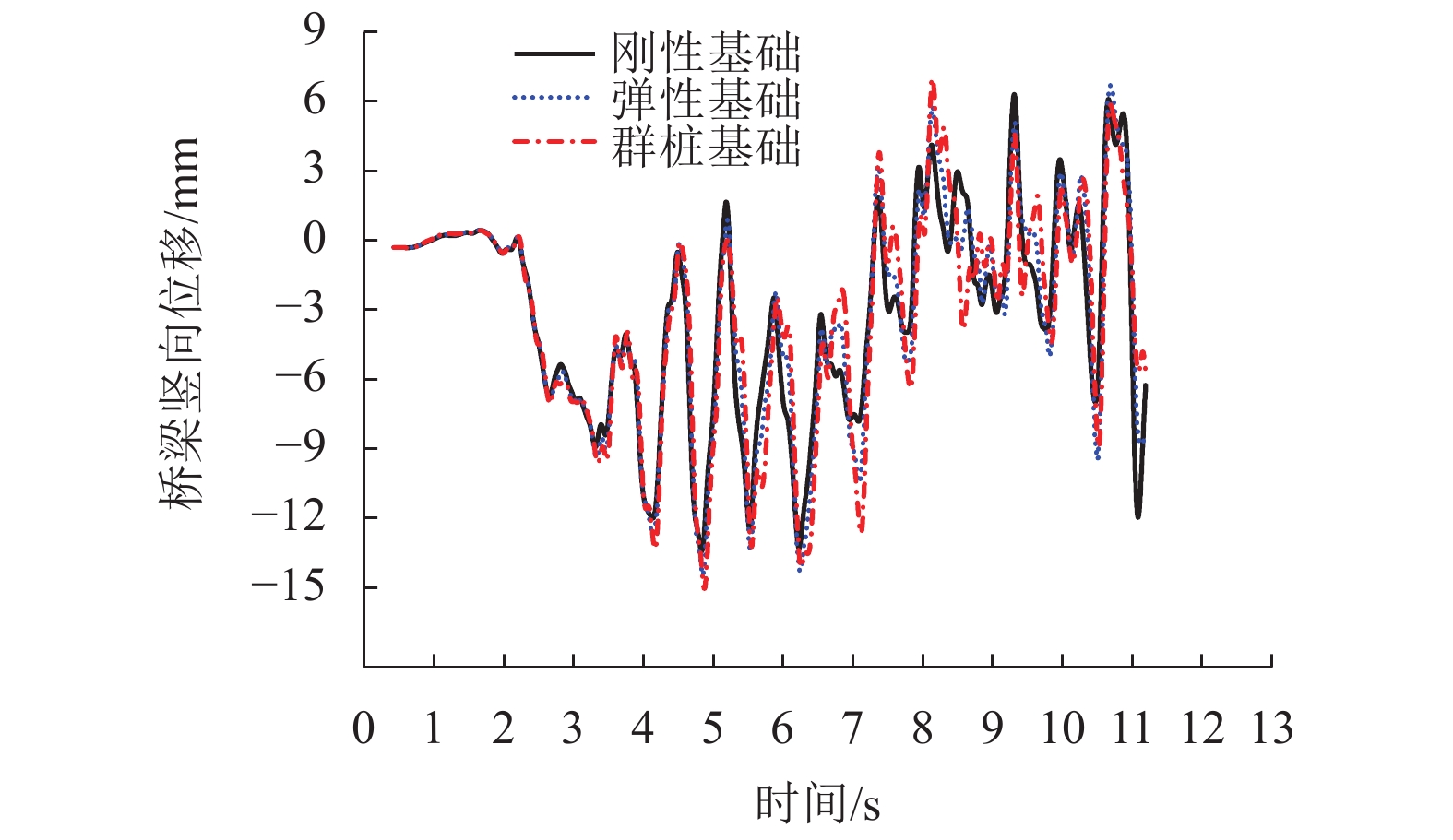
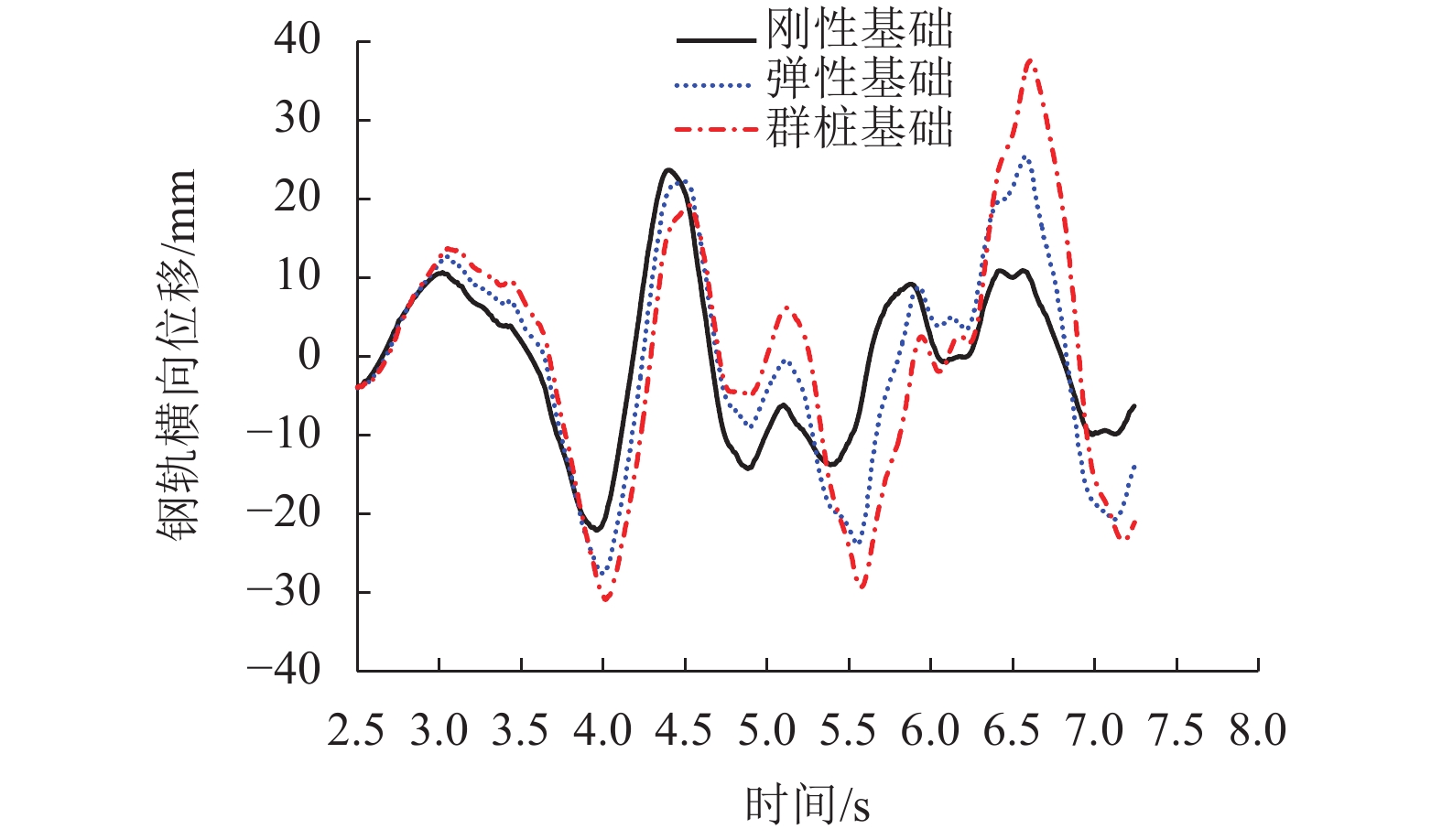
指标 工况 横向 竖向 刚性基础 弹性基础 群桩基础 刚性基础 弹性基础 群桩基础 桥梁位移/mm RSN15 50.700 55.000 60.400 12.700 13.600 14.200 RSN51 92.800 115.900 120.800 14.300 15.100 15.700 RSN78 142.900 190.900 212.100 20.700 21.300 21.800 平均值 95.500 120.600 131.100 15.900 16.700 17.200 相对值 1.000 1.263 1.373 1.000 1.050 1.086 桥梁加速度/(×g) RSN15 0.215 0.320 0.343 0.234 0.260 0.273 RSN51 0.383 0.457 0.521 0.289 0.305 0.312 RSN78 0.358 0.554 0.605 0.249 0.258 0.265 平均值 0.319 0.444 0.490 0.257 0.274 0.283 相对值 1.000 1.392 1.536 1.000 1.066 1.101 钢轨位移/mm RSN15 23.600 27.500 37.600 13.400 14.200 14.300 RSN51 95.400 107.600 113.900 14.600 15.200 16.900 RSN78 146.800 195.200 213.000 22.500 23.200 24.600 平均值 88.600 110.100 121.500 16.800 17.600 18.600 相对值 1.000 1.243 1.371 1.000 1.042 1.104 表 5 列车的3种行车安全性指标幅值对比
Table 5. Amplitudes comparison of the three running safety indices
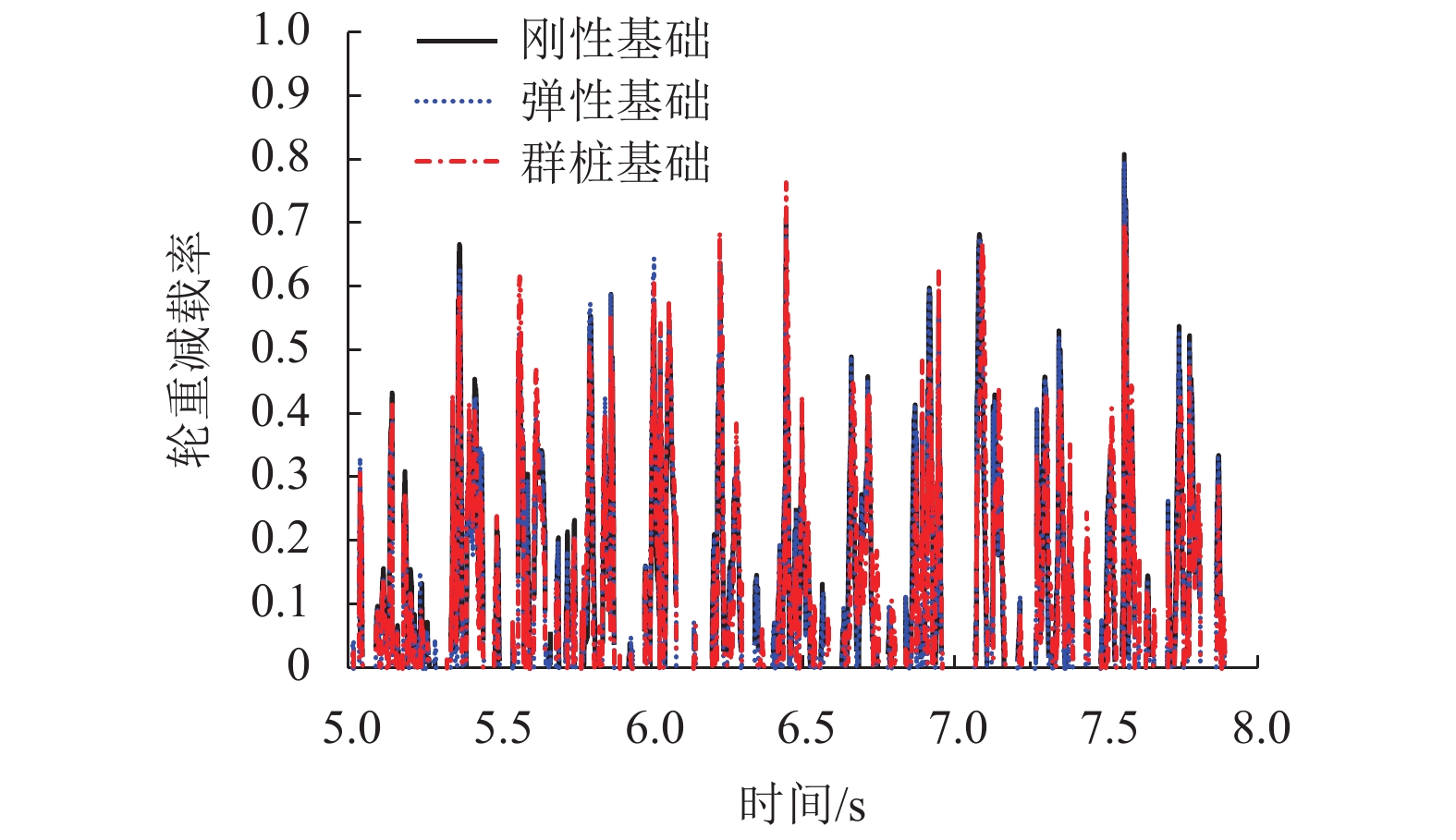
工况 脱轨系数 轮重减载率 轮轴横向力/kN 刚性基础 弹性基础 群桩基础 刚性基础 弹性基础 群桩基础 刚性基础 弹性基础 群桩基础 RSN15 0.785 0.832 0.838 0.503 0.526 0.532 86.200 91.100 93.800 RSN51 0.852 0.916 0.927 0.527 0.571 0.580 91.900 97.900 99.300 RSN78 0.865 0.876 0.883 0.534 0.570 0.586 92.800 98.800 102.300 平均值 0.834 0.875 0.883 0.521 0.556 0.566 90.300 95.900 98.500 相对值 1.000 1.049 1.058 1.000 1.066 1.086 1.000 1.062 1.090 注:列车的行车安全性指标幅值指所有编号车辆、所有轮对处该指标幅值的最大值. -
YANG Y B, WU Y S. Dynamic stability of trains moving over bridges shaken by earthquakes[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2002, 258(1): 65-94. doi: 10.1006/jsvi.2002.5089 XIA H, HAN Y, ZHANG N, et al. Dynamic analysis of train-bridge system subjected to non-uniform seismic excitations[J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 2006, 35(12): 1563-1579. JIN Z B, PEI S L, LI X Z, et al. Effect of vertical ground motion on earthquake-induced derailment of railway vehicles over simply-supported bridges[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2016, 383: 277-294. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2016.06.048 江博君,冼巧玲,周福霖. 桩土效应对高铁桥梁地震反应的影响分析[J]. 广州大学学报(自然科学版),2016,15(1): 57-63.JIANG Bojun, XIAN Qiaoling, ZHOU Fulin. The influence analysis of the effect of pile-soil contact on the seismic response of the high speed railway bridge[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 15(1): 57-63. 高昊,王君杰,苏俊省,等. 桩-土水平弹簧系数对桥梁地震反应影响的参数分析[J]. 振动与冲击,2017,36(14): 156-167.GAO Hao, WANG Junjie, SU Junsheng, et al. Parameter analysis on the influence of soil-pile horizontal spring coefficient on the seismic response of bridges[J]. Joural of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(14): 156-167. MAKRIS N, TAZOH T, YUN X, et al. Prediction of the measured response of a scaled soil-pile-superstructure system[J]. Soil Dynamics & Earthquake Engineering, 1997, 16(2): 113-124. 韦晓,范立础,王君杰. 考虑桩-土-桥梁结构相互作用振动台试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2002,35(4): 91-97. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2002.04.017WEI Xiao, FAN Lichu, WANG Junjie. Shake table test on soil-pile-structure interaction[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2002, 35(4): 91-97. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2002.04.017 谢文,孙利民. 桩-土-斜拉桥动力相互作用体系振动反应特性试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2019,41(7): 1319-1328.XIE Wen, SUN Limin. Experimental studies on seismic response characteristics of pile-soil-cable-stayed bridge dynamic interaction system[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(7): 1319-1328. 熊辉,谷亚东. 基于高速列车振动荷载的桩-土-结构相互作用分析[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2019,16(2): 302-309.XIONG Hui, GU Yadong. Pile-soil structure interaction analysis based on high-speed train vibration load[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2019, 16(2): 302-309. 边学成. 高速列车荷载作用下高架桥和地基振动分析[J]. 振动工程学报,2006,19(4): 438-445. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4523.2006.04.002BIAN Xuecheng. Analysis of viaduct-ground vibrations due to high-speed train moving loads[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2006, 19(4): 438-445. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4523.2006.04.002 李忠献,黄健,张媛,等. 地震作用对轻轨铁路车桥系统耦合振动的影响[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,2005,25(6): 183-188. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1301.2005.06.031LI Zhongxian, HUANG Jian, ZHANG Yuan, et al. Influence of seismic excitation on coupled vibration of train-bridge system in light railway[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2005, 25(6): 183-188. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1301.2005.06.031 李小珍,刘孝寒,刘德军. 考虑桩-土相互作用的连续刚构桥车桥耦合振动分析[J]. 振动与冲击,2011,30(12): 54-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.12.011LI Xiaozhen, LIU Xiaohan, LIU Dejun. Coupled vibration analysis of a railway coutinuous rigid-frame bridge and vehicles with soil-structure interaction[J]. Joural of Vibration and Shock, 2011, 30(12): 54-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.12.011 陈令坤,蒋丽忠,陶磊,等. 考虑桩-土作用的高速列车-桥梁地震响应分析[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(10): 3162-3170.CHEN Lingkun, JIANG Lizhong, TAO Lei, et al. Seismic response analysis of high-speed vehicle-bridge considering soil-structure interaction[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(10): 3162-3170. 乔宏,夏禾,杜宪亭. 考虑桩土相互作用的车桥耦合动力分析[J]. 振动与冲击,2018,37(3): 105-111.QIAO Hong, XIA He, DU Xianting. Dynamic analysis for a train-bridge coupled system considering soil-pile interaction[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(3): 105-111. 雷虎军. 非一致地震激励下列车-轨道-桥梁耦合振动及行车安全性研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2014. 翟婉明, 夏禾. 列车-轨道-桥梁动力相互作用理论与工程应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011: 32-88. 雷虎军,李小珍. 非一致地震激励下列车-轨道-桥梁耦合振动模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2013,48(5): 803-809. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.05.004LEI Hujun, LI Xiaozhen. Dynamic model for train-track-bridge coupling system subjected to non-uniform seismic excitation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013, 48(5): 803-809. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.05.004 ZHAI W M. Two simple fast integration methods for large scale dynamic problems in engineering[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1996, 39(24): 4199-4214. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(19961230)39:24<4199::AID-NME39>3.0.CO;2-Y 国家铁路局. 铁路桥涵地基和基础设计规范: TB 10093—2017[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2017. 李永乐,赵凯,蔡宪棠. 桥梁基础刚度有限元模拟的正交三梁模型[J]. 桥梁建设,2010(6): 17-20.LI Yongle, ZHAO Kai, CAI Xiantang. Three orthogonal-beam model for finite element simulation of bridge foundation stiffness[J]. Bridge Construction, 2010(6): 17-20. LI X Z, ZHANG Z J, ZHANG X. Using elastic bridge bearings to reduce train-induced ground vibrations:An experimental and numerical study[J]. Soil Dynamics & Earthquake Engineering, 2016, 85: 78-90. 冀昆,温瑞智,任叶飞,等. 我国抗震规范时程分析中地震动的输入数量[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(4): 743-751.JI Kun, WEN Ruizhi, REN Yefei, et al. Number of earthquake ground motion inputs for time-history analysis of seismic design code in china[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(4): 743-751. 李小珍,刘鸣,杨得海,等. 大跨度上承式钢桁架拱桥的地震损伤演化模拟[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(6): 1207-1214,1223.LI Xiaozhen, LIU Ming, YANG Dehai, et al. Seismic damage evolution simulation of long-span deck steel truss arch bridge[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(6): 1207-1214,1223. -




 下载:
下载: