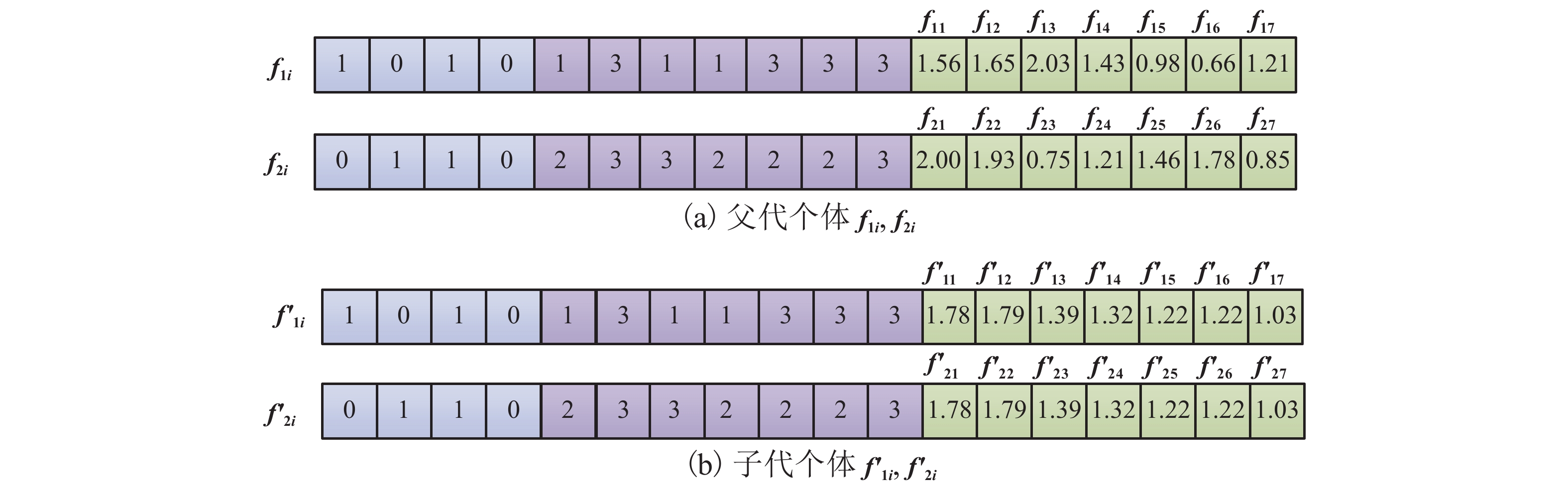
LIRP Joint Collaborative Optimization under Stochastic Demand and Time Constraints
-
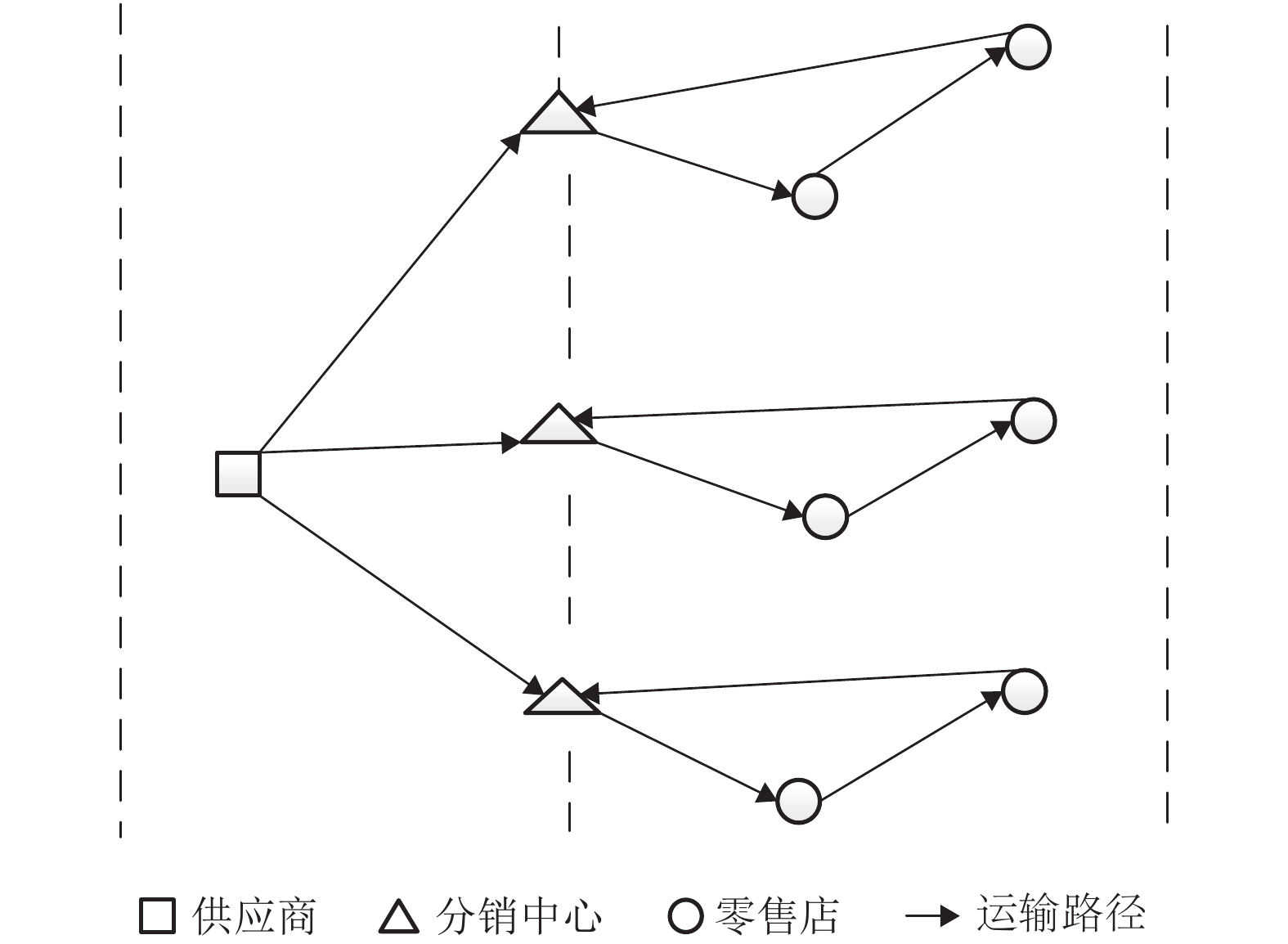
摘要: 针对多节点多层次多功能的供应链管理中整体效益亟待提高的问题,结合某连锁超市的单一供应商、多分销中心、多零售店所构成二级分销网络,建立以系统总成本和供货时间为目标的多目标选址-库存-路径问题(location-inventory-routing problem,LIRP)集成规划模型. 利用线性加权法将其转化为单目标规划模型,提出遗传算法和节约里程法相结合的两阶段启发式算法并求解模型,第1阶段用遗传算法求解选址-库存问题,第2阶段用节约里程算法求解车辆路径规划问题. 并结合某连锁超市实例,对不同总成本权重下的不同决策方案的分销网络进行LIRP集成优化,优化后的系统方案比原文献的总里程减少了3 606.9 km,系统总成本减小了6 526.2 元,缺货成本降低了124.6 元,只有19.7元,验证了模型和算法的有效性.Abstract: Aiming at improving the overall efficiency of the multi-node, multi-level, and multi-functional supply chain management, a secondary distribution network composed of a single supplier, multiple distribution centers, and multiple retail stores for a chain supermarket wasexplored to establish the multi-objective location-inventory-routing problem (LIRP) integrated planning model with the objectives of the total system cost and supply time. The linear weighting method was used to transform the model into the single-objective programming one. A two-stage heuristic algorithm combining genetic algorithm and mileage saving method was proposed to solve the model. In the first phase, the location-inventory problem was solved by the genetic algorithm, and in the second phase, vehicle routing problem was solved by the mileage saving method. A chain supermarket example was used for the LIRP integration optimization of the distribution network with different decision schemes and total cost weights. Compared the results from a reference, the optimized system scheme reduced the total mileage by 3 606.9 km, the total system cost by 6 526.2 yuan, and the cost of back orders by 124.6 yuan, being 19.7 yuan, which verifies the model and algorithm.
-
表 1 变量符号表
Table 1. Parametric symbols
参数 含义 参数 含义 参数 含义 $ K $ 车辆数量集合(k∈K, k=1,2,…,L,
L 为最大车辆数)$ {\zeta }_{i} $ 零售店 i 的惩罚成本 $ {O}_{j} $ 分销中心 j 每次的订货成本 $ c $ 物流节点间单位运费 $ {k}_{i} $ 零售店 i 的库存安全系数 $ {k}_{j} $ 分销中心 j 的库存安全系数 ${d_{ij}}$ 零售店 i 和分销中心 j 之间的运距 $ {S}_{i} $ 零售店 i 的最大库存量 $ {S}\!_{j} $ 分销中心 j 的最大库存水平 $ \alpha $ 系统总成本的权重系数 $ {T}_{i} $ 零售店 i 的库存周转时间 $ {T}_{j} $ 分销中心 j 的库存周转时间 $ {c}_{k} $ 使用 k 次车辆的固定成本 $ {d}_{sj} $ 供应商 s 和分销中心 j 间的运距 $ {Q}_{j} $ 分销中心 j 的订货量 $ {Q}_{k} $ 车辆的最大容量 $ {W}_{i} $ 零售店 i 无缺货量表示的服务水平 $ {I}_{j} $ 分销中心 j 平均库存 $ {Q}_{i} $ 零售店 i 的订货量 $ {E}_{i} $ 零售店 i 的平均缺货量 $ {F}_{j} $ 分销中心 j 的固定费用 V I 和 J 的集合 $ {\lambda }_{i} $ 零售店 i 的安全库存 $ {\gamma }_{j} $ 分销中心 j 的安全库存 I 零售店数量集合( i ∈I, i=1,2,…,m,m 为最大零售店数) $ J $ 候选分销中心数量集合( j ∈J, j=1,2,…,n,n 为最大分销中心数) 0-1 决策变量 $ {M}_{i} $ 零售店 i 的目标服务水平 $ {L}_{j} $ 分销中心 j 订货的提前期 $ {X}_{ijk} $ 车辆 k 从零售店 $ {i} $ 到分销中心 j $ {\mu }_{i} $ 零售店 i 每天的需求均值 $ {\mu }_{j} $ 分销中心 j 每天的需求均值 $ {Y}_{j} $ 分销中心 j 是否被选(Yj=1 选中,Yj=0 未选中) $ {\sigma }_{i}^{2} $ 零售店 i 每天的需求方差 $ {\mathrm{\sigma }}_{j}^{2} $ 分销中心 j 每天的需求方差 $ {Z}_{ij} $ 分销中心 j 服务零售店 i $ {B}_{i} $ 零售店 i 单位持有成本 $ {b}_{j} $ 分销中心 j 单位库存持有成本 $ {f}_{kj} $ 车辆 k 分配到分销中心 j 表 2 算法所用参数表
Table 2. Parameters in the algorithm
参数 说明 参数 说明 参数 赋值 说明 $ \mathrm{G}({x}) $ 适应度函数 $ {P}_{{\rm{c}}} $ 交叉概率函数 $ {e}_{1} $、${e}_{3}$ 1 $ {e}_{l}\in \left(0, 1\right), $ $ {G}_{\max} $ 最大适应值 $ {P}_{{\rm{m}}} $ 变异概率函数 $ {e}_{2} $、${e}_{4}$ 0.5 $ {G}_{{\rm{avg}}} $ 平均适应值 $ {C}_{{\rm{max}}} $ 每代较大的数 $ p $ 0.1 惩罚系数 $ {G}' $ 两交叉个体较大适值 $ \beta $ [0, 1]间的随机数 $ r $ 3 $ r\in \left(\mathrm{2,4}\right) $ $ {G}'' $ 变异个体适值 $ {\varepsilon } $ [0, 1]间的随机数 $ {T} $ 150 进化的最大代数 表 3 分销中心相关参数
Table 3. Relevant parameters of distribution center
参数 $ \mathrm{D}1 $ $ \mathrm{D}2 $ $ \mathrm{D}3 $ $ \mathrm{D}4 $ $ \mathrm{D}5 $ $ \mathrm{D}6 $ $ {F}_{j} /$元 5 000 4 000 4 000 6 000 5 000 4 000 $ {b}_{j} /$元 3.5 5.6 4.0 4.3 4.0 3.8 $ {O}_{j} /$元 100 100 100 120 120 100 $ {d}_{sj}/ $km 36 38 68 59 56 27 $ {L}_{j}/ $d 2 2 2 3 2 3 横坐标 524.7 532.2 506.3 518.7 525.0 521.2 纵坐标 39.7 41.0 70.2 62.4 59.5 31.1 表 4 不同
$ {\alpha } $ 下的方案Table 4. Schemes under different
$ {\alpha } $ $ {\alpha } $ 分销中心 TC/元 TT/d h 0 1、2 23 130 29.94 0.99 0.2 1、3、5、6 34 328 30.61 1.01 0.4 2、3、6 27 184 30.30 1.00 0.6 3、5、6 28 009 30.28 1.02 0.8 2、3、6 27 187 30.24 1.00 1.0 2、6 22 398 30.00 1.00 表 5 优化路径规划结果
Table 5. Results of optimal path planning
分销
中心路径
编号路径节点 载运
量满载
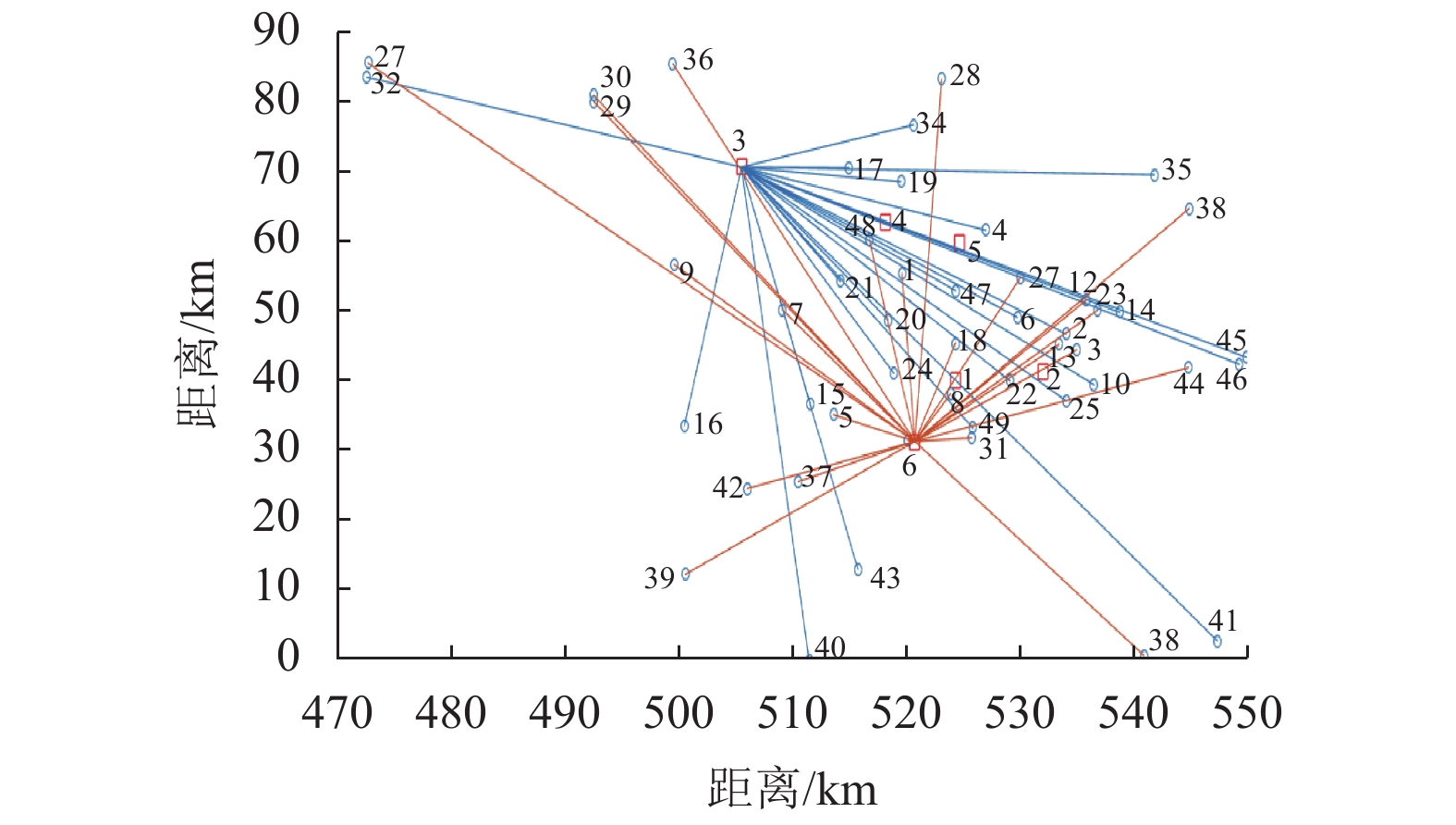
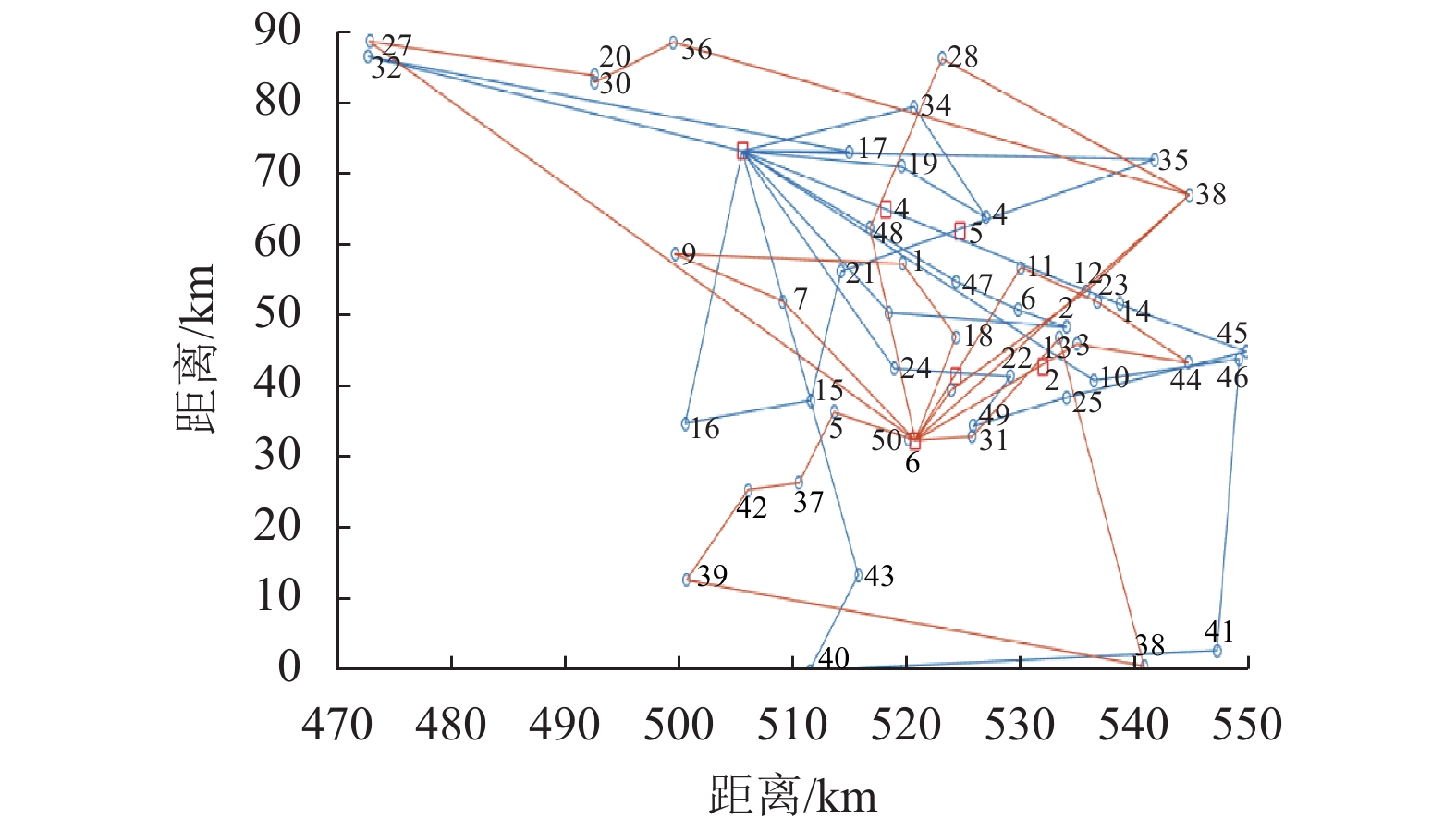
率/%D2 1 D2—41—38—43—16—D2 173 96 2 D2—34—28—30—20—39—D2 180 100 3 D2—11—4—35—33—D2 171 95 4 D2—8—49—50—42—
15—48—D2172 96 5 D2—14—47—1—18—22—D2 171 95 6 D2—25—44—2—D2 118 66 $ \mathrm{D}6 $ 1 D6—32—27—29—36—17—D6 171 95 2 D6—46—45—26—12—13—D6 172 96 3 D6—21—19—9—7—D6 164 91 4 D6—6—23—3—10—D6 173 96 5 D6—31—40—37—5—D6 95 53 6 D6—24—D6 41 23 表 6 结果对比(α=1)
Table 6. Result comparative (α=1)
模型 分销中
心数/个配送
车/辆总里
程/km运输总
成本/元零售店总持有成
本/元零售店缺货成本/元 分销中心固定费
用/元订货成
本/元分销中心
成本/元库存总
成本/元系统总
成本/元本文 2 12 1086.7 7509.4 4774.9 19.7 8000.0 918.9 1108.0 5902.5 22398.0 文献[14] 3 12 609.3 5643.0 4912.5 195.2 12000.0 1041.0 2926.7 7839.2 26144.7 原文 0 50 4693.6 13693.6 5292.7 144.3 0 5000.0 0 5292.7 28924.2 -
LIU S C, LEE S B. A two-phase heuristic method for the multi-depot location routing problem taking inventory control decisions into consideration[J]. International Journal Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2003, 22(11/12): 941-950. LIU S C, LIN C C. A heuristic method for the combined location routing and inventory problem[J]. International Journal Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2005, 26(4): 372-381. doi: 10.1007/s00170-003-2005-3 LIU Bailing, CHEN Hui, LI Yanhui, et al. A pseudo-parallel genetic algorithm integrating simulated annealing for stochastic LIRP with consideration of returns in e-commerce[J]. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2015, 2015: 586581.1-586581.15. YUCHI Q, HE Zhengwen, YANG Zhen, et al. A location-inventory-routing problem in forward and reverse logistics network design[J]. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2016, 2016: 3475369.1-3475369.18. ATIYE G, MOHAMMAD R A J. A hybrid imperialist competitive simulated annealing algorithm for a multi-source multi-product location-routing-inventory problem[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2016, 101: 116-127. FARNAZ R, MIR M M, ALI B A. Bi-objective reliable location-inventory-routing problem with partial backorder-ing under disruption risks:a modified ASOSA approach[J]. Applied Soft Comput-ing, 2017, 59: 622-643. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2017.06.036 FARHAD H, EHSAN A, SEYED J S. A location-inventory-routing optimization model for cost effective microalgae biofuel distribution system:a case study in Iran[J]. Energy Strategy Reviews, 2018, 22: 82-93. doi: 10.1016/j.esr.2018.08.006 NOVA I S, SENATOR N B, SUPRAYOGI, et al. A heuristic method for location-inventory-routing problem in a three-echelon supply chain system[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2019, 127: 875-886. ZHENG Xiaojin, YIN Meixia, ZHANG Yanxia. Integrated optimization of location,inventory and routing in supply chain network design[J]. Transpor- tation Research Part B, 2019, 121: 1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2019.01.003 崔广彬,李一军. 模糊需求下物流系统 CLRIP 问题研究[J]. 控制与决策,2007,22(9): 1001-1016.CUI Guangbin, LI Yijun. Research on CLRIP of logistics system under fuzzy demand[J]. Control and Decision, 2007, 22(9): 1001-1016. 杜丽敬,李延晖. 选址-库存-路径问题模型及其集成优化算法[J]. 运筹与管理,2014,23(4): 70-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3221.2014.04.010DU Lijing, LI Yanhui. Integrated models and approach for location inventory and routing problem[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2014, 23(4): 70-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3221.2014.04.010 吴迪,王诺,宋南奇,等. 边远群岛物流体系的选址-库存-路径优化[J]. 系统工程理论与实践,2016,36(12): 3175-3187. doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2016)12-3175-13WU Di, WANG Nuo, SONG Nanqi, et al. Location-inventory-path optimization of logistics system in remote islands[J]. System Engineering Theory and Practice, 2016, 36(12): 3175-3187. doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2016)12-3175-13 张得志,潘立红,李双艳. 考虑供应商选择的选址-库存-路径的联合优化[J]. 计算机应用研究,2019,36(8): 2338-2341.ZHANG Dezhi, PAN Lihong, LI Shuangyan. Joint optimization of location-inventory-path considering supplier selection[J]. Computer Application Research, 2019, 36(8): 2338-2341. 汪伟. J公司选址-库存-路径集成规划问题研究[D]. 长沙: 东南大学, 2018. -





 下载:
下载: