Bionic Design Method for Crane Box Girder Wind Load Reduction Based on Ostracion-Cubicus
-
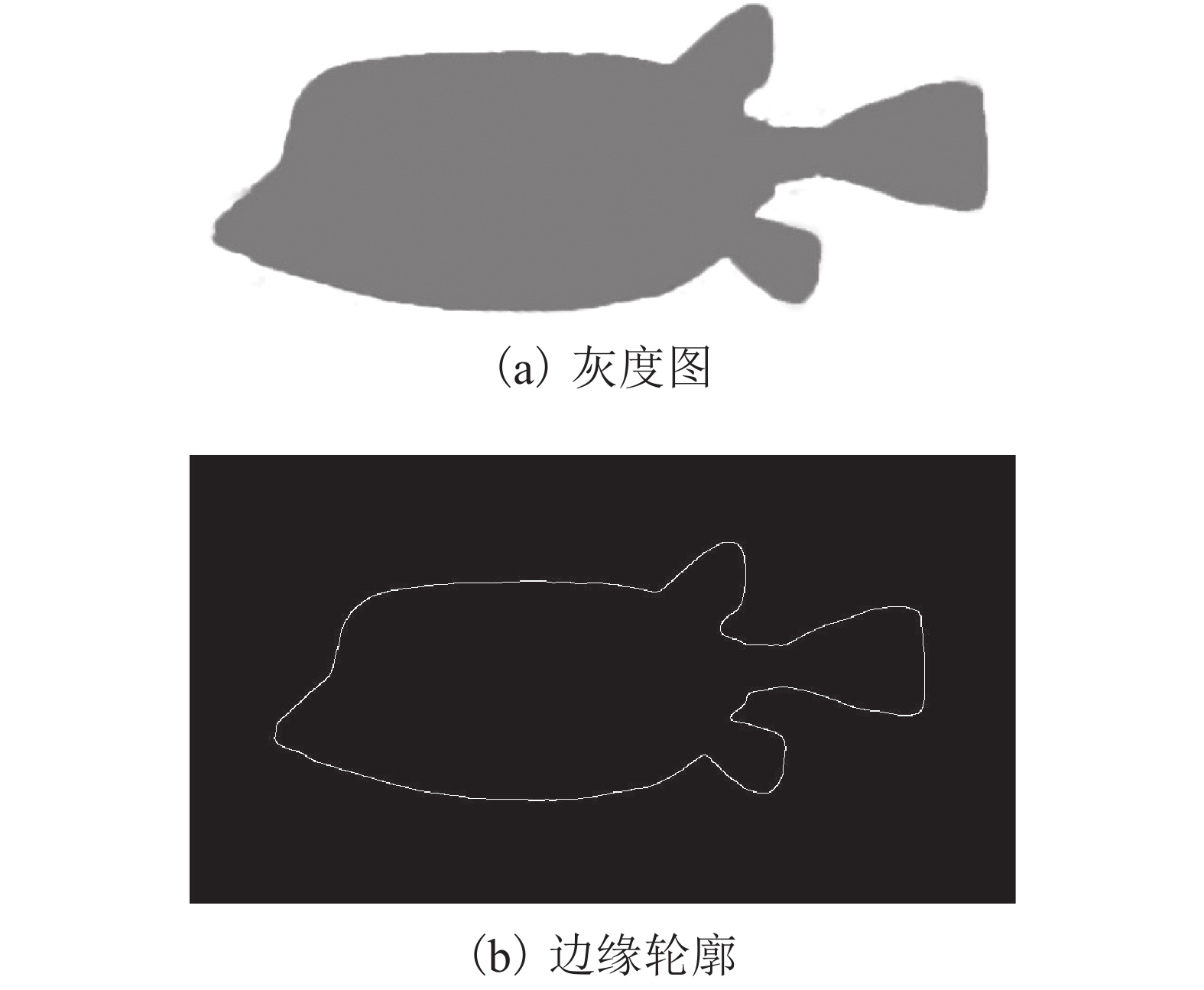
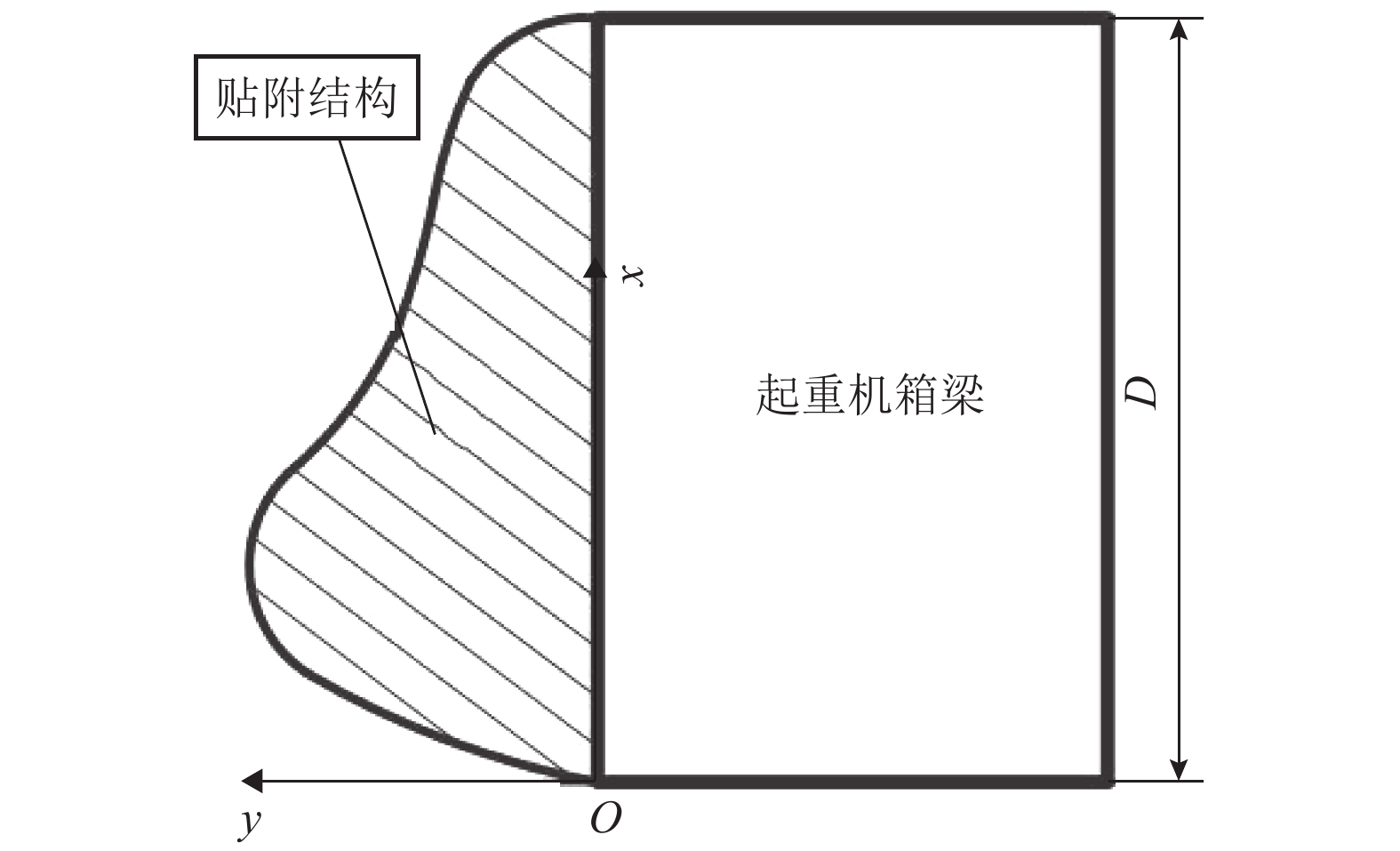
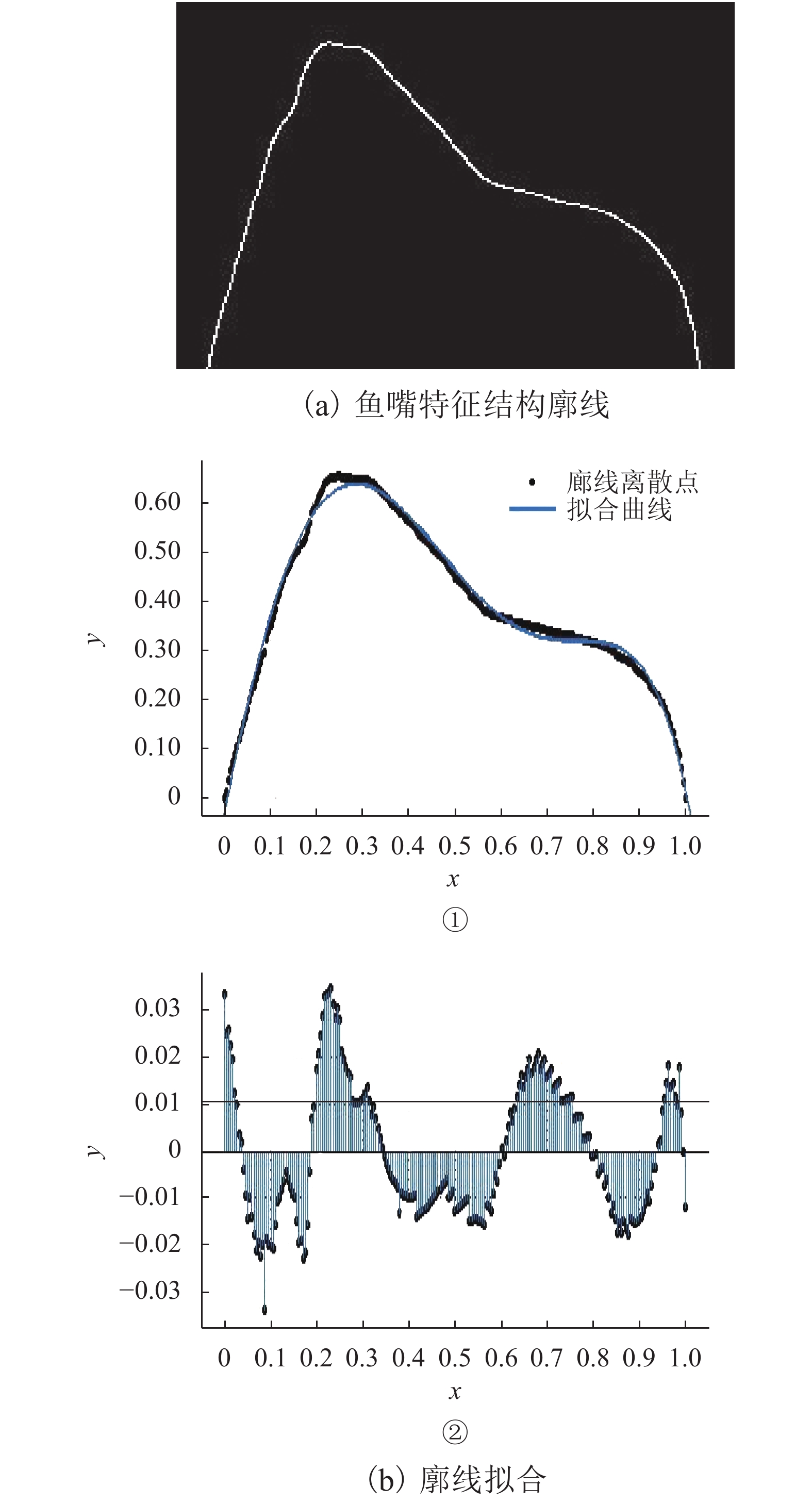
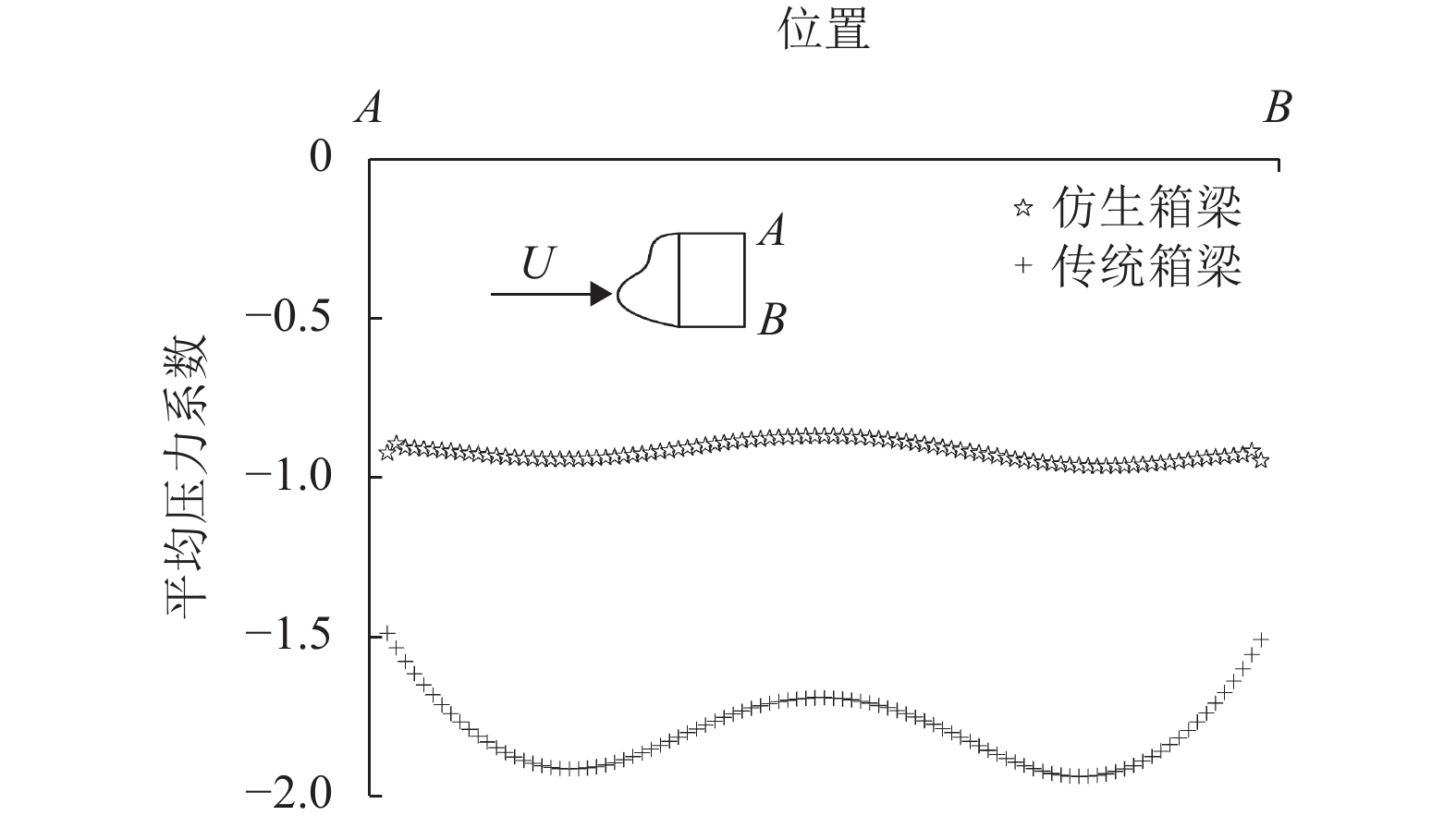
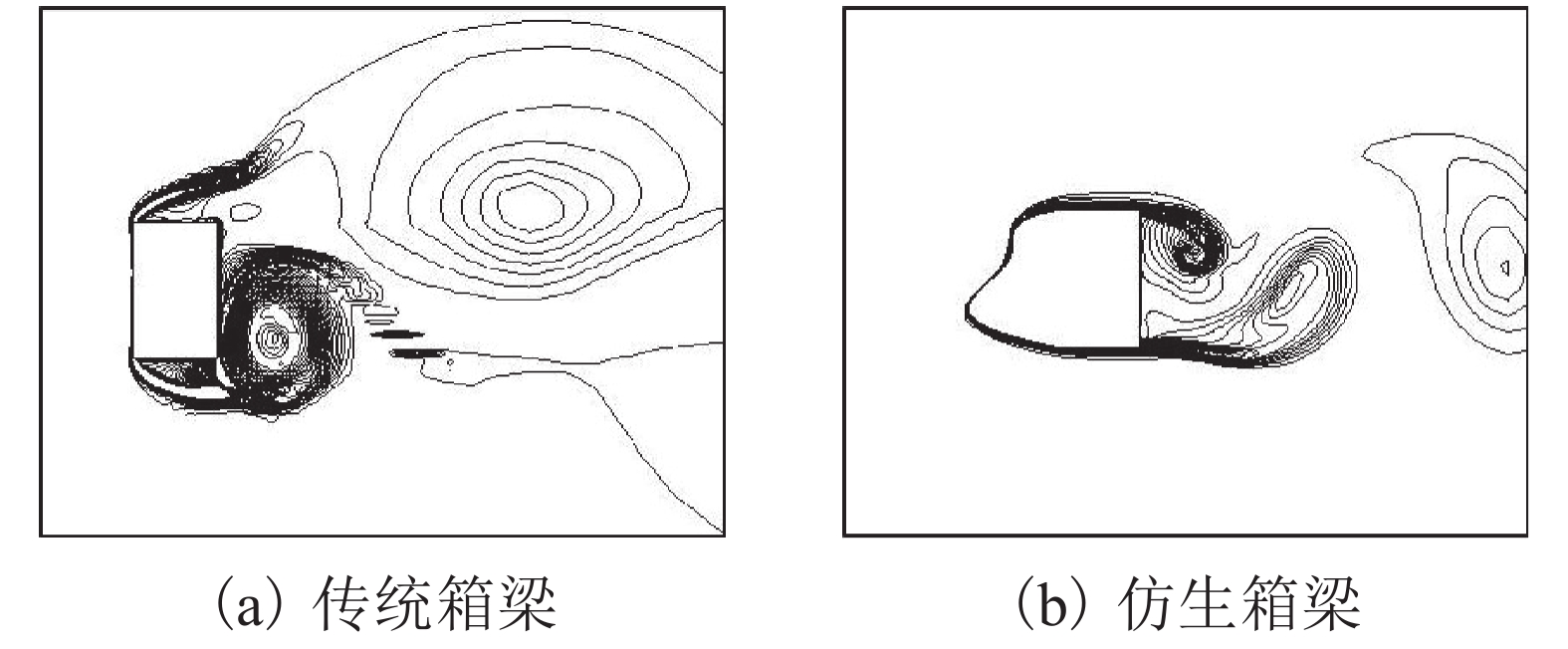
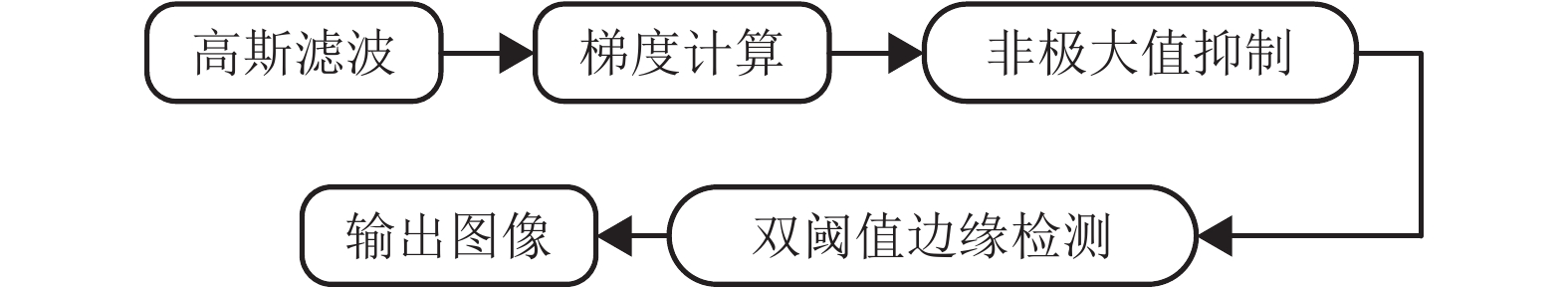
摘要: 风荷载是起重机大车运行时的重要载荷,主梁作为起重机的主要挡风构件,针对主梁的减载设计可以有效地降低起重机运行能耗,本文以粒突箱鲀的结构为启发,探究起重机箱梁风荷载的仿生减载设计方法. 首先运用灰度转换、二值图像转换及边缘检测方法提取箱鲀鱼嘴特征廓线,获得以箱梁特征高度为设计变量的仿生设计模型,然后通过箱梁迎风面附着轻质材料的方式实现传统起重机箱梁的仿生设计,并运用计算流体力学软件(FLUENT)对仿生设计进行评估. 研究结果表明:以某40 t集装箱起重机箱梁为例,采用聚苯乙烯泡沫作为轻质贴附材料的仿生箱梁较传统箱梁结构风阻减小65.77%,而仿生贴附结构仅使箱梁增重2.28%;仿生箱梁的流线外型减轻了由迎风面处边界层分离带来的流场扰动,降低了结构的气动力脉动值,提高了起重机在风场中运行的平稳性.Abstract: The wind load is an important load during the gantry crane operation, and the crane box girder is the major windshield component . Therefore the wind load reduction design for the crane box girder can decrease the crane energy consumption effectively. The bionic design method for the crane box girder wind load reduction based on the geometry of ostracion-cubicus was explored. Firstly, the ostracion-cubicus mouth feature profile was extracted through gray level conversion, binary image conversion and edge detection method. On this basis, a bionic model was built with the box girder height as the design variable. Secondly, the bionic design of the traditional crane box girder was realized by attaching the light material to the windward side of the box girder. Finally, aerodynamic characteristics of the bionic box girder was evaluated with FLUENT. A 40 t container crane was taken as an evaluation case, and comparison was made between the original and the bionic ones, expanded polystyrene (EPS) was selected as the attachment material. The research shows that the wind load decreases by 65.77% with the bionic girder , while the weigh is only 2.28% more than the original one. The flow field disturbance from the boundary layer separation reduces due to the streamlined structure of the bionic girder, which decreases the lift pulsation, improves the running stability of the crane in the wind field.
-
Key words:
- bionics /
- ostracion-cubicus /
- gantry crane /
- wind stress /
- load reduction design
-
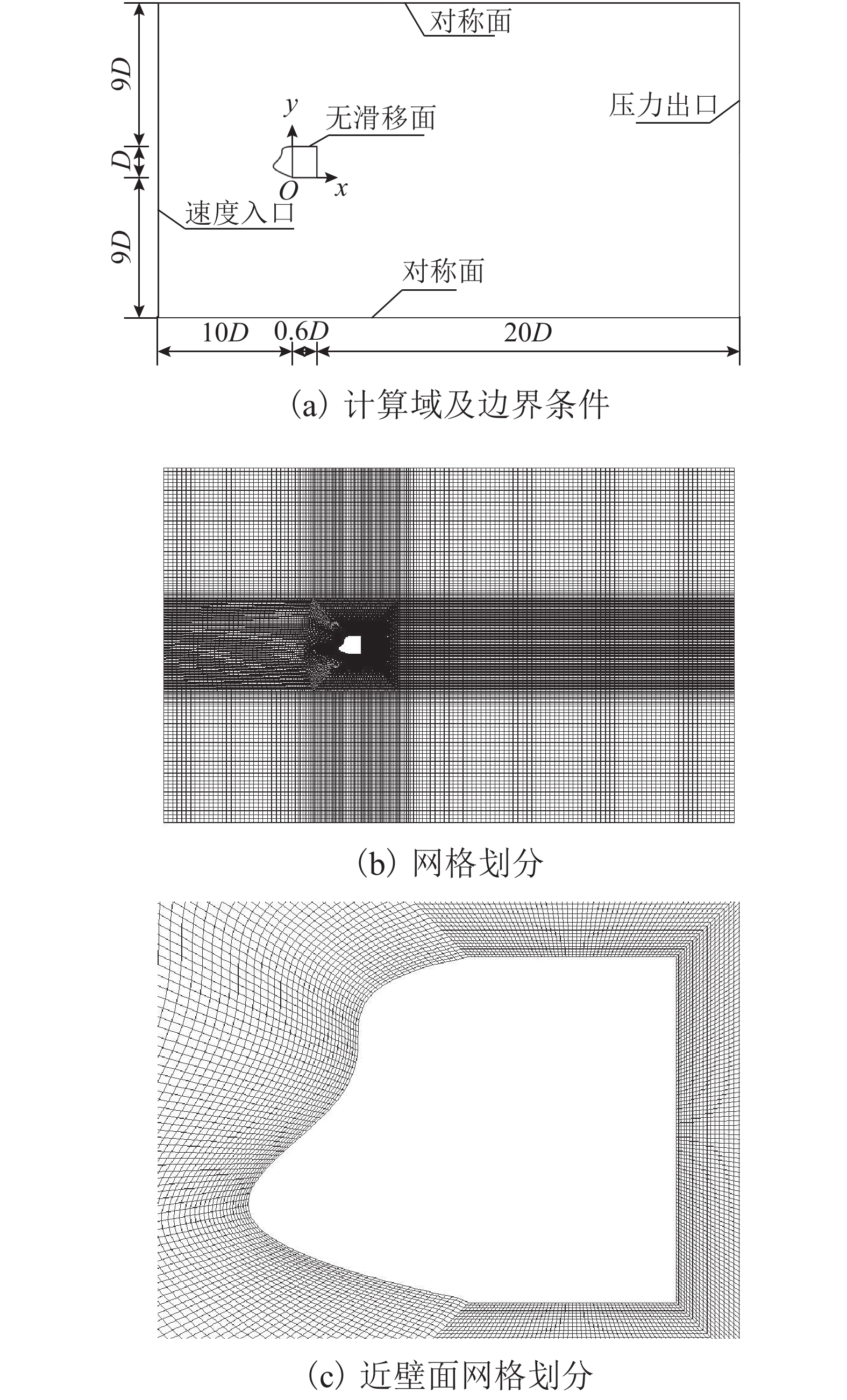
表 1 网格无关性验证
Table 1. Grids independence verification
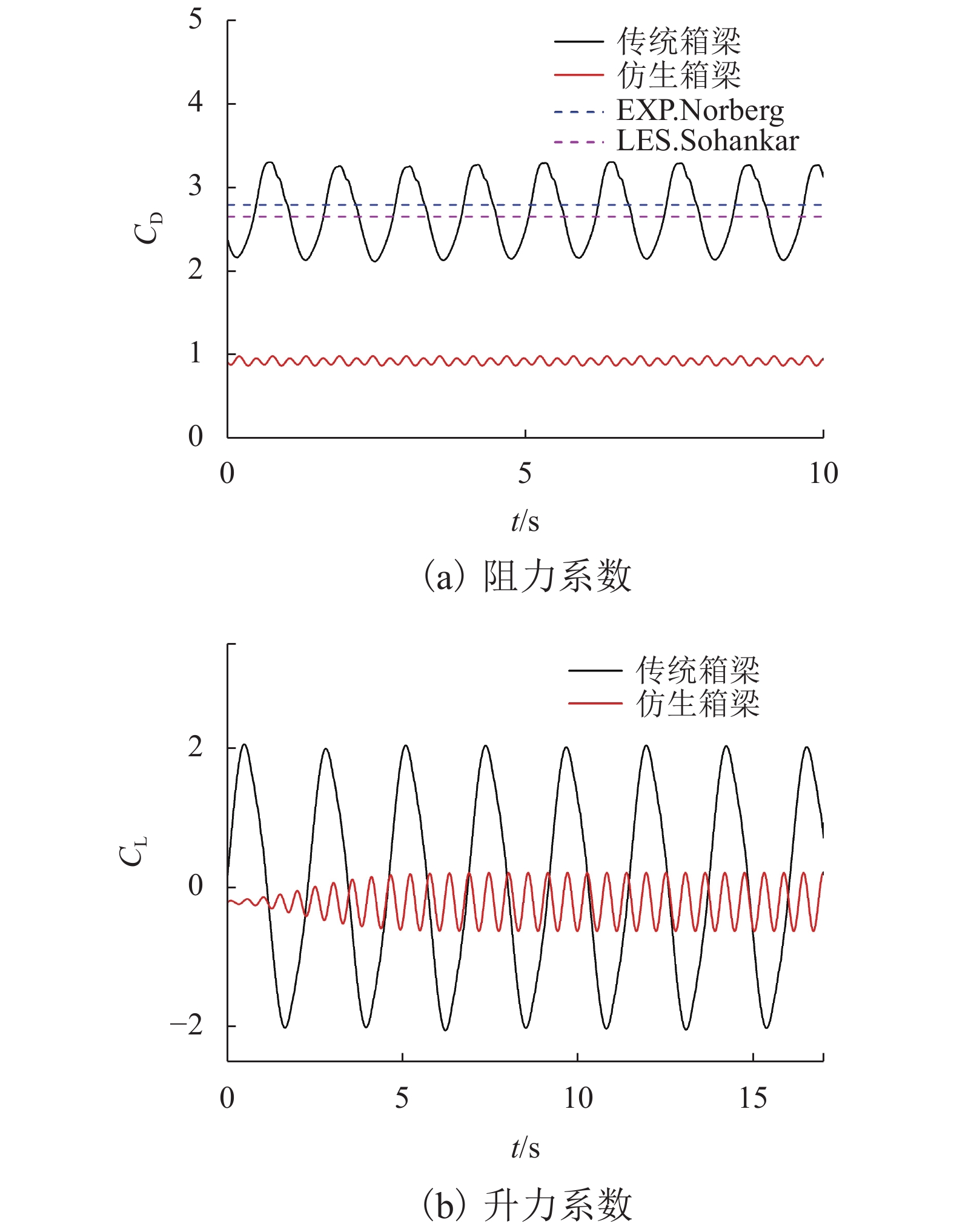
对象 网格精度名称 网格数量/个 平均阻力系数 升力系数均方根 背压系数 EXP.Norberg 2.79~2.82 2.023 LES.Sohankar 2.65 1.192 1.993 传统箱梁 G1 28 632 2.682 1.430 2.169 G2 47 128 2.699 1.458 2.167 G3 65 424 2.742 1.455 2.215 仿生箱梁 G1 28 040 1.210 0.535 1.146 G2 48 124 0.935 0.366 0.871 G3 72 144 0.966 0.353 0.913 表 2 箱梁风载荷
Table 2. Wind loads of crane box girder
对象 迎风面积/m2 重量/kg 风荷载/kN 阻力系数均方根 升力系数均方根 扭矩系数均方根 传统箱梁 80 27 361.00 13.24 2.694 1.458 1.399 仿生箱梁 80 27 998.44 4.53 0.936 0.366 0.214 减载比/% 2.28 −65.77 −65.26 −74.90 −84.70 -
ROSS B, MCDONALD B, SARAF S. E. V. Big blue goes down. the miller park crane accident[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2007, 14(6): 942-961. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2006.12.002 MCCARTHY P, SODERBERG E, DIX A. Wind damage to dockside cranes: recent failures and recommendations[C]//Technical Council on Lifeline Earthquake Engineering Conference. Oakland: ASCE, 2009, 357: 518-526. VOISIN D, GRILLAUAD G, SOLLIEC C, et al. Wind tunnel test method to study out-of-service tower crane behavior in storm winds[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics, 2004, 92(7/8): 687-697. 项海帆. 现代桥梁抗风理论与实践[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2005: 1-6. 朱小海,程文明,罗鹏. 基于CFD的大型门式起重机风载特性研究[J]. 机械设计,2014,31(8): 83-87.ZHU Xiaohai, CHENG Wenming, LUO Peng. CFD based study on wind-load characteristics of large gantry crane[J]. Journal of Machine Design, 2014, 31(8): 83-87. 吴学阳,程文明,王玉璞,等. 基于数值模拟的双箱梁起重机风载荷研究[J]. 机械设计与制造,2016(2): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2016.02.001WU Xueyang, CHENG Wenming, WANG Yupu, et al. Wind loading analysis of double box girder structured cranes based on numerical simulation[J]. Machinery Design&Manufacture, 2016(2): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2016.02.001 CHENG Wenming, FU Weigang, ZHANG Zeqiang, et al. The bionic lightweight design of the mid-rail box girder based on the bamboo structure[J]. Przeglad Elektrotechniczny, 2012, 88(9B): 113-117. 付为刚,程文明,濮德璋,等. 参数变化对简支斜板屈曲承载力的影响规律[J]. 华南理工大学学报,2013,41(3): 108-115.FU Weigang, CHENG Wenming, PU Dezhang, et al. Influence law of varying parameters on buckling bearing capacity of simply-supported skew plates[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology, 2013, 41(3): 108-115. 付为刚,程文明,王弘,等. 起重机上翼缘仿生简支板的局部稳定性分析[J]. 计算机仿真,2012,29(8): 396-400. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2012.08.095FU Weigang, CHENG Wenming, WANG Hong, et al. Local stability analysis of bionic simple supported plate for crane’s top flange[J]. Computer Simulation, 2012, 29(8): 396-400. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2012.08.095 REN Yangzhi, CHENG Wenming, Wu Xiao, et al. Torsional-flexural buckling of unevenly battened columns under eccentrical compressive loading[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2016, 142(1): 1-15. 付为刚,程文明,于兰峰,等. 正轨箱梁横向肋的竹子结构仿生学设计[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2013,48(2): 211-216. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.02.004FU Weigang, CHENG Wenming, YU Lanfeng, et al. Bionics design of transverse stiffener in the upright rail box girder based on bamboo structure[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013, 48(2): 211-216. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.02.004 HOU Minfeng, FU Liming. On auto bionic modeling design study based on cognitive psychology theories[C]//International Conference on Mechatronic Science. Jilin: IEEE, 2011: 1641-1644. CANNY J. A computational approach to edge detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1986, 8(6): 679-698. 罗文婷,李中轶,李林,等. 基于改进Canny算法的道路标线自动识别及定位[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2018,53(6): 1253-1260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.06.022LUO Wenting, LI Zhongyi, LI Lin, et al. Automated lane marking identification based on improved Canny edge detection algorithm[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(6): 1253-1260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.06.022 SHIH T H, LIOU W W, SHABIR A, et al. A new κ-ε eddy viscosity model for high Reynolds number turbulent flows[J]. Computers Fluids, 1995, 24(3): 227-238. doi: 10.1016/0045-7930(94)00032-T NORBERG C. Flow around rectangular cylinders:pressure forces and wake frequencies[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics, 1993, 49(1/2/3): 187-196. NAKAGUCHI H, HASHIMOTO K, MUTO S. An experimental study on aerodynamic drag of rectangular cylinders[J]. Japan Soc. Aeronaut. Space Sci., 1968, 16: 1-5. SOHANKAR A. Large eddy simulation of flow past rectangular-section cylinders:side ratio effects[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics, 2008, 96(5): 640-655. -




 下载:
下载: