Sensitivity Analysis for Transit Network with Distance Effect
-
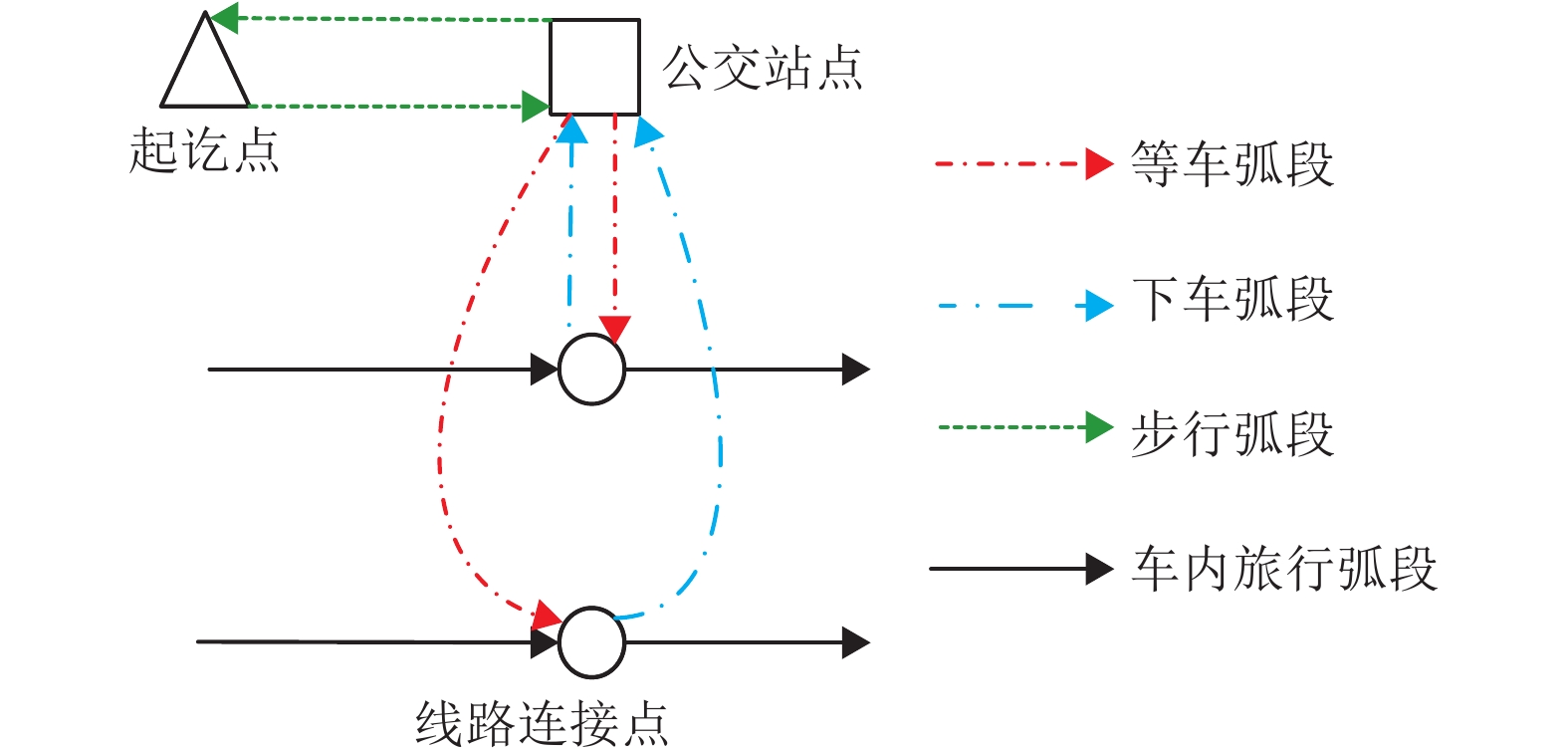
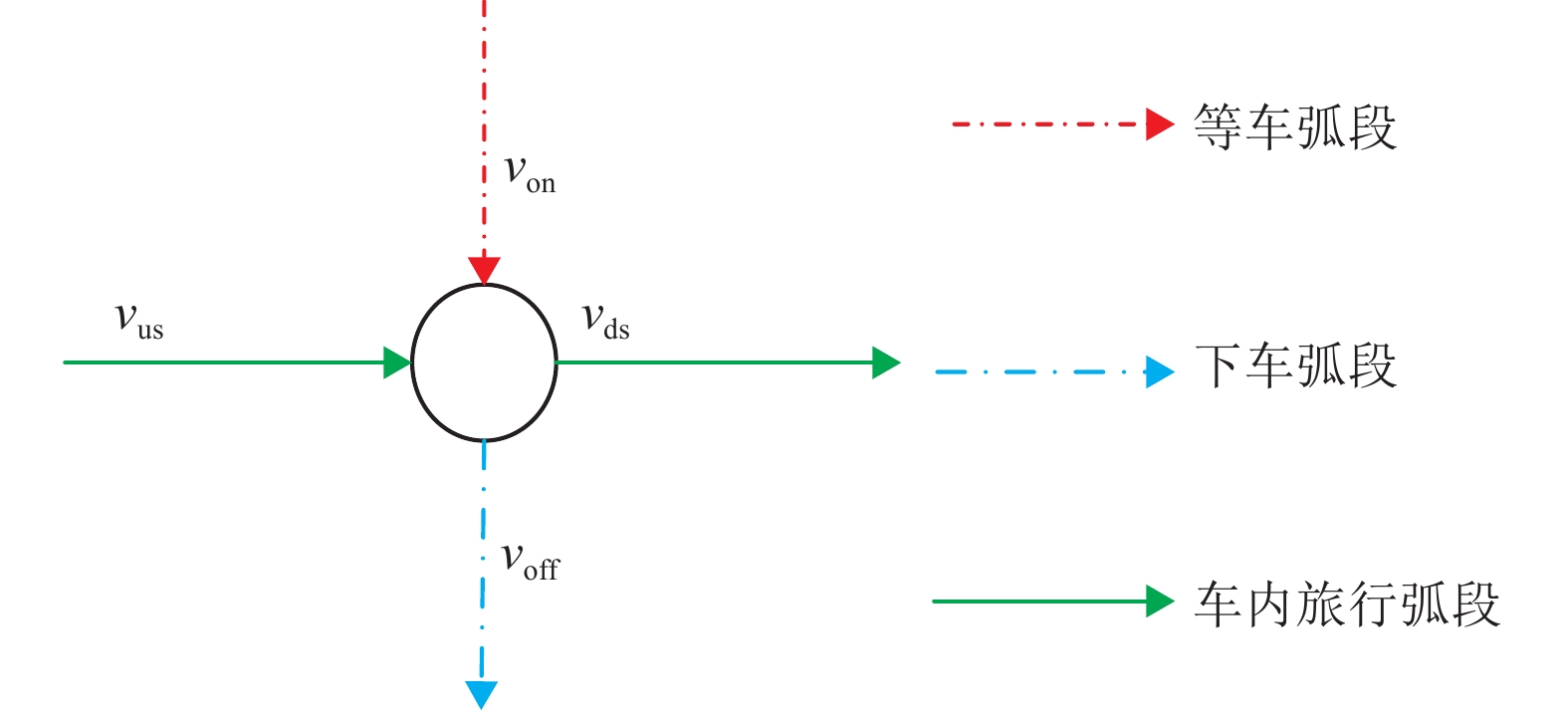
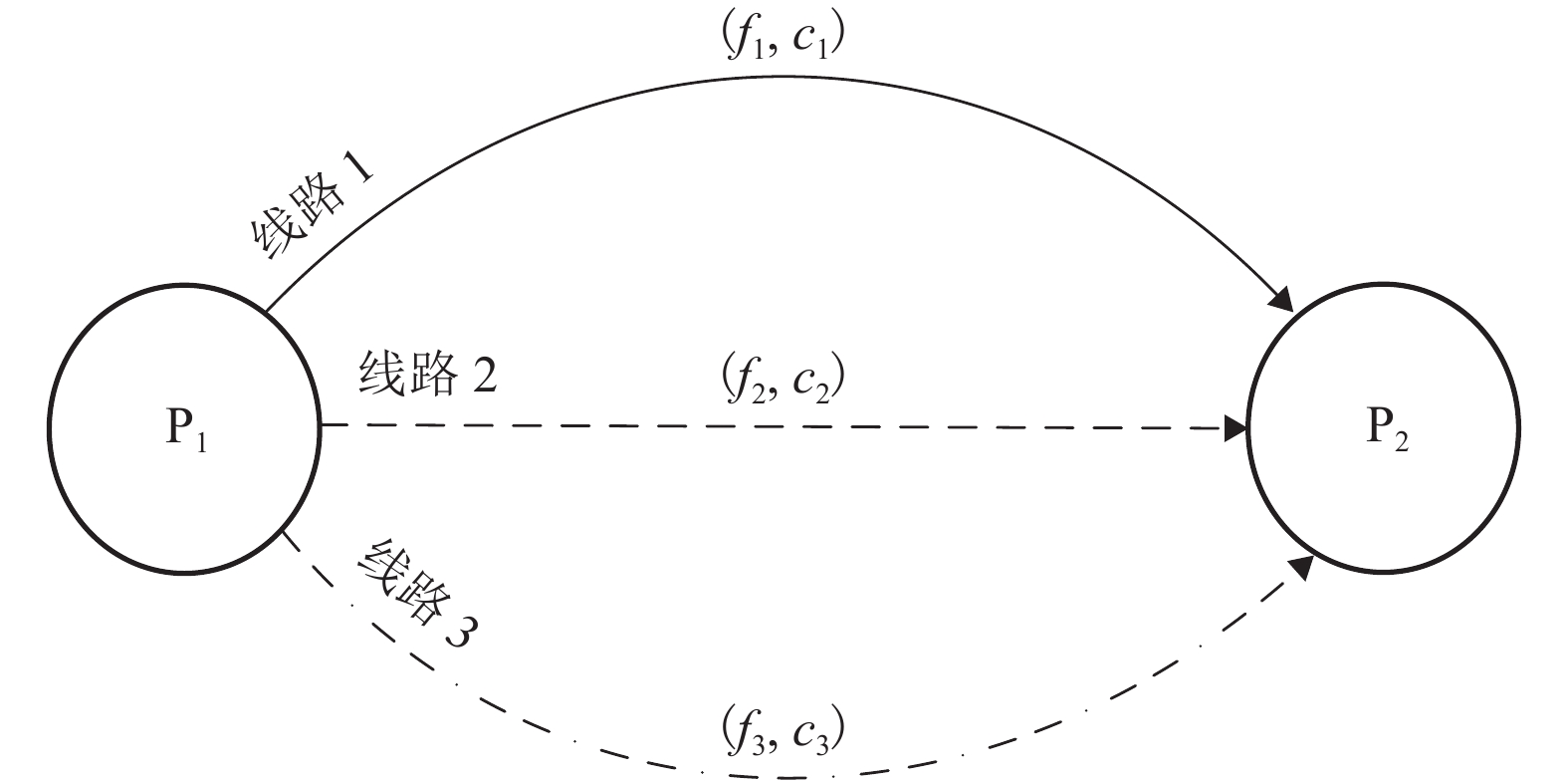
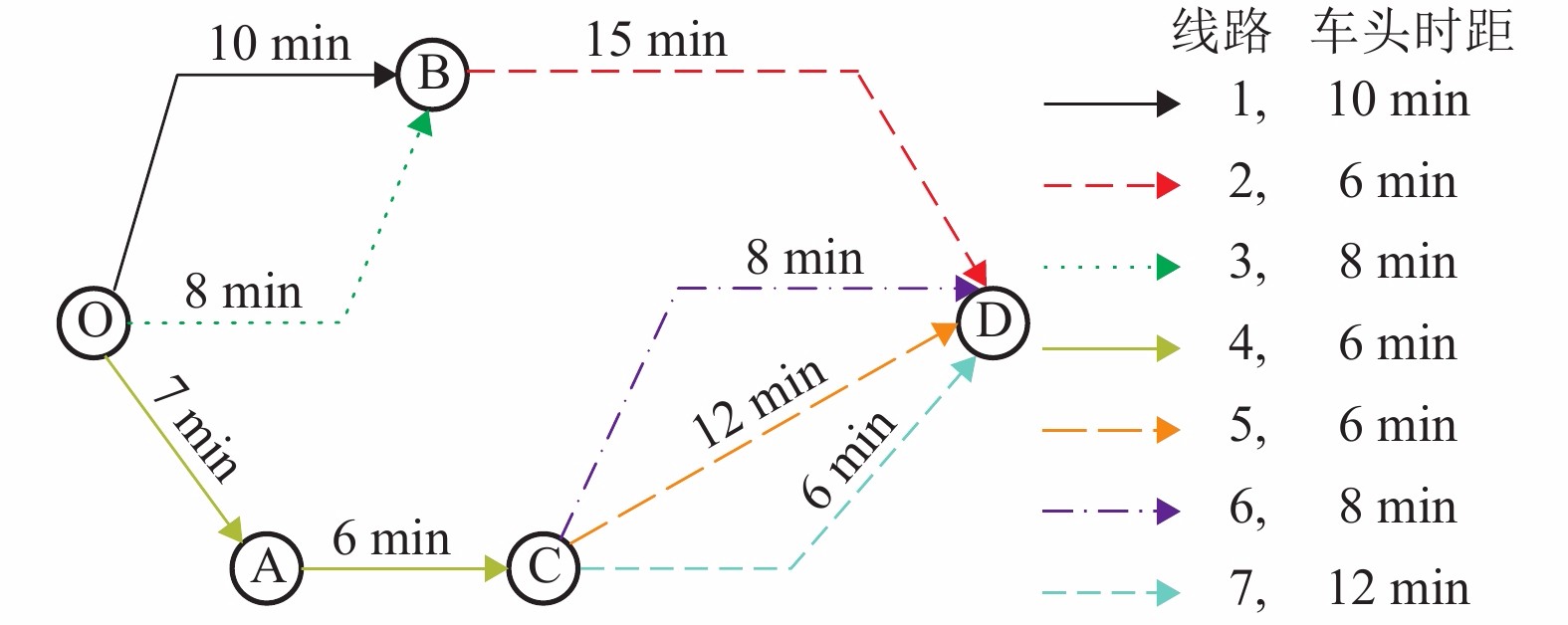
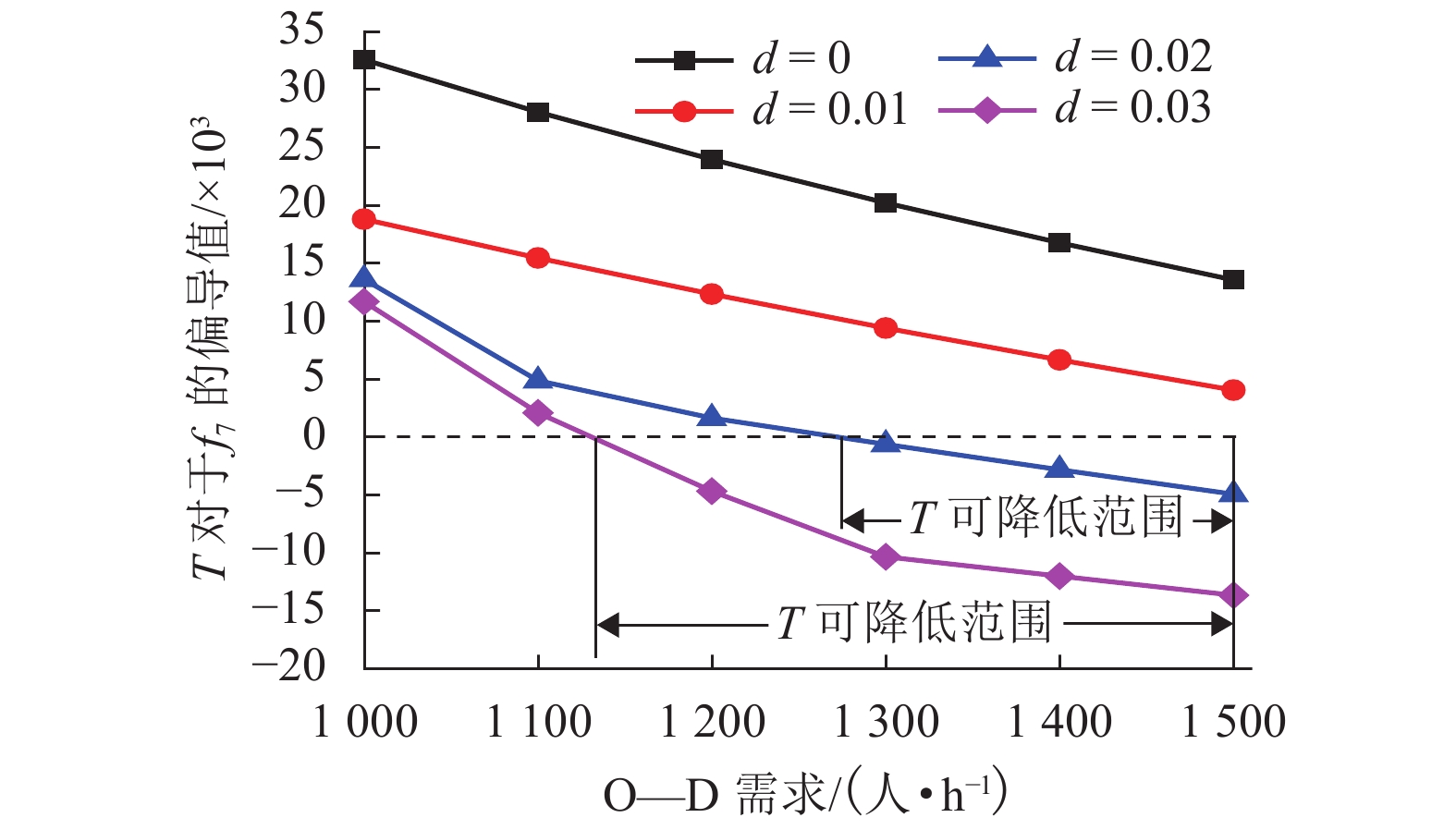
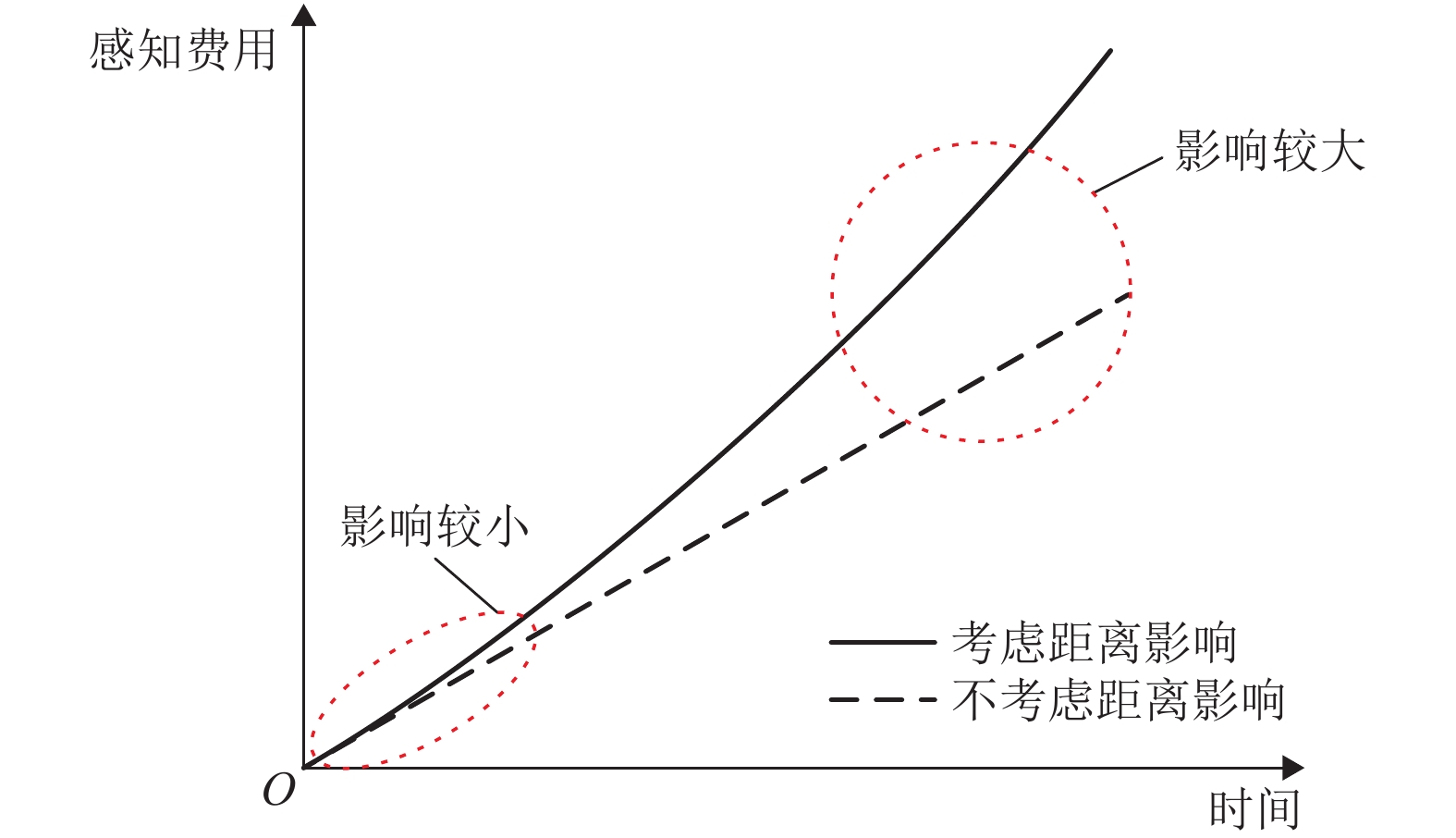
摘要: 为更加准确地分析公交网络的性能状况,考虑了距离对于出行者感知费用的放大作用,提出了一种广义出行费用函数对公交网络敏感度进行了分析. 首先,分析了距离的影响作用,建立了一个公交网络模型,并通过超路径理论解释了公交共线问题和乘客的选择行为. 其次,在均衡配流的公交网络基础上,根据变分不等式的扰动问题,构建了考虑距离因素的公交网络敏感度分析方法. 最后,以实际算例分析了公交网络在受到不同因素的影响时各个弧段以及网络性能的变化情况,并着重分析了距离因素的影响作用. 研究结果表明:需求从0增加到900人/h,考虑距离影响下的最优出行策略从原来的单一超路径变为多条超路径;在模型关键参数的识别中发现,距离因素是一个较为敏感的参数,需要更加准确地进行标定;在相同的需求水平下,距离参数取值从0变化至0.03时,总旅行费用关于公交服务频率的偏导数值不断减小,为寻找总旅行费用可降低区域提供依据.Abstract: In order to accurately analyze the performance of transit network, the amplification effect of distance on the travelers’ perceived travel cost is considered, and a generalized travel cost function is proposed in the sensitivity analysis of transit network. Firstly, as to the influence of distance effect, a transit network model is established. Then the problem of common bus line and the passengers' choice behaviors are coped with the hyperpath theory. Secondly, based on the equilibrium assignment of transit network, a sensitivity analysis method for transit network with distance effect is constructed in the perturbation problem of variational inequality. Finally, an example is used to analyze the changes in each arc and network performance when the transit network is affected by different factors, especially the distance. The results show that along with the demand increasing from 0 to 900 people per hour, the optimal travel strategy under the influence of distance is changed from the original single hyperpath to the multiple hyperpaths. In the identification of critical parameters, the distance factor is a sensitive parameter, which need more accurate calibration in practice. At the same level of demand, when the distance parameter changes from 0 to 0.03, the derivatives of the total travel cost to bus service frequency noticeably declines, which can be utilized for finding the region such that the total travel time is likely to reduce.
-
Key words:
- transit assignment /
- distance /
- sensitivity analysis /
- variational inequality
-
表 1 参数取值
Table 1. Parameter values
参数 取值 参数 取值 参数 取值 α1 1.0 β2 0.2 α4 1.1 β1 1.0 γ1 1.2 d 0.01 α2 1.0 ρ 2.0 m 1.0 表 2 T对于不同参数偏导数值
Table 2. Derivatives of T with respect to different parameters
ρ Cbus d α1 3556.05438 −335.2526 32169.70373 25465.71138 表 3 有无距离因素对比分析
Table 3. Comparative analysis with and without distance factors
变量 x 不考虑距离 (d = 0) 考虑距离 (d = 0.02) $\partial x/\partial {f_5} $ $\partial x/\partial {f_6} $ $\partial x/\partial {f_7} $ $\partial x/\partial {f_5} $ $\partial x/\partial {f_6} $ $\partial x/\partial {f_7} $ v5 3 345 −2 354 −9 032 2 732 −2 250 −9 046 v6 −1 005 707 2 713 −821 676 2 717 v7 −2 340 1 647 6 319 −1 911 1 575 6 329 T −28 775 −32 210 13 548 −19 855 −38 362 −4 951 -
程琳,李向阳,徐婷. 基于网络分解与叠加的用户均衡网络敏感度分析[J]. 系统工程理论与实践,2014,34(2): 502-508. doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2014)2-502CHEN Lin, LI Xiangyang, XU Ting. Sensitivity analysis of user equilibrium network based on network decomposition and composition[J]. Systems Engineering:Theory & Practice, 2014, 34(2): 502-508. doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2014)2-502 程琳,纪魁,蒲自源,等. 路段型随机用户均衡敏感度分析[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版),2013,43(1): 221-225.CHEN Lin, JI Kui, PU Ziyuan, et al. Sensitivity analysis for link-based stochastic user equilibrium network flows[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 43(1): 221-225. YANG H. Sensitivity analysis for queuing equilibrium network flow and its application to traffic control[J]. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 1995, 22(4): 247-258. YANG H. Sensitivity analysis for the elastic-demand network equilibrium problem with applications[J]. Transportation Research Part B:Methodological, 1997, 31(1): 55-70. doi: 10.1016/S0191-2615(96)00015-X 周豪,四兵锋,汪勤政. 考虑距离因素的多方式交通超级网络均衡配流模型及算法[J]. 山东科学,2018,31(3): 66-75. doi: 10.3976/j.issn.1002-4026.2018.03.011ZHOU Hao, SI Bingfeng, WANG Qinzheng. Equilibrium assignment model and algorithm for multi-modal traffic super network considering distance factor[J]. Shandong Science, 2018, 31(3): 66-75. doi: 10.3976/j.issn.1002-4026.2018.03.011 LEE Y, VUCHIC V R. Transit network design with variable demand[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2005, 131(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(2005)131:1(1) GAO Z, SUN H, SHAN L L. A continuous equilibrium network design model and algorithm for transit systems[J]. Transportation Research Part B:Methodological, 2004, 38(3): 235-250. doi: 10.1016/S0191-2615(03)00011-0 JIANG Y, SZETO W Y. Reliability-based stochastic transit assignment:formulations and capacity paradox[J]. Transportation Research Part B:Methodological, 2016, 93: 181-206. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2016.06.008 CEA J D, FERNÁNDEZ E. Transit assignment for congested public transport systems:an equilibrium model[J]. Transportation Science, 1993, 27(2): 133-147. doi: 10.1287/trsc.27.2.133 WU J H, FLORIAN M, MARCOTTE P. Transit equilibrium assignment: a model and solution algorithms[J]. Transportation Science, 1994, 28(3): 193-203. SPIESS H, FLORIAN M. Optimal strategies:a new assignment model for transit networks[J]. Transportation Research Part B:Methodological, 1989, 23(2): 83-102. doi: 10.1016/0191-2615(89)90034-9 CHRIQUI C, ROBILLARD P. Common bus lines[J]. Transportation Science, 1975, 9(2): 115-121. doi: 10.1287/trsc.9.2.115 王殿海,熊满初,章立辉,等. 基于舒适度的公交线网优化方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(4): 789-795. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.04.018WANG Dianhai, XIONG Manchu, ZHANG Lihui, et al. Optimization of public traffic network based on comfort improvement[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(4): 789-795. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.04.018 NGUYEN S, PALLOTTINO S. Equilibrium traffic assignment for large scale transit networks[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 1988, 37(2): 176-186 TOBIN R L, FRIESZ T L. Sensitivity analysis for equilibrium network flow[J]. Transportation Science, 1988, 22(4): 242-250. doi: 10.1287/trsc.22.4.242 杜牧青. 道路网络容量模型及算法[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2014. 黄海军. 城市交通网络平衡分析理论与实践[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 1994: 107-120. DU M, CHENG L, RAKHA H. Sensitivity analysis of combined distribution–assignment model with applications[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2012, 2284(1): 10-20 祁宏生,王殿海,徐程. 基于合理路径的拥挤路网交通状态分析方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2011,46(1): 175-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2011.01.028QI Hongsheng, WANG Dianhai, XU Cheng. Method of congested traffic network state analysis based on reasonable routes[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2011, 46(1): 175-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2011.01.028 陈学武, 李海波, 候现耀. 城市公交IC卡数据分析方法及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014: 110-112. -




 下载:
下载: