Comparative Analysis of Shear Strength Models in Plastic Hinge Region for Concrete Hollow Piers
-
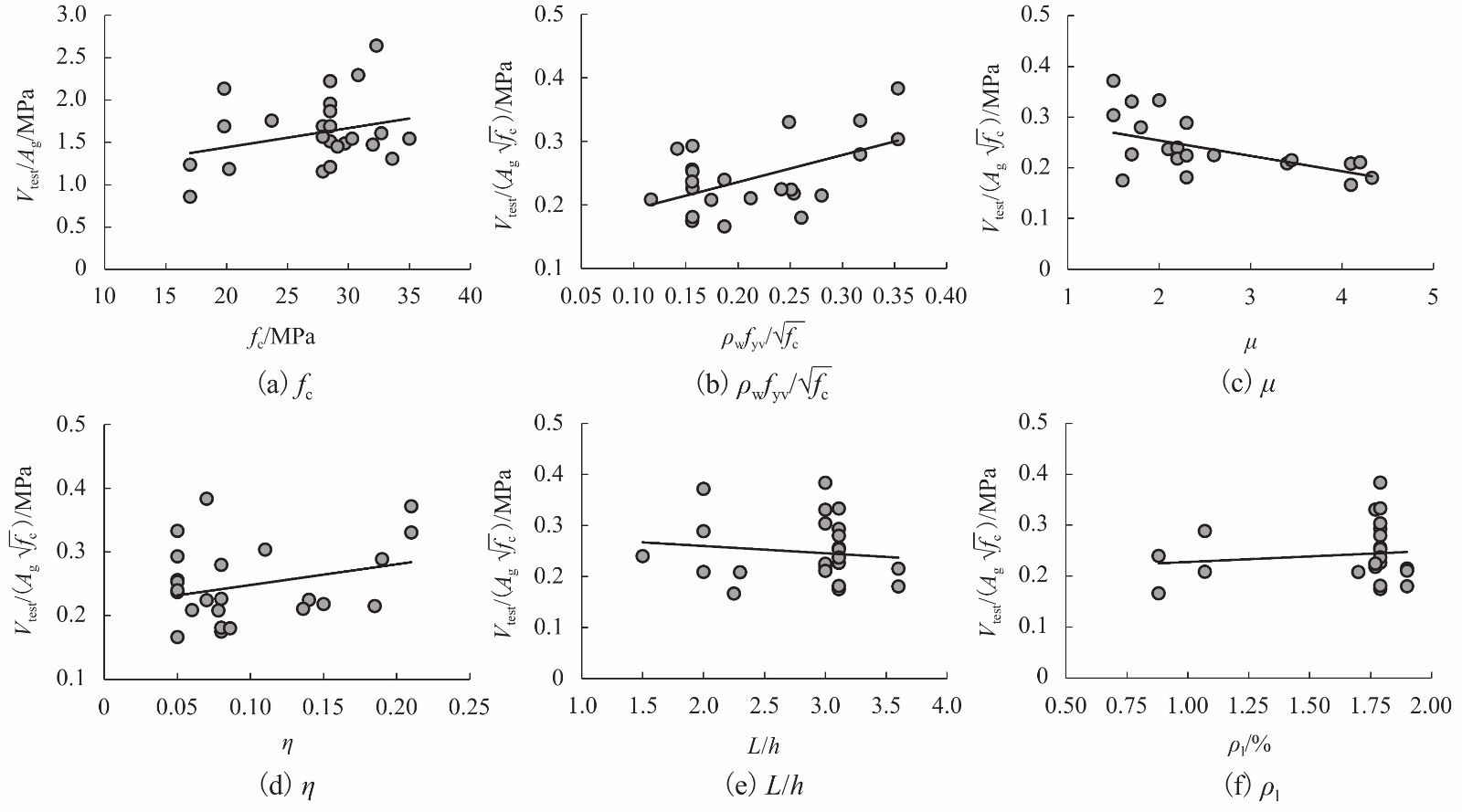
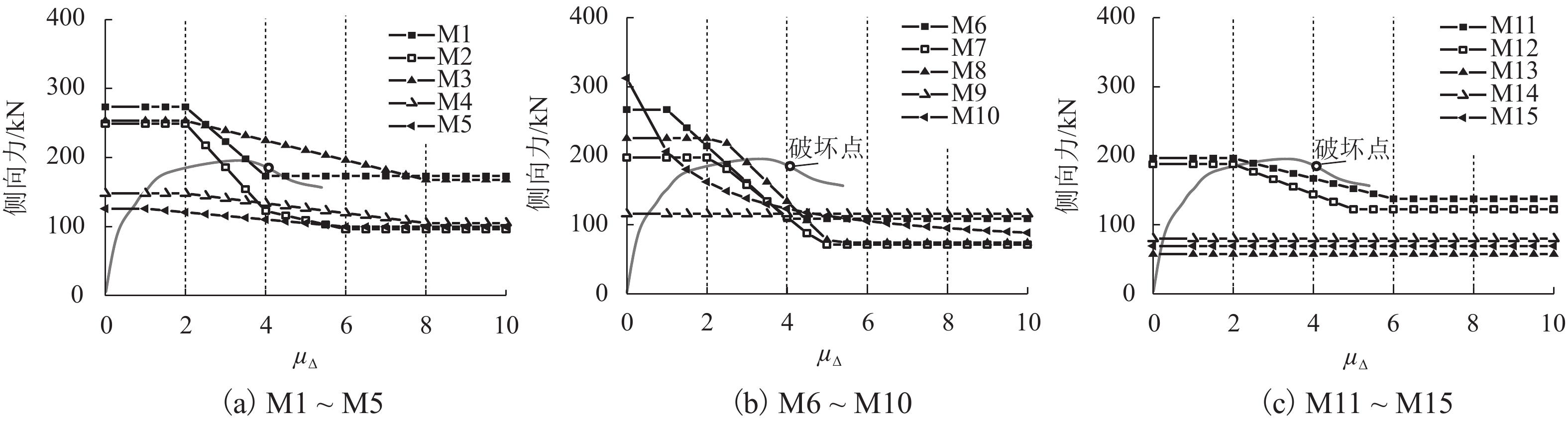
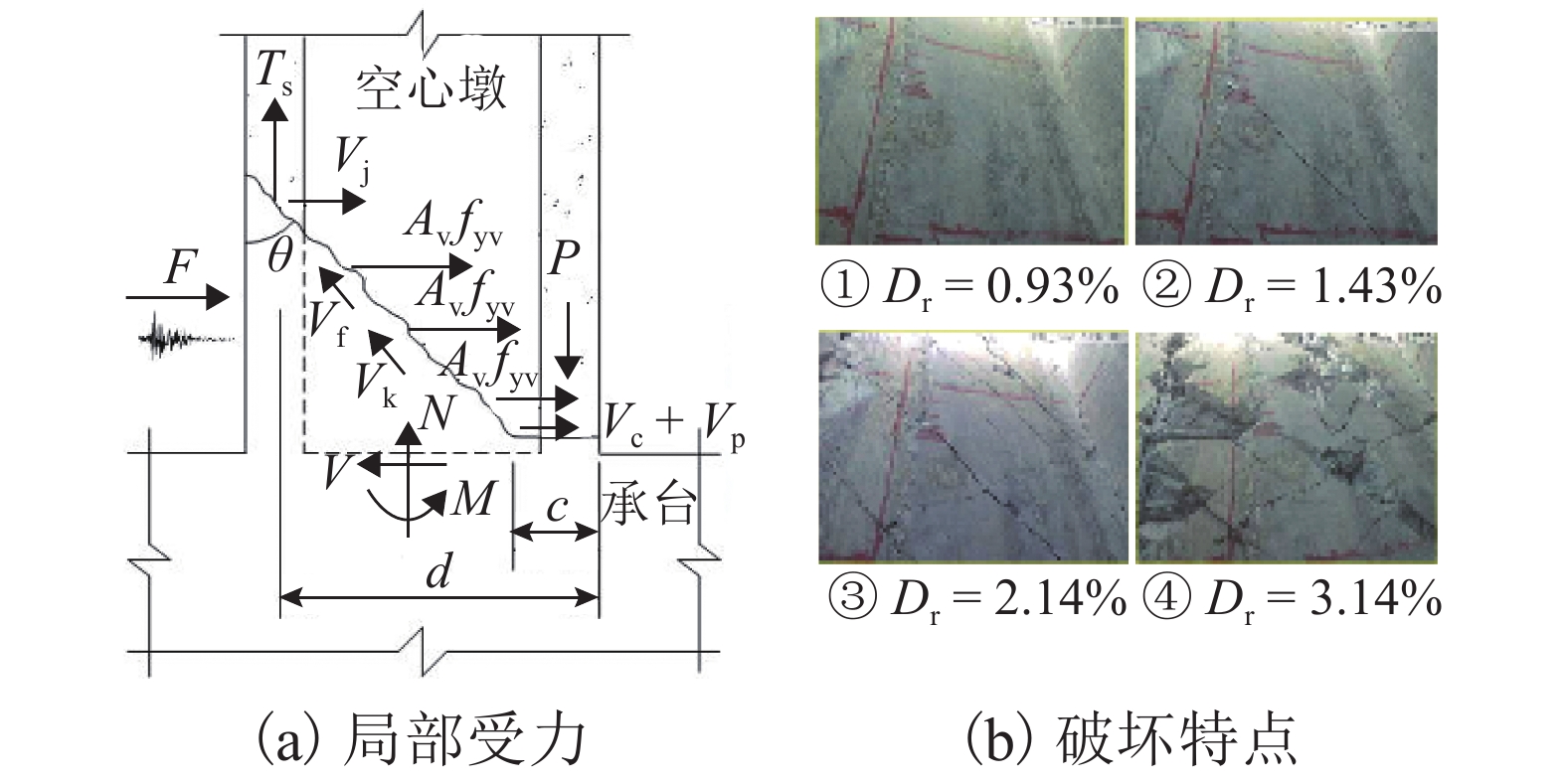
摘要: 准确评估空心墩塑性铰区的抗剪能力是高墩大跨桥梁抗震设计的重要内容. 目前国内外规范中并未明确给出空心墩的抗剪计算模型,规范中已有的实心墩抗剪公式能否直接应用、其它文献中实心墩或空心墩抗剪强度计算方法的适用性等均有待深入研究. 为此,基于25个发生剪切或弯剪破坏的空心墩试验数据,分析塑性铰区抗剪能力的影响因素,并将抗剪强度试验值与已有15个抗剪公式计算结果进行比较. 结果表明:混凝土空心墩抗剪能力随混凝土强度、配箍率和轴压比的增加而提高,一定范围内随位移延性系数和剪跨比的增加而降低,纵向配筋率的影响不显著;Aschheim、Caltrans、Sezen和Shin公式的计算值与试验结果误差不超过5%,其中Sezen模型计算效果最佳,可用于评估空心墩塑性铰区抗剪能力;NZS3101、JRA、JTG/TB 02-01—2008、Eurocode 8和ACI-318等规范公式计算结果略显保守,可作为空心墩抗剪设计的依据;其余公式过高估算了抗剪强度,不适于混凝土空心墩塑性铰区的抗剪设计.Abstract: Accurate evaluation of shear strength in plastic hinge region is of great significance for seismic design of long-span bridges with tall piers. However, the shear design models for hollow piers are not directly listed in the current codes in China and abroad. The applicability of both the existing formulas for solid piers in the codes and the formulas for solid or hollow columns in literature needs to be further studied. Thus, based on the test results of 25 hollow piers with shear or flexural-shear failure modes, the influencing factors of shear strength in plastic region are analyzed, and the experimental values of shear strength are compared with the calculation results of 15 formulas. The results show that the shear strength of concrete hollow piers increases with an increase in concrete strength, stirrup ratio and axial load ratio, and decreases with an increase in displacement ductility factor and aspect ratio within a certain range, while the influence of the longitudinal reinforcement ratio is not significant. The errors between the test results and the calculated values by formulas of Aschheim, Caltrans, Sezen and Shin are all less than 5%, among which the Sezen model is the most suitable to assess the shear strength in plastic hinge region for hollow piers. The formulas in NZS3101, JRA, JTG/TB 02-01—2008, Eurocode 8, and ACI-318 lead to slightly conservative results, which can be used for shear design of hollow piers; the rest of equations, for overestimation of the shear strength in plastic hinge region, are inappropriate to concrete hollow piers.
-
表 1 空心墩的设计参数
Table 1. Design parameters of hollow piers
来源 试件编号 试件
名称破坏模式 L/
mmh/
mmtw/
mmL/h η fc/
MPafyl/
MPaρl/% fw/
MPas/
mmρw/% μmax μΔ Vmax/
kNVM/
kNVM/
VmaxYeh等[23] S1 PI2 弯剪 3500 1500 300 2.3 0.078 32.0 418 1.70 420 200 0.24 2.6 4.1 2650 2512 0.95 Yeh等[24] S2 MI1 弯剪 5400 1500 300 3.6 0.086 33.6 476 1.90 480 150 0.31 2.4 4.3 2350 1824 0.78 S3 MI2 弯剪 5400 1500 300 3.6 0.185 29.1 476 1.90 480 150 0.31 1.9 3.5 2610 1827 0.78 Mo等[25] S4 NI1-b 弯剪 1500 500 120 3.0 0.136 20.2 476 1.90 405 50 0.24 2.1 4.2 270 267 0.99 Calvi等[26] S5 S250 弯剪 900 450 75 2.0 0.06 35.0 550 1.07 550 75 0.13 3.4 3.4 217 197 0.91 S6 S500 弯剪 900 450 75 2.0 0.19 23.7 550 1.07 550 75 0.13 1.2 2.3 247 229 0.93 S7 S750 弯剪 900 450 75 2.0 0.21 32.3 550 1.07 550 75 0.13 1.3 1.5 297 278 0.94 S8 T250 弯剪 1350 450 75 3.0 0.07 30.3 550 1.77 550 75 0.25 1.9 2.3 217 190 0.88 S9 T500A 弯剪 1350 450 75 3.0 0.15 29.7 550 1.77 550 75 0.25 1.1 2.2 209 219 1.05 S10 T500B 弯剪 1350 450 75 3.0 0.14 32.7 550 1.77 550 75 0.25 2.2 2.6 226 220 0.97 S11 T750 弯剪 1350 450 75 3.0 0.21 30.8 550 1.77 550 75 0.25 1.7 1.7 258 244 0.95 Delgado[27] S12 PO1-N1 弯剪 1350 450 75 3.0 0.11 19.8 625 1.79 390 75 0.4 1.4 1.5 190 199 1.05 S13 PO1-N2 弯剪 1400 450 75 3.1 0.08 27.9 435 1.79 437 75 0.19 1.1 1.6 130 142 1.09 S14 PO1-N3 弯剪 1400 450 75 3.1 0.08 27.9 435 1.79 437 75 0.19 1.3 1.6 130 142 1.09 S15 PO1-N4 弯剪 1400 450 75 3.1 0.08 28.5 560 1.79 443 75 0.19 1.5 1.7 170 178 1.05 S16 PO1-N5 弯剪 1400 450 75 3.1 0.08 28.5 560 1.79 443 75 0.19 2.1 2.3 170 178 1.05 S17 PO1-N6 弯剪 1400 450 75 3.1 0.08 28.5 560 1.79 443 75 0.38 1.4 1.8 210 193 0.92 S18 PO2-N1 剪切 1350 450 75 3.0 0.07 19.8 625 1.79 390 75 0.40 − − 240 249 1.04 S19 PO2-N2 剪切 1400 450 75 3.1 0.05 27.9 435 1.79 437 75 0.19 − − 190 221 1.16 S20 PO2-N3 弯剪 1400 450 75 3.1 0.05 27.9 435 1.79 437 75 0.19 2.0 2.1 220 221 1.01 S21 PO2-N4 剪切 1400 450 75 3.1 0.05 28.5 560 1.79 443 75 0.19 − − 190 224 1.18 S22 PO2-N5 剪切 1400 450 75 3.1 0.05 28.5 560 1.79 443 75 0.19 − − 200 224 1.02 S23 PO2-N6 弯剪 1400 450 75 3.1 0.05 28.5 560 1.79 443 75 0.38 1.0 2.0 250 245 0.98 Cassese等[11] S24 P3 弯剪 900 400 100 1.5 0.05 17.0 540 0.88 655 120 0.12 2.0 2.2 278 256 0.92 S25 P4 弯剪 900 600 100 2.25 0.05 17.0 540 0.88 655 120 0.12 3.6 4.1 193 165 0.86 表 2 轴力考虑为单独项Vp的抗剪模型
Table 2. Shear strength models considering axial-load in Vp
公式编号 来源 混凝土部分Vc 箍筋部分Vs M1 Priestley等[8] $\gamma \sqrt {{f_{\rm{c}}}} \left( {0.8{A_{\rm{g}}}} \right)$ $\dfrac{ { {A_{\rm{v} } }{f_{ {\rm{yv} } } }d} }{s}\cot \;30^\circ$ M2 Xiao等[9] $\gamma \sqrt {{f_{\rm{c}}}} \left( {0.8{A_{\rm{g}}}} \right)$ $\dfrac{{{A_{\rm{v}}}{f_{{\rm{yv}}}}\left( {d - {c_{\rm cov}}} \right)}}{s}\cot \;\theta $ M3 Kowalsky等[10] $\alpha \beta \gamma \sqrt {{f_{\rm{c}}}} \left( {0.8{A_{\rm{g}}}} \right)$ $\dfrac{ { {A_{\rm{v} } }{f_{ {\rm{yv} } } }\left( {h - c - {c_{\rm cov}} } \right)} }{s}\cot \;\theta$ M4 Cassese等[11] $\alpha \beta \gamma \sqrt {{f_{\rm{c}}}} \left( {1.6{t_{\rm{w}}}h} \right)$ $\dfrac{ { {A_{\rm{v} } }{f_{ {\rm{yv} } } }\left( {h - c - {c_{\rm cov}} } \right)} }{s}\cot \;\theta$ M5 Eurocode 8[12] $\alpha \beta \gamma {\sqrt {{f_{\rm{c}}}} _{}}{b_{\rm{w}}}d$ $\dfrac{{\gamma {A_{\rm{v}}}{f_{{\rm{yv}}}}\left( {d - {c_{\rm cov}}} \right)}}{s}$ 表 3 轴力贡献计入混凝土分项Vc的抗剪模型
Table 3. Shear strength models with the effect of load P in Vc
公式
编号来源 混凝土部分Vc M6 Aschheim等[13] $0.3\left( {\gamma + \dfrac{P}{{13.8{A_{\rm{g}}}}}} \right)\sqrt {{f_{\rm{c}}}} \left( {0.8{A_{\rm{g}}}} \right)$ M7 Caltrans[14] $\lambda \left( {1 + \dfrac{P}{{13.8{A_{\rm{g}}}}}} \right)\sqrt {{f_{\rm{c}}}} \left( {0.8{A_{\rm{g}}}} \right)$ M8 《城规》[15] $\lambda \left( {1 + \dfrac{P}{{13.8{A_{\rm{g}}}}}} \right)\sqrt {{f_{\rm{c}}}} \left( {0.8{A_{\rm{g}}}} \right)$ M9 ACI-318[16] $0.167\left( {1 + \dfrac{P}{{13.8{A_{\rm{g}}}}}} \right){\sqrt {{f_{\rm{c}}}} _{}}{b_{\rm{w}}}d$ M10 顾毅云[17] $0.058\gamma \left( {3.6\eta + 1} \right){f_{\rm{c}}}\left( {0.8{A_{\rm{g}}}} \right)$ M11 Sezen等[18] $\gamma \left( {\dfrac{{0.5\sqrt {{f_{\rm{c}}}} }}{{L/d}}\sqrt {1 + \dfrac{P}{{0.5\sqrt {{f_{\rm{c}}}} {A_{\rm{g}}}}}} } \right)\left( {0.8{A_{\rm{g}}}} \right)$ M12 Shin等[19] $\left( {\alpha \beta \gamma } \right)0.5\sqrt {{f_{\rm{c}}}} \sqrt {1 + \dfrac{P}{{0.5\sqrt {{f_{\rm{c}}}} {A_{\rm{g}}}}}} \left( {0.8{A_{\rm{g}}}} \right)$ M13 NZS3101[20] $\left[ {4\left( {0.07 + 10{p_{\rm{w}}}} \right)\sqrt {{f_{\rm{c}}}} \sqrt {\dfrac{P}{{{f_{\rm{c}}}{A_{\rm{g}}}}} - 0.1} } \right]{b_{\rm{w}}}d$ 表 4 不考虑轴力变化影响的抗剪模型
Table 4. Shear strength models without the effect of varying P
表 5 各抗剪模型影响参数
Table 5. Influencing factors in each shear strength model
公式
编号来源 fc/MPa Avfyv/MPa η/P μΔ L/h ρl/% ρsfyv 计算
角度/(°)截面计算高度 有效剪切面积 M1 Priestley等[8] ○ ○ ○ 2.0~4.0 × × × 30 d 0.8Ag M2 Xiao等[9] ○ ○ ○ 2.0~6.0 × × × 30 d−c 0.8Ag M3 Kowalsky等[10] ○ ○ ○ 2.0~8.0 1.5~2.0 ○ × 30 h−c−ccov 0.8Ag M4 Cassese等[11] ○ ○ ○ 2.0~8.0 1.5~2.0 ○ × 30 h−c−ccov 1.6twh M5 Eurocode 8[12] ○ ○ ○ 1.0~6.0 ≤5.0 ○ × 45 d−c bwd M6 Aschheim等[13] ○ ○ ○ 1.0~4.0 × × × 45 d 0.8Ag M7 Caltrans[14] ○ ○ ○ 1.0~5.7 × × ○ 45 d 0.8Ag M8 《城规》[15] ○ ○ ○ ○ × × ○ 45 d 0.8Ag M9 ACI-318[16] ○ ○ ○ × × × × 45 d bwd M10 顾毅云[17] ○ ○ ○ ○ × × × 45 d 0.8Ag M11 Sezen等[18] ○ ○ ○ 2.0~6.0 2.0~4.0 × × 45 d 0.8Ag M12 Shin等[19] ○ ○ ○ 2.0~5.0 1.5~3.0 ○ × 45 d 0.8Ag M13 NZS 3101[20] ○ ○ ○ × × ○ × 45 d bwd M14 JRA[21] ○ ○ × × × ○ × 45 d bwd M15 《细则》[22] ○ ○ × × × × × 45 h 0.8Ag 注:表中○表示在该模型中考虑了某一参数,× 表示在该模型中没有考虑某一参数;利用桁架模型计算箍筋抗剪贡献时,截面计算高度的4种取法分别为d、d−c、h−c−ccov、h. 表 6 抗剪能力计算值与试验值比值的平均值和变异系数
Table 6. Mean value and variation coefficient of the ratio of calculated shear strength to test results
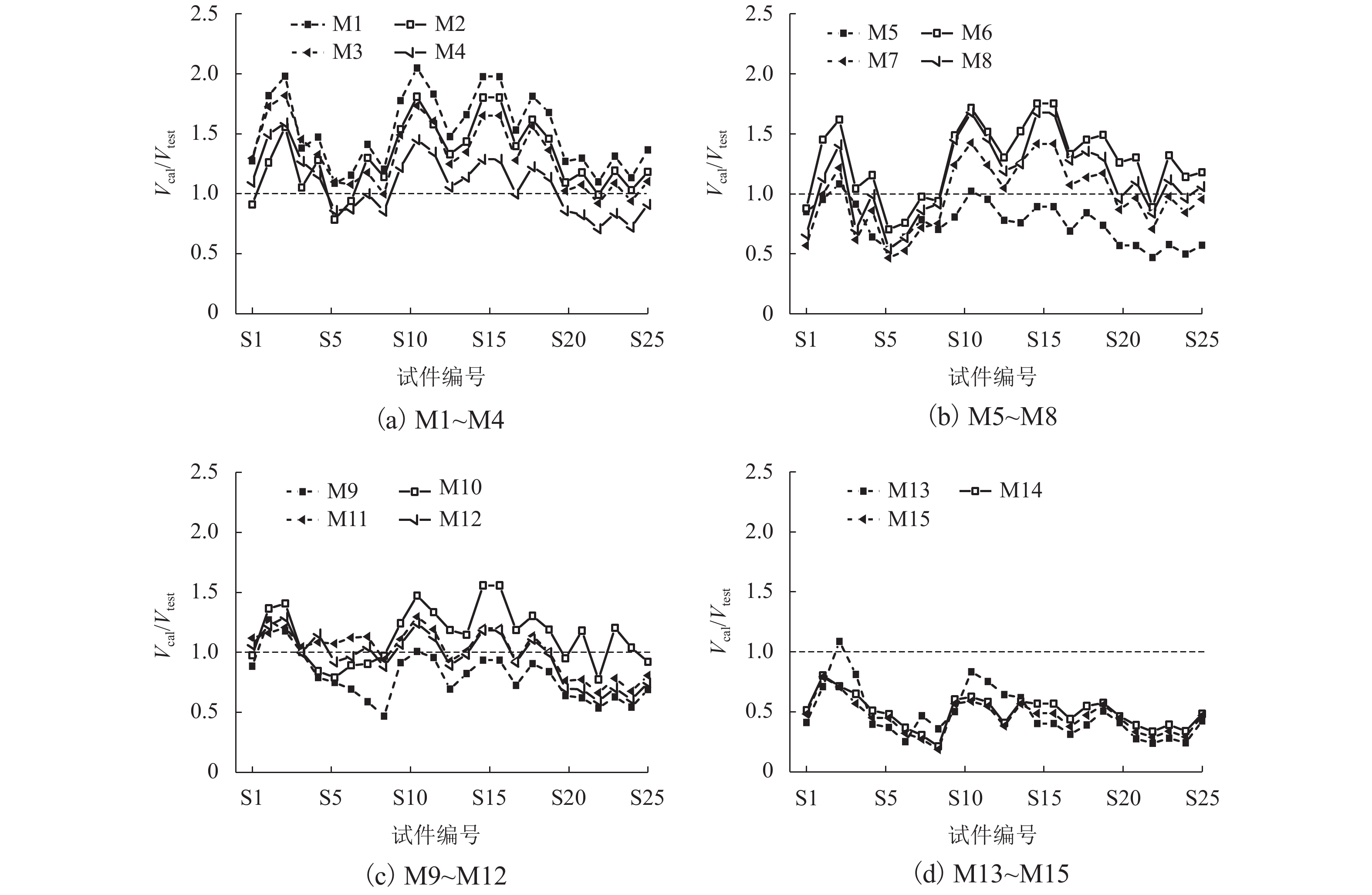
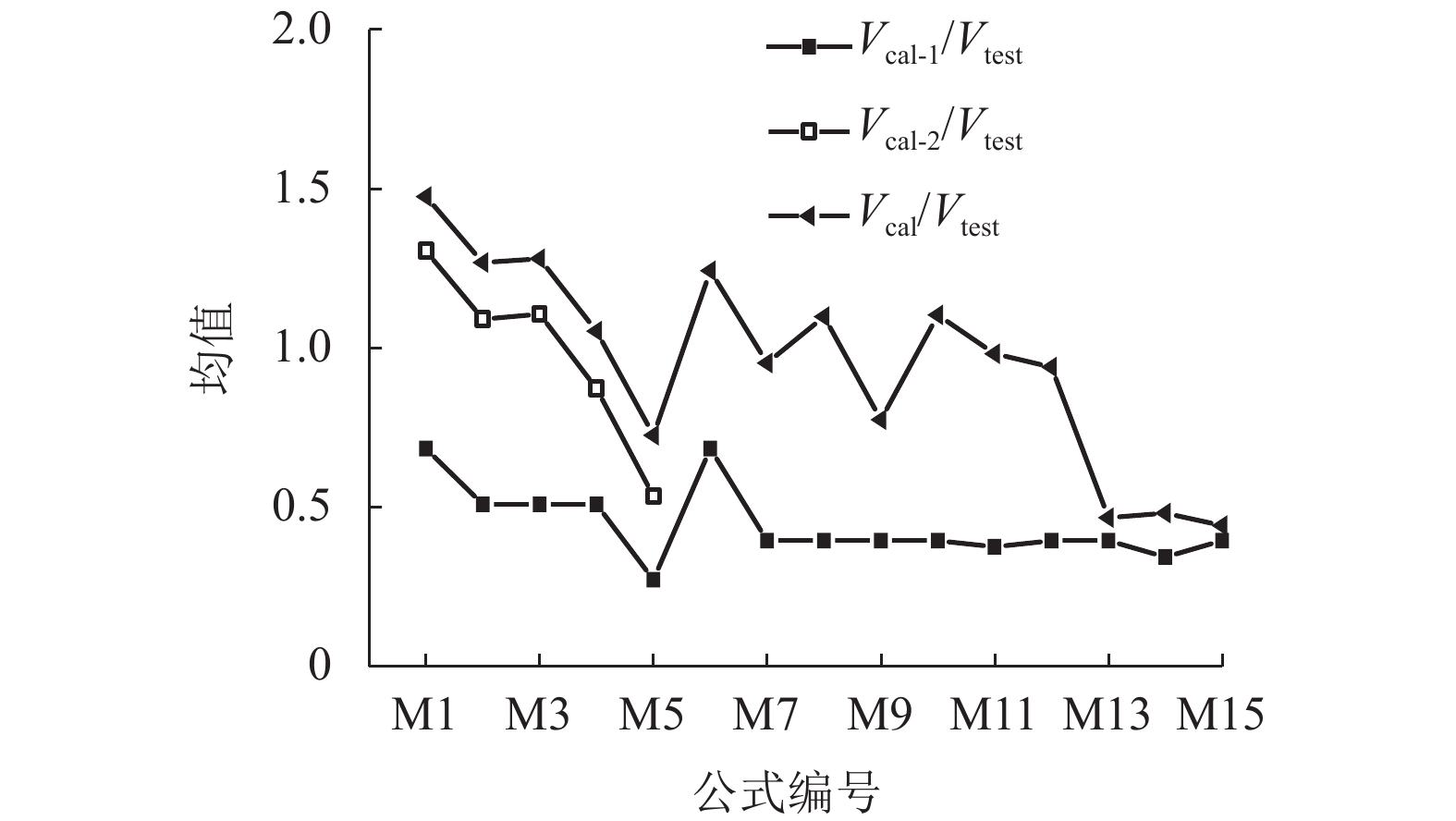
项目 M1 M2 M3 M4 M5 M6 M7 M8 M9 M10 M11 M12 M13 M14 M15 Vcal/Vtest平均值 1.52 1.30 1.32 1.09 0.75 0.99 0.98 1.13 0.80 1.14 1.01 0.97 0.48 0.50 0.46 变异系数 0.204 0.221 0.207 0.225 0.229 0.266 0.290 0.291 0.250 0.205 0.178 0.211 0.447 0.274 0.307 -
MO Y L, NIEN I C. Seismic performance of hollow high-strength concrete bridge columns[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2002, 7(6): 338-349. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0702(2002)7:6(338) 宗周红,夏坚,徐绰然. 桥梁高墩抗震研究现状及展望[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版),2013,43(2): 445-452.ZONG Zhouhong, XIA Jian, XU Chaoran. Seismic study of high piers of large-span bridges:an overview and research development[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 43(2): 445-452. 王东升,郭迅,孙治国,等. 汶川大地震公路桥梁震害初步调查[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,2009,29(3): 84-94.WANG Dongsheng, GUO Xun, SUN Zhiguo, et al. Damage to highway bridges during wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2009, 29(3): 84-94. 孙治国,王东升,郭迅,等. 汶川大地震绵竹市回澜立交桥震害调查[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,2009,29(4): 132-138.SUN Zhiguo, WANG Dongsheng, GUO Xun, et al. Damage investigation of huilan interchange in mianzhu after wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2009, 29(4): 132-138. KIM I H, SUN C H, SHIN M. Concrete contribution to initial shear strength of RC hollow bridge columns[J]. Structural Engineering and Mechanics, 2012, 41(1): 43-65. doi: 10.12989/sem.2012.41.1.043 LI B, CAO T N T. Reinforced concrete beam analysis supplementing concrete contribution in truss models[J]. Engineering Structures, 2008, 30: 3285-3294. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2008.05.002 TURMO J, RAMOS G, APARICIO A C. Shear truss analogy for concrete members of solid and hollow circular cross section[J]. Engineering Structures, 2009, 31: 455-465. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2008.09.002 PRIESTLEY M J N, VERMA R, XIAO Y. Seismic shear strength of reinforced concrete columns[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1994, 120(8): 2310-2329. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1994)120:8(2310) XIAO Y, MARTIROSSYAN A. Seismic performance of high-strength concrete columns[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1998, 124(3): 241-251. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1998)124:3(241) KOWALSKY M J, PRIESTLEY M J N. Improved analytical model for shear strength of circular reinforced concrete columns in seismic regions[J]. ACI Structural Journal, 2000, 97(3): 388-396. CASSESE P, RICCI P, VERDERAME G M. Experimental study on the seismic performance of existing reinforced concrete bridge piers with hollow rectangular section[J]. Engineering Structures, 2017, 144: 88-106. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2017.04.047 European Committee for Standardization. Design of structures for earthquake resistance-part 3: assessment and retrofitting of buildings: Eurocode 8—2005[S]. Brussels: Committee European de Normalization, 2005. ASCHHEIM A M, MOEHLE J P. Shear strength and deformability of RC bridge columns subjected to inelastic cyclic displacements[R]. Berkeley: University of California at Berkeley, 1992. Caltrans. Seismic design criteria (version 1.7): caltrans V1.7—2013[S]. Sacramento: California Department of Transportation, 2013. 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 城市桥梁抗震设计规范: CJJ 166—2011[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2011. ACI Committee 318. Building code requirements for structure concrete: ACI-318—2014[S]. Farmington Hills: American Concrete Institute, 2014. 顾毅云. 强震动下钢筋混凝土桥墩的残余剪切能力研究[D]. 福州: 福州大学, 2003. SEZEN H, MOEHLE J P. Shear strength model for lightly reinforced concrete columns[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2004, 130(11): 1692-1703. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2004)130:11(1692) SHIN M, CHOI Y Y, SUN C H, et al. Shear strength model for reinforced concrete rectangular hollow columns[J]. Engineering Structures, 2013, 56: 958-969. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2013.06.015 Concrete Design Committee P 3101. Concrete structures standard: NZS 3101—2006[S]. Wellington: Standards New Zealand, 2006. Japan Road Association. Design specifications for highway bridges, part V: seismic design: JRA—2002[S]. Tokyo: Japan Road Association, 2002. 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 公路桥梁抗震设计细则: JTG/TB 02-01—2008[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2008. YEH Y K, MO Y L, YANG C Y. Full-scale tests on rectangular hollow bridge piers[J]. Materials and Structures, 2002, 35: 117-125. doi: 10.1007/BF02482111 YEH Y K, MO Y L, YANG C Y. Seismic performance of rectangular hollow bridge columns[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2002, 128(1): 60-68. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2002)128:1(60) MO Y L, YEH Y K, HSIEH D M. Seismic retrofit of hollow rectangular bridge columns[J]. Journal of Composites for Construction, 2004, 8(1): 43-51. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0268(2004)8:1(43) CALVI G M, PAVESE A, RASULO A, et al. Experimental and numerical studies on the seismic response of RC hollow bridge piers[J]. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 2005, 3(3): 267-297. doi: 10.1007/s10518-005-2240-0 DELGADO P. Avaliação da segurança estruturalem pontes[D]. Porto: FEUP, 2009. Applied Technology Council. Seismic design guidelines for highway bridges: ATC—6[R]. Berkeley: Federal Highway Administration Department of Transtation, 1981. Applied Technology Council (ATC-33 Project). NEHRP guidelines for the seismic rehabilitation of buildings: FEMA 273[S]. Washington D. C.: Federal Emergency Management Agency, 1997. -




 下载:
下载: