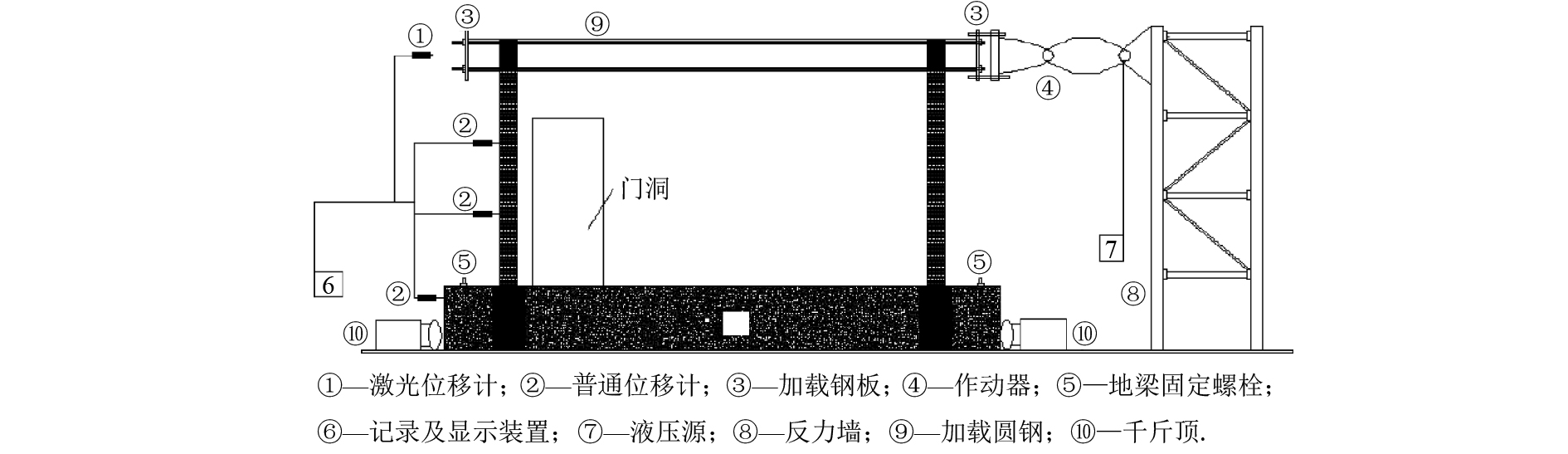
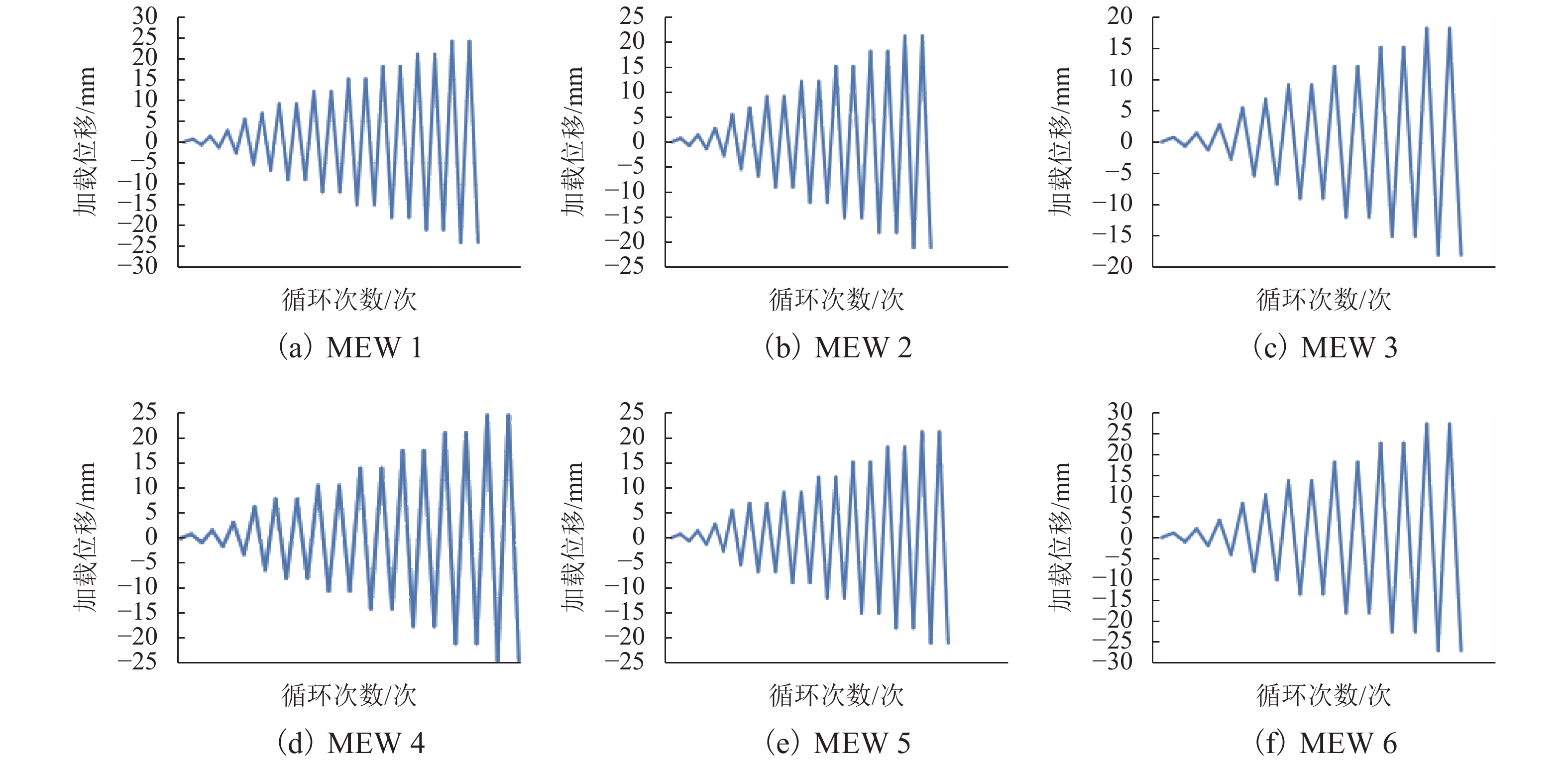
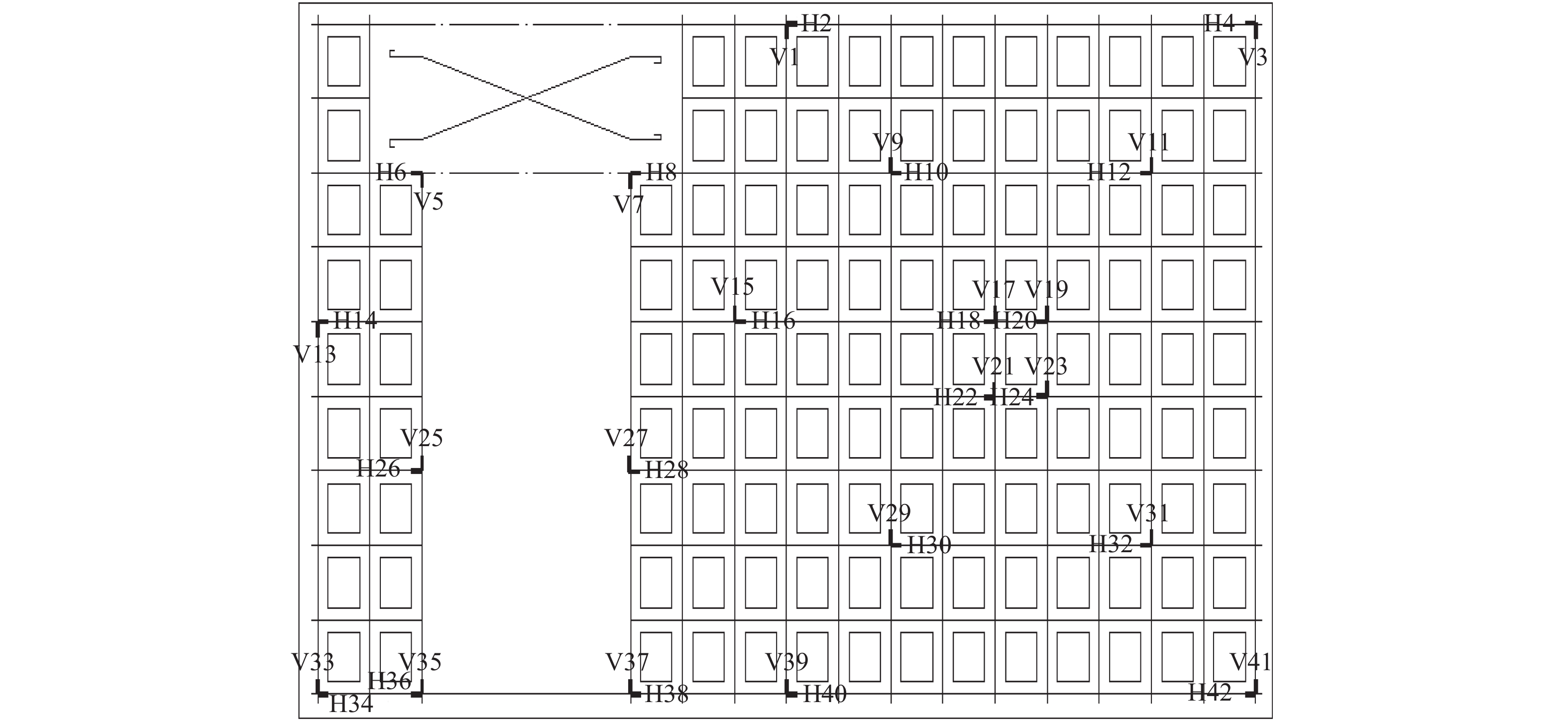
Seismic Behavior of Energy-Saving Block & Invisible Multi-ribbed Frame Composite Walls with Different Opening Positions
-
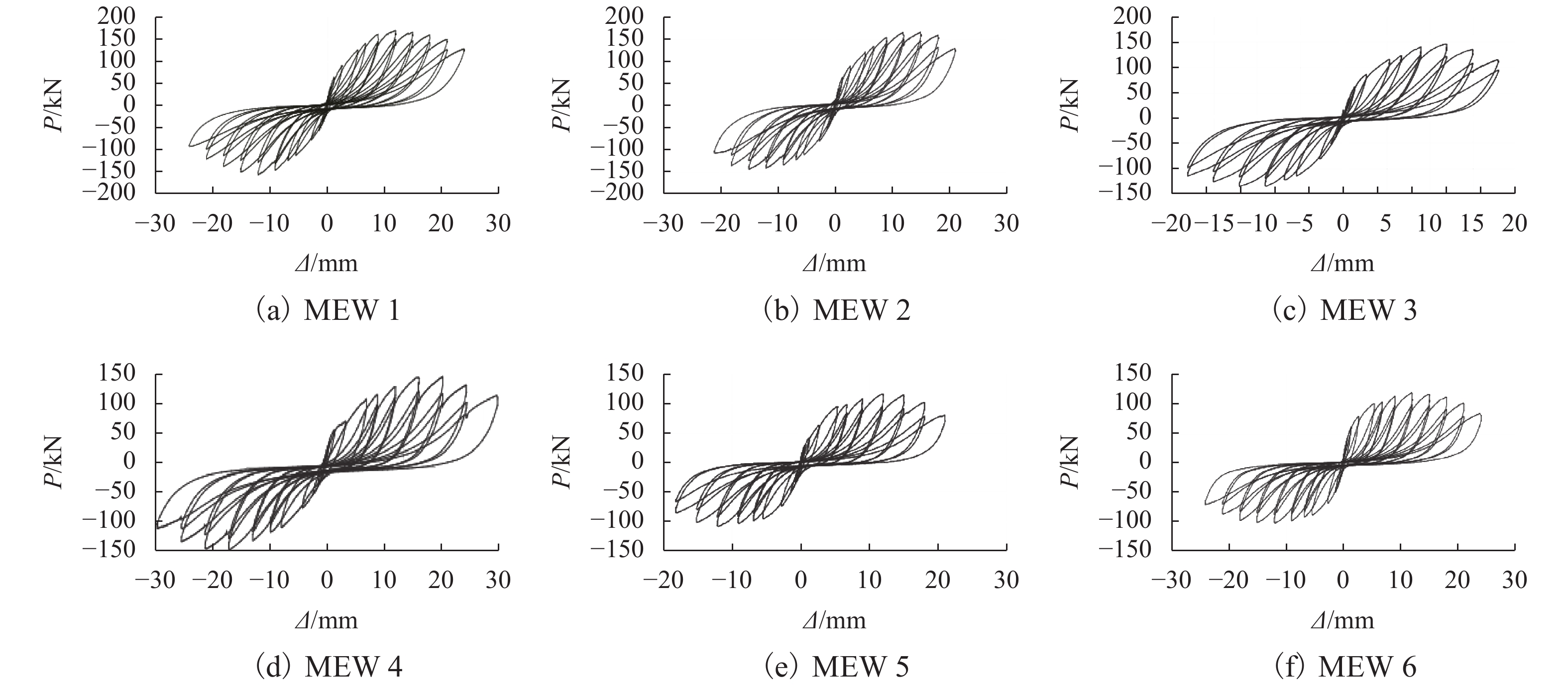
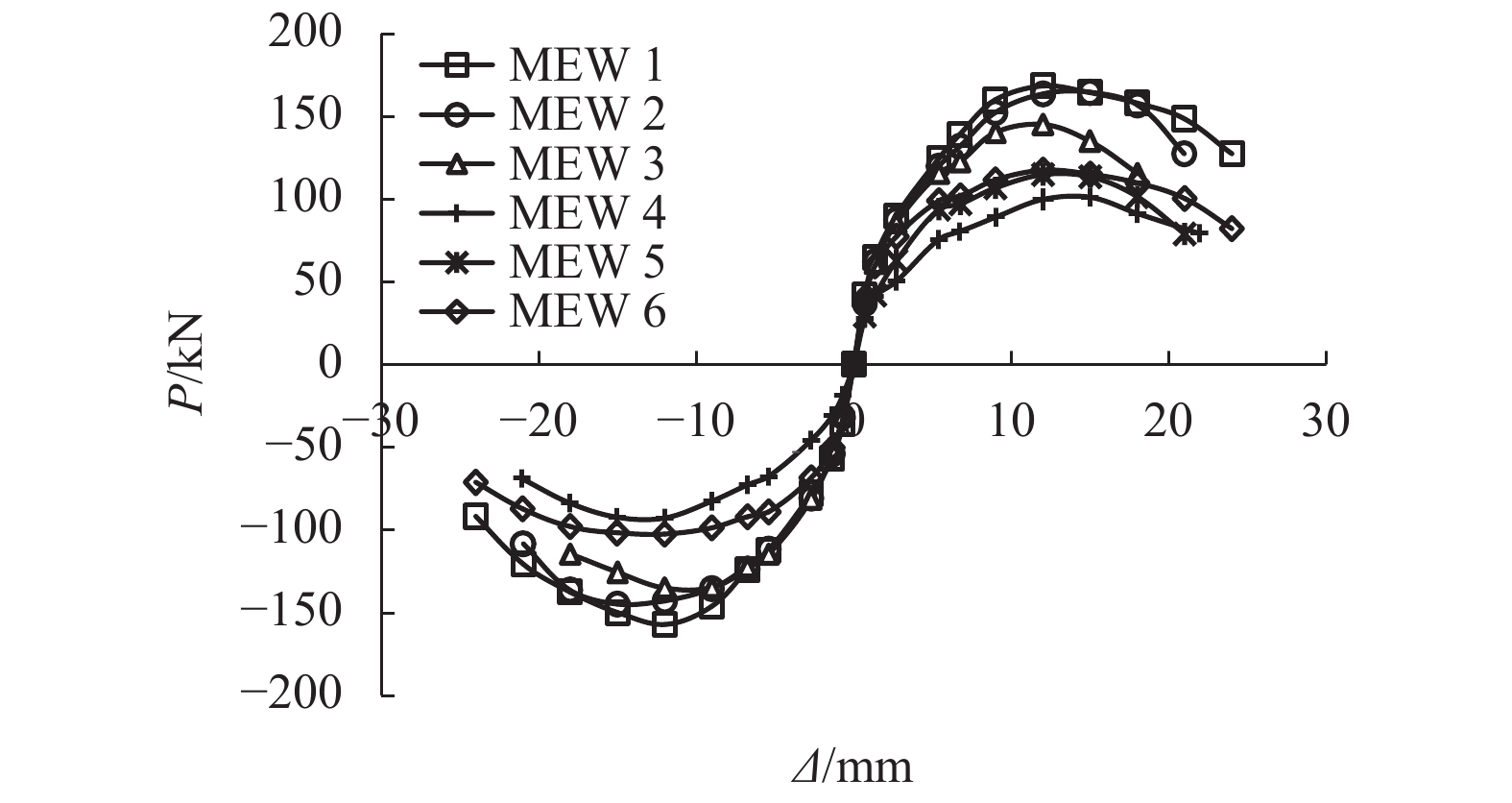
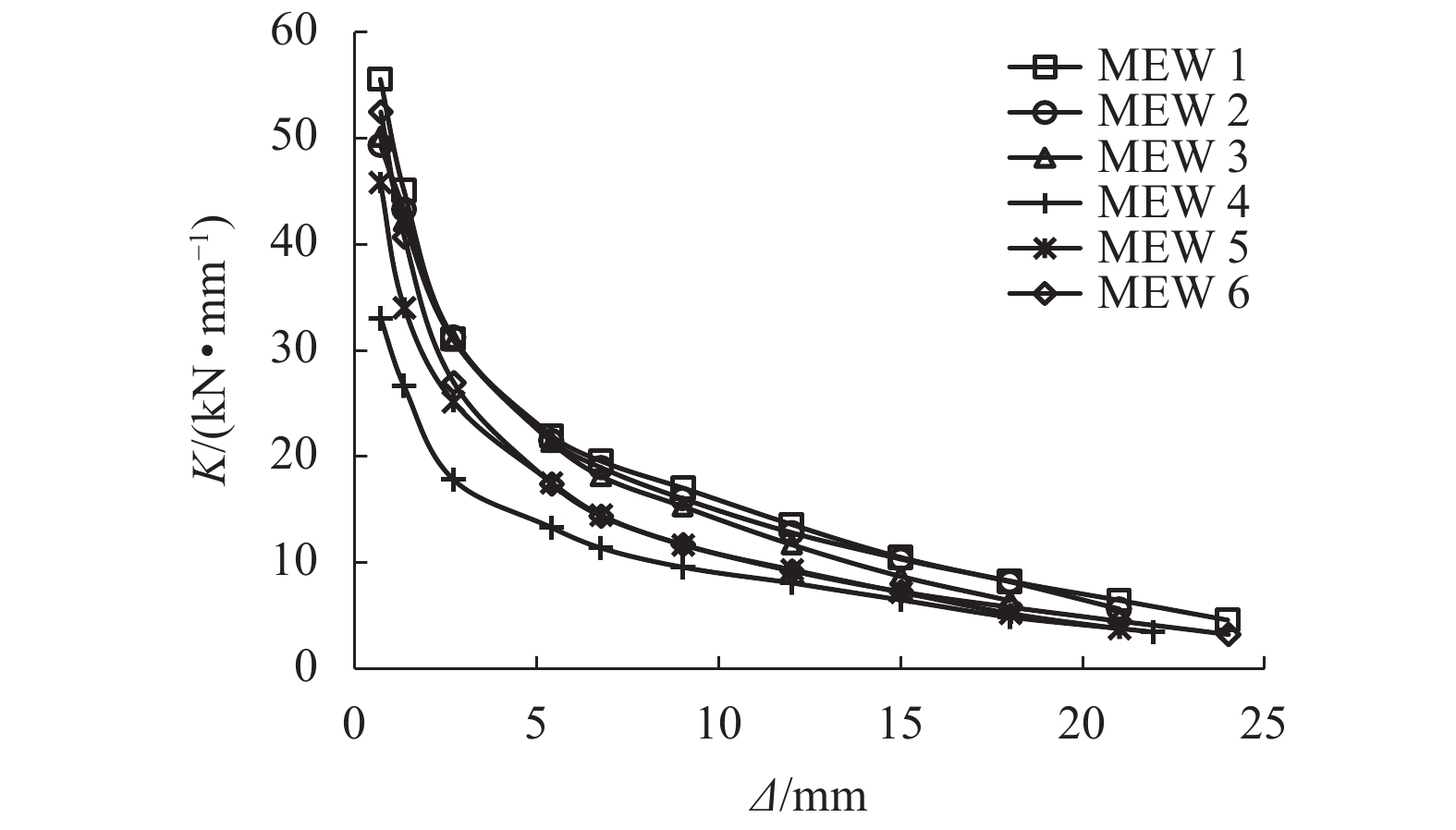
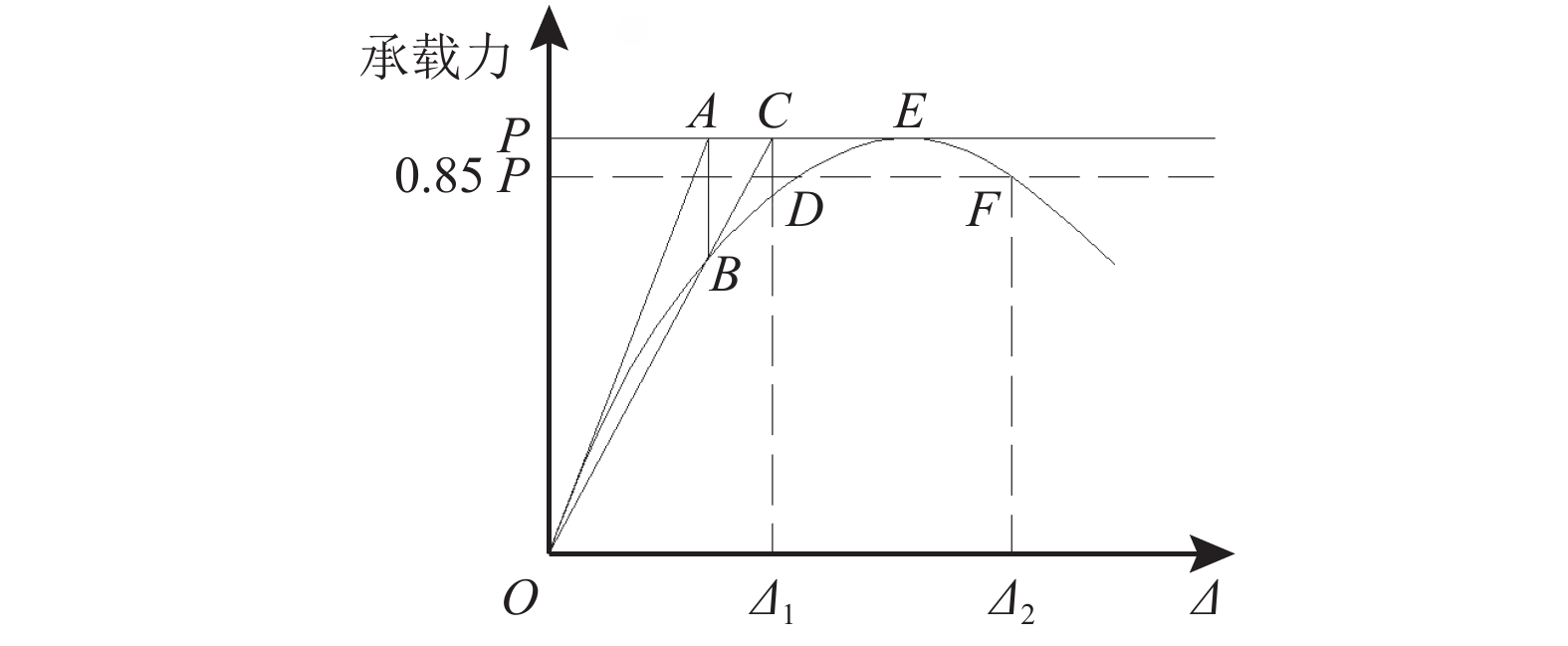
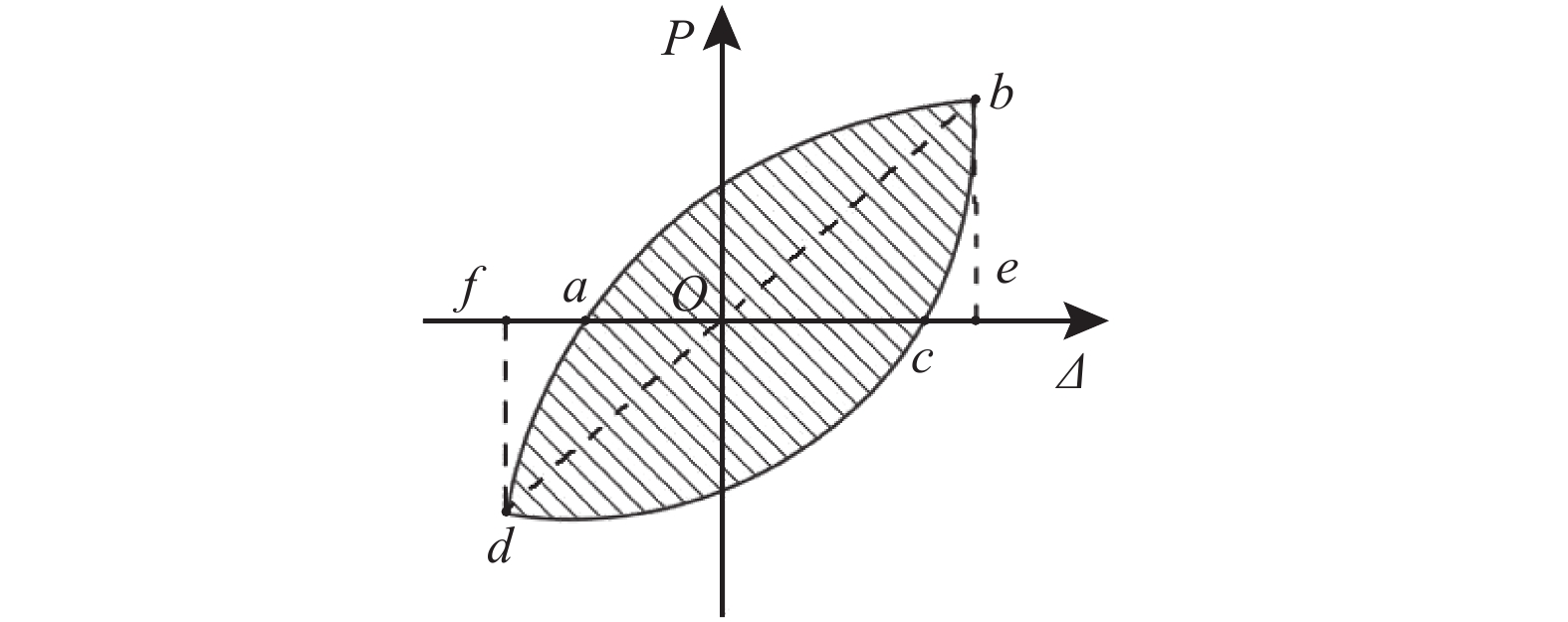
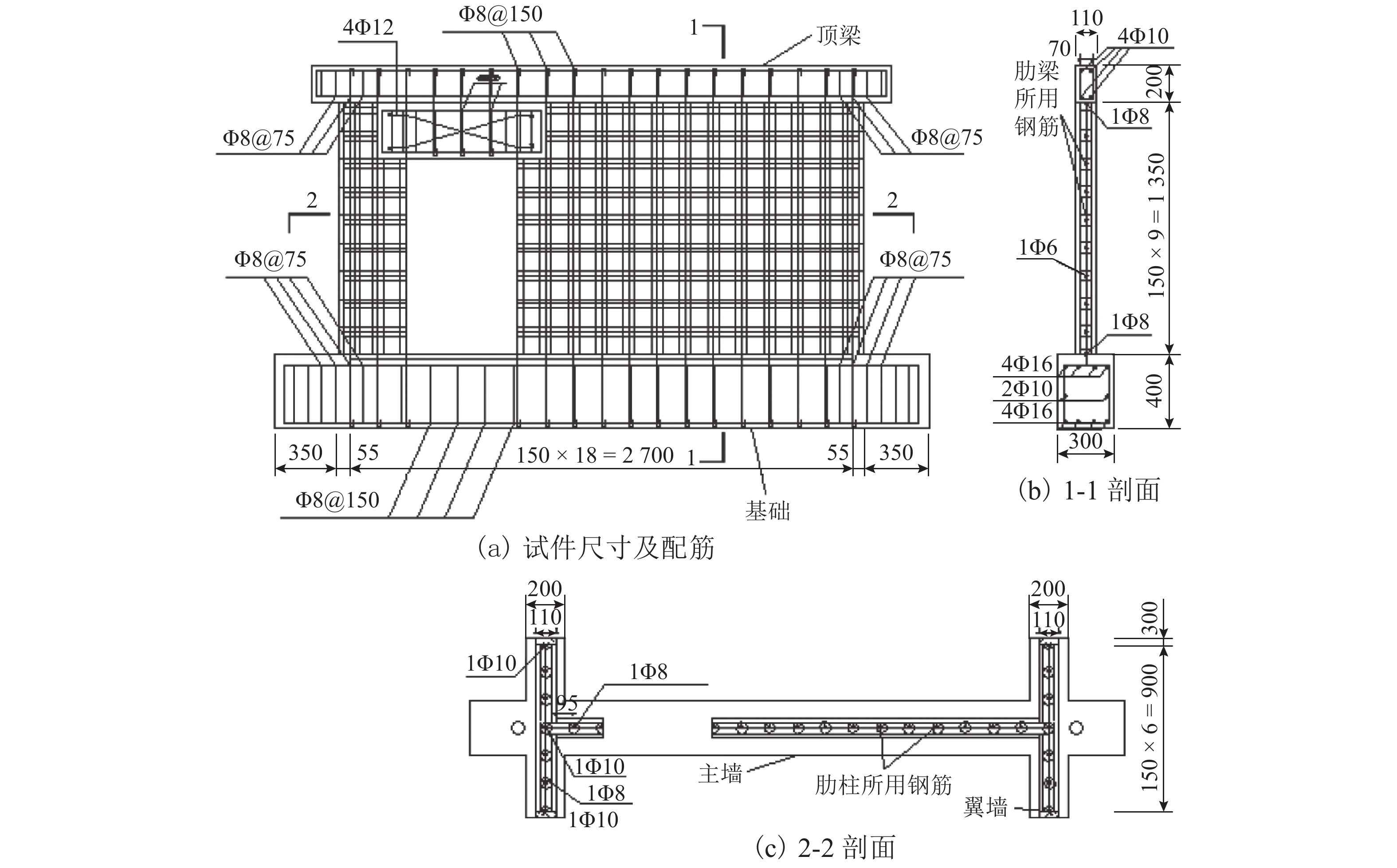
摘要: 为了研究节能砌块隐形密框复合墙体的破坏形态及滞回性能、刚度退化、延性和耗能能力等抗震性能,以门洞位置为变化参数,设计制作了6个缩尺比例为1/2的墙体试件,进行了低周往复加载试验. 首先,通过对比、总结的方法,得出了试件的破坏形态并分析了其滞回性能;其次,采用切线刚度计算方法,对比分析了各试件刚度退化规律;然后,通过图解法确定屈服位移,并利用公式计算位移延性系数,从而分析判断各试件的延性性能;最后,采用等效粘滞阻尼系数的计算方法研究试件的耗能能力. 研究结果表明:在低周往复加载下,配筋合适的开洞复合墙体往往会发生剪压破坏,其破坏过程可分为弹性、弹塑性和破坏3个阶段;墙体试件的滞回曲线形状较为饱满,能表现出开洞的墙体会有良好抗震性能;中开洞墙体其骨架曲线下降段更为平缓,比偏开洞墙体的抗震性能更好;开洞位置越接近墙体的中间部位,墙体在弹塑性阶段刚度的有利贡献就越大,其变形能力也会越强;6个试件的延性系数均大于3,满足抗震规范要求,开洞位置越接近墙体中间的试件延性越好,其等效粘滞阻尼系数也越大,其耗能性能也越好;确定了墙体在不同性能目标时的变形容许值,为设计该类墙体提供理论基础.Abstract: In order to study the failure modes and seismic performance of energy-saving block & invisible multi-ribbed frame composite wall (EBIMFCW) in terms of hysteretic behavior, stiffness degradation, ductility, energy dissipation capacity, etc., low cyclic reversed loading tests were conducted on six test specimens of EBIMFCW designed in a scale of 1/2 and manufactured with varied opening positions. First, the test results of the specimens were compared and analyzed to determine their failure modes and hysteretic behaviors. Then, the stiffness degradation of each specimen was analyzed using the tangent stiffness calculation method and compared with others, the yield displacement was determined by the graphic method, and the displacement ductility coefficient was calculated using a formula to judge the ductility of each specimen. Finally, the energy dissipation capacity of specimens was studied using the equivalent viscous damping coefficient. Results show that under the horizontal low cyclic reversed loading, a shear-compression failure often occurs to the EBIMFCW with appropriate reinforcement and the failure process can be divided into elastic, elastoplastic and failure stages. The shape of hysteretic loop curve of specimens is relatively full, suggesting that the wall with holes has good seismic performance. Besides, the skeleton curve of the wall with a central opening is descending more slowly and the wall has better seismic performance than those with a non-central opening; a closer opening position to the wall center results in a more favorable contribution of the wall stiffness in the elastoplastic stage and thus a bigger deformation ability of the wall. In addition, the ductility coefficients of the six specimens are all greater than 3, meeting the requirements of the seismic design code; when the opening position is closer to the wall center, the specimen has a better ductility, a larger equivalent viscous damping coefficient, and better energy dissipation performance. Based on the test data, the allowable deformation values of the wall under different performance targets are determined, which provides a theoretical basis for design of EBIMFCWs.
-
Key words:
- opening position /
- stiffness /
- ductility /
- energy dissipation /
- allowable value of deformation /
- EBIMFCW
-
表 1 钢筋的力学性能
Table 1. Mechanical properties of steel reinforcement
规格 屈服强度
/MPa极限强度
/MPa弹性模量
/(× 105 N•mm−2)Φ6 476.3 558.6 2.08 Φ8 443.7 525.3 2.07 Φ10 428.6 517.6 2.06 表 2 自密实混凝土的力学性能
Table 2. Mechanical properties of fine aggregate concrete
试件
编号构件
类型强度
等级fcu.m/MPa fcm/MPa MEW1 密框 C20 23.34 17.75 MEW2 密框 C20 26.44 20.09 MEW3 密框 C20 24.54 18.65 MEW4 密框 C20 20.32 15.44 MEW5 密框 C20 19.66 14.94 MEW6 密框 C20 22.23 16.89 注:f cu.m为混凝土立方体抗压强度平均值;f cm为混凝土 轴心抗压强度平均值,fcm= 0.76 fcu.m. 表 3 节能砌块的材料性能
Table 3. Physical and mechanical properties of the block
砌块
材料抗压强度
/MPa抗拉强度
/MPa干容重
/(kN•m−3)弹性模量
/(N•mm−2)石膏
砌块15.8 1.6 10.15 1 950 表 4 试验结果汇总表
Table 4. Summary sheet of test result
试件编号 幵裂荷载点 屈服的荷载点 极限的荷载点 破坏的荷载点 μ 荷载/kN 位移/mm 荷载/kN 位移/mm 荷载/kN 位移/mm 荷载/kN 位移/mm MEW1 60.78 1.35 118.98 5.51 162.78 12.01 13836 20.25 3.68 MEW2 57.23 1.35 116.00 5.43 154.77 15.01 131.55 19.58 3.60 MEW3 56.47 1.34 106.45 4.66 140.23 12.01 119.19 17.36 3.73 MEW4 35.95 1.35 72.56 5.73 96.96 13.51 82.41 19.40 3.39 MEW5 46.06 1.36 85.11 4.33 111.53 12.02 94.80 18.88 4.36 MEW6 54.87 1.35 79.62 3.56 110.01 12.02 93.50 21.07 5.91 表 5 等效粘滞阻尼系数
Table 5. Equivalent viscous damping coefficients
% 试件编号 开裂 屈服 极限 破坏 NEW1 8.26 8.56 8.92 8.76 NEW2 8.33 8.78 9.05 8.83 NEW3 8.44 8.99 935 9.13 NEW4 7.82 8.46 9.15 8.94 NEW5 9.23 10.15 11.25 10.77 NEW6 10.56 11.87 12.96 12.23 表 6 试件的变形容许值
Table 6. Deformation limit of the specimens
试件编号 弹性位移角 [θe] 弹塑性位移角 [θp] MEW1 1/1 000 1/800 1/67 1/80 MEW2 1/1 000 1/800 1/69 1/80 MEW3 1/1 000 1/800 1/78 1/80 MEW4 1/1 000 1/800 1/70 1/80 MEW5 1/1 000 1/800 1/72 1/80 MEW6 1/1 000 1/800 1/64 1/80 -
张微敬,王金金,张倩. 带窗洞配筋砌块砌体剪力墙抗震性能试验研究[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,2016,36(5): 92-98.ZHANG Weijing, WANG Jinjin, ZHANG Qian. Experimental study of seismic performance of reinforced block masonry shear walls with opening[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2016, 36(5): 92-98. 常鹏,张凯,李强军. 开洞对密肋复合墙体抗侧刚度的影响[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2015,43(11): 127-132.CHANG Peng, ZHANG Kai, LI Qiangjun. Influence of openings on lateral stiffness of multi-ribbed composite walls[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Nature Science Edition), 2015, 43(11): 127-132. 贾穗子,曹万林,袁泉. 底框-密肋复合板结构非线性有限元分析[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版),2015,47(5): 30-37.JIA Suizi, CAO Wanlin, YUAN Quan. Nonlinear finite element analysis on multi-ribbed composite slab structure with framework at the bottom[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2015, 47(5): 30-37. 贾益纲,钟亚曦. 水平荷载作用下洞口对填充墙RC框架结构受力性能影响的非线性分析[J]. 建筑结构,2012,42(9): 98-102.JIA Yigang, ZHONG Yaxi. Nonlinear analysis on influence of opening of infilled wall on the mechanical behaviors of RC framework under the horizontal load[J]. Building Structure, 2012, 42(9): 98-102. 刘宏波,曹万林,乔崎云,等. 框架内填带洞单排配筋墙体结构抗震试验[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2018,50(6): 56-63. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201708043LIU Hongbo, CAO Wanlin, QIAO Qiyun, et al. Experimental study on seismic performance of reinforced concrete frame infilled single row of steel bars shear wall with openings[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018, 50(6): 56-63. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201708043 吴会阁,凌沛春,陈继华. 不同构造措施的加气混凝土砌块墙抗震性能比较[J]. 工业建筑,2017,47(12): 101-105.WU Huige, LING Peichun, CHEN Jihua. A comparison of seismic behavior of aerated concrete block composite walls with different constructional measures[J]. Industrial Construction, 2017, 47(12): 101-105. DAVORIN P, VASILIS S, IVICA K, et al. Contribution of RC columns and masonry wall to the shear resistance of masonry infilled RC frames containing different in size window and door openings[J]. Engineering Structures, 2018, 172: 105-130. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.06.007 BEDON C, RINALDIN G, IZZI M, et al. Assessment of the structural stability of blockhaus timber log-walls under in-plane compression via full-scale buckling experiments[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 78: 474-490. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.01.049 MOSAAD E D, HUSSEIN O, OSAMA K, et al. Structural performance of confined masonry walls retrofitted using ferrocement and GFRP under in-plane cyclic loading[J]. Engineering Structures, 2015, 94: 54-69. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2015.03.035 CHIARA B, GIOVANNI R, MASSIMO F. Non-linear modelling of the in-plane seismic behaviour of timber Blockhaus log-walls[J]. Engineering Structures, 2015, 91: 112-124. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2015.03.002 张莹,孙广俊,李鸿晶. 开洞填充墙对混凝土框架柱地震损伤影响分析[J]. 振动测试与诊断,2014,34(5): 932-937.ZHANG Ying, SUN Guangjun, LI Hongjing. Numerical simulation on seismic damage of reinforced concrete frame columns considering the influence of infill walls with opening[J]. Journal of Vibration,Measurement & Diagnosis, 2014, 34(5): 932-937. 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 金属材料拉伸试验第1部分: 室温试验方法: GB/T 288.1—2010[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011 中华人民共和国建设部. 普通混凝土力学性能试验法方标准: GB/T 50081—2002[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2003 邱法维, 钱稼茹, 陈志鹏. 结构抗震试验方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000: 9-15. 张新培. 钢筋混凝土抗震结构非线性分析[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 6-11. -




 下载:
下载: