Review on Network Virtualization Simulation Software
-
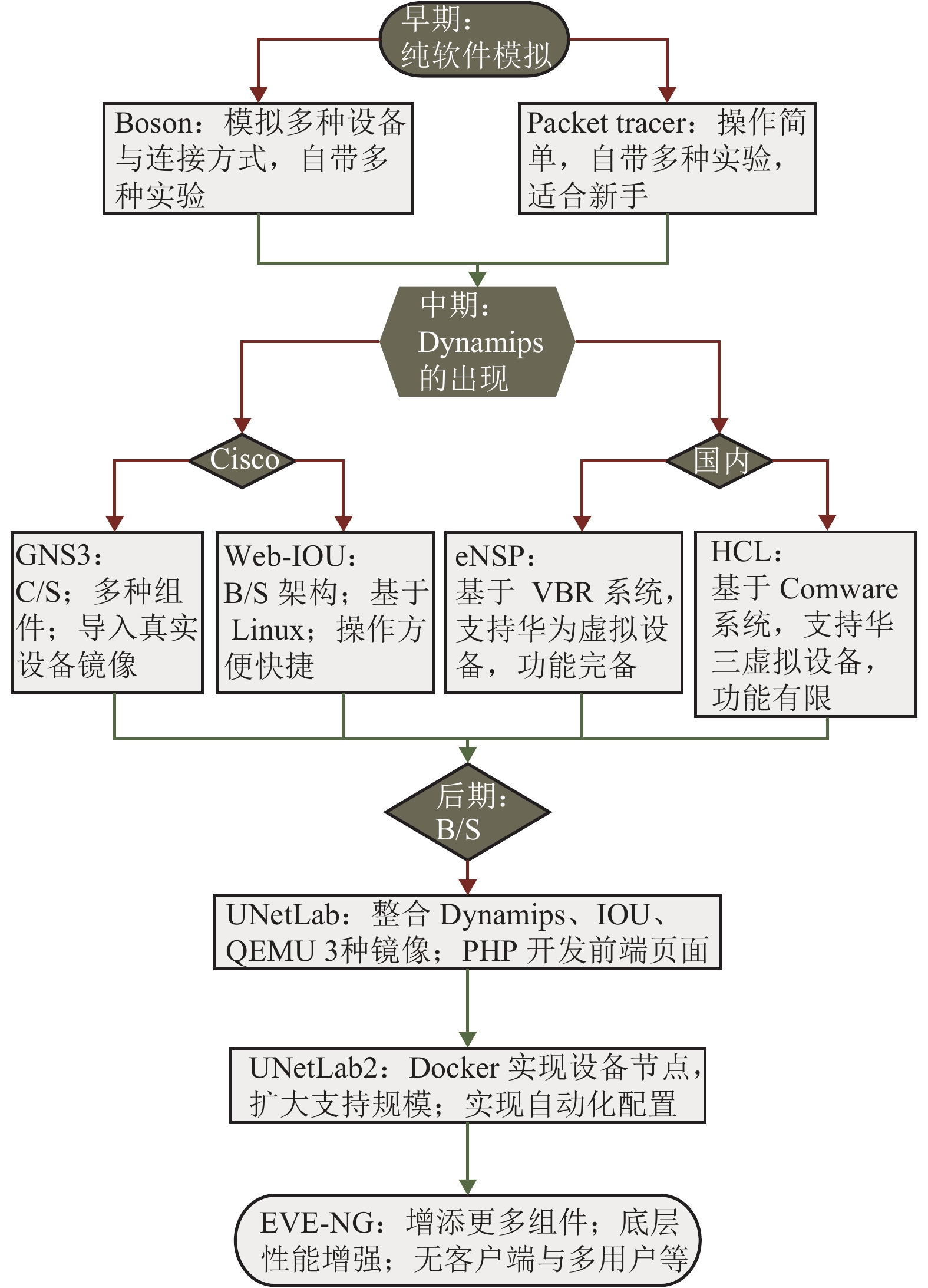
摘要: 网络虚拟化模拟软件是网络虚拟化和虚拟化软件两种概念的集合体,通过虚拟化技术在主机上实现了网络设备的虚拟化,帮助用户自定义地构建与配置网络拓扑,是网络工程师学习培训以及学术研究者进行实验验证的重要辅助工具. 为帮助读者针对需求选择合适的网络虚拟仿真软件,在归纳整理了有关研究文献的基础上,以软件架构与技术演化为脉络,系统地介绍了网络虚拟化软件的诞生和发展历程,以及国内外学者对网络虚拟化仿真软件的研究现状,介绍了不同时期具有代表性的网络虚拟化仿真软件,如GNS3 (graphical network simulator 3),EVE-NG (emulated virtual environment-next generation)等,阐述了这些软件的功能、性能、特点以及适用范围等. 最后展望了在技术与需求不断发展的未来,网络虚拟化模拟软件将具有兼容性、交互性和智能化的特点,并将在各个行业得到应用.Abstract: Network virtualization simulation software (NVSS) is an integration of network virtualization and virtualization software, serving as an important auxiliary tool for network engineers in learning and training, and researchers in experimental verification. It realizes the virtualization of network equipment on the host through virtualization technology, which helps to build and configure user-defined network topology. In order to help users choose the suitable NVSS as desired, this paper systematically introduces its birth and development as well as domestic and foreign research status, based on relevant research literature and the evolution of software architecture and technology. Furthermore, representatives of NVSS in different periods, such as graphical network simulator 3 (GNS3) and emulated virtual environment-next generation (EVE-NG), are listed with a focus on the functions, performances, properties, characteristics and application scope. Finally, the prospects of NVSS technology and demand are discussed. NVSS will be characterized by compatibility, interactivity and intelligence, and may be applied in various industries.
-
Key words:
- network virtualization /
- simulator /
- EVE-NG
-
表 1 GNS3与UNetLab比较
Table 1. Comparison of GNS3 and UNetLab
UNetLab GNS3 用户界面为 Web 形式 用户必须安装客户端 除 Wireshark,putty/SecureCRT 及 UltraVNC 外,无需安装任何程序 必须安装组件程序 不依赖操作系统类型 不同系统都有不同的问题 除厂商镜像外的全部内容都集成到一个虚拟机中 很多组件程序需要安装在 PC 上 QEMU 无 RAM 限制 Windows 中限制了 QEMU 内存大小为 2 G QEMU 网络无限制 QEMU 的网络数限制在 16 个 所有镜像都在一个 VM 中运行 IOU/IOL 需要另起一台虚拟机才能同 GNS3 搭配运行 -
ZHANG Hongjing, WANG Ying, QIU Xuesong, et al. Network operation simulation platform for network virtualization environment[C]//The 17th Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS 2015). Busan: IEEE, 2015: 400-403. IEEE. IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan area networks–bridges and bridged networks–amendment 23: application virtual local area network (VLAN) type, length, value (TLV): 978-0-7381-9565-0[S]. New York: IEEE, 2015 ABDULLAH A, SANDEEP P, HUANG Dijiang. A survey of mobile VPN technologies[C]//IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials. New York: IEEE, 2016: 1177-1196 SHALMALI S S, SHILPA S. S. Comparing OpenStack and VMware[C]//2014 International Conference on Advances in Electronics Computers and Communications. Bangalore: IEEE, 2014: 1-4 BABU K M, KIRAN P S. A secure virtualized cloud environment with pseudo-hypervisor IP based technology[C]//The 2nd International Conference on Next Generation Computing Technologies (NGCT 2016) . Dehradun: IEEE, 2016: 626-630 袁展. 基于Boson NetSim的小型网络虚拟实现[J]. 现代电子技术,2007,246(7): 89-91.YUAN Zhan. Implication of miniature virtual network based on Boson Netsim[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2007, 246(7): 89-91. VIJAYALAKSHMI M, DESAI P, RAIKAR M M. Packet tracer simulation tool as pedagogy to enhance learning of computer network concepts[C]//2016 IEEE 4th International Conference on MOOCs, Innovation and Technology in Education. Madurai: IEEE, 2016: 71-76 MOHTASIN R, PRASAD P W C, ABEER A, et al. Development of a virtualized networking lab using GNS3 and VMware workstation[C]//2016 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking. Chennai: IEEE, 2016: 603-609 FECIL'AK P, KLEINOVA K. Virtual laboratory environment based on Dynamips platform[C]//2012 IEEE 10th International Conference on Emerging Learning Technologies and Applications. Stara Lesna: IEEE, 2012: 105-109 DENG Xinxin, QIU Zhongpan, YANG Xiaofang. Research and design of network behavior management system based on B/S architecture[C]//The 6th International Conference on Computer Science & Education (ICCSE 2011). Singapore: IEEE, 2011: 129-132 GANNA V, OLENA S, KOSTIANTYN H, et al. Approaches and algorithms of virtual telecommunication networks analysis in UNetLab environment[C]//The Third International Scientific-Practical Conference Problems of Infocommunications Science and Technology. Kharkiv: IEEE, 2016: 181-184 BIAN Xiaoxiao. Implement a virtual development platform based on QEMU[C]//2017 International Conference on Green Informatics. Fuzhou: IEEE, 2017: 93-97 ALEXANDRE M S P M. Cisco firewalls[M]. Hoboken: Cisco Press, 2011: 47-49 DIRK M, LINUX J. Docker: lightweight Linux containers for consistent development and deployment[EB/OL]. (2014-03-01)[2019-03-16]. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2600239.2600241 PAVEL M, MARTIN S, JAN K, et al. Unleashing full potential of ansible framework: university labs administration[C]//The 22nd Conference of Open Innovations Association. Jyvaskyla: IEEE, 2018: 144-150 BUJOR A C, DOBRE R. KVM IO profiling[C]//IEEE 2013 RoEduNet International Conference 12th Edition: Networking in Education and Research. Iasi: IEEE, 2013: 1-6 SONONE S, SONI A, NATHAN S, et al. On exploiting page sharing in a virtualised environment —an empirical study of virtualization versus lightweight containers[C]//2015 IEEE 8th International Conference on Cloud Computing. New York: IEEE, 2015: 49-56 -




 下载:
下载:

