Automatic Volume Calculation System for Sand and Gravel Carried by Ship Based on LiDAR Point Cloud
-
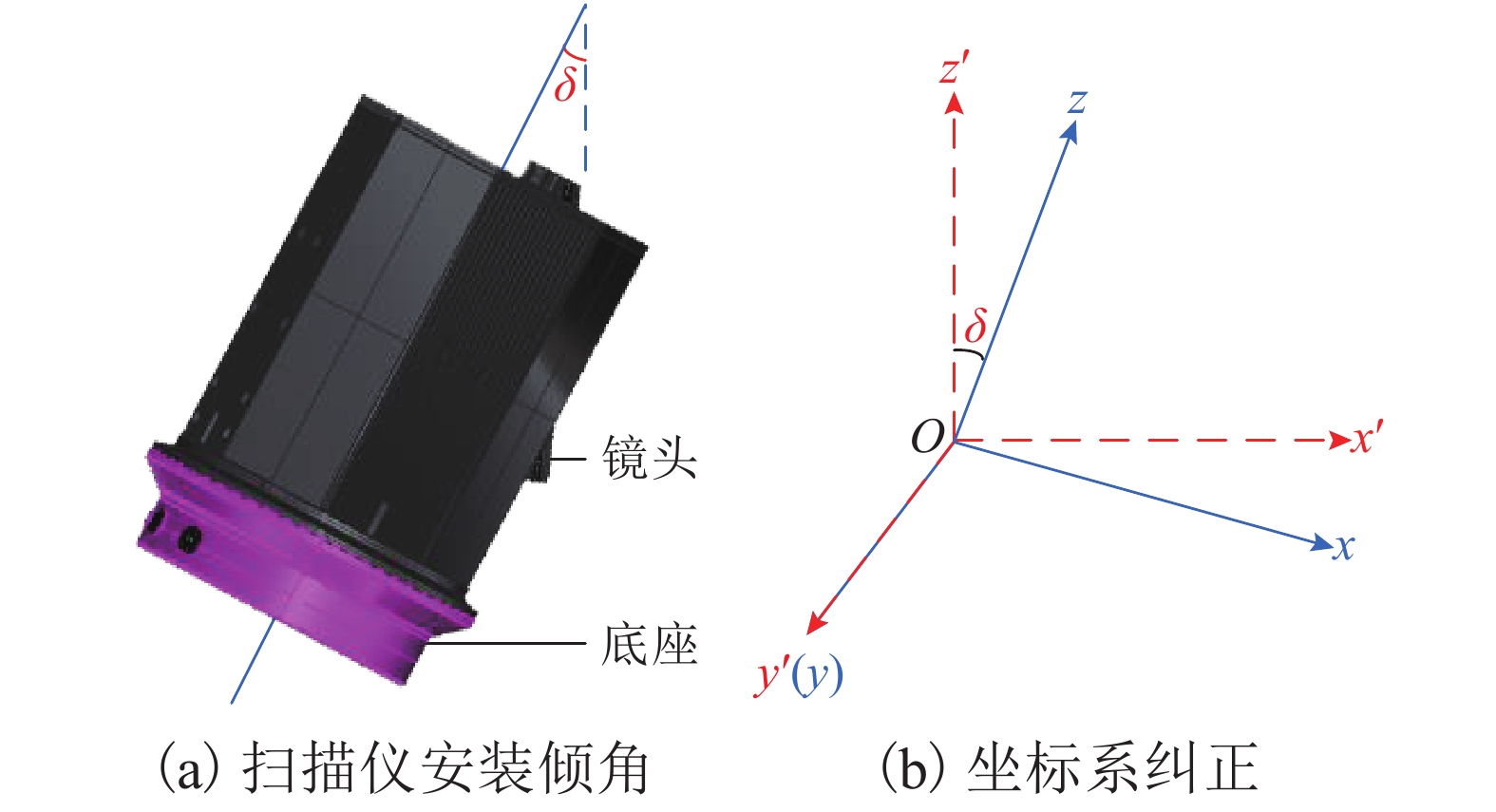
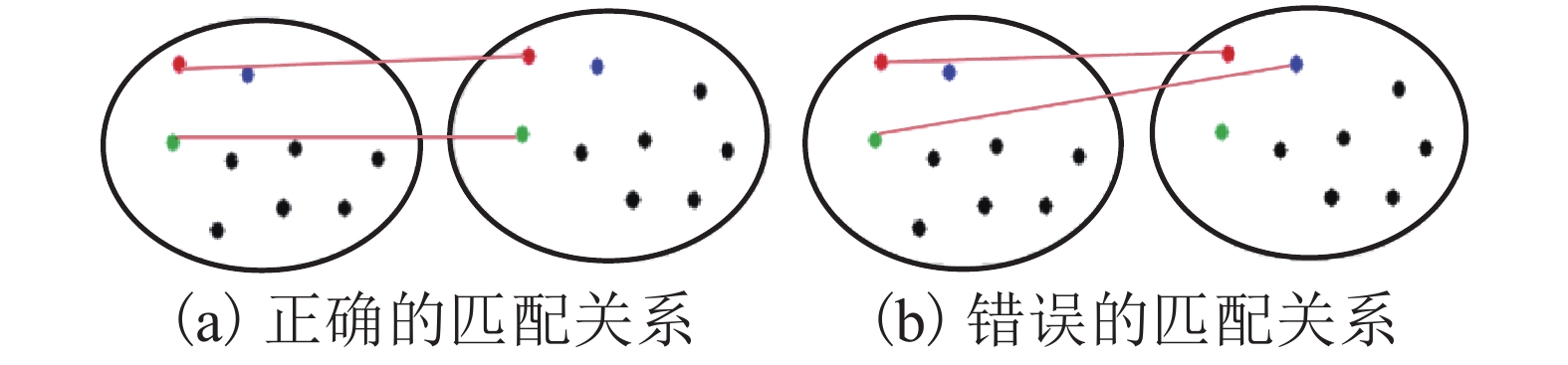
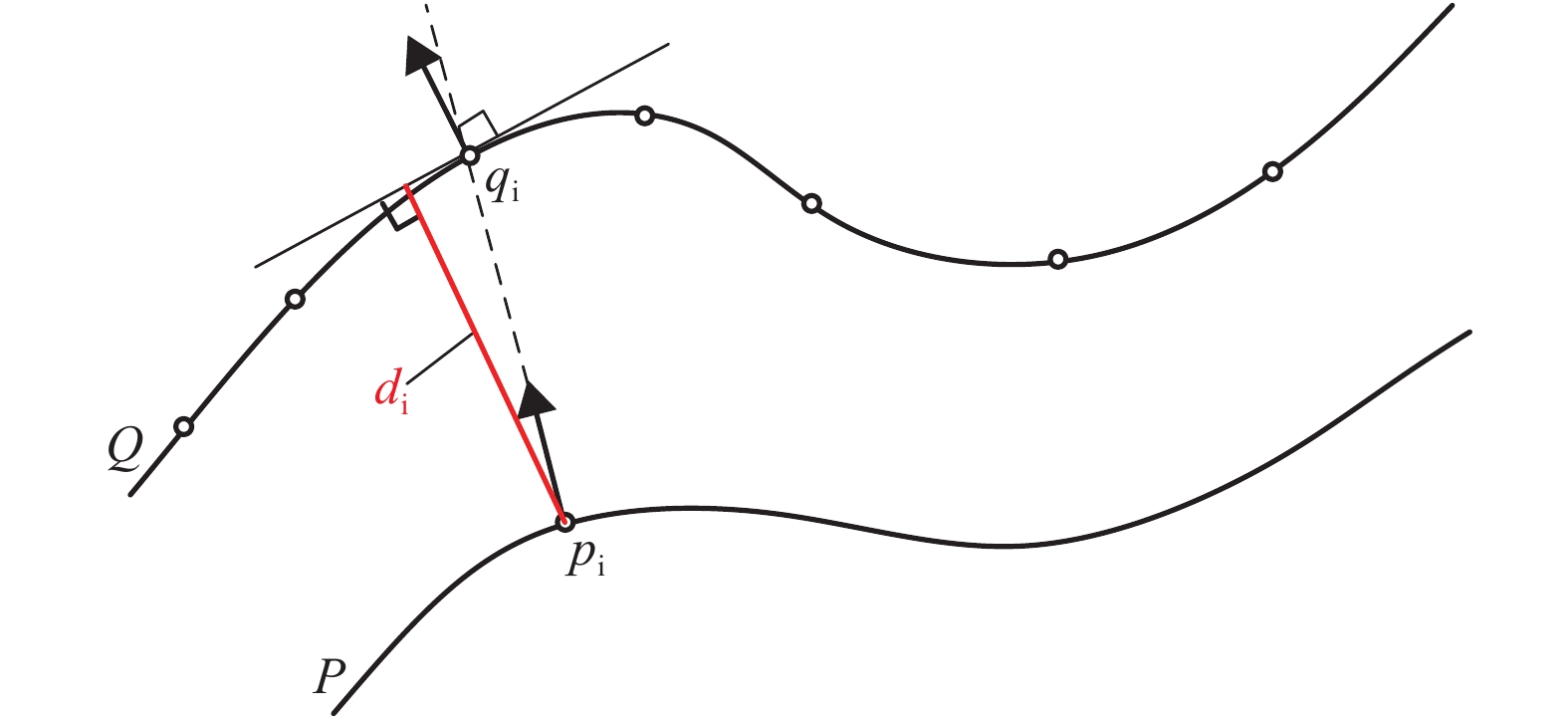
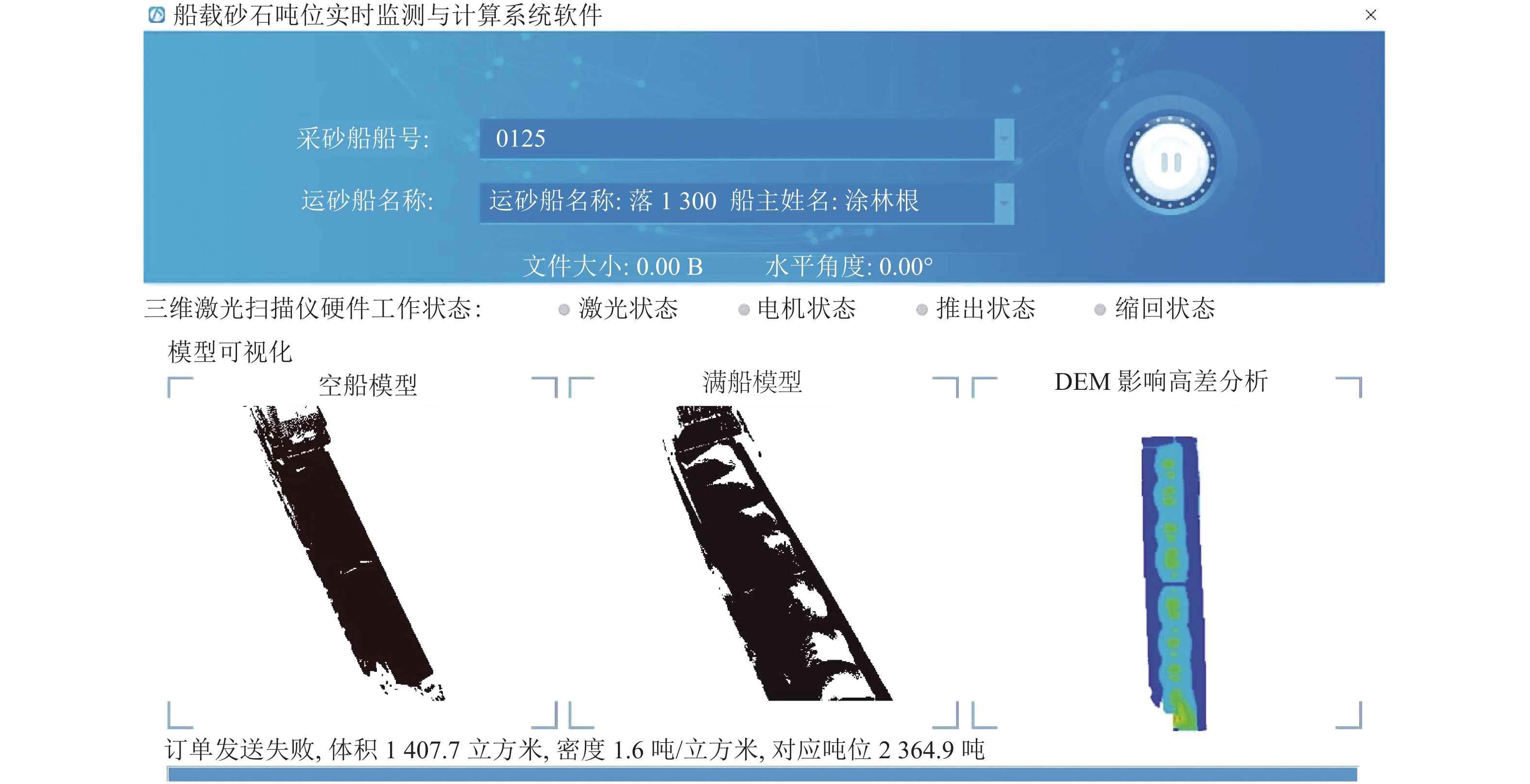
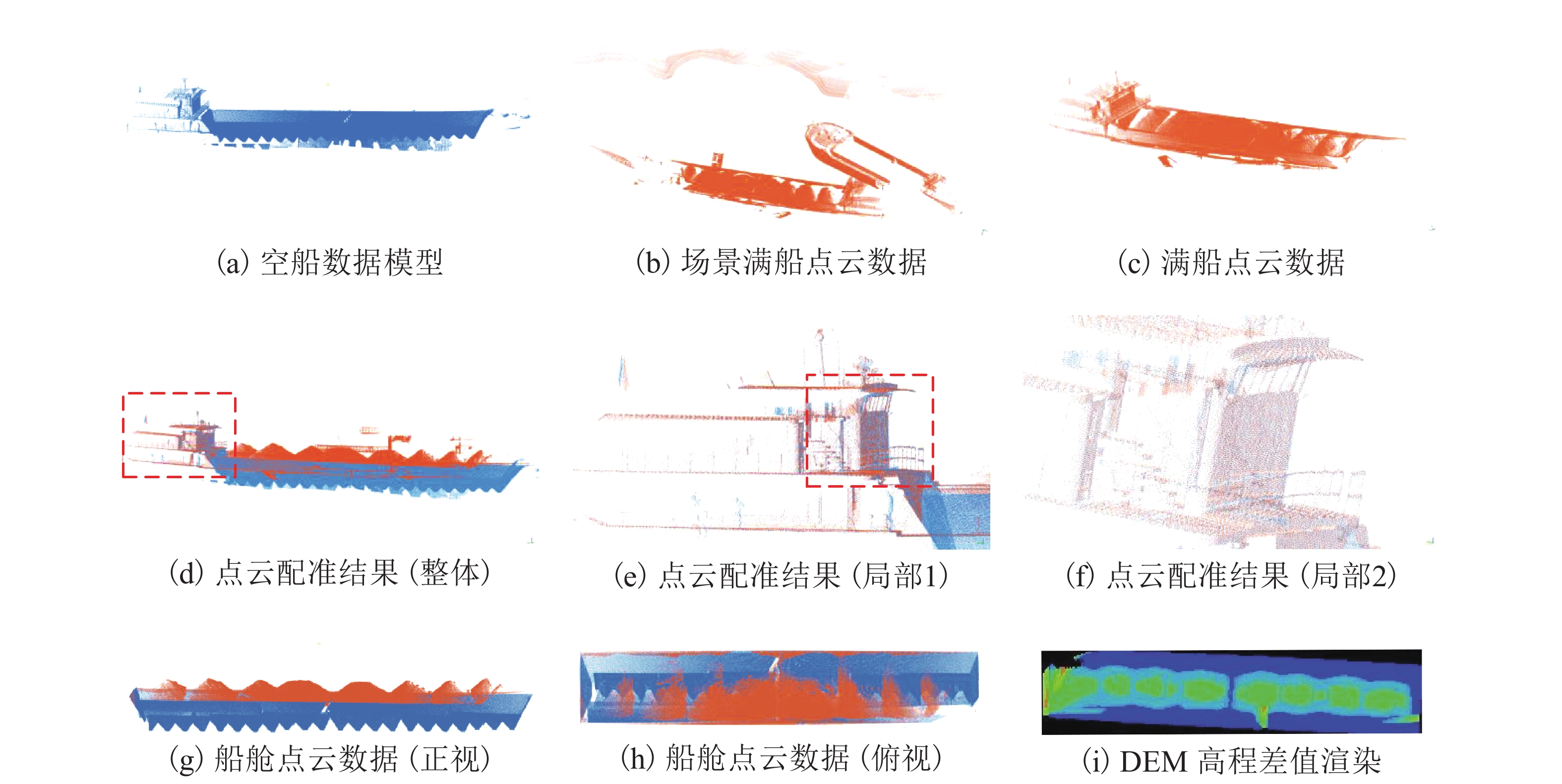
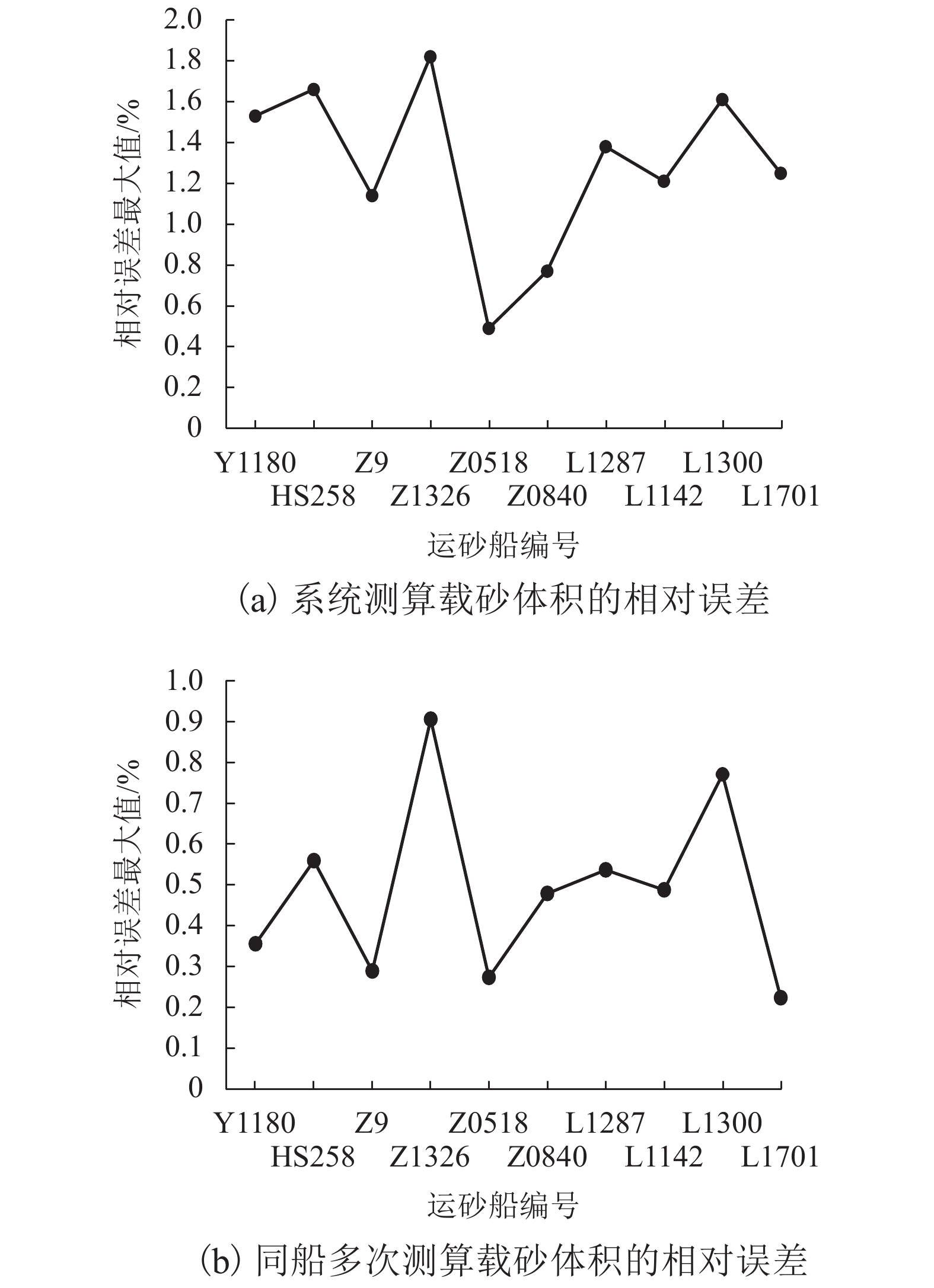
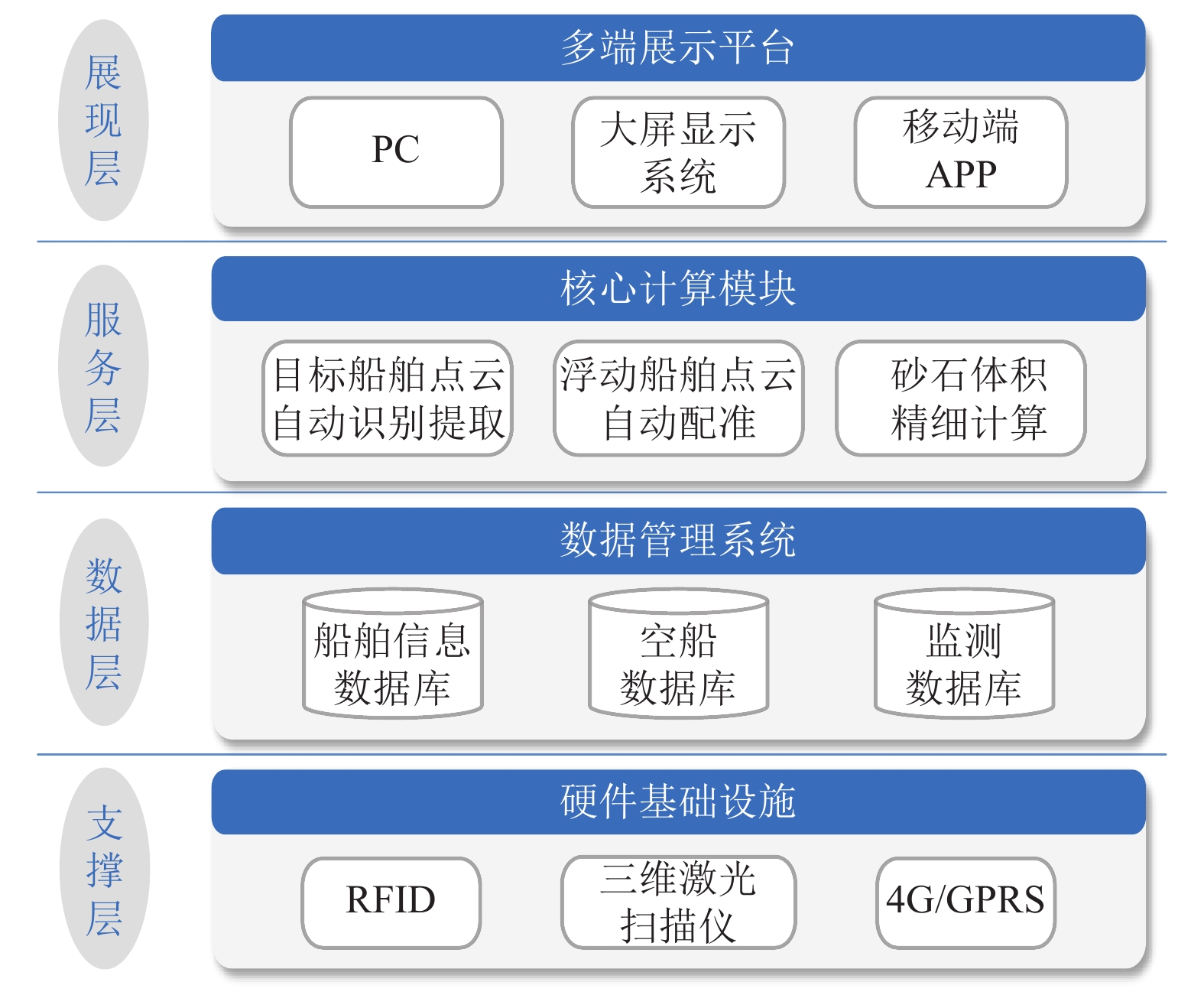
摘要: 针对现有船舶运输砂石体积计算主要依赖人工方式称重和纸质运单流转、精度不高且效率很低的难题,采用基于八叉树的点云精简和聚类分析进行复杂环境下船舶点云的自动识别和提取;采用基于改进SK-4PCS (semantic-keypoint-based 4-points congruent sets)的粗配准和基于Point-to-Plane ICP (iterative closest point)的精配准进行空载和满载两期点云由粗到精的高效配准,设计实现了一种利用LiDAR (light detection and ranging)点云数据进行船载砂石自动测算的系统. 采集了江西南昌赣江运砂船数据进行实验验证,从扫描到出结果一艘船的砂石体积自动测算时间少于2 min,同船多次测算结果最大相对误差小于1.00%,砂石体积与实际真值相比的最大误差小于2.00%,满足实际业务需求.Abstract: The current volume calculation method of sand and gravel carried by ship mainly relies on manual weighing and waybill transfer, which has the problem of low precision and low efficiency. To deal with this, an automatic volume calculation system of sand and gravel carried by ship is developed on the basis of LiDAR (light detection and ranging) point cloud. It uses the cluster analysis and the octree-based point cloud reduction to realize automatic identification and extraction of the point cloud for the target ship in a complex environment. It adopts the coarse registration based on the improved SK-4PCS (semantic-keypoint-based 4-points congruent sets) and fine registration based on the point-to-plane ICP (iterative closest point) to realize the high-efficient registration of no-load and full-load point clouds from coarse to fine level. The experiment is conducted with the data from the gravel transport ships on the Ganjiang River in Nanchang, Jiangxi, showing that the automatic measurement and calculation time of sand and gravel volume for one ship is less than 2 min, the maximum relative error of multiple calculation results is less than 1.00%, and the maximum error between the volume calculation results and real values is less than 2.00%, which meet practical requirements.
-
Key words:
- 3D laser scanning /
- sand and gravel volume /
- point cloud registration /
- ship transport
-
表 1 船载砂石体积自动测算系统测试统计结果
Table 1. Statistical results of automatic volume calculation system of sand and gravel carried by ship
船只类型 运砂船编号 点云扫描
时间/s系统计算最长时间/s 体积计算最大值/m3 体积计算最小值/m3 转换系
数/(kg•m−3)载砂方
量值/kgδ1最大值/% δ2最大值/% 自卸驳 Y1180 40 59 1270.15 1265.65 1.43 1838 1.53 0.36 自卸驳 HS258 40 56 1138.27 1131.94 1.43 1646 1.66 0.56 自卸驳 Z9 40 42 773.76 771.53 1.43 1094 1.14 0.29 自卸驳 Z1326 40 63 1541.45 1527.63 1.43 2225 1.82 0.91 自卸驳 Z0518 40 51 829.92 827.66 1.43 1181 0.49 0.27 自卸驳 Z0840 40 50 880.15 875.96 1.43 1249 0.77 0.48 落舱驳 L1142 40 46 753.41 749.39 1.62 1231 1.38 0.54 落舱驳 L1287 40 49 754.34 750.68 1.62 1231 1.21 0.49 落舱驳 L1300 40 54 960.88 953.53 1.62 1570 1.61 0.77 落舱驳 L1701 40 45 695.85 694.30 1.62 1139 1.25 0.22 -
王洁军,郎营. 新形势下我国砂石行业发展现状及对策研究[J]. 建材发展导向,2018,16(8): 3-8. 张学朴,赵丹. 砂石采砂量核定方法的一些探讨[J]. 河南科技,2014,44(14): 41-42. 张吉星,程效军,程小龙. 三维激光扫描技术在船舶排水量计量中的应用[J]. 中国激光,2016,43(12): 162-168.ZHANG Jixing, CHENG Xiaojun, CHENG Xiaolong. Application of three-dimensional laser scanning technology in measurement of ship displacement[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2016, 43(12): 162-168. 冯亮. 河道采砂管理存在的问题及对策[J]. 珠江水运,2017,25(13): 57-58. 陈俊发,罗东浩. 三维激光扫描技术在船舶行业的应用[J]. 广东造船,2018,38(4): 68-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6622.2018.04.021CHEN Junfa, LUO Haodong. Application of 3D laser scanning technology in ship engineering[J]. Guangdong Shipbuilding, 2018, 38(4): 68-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6622.2018.04.021 国策,杨国东,王民水,等. 三维激光扫描装置设计与数据处理[J]. 世界地质,2018,37(4): 1231-1238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2018.04.023GUO Ce, YANG Guodong, WANG Minshui, et al. 3D laser scanning device design and data processing[J]. Global Geology, 2018, 37(4): 1231-1238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2018.04.023 朱庆,李世明,胡翰,等. 面向三维城市建模的多点云数据融合方法综述[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2018,43(12): 1962-1971.ZHU Qing, LI Shiming, HU Han, et al. Multiple point clouds data fusion method for 3D city modeling[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(12): 1962-1971. 朱曙光,何宽,周建郑. 徕卡三维激光扫描系统在建筑物精细建模中的应用[J]. 测绘通报,2018,65(2): 154-156.ZHU Shuguang, HE Kuan, ZHOU Jianzheng. Research on the application of Leica 3D laser scanning system in the fine modeling of buildings[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2018, 65(2): 154-156. 邬镇伦,程效军,辛佩康,等. 基于激光点云与建筑信息模型技术的复杂船舱容积计算方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2019,56(5): 234-242.WU Zhenlun, CHENG Xiaojun, XIN Peikang, et al. Calculating method of the capacity measurement of complex tank based on point cloud data and BIM technology[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(5): 234-242. 杨志华,张云生. 一种基于特征点的地面激光点云全局配准方法[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息,2018,41(4): 66-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2018.04.019YANG Zhihua, ZHANG Yunsheng. A global registration method of terrestrial laser point cloud based on feature points[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2018, 41(4): 66-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2018.04.019 MELLADO N, AIGER D, MITRA N J. Super 4PCS fast global point cloud registration via smart indexing[J]. Computer Graphics Forum, 2015, 33(5): 205-215. THEILER P W, WEGNER J D, SCHINDLER K. Keypoint-based 4-points congruent sets–automated marker-less registration of laser scans[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2014, 96(11): 149-163. BOGDAN R R, NICO B, MICHAEL B. Fast point feature histograms (FPFH) for 3D registration[C]//2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Kobe: IEEE, 2009: 3212-3217 周波,陈银刚,顾泽元. 基于八叉树网格的点云数据精简方法研究[J]. 现代制造工程,2008,33(3): 64-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3133.2008.03.019ZHOU Bo, CHEN Yingang, GU Zeyuan. Data point reduction on octree cube algorithm[J]. Modern Manufacturing Engineering, 2008, 33(3): 64-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3133.2008.03.019 GE Xuming. Automatic markerless registration of point clouds with semantic-keypoint-based 4-points congruent sets[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2017, 130: 344-357. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.06.011 戴静兰,陈志杨,叶修梓. ICP算法在点云配准中的应用[J]. 中国图象图形学报,2007,12(3): 517-521. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2007.03.023DAI Jinglan, CHEN Zhiyang, YE Xiuzi. The application of ICP algorithm in point cloud alignment[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2007, 12(3): 517-521. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2007.03.023 杨现辉,王惠南. ICP算法在3D点云配准中的应用研究[J]. 计算机仿真,2010,27(8): 235-238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2010.08.058YANG Xianhui, WANG Huinan. Application research of ICP algorithmin 3D point cloud alignment[J]. Computer Simulation, 2010, 27(8): 235-238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2010.08.058 张星,张双星. 基于Point-to-Plane ICP的点云与影像数据自动配准[J]. 计算机与数字工程,2017,45(12): 2510-2514. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2017.12.039ZHANG Xing, ZHANG Shuangxing. Automatic registration of point cloud and image data based on point-to-plane ICP[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2017, 45(12): 2510-2514. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2017.12.039 张宏伟,张保明,郭海涛,等. 一种基于点云数据的DEM生成方法[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息,2015,38(5): 4-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2015.05.002ZHANG Hongwei, ZHANG Baoming, GUO Haitao, et al. A DEM generation method based on point cloud data[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2015, 38(5): 4-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2015.05.002 -




 下载:
下载: