Dynamic Characteristics of Silt Considering Time Intermittent Effect
-
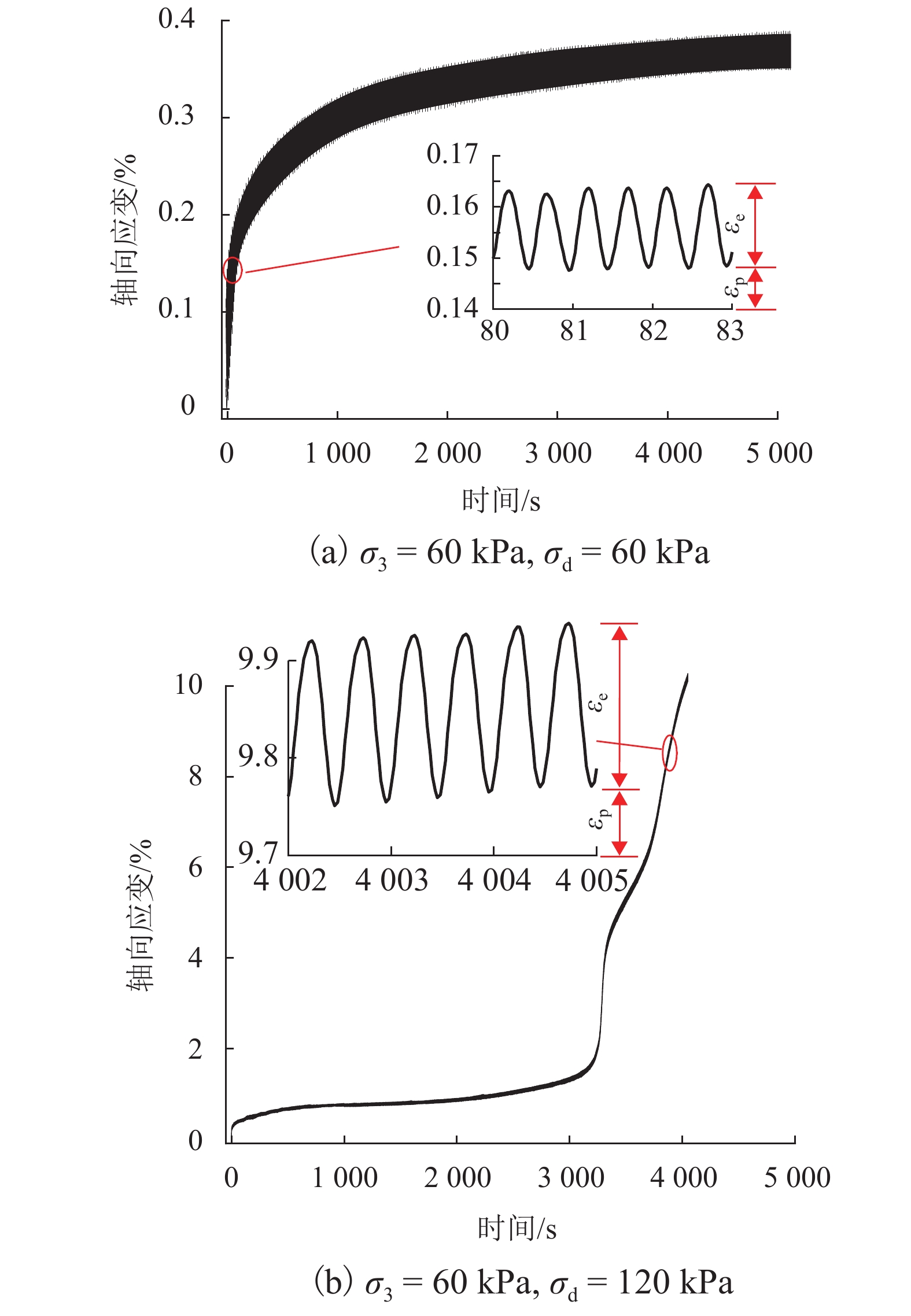
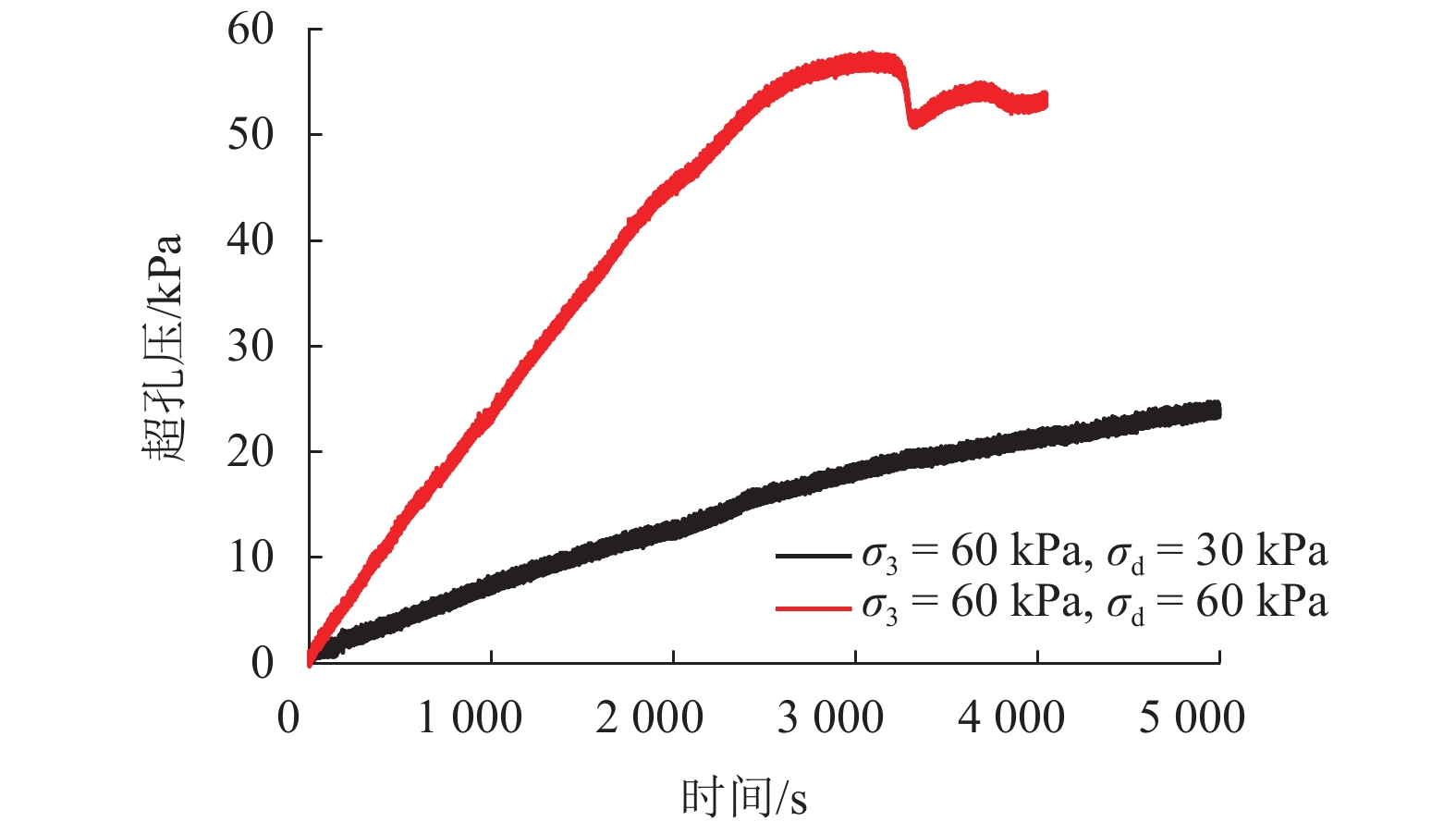
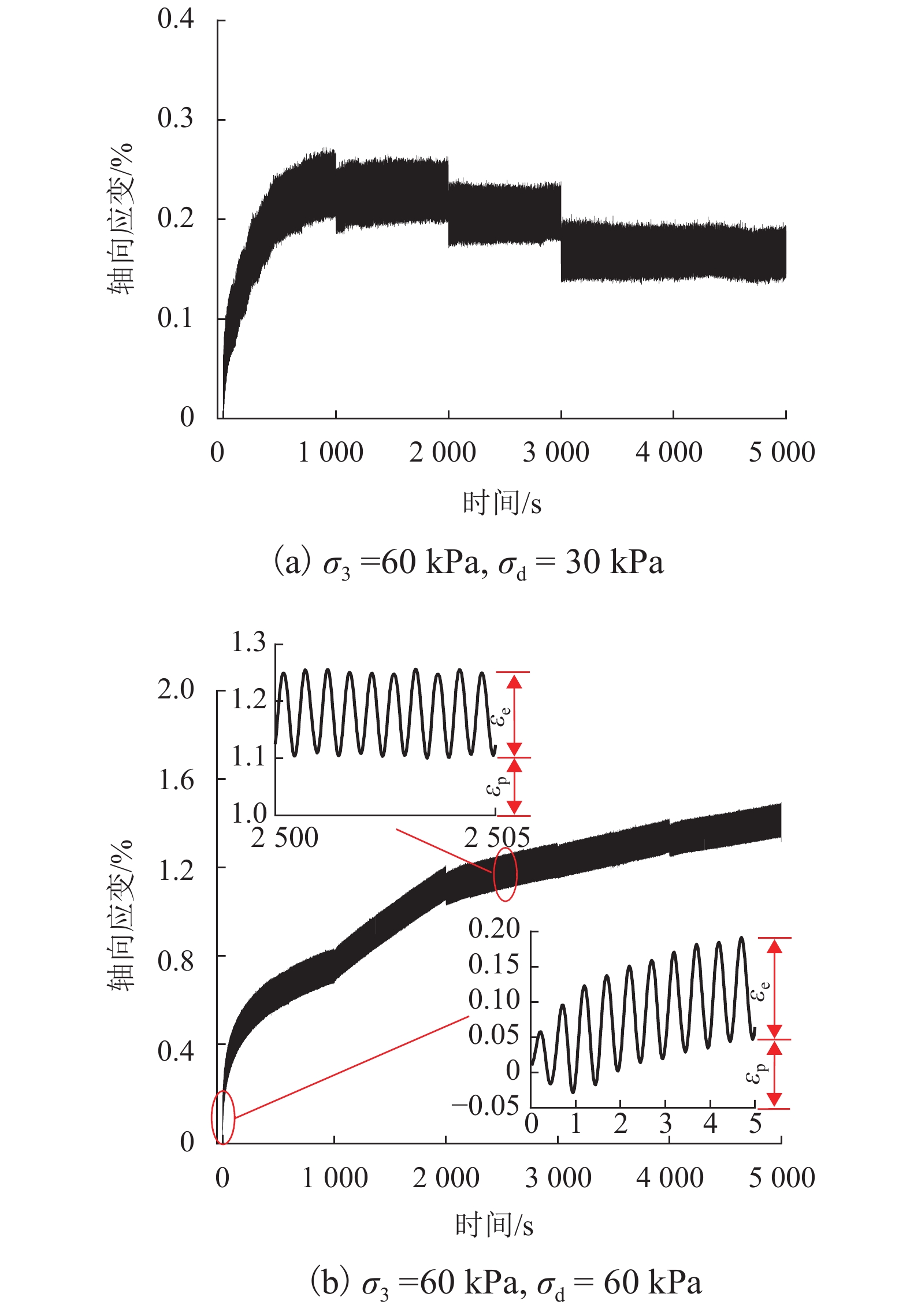
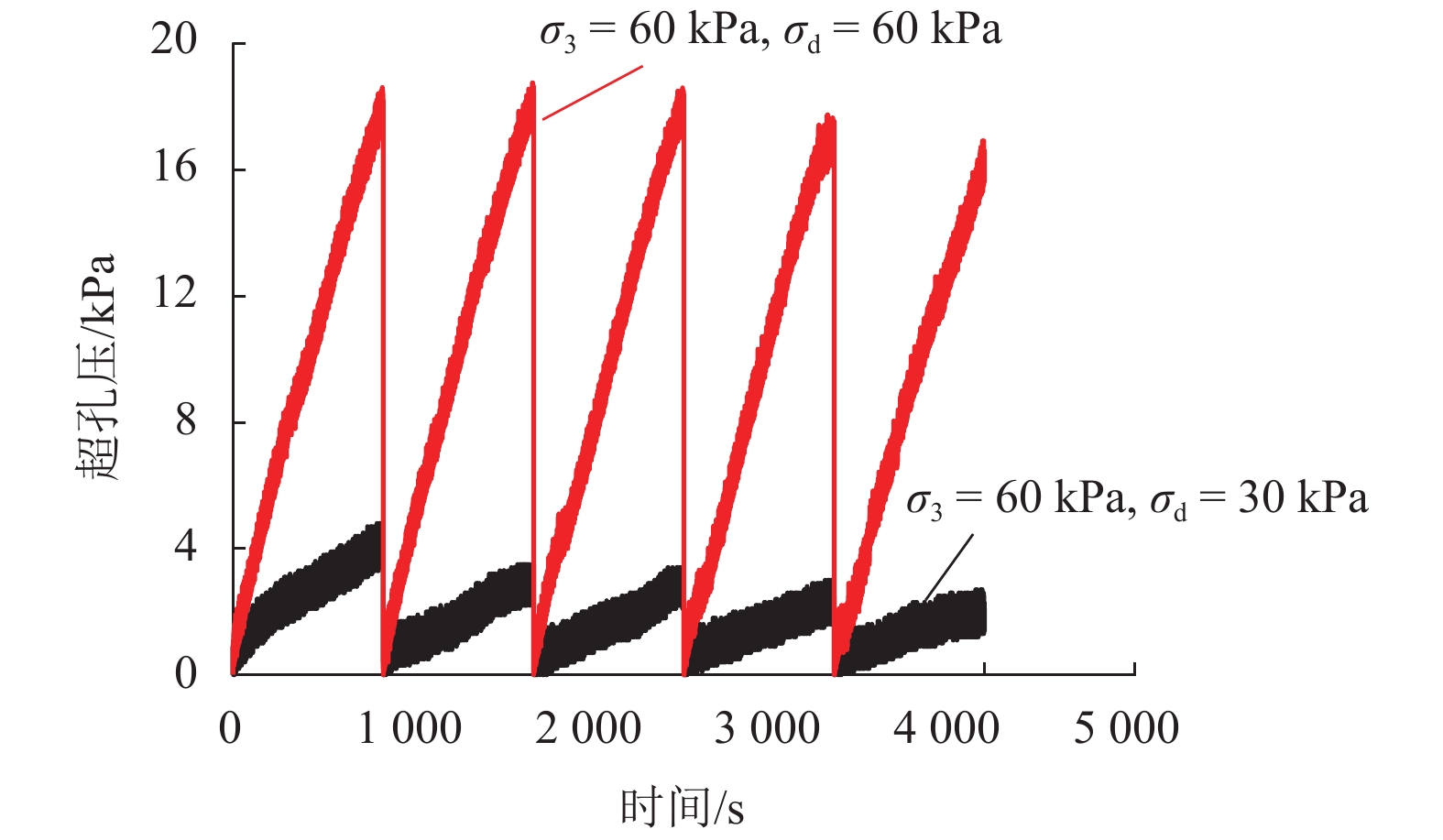
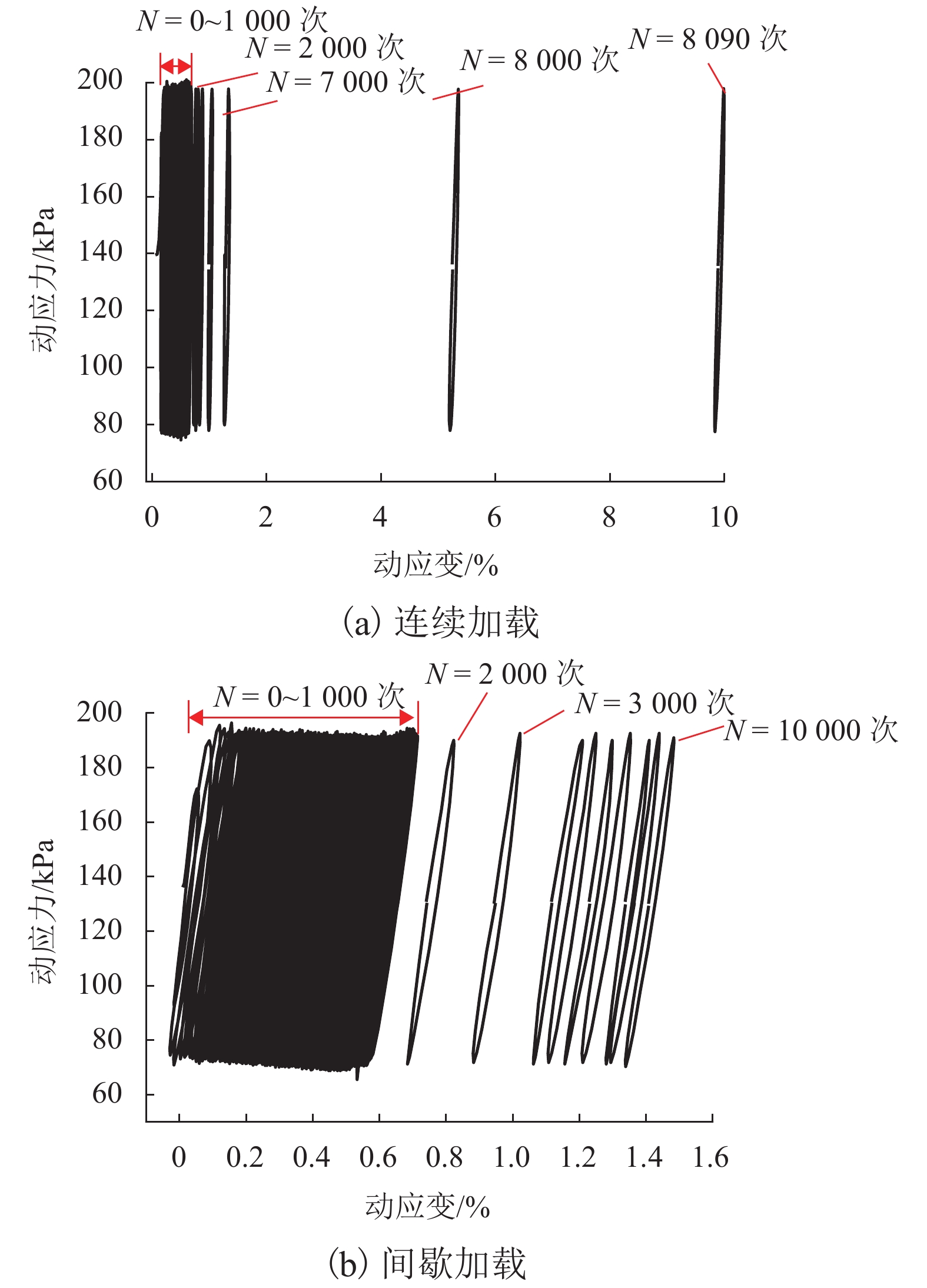
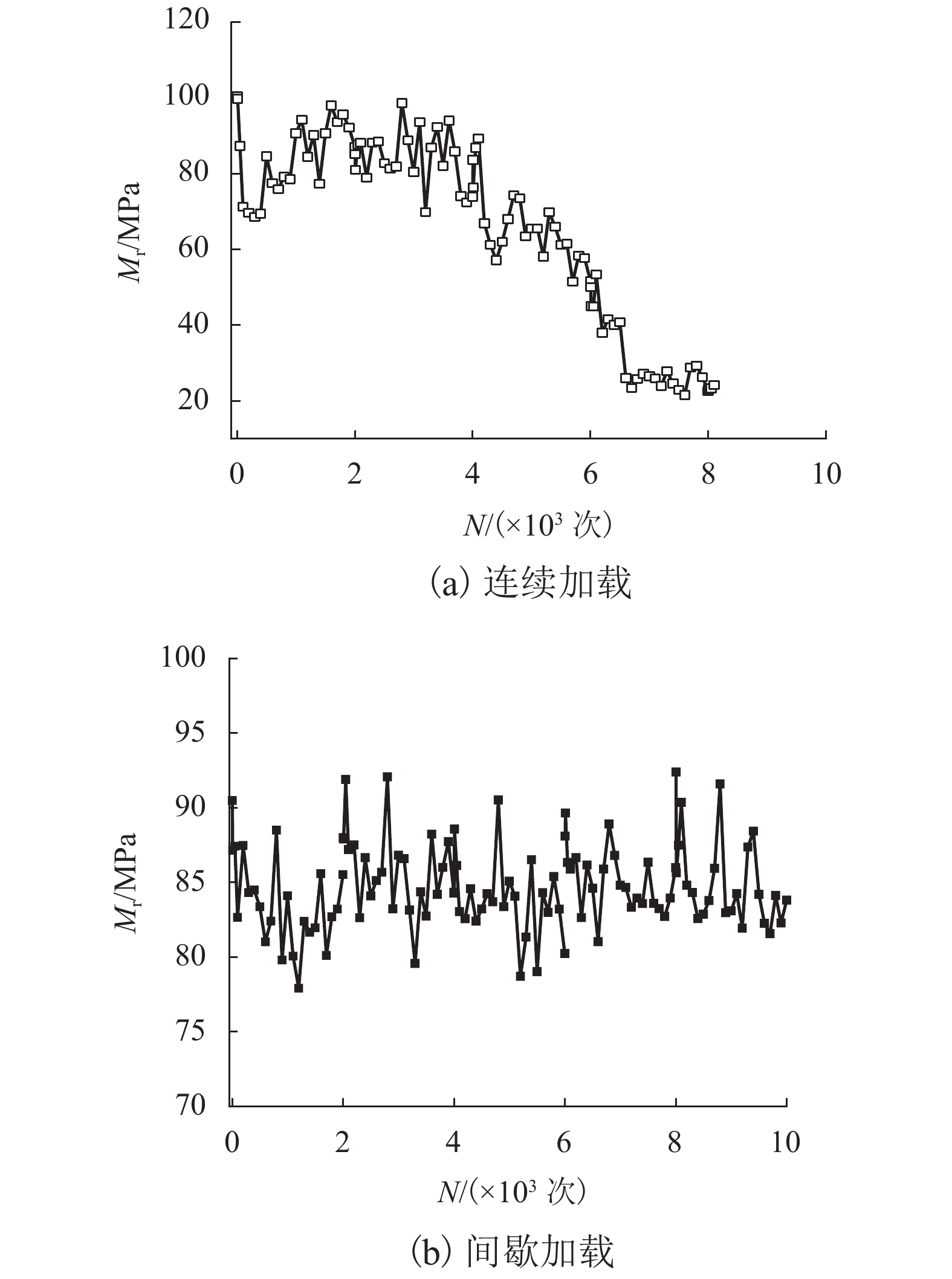
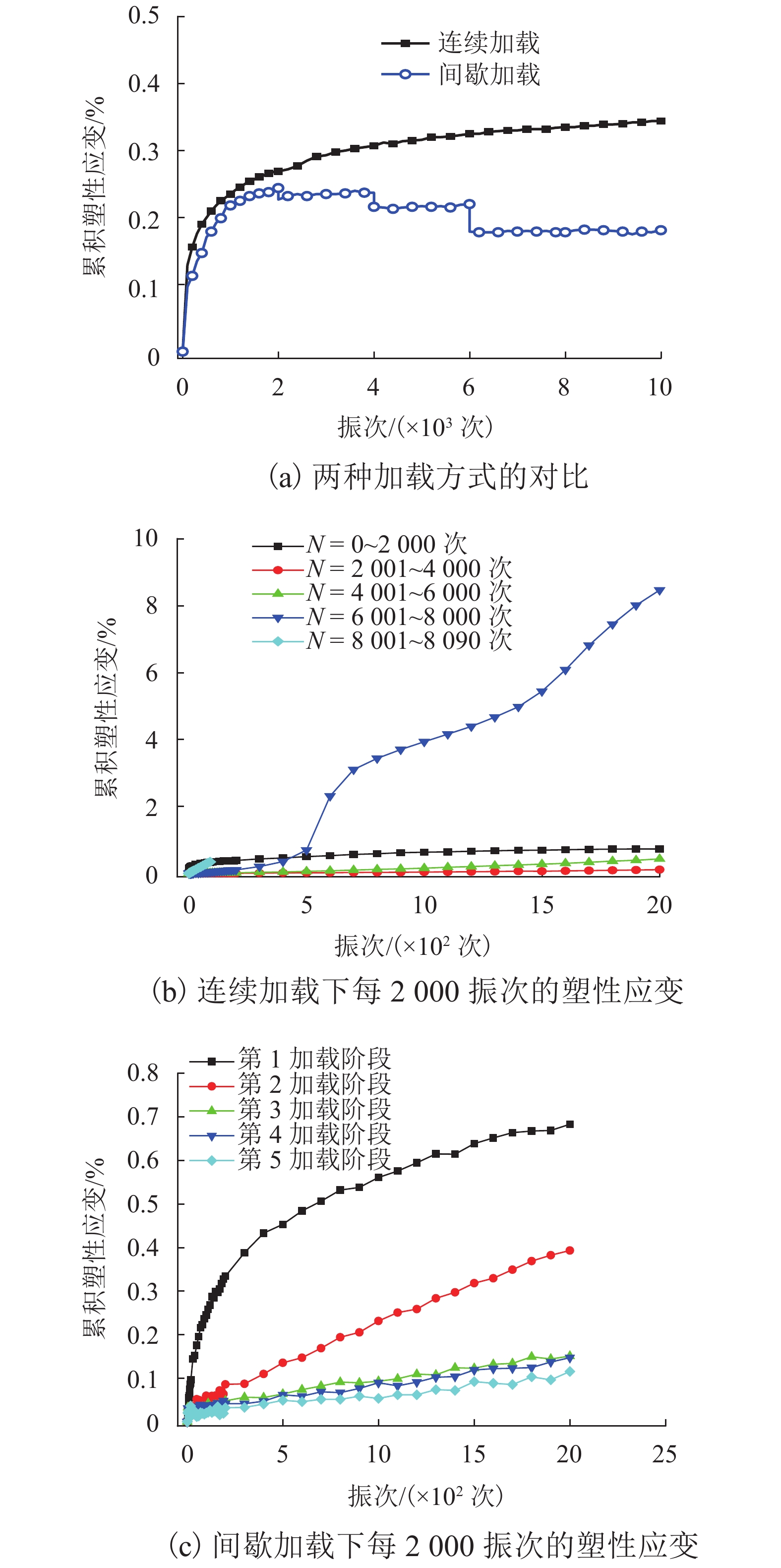
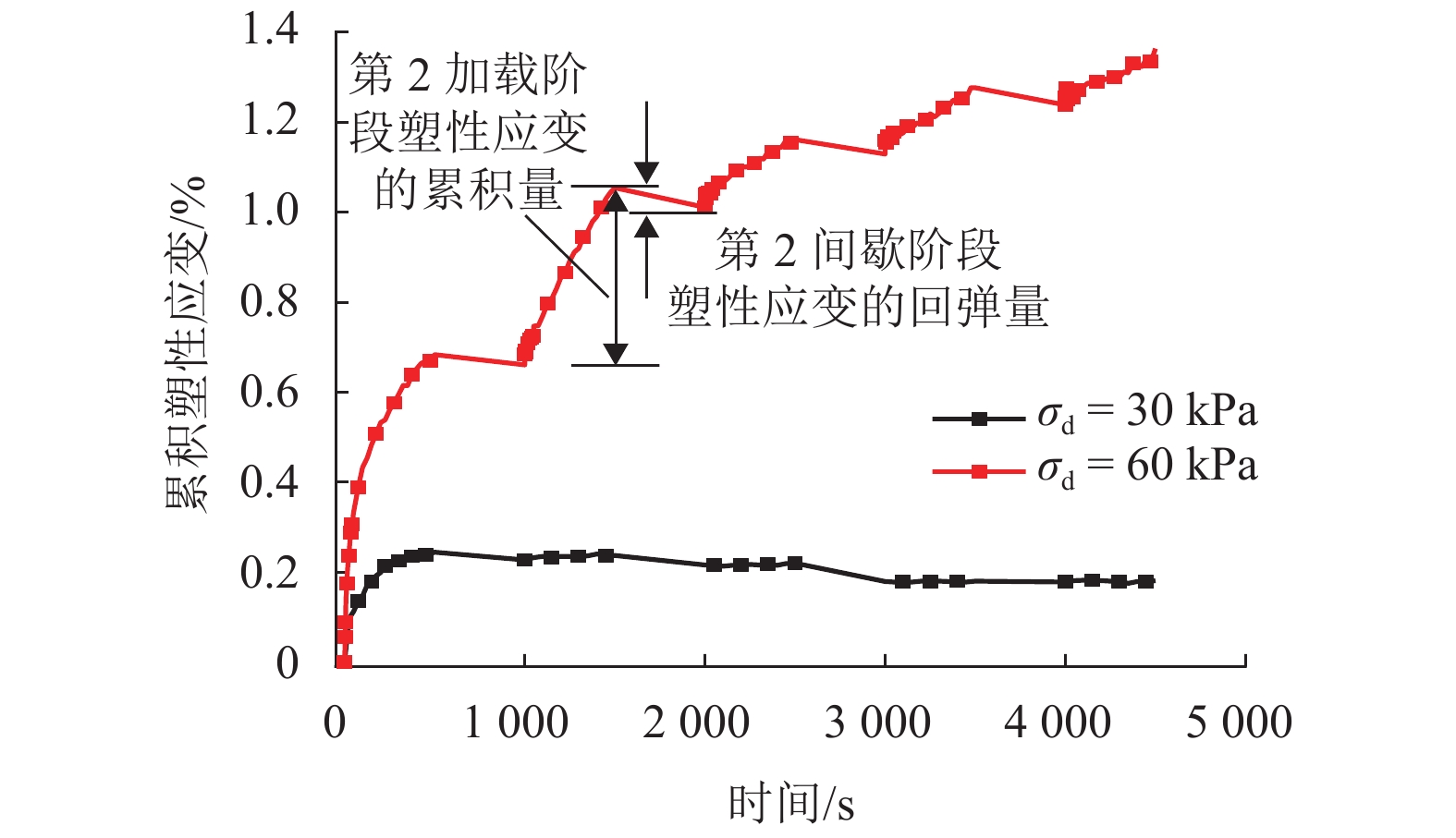
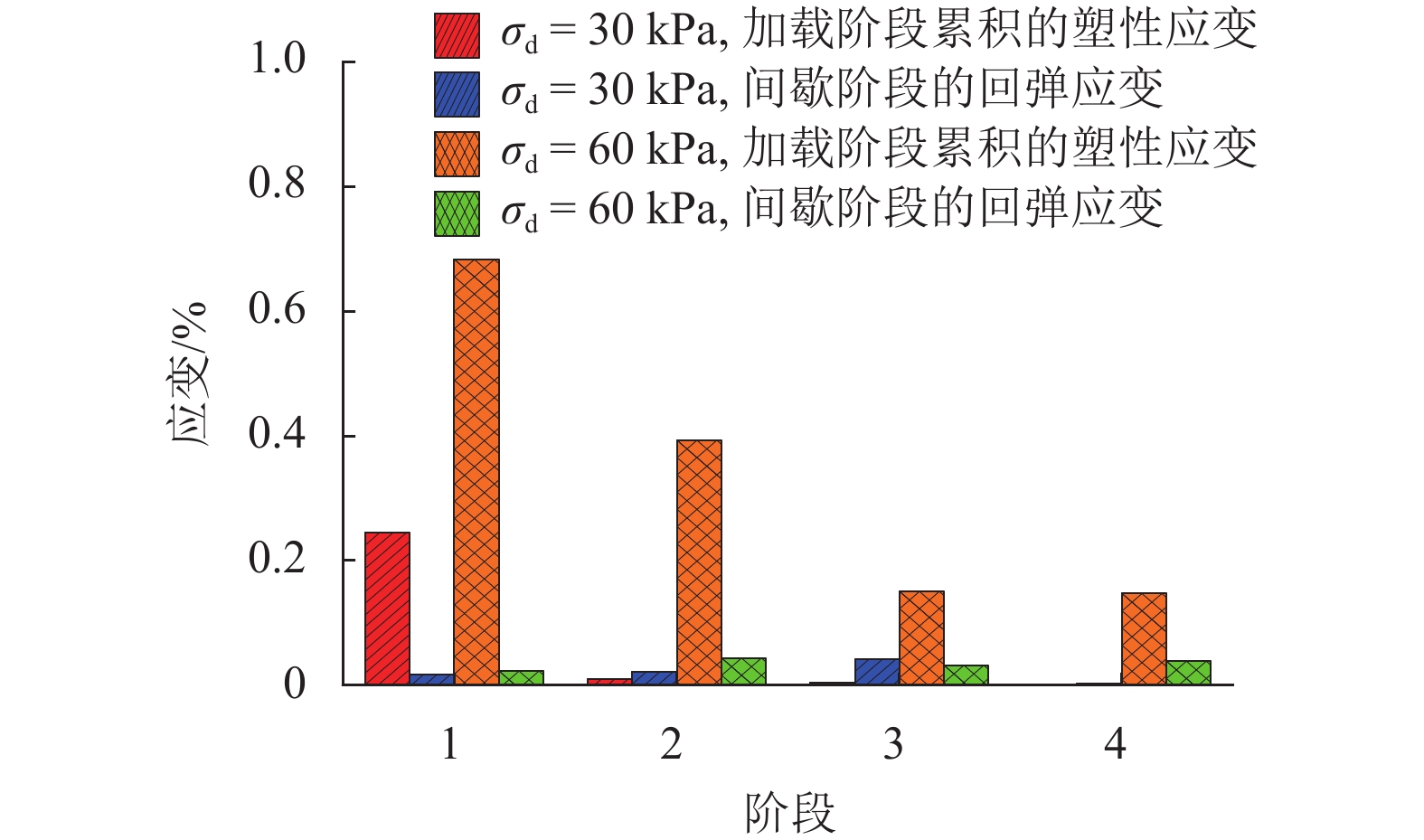
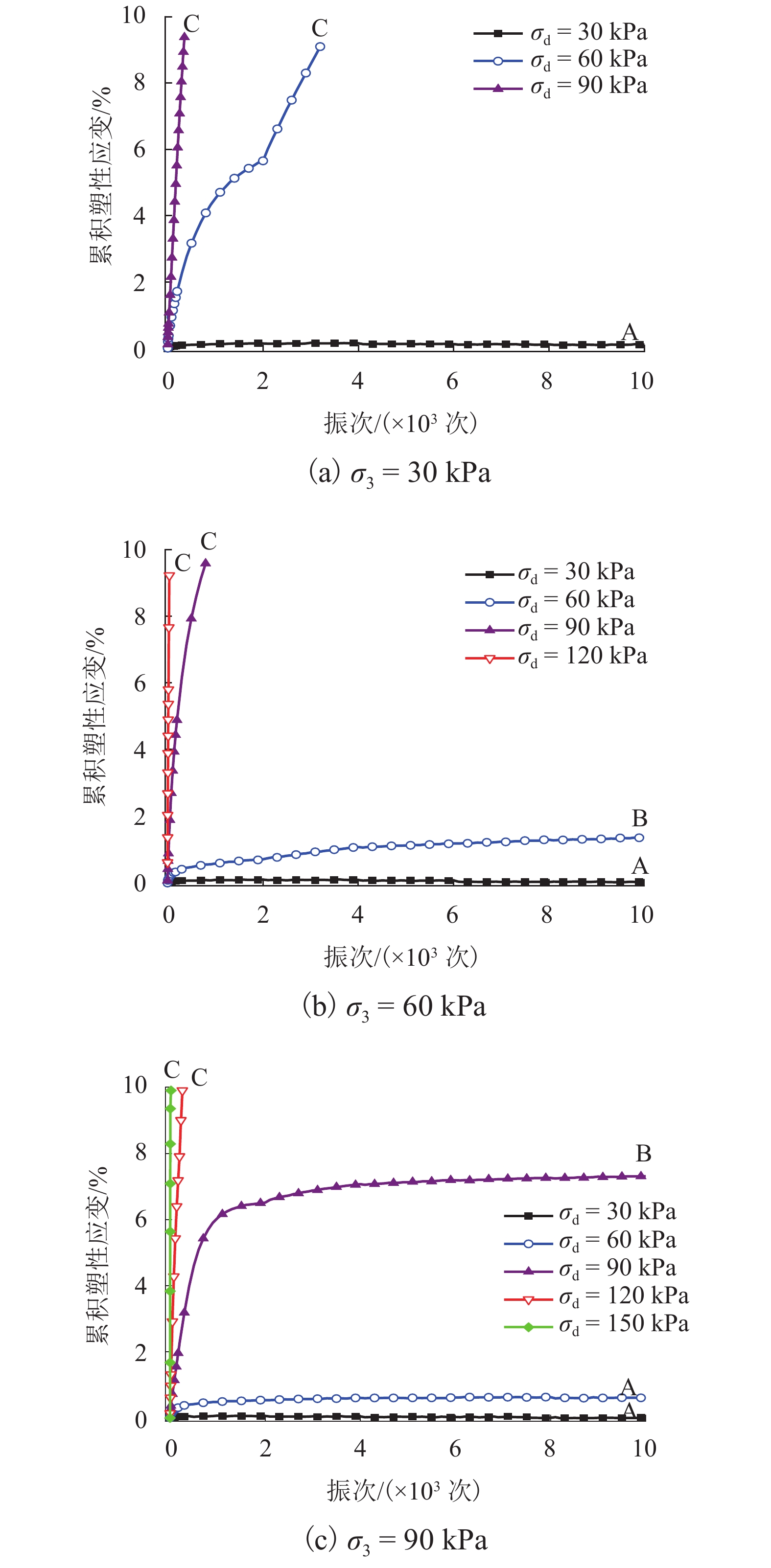
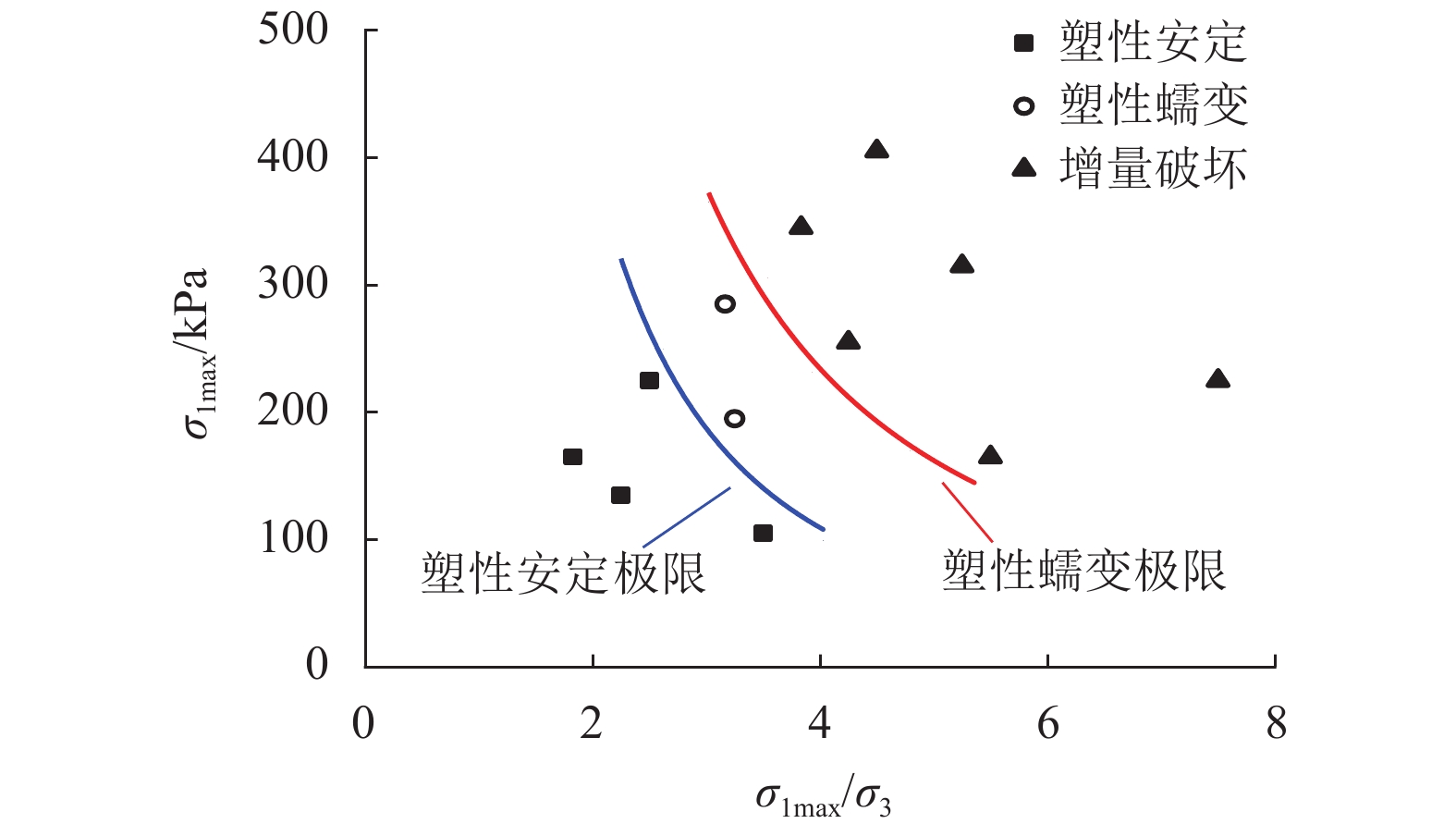
摘要: 列车荷载是揭示路基真实动力响应特性的前提,以往的动三轴试验将列车荷载视为连续动荷载,忽略了追踪列车间隔时间对路基土体动力特性的影响. 利用室内动三轴仪对粉土开展了连续加载和间歇加载(连续加载与间歇交替循环)的动三轴试验,分析了两种加载方式下粉土超孔隙水压力、回弹模量、累积塑性应变等的发展规律. 研究结果表明:持续动荷载作用下累积的超孔隙水压力在间歇阶段会发生消散,轴向应变在间歇阶段得到一定程度恢复,进而提高了试样抵抗变形的能力;室内动三轴试验忽略间歇效应将高估列车动荷载作用下试样超孔压和塑性应变的累积量及发生破坏的可能性;间歇加载下试样的永久变形行为可依据安定理论划分为塑性安定、塑性蠕变和增量破坏.Abstract: Train dynamic load is the premise to reveal the real dynamic response characteristics of subgrade. The train load is regarded as a continuous dynamic load in previous cyclic triaxial tests without considering the time intermittent effect. Dynamic triaxial tests of silt under continuous loading and intermittent loading (continuous loading and intermittent alternating circulation) were carried out by using indoor dynamic triaxial apparatus, and the development laws of excess pore water pressure, modulus of resilience and accumulated plastic strain of silt under two loading modes were analyzed. The accumulated excess pore water pressure under continuous dynamic load will dissipate in the intermittent stage, and the axial strain will be restored to a certain extent in the intermittent stage, thus improving the ability of the sample to resist deformation. Ignoring intermittent effect in indoor dynamic triaxial tests will overestimate the cumulative amount of excess pore pressure and plastic strain and the possibility of failure. The permanent deformation behavior of specimens under intermittent loading can be divided into plastic stability, plastic creep, and incremental failure according to stability theory.
-
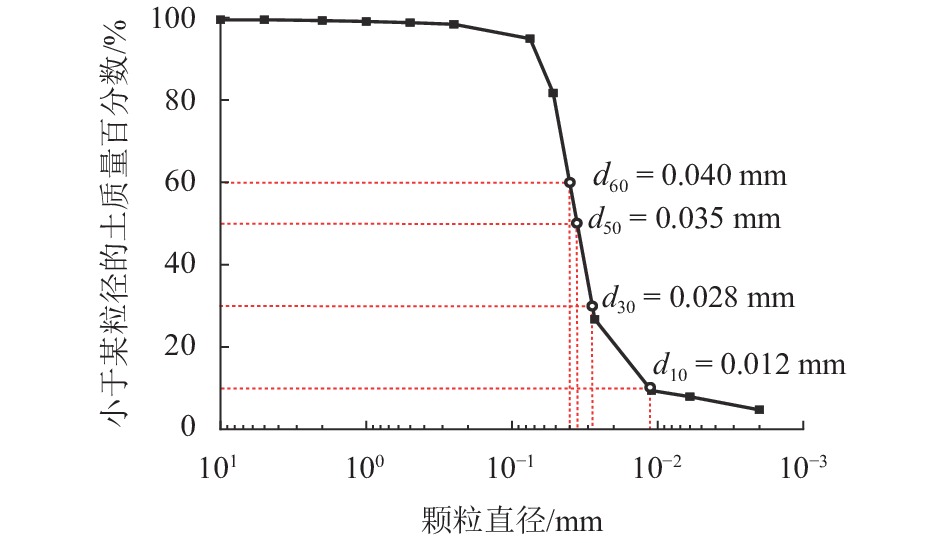
表 1 低液限粉土的基本物理参数
Table 1. Basic physical parameters of silt with low liquid limit
颗粒密度/(g•cm−3) 最大干
密度/(g•cm−3)最优
含水率/%饱和
含水率/%塑限/% 塑性
指数渗透系数k/(cm•s−1) 2.71 1.96 11.80 19.75 18.2 7.8 1.238 × 10−7 表 2 动三轴试验方案
Table 2. Test scheme of dynamic triaxial
kPa 试验序列 试验类型 σ3 σd 1 连续加载 60 30,60 2 30 30,60,90 3 分阶段循环加载 60 30,60,90,120 4 90 30,60,90,120,150 -
MONISMITH C L, OGAWA N, FREEME C R. Permanent deformation characteristics of subgrade soils due to repeated loading[R]. Washington D. C.: Transportation Research Board, 1975. KAZUYA Y, KAZUTOSHI H, ADRIAN F L H. Effects of cyclic loading on undrained strength and compressibility of clay[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1992, 32(1): 100-116. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.32.100 XIAO J H, JUANG C H, XU C J, et al. Strength and deformation characteristics of compacted silt from the lower reaches of the Yellow River of China under monotonic and repeated loading[J]. Engineering Geology, 2014, 178: 49-57. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.06.008 GU C, GU Z Q, CAI Y Q, et al. Dynamic modulus characteristics of saturated clays under variable confining pressure[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2017, 54: 729-735. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2016-0441 CAI Y Q, GUO L, JARDINE R J, et al. Stress-strain response of soft clay to traffic loading[J]. Géotechnique, 2017, 67(5): 446-451. FREDRICK L, ULF I, ANDREW D. State of the art. I:resilient response of unbound aggregates[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2000, 126(1): 66-75. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(2000)126:1(66) SWEERE G T H. Unbound granular bases for roads[D]. [S.l.]: University of Delft, 1990. WOLFF H, VISSER A T. Incorporating elasto-plasticity in granular layer pavement design[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers Transport, 1994, 105: 259-72. doi: 10.1680/itran.1994.27137 BARKSDALE R D. Laboratory evaluation of rutting in base course materials[C]//Third International Conference on the Structural Design of Asphalt Pavements. [S.l.]: Michigan State University, 1972: 161-74. WERKMEISTER S, DAWSON A, WELLNER F. Permanent deformation behaviour of granular materials[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2005, 6: 31-51. doi: 10.1080/14680629.2005.9689998 YILDIRIM H, ERSAN H. Settlements under consecutive series of cyclic loading[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2007, 27: 577-585. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2006.10.007 王军,蔡袁强,郭林,等. 分阶段循环加载条件下温州饱和软黏土孔压和应变发展规律[J]. 岩土工程学报,2012,34(7): 1349-1354.WANG Jun, CAI Yuanqiang, GUO Lin, et al. Pore pressure and strain development of Wenzhou saturated soft soil under cyclic loading by stages[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(7): 1349-1354. 何绍衡,郑晴晴,夏唐代,等. 考虑时间间歇效应的地铁列车荷载下海相软土长期动力特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(2): 353-364.HE Shaoheng, ZHENG Qingqing, XIA Tangdai, et al. Experimental on long-term dynamic characteristics of marine soft soil under metro train load considering time intermittent effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(2): 353-364. 梅慧浩,冷伍明,聂如松,等. 重载铁路路基面动应力峰值随机分布特征研究[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(4): 1603-1613.MEI Huihao, LENG Wuming, NIE Rusong, et al. Random distribution characteristics of peak dynamic stress on subgrade surface of heavy haul railway[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(4): 1603-1613. CAI Y Q, CHEN J Y, CAI Z G, et al. Influence of grain gradation on permanent strain of unbound granular materials under low confining pressure and high-cycle loading[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 18(3): 04017156.1-04017156.10. LI D Q, HYSLIP J, SUSSMANN T, et al. Railway Geotechnics[M]. [S.l.]: CRC Press, 2016: 40. 聂如松,梅慧浩,冷伍明,等. 重载铁路过渡段路基动力响应特性试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2019,52(5): 101-115.NIE Rusong, MEI Huihao, LENG Wuming, et al. Experimental research on dynamic response characteristics of transition subgrade induced by heavy-haul trains[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2019, 52(5): 101-115. WERKMEISTER S. Permanent deformation behavior of unbound granular materials in pavement constructions[D]. Dresden: Dresden University, 2003. WERKMEISTER S, NUMRICH R, DAWSON A R, et al. Deformation behavior of granular materials under repeated dynamic load[J]. Environmental Geomechanics, 2002, 2: 1-9. PEREZ I, MEDINA L, ROMANA M G. Permanent deformation modals for a granular material used in road pavements[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2006, 20(9): 790-800. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.01.050 WERKMEISTER S, ANDREW R D, FROHMUT W. Permanent deformation behavior of granular materials and the shakedown concept[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2001, 1757(1): 75-81. doi: 10.3141/1757-09 WERKMEISTER S, DAWSON A R, WELLNER F. Pavement design model for unbound granular materials[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2004, 130(5): 665-674. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(2004)130:5(665) DAWSON A, MUNDY M, HUHTALA M. European research into granular material for pavement bases and subbases[C]//Transportation Research Record 1721, TRB. Washington D.C.: National Research Council, 2000, 1721(1): 91-99. -




 下载:
下载: