Finite Element Analysis of Rolling Strengthening Process for Wheel Tread of High-Speed Trains
-
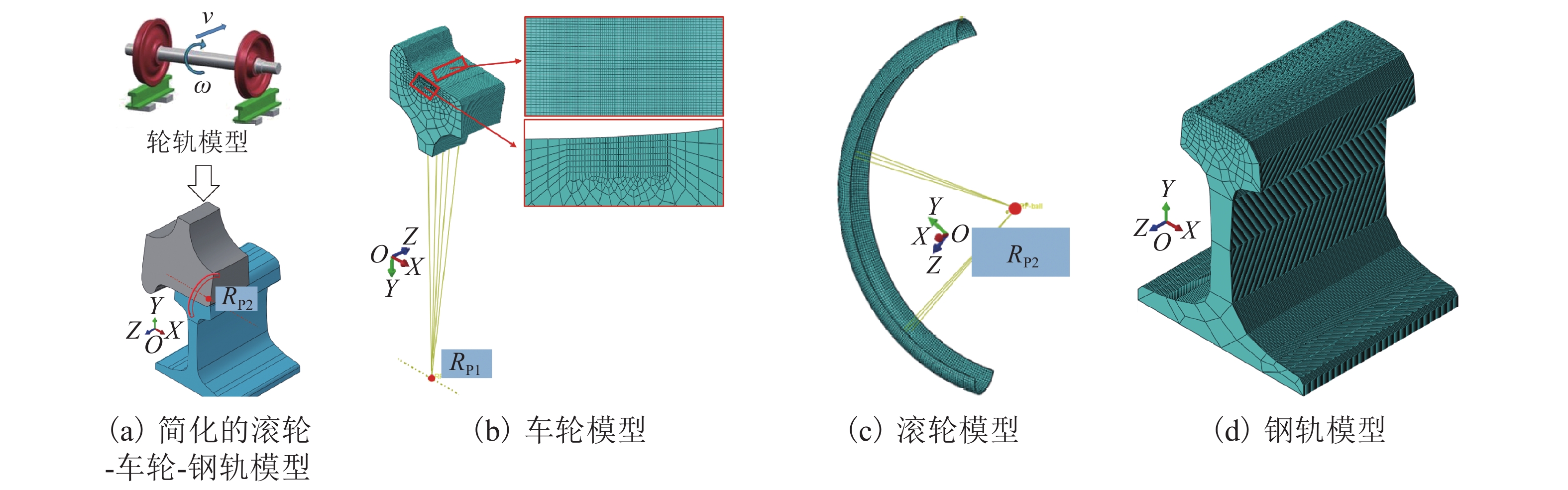
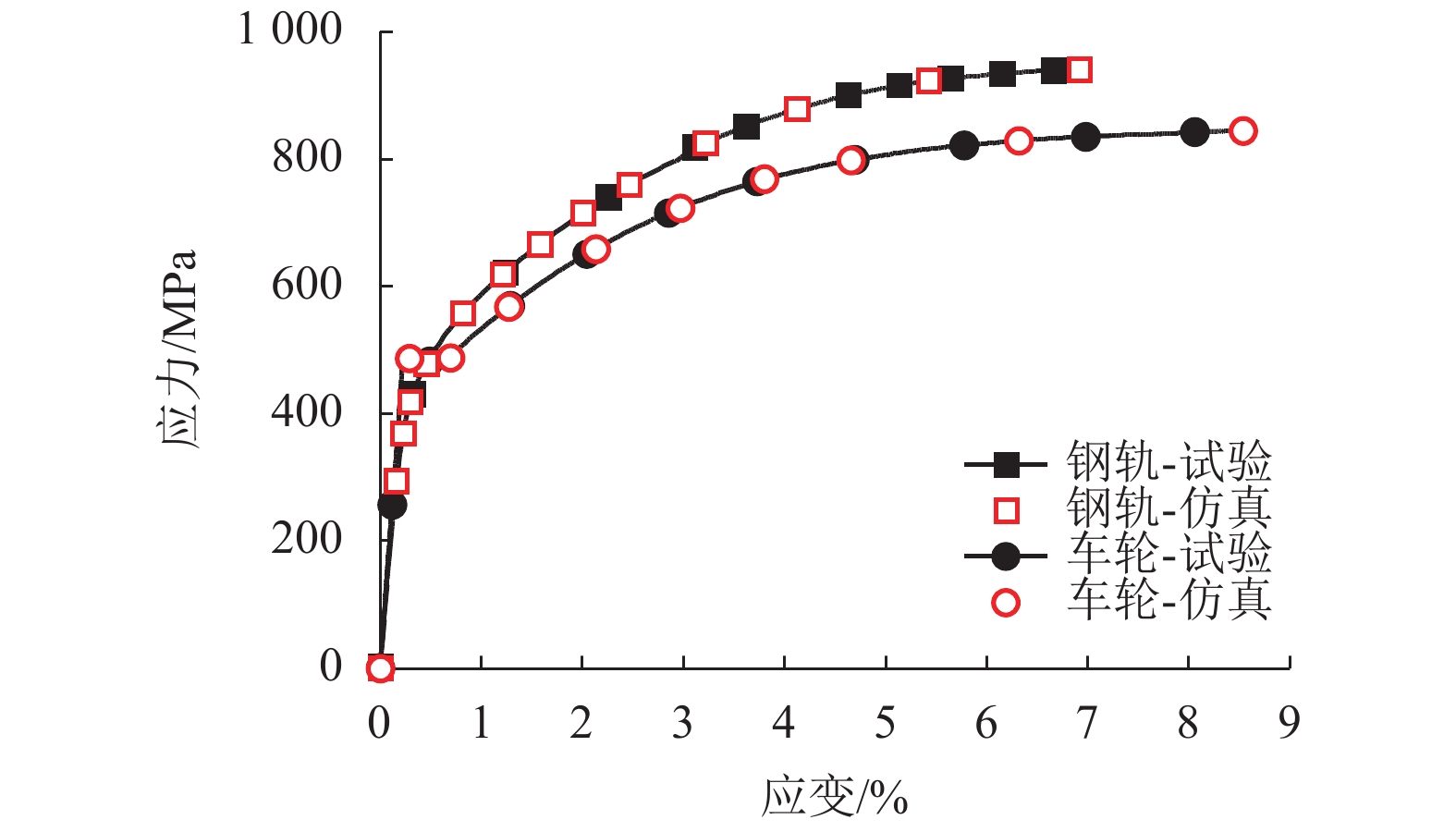
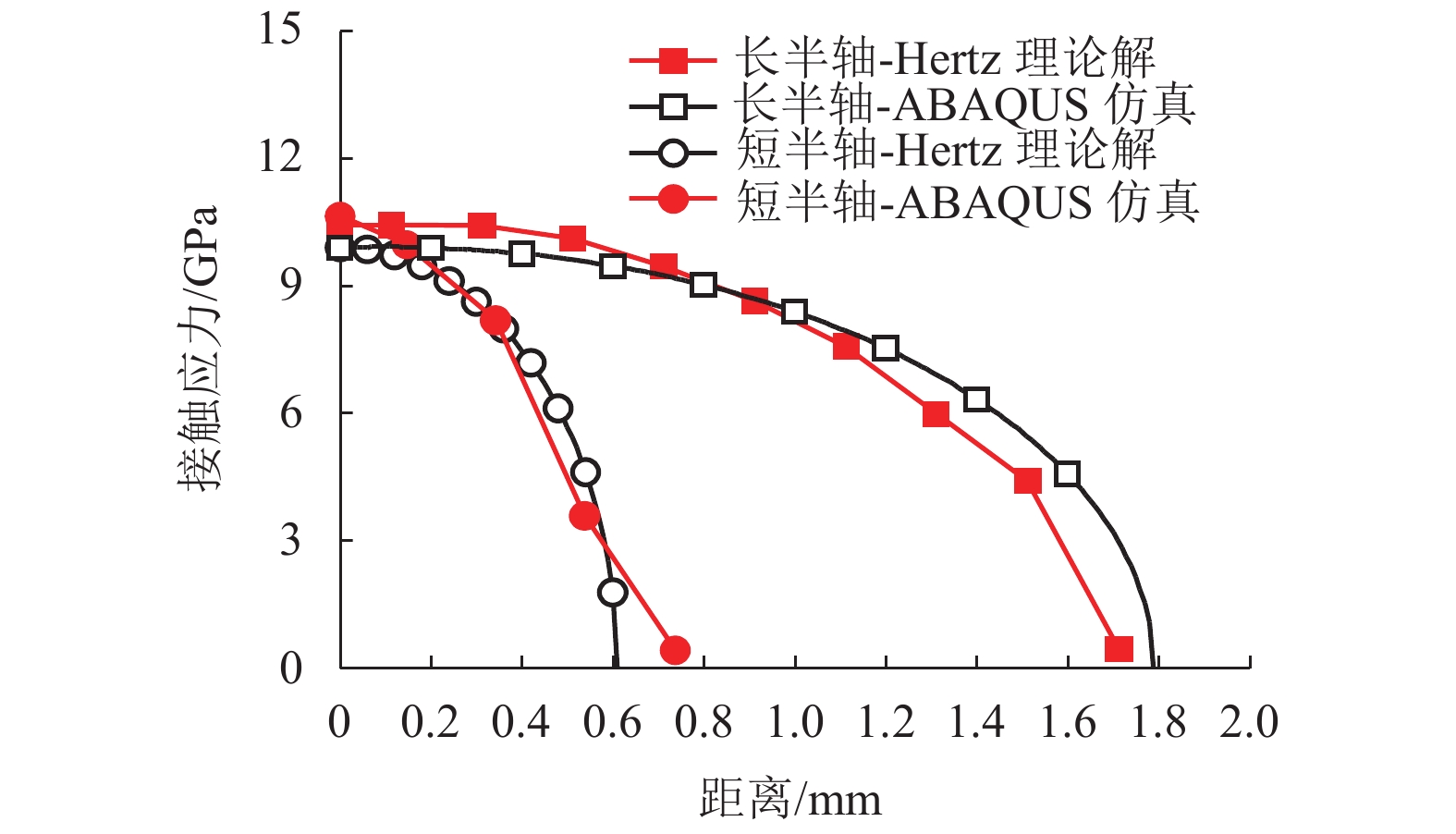
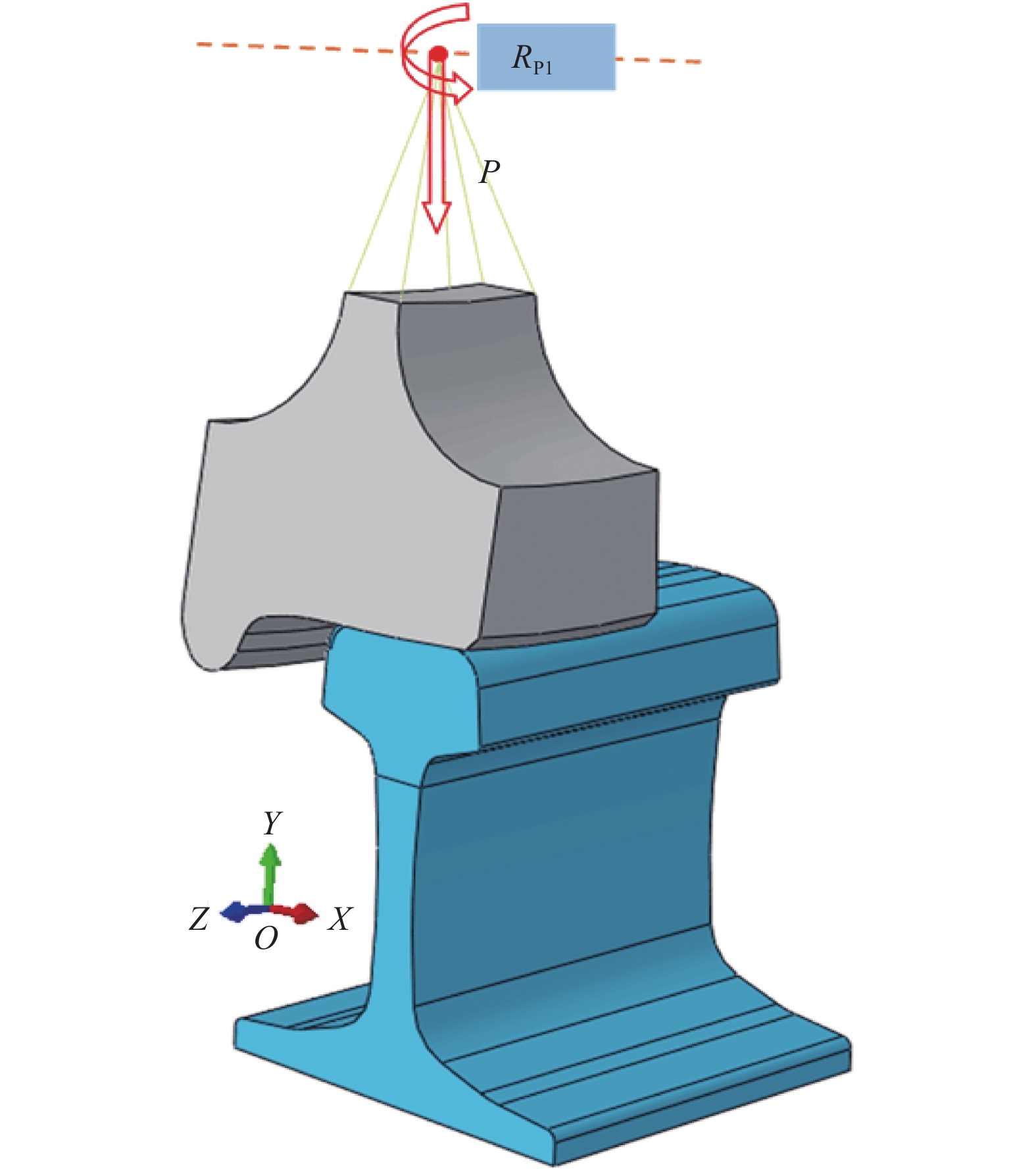
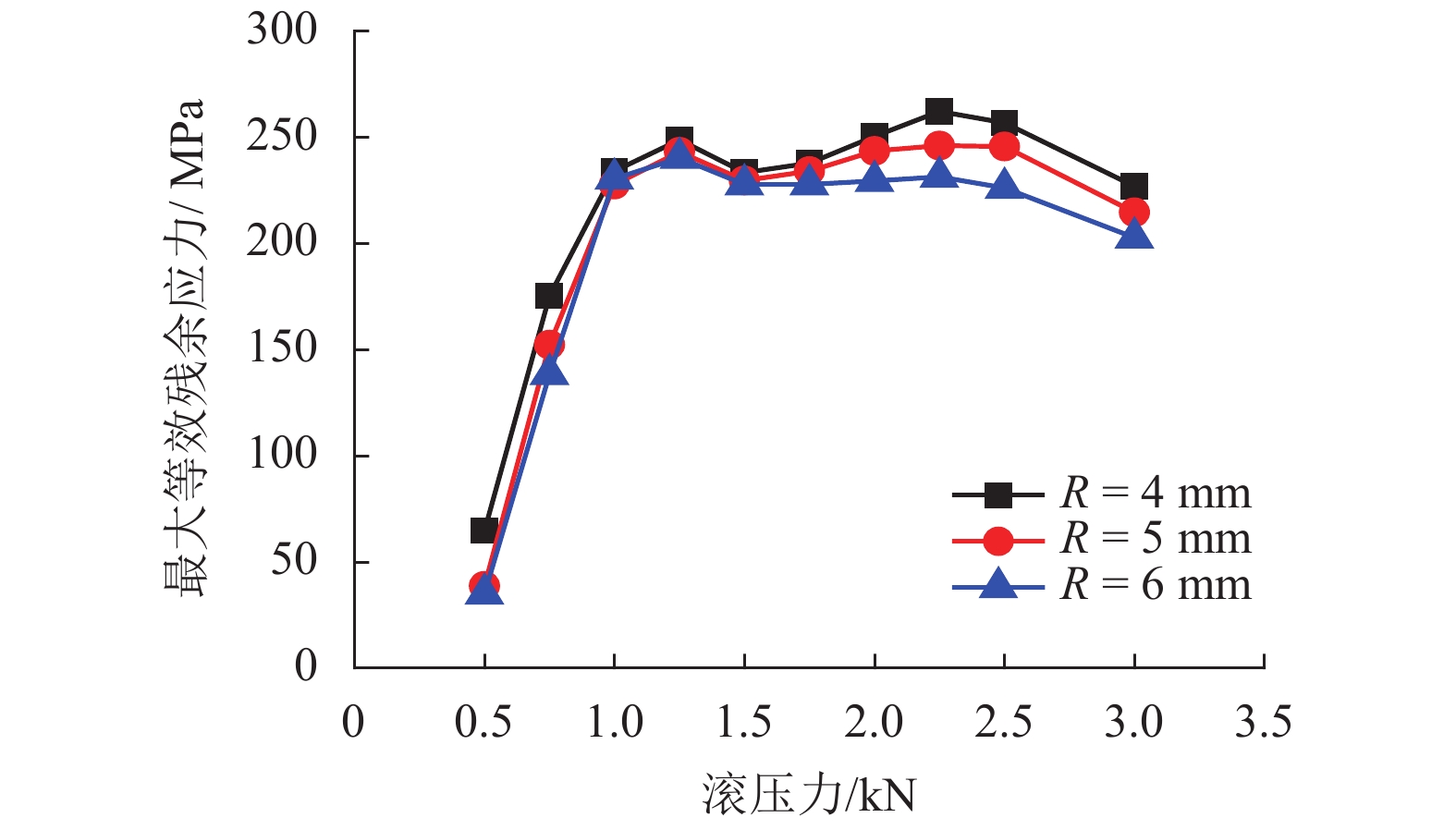
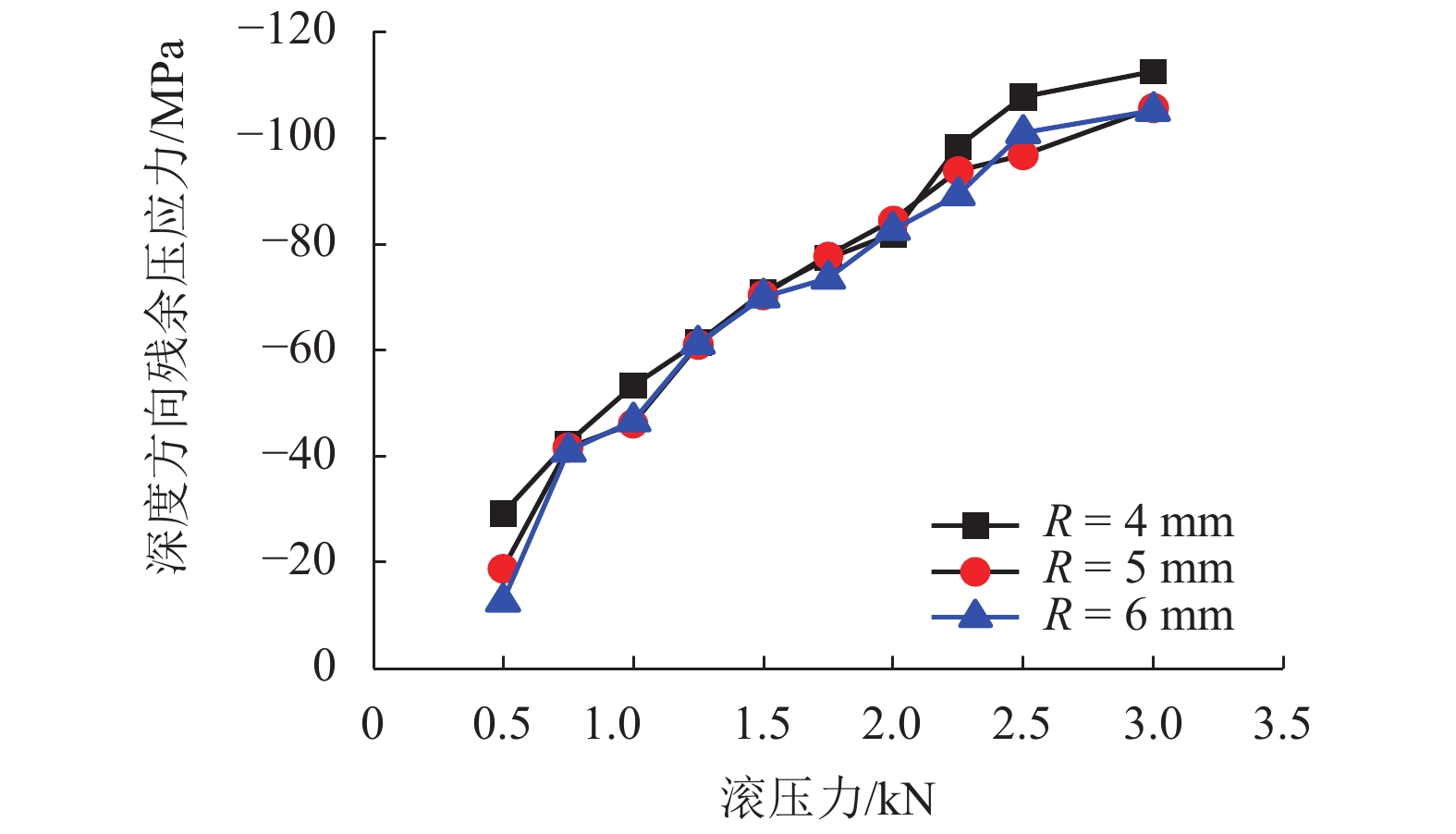
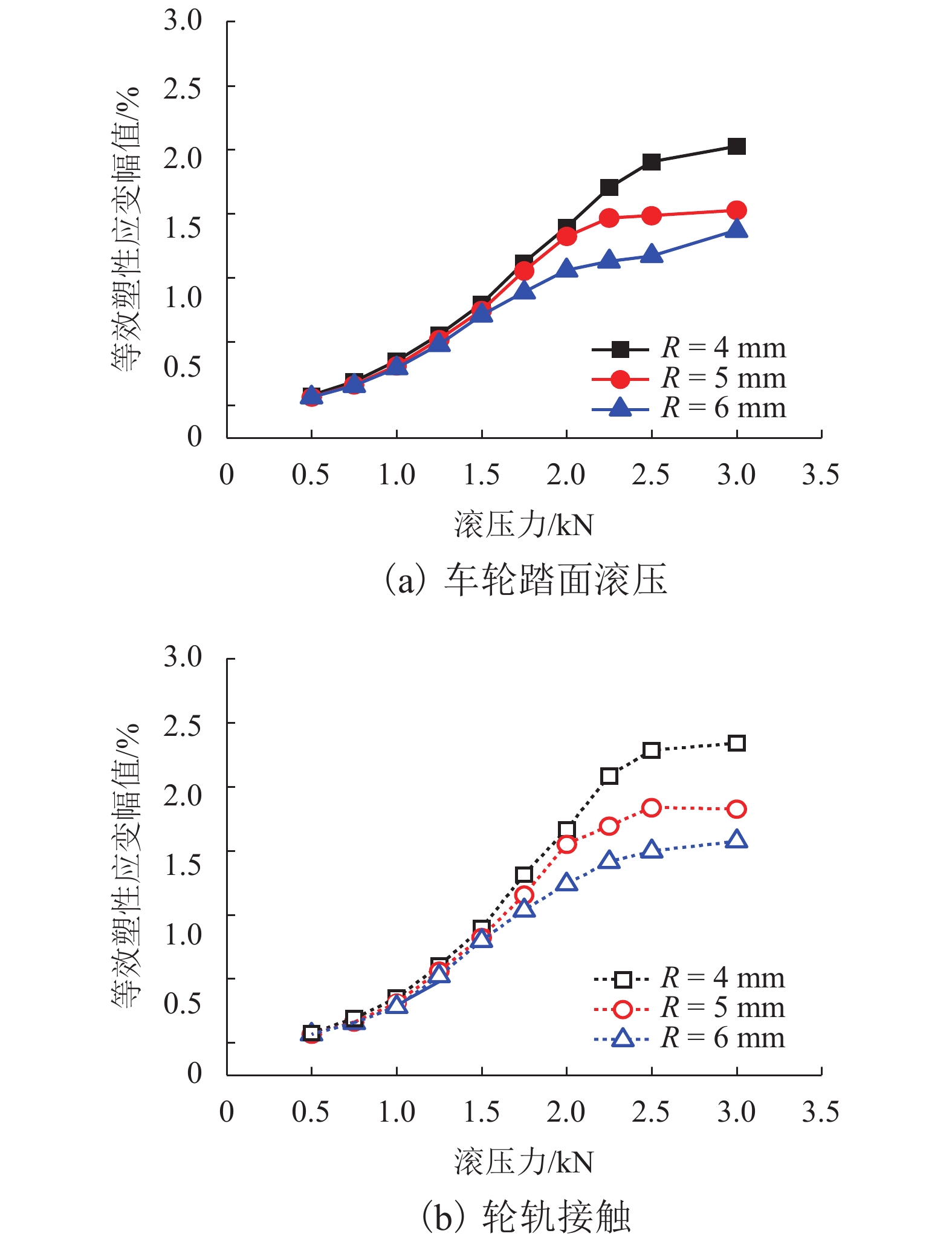
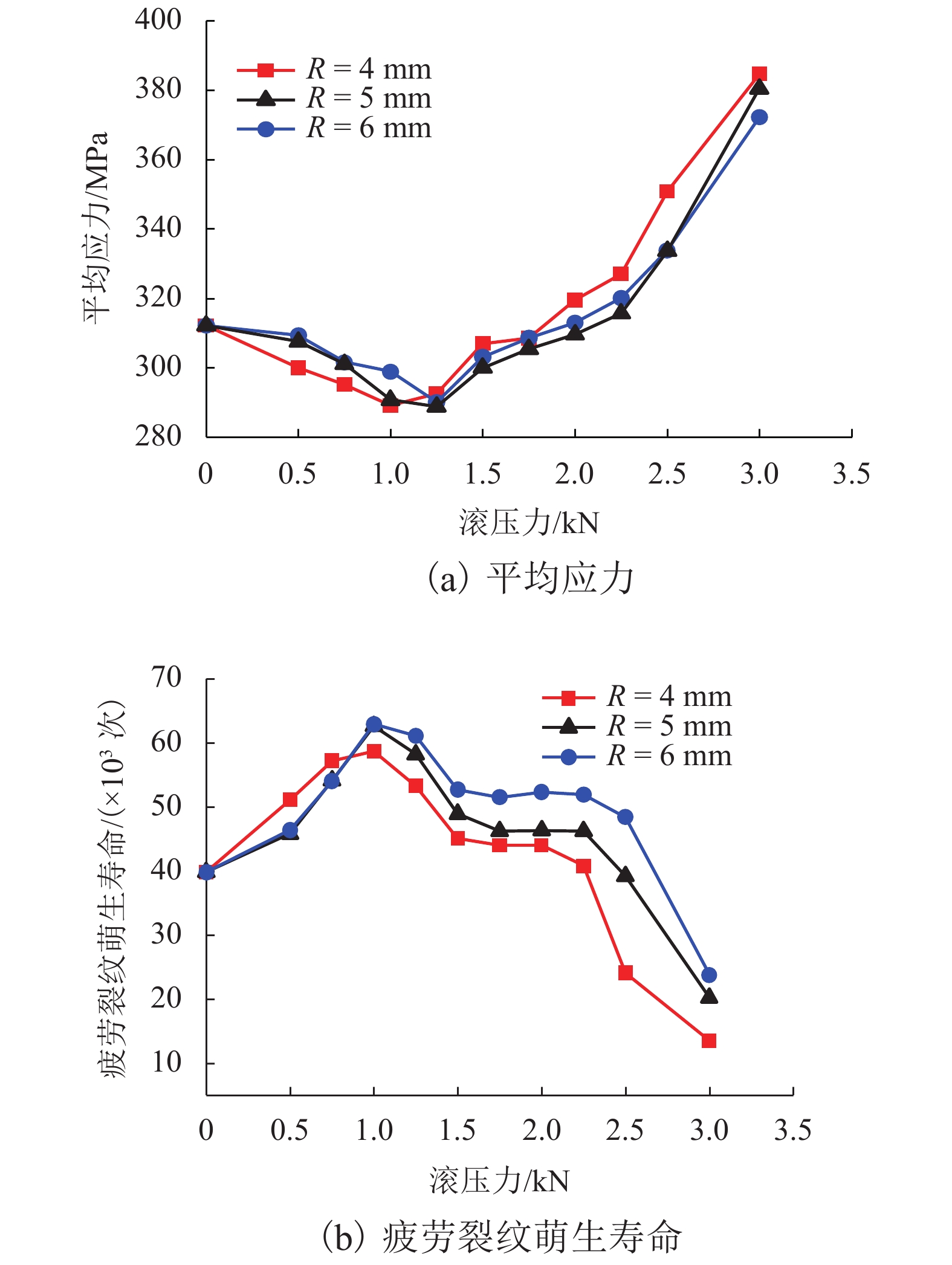
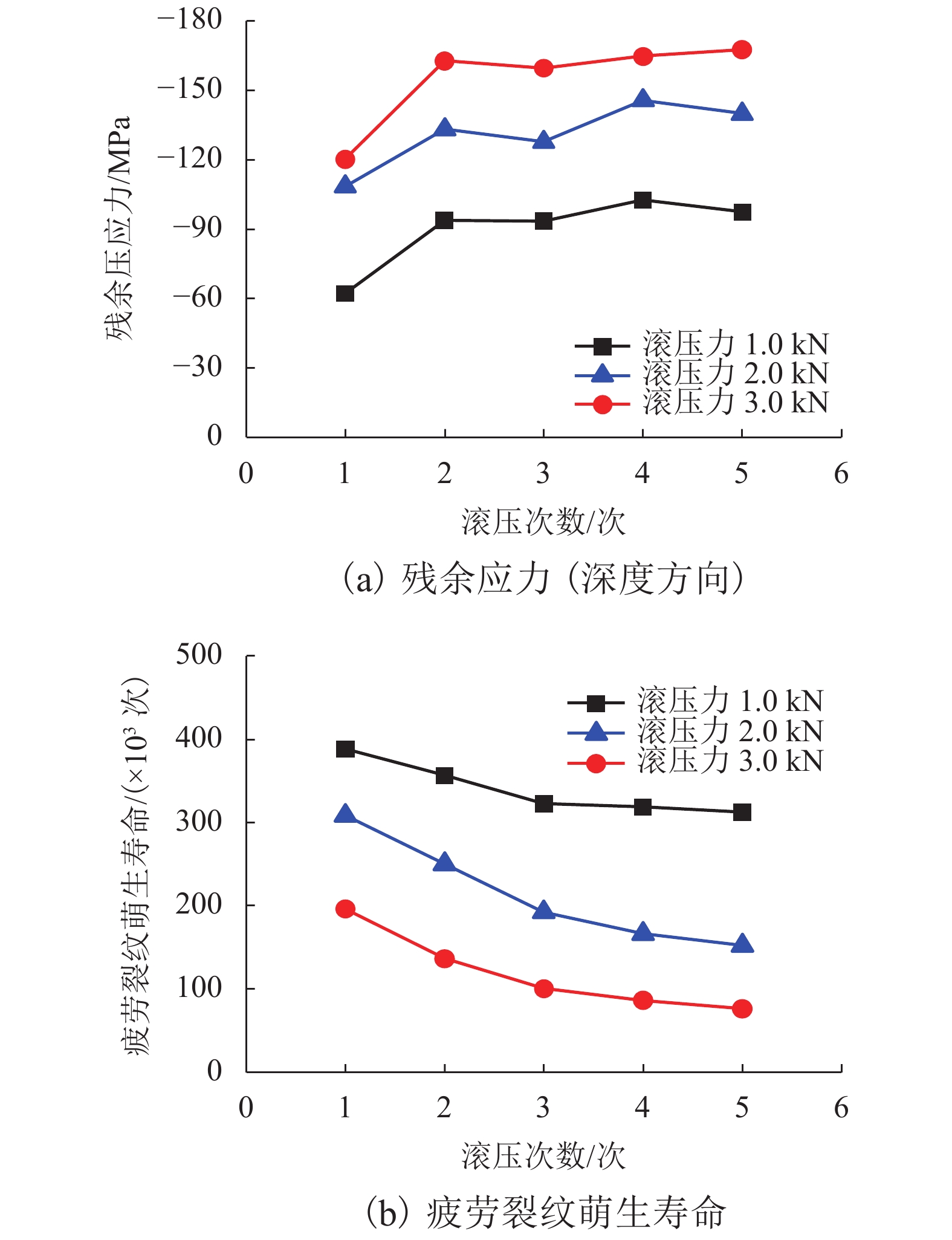
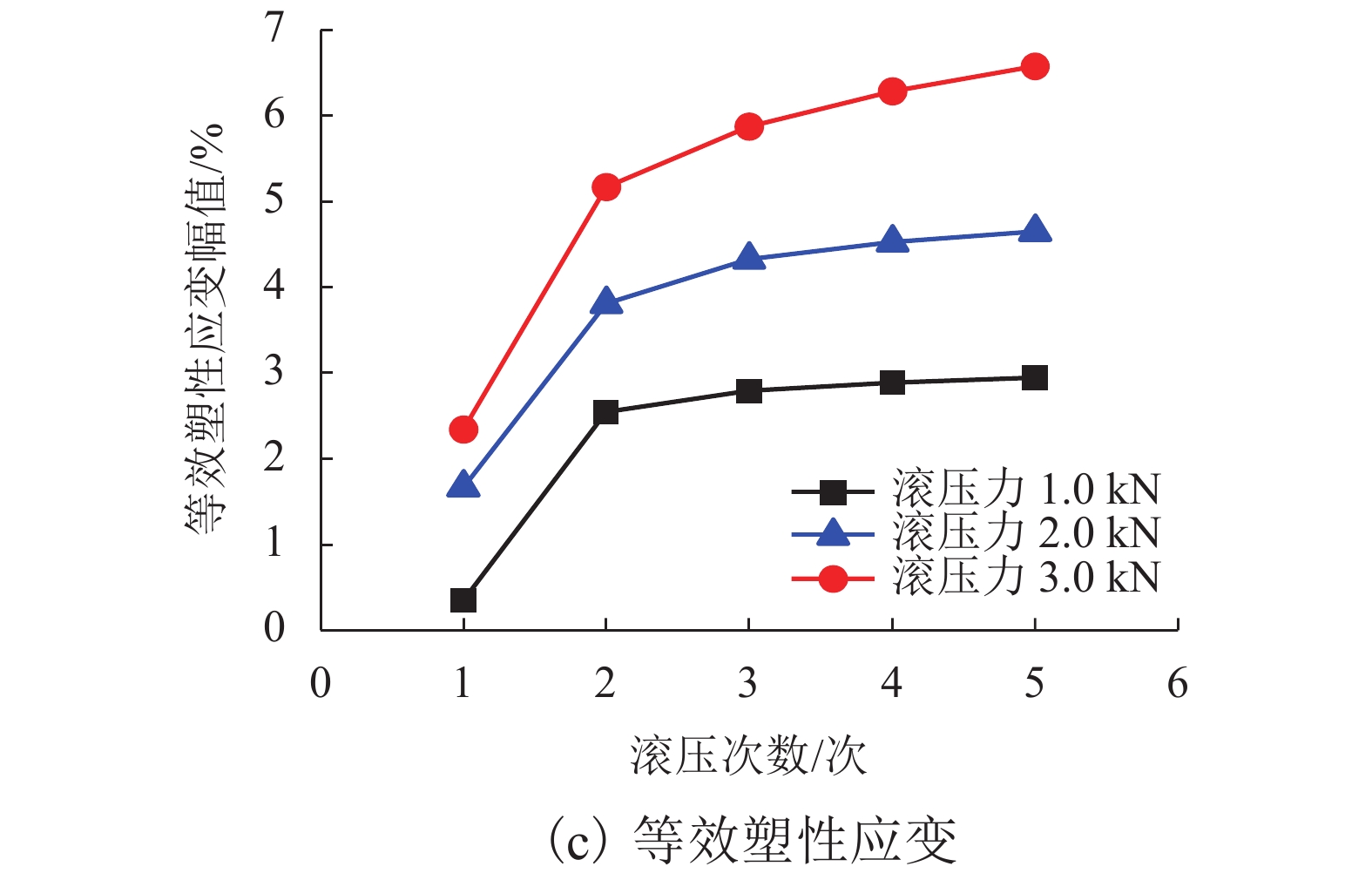
摘要: 为提高镟修后高速列车车轮踏面强度和使用寿命,进行了车轮踏面滚压强化过程的数值模拟,并对滚压强化的工艺参数进行了优化. 以CRH3高速列车车轮为研究对象,建立了滚压轮-车轮-钢轨三维滚动接触有限元模型;通过计算不同滚压轮尺寸、滚压力及滚压道次对车轮踏面残余应力和等效塑性应变场分布的影响来分析滚压强化机理;采用Borrow-Miller准则修正的Manson-Coffin公式计算了滚压后轮轨接触时车轮踏面的疲劳裂纹萌生寿命,进而对车轮踏面滚压强化工艺参数进行优化. 研究结果表明:随着滚压力的增加,车轮踏面的疲劳裂纹萌生寿命先增后减,且随着滚压道次的增加而下降,即滚压道次的增加反而会降低车轮踏面的疲劳裂纹萌生寿命;滚压道次的增加对残余应力的影响不大,滚压轮圆弧半径的增加会导致疲劳裂纹萌生寿命小幅度增大;综合考虑,以滚压道次为3次、滚压力为1 kN、滚压轮圆弧半径为6 mm时的滚压效果最佳,此时车轮踏面的疲劳裂纹萌生寿命可提升约58%.Abstract: To improve the wheel tread strength and service life of high-speed trains after reprofiling, the numerical simulation of rolling strengthening for the wheel tread was carried out, and the process parameters of rolling strengthening were optimized. Focusing on the wheel of the CRH3 high-speed train, a three-dimensional rolling contact finite element model was established which combines the roller, wheel, and rail. According to the influences of roller size, rolling pressure and rolling time on the distributions of residual stress and equivalent plastic strain fields of the wheel tread, the rolling strengthening mechanism were numerically investigated. The fatigue crack initiation life of the wheel tread after rolling strengthening in wheel-rail contact were estimated by the Manson-Coffin model modified by Borrow-Miller criterion, and the process parameters of rolling strengthening were optimized. The results show that, with the increase of rolling force, the fatigue crack initiation life of the wheel tread increases at first and then decreases, and it decreases with the increasing rolling time, which implies that the increasing rolling time reduces the fatigue crack initiation life of the wheel tread. Meanwhile, increasing the rolling time has little effect on the residual stress, and the increasing roller radius leads to a small increase of the fatigue crack initiation life. In summary, the optimal rolling strengthening parameters can be considered as the rolling times of 3 times, rolling force of 1 kN and roller radius of 6 mm, which can increase the fatigue crack initiation life of the wheel tread by about 58%.
-
表 1 网格敏感性分析
Table 1. Mesh sensitivity analysis
网格尺寸/mm 等效应力/MPa 计算时间/min 计算误差/% 0.3 608.8 152.0 0 0.4 608.3 123.0 0.08 0.5 587.4 98.0 3.50 表 2 疲劳裂纹萌生寿命预测模型材料参数
Table 2. Material parameters using in fatigue crack initiation life prediction model
σf/MPa b c $\varepsilon _{\rm{f}}^{0.6}$ 1 425 −0.113 4 −0.597 6 0.450 5 -
金学松,张雪珊,张剑,等. 轮轨关系研究中的力学问题[J]. 机械强度,2005,27(4): 408-418. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9669.2005.04.002JIN Xuesong, ZHANG Xueshan, ZHANG Jian, et al. Mechanics in performance of wheel-rail[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2005, 27(4): 408-418. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9669.2005.04.002 CARTER F W. On the action of a locomotive driving wheel[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, 1926, 112(760): 151-157. JOHNSON K L. The effect of a tangential contact force on the rolling motion of an elastic sphere on a plane[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1958, 25: 339-346. VERMEULEN P J, JOHNSON K L. Contact of nonspherical elastic bodies transmitting tangential forces[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1964, 17: 338-340. SHEN Z Y, HEDRICK J K, ELKINS J A. A comparison of alternative creep force models for rail vehicle dynamic analysis[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 1983, 12(1/2/3): 79-83. KALKER J J. On the rolling contact of two elastic bodies in the presence of dry friction[D]. Delft: Delft University, 1967. KALKER J J. A fast algorithm for the simplified theory of rolling contact[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 1982, 11(1): 1-13. doi: 10.1080/00423118208968684 KALKER J J. Three-dimensional elastic bodies in rolling contact[M]. The Netherlands: Dordrecht, Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1990: 137-184. 张焱,孔祥安,金学松,等. 轮轨三维弹塑性接触应力的算法研究[J]. 力学与实践,2000,22(1): 23-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0879.2000.01.007ZHANG Yan, KONG Xiang’an, JIN Xuesong, et al. The algorithm study of three-dimensional elasto-plastic contact stress of wheel-rail[J]. Mechanics in Engineering, 2000, 22(1): 23-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0879.2000.01.007 张军,吴昌华. 轮轨接触问题的弹塑性分析[J]. 铁道学报,2000,22(3): 16-21. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.2000.03.004ZHANG Jun, WU Changhau. Elasto-plastic analysis of wheel-rail contact problem[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2000, 22(3): 16-21. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.2000.03.004 ZHAO Xin, LI Zili. The solution of frictional wheel–rail rolling contact with a 3D transient finite element model:validation and error analysis[J]. Wear, 2011, 271(1): 444-452. MAI S H, GRAVOUIL A, NGUYEN-TAJAN M L, et al. Numerical simulation of rolling contact fatigue crack growth in rails with the rail bending and the frictional contact[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2017, 174: 196-206. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2016.12.019 LUNDÉN R. Contact region fatigue of railway wheels under combined mechanical rolling pressure and thermal brake loading[J]. Wear, 1991, 144(1/2): 57-70. 张澎湃. 动车组车轮疲劳性能数值仿真和评定方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国铁道科学研究院, 2014. LIU Y, STRATMAN B, MAHADEVAN S. Fatigue crack initiation life prediction of railroad wheels[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2006, 28(7): 747-756. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2005.09.007 HUANG Y B, SHI L B, ZHAO X J, et al. On the formation and damage mechanism of rolling contact fatigue surface cracks of wheel/rail under the dry condition[J]. Wear, 2018, 400/401: 62-73. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2017.12.020 孙华东. 考虑滚压强化效应的参数化曲轴有限元分析系统的研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2009. 潘玉祥. TC4钛合金表面温滚压强化及其微动磨损性能研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2016. 王迎,康达昌. 抽油杆表面滚压强化的实验研究[J]. 热加工工艺,2004(6): 16-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3814.2004.06.008WANG Ying, KANG Dachang. Experimental study on surface peening of pumping rod by rolling technology[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2004(6): 16-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3814.2004.06.008 宋玉泉,徐振国,赵泼,等. 金属平面滚压塑性精加工的实验分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版),2006,36(2): 188-194.SONG Yuquan, XU Zhenguo, ZHAO Po, et al. Expermental analysis of ro ller burnish ing process form etal plane[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2006, 36(2): 188-194. 刘福超,雷丽萍,曾攀. 滚压有限元模型数值模拟[J]. 塑性工程学报,2012,19(2): 17-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2012.02.004LIU Fuchao, LEI Liping, ZENG Pan. Surface rolling FE model for numerical simulation[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2012, 19(2): 17-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2012.02.004 陈利钦,项彬,任学冲,等. 表面超声滚压处理工艺对高速列车车轴钢表面状态的影响[J]. 中国表面工程,2014,27(5): 96-101.CHEN Liqin, XIANG Bin, REN Xuechong, et al. Influences of surface ultrasonic rolling processing parameters on surface condition of axle steel used in high speed trains[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2014, 27(5): 96-101. 于鑫,孙杰,李世涛,等. 滚压工艺对EA4T车轴表面质量完整性的影响及预测模型建立[J]. 中国表面工程,2014,27(5): 87-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9289.2014.05.011YU Xin, SUN Jie, LI Shitao, et al. Influences of burnishing process on surface quality integrity of ea4t axles and establishment of prediction model[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2014, 27(5): 87-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9289.2014.05.011 陈水友,刘吉华,郭俊,等. 车轮材料特性对轮轨磨损与疲劳性能影响的研究[J]. 摩擦学学报,2015,35(5): 531-537.CHEN Shuiyou, LIU Jihua, GUO Jun, et al. Effect of wheel material characteristics on wear and fatigue property of wheel-rail[J]. Tribology, 2015, 35(5): 531-537. 刘旭阳. TC4钛合金动态本构关系研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2010. 吴超,赵娟,姚福钦,等. 车轴滚压刀具的设计和滚压工艺试验分析[J]. 工具技术,2018,52(4): 96-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2018.04.021WU Chao, ZHAO Juan, YAO Fuqin, et al. Design of axle rolling tool and rolling test analysis[J]. Tool Engineering, 2018, 52(4): 96-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2018.04.021 沈文林,宋春元,李国栋,等. 高速动车组车轮硬度与车轮多边形形成关系及解决措施研究[J]. 铁道机车车辆,2018,38(4): 18-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7842.2018.04.04SHEN Wenlin, SONG Chunyuan, LI Guodong, et al. Research for high-speed EMU wheel hardness and polygon-form relationships with solutions[J]. Railway Locomotive & Car, 2018, 38(4): 18-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7842.2018.04.04 MANSON S S, HALFORD G R. Fatigue and durability of structural materials[M]. Ohio: ASM International, 2006: 76-103. SOCIE D. Multiaxial fatigue damage models[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 1987, 324/325(4): 747-750. WEI S S, WILLIAMS E J, LEEN S B. Finite element, critical-plane, fatigue life prediction of simple and complex contact configurations[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2005, 27(4): 403-416. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2004.08.001 SMITH K N, WATSON P, TOPPER T H. A stress-strain function for the fatigue of metals[J]. Journal of Materials, 1970, 5(4): 767-778. XIA Z, KUJAWSKI D, ELLYIN F. Effect of mean stress and ratcheting strain on fatigue life of steel[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 1996, 18(5): 335-341. doi: 10.1016/0142-1123(96)00088-6 雷冬. 疲劳裂纹萌生寿命预测若干方法的研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2006. 何嘉武,马世宁,巴德玛. 表面滚压强化技术研究与应用进展[J]. 装甲兵工程学院学报,2013,27(3): 75-81. doi: 10.11732/j.issn.1672-1497.2013.03.018HE Jiawu, MA Shining, BA Dema. Research and application progress of surface rolling strengthening technology[J]. Journal of Academy of Armored Force Engineering, 2013, 27(3): 75-81. doi: 10.11732/j.issn.1672-1497.2013.03.018 -




 下载:
下载: