Experimental Study on Frost Heave, Thaw Settlement and Thermal Properties of Foundation Soils along China-Russia Crude Oil Pipeline
-
摘要: 中俄原油管道是我国能源战略通道之一,管道穿越大兴安岭多年冻土区,工程地质条件十分复杂,尤其是在伊勒呼里山附近,冻胀和融沉严重影响了管道的正常运营. 为了研究伊勒呼里山附近多年冻土的冻融性质与热学性质,对该区段内的冻土进行冻胀、融沉及导热系数试验,并对试验数据进行回归分析与影响因素分析. 研究结果表明:细粒土塑性指数小于10时,冻胀率不一定随初始含水量的增加而增加,在研究区域内进行管道垫层施工或挖填材料选择时应选用砂砾或碎石,并做好防排水措施;融沉系数随含水量的增加而增大,随干密度的增加而减小,其中粉土对融沉作用十分敏感,不适合作为管道地基,而细砾才是最佳的冻土地基;导热系数分别随总含水量和干密度的增大而增大,其中粗粒土的导热系数大于细粒土,而冻土的导热系数则比融土的高;当含水量小于10%时,融土的导热系数则高于冻土. 不同试验方法所得的结果也具有显著的差异,粗粒土扰动样的导热系数宜采用热流计法测量,细粒土扰动样的导热系数宜采用热线法测量,而原状样的导热系数宜采用比较法测量.Abstract: The China-Russia crude oil pipeline is one of the strategic energy channels of China. The pipeline passes through the permafrost region of the Da Hinggan Mountains, where the engineering geological conditions are very complex, especially near the Yilehuli Mountains, and frost heave and thaw settlement seriously affect the normal operation of the pipeline. Experiments were therefore conducted on soils in this area to study their properties of frost heave, thaw settlement and thermal conductivity, and the test data were subjected to the regression analysis and influencing factors analysis. Results show that when the plasticity of fine-grained soils is less than 10, the frost heave ratio of soils does not necessarily increase with an increase in the initial water content. Thus, gravel and breakstone should be used as cushion and filling materials, and waterproof and drainage measures should be taken. Meanwhile, the coefficient of thaw settlement increases with water content and decreases with dry density. The silt is very sensitive to the thawing action, hence not suitable for pipe foundation, and fine gravel is the best frozen soil foundation. Besides, the thermal conductivity increases with the increase of total water content and dry density. The thermal conductivity of coarse-grained soil is higher than that of fine-grained soil, and the thermal conductivity of frozen soil is higher than that of thawed soil. However, when the water content is less than 10%, the thermal conductivity of the thawed soil is higher than that of the frozen soil. In addition, the results of thermal conductivity obtained by different test methods are significantly different. Generally, the thermal conductivity of disturbed coarse-grained soil sample should be measured by heat flow meter method, that of disturbed fine-grained soil sample should be measured by hot wire method, and that of undisturbed sample should be measured by comparison method.
-
表 1 冻胀试验土样物理力学性质指标
Table 1. Physical and mechanical indexes of test soils
土样编号 含水率 w/% 干密度 γd/(g•cm−3) 塑性指数 含泥量/% 土样名称 1# 10.0~25.0 1.5~1.7 10.0~13.0 粉质黏土(含砂砾) 2# 20.0~25.0 1.4~1.6 13.0~15.0 粉质黏土 3# 10.0~25.0 1.6~1.8 7.0~9.0 粉土(黏砂土) 4# 4.0~12.0 1.7~1.8 2.0~5.0 中砂 5# 6.0~11.0 1.7~1.8 10.0~15.0 细粒土质角砾 表 2 融沉试验土料基本物理力学指标
Table 2. The physical and mechanical indexes of test soils
土样
名称含水率/
%干密度/
(g•cm−3)塑性
指数含泥量/
%粉质黏土 10.0~65.0 0.8~1.8 10.0~27.0 粉土 15.0~115.0 0.5~1.8 4.5~9.0 砂土 10.0~115.0 0.2~2.0 2.0~40.0 表 3 试验土料基本物理力学指标
Table 3. The physical and mechanical indexes of soils
土样
名称含水率/
%干密度/
(g•cm−3)塑性
指数含泥量/
%粉质黏土 10.0~65.0 0.8~1.8 10.0~27.0 细粒土质
砂土18.0~26.0 1.3~2.0 细粒土质
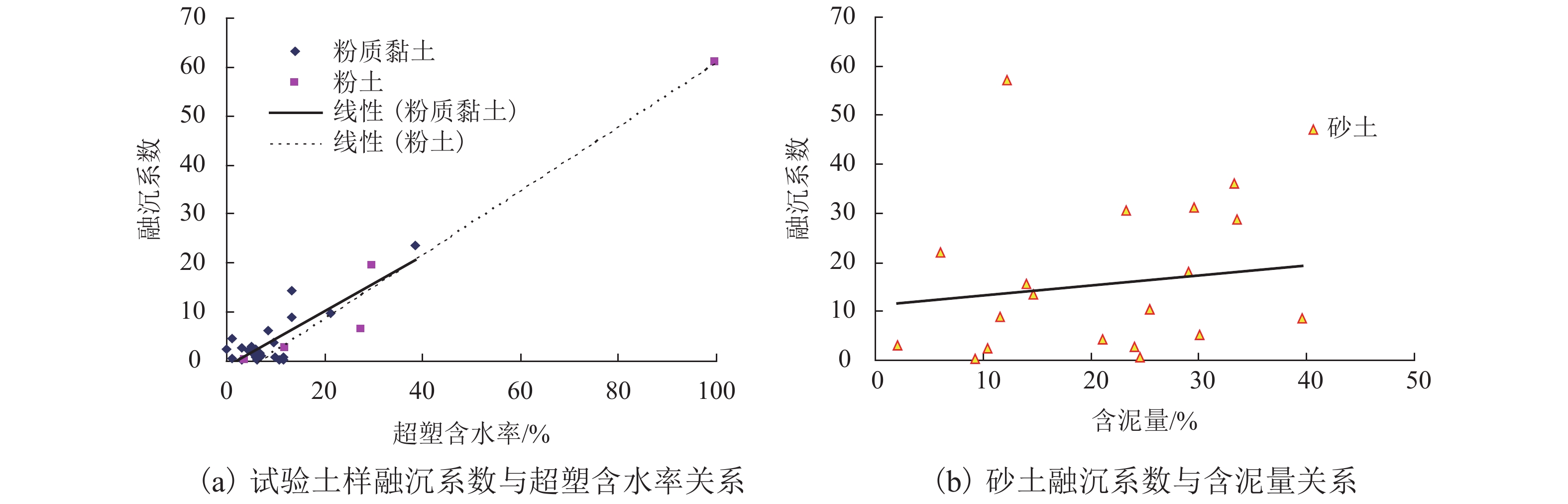
砾石5.0~15.0 1.6~1.7 2.0~40.0 表 4 各种土料η-w线性回归分析
Table 4. Unary linear regression analysis on η-w of soils
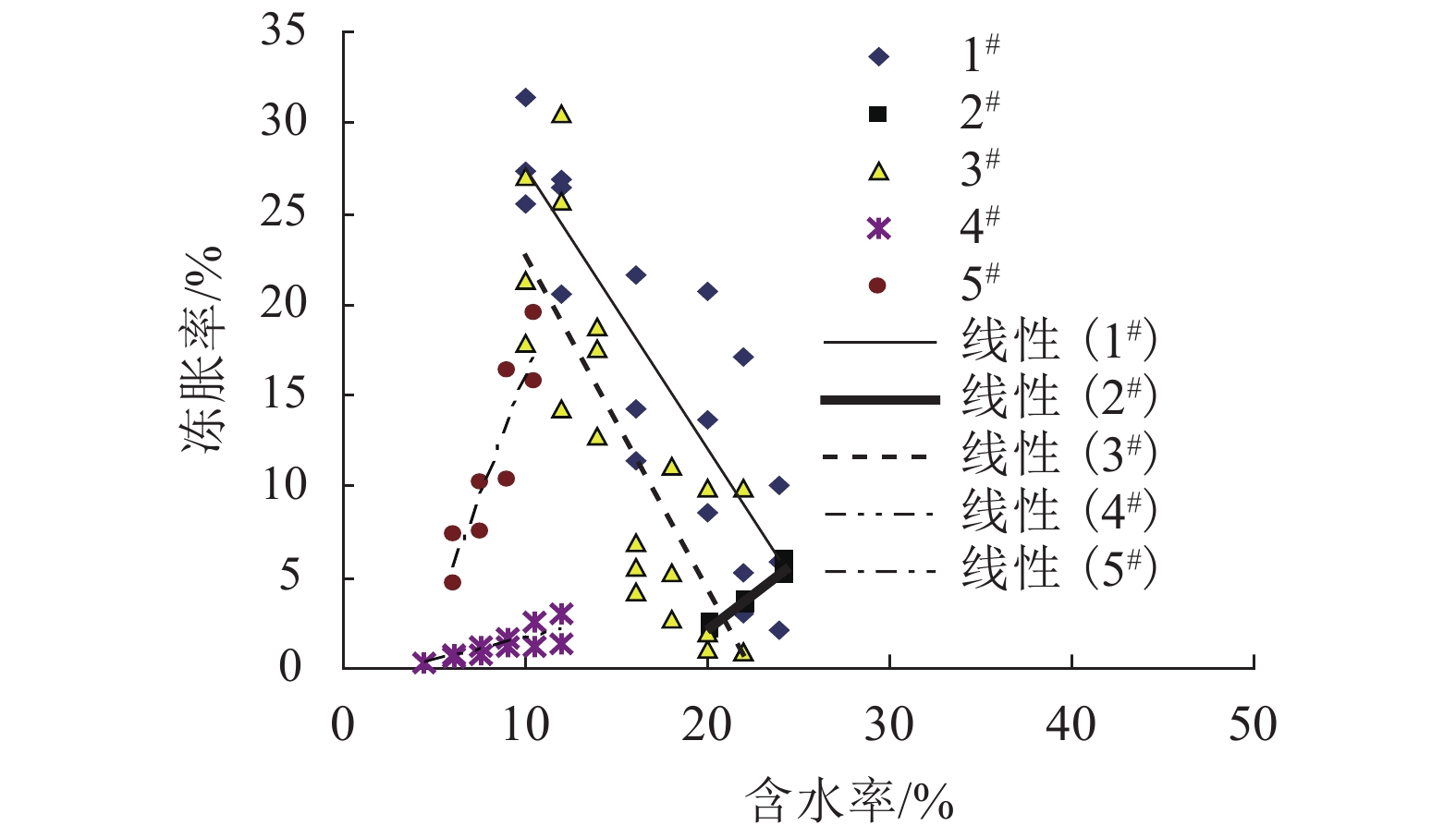
土样编号 回归方程 R2 n F 显著性 1# η = −1.882w + 51.856 0.516 18 F = 17.07 > F0.01(1,16) = 8.53 高度显著 2# η = 0.804w – 13.998 0.944 6 F = 67.00 > F0.01(1,4) = 21.20 高度显著 3# η = −1.780w + 39.877 0.446 21 F = 15.29 > F0.01(1,19) = 8.18 高度显著 4# η = 0.171w − 0.187 0.382 10 F = 3.74 > F0.10(1,8) = 3.46 显著 5# η = 1.798w – 4.522 0.570 8 F = 7.95 > F0.05(1,6) = 5.99 显著 表 5 试验土样回归方程汇总
Table 5. The regression equations of each soil
土样
名称含水率/
%干密度范围/
(g•cm−3)回归
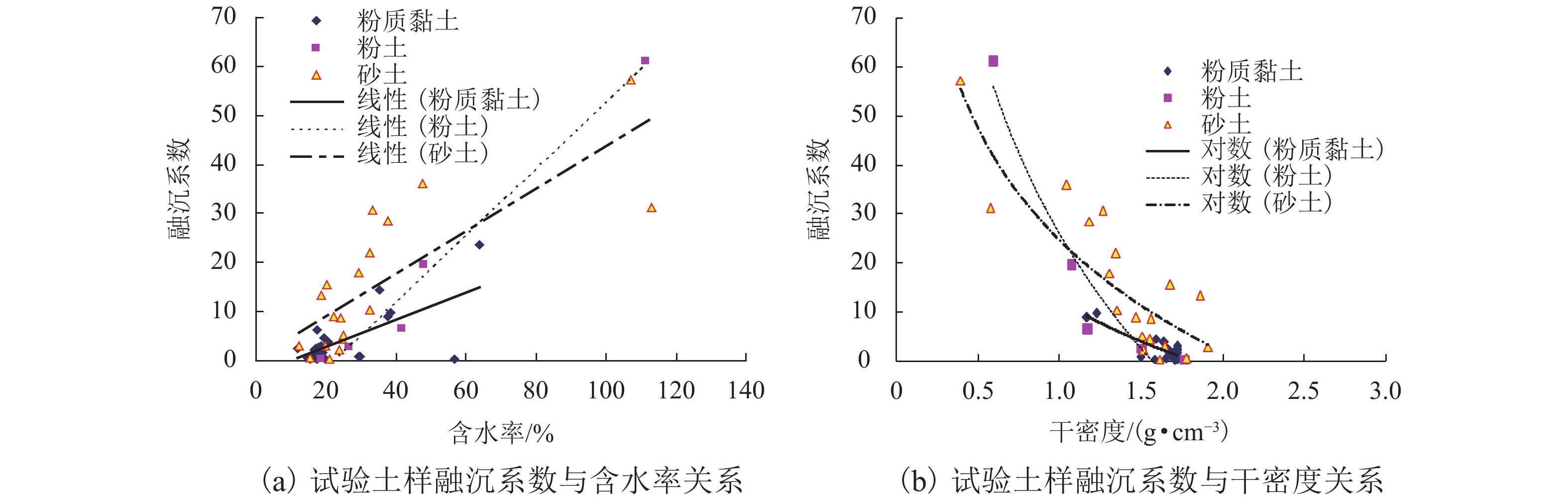
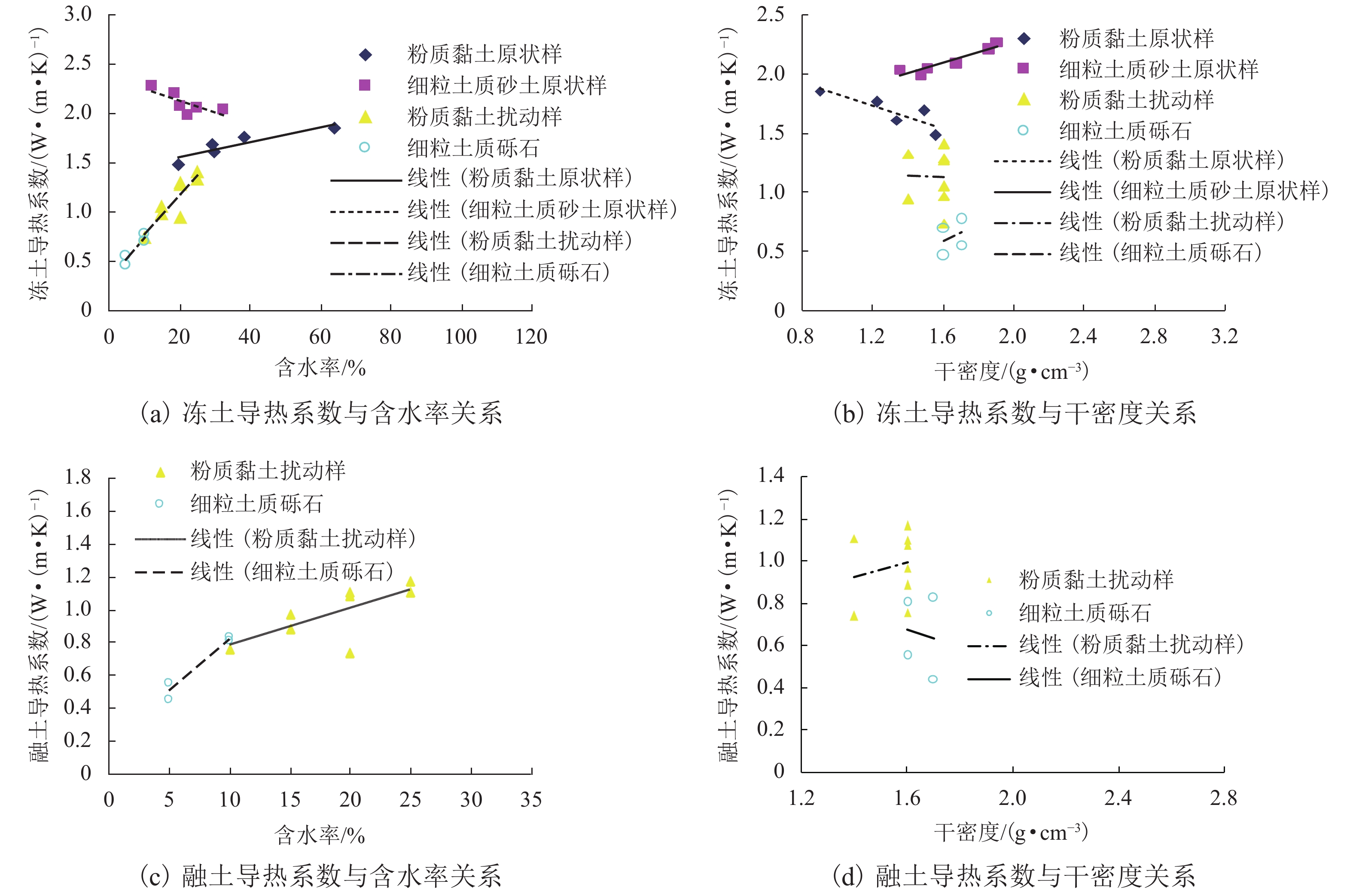
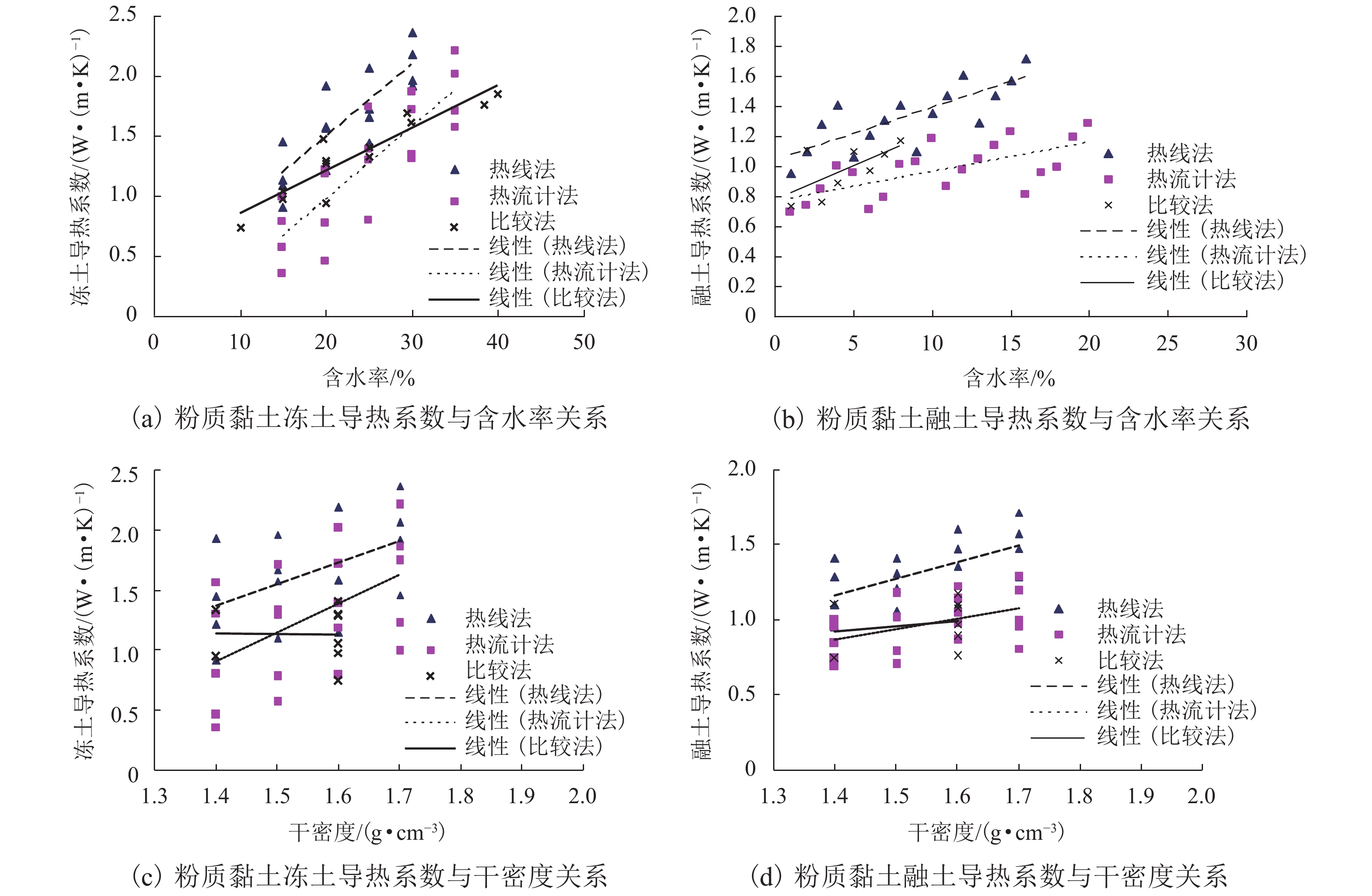
方程n R2 F 显著性 粉质黏土 12.0~38.4 1.165~1.720 a0 = 0.296w − 3.377 18 0.620 F = 26.11 > F0.01(1,16) = 8.53 显著 a0 = 0.565(w−wp) − 0.965 23 0.666 F = 41.85 > F0.01(1,21) = 8.02 显著 a0 = −20.161ln γd + 12.177 18 0.705 F = 38.31 > F0.01(1,16) = 8.53 显著 粉土 11.6~66.9 0.570~1.880 a0 = 0.640w − 11.472 34 0.971 F = 519.06 > F0.01(1,32) = 7.56 高度显著 a0 = −47.223ln γd + 23.164 34 0.930 F = 205.00 > F0.01(1,32) = 7.56 高度显著 砂土 12.1~113.0 0.392~1.911 a0 = 0.434w + 0.461 20 0.625 F = 30.04 > F0.01(1,18) = 8.28 显著 a0 = −33.030ln γd + 24.629 20 0.736 F = 50.28 > F0.01(1,18) = 8.28 显著 表 6 粉质黏土λ-w-γd回归方程汇总表
Table 6. Summary of the regression equation of λ-w-γd of the silty clay
土样名称 含水率
范围/%干密度范围/ (g•cm−3) 冻土回归方程 融土回归方程 显著性 粉质黏土(2008 年) 15.0~35.0 1.4~1.7 λf = 2.408γd + 0.061w − 3.988
(R2 = 0.975,n = 20,
F = 332.45 > F0.01(1,18) = 8.28)λu = 0.708γd + 0.020w − 0.633
(R2 = 0.914,n = 20,
F = 90.39 > F0.01(1,18) = 8.28)高度显著 粉质黏土(2010 年) 15.0~30.0 1.4~1.7 λf = 1.824γd + 0.061w − 2.550
(R2 = 0.955,n = 16,
F = 137.73 > F0.01(1,14) = 8.86)λu = 1.113γd + 0.063w − 1.035
(R2 = 0.970,n = 16,
F = 210.00 > F0.01(1,14) = 8.86)高度显著 粉质黏土
(本文)15.0~25.0 1.4~1.6 λf = 1.359γd + 0.039w − 1.642
(R2 = 0.751,n = 13,
F = 15.08 > F0.01(1,11) = 9.65)λu = 1.153γd + 0.032w − 1.411
(R2 = 0.840,n = 8,
F = 13.09 > F0.01(1,6) = 11.26)显著 表 7 粗粒土λ-w-γd回归方程汇总表
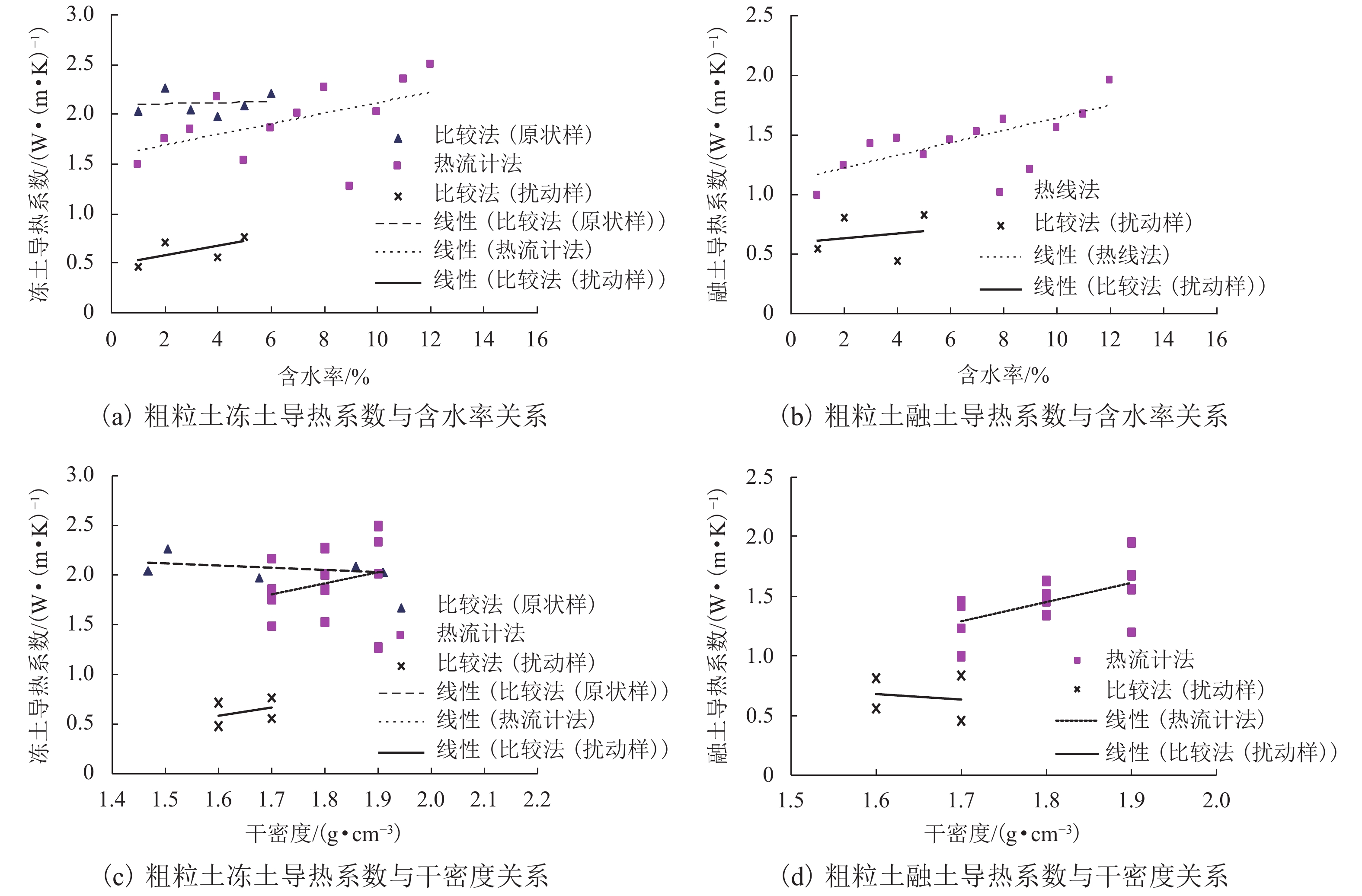
Table 7. Summary of the regression equation of λ-w-γd of the coarse grained soils
土样名称 含水率/% 干密度/ (g•cm−3) 冻土回归方程 融土回归方程 显著性 含细粒土砾石(2008年) 8.0~20.0 1.7~1.9 λf = 1.071γd + 0.071w − 0.999
(R2 = 0.857,n = 12,
F = 27.07 > F0.01(1,10) = 10.04)λu = 1.584γd + 0.041w − 1.974
(R2 = 0.891,n = 12,
F = 36.80 > F0.01(1,10) = 10.04)显著 细粒土质砾石(本文) 5.0~15.0 1.6~1.7 λf = 0.548γd + 0.059w − 0.712
(R2 = 0.965,n = 5,
F = 27.67 > F0.05(1,3) = 10.13)λu = −0.402γd + 0.062w + 0.853
(R2 = 0.986,n = 5,
F = 69.81 > F0.05(1,3) = 10.13)显著 细粒土质砂土(本文) 12.0~33.0 1.3~2.0 λf = 0.656γd + 0.008w + 0.871
(R2 = 0.882,n = 6,
F = 11.19 > F0.05(1,4) = 7.71)显著 -
李国玉,金会军,盛煜,等. 中国-俄罗斯原油管道工程(漠河—大庆段)冻土工程地质考察与研究进展[J]. 冰川冻土,2008,30(1): 170-175.LI Guoyu, JIN Huijun, SHENG Yu, et al. Recent advances in frozen ground engineering geology survey along the China-Russia crude oil pipeline route (Mohe−Daqing section)[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2008, 30(1): 170-175. 李国玉,马巍,王学力,等. 中俄原油管道漠大线运营后面临一些冻害问题及防治措施建议[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(10): 2963-2973.LI Guoyu, MA Wei, WANG Xueli, et al. Frost hazards and mitigative measures following operation of Mohe-Daqing line of China-Russia crude oil pipeline[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(10): 2963-2973. 金会军,喻文兵,陈友昌,等. 多年冻土区输油管道工程中的(差异性)融沉和冻胀问题[J]. 冰川冻土,2005,27(3): 454-464. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2005.03.021JIN Huijun, YU Wenbing, CHEN Youchang, et al. (Differential) frost heave and thaw settlement in the engineering design and construction of oil pipelines in permafrost regions:a review[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2005, 27(3): 454-464. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2005.03.021 金会军,于少鹏,吕兰芝,等. 大小兴安岭多年冻土退化及其趋势初步评估[J]. 冰川冻土,2006,28(4): 467-476. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2006.04.002JIN Huijun, YU Shaopeng, LÜ Lanzhi, et al. Degradation of permafrost in the Da and Xiao Hinggan Mountains,Northeast China,and preliminary assessment of its trend[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2006, 28(4): 467-476. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2006.04.002 何瑞霞,金会军,赵淑萍,等. 冻土导热系数研究现状及进展[J]. 冰川冻土,2017,39(5): 1-11.HE Ruixia, JIN Huijun, ZHAO Shuping, et al. Review of status and progress of the study in thermal conductivity of frozen soil[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2017, 39(5): 1-11. 吉延峻,金会军,张建明,等. 中俄原油管道沿线典型土样冻胀性试验研究[J]. 冰川冻土,2008(2): 296-300.JI Yanjun, JIN Huijun, ZHANG Jianming, et al. Experimental study of the frost-heaving ratio of the typical soil samples along the China-Russia crude oil pipeline[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2008(2): 296-300. 吉延峻,金会军,王国尚,等. 中俄原油管道(漠河-大庆段)地基土融沉稳定性评价研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2010(2): 241-251. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.02.015JI Yanjun, JIN Huijun, WANG Guoshang, et al. Thaw stability assessment of the permafrost foundation soil along the proposed China-Russia crude oil pipeline from Mo ’he to Daqing[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010(2): 241-251. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.02.015 董斌. 中俄石油管道漠河-塔河段冻土融沉特性及工程措施研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2008. 郭高峰. 影响多年冻土融沉特性的因素研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2008. 陈义民. 多年冻土融沉特性统计分析与分类研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2008. 逯兰. 冻土融化下沉特性试验分析研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2009. 陶兆祥,张景森. 大含水(冰)量融土冻土导热系数的测定研究[J]. 冰川冻土,1983,5(2): 75-80.TAO Zhaoxiang, ZHANG Jingsen. The thermal conductivity of thawed and frozen soils with high water (ice) content[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 1983, 5(2): 75-80. 肖琳,李晓昭,赵晓豹,等. 含水量与孔隙率对土体热导率影响的室内实验[J]. 解放军理工大学学报(自然科学版),2008,9(3): 242-247.XIAO Lin, LI Xiaozhao, ZHAO Xiaobao, et al. Laboratory on influences of moisture content and porosity on thermal conductivity of soils[J]. Journal of PLA University of Science and Technology, 2008, 9(3): 242-247. 袁喜忠,李宁,赵秀云,等. 非饱和(冻)土导热系数预估模型研究[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(9): 2689-2694. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.09.001YUAN Xizhong, LI Ning, ZHAO Xiuyun, et al. Study of thermal conductivity model for unsaturated unfrozen and frozen soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(9): 2689-2694. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.09.001 周家作,韦昌富,魏厚振,等. 热线源法测量冻土热参数的适用性分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2016,38(4): 681-687.ZHOU Jiazuo, WEI Changfu, WEI Houzhen, et al. Applicability of line heat source method in measuring thermal parameters of frozen soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(4): 681-687. 王伟,张喜发,吕岩. 多年冻土区管道地基土开式冻胀试验研究[J]. 天然气工业,2017,37(10): 93-99. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.10.013WANG Wei, ZHANG Xifa, LÜ Yan. Investigation on the open frozen-heave test of the foundation of pipelines in the permafrost regions[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(10): 93-99. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.10.013 中国科学院数学研究所数理统计组. 回归分析方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1974: 132-134. 张喜发, 杨风学, 冷毅飞, 等. 冻土试验与冻害调查[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013: 55-56. 孙振华. 多年冻土原状样热学性质研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2008. 王伟. 冻土传热性质试验研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2010. 孙克国, 李思, 许炜萍, 等. 导热系数对寒区隧道温度场时空分布的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2020, 55(2): 256-264, 289.SUN Keguo, LI Si, XU Weiping, et al. Influence of thermal conductivity on temporal and spatial distributions of temperature filed in cold region tunnel[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(2): 256-264, 289. -




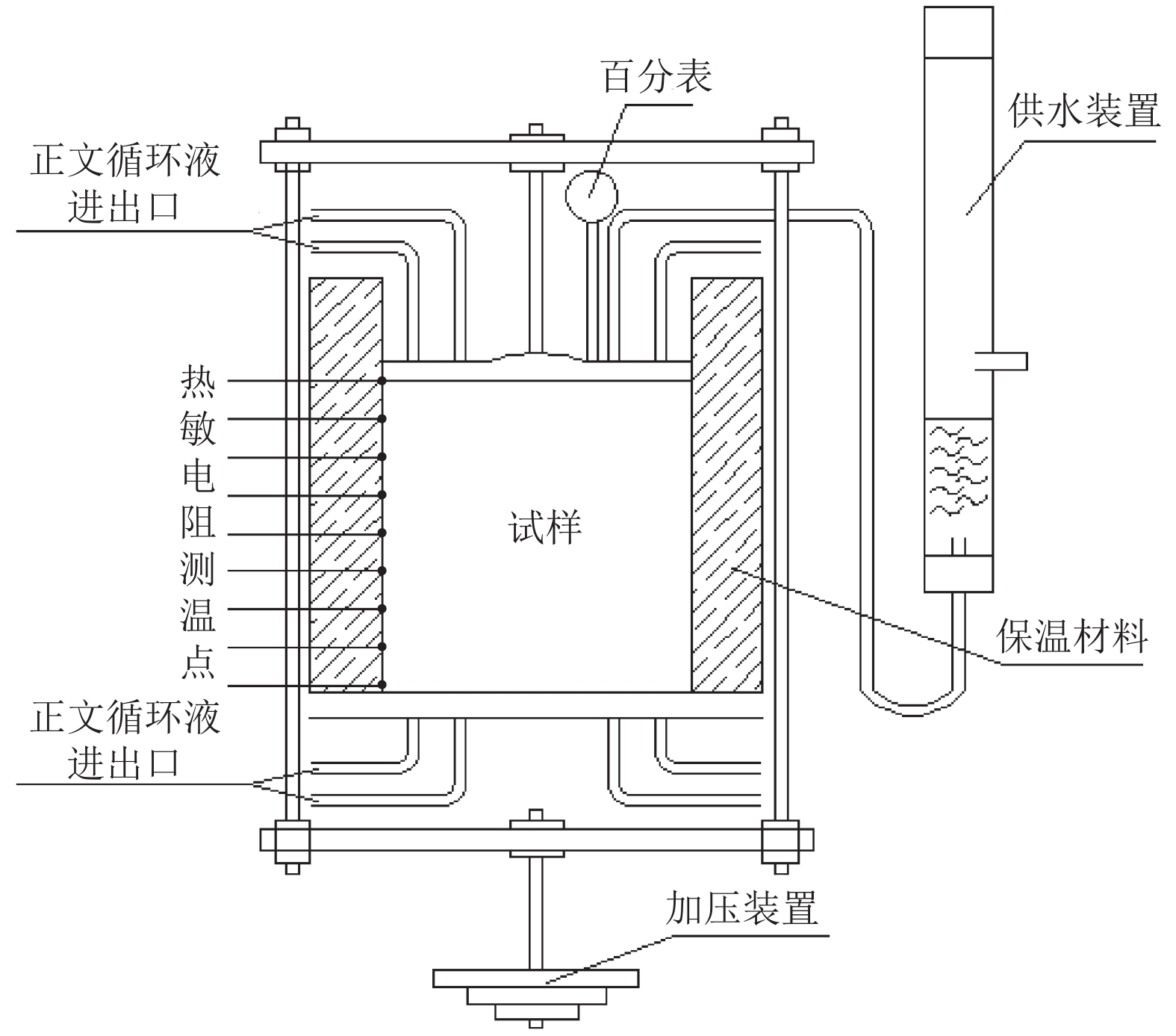
 下载:
下载: