Three-Dimensional High-Precision Laser Non-contact Detection of Asphalt Pavement Surface Texture
-
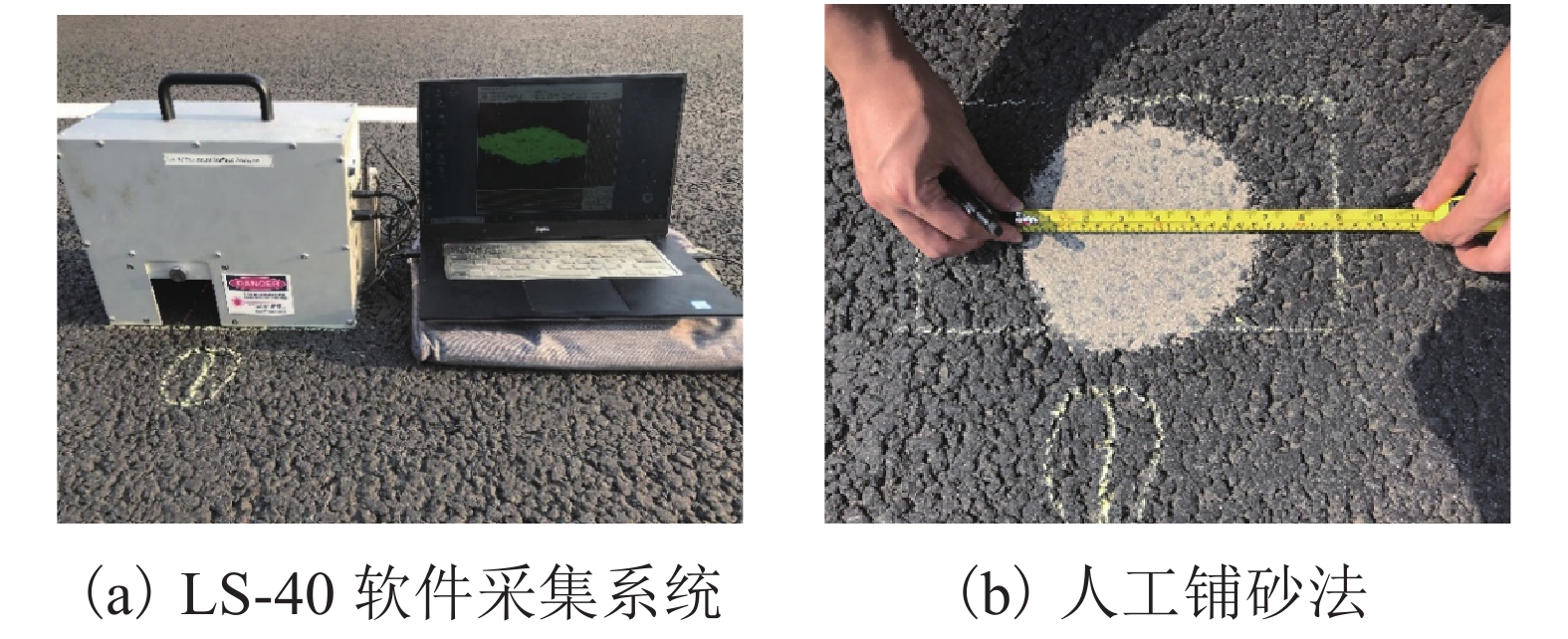
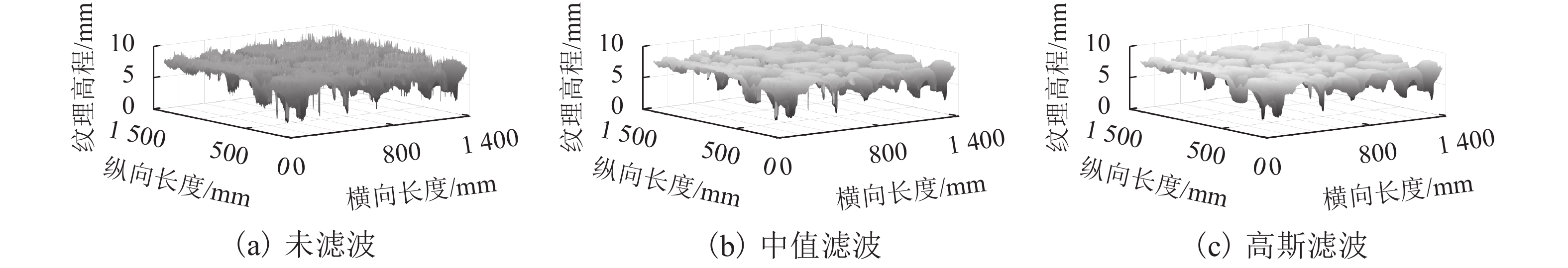
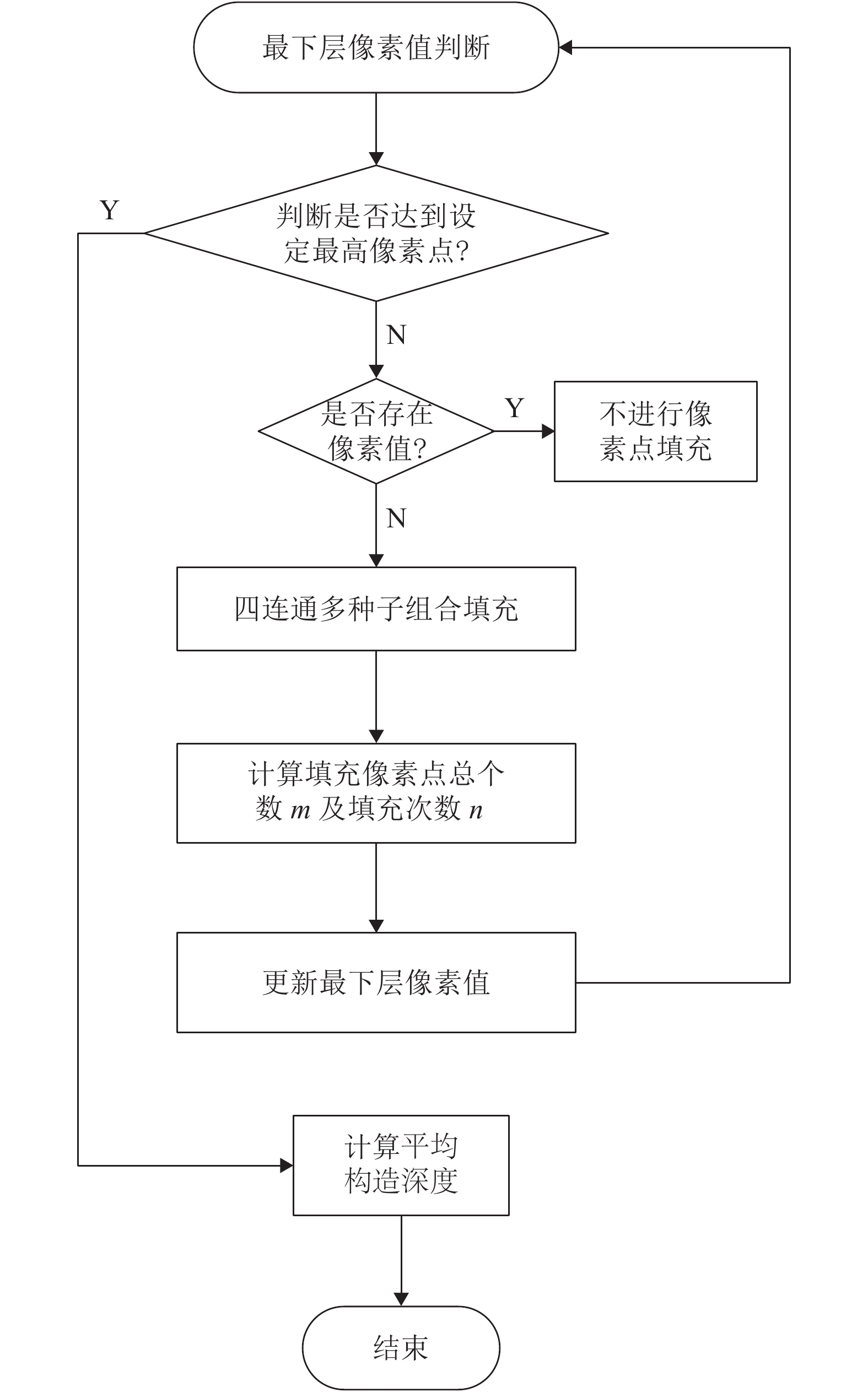
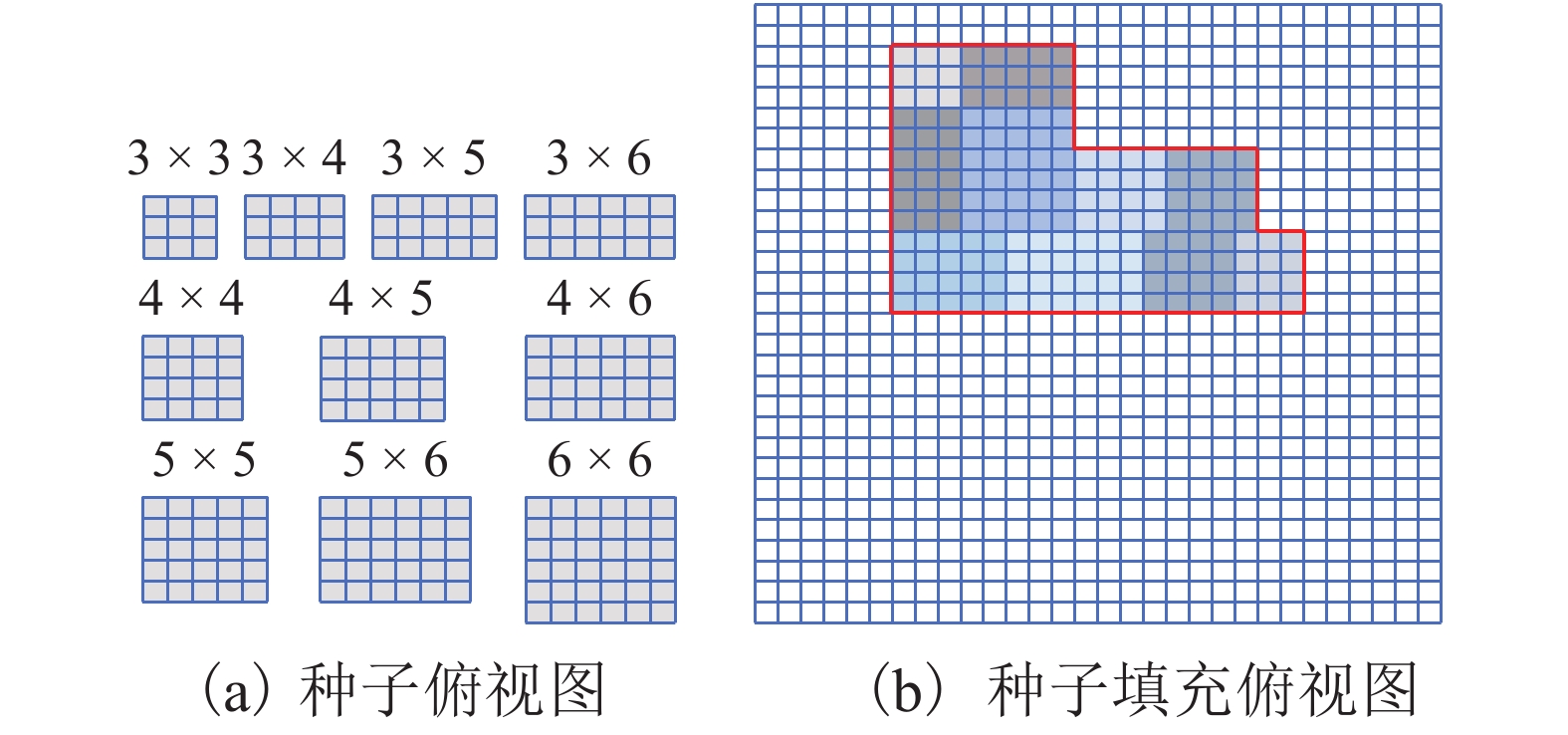
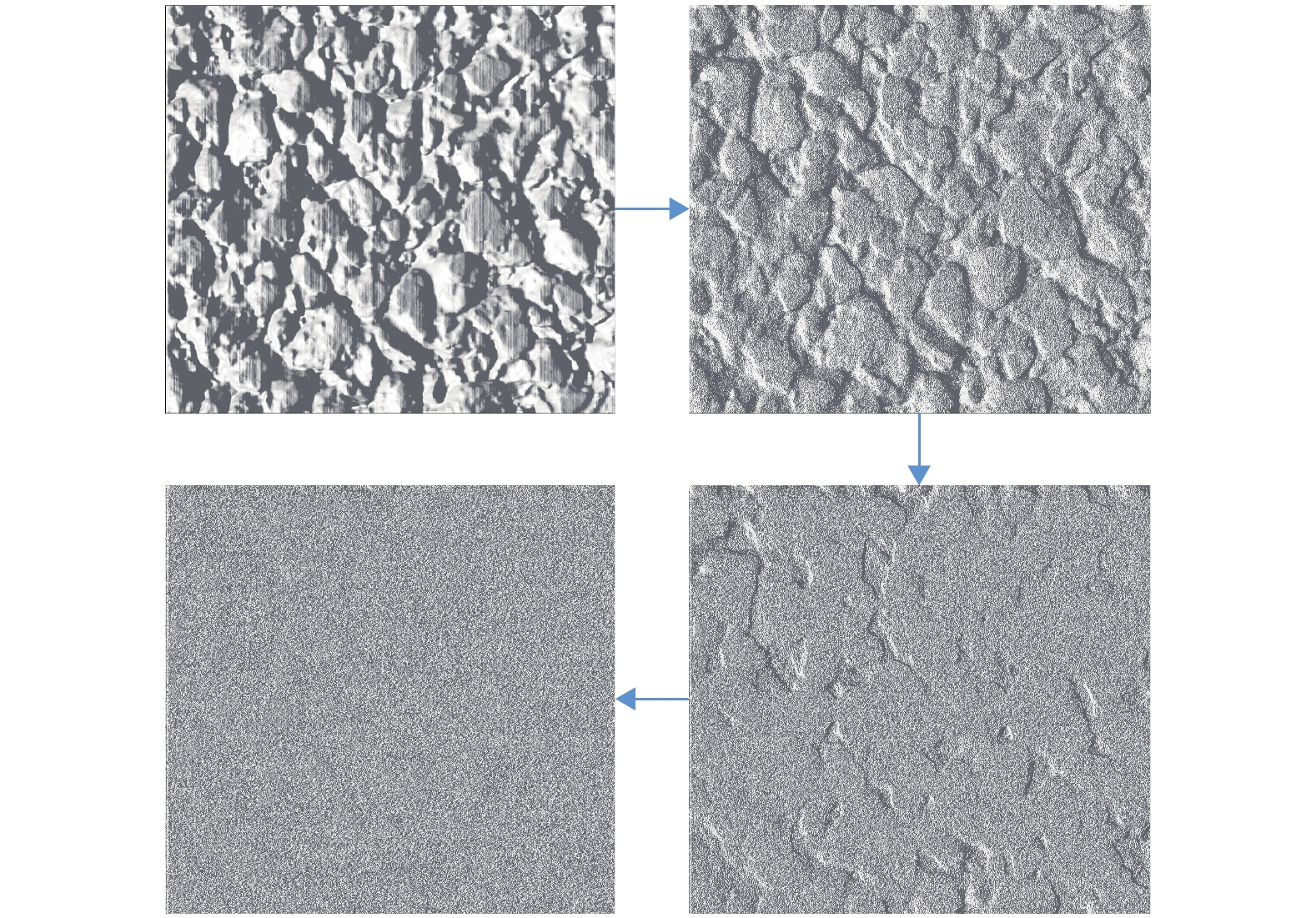
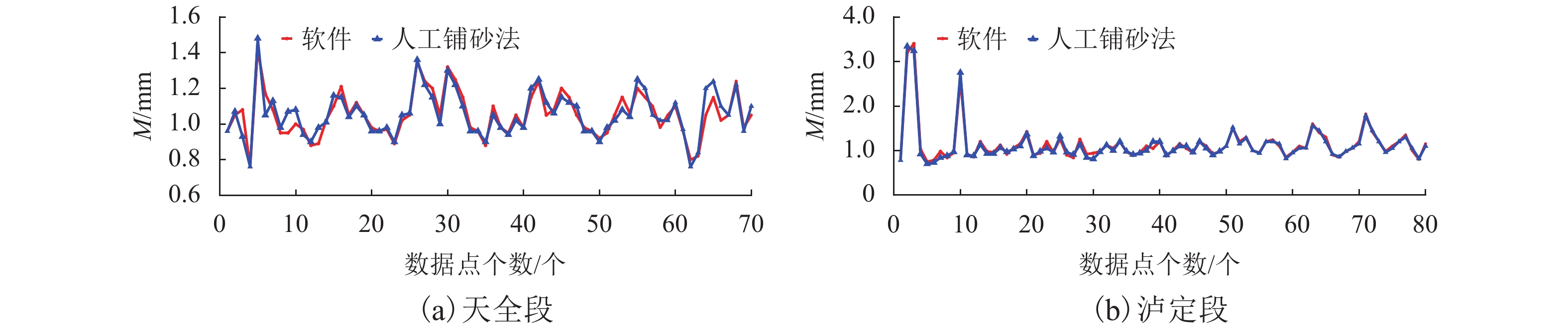
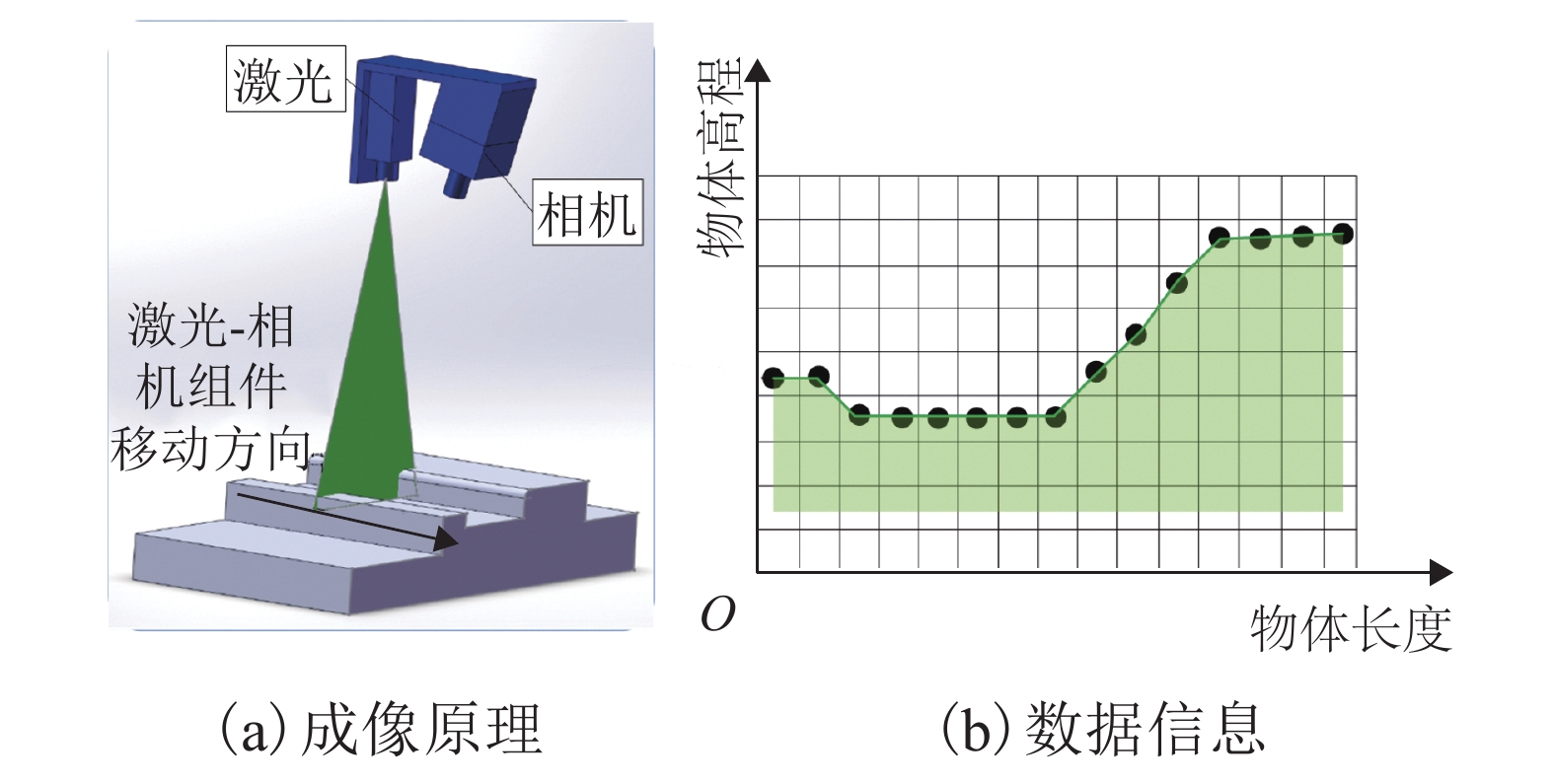
摘要: 为实现沥青路面纹理构造高精度自动检测,借助三维激光技术实现路面纹理三维重构,提出模拟铺砂的沥青路面构造深度测量方法. 首先采用高精度三维激光扫描仪获取雅康高速公路沥青路面0.1 mm精度三维高程数据,同时人工铺砂法获取对应区域的宏观构造深度值;其次通过数字图像处理技术实现重构沥青路面三维云图并进行数据噪声处理;最后设计四连通多种子组合填充算法,实现在滤波后的三维路面纹理云图上自动铺砂并获取路面纹理宏观构造深度值. 研究结果表明:模拟铺砂测量方法与人工铺砂法测量的平均构造深度(MTD,M)的平均绝对误差为0.052 mm,两者相关系数为0.96. 研究成果验证了用非接触式路面纹理测试替代现有的接触式路面摩擦性能测试的可行性,为道路交通安全网级监测与管理奠定基础.Abstract: In order to realize the high-precision automatic detection of asphalt pavement textures and the 3D reconstruction of pavement textures with the help of 3D laser technology, a method for measuring the depth of the asphalt pavement structure by simulating the sand patch test was proposed. First, a high-precision 3D laser scanner was used to obtain the 0.1 mm-precision 3D elevation data of asphalt pavement of Ya’an–Kangding expressway, and the artificial sand patch method was used to measure the macro-structure depth value in the same area. Second, the digital image processing technology was used to reconstruct the 3D cloud image of the asphalt pavement and perform data noise processing. Finally, a four-connected multi-seed combination filling algorithm was designed to automatically pave sand on the filtered 3D road texture cloud map and obtain the macro structure depth of road texture. The results show that the average absolute error between the mean texture depth (MTD) values measured by the simulation method and the artificial method is 0.052 mm, and the correlation coefficient between them is 0.96, which verifies the feasibility of replacing the existing contact road surface friction performance test with a non-contact road surface texture test, and can lay a foundation for network-level monitoring and management of road traffic safety.
-
表 1 M值的结果分析
Table 1. Comparative analysis of M values
测试
路段数据点
个数/个平均绝对
误差/mm相对
误差/%r 天全段 70 0.055 4.6 0.95 泸定段 80 0.050 5.2 0.97 汇总/平均值 150 0.052 4.9 0.96 -
董斌, 唐伯明, 刘唐志. 冰雪路面事故成因分析及对策探讨[J]. 交通运输研究, 2010(22): 137-140.DONG Bin, TANG Baiming, LIU Tangzhi. Cause analysis and countermeasure study on snow-icing road pavement accidents[J]. Transport Research, 2010(22): 137-140. 朱洪洲,廖亦源. 沥青路面抗滑性能研究现状[J]. 公路,2018(1): 35-46.ZHU Hongzhou, LIAO Yiyuan. Present situations of research on anti-skid property of asphalt pavement[J]. Highway, 2018(1): 35-46. 桂志敬,刘恒权,张智勇. 路面纹理构造特征表征与抗滑性能检测技术研究进展[J]. 公路交通科技(应用技术版),2012,5(4): 55-59. 刘建华. 路面抗滑性能检测与评价技术研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2002. 张艳玲. 全国公路总里程477.35万公里 高速公路13.65万公里[DB/OL]. (2018-08-24)[2018-11-23]. http://www.chinahighway.com/news/2018/1183657.php 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 公路路基路面现场测试规程: JTG E60—2008[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社. 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 公路工程质量检验评定标准: JTG F80/1—2004[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社. WANG K C P. Design and implementations of automated systems for pavement surface distress survey[J]. Journal of Infrastructure Systems, 2000, 6(1): 24-32. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1076-0342(2000)6:1(24) FUKUHARA T, TERADA K, NAGAO M, et al. Automatic pavement-distress-survey system[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 1990, 116(3): 280-286. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(1990)116:3(280) 王端宜,李维杰,张肖宁. 用数字图像技术评价和测量沥青路表面构造深度[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2004,32(2): 42-45. 宋永朝,闫功喜,隋永芹,等. 基于数字图像处理技术的沥青路面表面纹理构造分布[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2014,45(11): 4075-4080.SONG Yongchao, YAN Gongxi, SUI Yongqing, et al. Texture structure distribution of asphalt pavement surface based on digital image processing technology[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(11): 4075-4080. 李伟,孙朝云,呼延菊,等. 基于激光3D数据的沥青路面构造深度检测方法[J]. 中外公路,2016,36(5): 9-12. 周兴林,蒋难得,肖旺新,等. 基于激光视觉的沥青路面构造深度测量方法[J]. 中国公路学报,2014,27(3): 11-16.ZHOU Xinglin, JIANG Nande, XIAO Wangxin, et al. Measurement method for mean texture depth of asphalt pavement based on laser vision[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2014, 27(3): 11-16. 文静. 数字化技术评价沥青路面构造深度研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2009. 窦光武. 基于断面高程的路面构造深度计算模型研究[J]. 公路交通科技,2015,32(1): 50-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2015.01.009DOU Guangwu. Research of calculation model of pavement texture depth based on profile elevation[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2015, 32(1): 50-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2015.01.009 ALFREDO C, FEDERICO M, STEFANO M. Laser-triangulation device for in-line measurement of road texture at medium and high speed[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2010, 5(7): 2225-2234. YANG G, LI Q, ZHAN Y, et al. Convolutional neural network–based friction model using pavement texture data[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2018, 32(6): 165-176. LI Q, YANG G, WANG C P, et al. Novel macro- and micro texture indicators for pavement friction by using high-resolution three-dimensional surface data[J]. Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2017, 26(41): 164-176. ALAMDARLO M N, HESAMI S. Optimization of the photometric stereo method for measuring pavement texture properties[J]. Measurement, 2018, 10(127): 406-413. 王晓嘉,高隽,王磊. 激光三角法综述[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2004,25(4): 601-604.WANG Xiaojia, GAO Jun, WANG Lei. Survey on the laser triangulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2004, 25(4): 601-604. WANG C P. Elements of automated survey of pavements and a 3D methodology[J]. Journal of Modern Transportation, 2011, 19(1): 51-57. doi: 10.1007/BF03325740 TSAI Y C J, LI F. Critical assessment of detecting asphalt pavement cracks under different lighting and low intensity contrast conditions using emerging 3D laser technology[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2012, 138(5): 649-656. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)TE.1943-5436.0000353 OUYANG W, XU B. Pavement cracking measurements using 3D laser-scan images[J]. Measurement Science & Technology, 2013, 24(10): 105204.1-105204.9. 李少斌. MLS_13PTR多功能激光路面检测仪检测指标的相关性研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学, 2013. -




 下载:
下载: