Parallel Interaction Influence of Single-Stage Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Multi-Inverter System
-
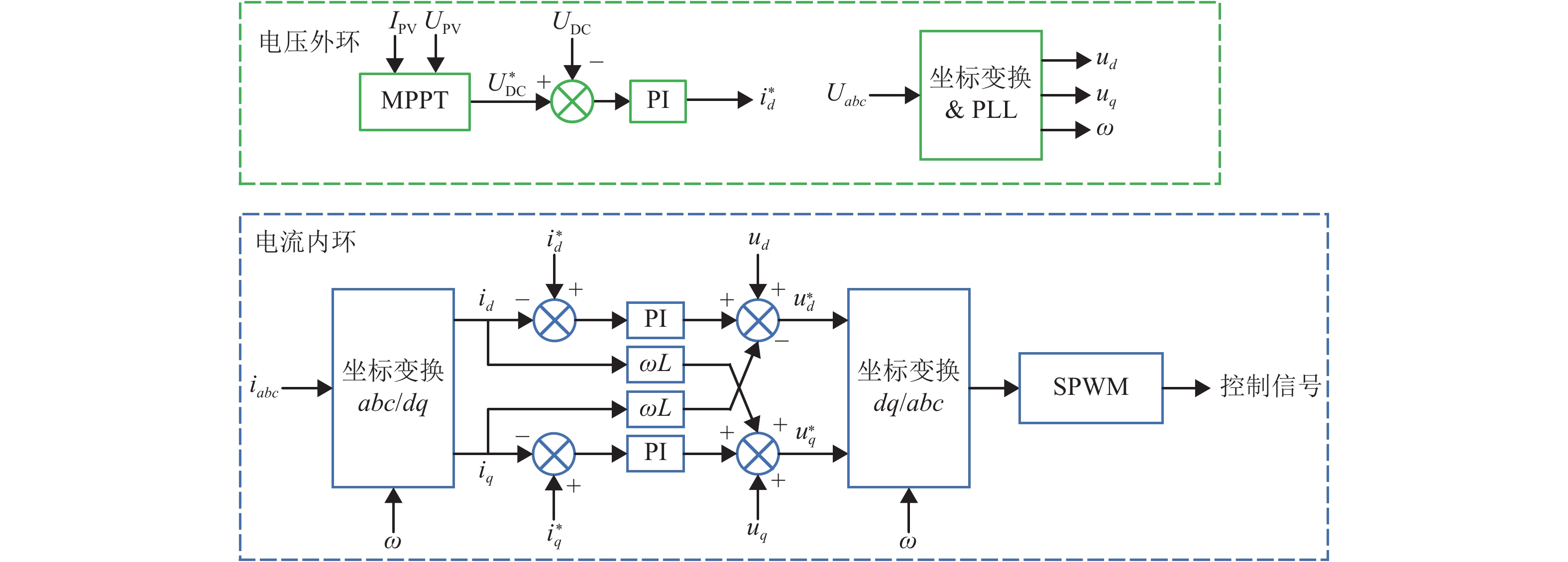
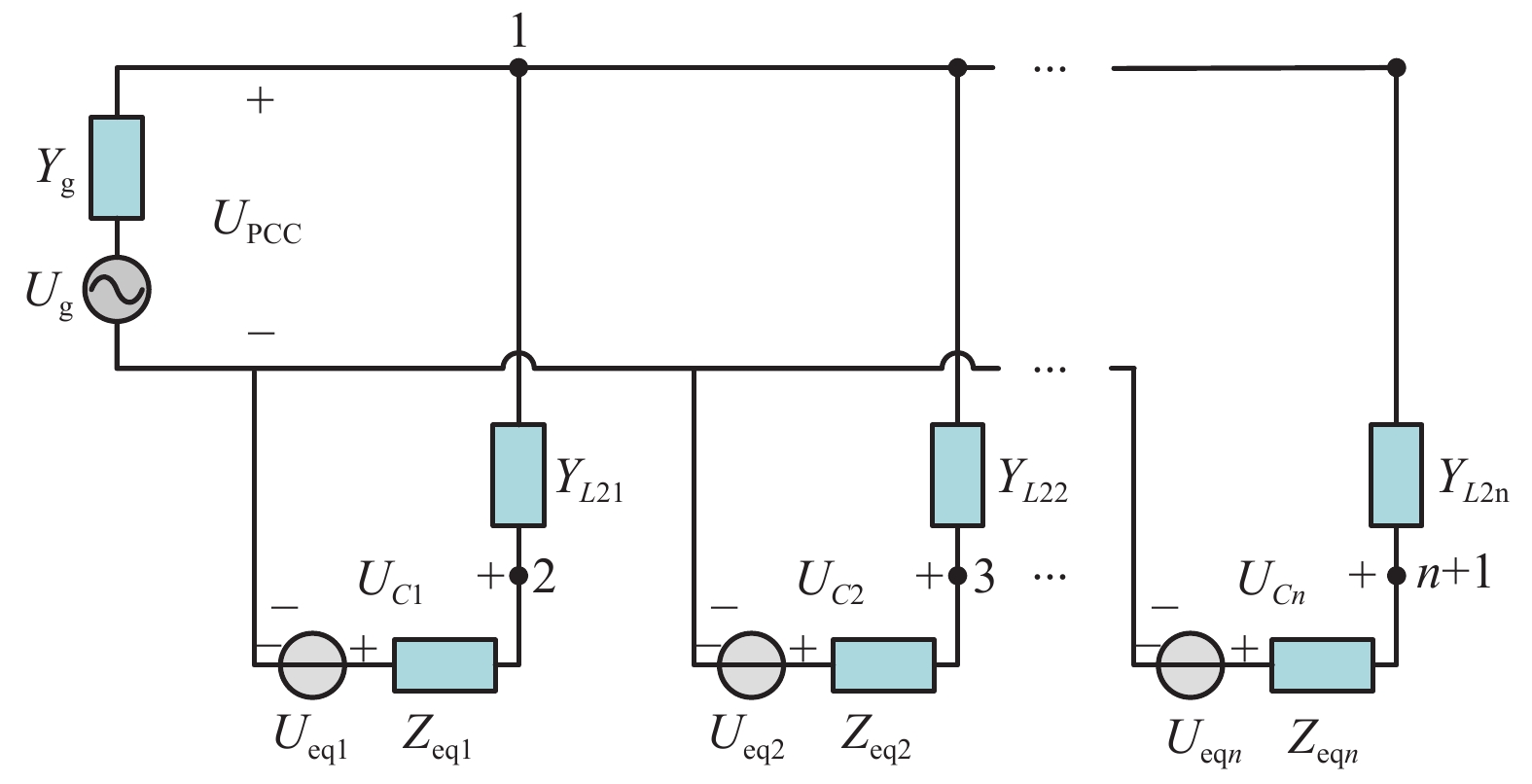
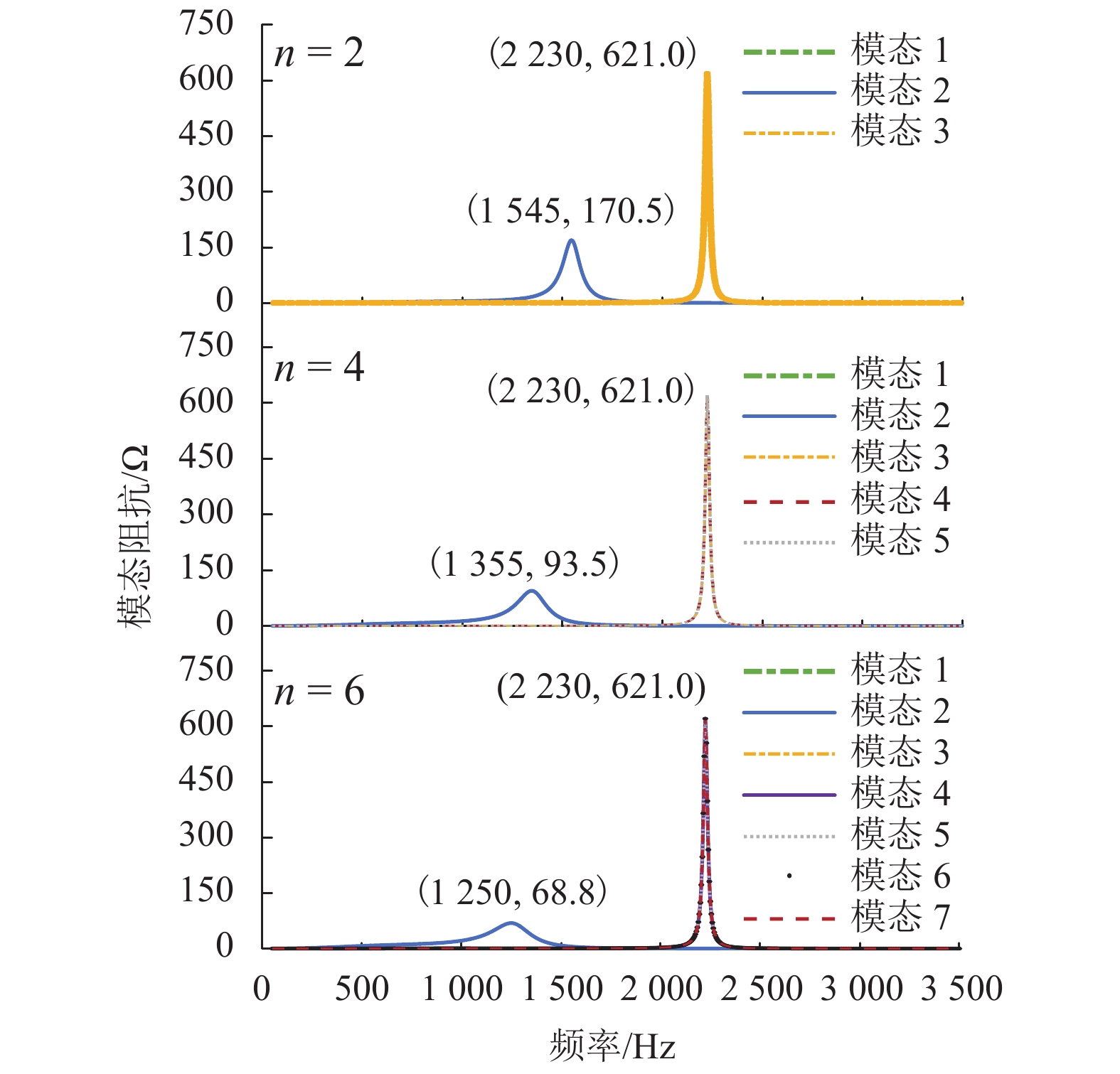
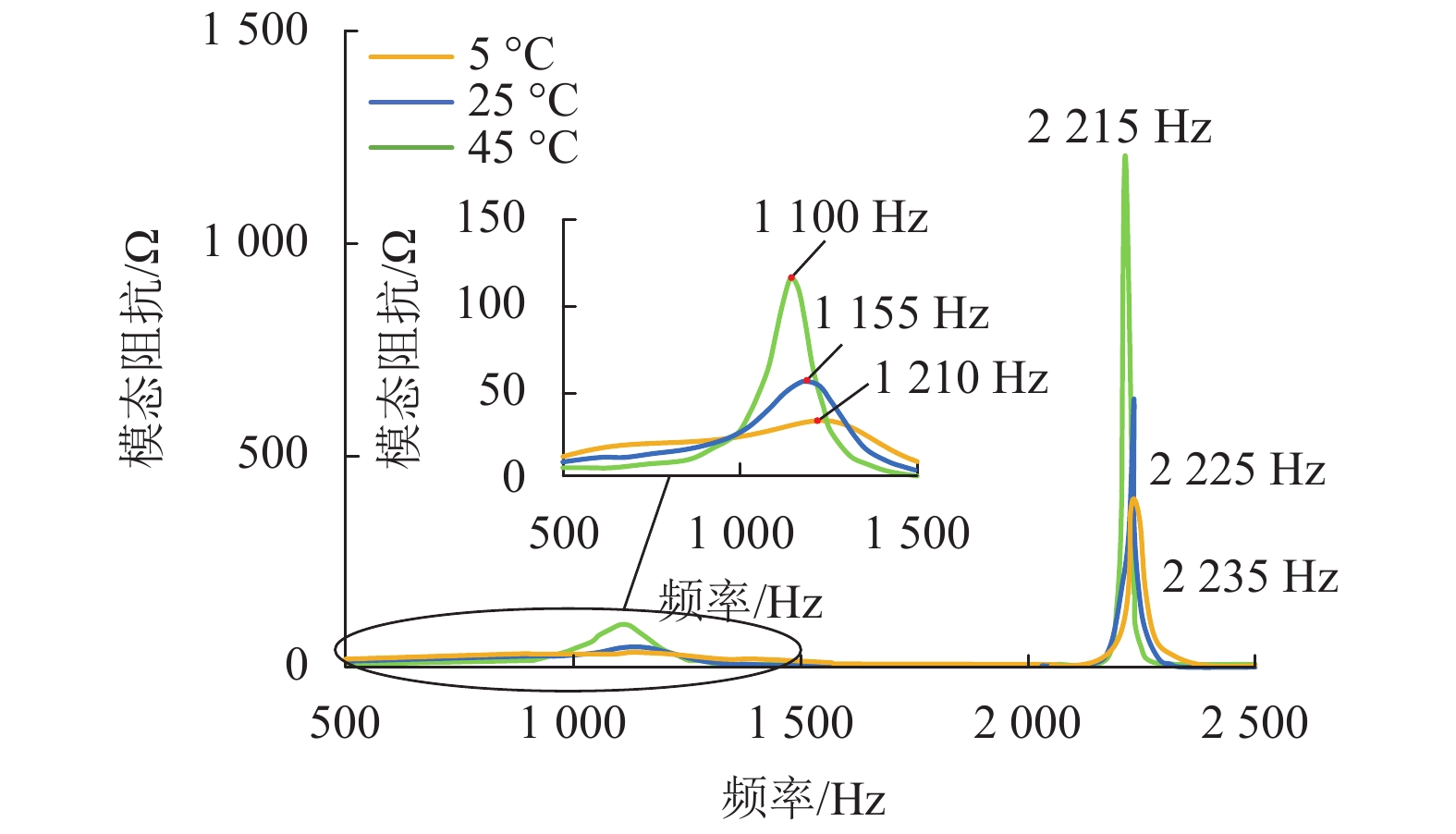
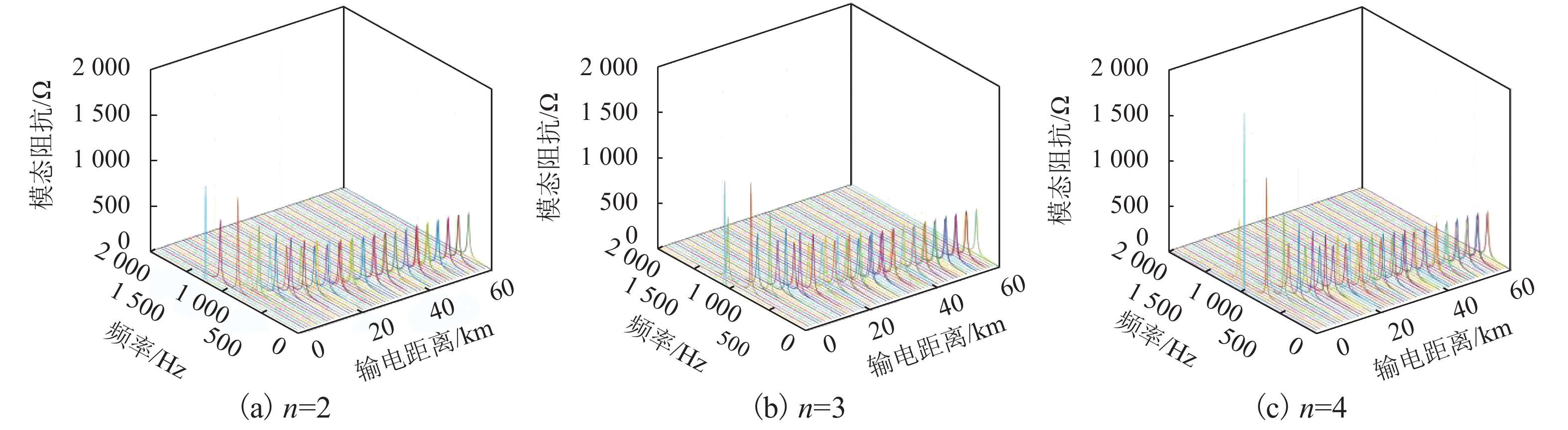
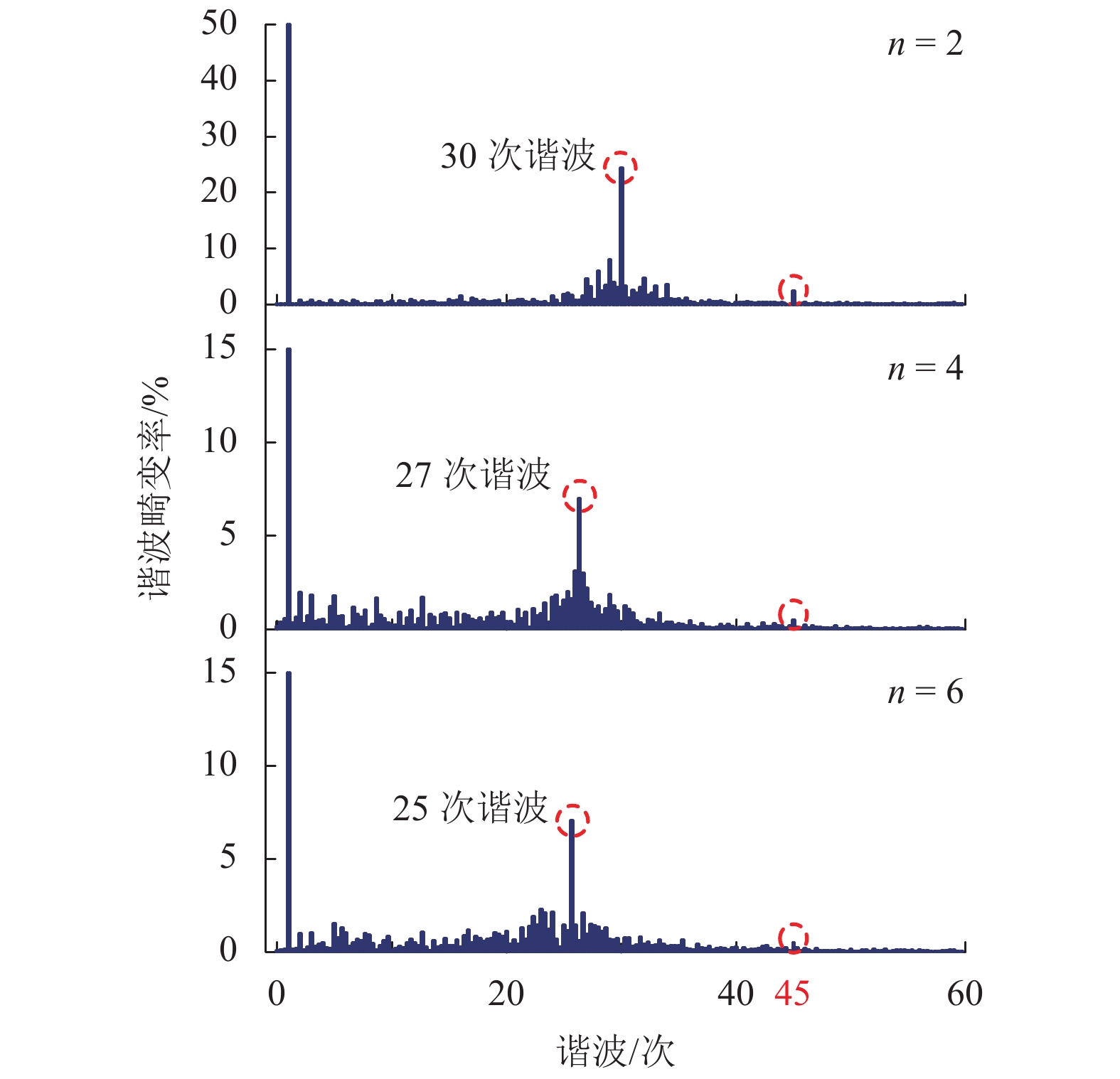
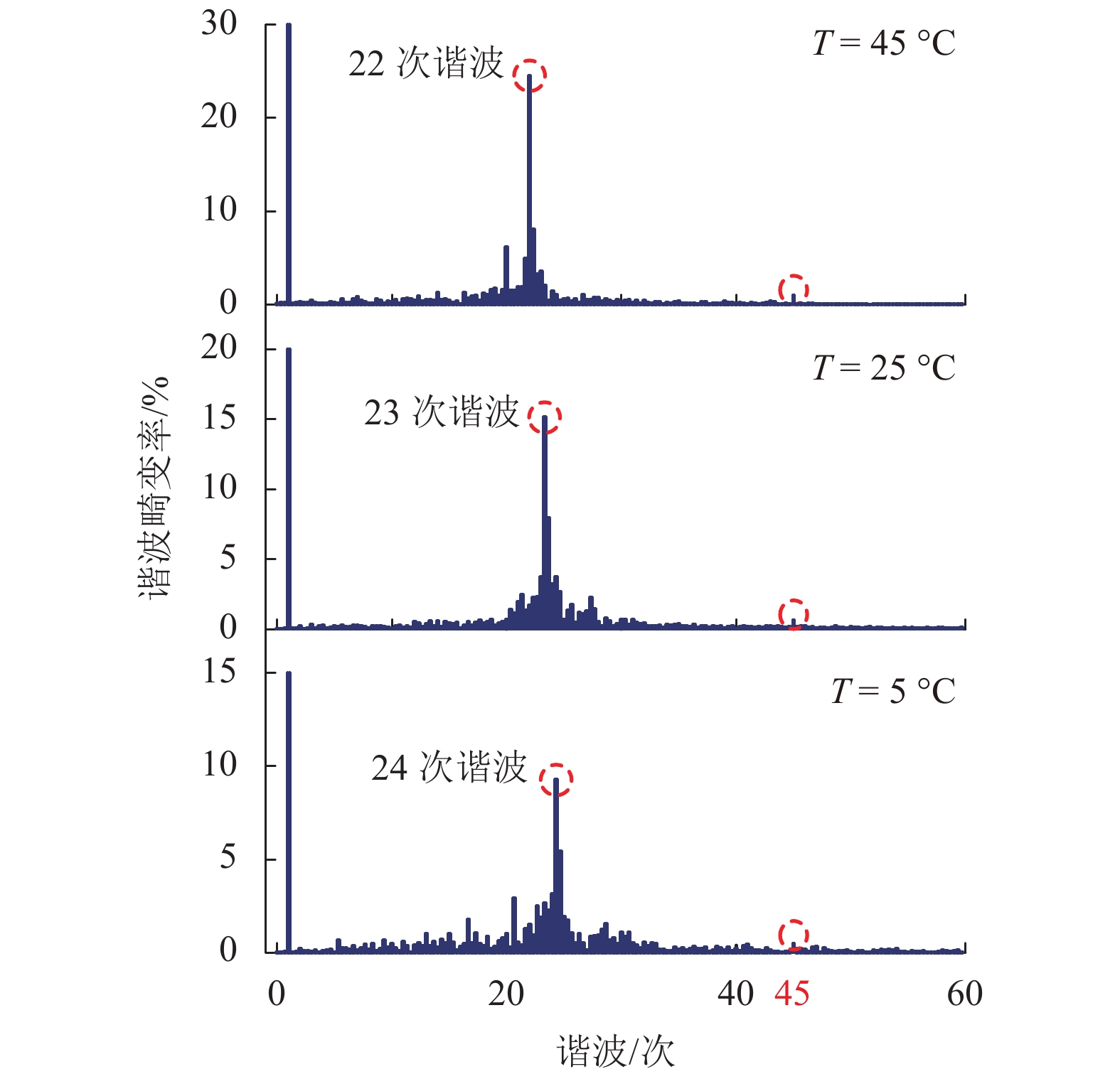
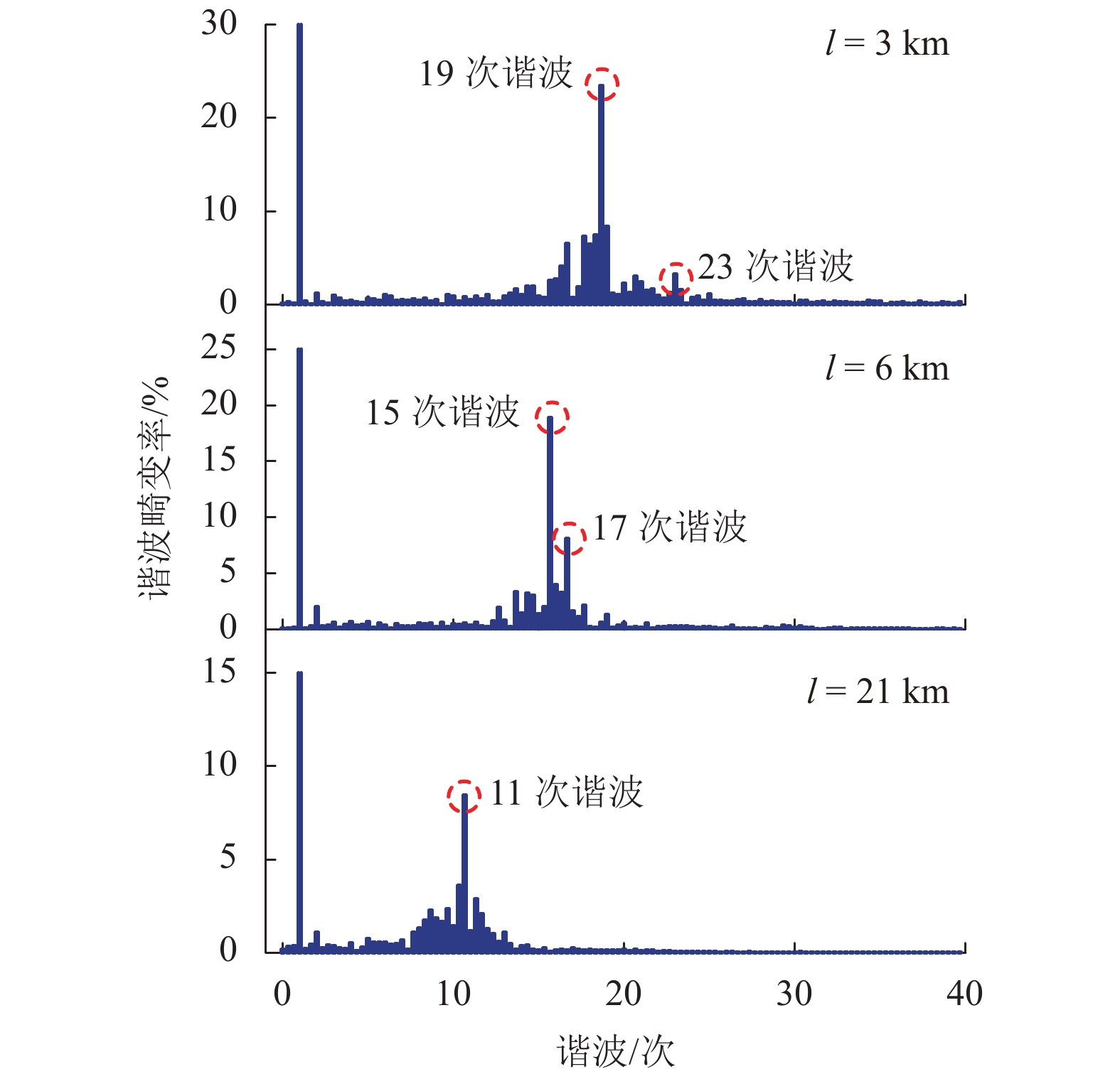
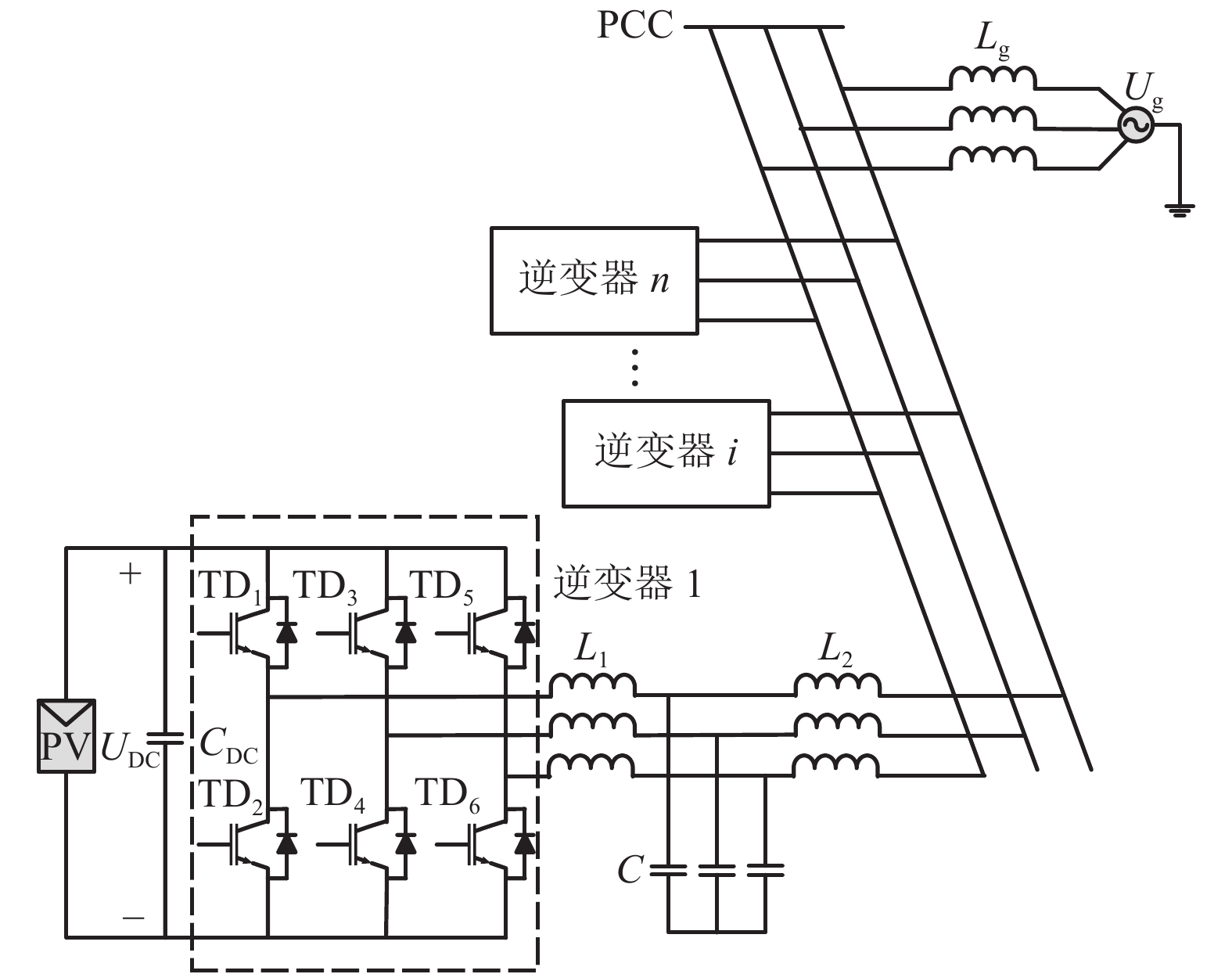
摘要: 在弱电网条件下,多逆变器间、多逆变器与电网间的动态交互作用影响着电力系统的电能质量和稳定性,易引发谐波谐振等问题. 为了研究单级光伏并网多逆变器系统的谐波谐振特性,考虑光伏源与系统之间的交互作用,采用模态分析法对谐振问题进行了系统的分析与讨论. 首先,根据三相单级式光伏并网系统结构及控制策略,建立了多逆变器戴维南等效模型;其次,通过构建多逆变器系统节点导纳矩阵,应用了一种能够确定系统谐振频率、谐振中心以及各节点参与程度的模态分析方法,从逆变器台数、外界环境、输电距离3个方面研究了系统谐振特性与变化规律;最后,基于MATLAB/Simulink仿真平台,通过搭建三相单级式光伏并网多逆变器系统仿真模型,验证了模态分析法的正确性与有效性. 研究结果表明:当逆变器台数增加时,低频谐振频率呈降低趋势,依次为30、27、25次谐波,高频谐振频率为2 230 Hz保持不变;当外界环境温度降低时,低频谐振频率逐渐升高,依次为22、23、24次谐波,高频谐振频率固定约为2 225 Hz;当输电距离增长时,低频与高频谐振频率均逐渐降低且变得接近.Abstract: Under the condition of weak grid, the dynamic interactions between multi-inverters and between multi-inverters and the grid affect the power quality and stability of the power system, which is likely to cause harmonic resonance. In order to study the harmonic resonance characteristics of the single-stage photovoltaic grid-connected multi-inverter system, the modal analysis method is used for systematical analysis and discussion on the resonance problem while the interaction between the photovoltaic generation and the system is considered. Firstly, according to the structure and control strategy of three-phase single-stage photovoltaic grid-connected system, the Thevenin equivalent model for the multi-inverter system is established. Secondly, a modal analysis method is applied, which can determine the system resonance frequency, resonance center and the participation degree of each node by constructing node admittance matrix of the multi-inverter system. The resonance characteristics and variation laws of the system are studied from three aspects: the number of inverters, external environment and transmission distance. Finally, with the use of MATLAB/Simulink simulation platform, the correctness and effectiveness of the modal analysis method are validated by a simulation model of a three-phase single-stage photovoltaic grid-connected multi-inverter system. The results show that when the number of inverters increases, the low resonance frequency tends to decrease, which is 30th, 27th, and 25th harmonics respectively, while the high resonance frequency remains unchanged at 2 230 Hz. When the ambient temperature decreases, the low resonance frequency increases gradually, which is 22th, 23th, and 24th harmonics respectively, and the high resonance frequency is stable at about 2 225 Hz. When the transmission distance increases, the low and high resonance frequencies gradually decrease and become close to each other.
-
Key words:
- harmonic resonance /
- modal analysis /
- multi-inverter /
- single-stage photovoltaic
-
表 1 系统仿真参数
Table 1. Parameters of system simulation
参数 数值 参数 数值 光伏开路电压 Uoc/V 880 光伏 MPP 电压 Um/V 700 光伏短路电流 Isc/A 15.9 光伏 MPP 电流 Im/A 14.7 电网电压 Ug/V 220 逆变器侧电感 L1/mH 4 电网频率 fg/Hz 50 网侧电感 L2/mH 0.6 电网阻抗 Lg/mH 0.5 滤波电容 C/μF 10 开关频率 fs/kHz 10 直流链电容 CDC/μF 2 000 注:MPP—maximum power point. 表 2 逆变器台数变化时各节点参与因子
Table 2. Participation factor with variable inverter number
节点 n = 2 n = 4 n = 6 f = 1 545 Hz f = 2 230 Hz f = 1 355 Hz f = 2 230 Hz f = 1 250 Hz f = 2 230 Hz 1 0.082 0.063 0.032 0.026 0.017 0.014 2 0.418 0.437 0.218 0.224 0.149 0.152 3 0.500 0.500 0.565 0.083 0.833 0.040 4 0.190 0.569 0 0.091 5 0 0.098 0 0.415 6 0 0.046 7 0 0.325 表 3 不同输电距离下模态分析结果
Table 3. Modal analysis results underdifferent transmission distances
l/km f/Hz 模态阻抗/Ω 3 955 975.5 1 160 686.2 6 745 764.7 880 584.2 21 525 562.3 550 501.3 -
JALILI K, BERNET S. Design of LCL filters of active-front-end two level voltage-source converters[J]. IEEE Trans on Industrial Electronics, 2009, 56(5): 1674-1689. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2008.2011251 丁明,王伟胜,王秀丽,等. 大规模光伏发电对电力系统影响综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2014,34(1): 1-14.DING Ming, WANG Weisheng, WANG Xiuli, et al. A review on the effect of large-scale PV generation on power systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34(1): 1-14. 刘怀远,徐殿国,武健,等. 并网换流器系统谐振的分析、检测与消除[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2016,36(4): 1061-1074.LIU Huaiyuan, XU Dianguo, WU Jian, et al. Analysis,detection and mitigation of resonance in grid-connected converter systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(4): 1061-1074. 张兴,余畅舟,刘芳,等. 光伏并网多逆变器并联建模及谐振分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2014,34(3): 336-345.ZHANG Xing, YU Changzhou, LIU Fang, et al. Modeling and resonance analysis of multi-paralleled grid-tied inverters in PV systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34(3): 336-345. 王振浩,孙玮澳,孙福军. 光伏系统并网的多逆变器并联交互影响分析[J]. 电力电子技术,2017,51(2): 29-32.WANG Zhenhao, SUN Weiao, SUN Fujun. Interaction analysis of multiple paralleled inverters in photovoltaic system[J]. Power Electronics, 2017, 51(2): 29-32. 唐振东,杨洪耕,袁林. 弱电网下多逆变器并网控制通道间的交互影响分析[J]. 电网技术,2016,40(11): 3524-3531.TANG Zhendong, YANG Honggeng, YUAN Lin. Analysis on interactive influences among control loops of multi inverters connected to weak-structured power system[J]. Power System Technology, 2016, 40(11): 3524-3531. 胡伟,孙建军,马谦,等. 多个并网逆变器间的交互影响分析[J]. 电网技术,2014,38(9): 2511-2518.HU Wei, SUN Jianjun, MA Qian, et al. Analysis on interactive influences among multi grid-connected inverters[J]. Power System Technology, 2014, 38(9): 2511-2518. HE J. Investigation and active damping of multiple resonances in a parallel-inverter-based microgrid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2013, 28(1): 234-246. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2012.2195032 严干贵,常青云,黄亚峰,等. 弱电网接入下多光伏逆变器并联运行特性分析[J]. 电网技术,2014,38(4): 933-940.YAN Gangui, CHANG Qingyun, HUANG Yafeng, et al. Analysis on parallel operational characteristics of multi photovoltaic inverters connected to weak-structured power system[J]. Power System Technology, 2014, 38(4): 933-940. 许德志,汪飞,毛华龙,等. 多并网逆变器与电网的谐波交互建模与分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2013,33(12): 64-71,187.XU Dezhi, WANG Fei, MAO Hualong, et al. Modeling and analysis of harmonic interaction between multiple grid-connected inverters and the utility grid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33(12): 64-71,187. 孙振奥,杨子龙,王一波,等. 光伏并网逆变器集群的谐振原因及其抑制方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2015,35(2): 418-425.SUN Zhenao, YANG Zilong, WANG Yibo, et al. The cause analysis and suppression method of resonances in clustered grid-connected photovoltaic inverters[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35(2): 418-425. XU W, HUANG Z Y, CUI Y, et al. Harmonic resonance mode analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2005, 20(2): 1182-1190. doi: 10.1109/TPWRD.2004.834856 仰彩霞, 刘开培, 李建奇, 等. 谐波谐振模态灵敏度分析[J]. 电工技术学报, 2011, 26(增刊1): 207-212.YANG Caixia, LIU Kaipei, LI Jianqi, et al. Modal sensitivity analysis for harmonic resonance[J]. Transac-tions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2011, 26(S1): 207-212. 孙东,姚玉洁,刘玉林,等. 配电网谐波谐振改进模态分析方法的研究[J]. 电力电容器与无功补偿,2017,38(2): 105-110.SUN Dong, YAO Yujie, LIU Yulin, et al. Study on improved mode analysis method of harmonic resonance in distribution grid[J]. Power Capacitor & Reactive Power Compensation, 2017, 38(2): 105-110. 艾欣,雷之力,崔明勇. 微电网谐波谐振的模态检测法研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2009,29(增刊1): 55-60.AI Xin, LEI Zhili, CUI Mingyong. Study on modal survey method of the harmonic resonance in micro-grid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2009, 29(S1): 55-60. 谈萌,彭祥华,王同勋,等. 基于模态分析的半波长交流输电系统与风电场并网谐振研究[J]. 高电压技术,2018,44(1): 90-98.TAN Meng, PENG Xianghua, WANG Tongxun, et al. Study on the harmonic resonance of grid-connected of wind farms and half-wavelength AC transmission system based on modal analysis method[J]. High Voltage Engineering,Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2018, 44(1): 90-98. 唐振东,杨洪耕. 基于模态分析的风电场并网谐波谐振研究[J]. 电力自动化设备,2017,37(3): 87-92,99.TANG Zhendong, YANG Honggeng. Research on wind farm harmonic resonance based on modal analysis[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2017, 37(3): 87-92,99. -




 下载:
下载: