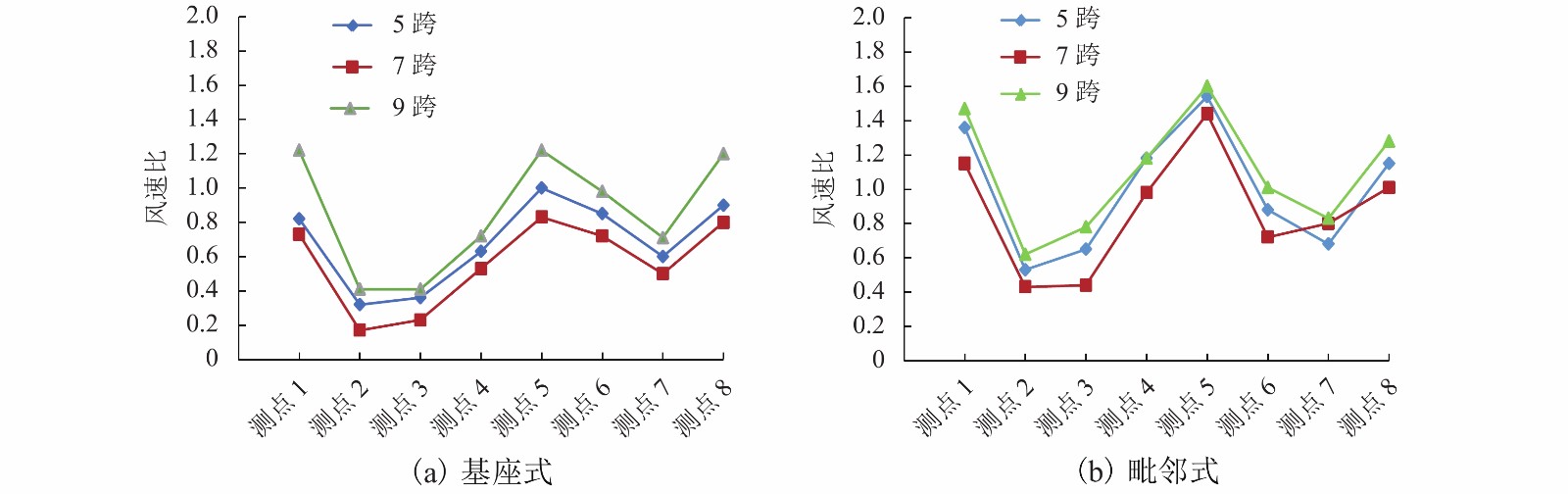
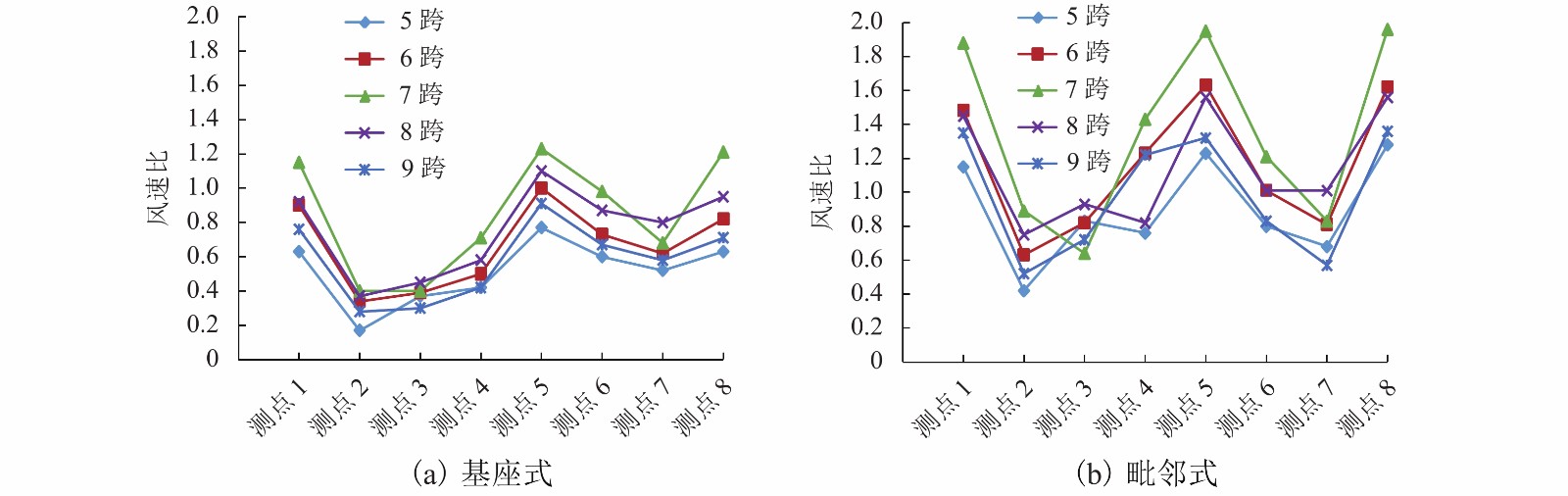
|
MURAKAMI S. Current status and future trends in computational wind engineering[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1986, 1: 3-34.
|
|
牛海燕,刘敏,陆敏,等. 中国沿海地区近20年台风灾害风险评价[J]. 地理科学,2011,31(6): 764-768.NIU Haiyan, LIU Min, LU Min, et al. Risk assessment of typhoon disasters in China coastal area during last 20 years[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2011, 31(6): 764-768.
|
|
温家洪,黄蕙,陈珂,等. 基于社区的台风灾害概率风险评估——以上海市杨浦区富禄里居委地区为例[J]. 地理学,2012,32(3): 348-355.WEN Jiahong, HUANG Hui, CHEN Ke, et al. Probabilistic community-based typhoon disaster risk assessment:a case of Fululi community,Shanghai[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2012, 32(3): 348-355.
|
|
应小宇,朱炜,外尾一则. 高层建筑群平面布局类型对室外风环境影响的对比研究[J]. 地理科学,2013,33(9): 97-101.YING Xiaoyu, ZHU Wei, HOKAO K. Comparative study of the effect on outdoor wind environment by high-rise buildings layout types[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2013, 33(9): 97-101.
|
|
香港中文大学. 都市气候图及风环境评价标准——可行性研究(最终报告)[R]. 香港: 香港特别行政区规划署, 2013
|
|
江亿. 科学发展实现中国特色建筑节能[J]. 城市住宅,2009(1): 38-41,22.
|
|
吴义章,张幸涛,李会知,等. 高层建筑周围行人高度风环境的数值模拟研究[J]. 郑州大学学报(理学版),2011,43(4): 110-115.WU Yizhang, ZHANG Xingtao, LI Huizhi, et al. Numerical simulation of the pedestrian level wind environment around high-rise buildings[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 43(4): 110-115.
|
|
TSANG C W, KWOK K C S, HITCHCOCK P A. Wind tunnel study of pedestrian level wind environment around tall buildings:effects of building dimensions,separation and podium[J]. Building and Environment, 2012, 49: 167-181. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2011.08.014
|
|
DYE R C F. Comparison of full-scale and wind-tunnel model measurements of ground winds around a tower building[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1980, 6(3/4): 311-326.
|
|
王辉. 基于风环境的深圳前海三四单元高层建筑形态控制研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013;
|
|
姚征,陈康民. CFD通用软件综述[J]. 上海理工大学学报,2002,24(2): 137-144.YAO Zheng, CHEN Kangming. Review on the commercial CFD softwares[J]. Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, 2002, 24(2): 137-144.
|
|
HANG J, LI Y, SANDBERG M. Experimental and numerical studies of flows through and within high-rise building arrays and their link to ventilation strategy[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics, 2011, 99(10): 1036-1055.
|
|
CHAN A T, SO E S P, SAMAD S C. Strategic guidelines for street canyon geometry to achieve sustainable street air quality[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2001, 35(24): 4089-4098. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00212-6
|
|
FRANKE J, HELLSTEN A, SCHLTLNZEN H, et al. The COST 732 best practice guideline for CFD simulation of flows in the urban environment:a summary[J]. International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 2011, 44(1/2/3/4): 419-427. doi: 10.1504/IJEP.2011.038443
|
|
TOMINAGA Y, MOCHIDA A, YOSHIE R, et al. AIJ guidelines for practical applications of CFD to pedestrian wind environment around buildings[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2008, 96(10/11): 1749-1761.
|
|
齐庆梅. 中国建筑热环境分析专用气象数据集[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2005
|
|
曹象明,王超. 基于风环境的西安市高层建筑区规划布局策略−以曲江新区为例[J]. 城市发展研究,2017,24(8): 20-26.CAO Xiangming, WANG Chao. The planning strategy of the high-rise buildings layout in Xi’an city based on the wind environment:a case of Qujiang new district[J]. Urban Development Studies, 2017, 24(8): 20-26.
|
|
KUBOTAA T, MIURAB M, TOMINAGAC Y, et al. Wind tunnel tests on the relationship between building density and pedestrian-level wind velocity:development of guidelines for realizing acceptable wind environment in residential neighborhoods[J]. Building and Environment, 2008, 43(10): 1699-1708. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2007.10.015
|
|
周美丽. 高层居住建筑的建筑洞口及建筑间洞口对风环境的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016;
|
|
赖林凤,冉茂宇. 高层建筑及裙房对人行区域风环境影响的研究现状与发展[J]. 福建建筑,2016,215(5): 20-24.LAI Linfeng, RAN Maoyu. Effects of high-rise building and podium on pedestrian-level wind environment:a systematic review[J]. Fujian Architecture & Construction, 2016, 215(5): 20-24.
|
|
YING Xiaoyu, ZHU Wei, GE Jian, et al. Numerical research of layout effect on wind environment around high-rise buildings[J]. Architectural Science Review, 2013, 4(12): 272-278.
|
|
YING Xiaoyu, DING Grace, HU Xiaojun, et al. Developing planning indicators for outdoor wind environments of high-rise residential buildings[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University—Science A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 2016, 17(5): 378-388.
|




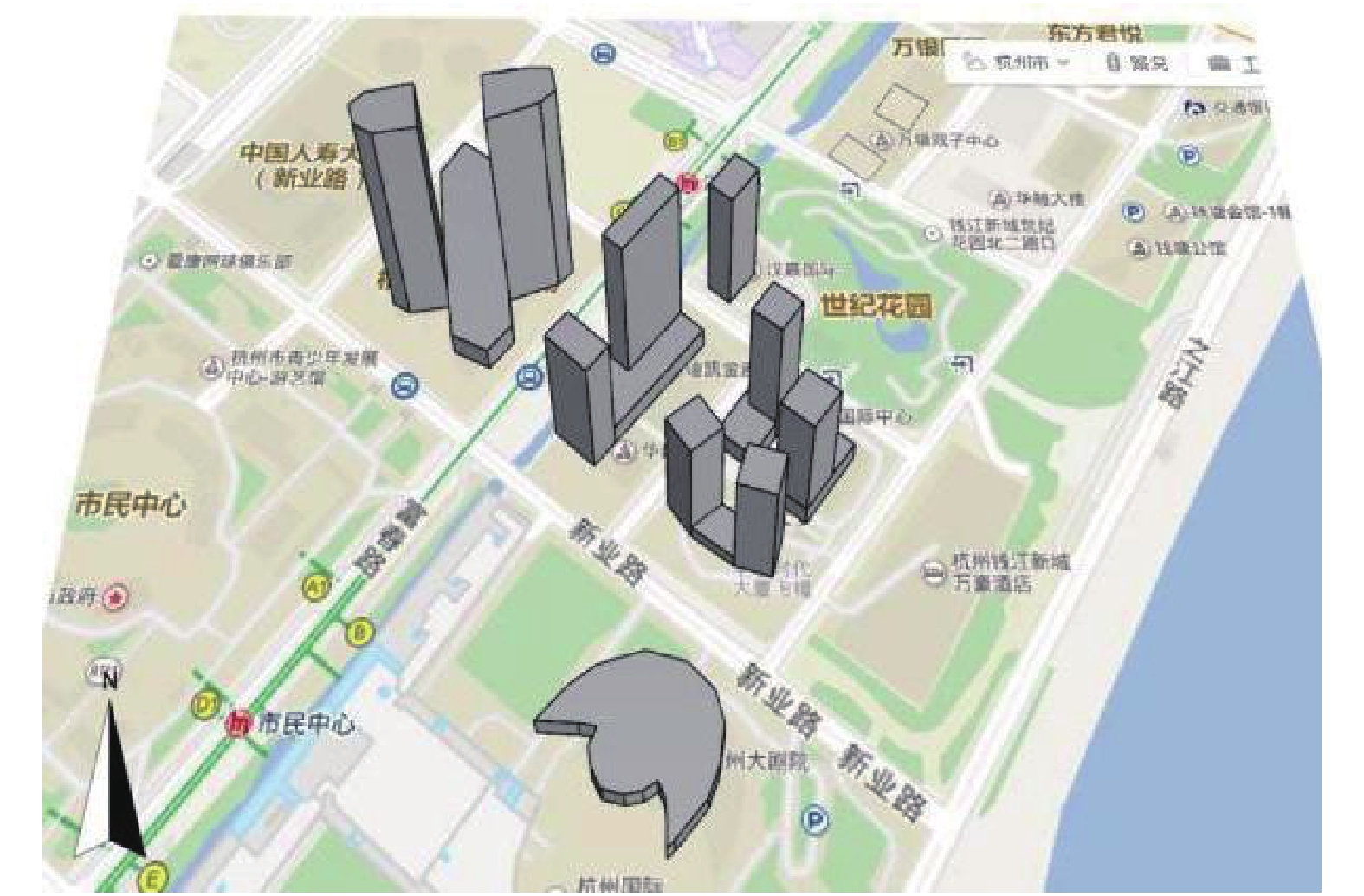
 下载:
下载: