Effect of Turbulence Integral Scale on Fluctuating Wind Pressure and Its Distribution Characteristics on Rectangular Upwind Surface
-
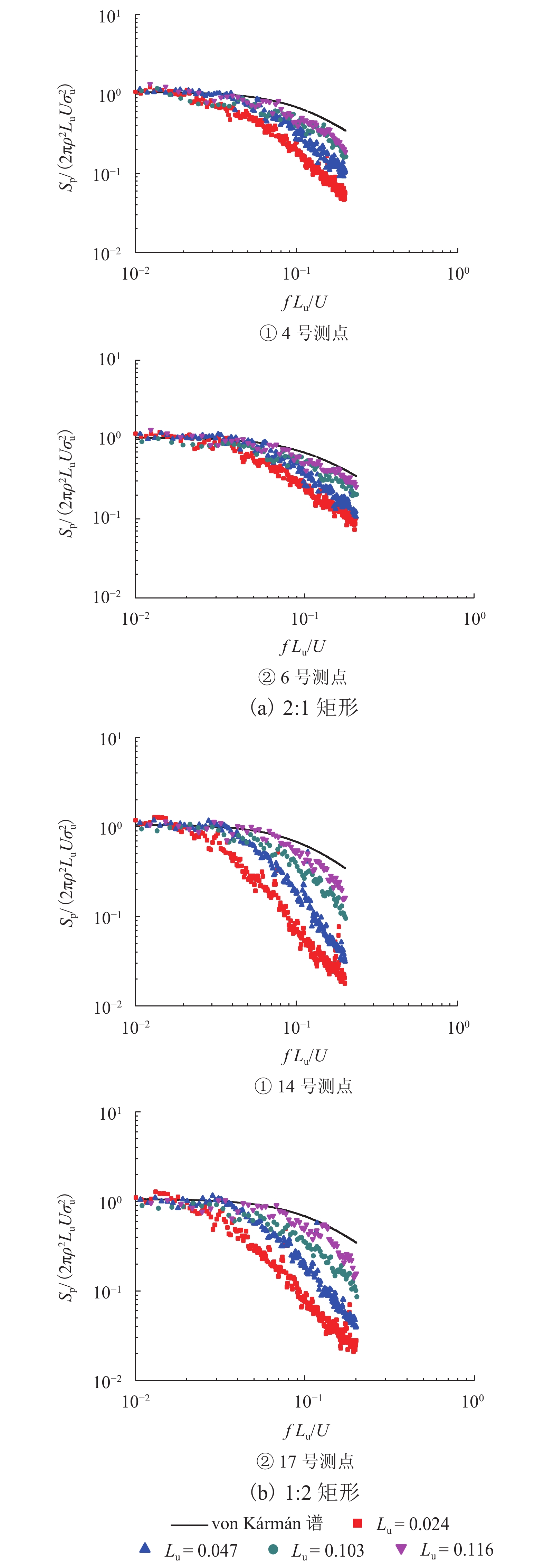
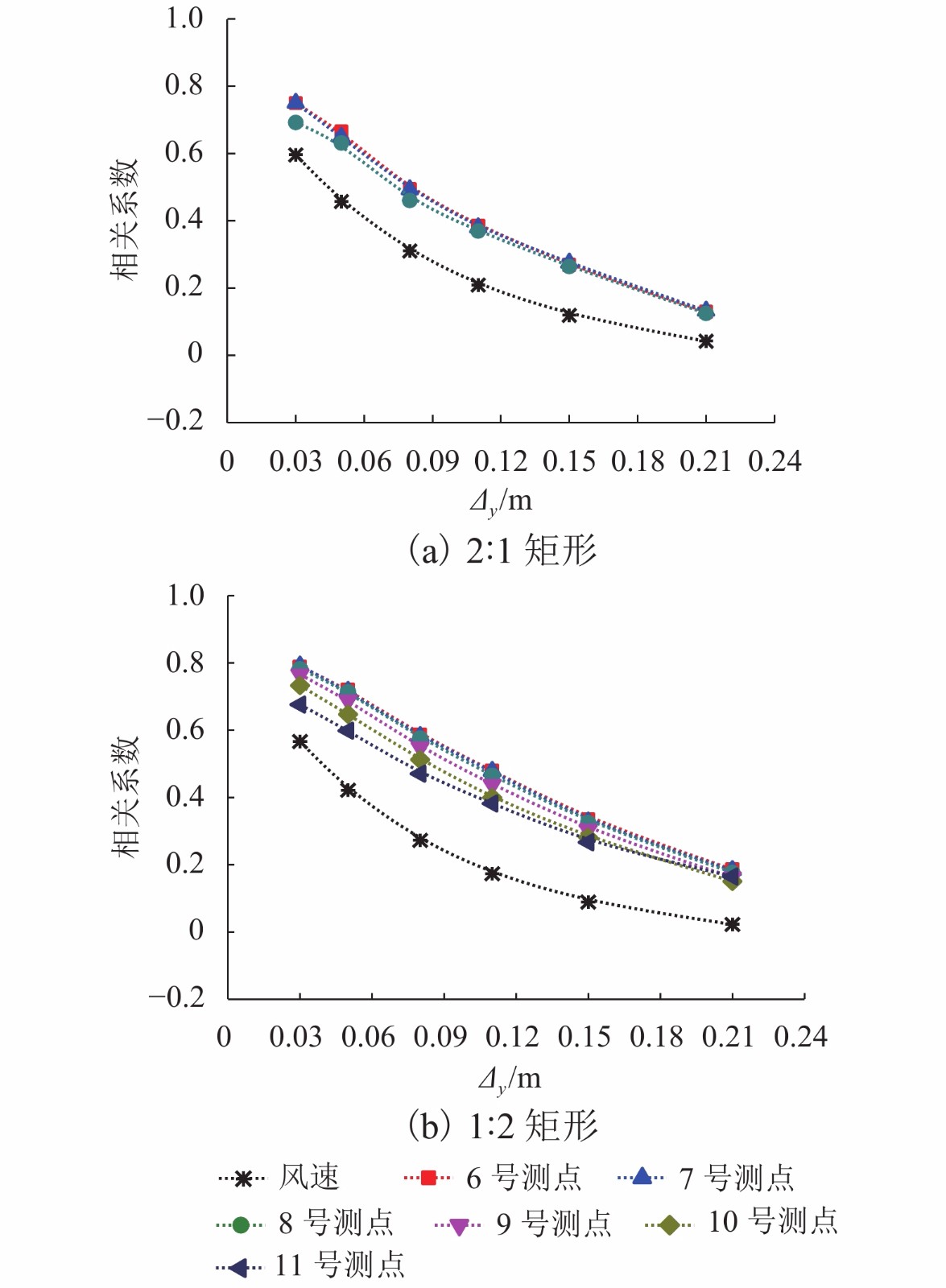
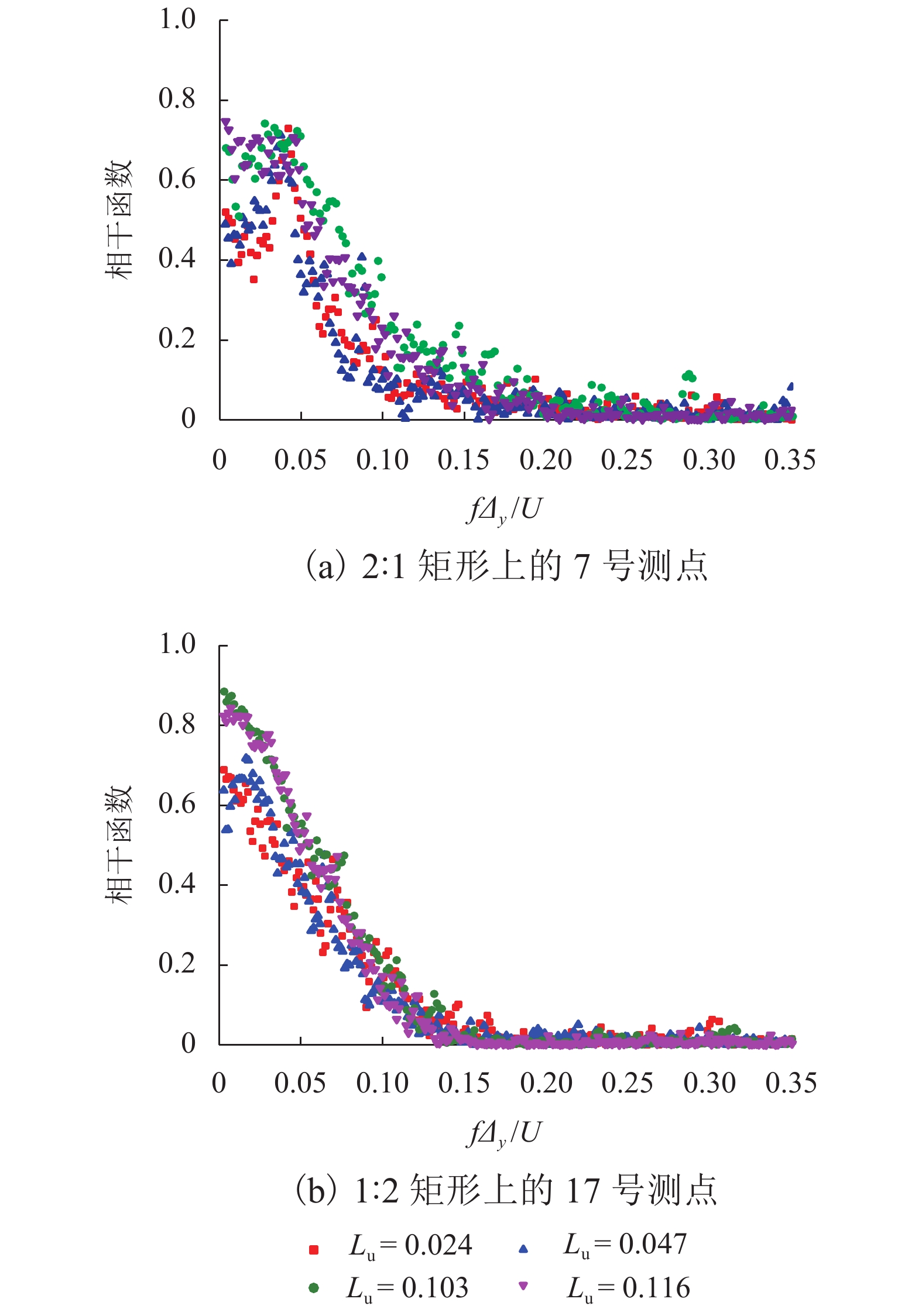
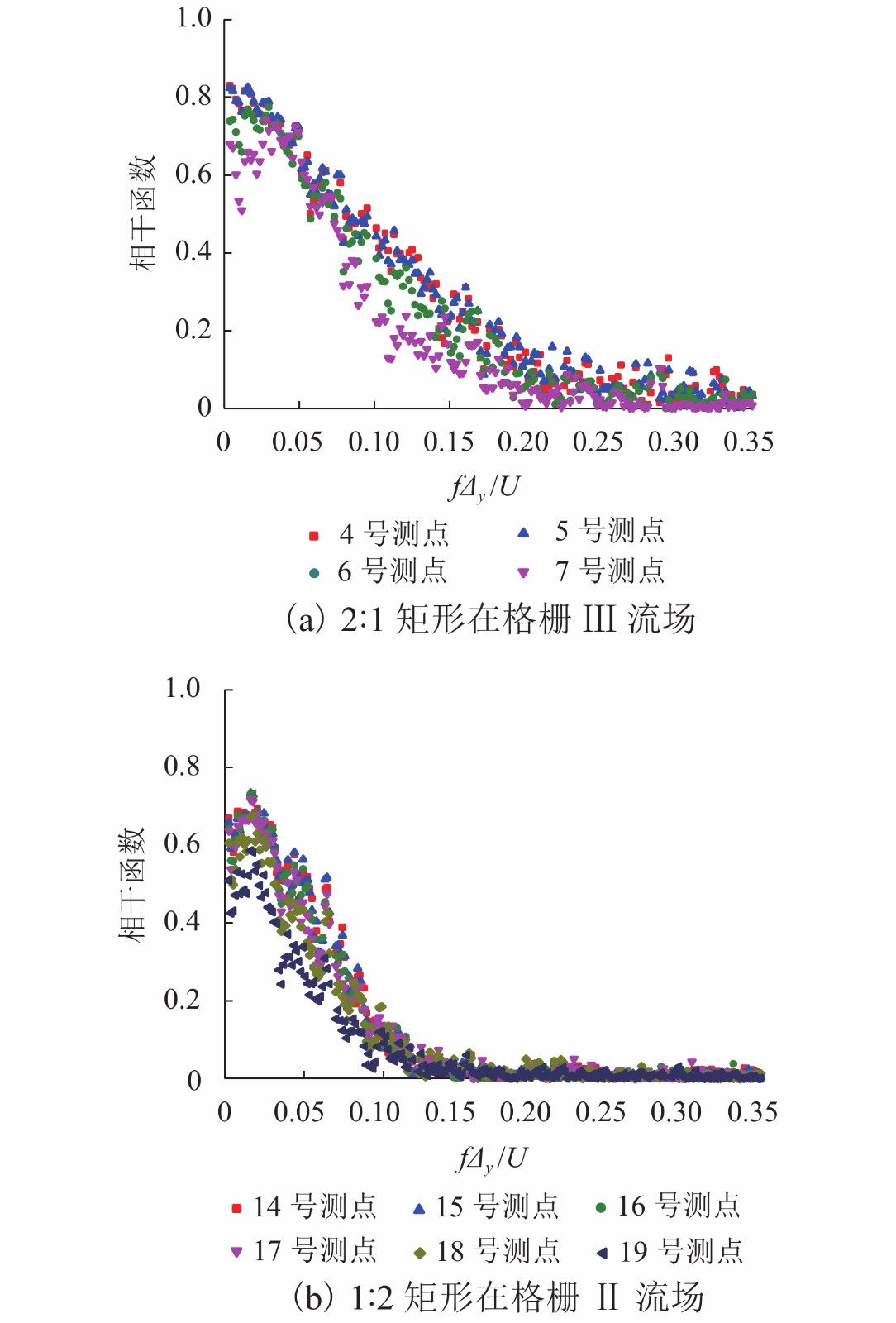
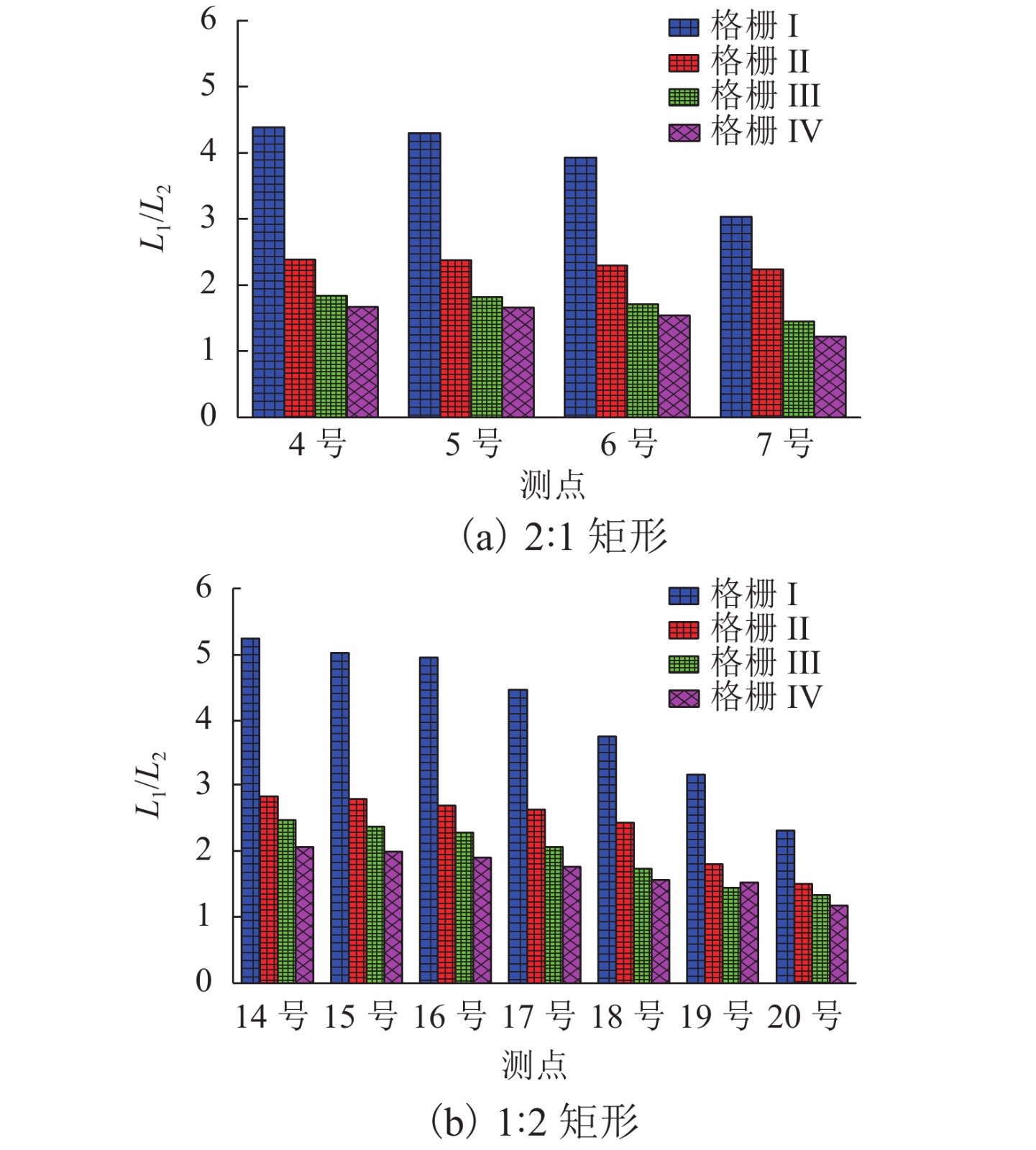
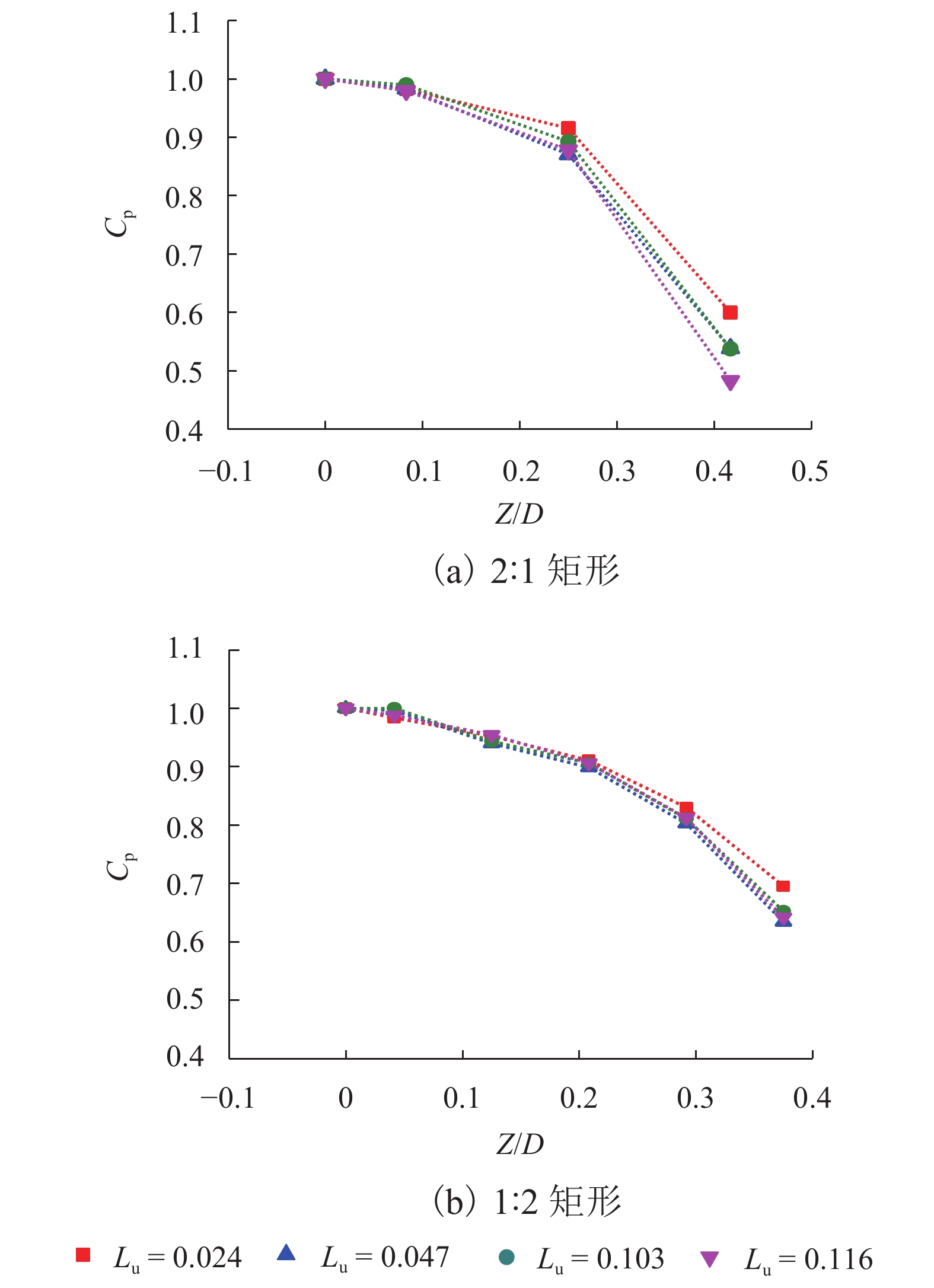
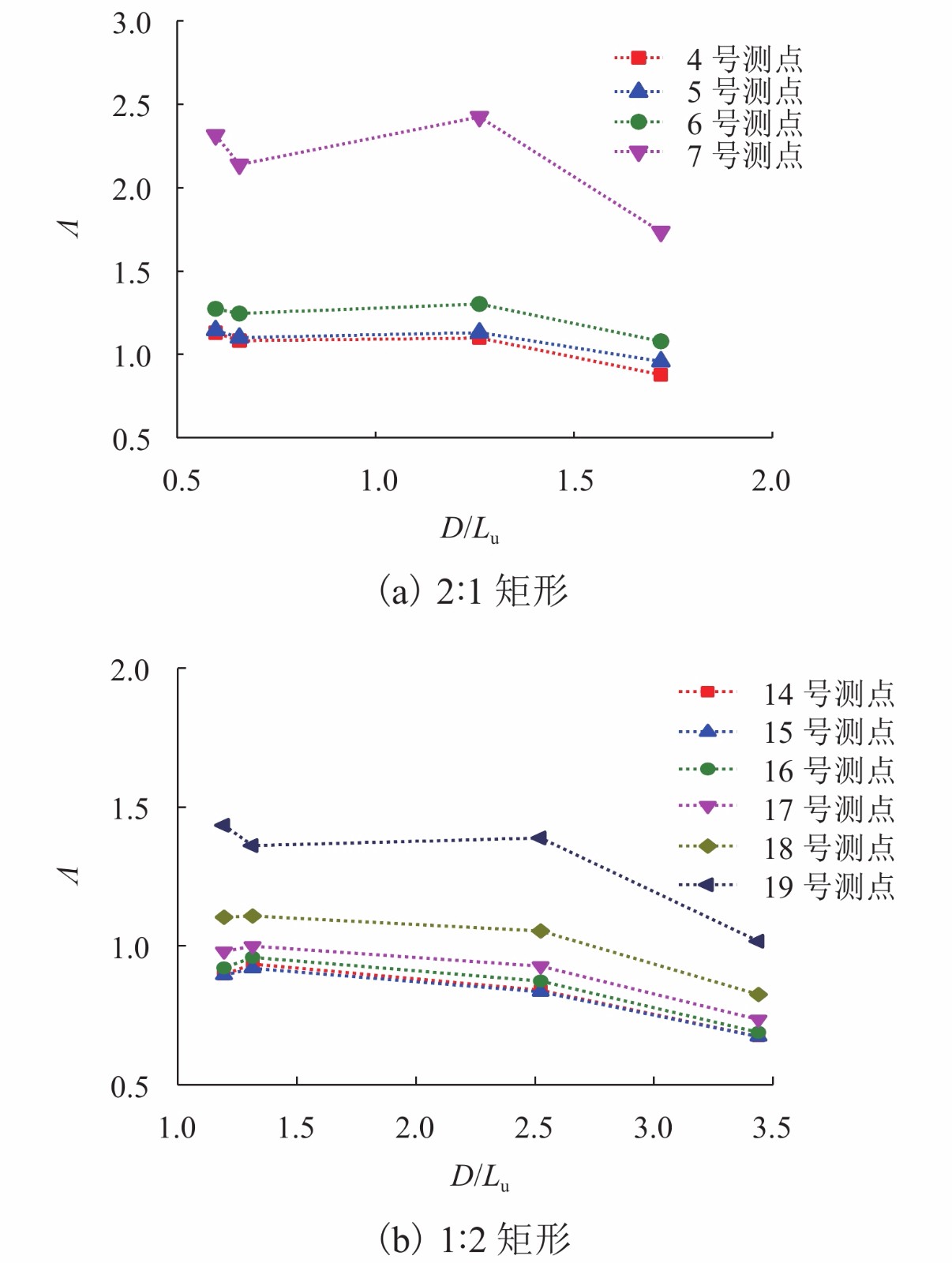
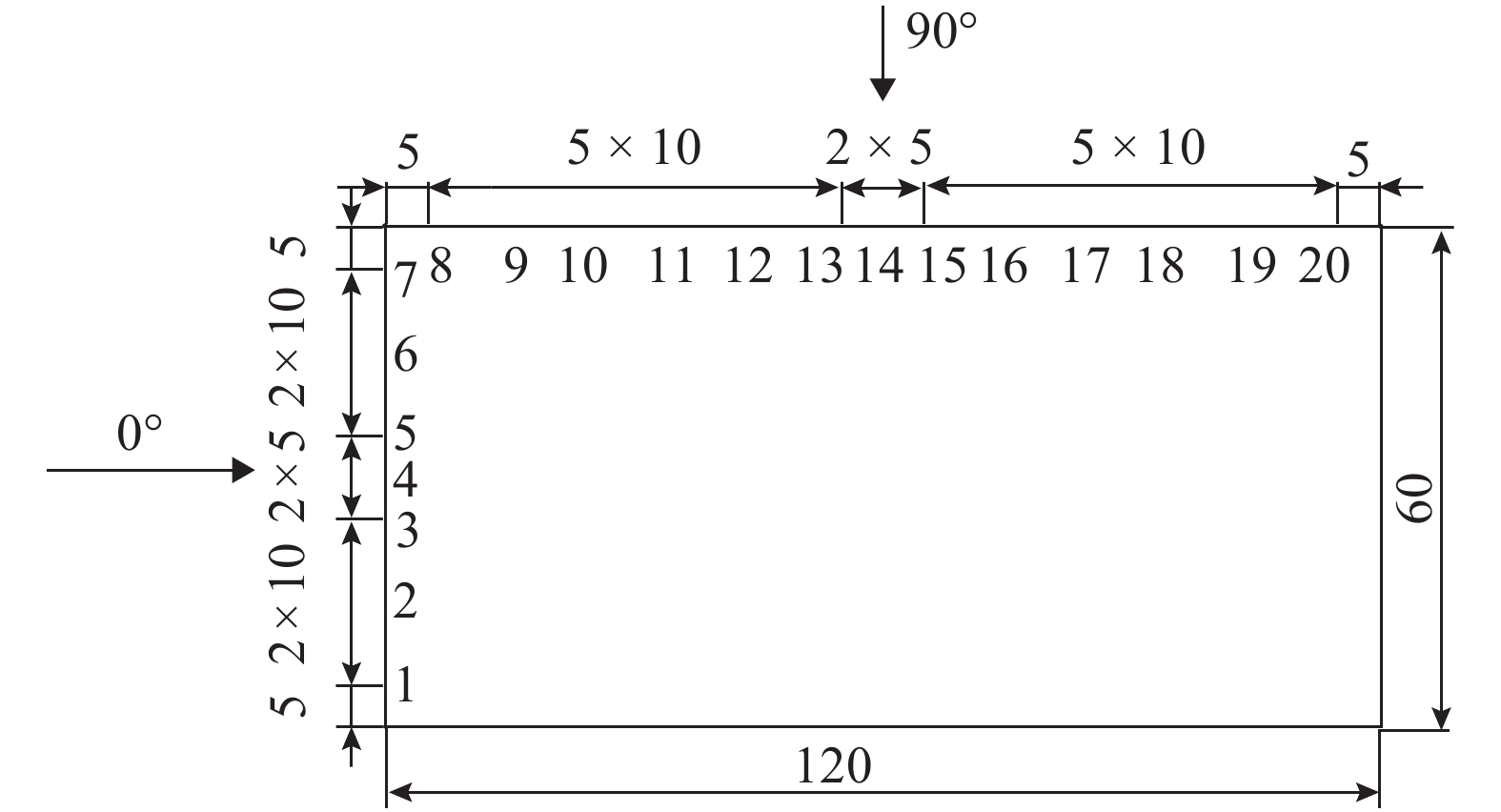
摘要: 为了研究来流紊流积分尺度对矩形断面高层建筑迎风面脉动风压及其分布特性的影响,选取2∶1和1∶2矩形为对象,通过风洞测压试验,对不同积分尺度紊流场中矩形迎风面的平均风压系数及脉动风压均方根系数、脉动风压相关函数和相干函数、脉动风压功率谱进行了对比分析. 研究结果表明:对于矩形同一高度处,脉动风压功率谱在低频区始终受准定常效应控制,而在高频区脉动风压功率谱随积分尺度的增大而增大;风压的相关性高于风的相关性,风压的相关函数与相干函数也随积分尺度的增大而增大,但相关宽度随积分尺度的增大而减小;脉动风压均方根系数随积分尺度的增大而增大;对于同一流场中矩形不同测点处,离驻点越远,风压相关函数和相干函数越小,脉动风压均方根系数越大;来流紊流积分尺度对平均风压系数的影响较小.Abstract: In order to study the influence of turbulence integral scale on the fluctuating wind pressure and its distribution characteristics on the rectangular windward surface of a high-rise building, rectangular models with 2∶1 and 1∶2 width-depth ratios were put in a wind tunnel to obtain statistical features of wind pressure in turbulent flow fields with different integral scales for comparative analysis, including the mean wind pressure coefficient, root mean square coefficient, correlation coefficient and coherence function, and power spectrum of fluctuating wind pressure. Results are as follows: At the same height of the rectangular model in different turbulence flow fields, the wind pressure power spectrum is dominated by a quasi-steady effect in low-frequency regions, but it increases as the integral scale increases in high-frequency regions. The correlation and coherence of wind pressure increases with the integral scale increasing, and wind pressure is always more correlated than the turbulence flow. However, as the integral scale increases, the correlation width of wind pressure decreases, and the root mean square coefficient of fluctuating wind pressure increases. On the other hand, at different heights of the rectangular model in the same turbulence flow field, the farther away from the stagnation point, the smaller the wind pressure correlation function and coherence function, and the larger the root mean square coefficient of fluctuating wind pressure. In addition, the mean wind pressure coefficient is rarely affected by turbulence integral scale.
-
表 1 试验工况
Table 1. Test conditions
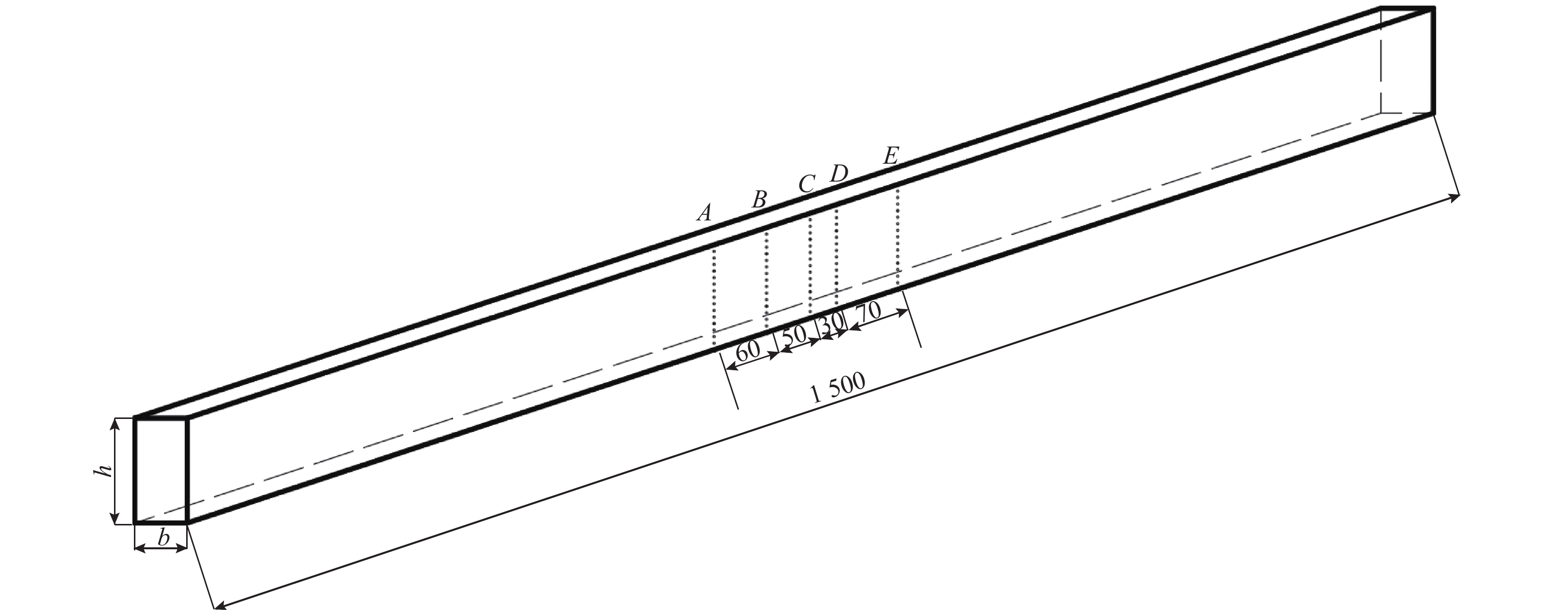
工况 格栅编号 格栅网格尺寸/m 格栅杆件尺寸/mm 测量点与格栅间距离 x/m 来流风速U/(m•s−1) 1 Ⅰ 0.08 20 2.5 9.5 2 Ⅱ 0.16 25 3.0 9.5 3 Ⅲ 0.33 70 4.2 9.5 4 Ⅳ 0.45 85 4.2 9.5 表 2 格栅紊流场参数
Table 2. Parameters of grid-generated turbulent flow fields
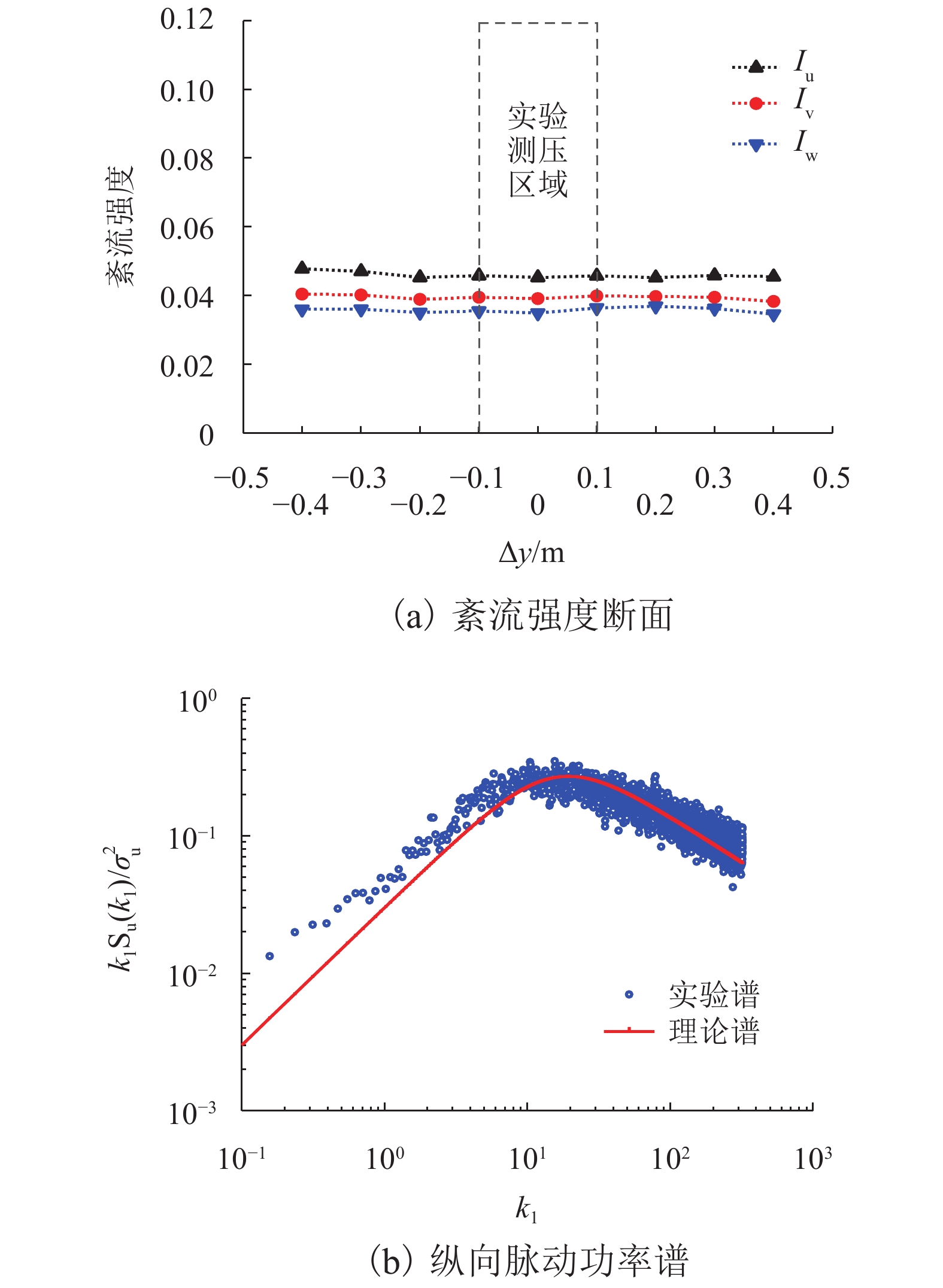
工况 $L_{\rm{u} }/{\rm{m}}$ $L_{\rm{v} }/{\rm{m}}$ $L_{\rm{w} }/{\rm{m}}$ Iu Iv Iw 1 0.024 0.009 0.014 0.066 0.056 0.061 2 0.047 0.019 0.020 0.044 0.037 0.039 3 0.103 0.037 0.036 0.081 0.070 0.070 4 0.116 0.045 0.045 0.112 0.099 0.100 -
FARELL C, IYENGAR A K S. Experiments on the wind tunnel simulation of atmospheric boundary layers[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1999, 79(1/2): 11-35. KATO N, OHKUMA T, KIM J R, et al. Full-scale measurements of wind velocity in two urban areas using an ultrasonic anemometer[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1992, 41(1/2/3): 67-78. MAEDA J, MAKINO M. Power spectra of longitudinal and lateral wind speed near the ground in strong winds[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1988, 28(1/2/3): 31-40. SHU Z R, LI Q S. An experimental investigation of surface pressures in separated and reattaching flows:effects of freestream turbulence and leading-edge geometry[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2017, 165: 58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2017.03.004 ABUL F A, GREGORY A K. Mean pressure distributions and reattachment lengths for roof-separation bubbles on low-rise buildings[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2016, 155: 115-125. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2016.05.008 MORRISON M J, KOPP G A. Effects of turbulence intensity and scale on surface pressure fluctuations on the roof of a low-rise building in the atmospheric boundary layer[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2018, 183: 140-151. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2018.10.017 BEARMAN P W. Some measurements of the distortion of turbulence approaching a two-dimensional bluff body[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1972, 53(3): 451-467. doi: 10.1017/S0022112072000254 KAWAI, KATSURA J, ISHIZAKI H. Characteristics of pressure fluctuation on the windward wall of a tall building[C]//Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Wind Engineering. Colorado: Pergamon Press, 1980: 519-521 HOLMES J D. Pressure fluctuations on a large building and along-wind structural loading[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1975, 1: 249-278. doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(75)90020-3 MATSUI G, SUDA K, HIGUCHI K. Full-scale measurement of wind pressures acting on a high-rise building of rectangular plan[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1982, 10(3): 267-286. doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(82)90002-2 曾加东,李明水,李少鹏. 矩形高层建筑顺风向脉动风荷载空间相关性[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2017,49(6): 150-155. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201604087ZENG Jiadong, LI Mingshui, LI Shaopeng. Spatial correlation analysis of fluctuating along-wind loads on high-rise buildings with rectangular section[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017, 49(6): 150-155. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201604087 顾明,张建国. 高层建筑顺风向脉动荷载相干性研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2008,41(11): 18-22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2008.11.004GU Ming, ZHANG Jianguo. Coherence analysis of along-wind fluctuating loads on high-rise buildings[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2008, 41(11): 18-22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2008.11.004 HUNT J C R, KAWAI H, RAMSEY S R, et al. A review of velocity and pressure fluctuations in turbulent flows around bluff bodies[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1990, 35: 49-85. doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(90)90210-4 LAVOIE P, DJENIDI L, ANTONIA R A. Effects of initial conditions in decaying turbulence generated by passive grids[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2007, 585: 395-420. doi: 10.1017/S0022112007006763 DJENIDI L, TARDU S F. On the anisotropy of a low-reynolds-number grid turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2012, 702: 332-353. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2012.179 HUNT J C R. A theory of turbulent flow round two-dimensional bluff bodies[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1973, 61(4): 625-706. doi: 10.1017/S0022112073000893 LAROSE G L, MANN J. Gust loading on streamlined bridge decks[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 1998, 12(5): 511-536. doi: 10.1006/jfls.1998.0161 DAVENPORT A G. The response of slender,line-like structures to a gusty wind[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers, 1962, 23(3): 389-408. doi: 10.1680/iicep.1962.10876 LI M, YANG Y, LI M, et al. Direct measurement of the sears function in turbulent flow[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2018, 847(25): 768-785. LAROSE G L. The spatial distribution of unsteady loading due to gusts on bridge decks[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2003, 91(12/13/14/15): 1431-1443. 李少鹏,李明水,马存明. 矩形断面抖振力展向相关性的试验研究[J]. 工程力学,2016,33(1): 39-46. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.05.0458LI Shaopeng, LI Mingshui, MA Cunming. Experimental investigation of the span-wise correlation of buffeting forces on a rectangular section[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2016, 33(1): 39-46. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.05.0458 DURBIN P A, HUNT J C R. On surface pressure fluctuations beneath turbulent flow round bluff bodies[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1980, 100(1): 161-184. doi: 10.1017/S0022112080001061 -




 下载:
下载: