Effect of Brace-to-Chord Angle on Performance of Unstiffened Circular Hollow Section X-Joints under Brace Axial Force
-
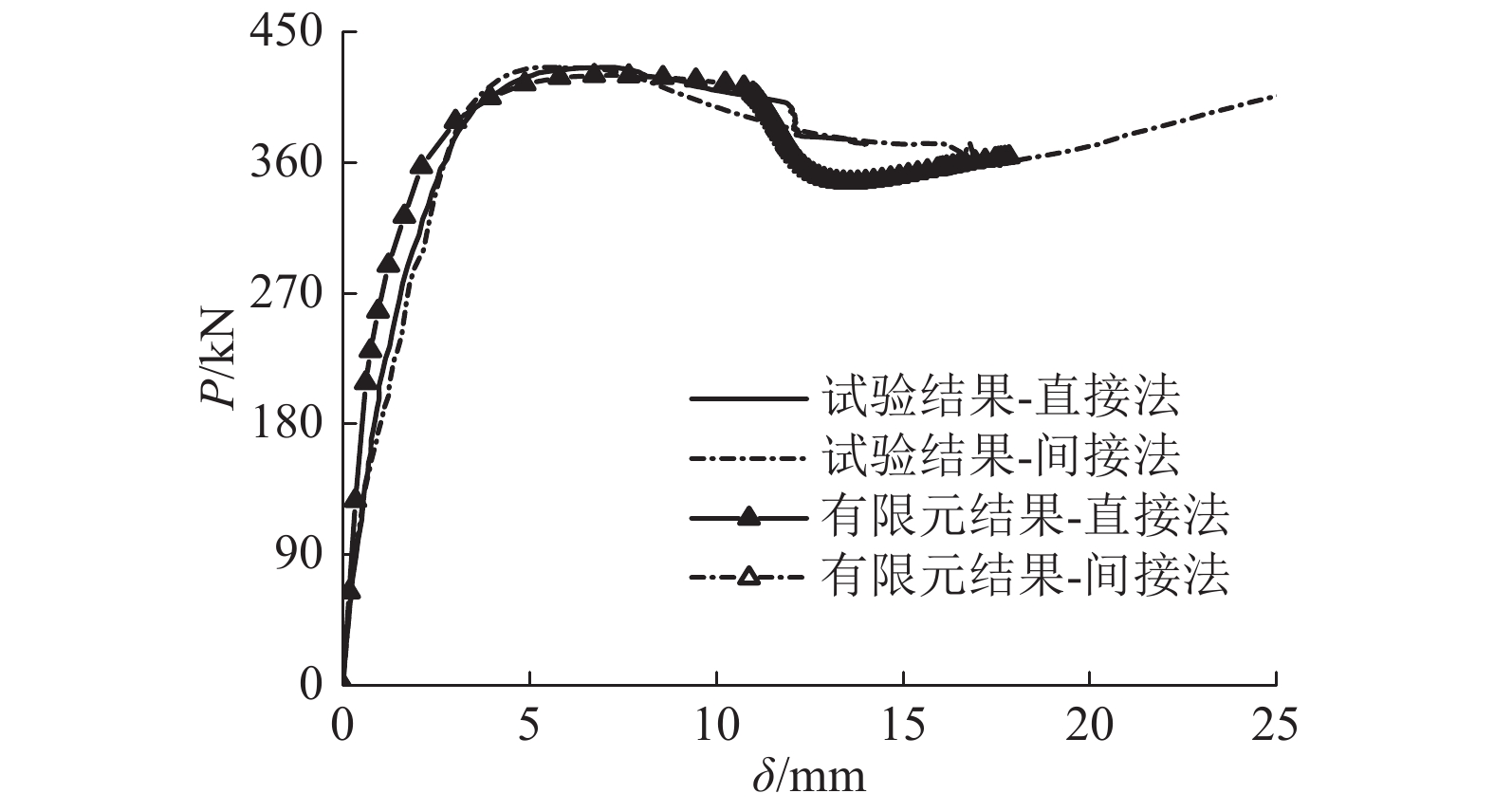
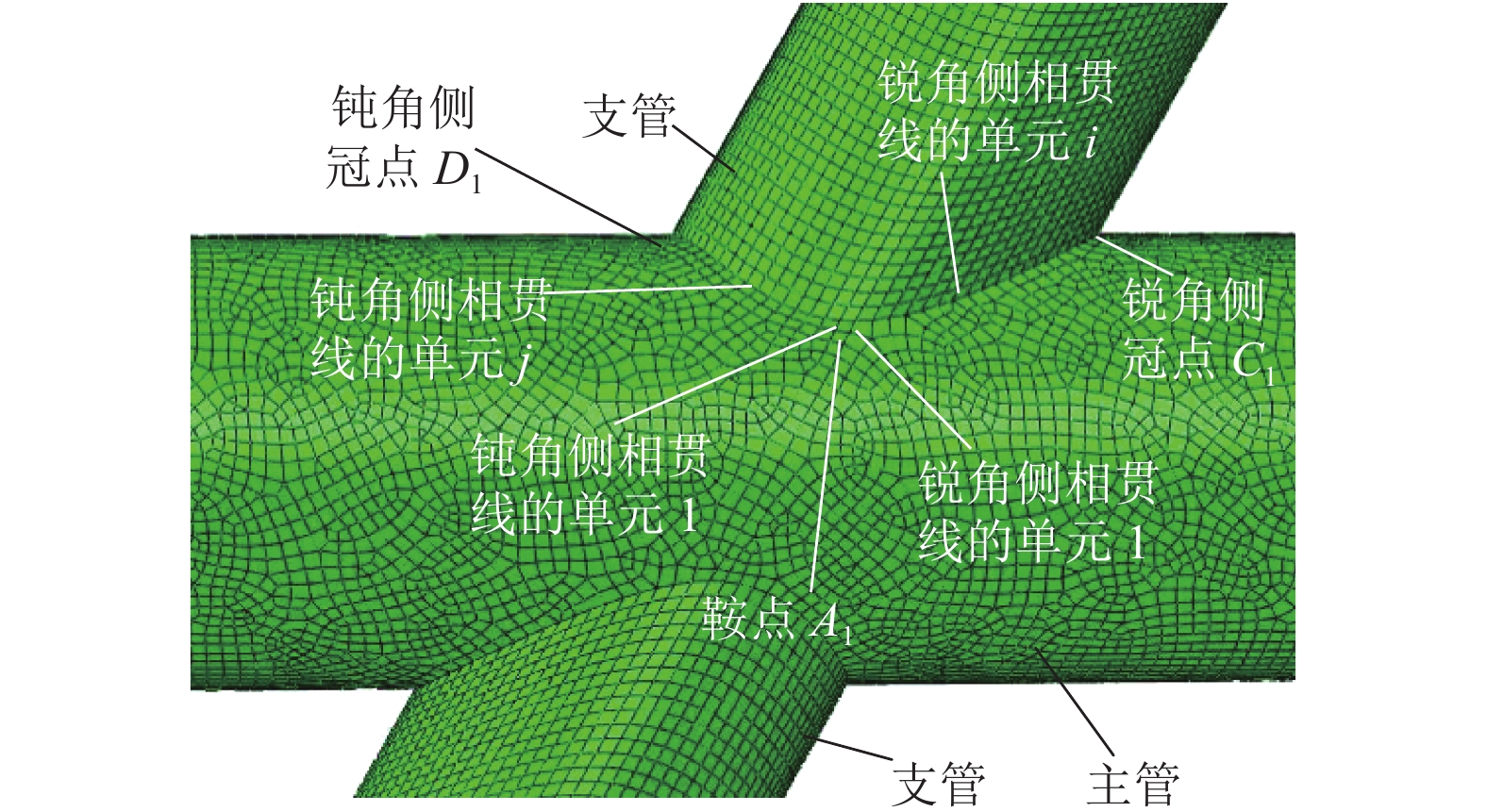
摘要: 为了研究支主管夹角对X形圆钢管相贯节点轴向受力性能的影响,进行相关试验来校验有限元模型,以有限元为手段分析了支主管夹角对X形节点在支管轴力作用下的传力特性和承载力的影响;根据有限元参数分析结果,对支主管夹角较小的节点的承载力提出了改进建议. 研究结果表明:节点试件的破坏模式为相贯线附近主管管壁局部屈曲;当支主管非正交但夹角大于60° 时,节点的传力特性与支主管正交节点的相近,符合Togo模型的假定,现行规范中的夹角正弦的倒数项能精准地反映夹角对节点承载力的影响;但当节点的支主管夹角小于45° 时,其传力特性与Togo模型的假定有较大的差异,夹角正弦的倒数也低估了支主管夹角对节点承载力的提高,对于夹角接近30° 的节点甚至低估了30%;因此建议当夹角小于45° 时,在规范已有的节点承载力计算式的基础上乘以修正系数.Abstract: In order to study the effect of brace-to-chord angle (BCA) on the performance of unstiffened circular hollow section (CHS) X-joints under brace axial force, experimental test was carried out to verified finite element (FE) model. Then FE parameter analysis were used to study the effect of BCA on the stress transfer and bearing capacity of the X-joints under brace axial force, and the capacity prediction accuracy of the X-joints with small BCA was improved. The results show that the failure pattern of test is local buckling of chord wall near brace-to-chord intersection. The incline X-joints (brace-to-chord non-orthogonal) with BCA greater than 60° have the similar stress transfer characteristic to that of the brace-to-chord orthogonal X-joints, which is consistent with the assumption of the Togo model. Moreover, the reciprocal of the sine of BCA (RSBCA) in the current specification can accurately reflect the influence of BCA on the capacity. However, the stress transfer characteristics of the incline X-joints with BCA less than 45° are quite different from the assumption of the Togo model, and RSBCA underestimates the beneficial effect of BCA on the capacity of these X-joints (even 30% for the X-joint with BCA near to 30°). Hence, it is recommended to multiply a correction coefficient on the existing capacity prediction formula of these CHS X-joints with BCA less than 45°, to improve the prediction accuracy.
-
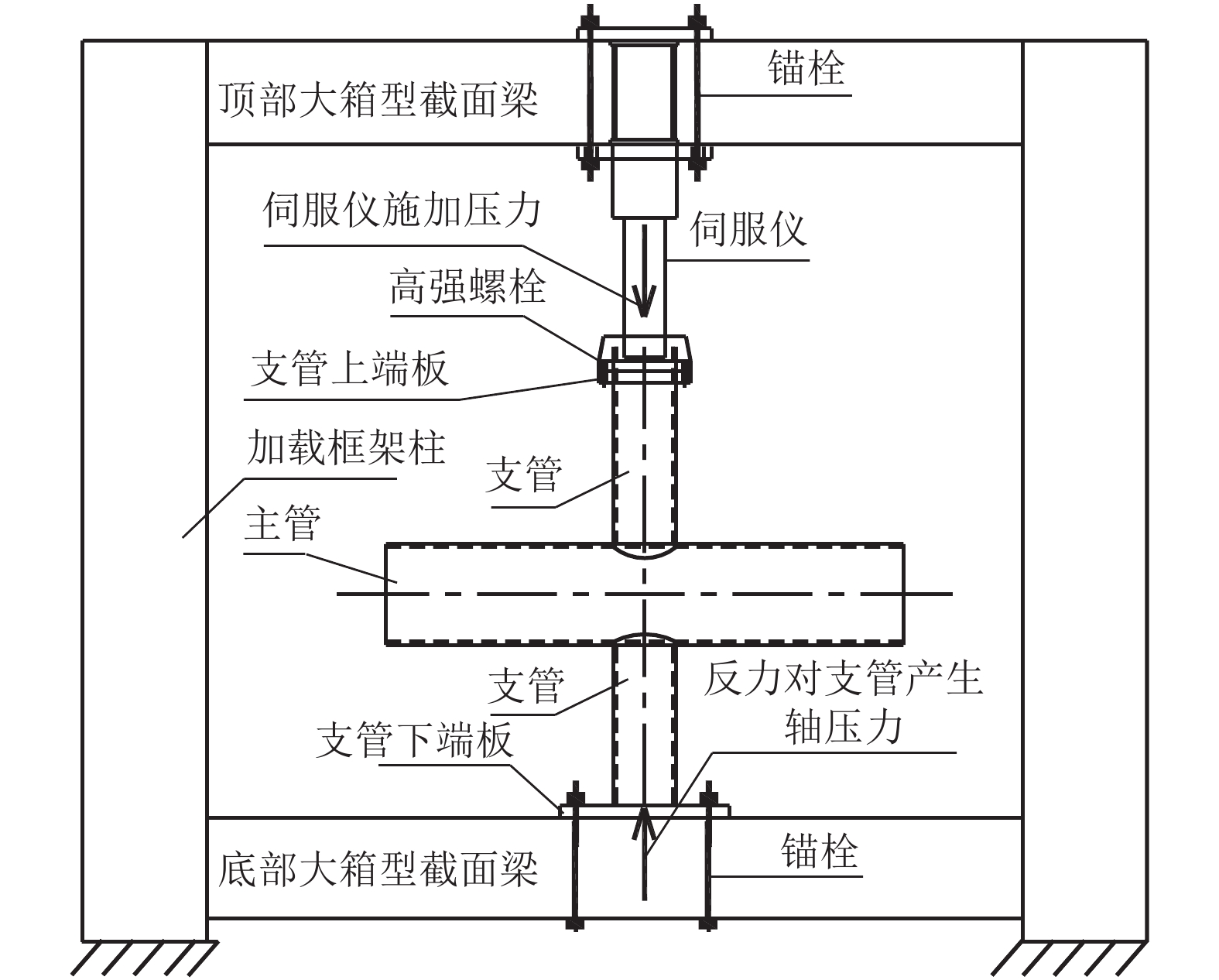
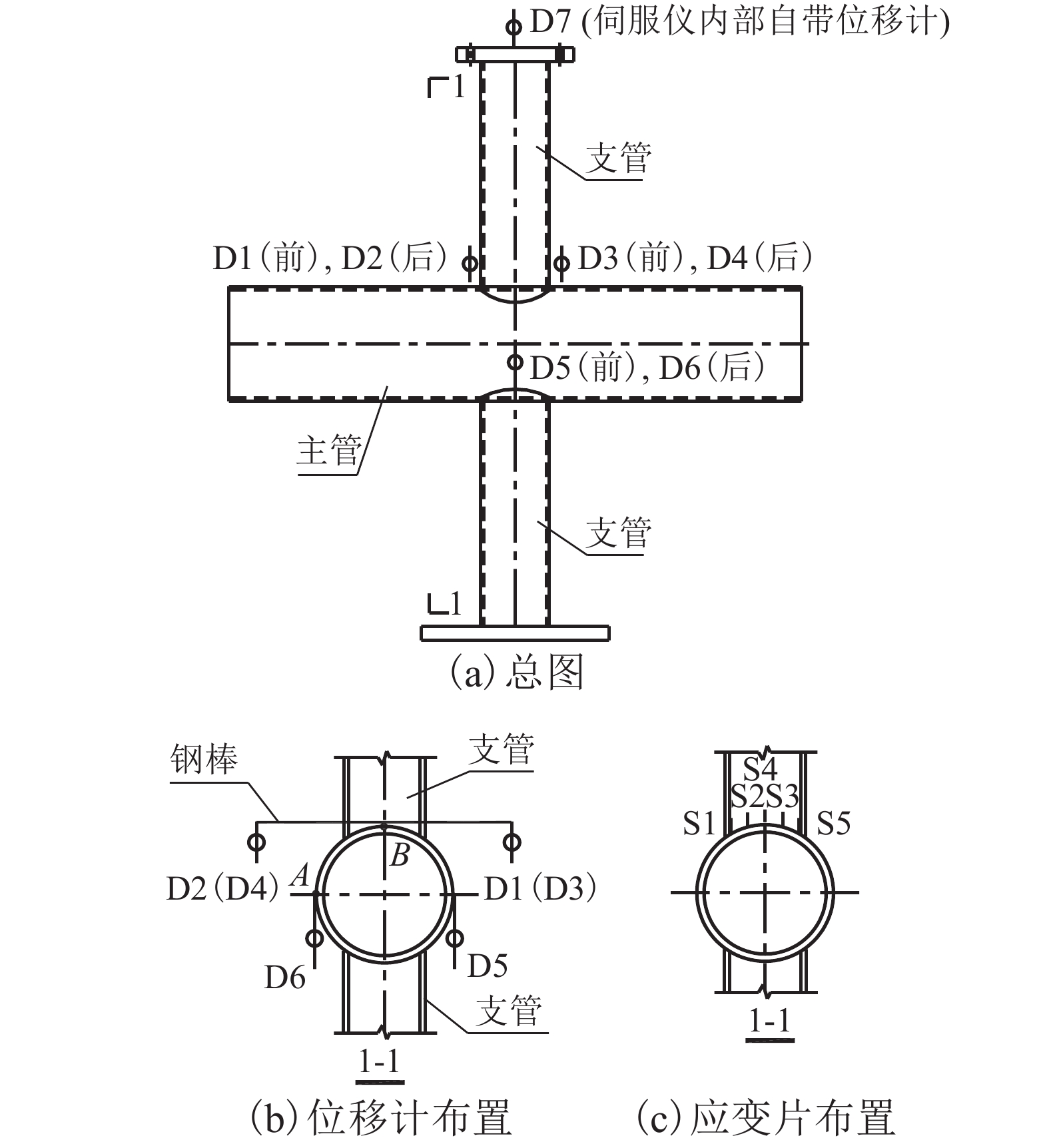
表 1 试件的几何特征
Table 1. Geometry of the specimen
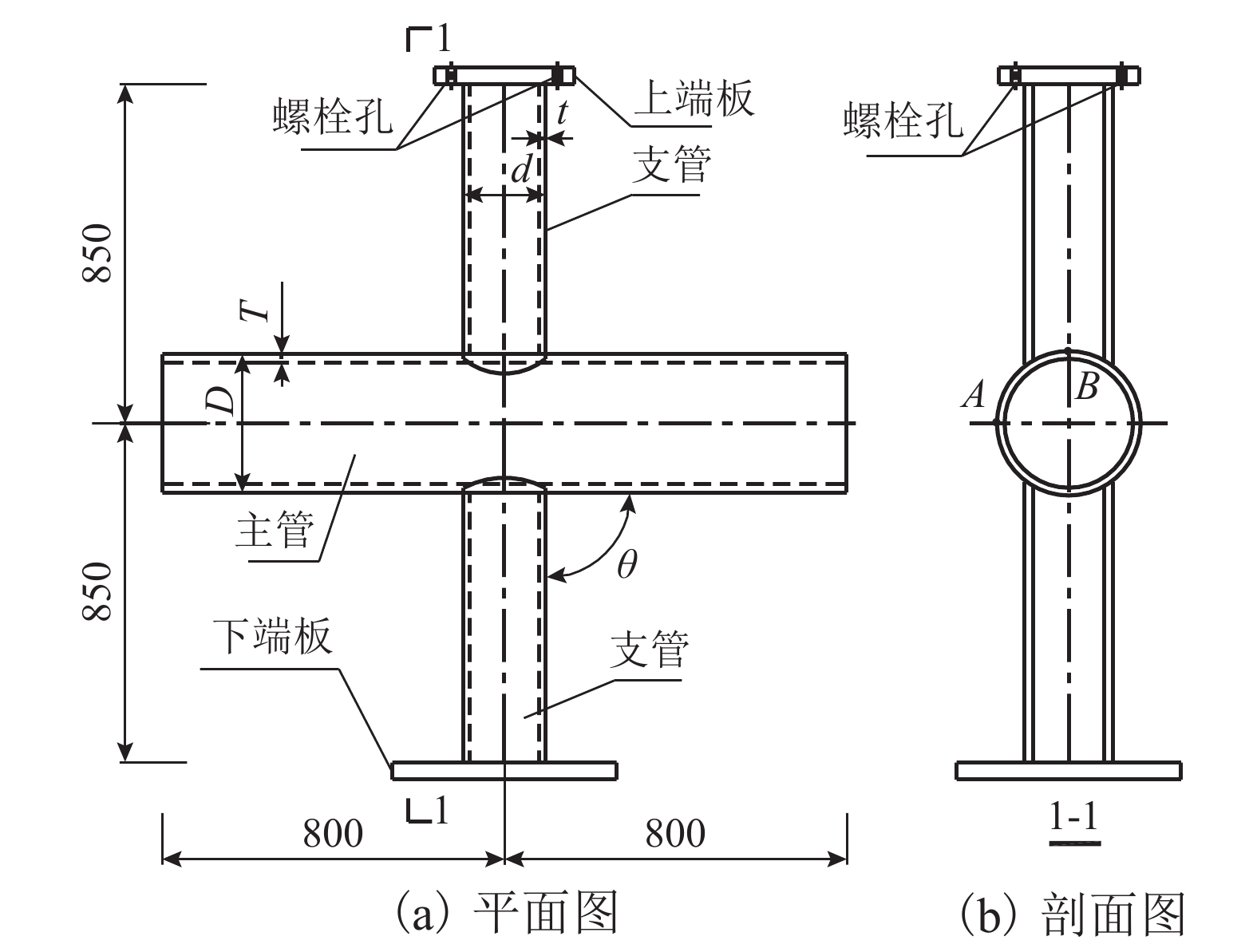
试件 D/mm d/mm T/mm t/mm β γ τ θ/(°) XPA 244.6 202.8 8.0 6.8 0.83 15.3 0.85 90 表 2 钢管材性试验结果(平均值)
Table 2. Test results of steel tubing properties (average value)
钢管直径(壁厚)/mm fy/MPa fu/MPa E/GPa ζ/% 244.6(8.0) 375.3 545.1 209 32.7 202.8(6.8) 372.1 550.3 213 31.3 表 3 θ
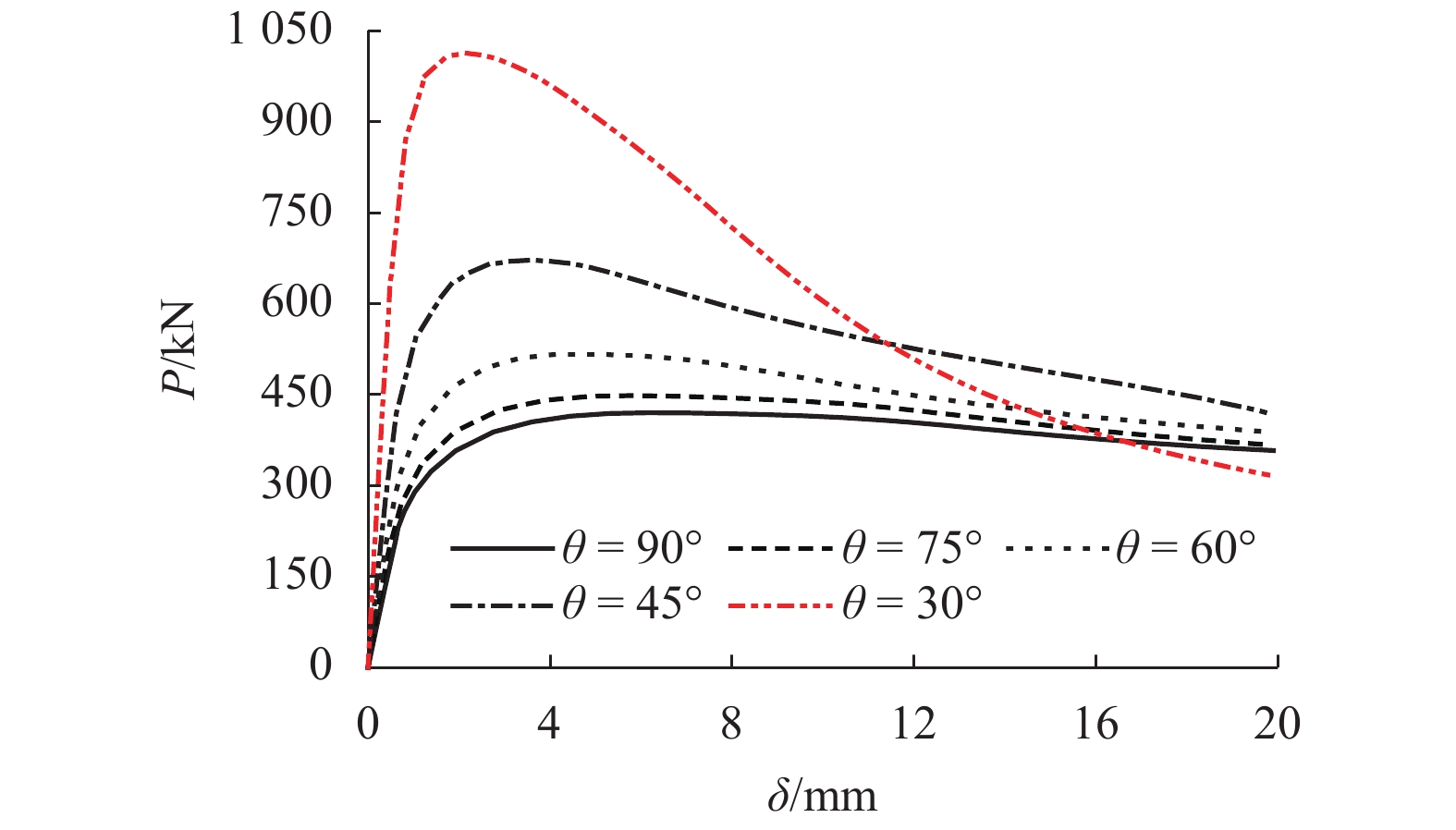
对节点受压承载力的影响 Table 3. Effect of θ on the Puc
项目 90° 75° 60° 45° 30° Puc/kN 419.9 441.3 516.4 671.3 1013.2 Pucsin θ/kN 419.9 426.3 447.2 474.7 506.6 Pucsin θ/Puc90 1.00 1.01 1.06 1.13 1.21 表 4 θ对ηt的影响
Table 4. Effect of θ on the ratio ηt
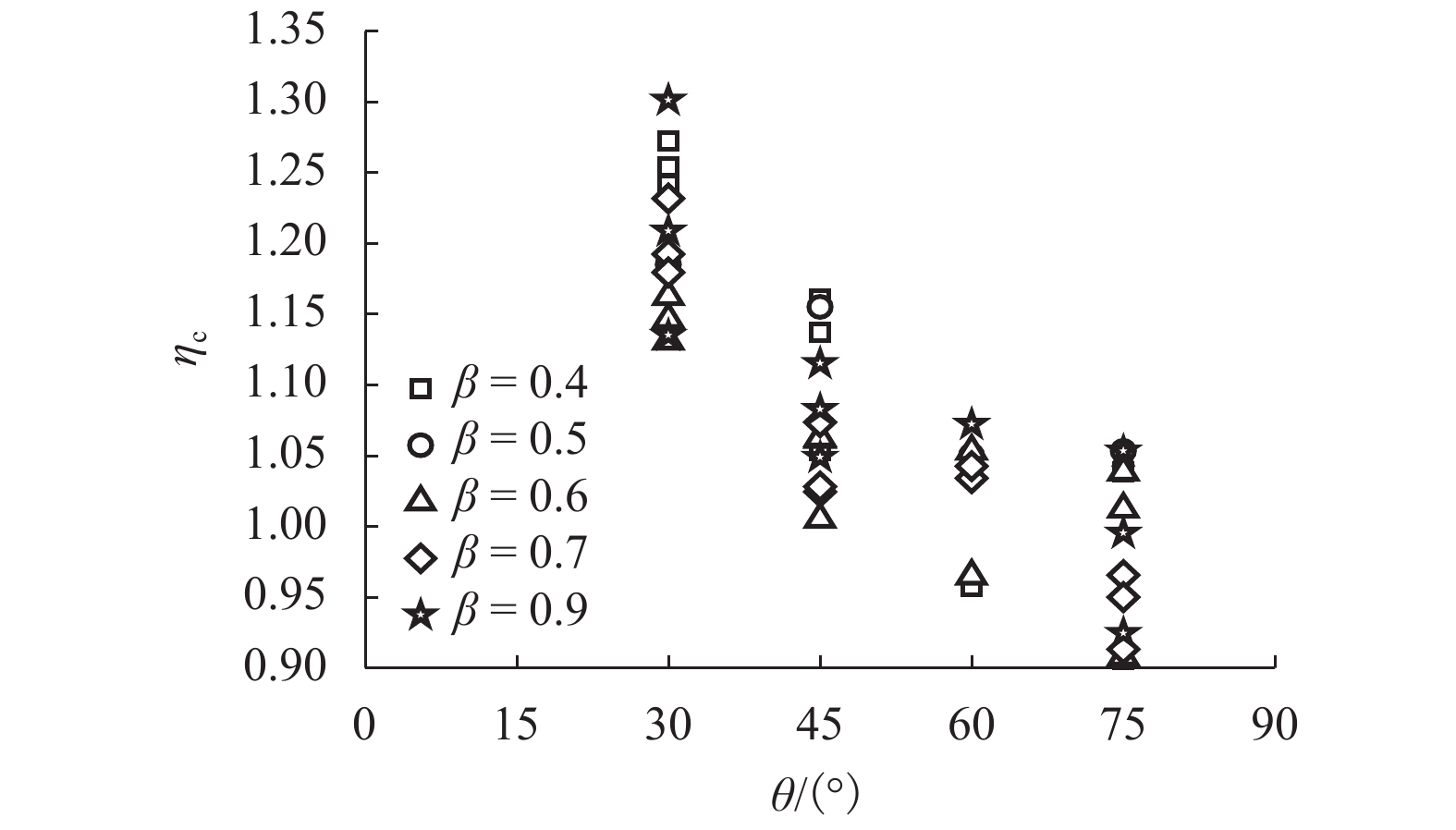
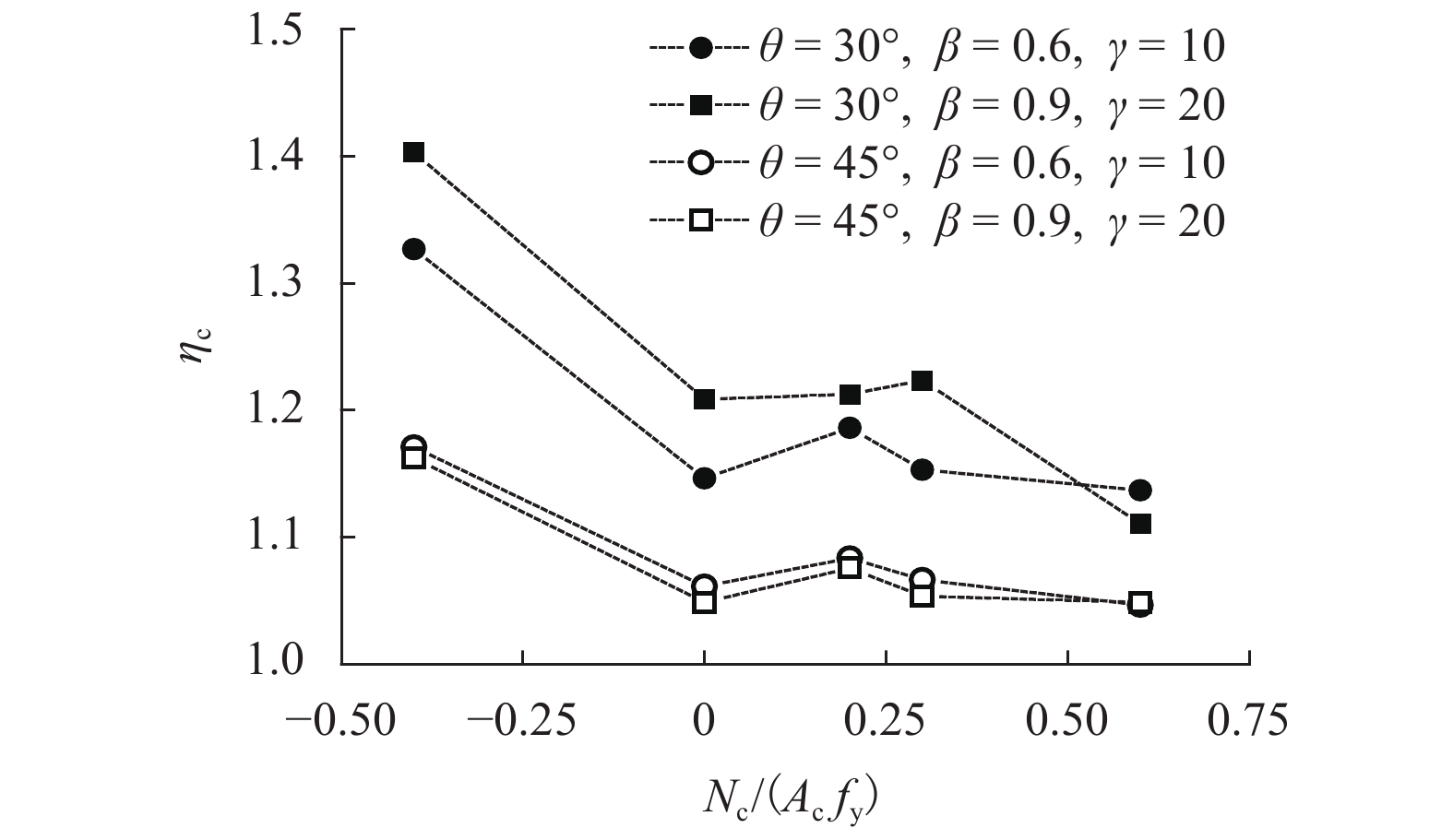
D/mm fy/MPa β γ θ/(°) Put/kN ηt 245 375 0.83 15.3 75 901.1 1.04 245 375 0.83 15.3 60 1016.4 1.05 245 375 0.83 15.3 45 1291.3 1.09 245 375 0.83 15.3 30 1860.5 1.12 250 345 0.90 10.0 75 2646.2 0.96 250 345 0.90 20.0 45 1491.1 0.98 250 345 0.90 40.0 30 932.2 1.11 250 345 0.70 10.0 45 1891.7 1.12 250 345 0.70 20.0 30 1062.8 1.34 250 345 0.70 40.0 75 107.6 1.03 250 345 0.40 10.0 30 1650.6 1.27 250 345 0.40 20.0 75 202.9 1.01 250 345 0.40 40.0 45 106.2 1.00 -
KUROBANE Y, MAKINO Y, OCHI K. Ultimate resistance of unstiffened tubular joints[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1984, 110(2): 385-40. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1984)110:2(385) LU L H, WINKEL G D, YU Y, et al. Deformation limit for the ultimate strength of hollow section joints[C]// Sixth International Symposium on Tubular Structures. Melbourne: University of Melbourne, 1994: 341-347. PECKNOLD D, MARSHALL P, BUCKNELL J. New API RP2A tubular joint strength design provisions[J]. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 2007, 129(3): 177-189. doi: 10.1115/1.2748811 王伟,陈以一,杜纯领,等. 上海光源工程屋盖钢管节点平面外受弯性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报,2009,30(1): 75-81. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6869.2009.01.011WANG Wei, CHEN Yiyi, DU Chunling. et al. Experimental study on out-of-plane bending performance of tubular joints in steel roof for the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2009, 30(1): 75-81. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6869.2009.01.011 RAN Feng, BEN Young. Theoretical analysis of cold-formed stainless steel tubular joints[J]. Engineering Structures, 2015, 83(1): 99-115. 赵必大,刘成清,章圣冶,等. Y型圆钢管相贯节点的轴向刚度计算模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(5): 872-878. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.05.016ZHAO Bida, LIU Chengqing, ZHANG Shenye, et al. Calculation model for axial rigidity of CHS Y-type joints[J]. Journal of southwest jiaotong university, 2015, 50(5): 872-878. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.05.016 马昕煦,陈以一. 支方主圆T形相贯节点轴压承载力计算公式[J]. 工程力学,2017,34(5): 163-170.MA Xinxu, CHEN Yiyi. Ultimate strength formulae for RHS-CHS T-joints under axial compression[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2017, 34(5): 163-170. 吴亮秦,李自林,韩庆华. 垫板加强N形圆钢管相贯节点静力性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报,2010,31(10): 83-88.WU Liangqin, LI Zilin, HAN Qinghua. Experimental study on static behavior of plate reinforced tubular N- joints[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2010, 31(10): 83-88. LEI Zhu, KAI Yang, YU Bai, et al. Capacity of steel CHS X-joints strengthened with external stiffening ring in compression[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2017, 115(6): 110-118. TOGO T, Experimental study on mechanical behavior of tubular joints[D]. Osaka: Osaka University, 1967. European Committee for Standardization. Eurocode3-design of steel structures-part 1.8: design of joints[S]. Brussels: CEN Press, 2005. 中冶建筑研究总院有限公司, 同济大学. 钢管结构技术规程: CECS280—2010[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2011. 中冶京诚工程技术有限公司. 钢结构设计标准: GB 50017—2017[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2018. Health and Safety Executive. Offshore installations, guidance on design, construction and certification: L85 HSE[S]. Britain: HSE Press, 1998. International Standards Organization. Petroleum and natural gas industries-offshore structures: ISO 13819-2—1955[S]. London: BIS Press, 1996. 中冶建筑研究总院有限公司. 钢结构焊接规范: GB 50661—2011[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012. ANDREW P V, JEFFREY A P. Numerical study and design of skewed X-type branch plate-to-circular hollow section connections[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2012, 68(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2011.06.005 -




 下载:
下载: