Application of Hierarchical Extreme Learning Machine in Prediction of Insulator Pollution Degree Using Hyperspectral Images
-
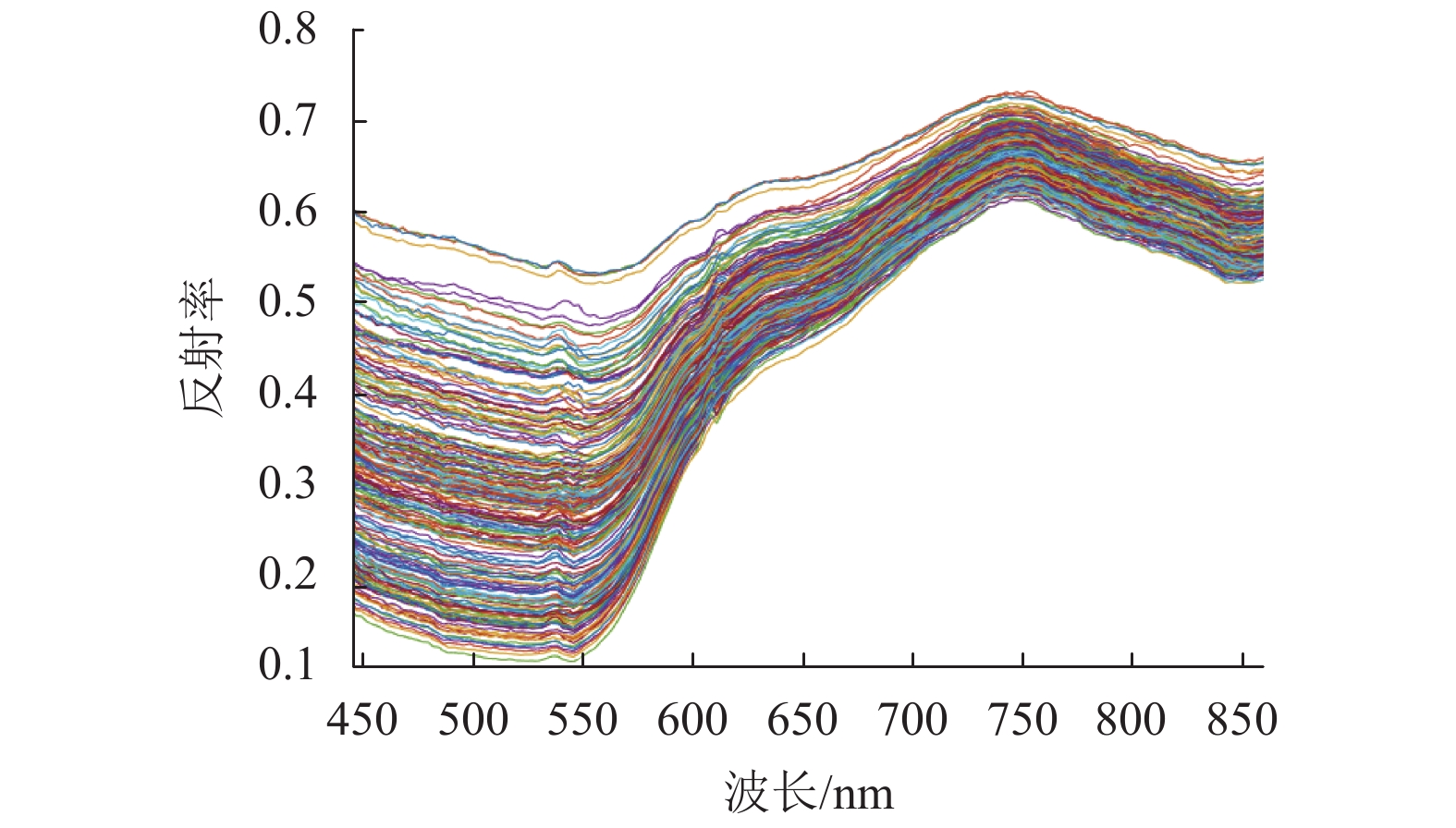
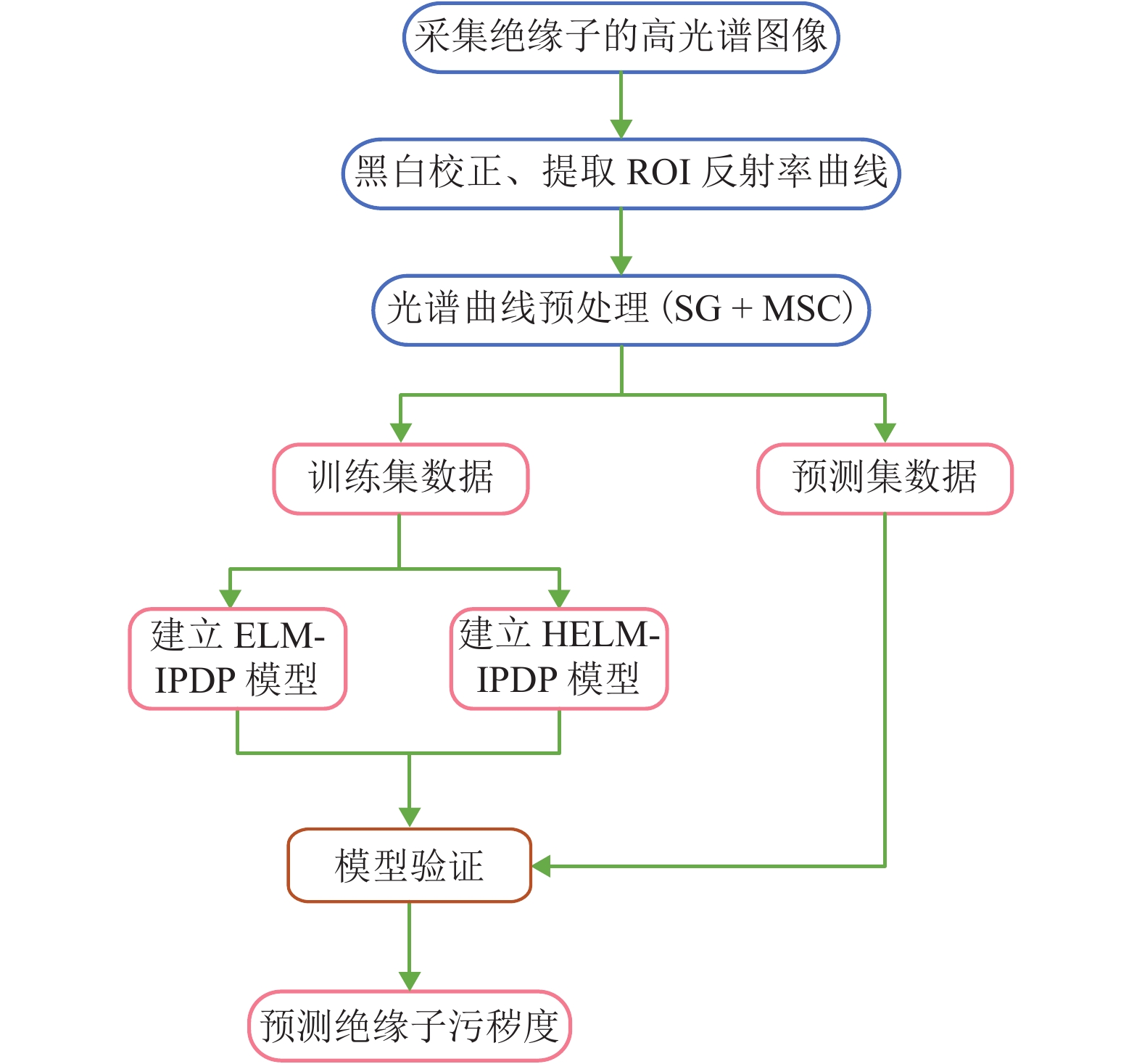
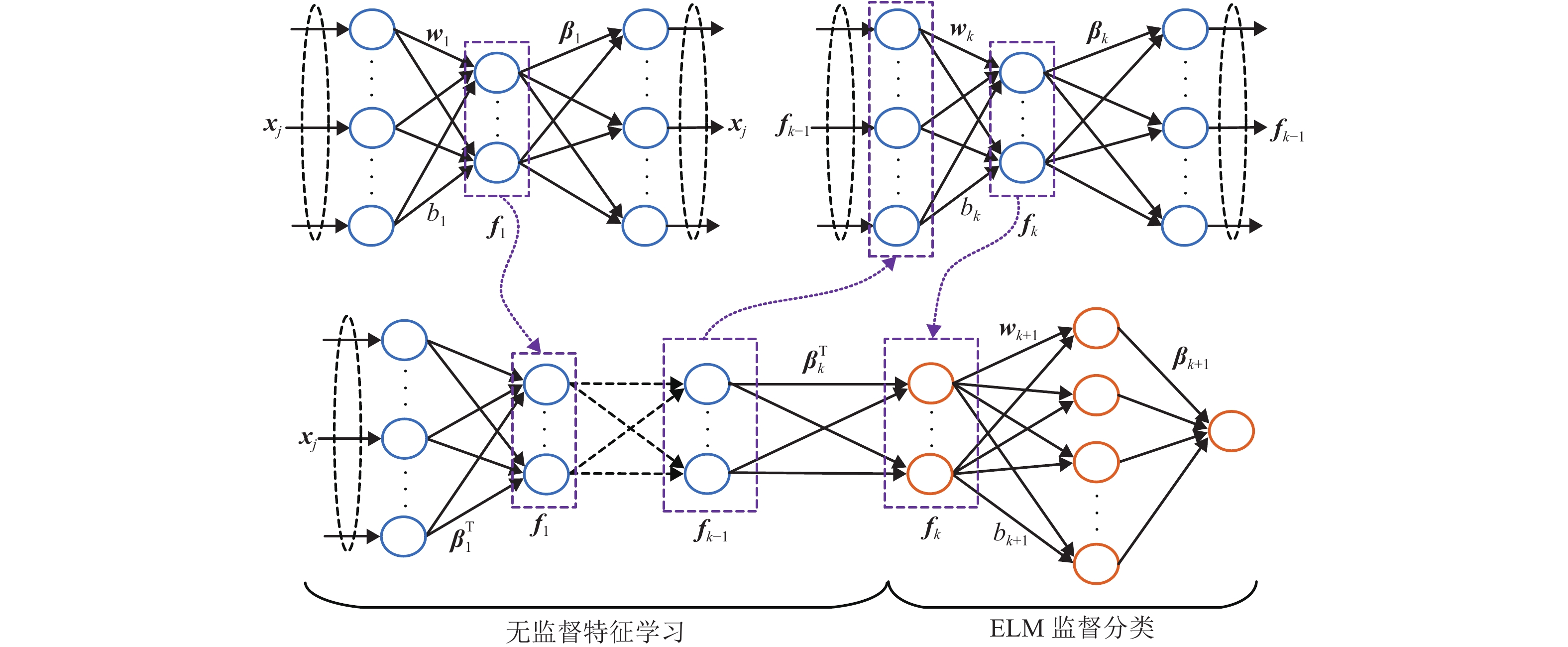
摘要: 高光谱图像具有图谱合一、光谱范围广及分辨率高等优势,能精细化地反映物质微观特性. 为此,引入高光谱成像技术以非接触式预测绝缘子污秽度. 考虑到极限学习机具有学习效率高和泛化能力强等优点,提出基于正则化约束极限学习机的绝缘子污秽度预测(extreme learning machine-insulator pollution degree prediction,ELM-IPDP)模型. 此外,为进一步提升预测性能,引入层次极限学习机从复杂的高光谱图像中学习出有效、抽象、判决性特征表示,继而建立基于层次极限学习机的绝缘子污秽度预测(hierarchical ELM-IPDP,HELM-IPDP)模型. 在不同的训练集与测试集比例和不同隐含层神经元个数的情况下分别进行实验,从实验结果可知:ELM-IPDP模型和HELM-IPDP模型的预测性能基本上随着隐含层神经元个数和训练样本的增加而不断提高;当训练集与测试集比例为9∶1时,ELM-IPDP模型的均方根误差和相关系数分别为0.040 3和0.944 7,而HELM-IPDP模型的均方根误差和相关系数分别提升到0.022 3和0.972 0.Abstract: Hyperspectral images possess merging properties of image and spectrum, wide spectral range, and high spectral resolution, which can finely reflect the material microscopic characteristics. To this end, hyperspectral imaging technology is introduced to research the insulator pollution degree in a non-contact way. Considering that extreme learning machine (ELM) has high learning efficiency and strong generalization ability, we construct a ELM with regularization constraint based insulator pollution degree prediction (ELM-IPDP) model. Besides, in order to further improve the prediction performance, hierarchical ELM (HELM) is utilized to learn the effective, abstract, and discriminative feature representations from the complex hyperspectral images, and the HELM based insulator pollution degree prediction (HELM-IPDP) model is proposed. Experiments are performed with different amounts of training data and numbers of neurons in hidden layers. Experimental results show that the prediction performance is basically improved with the increase of numbers of neurons in hidden layer and training samples. Specifically, when the proportion of training sample and test sample is 9∶1, root mean squared error (RMSE) and correlation coefficient of the ELM-IPDP model are 0.040 3 and 0.944 7, while those of the HELM-IPDP model are up to 0.022 3 and 0.972 0, respectively.
-
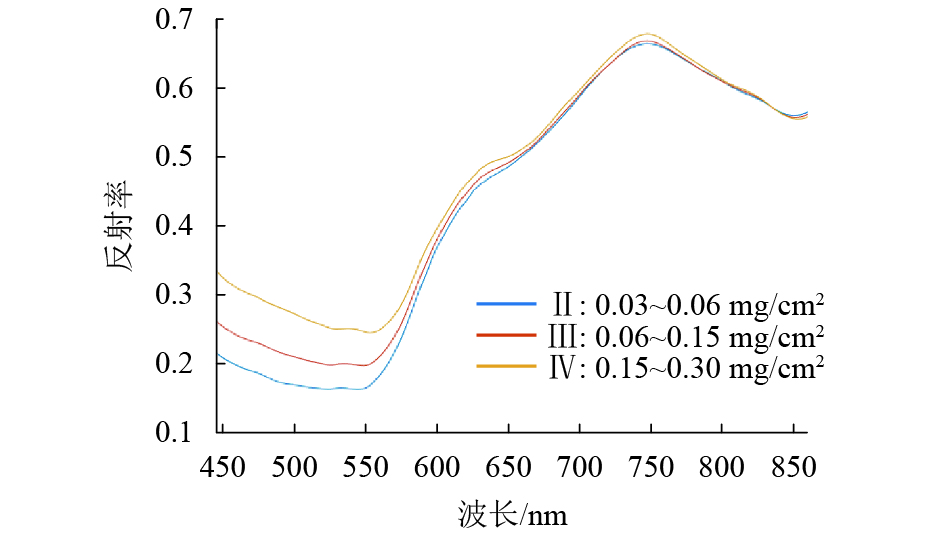
表 1 第Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ级间的SAD值
Table 1. SAD values between the Ⅱ,Ⅲ,and Ⅳ levels
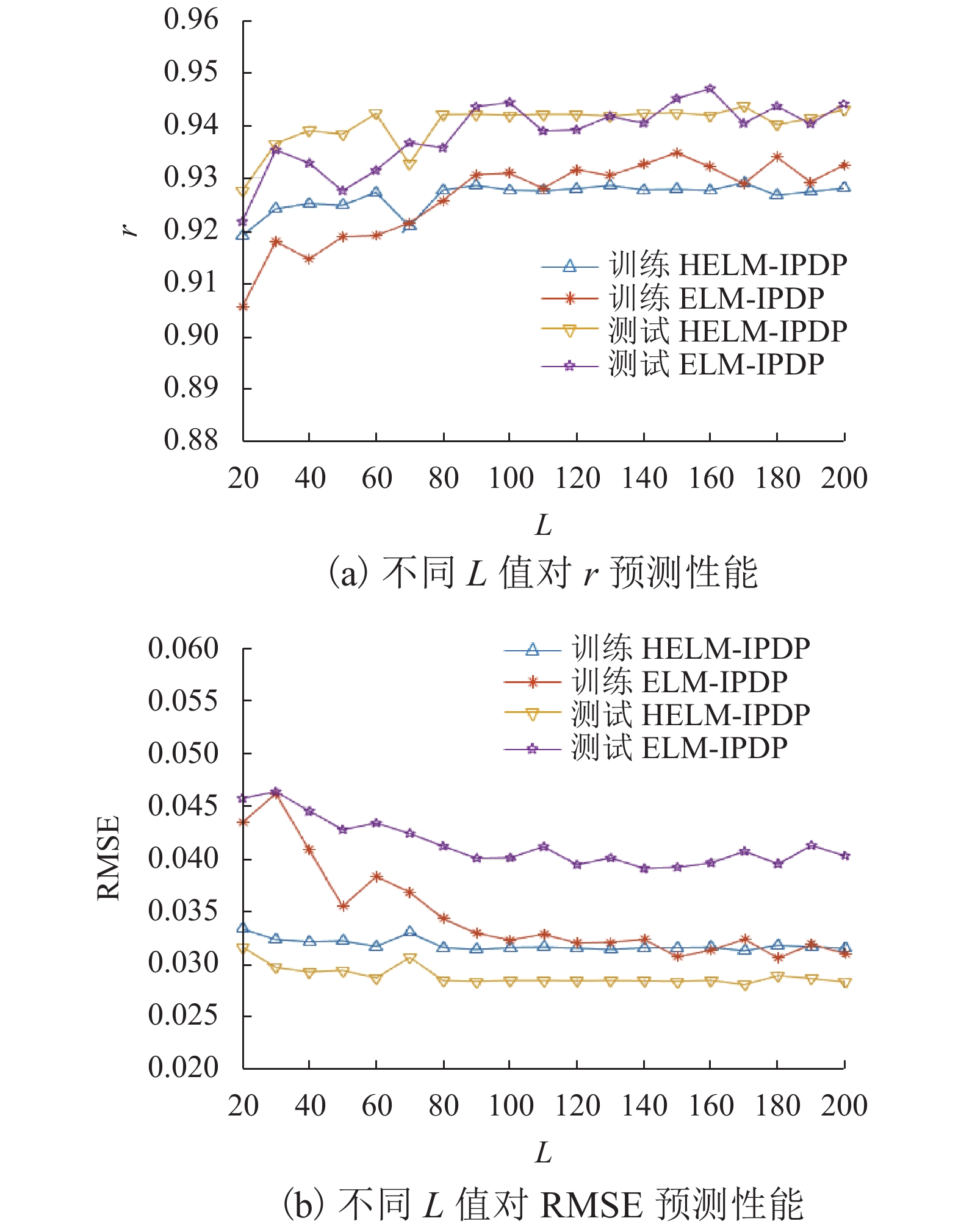
污秽级 第Ⅱ级 第Ⅲ级 第Ⅳ级 第Ⅱ级 0 0.103 7 0.208 4 第Ⅲ级 0.103 7 0 0.104 7 第Ⅳ级 0.208 4 0.104 7 0 表 2 不同训练集样本量下ELM-IPDP和HELM-IPDP模型的预测结果
Table 2. Predicted results of training sets with different train sample sizes for ELM-IPDP and HELM-IPDP models
比值(训练集组数/
测试集组数)ELM-IPDP模型 HELM-IPDP模型 eRMSE-T rT eRMSE-P rP eRMSE-T rT eRMSE-P rP 5∶5 (108/108) 0.035 7 0.909 9 0.044 2 0.927 9 0.031 7 0.919 8 0.035 4 0.921 9 6∶4 (130/86) 0.034 6 0.918 5 0.044 5 0.933 0 0.033 7 0.913 9 0.033 7 0.925 1 7∶3 (151/65) 0.034 3 0.920 6 0.042 5 0.932 8 0.030 0 0.934 6 0.031 2 0.934 8 8∶2 (173/43) 0.034 1 0.921 0 0.042 9 0.932 0 0.031 6 0.927 6 0.028 5 0.942 1 9∶1 (194/22) 0.034 4 0.919 2 0.040 3 0.944 7 0.031 0 0.930 7 0.022 3 0.972 0 注:eRMSE-T 和 eRMSE-P 为训练集和测试集的 RMSE;rT 和 rP 为训练集和测试集的 r. -
汪万平,陈伟根,刘凡,等. 基于泄漏电流特征信息及概率神经网络的绝缘子污秽度预测模型[J]. 高压电器,2017,53(9): 198-203.WANG Wanping, CHEN Weigen, LIU Fan, et al. Con-tamination level forecast model of insulators based on leakage current characteristics and probabilistic neural network[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2017, 53(9): 198-203. 王健,杨志超,葛乐,等. 基于BP神经网络和模糊逻辑的绝缘子污秽等级预测[J]. 南京工程学院学报(自科版),2013,11(4): 17-22.WANG Jian, YANG Zhichao, GE Le, et al. Prediction of insulator pollution severity class based on BP neural network and fuzzy logic[J]. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 11(4): 17-22. 文志科,孔晨华,闵绚,等. 高光谱遥感检测复合绝缘子运行状态技术研究[J]. 高压电器,2014,50(2): 75-79.WEN Zhike, KONG Chenhua, MIN Xuan, et al. Working state detection of composite insulator by hyperspectral remote sensing[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2014, 50(2): 75-79. 黄锋华,张淑娟,杨一,等. 油桃外部缺陷的高光谱成像检测[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(11): 252-259. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2015.11.034HUANG Fenghua, ZHANG Shujuan, YANG Yi, et al. Application of hyperspectral imaging for detection of de-fective features in nectarine fruit[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machine, 2015, 46(11): 252-259. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2015.11.034 岳学军,全东平,洪添胜,等. 柑橘叶片叶绿素含量高光谱无损检测模型[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(1): 294-302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.01.039YUE Xuejun, QUAN Dongping, HONG Tiansheng, et al. Non-destructive hyperspectral measurement model of chlorophyll content for citrus leaves[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(1): 294-302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.01.039 易秋香,黄敬峰,王秀珍. 玉米粗纤维含量高光谱估算模型研究[J]. 红外与毫米波学报,2007,26(5): 393-395. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9014.2007.05.018YI Qiuxiang, HUANG Jingfeng, WANG Xiuzhen. Hyper-spectral estimation models for crude fibre concentration of corn[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2007, 26(5): 393-395. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9014.2007.05.018 张初,刘飞,章海亮,等. 近地高光谱成像技术对黑豆品种无损鉴别[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2014,34(3): 746-750. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2014)03-0746-05ZHANG Chu, LIU Fei, ZHANG Hailiang, et al. Identifi-cation of varieties of black bean using ground based hyperspectral imaging[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2014, 34(3): 746-750. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2014)03-0746-05 贾仕强,刘哲,李绍明,等. 基于高光谱图像技术的玉米杂交种纯度鉴定方法探索[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2013,33(10): 2847-2852. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)10-2847-06JIA Shiqiang, LIU Zhe, LI Shaoming, et al. Study on method of maize hybrid purity identification based on hyperspectral image technology[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2013, 33(10): 2847-2852. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)10-2847-06 李庆利,薛永祺,王建宇,等. 高光谱成像系统在中医舌诊中的应用研究[J]. 红外与毫米波学报,2006,25(6): 465-468. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9014.2006.06.016LI Qingli, XUE Yongqi, WANG Jianyu, et al. Application of hyperspectral imaging system in tongue analysis of tradi-tional chinese medicine[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2006, 25(6): 465-468. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9014.2006.06.016 周霄,高峰,张爱武,等. VIS/NIR高光谱成像在中国云冈石窟砂岩风化状况分布研究中的进展[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2012,32(3): 790-794. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2012)03-0790-05ZHOU Xiao, GAO Feng, ZHANG Aiwu, et al. Advance in the study of the powdered weathering profile of sand-stone on china yungang grottoes based on VIS/NIR hyperspectral imaging[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2012, 32(3): 790-794. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2012)03-0790-05 孙美君,柴勃隆,张冬,等. 基于近红外高光谱技术的敦煌莫高窟壁画起甲病害风险评估方法[J]. 文物保护与考古科学,2016,28(4): 1-8.SUN Meijun, CHAI Bolong, ZHANG Dong, et al. As-sessing the degree of flaking of the murals in the Dunhuang Mogao Grottoes using near-infrared hyper-spectral imaging[J]. Sciences of Conservation and Ar-chaeology, 2016, 28(4): 1-8. 邵瑰玮,付晶,陈怡,等. 基于图谱特征的复合绝缘子老化神经网络评估方法[J]. 高电压技术,2014,40(3): 861-867.SHAO Guiwei, FU Jing, CHEN Yi, et al. Aging assess-ment method of composite insulator using neural network based on image and spectra characteristics[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2014, 40(3): 861-867. 向文祥,王星超,罗洋,等. 复合绝缘子粉化状态非接触检测技术研究[J]. 中国电业(技术版),2015(10): 3-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1140.2015.11.002XIANG Wenxiang, WANG Xingchao, LUO Yang, et al. Research of composite insulator powder status non-contact detection technology[J]. China Electric Power (Technology Edition), 2015(10): 3-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1140.2015.11.002 孙志军,薛磊,许阳明,等. 深度学习研究综述[J]. 计算机应用研究,2012,29(8): 2806-2810. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2012.08.002SUN Zhijun, XUE Lei, XU Yangming, et al. Overview of deep learning[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2012, 29(8): 2806-2810. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2012.08.002 王璨,武新慧,李恋卿,等. 卷积神经网络用于近红外光谱预测土壤含水率[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2018,38(1): 36-41.WANG Can, WU Xinhui, LI Lianqiang, et al. Convolu-tional neural network application in prediction of soil moisture content[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(1): 36-41. HUANG G B, ZHU Q Y, SIEW C K. Extreme learning machine:theory and applications[J]. Neurocomputing, 2006, 70: 489-501. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126 TANG J, DENG C, HUANG G B. Extreme learning machine for multilayer perceptron[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(4): 809-821. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2424995 BECK A, TEBOULLE M A. Fast iterative shrink-age-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems[J]. Siam Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(1): 183-202. doi: 10.1137/080716542 国家电网公司. 电力系统污区分级与外绝缘选择标准: Q/GDW 152—2006[S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2006. 李佐胜,姚建刚,杨迎建,等. 绝缘子污秽等级红外热像检测的视角影响分析[J]. 高电压技术,2008,34(11): 2327-2331.LI Zuosheng, YAO Jiangang, YANG Yingjian, et al. Analysis of visual angle influence on infrared thermal image detecting of insulator contamination grades[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2008, 34(11): 2327-2331. 刘平,马美湖. 基于高光谱技术检测全蛋粉掺假的研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2018,38(1): 246-252.LIU Ping, MA Meihu. Application of hyperspectral technology for detecting adulterated whole egg powder[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(1): 246-252. -




 下载:
下载: