Load Forecasting and Transformer Capacity Optimization for Newly-built Traction Substation
-
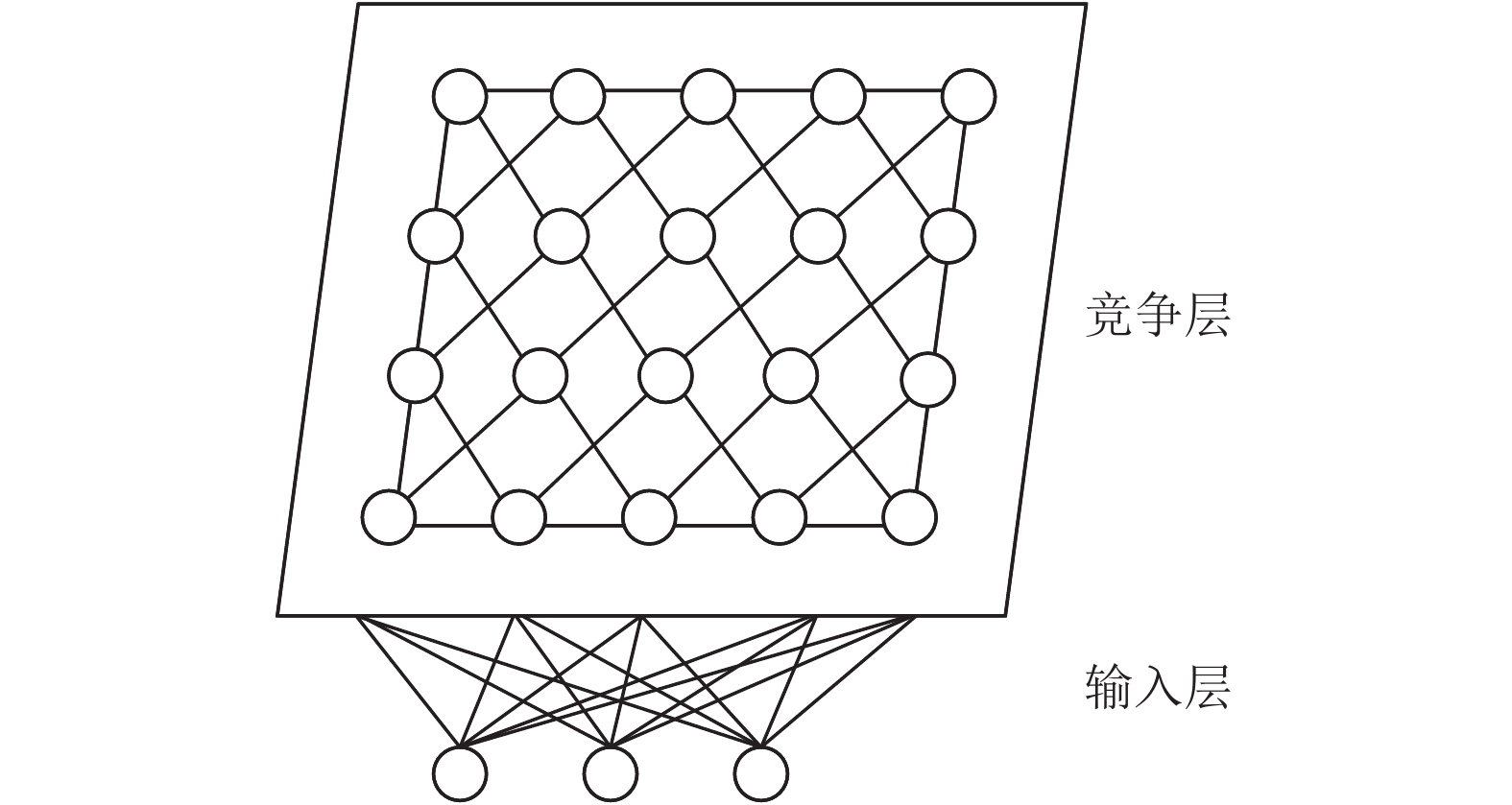
摘要: 为了获得新建牵引变电所的负荷情况并校验优化所内牵引变压器的配置容量,将高斯混合模型用于牵引变电所实测数据聚类,然后引入神经网络对新建牵引负荷进行匹配分类. 依据聚类和分类结果,结合概率密度及蒙特卡洛抽样方法,实现新建电气化铁路牵引负荷的预测. 根据热传递原理和相对老化计算,建立新建牵引变电所牵引变压器温升与寿命损失的差分方程模型,对新建牵引变电所的牵引变压器容量进行优化配置. 通过对大量牵引变电所实测数据的分析,聚类后伪-F统计量达12.81,匹配分类后伪-F统计量进一步上升至12.90,表明本文聚类分类方法效果良好. 通过牵引变压器建模,将算例中变压器容量利用率从60%提高到96%,即使考虑安全裕度适当提高安装容量也能使容量利用率达到75%,实现了变压器容量的优化,充分利用了变压器的温度指标和寿命损失.
-
关键词:
- 高斯混合模型 /
- 有监督Kohonen网络 /
- 伪-F统计量 /
- 负荷预测 /
- 容量配置
Abstract: In order to predict the load of a newly-built traction substation and optimize the traction transformer capacity, Gaussian mixture model was employed for clustering the measured data of traction loads, and then the neural network is introduced to match and assign the new traction load. According to the results of clustering and matching, the new load process for new electrified railway is evaluated by the probability density and Monte Carlo method. Then based on the theory of heat transfer and the calculation of aging rates, the difference equation models of the temperature rise and loss of life is proposed to optimize the capacity of new transformer. After analyzing large amount of measured data from traction substations, the pseudo-F value of the clustered data is 12.81, and rises to 12.90 when new load is matched and assigned, indicating that the clustering and assigning methods are effective. The capacity utilization ratio in case study rises from 60% to 96% by modeling the traction transformers. Even with safety margin, the capacity should be expanded and the capacity utilization ratio is also 75%, which achieves the goal of capacity optimization and makes the best of the temperature rise and loss of life. -
表 1 各模型的权重
Table 1. Proportion of all models
模型 1 2 3 4 5 6 权重 0.17 0.24 0.11 0.22 0.11 0.15 表 2 各模型均值向量
Table 2. Mean vectors of all models
模型 空载概率 平均值 有效值 有效系数 方差 偏度 峰度 1 0.57 0.15 0.20 0.11 0.14 0.58 0.57 2 0.54 0.24 0.32 0.11 0.22 0.29 0.14 3 0.83 0.13 0.26 0.57 0.22 0.71 0.52 4 0.21 0.15 0.21 0.11 0.14 0.50 0.42 5 0.53 0.17 0.26 0.23 0.20 0.48 0.27 6 0.65 0.34 0.43 0.05 0.26 0.21 0.16 表 3 模型1的特征量
Table 3. Characteristic quantity of Gauss model 1
特征量 空载概率/ × 10−2 平均值/ × 10−3 有效值/ × 10−3 有效系数/ × 10−4 方差/ × 10−4 偏度/ × 10−3 峰度/ × 10−4 空载概率 1.360 2.440 2.690 −23.000 13.300 −2.900 −74.300 平均值 0.244 0.722 0.774 −7.050 3.700 −1.580 −30.600 有效值 0.269 0.774 0.900 −5.750 4.760 −1.870 −40.800 有效系数 −0.230 −0.705 −0.575 14.900 −0.834 0.863 −0.417 方差 0.133 0.370 0.476 −0.834 31.200 0 −1.050 −27.300 偏度 −0.290 −1.580 −1.870 8.630 −10.500 6.100 123.000 峰度 −0.743 −3.060 −4.080 −0.417 −27.300 12.300 301.000 表 4 部分类别的部分负荷的特征值
Table 4. Characteristic values of some loads in different groups
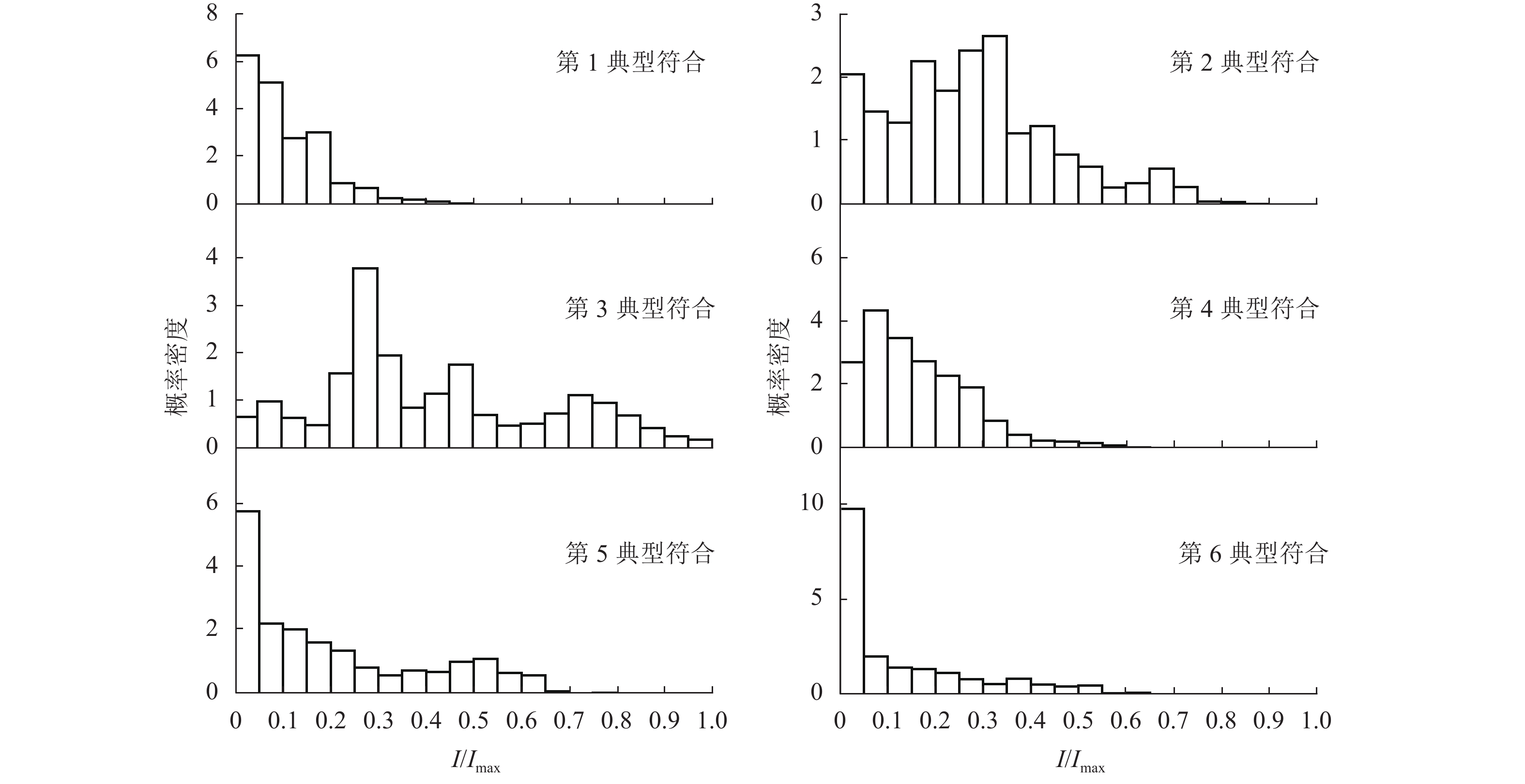
负荷 空载概率 平均值 有效值 有效系数 方差 偏度 峰度 1-1 0.46 0.16 0.21 0.11 0.14 0.53 0.46 1-2 0.53 0.15 0.20 0.11 0.14 0.53 0.47 1-3 0.52 0.13 0.18 0.17 0.14 0.62 0.62 1-4 0.56 0.15 0.21 0.14 0.15 0.60 0.52 2-1 0.91 0.27 0.38 0.14 0.27 0.25 0.06 2-2 0.87 0.24 0.36 0.20 0.28 0.29 0.08 2-3 0.91 0.23 0.32 0.12 0.22 0.23 0.12 3-1 0.82 0.16 0.29 0.32 0.24 0.52 0.26 3-2 0.86 0.18 0.33 0.36 0.27 0.52 0.23 3-3 0.85 0.12 0.24 0.47 0.21 0.66 0.40 注:负荷 1-2 表示第 1 类第 2 个负荷,其他类推. 表 5 各负荷所属类别统计
Table 5. Groups of all loads
类别 负荷编号 1 13,17,18,24,25,31,32,35,36 2 1,2,5,9,22,26,30,34,37,46,49,50 3 11,12,41,43,45 4 3,4,7,16,20,21,27,38,39,47,48 5 6,10,15,28,29,33 6 8,14,19,23,40,42,44 表 6 S_Kohonen网络各参数值
Table 6. Parameter values of S_Kohonen neural network
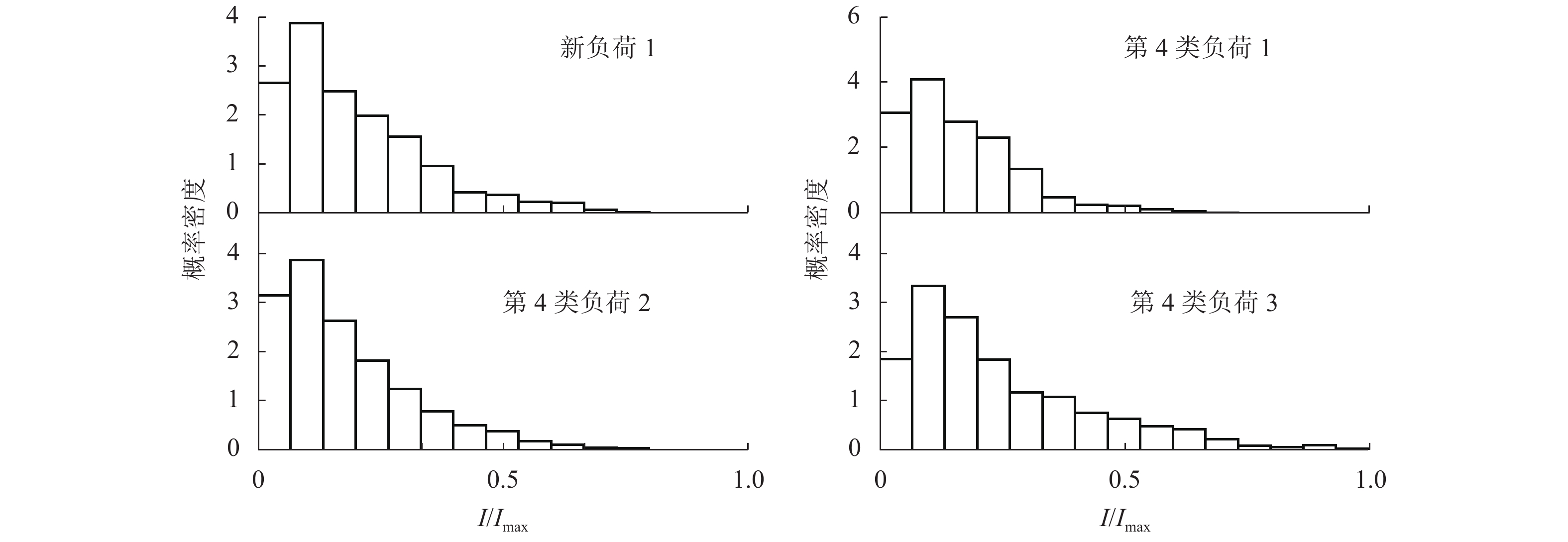
新建负荷编号 负荷的获胜节点 获胜节点与负荷的距离 输出节点(类别) 获胜节点与输出节点的最大权值 新1 10(2,4) 0.05 4 1 新2 36(6,6) 0.10 3 1 新3 25(5,1) 0.30 6 1 新4 9(2,3) 0.19 2 1 注:负荷的获胜节点中括号为获胜节点的位置. 表 7 新建牵引负荷与数据库负荷特征值对比表
Table 7. Characteristic values of new traction loads and database loads
负荷 空载概率 平均值 有效值 有效系数 方差 偏度 峰度 新 1 0.37 0.18 0.23 0.08 0.15 0.39 0.28 4-1 0.27 0.13 0.18 0.11 0.12 0.47 0.41 4-2 0.38 0.16 0.23 0.12 0.16 0.38 0.24 4-3 0.33 0.15 0.21 0.12 0.15 0.45 0.32 新 2 0.87 0.15 0.25 0.29 0.21 0.63 0.41 3-1 0.82 0.16 0.29 0.32 0.24 0.52 0.26 3-2 0.86 0.18 0.33 0.36 0.27 0.52 0.23 3-3 0.85 0.12 0.24 0.47 0.21 0.66 0.40 注:新 1、新 2 分别表示新建负荷 1、新建负荷 2. 表 8 伪-F统计法各项指标值
Table 8. Index values calculated with pseudo-F statistic methods
方法 SSB SSE MSB MSE 伪-F 统计值 GMM 19.32 14.48 3.86 0.30 12.81 S_Kohonen 18.26 13.59 3.65 0.28 12.90 表 9 不同约束下牵引变压器对应绕组最小容量
Table 9. Minimum capacity of corresponding winding of traction transformer under different constraint conditions
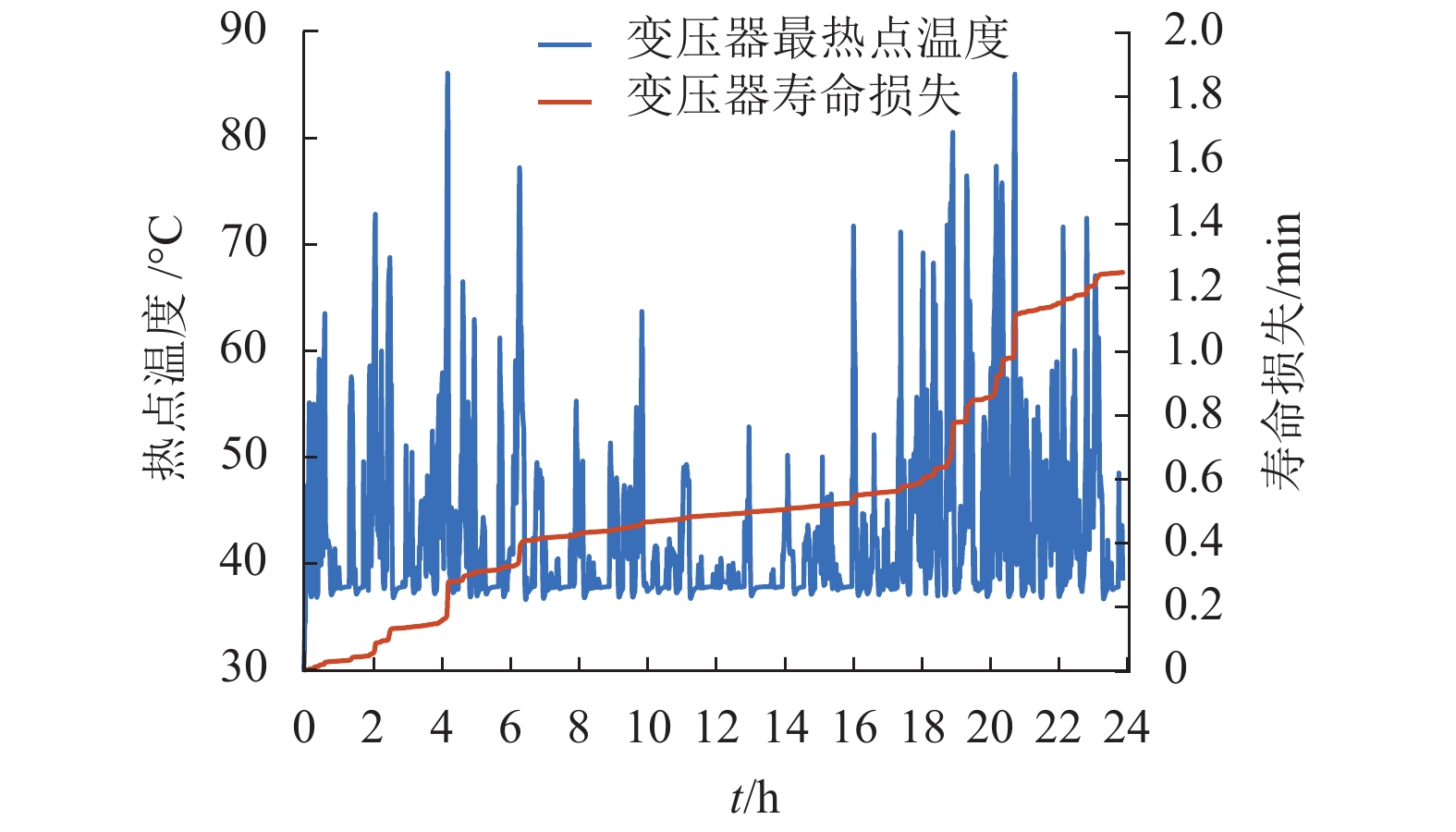
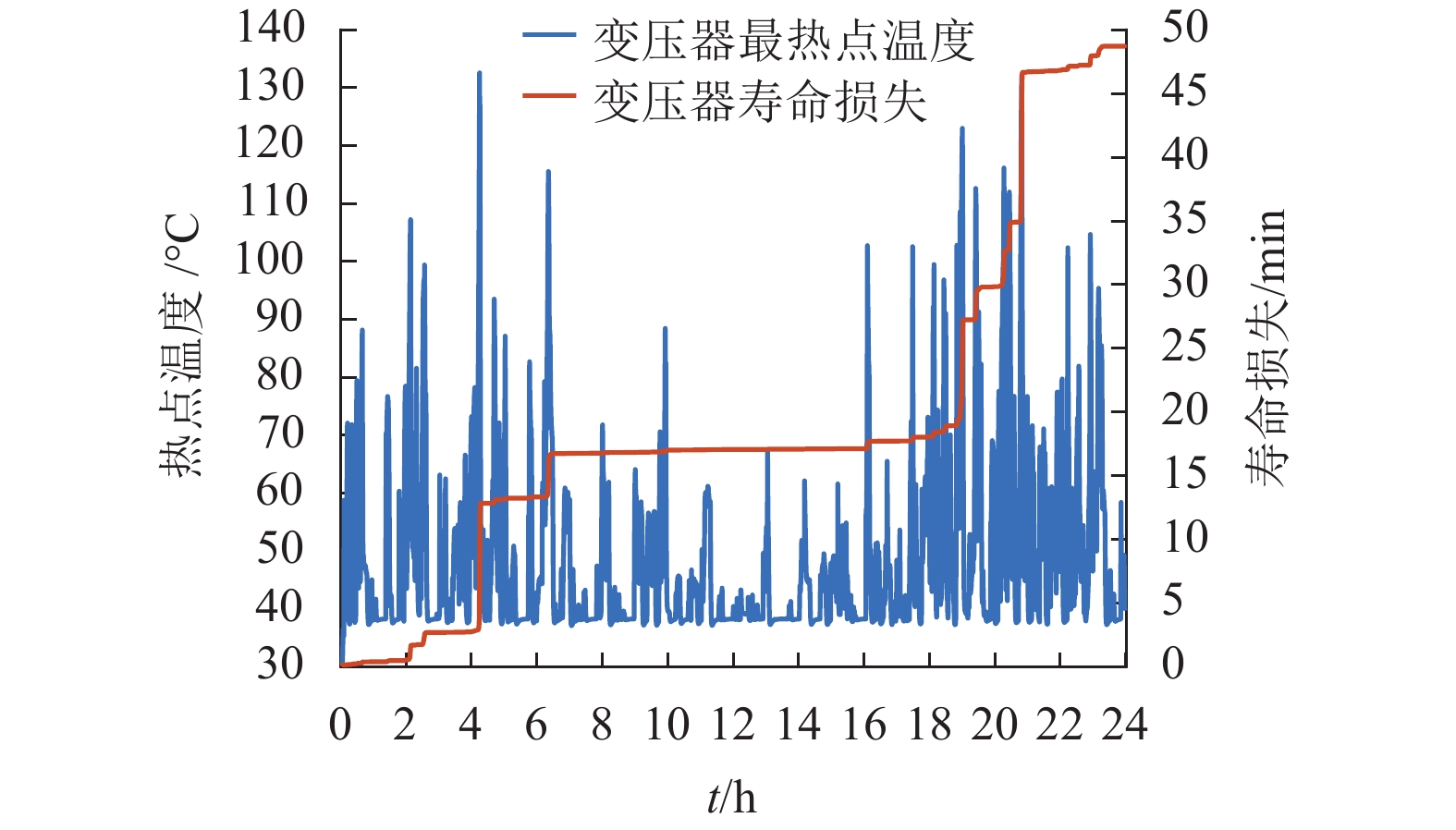
约束条件 最小容量/(MV•A) 最热点温度 140 ℃ 9.54 顶层油温 105 ℃ 8.57 寿命损失 24 h/d 11.99 -
张丽艳,陈映月,韩正庆. 基于改进聚类方式的牵引负荷分类方法研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(1): 27-33,40.ZHANG Liyan, CHEN Yingyue, HAN Zhengqing. Research on traction load classification method Bbased on iImproved clustering method[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(1): 27-33,40. 陈明等. 神经网络原理与实例精解[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2013: 246-247. 张烨,黄新波,陈小雄,等. 输电线路防外力破坏智能预警系统研究[J]. 高压电器,2015,51(8): 54-61.ZHANG Ye, HUANG Xinbo, CHEN Xiaoxiong, et al. Intelligent early-warning system for preserving transmission line from external damage[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2015, 51(8): 54-61. 郎坤. 电力系统短期负荷预测及经济调度决策优化研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2016. 朱晓露. 基于BP神经网络的电力负荷中长期预测[D]. 保定: 华北电力大学, 2017. 陈宇杰. 基于BP神经网络的区域配电网中期电力负荷预测[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017. 林麒麟. 基于神经网络智能算法的电力系统短期负荷预测研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2017. 黄钰淇. 贯通式同相牵引供电系统故障识别研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2017. 秦臻. 基于级联变换器的贯通式牵引供电系统故障诊断与系统重构策略研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. 邢小丽. 电铁牵引供电系统谐波检测及背景谐波分析方法的研究[D]. 保定: 华北电力大学, 2008. 解绍锋,李群湛,王杰文,等. 基于统计的牵引变压器典型负荷曲线分析[J]. 机车电传动,2004(6): 24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-128X.2004.06.008XIE Shaofeng, LI Qunzhan, WANG Jiewen, et al. Analysis on typical load curve of traction transformer based on statistics[J]. Electric Drive for Locomotives, 2004(6): 24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-128X.2004.06.008 王杰文. 牵引变压器典型负荷曲线的建模、仿真与应用[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2004. 吴羽生. 高速铁路牵引变压器典型负荷曲线与容量优化研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2011. 李航. 统计学习方法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2012: 160-162. 周英, 卓金武, 卞月青. 大数据挖掘: 系统方法与实例分析[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2016: 206-208. 张燕杰. 基于混合高斯模型的聚类分析[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2014. 谢中华. MATLAB统计分析与应用: 40个案例分析[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2015: 333. 茆诗松, 王静龙, 濮晓龙. 高等数理统计[M]. 上海: 高等教育出版社, 2004: 427-431. 石若颖. 新建电气化铁路牵引负荷统计预测研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. 郭欣,王蕾,宣伯凯,等. 基于有监督Kokonen神经网络的步态识别[J]. 自动化学报,2017,43(3): 430-438.GUO Xin, WANG Lei, XUAN Bokai, et al. Gait recognition based on supervised Kohonen neural network[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(3): 430-438. LAROSE D T, LAROSE C D. Data mining and predictive analysis[M]. Peking: Tsinghua University Press, 2017. LAROSE D. Discovering statistics[M]. 2nd ed. New York: W. H. and Freeman Company Publisher, 2013. 张丽艳. 新建电气化铁路对电网电能质量影响的预测与对策分析研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2012. 全国变压器标准化技术委员会. 电力变压器第7部分: 油浸式电力变压器负载导则: GB/T 1094.7—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. 陈民武,尚国旭,智慧,等. 高速铁路牵引变压器容量与配置方案优化研究[J]. 中国铁道科学,2013,34(5): 38-41.CHEN Minwu, SHANG Guoxu, ZHI Hui, et al. Study on the scheme for capacity and configuration of traction transformer in high speed railway[J]. China Railway Science, 2013, 34(5): 38-41. MCSHANE C P, RAPP K J, CORKRAN J L, et al. Aging of kraft paper in natural ester dielectric fluid[C]//Proceedings of 2002 IEEE 14th International Conference on Dielectric Liquid. Graz: IEEE, 2002: 173-177. MCSHANE C P, RAPP K J, CORKRAN J L, et al. Aging of paper insulation in natural ester dielectric fluid[C]//2001 IEEE/PES Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition. Atlanta: IEEE, 2001, 2: 675-679. 中铁电气化局集团有限公司. 电气化铁路牵引变压器技术条件: TB/T 3159—2007[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2007. -




 下载:
下载: