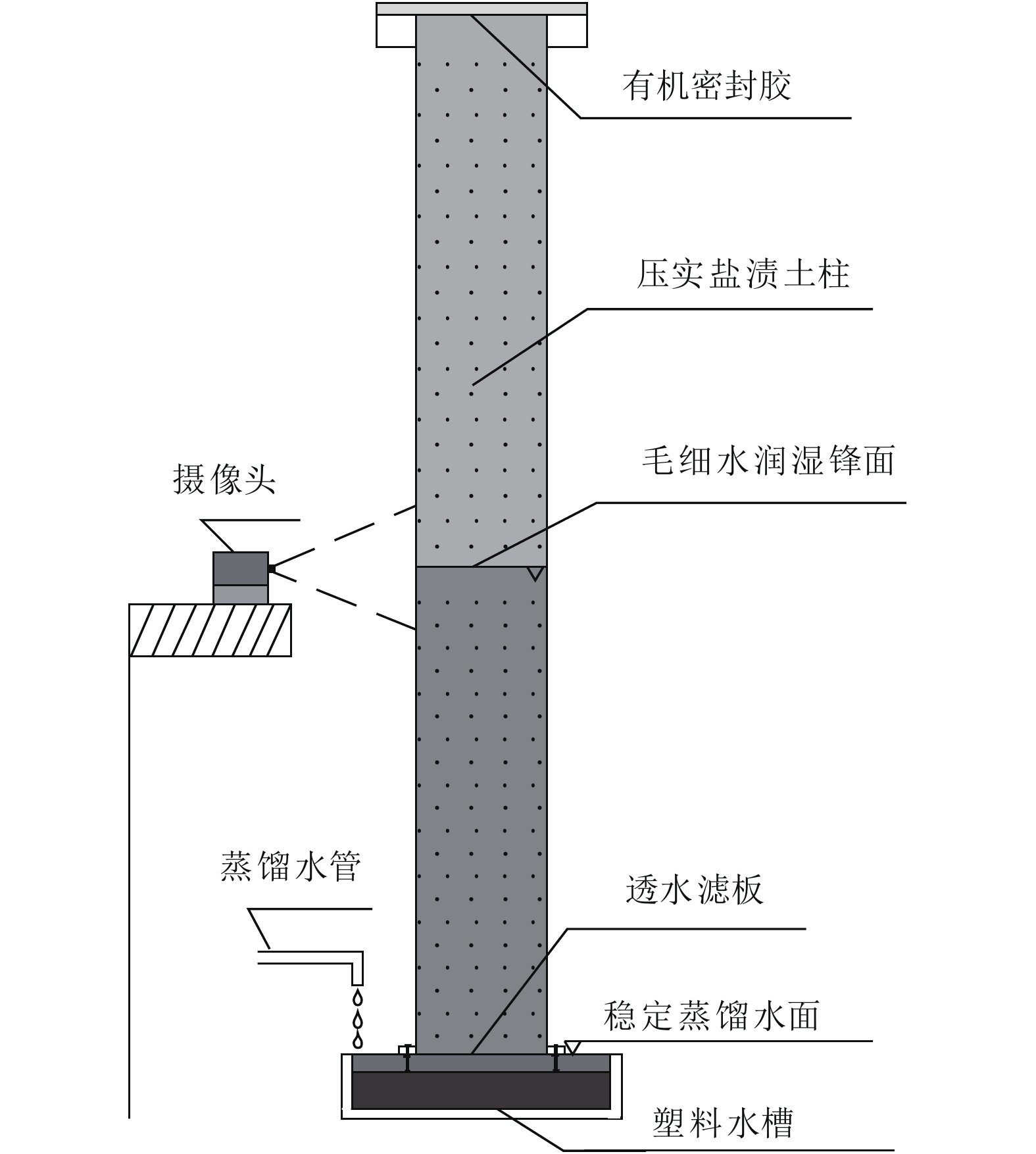
Gradation of Subgrade Soil and Its Salt-Resistance Effect in Salt Lake Area in Qinghai
-
摘要: 青海盐湖地区的路基工程处于隐蔽性盐风化作用强烈的寒旱岩土环境. 分别采取青海茶卡盐湖地区工程建设层天然盐渍土土样和已建路基结构土层土样,研究青海盐渍土地区路基结构防护盐风化作用的效果. 通过易溶盐含量测定、颗粒分析实验和毛细管水上升实验,对青海茶卡盐渍土区路基结构土层中的毛细管水上升最大高度开展理论计算. 研究表明:青海茶卡地区盐渍土中毛细水上升高度大于一般土中毛细水上升高度,细粒组(0.250~0.075 mm)含量有利于水盐运移上升,粗粒组(> 0.250 mm)含量不利于水盐运移上升;在水盐运移和汽盐运移双重作用下,茶卡盐渍土地区路基结构土层均出现次生盐渍化现象,建议在茶卡盐渍土地区的路基工程中,设置卵砾石阻盐隔断层的粒组级配范围控制在2.0~5.0 mm之间,该粒组含量大于75%,厚度在300.0~1000.0 mm为宜;阻盐隔断层的设置位于路堤上部,高于一般路基规范中规定的高度,可以提高阻止水盐运移上升、增强汽盐淋滤作用的效果.Abstract: A subgrade project in Qinghai salt lake area, China was in a cold and dry geotechnical environment with strong concealed salt weathering. Taking the natural saline soil samples of the above subgrade construction project and soil samples of the built subgrade structure in Chaka Salt Lake area of Qinghai, comparative tests were conducted to study the effect of the subgrade structure protection against salt weathering in the saline soil area of Qinghai province. On the basis of soluble salt content measurements, particle analysis and capillary water rising experiment, the maximum height of capillary water rising in subgrade soil layer in Chaka saline soil area was calculated theoretically. The results indicate that the rising height of capillary water in the saline soil was higher than that in the general soil; the content of fine grains (0.250–0.075 mm) was conducive to the increase of water and salt migration, while the content of coarse grains (> 0.250 mm) would inhibit water and salt migration. Under the dual action of water and salt migration and vapor salt migration, secondary salinization occurred in the subgrade soil layer of Chaka saline soil area. It was suggested to set up the gravel salt-blocking layer in the subgrade project of the Chaka saline land area; the grading range of particles should be controlled between 2.0 and 5.0 mm, and the fraction of grains in this size range should be greater than 75%, while the thickness of the gravel salt-blocking layer should be between 300.0 and 1000.0 mm. Besides, the location of the blocking layer should be on the upper part of the embankment, higher than the height specified in the general subgrade code, which can improve the effect of preventing the movement of water-salt and enhancing the effect of vapor-salt leaching.
-
表 1 研究区盐渍土易溶盐含量
Table 1. Soluble salt content in saline soil of chaqia lake
取样深
度/mCl−/
(mol•kg−1)SO42−/
(mol•kg−1)离子比 含盐
量/%盐渍
土类0 24 12.0 1.000 0.42 A 0.2 24 25.2 0.476 0.55 B 0.4 16 25.6 0.313 0.52 B 0.6 28 34.8 0.402 0.70 B 0.8 16 45.0 0.178 0.78 C 1.0 28 18.0 0.778 0.51 B 1.2 16 12.8 0.625 0.36 B 1.4 20 12.4 0.806 0.32 B 1.7 12 18.4 0.326 0.42 B 2.0 16 12.4 0.645 0.34 B 2.3 12 86.8 0.069 1.33 C 2.6 16 36.0 0.222 0.64 C 3.0 20 70.4 0.142 1.18 C 注:A为亚氯盐渍土;B为亚硫酸盐渍土;C为硫酸盐
渍土.表 2 研究区盐渍土的毛细管实验土样粒级配情况
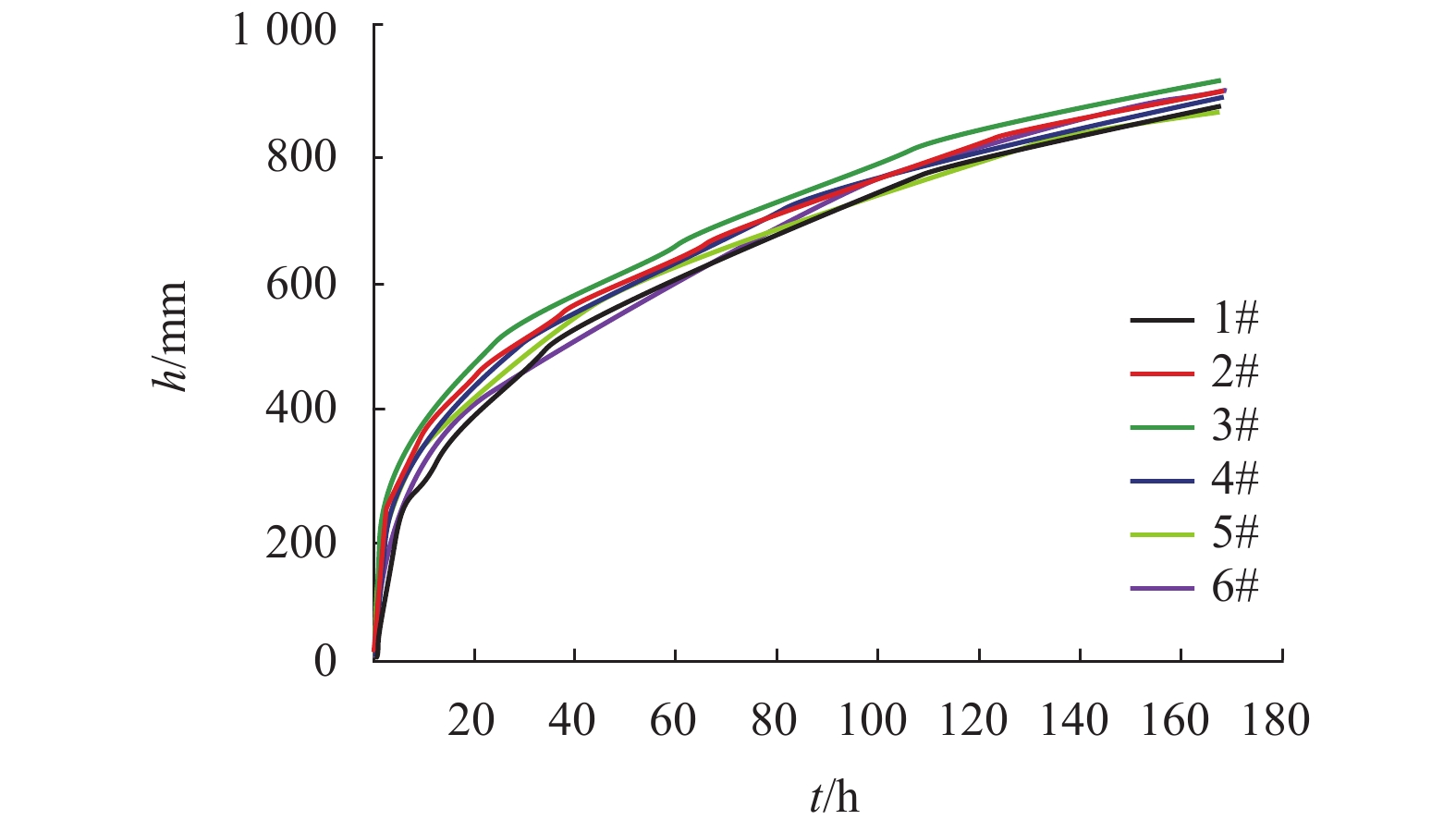
Table 2. Grading of soil samples in capillary experiment of saline soil in the study area
试验编号 粒组的含量/% 装土质量/g 含水
率/%(2.000~
0.250] mm
(粗粒组)(0.250~
0.100] mm
(中粒组)(0.100~
0.075] mm
(细粒组)1# 75 25 1783 0.2 2# 75 25 1812 0.2 3# 25 75 1833 0.2 4# 75 25 1866 0.2 5# 50 25 25 1877 0.2 6# 25 50 25 1880 0.2 表 3 路基结构层级配粒径及参数
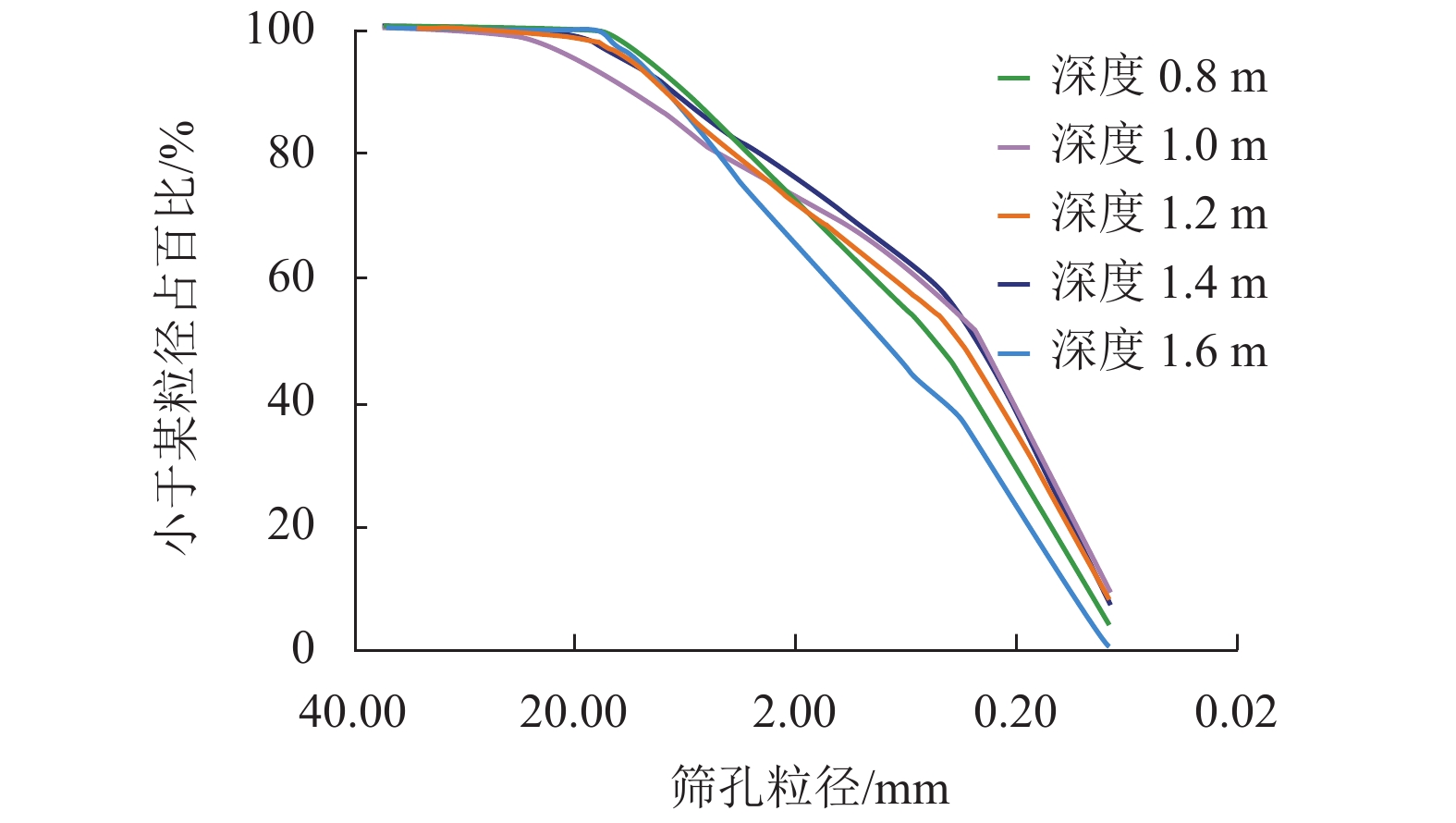
Table 3. Characteristic particle sizesand parameters of subgrade soil layer at different depths
取样深
度/md60/mm d30/mm d10/mm Cu Cc 0.2 0.360 0.150 0.066 5.455 0.947 0.4 0.850 0.210 0.120 7.083 0.432 0.6 0.480 0.164 0.086 5.581 0.652 0.8 0.460 0.160 0.087 5.287 0.640 1.0 0.260 0.140 0.084 3.095 0.897 1.2 0.260 0.140 0.080 3.250 0.942 1.4 0.280 0.140 0.080 3.500 0.875 1.6 0.600 0.160 0.082 7.317 0.520 1.8 0.460 0.138 0.080 5.750 0.518 2.0 0.470 0.165 0.086 5.465 0.674 2.2 0.480 0.165 0.087 5.517 0.652 2.4 0.620 0.148 0.086 7.209 0.411 2.6 0.270 0.126 0.075 3.600 0.784 表 4 路基结构土层级配及水盐运移上升高度计算结果
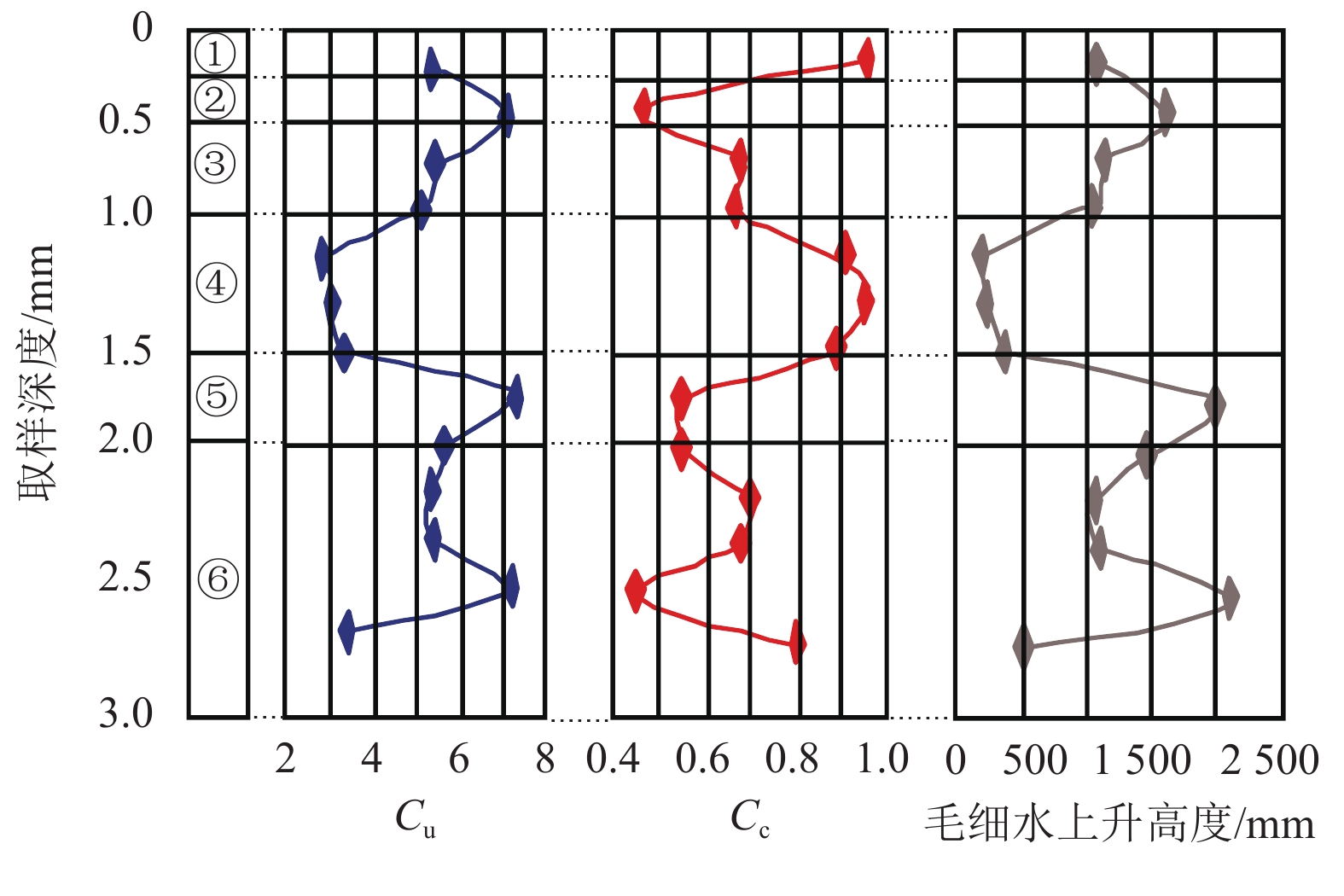
Table 4. Calculation results of soil gradation and rise height of water and salt migration in subgrade soil layers
路基结构层 取样深度/m d60/mm d30/mm d10/mm Cu h/mm ① 0.2 0.360 0.150 0.066 5.455 989.3 ② 0.4 0.850 0.210 0.120 7.083 1521.7 ③ 0.6 0.480 0.164 0.086 5.581 1047.3 0.8 0.460 0.160 0.087 5.287 957.1 ④ 1.0 0.260 0.140 0.084 3.095 92.2 ⑤ 1.2 0.260 0.140 0.080 3.250 136.7 1.4 0.280 0.140 0.080 3.500 258.5 1.6 0.600 0.160 0.082 7.317 1907.7 1.8 0.460 0.138 0.080 5.750 1377.8 ⑥ 2.0 0.470 0.165 0.086 5.465 979.4 2.2 0.480 0.165 0.087 5.517 1012.5 2.4 0.620 0.148 0.086 7.209 2022.1 2.6 0.270 0.126 0.075 3.600 427.2 表 5 研究区开挖路基结构土层含盐量
Table 5. Salt content of subgrade soil in chaqia lake
路基
结构层取样深度/m Cl−/
(mol•kg−1)SO42−/
(mol•kg−1)离子比 含盐
量/%盐渍土类型 ① 0.2 2 1.13 0.89 0.55 A ② 0.4 1.6 0.55 1.44 0.52 A ③ 0.6 1.6 1.32 0.60 0.70 A 0.8 5.4 7.46 0.36 0.78 A ④ 1.0 6.2 10.37 0.30 0.71 A 1.2 145 50.08 1.45 1.57 A 1.4 39 34.77 0.56 0.74 B ⑤ 1.6 31.8 35.89 0.44 0.71 B 1.8 3.2 20.40 0.80 0.33 B ⑥ 2.0 62.1 43.67 0.71 1.00 B 2.2 89 48.28 0.92 1.19 B 2.4 17.4 14.11 0.62 0.32 B 2.6 83 48.29 0.86 1.17 B -
BUI E. Soil salinity:a neglected factor in plant ecology and biogeography[J]. Journal of Arid Environ-Ments, 2013, 92: 14-25. 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 公路路基设计规范∶ JTG D30—2015 [S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社股份有限公司, 2015. SINITSYN AO, LØSET S. Problems of construction on saline silts[J]. Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engin-eering, 2011, 48(5): 196-202. SOZHAN G, RENGARAJAN B, GOPALACHARI V. Effect of chlorate on pitting corrosion of 316 and 304 stainless steel weldments[C]//Meeting abstracts. The Electrochemical Society (United States). San Francisco: IEEE, 2009: 1715-1715. PFLETSCHINGER H, PROMMEL K, SCHUTH C, et al. Sensitivity of vadose zone water fluxes to climate shifts in arid settings[J]. Vadose Zone Journal, 2014, 13(1): 246-250. AKSENOV V I, KAL’BERGENOV R G, LEONOV A R. Strength characteristics of frozen saline soils[J]. Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, 2003, 40(2): 55-59. doi: 10.1023/A:1024436118466 ROGOBETE G, GROZAV A, TARAU D. Solute transport[J]. Swelling and shrinking in salt-affected soils Science, 2011(43): 166-173 MIRONOV V L, KOMAROV S A, KLESHCHENKO V N. Microwave dielectric spectroscopy for bound water in saline soil[C]//Proceedings. 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Seoul: IEEE, 2005: 3196-3199. 王兆东,张雷. 盐渍土对路基的危害及防治[J]. 辽宁交通科技,2005(1): 35-37.WANG Zhaodong, ZHANG Lei. Harmfulness of salty soil to subgrade and its preventing and treating[J]. Northern Communications, 2005(1): 35-37. 乔宏霞, 王鹏辉, 李元可, 等. 基于Wienen退化对镁水泥混凝土中钢筋的锈蚀预测[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2019, 54(6): 1252-1257.QIAO Hongxia, WANG Penghui, LI Yuanke, et al. Corrosion prediction of coated steel in magnesium cement concrete based on Wiener degradation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(6): 1252-1257. 苏成光, 刘丹, 赵坪锐, 等. 道床板钢筋锈蚀的细观力学影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2020, 52(2): 273-281.SU Chengguang, LIU Dan, ZHAO Pingrui, et al. Meso-mechanical effect of track slab rebar corrosion[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(2): 273-281. FREDLUND D G, XING A Q, HUANG S Y. Predicting the permeability function for unsaturated soils using the soil-water characteristic curve[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Engineering, 1994, 31(4): 533-546. doi: 10.1139/t94-062 XING A Q, FREDLUND D G. Equations for the soil-water characteristic curve[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1994, 31(4): 52l-532. FREDLUND M D, FREDLUND D G, WILSON G W. Prediction of the soil-water characteristic curve from grain size distribution and volume-mass properties[C]// Proceedings of the Third Brazilian Symposium on Unsaturated Soils. Rio de Janeiro: Springer, 1997: 13-23 EVERETT D H. The thermodynamics of frost damage to porous solids[J]. Ransactions of the Faraday Sicuety, 1961, 57(5): 1541-1551. 张平,吴昊,殷洪建,等. 颗粒级配对毛细管水上升影响的研究[J]. 节水灌溉,2010(7): 24-26.ZHANG Ping, WU Hao, YIN Hongjian, et al. Effect of particle size distribution on capillary water upward movement[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2010(7): 24-26. 魏凯,张文,刘昕,等. 青海东部盐渍土颗粒级配对毛细管水上升影响的研究[J]. 青海大学学报(自然科学版),2016,34(3): 1-8.WEI Kai, ZHANG Wen, LIU Xin, et al. Effects of particle size distribution on capillary water upward movement in saline soil of Eastern Qinghai area[J]. Journal of Qinghai University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 34(3): 1-8. 金培杰,戴玉. 南疆铁路库喀段盐渍土路基病害与防治措施研究[J]. 路基工程,2006(1): 116-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2006.01.044JIN Peijie, DAI Yu. Research on salinized soil subgrade disease and control measures in kuqa section of southern Xinjiang railway[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2006(1): 116-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2006.01.044 谌文武,董兰凤. 公路盐渍土路基处理与病害防治[J]. 天津城建大学学报,1999(1): 61-65.CHEN Wenwu, DONG Lanfeng. Highway roadbed treatment and disaster prevention in the salty soil region[J]. Journal of Tianjin Chengjian University, 1999(1): 61-65. 赵中党. 天然级配卵砾石土毛细水隔断厚度的研究[J]. 铁道工程学报,1992(2): 51-54.ZHAO Zhongdang. Study on capillary water partition thickness of natural graded gravel soil[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 1992(2): 51-54. 王丁,费良军. 层状土壤上升毛管水运移特性试验研究[J]. 地下水,2009,31(1): 35-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2009.01.010WANG Ding, FEI Liangjun. Rising capillary water transported characteristics of layered soil[J]. Groundwater, 2009, 31(1): 35-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2009.01.010 何克瑾,费良军,尹娟. 均质土壤上升毛管水运动特性试验[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报,2007,38(4): 581-585. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2007.04.030HE Kejin, FEI Liangjun, YI Juan. Rising capillary water transport characteristics of homogeneous soil[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2007, 38(4): 581-585. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2007.04.030 陈先华, 马丽莉, 杨国涛, 等. 寒区高铁沥青混凝土基床表层的温度场特性[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2019, 54(6): 1196-1202.CHEN Xianhua, MA Lili, YANG Guotao, et al. Temperature field characteristics of high-speed railway subgrade surface with asphalt concrete layer in cold regions[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(6): 1252-1257. 虞卫国,房建宏. 盐渍土中固相相态变化规律的研究[J]. 公路工程,2013,38(4): 94-98.YU Weiguo, FANG Jianhong. Study on solid phases change regularities of saline soil[J]. Highway Engineering, 2013, 38(4): 94-98. 王明甫,李玉坤. 酒泉地区盐渍土地基处理措施及工程特性研究[J]. 山西建筑,2013,39(30): 79-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2013.30.041WANG Mingfu, LI Yukun. Research on salinized soil foundation treatment measures and engineering characteristics in Jiuquan region[J]. Shanxi Architecture, 2013, 39(30): 79-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2013.30.041 YU W G, FANG J H. Study on the phase change law of solid state in saline soil[J]. Ighway Engineering, 2013, 38(4): 94-98. SHI W, SHEN B, WANG Z, et al. Water and salt transport in sand-layered soil underevaporation with the shallow under ground water table[J]. Ransactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2005, 21(9): 23-26. ODONG J. Evaluation of empirical formulae for determination of hydraulic conductivity based on grain-Size analysis[J]. The Journal of American Science, 2007, 3(4): 105-113. LI S G. Special report on the code for design of railway special soil subgrade:a discussion on the formula for calculating the strong rising height of capillary water in salted land[J]. Ubgrade Engineering, 1989(5): 83-90. 杨仲全. 盐渍土地区路基隔断层设置研究[J]. 中国水运,2012,12(11): 218-220.YANG Zhongquan. Study on the setting of subgrade partition in saline soil area[J]. China Water Transport, 2012, 12(11): 218-220. -





 下载:
下载: