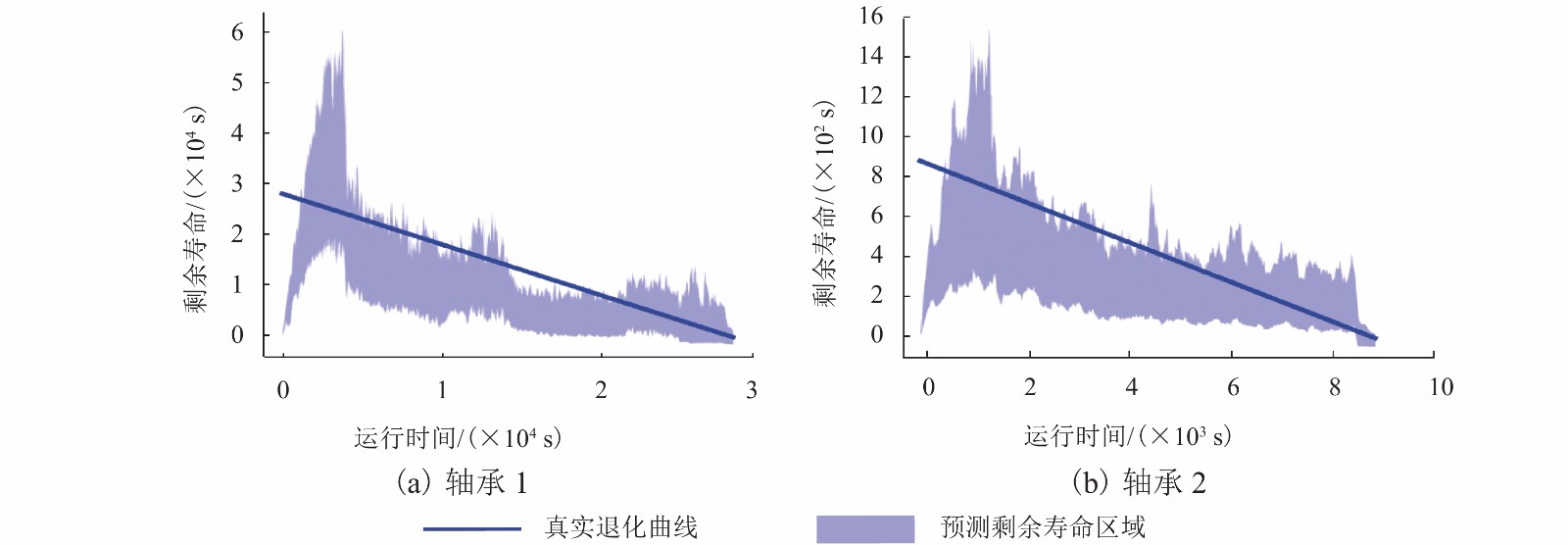
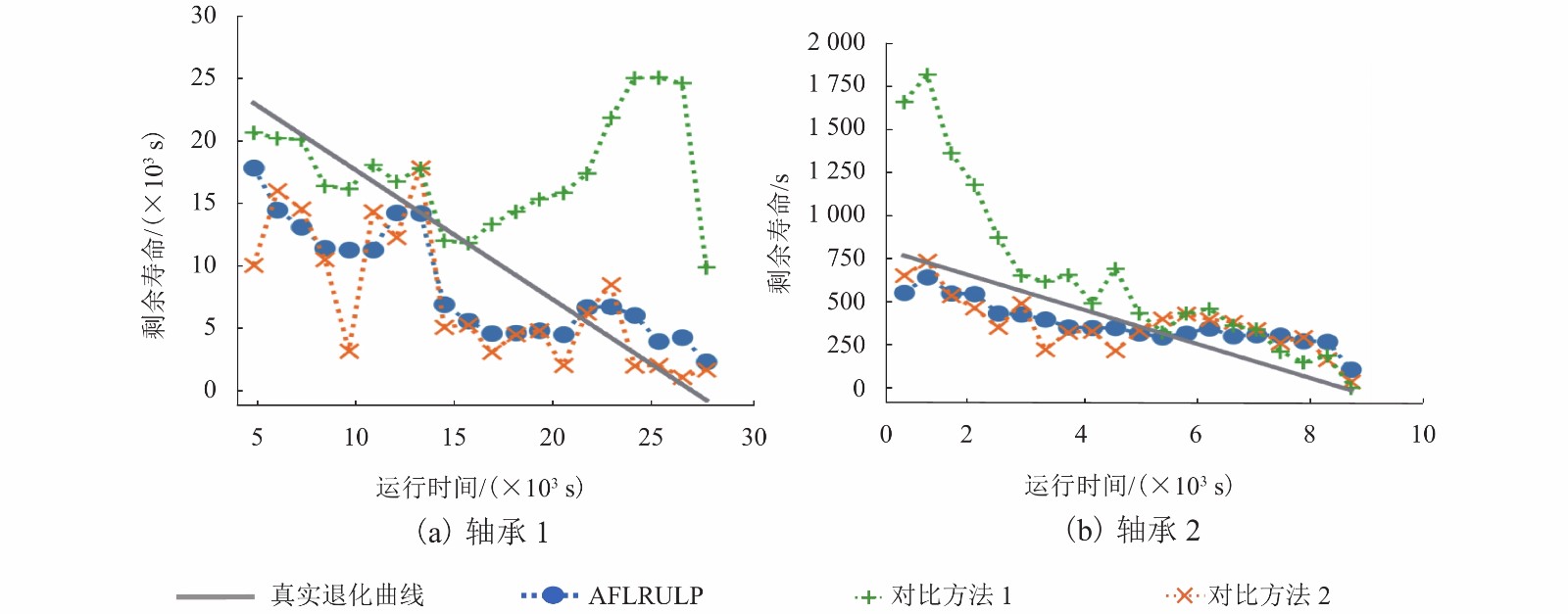
|
LEI Y, LI N, GUO L, et al. Machinery health prognostics:a systematic review from data acquisition to RUL prediction[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 104: 799-834. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.11.016
|
|
司小胜, 胡昌华. 数据驱动的设备剩余寿命预测理论及应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2016.
|
|
LEI Y. Intelligent fault diagnosis and remaining useful life prediction of rotating machinery[M]. Oxford: Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, 2016: 102-108.
|
|
陈雪峰, 訾艳阳. 智能运维与健康管理[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2018: 25-28.
|
|
GUO L, LEI Y, XING S, et al. Deep convolutional transfer learning network:a new method for intelligent fault diagnosis of machines with unlabeled data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(9): 7316-7325. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2877090
|
|
GUO L, LEI Y, LI N, et al. Machinery health indicator construction based on convolutional neural networks considering trend burr[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 292: 142-150. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.02.083
|
|
裴洪,胡昌华,司小胜,等. 基于机器学习的设备剩余寿命预测方法综述[J]. 机械工程学报,2019,55(8): 1-8. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.08.001FEI Hong, HU Changhua, SI Xiaosheng, el al. Review of machine learning based remaining useful life prediction methods for equipment[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(8): 1-8. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.08.001
|
|
XIN W L, ZHEN H W, YU D F. Remaining life predictions of fan based on time series analysis and BP neural networks[C]//2016 IEEE Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2016: 607-611.
|
|
HUANG C G, HUANG H Z, PENG W W, et al. Improved trajectory similarity-based approach for turbofan engine prognostics[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2019, 33(10): 1-14.
|
|
WANG B, LEI Y, LI N, et al. A hybrid prognostics approach for estimating remaining useful Life of rolling element bearings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2020, 69(1): 401-402. doi: 10.1109/TR.2018.2882682
|
|
BYINGTON M. WATSON D E. Data-driven neural network methodology to remaining life predictions for aircraft actuator components[C]//2004 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2004: 3581-3589.
|
|
HUANG C G, HUANG H Z, LI Y F. A bidirectional LSTM prognostics method under multiple operational conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(11): 8792-8802. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2891463
|
|
GEBRAEEL N, LAWLEY M, LIU R. Residual life predictions from vibration-based degradation signals:a neural network approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on industrial electronics, 2004, 51(3): 694-700. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2004.824875
|
|
高宏力,李登万,许明恒. 基于人工智能的丝杠寿命预测技术[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2010,45(5): 685-691.GAO Hongli, LI Dengwan, XU Mingheng. Intelligent monitoring system for screw life evaluation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010, 45(5): 685-691.
|
|
TIAN Z. An artificial neural network method for remaining useful life prediction of equipment subject to condition monitoring[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2012, 23(2): 227-237. doi: 10.1007/s10845-009-0356-9
|
|
GUO L, LI N, JIA F, et al. A recurrent neural network based health indicator for remaining useful life prediction of bearings[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 240: 98-109. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.02.045
|
|
HINTON G E, SALAKHUTDINOV R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks[J]. Science, 2006, 313(5786): 504-507. doi: 10.1126/science.1127647
|
|
HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, ET AL. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. [S.l.]: IEEE Computer Society, 2016: 770-778.
|
|
HINTON G, DENG L, YU D, et al. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2012, 29(6): 82. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2012.2205597
|
|
YAN H, WAN J, ZHANG C, et al. Industrial big data analytics for prediction of remaining useful life based on deep learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 17190-17197. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2809681
|
|
REN L, SUN Y, WANG H, et al. Prediction of bearing remaining useful life with deep convolution neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 13041-13049. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2804930
|




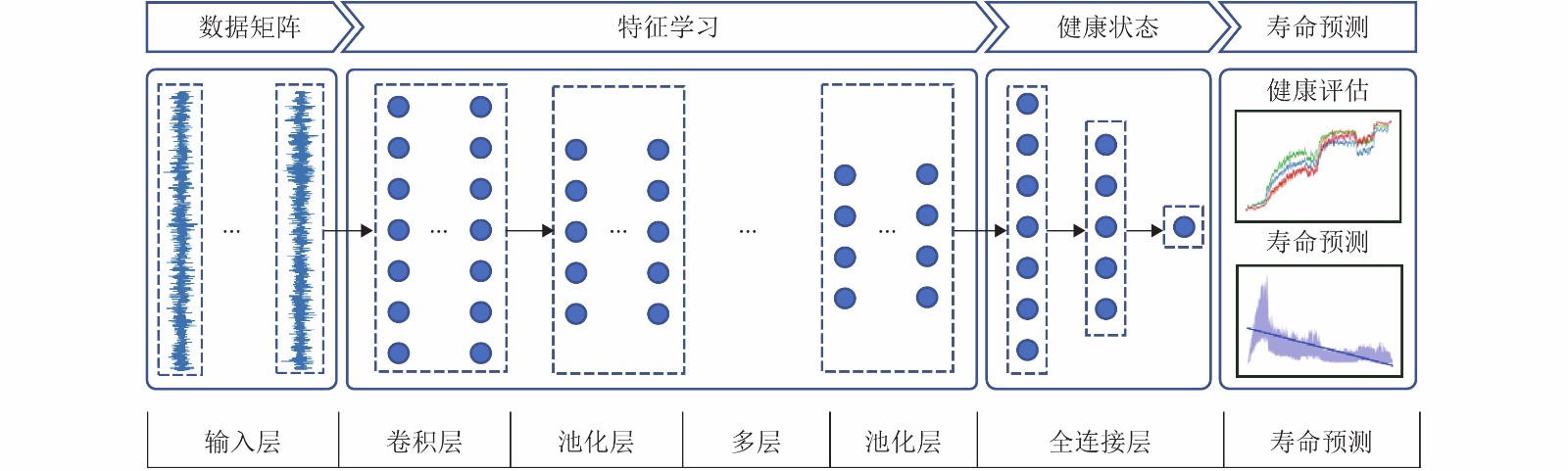
 下载:
下载: