Analysis of Power Tracking Management Strategy for Fuel Cell Hybrid System
-
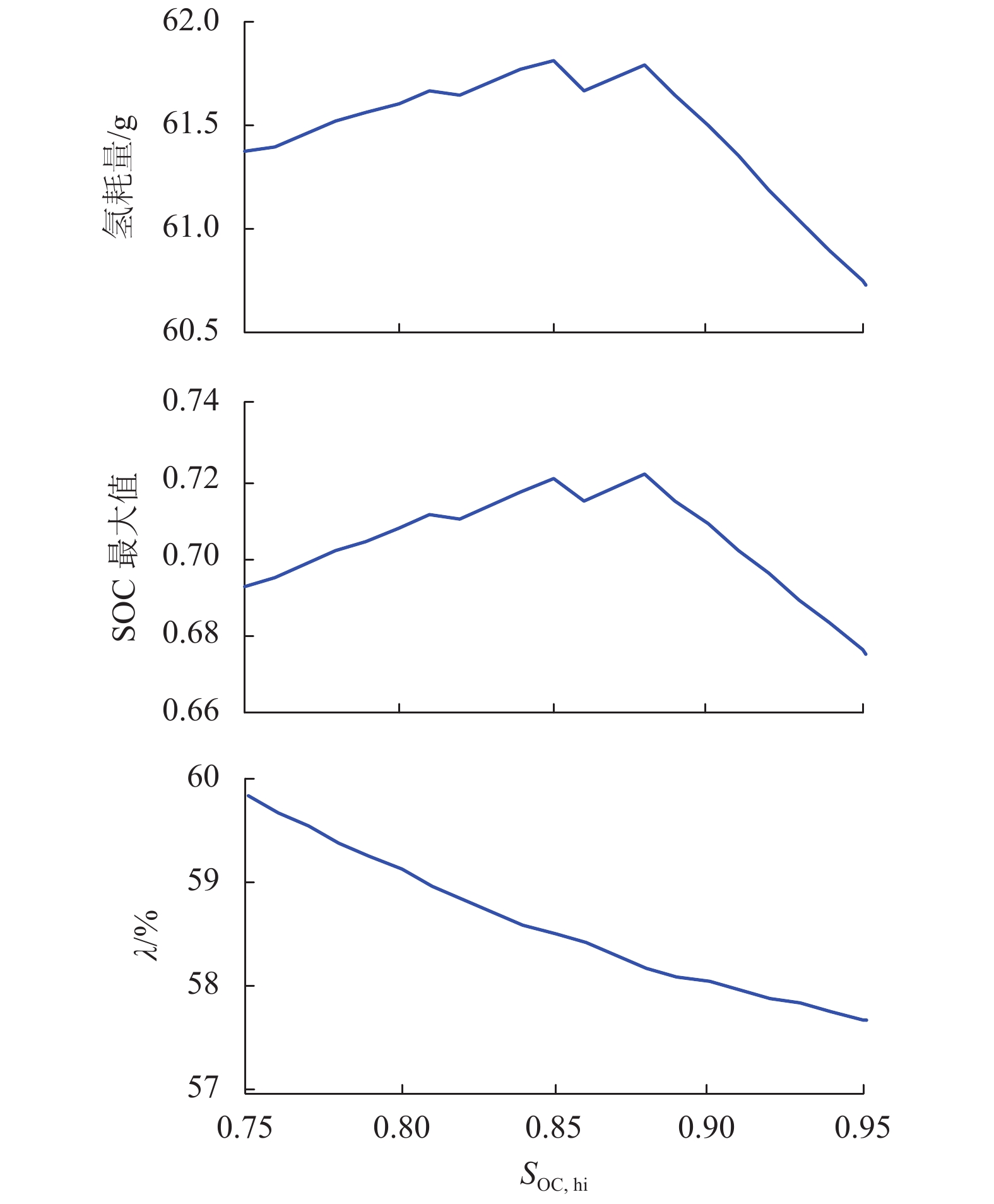
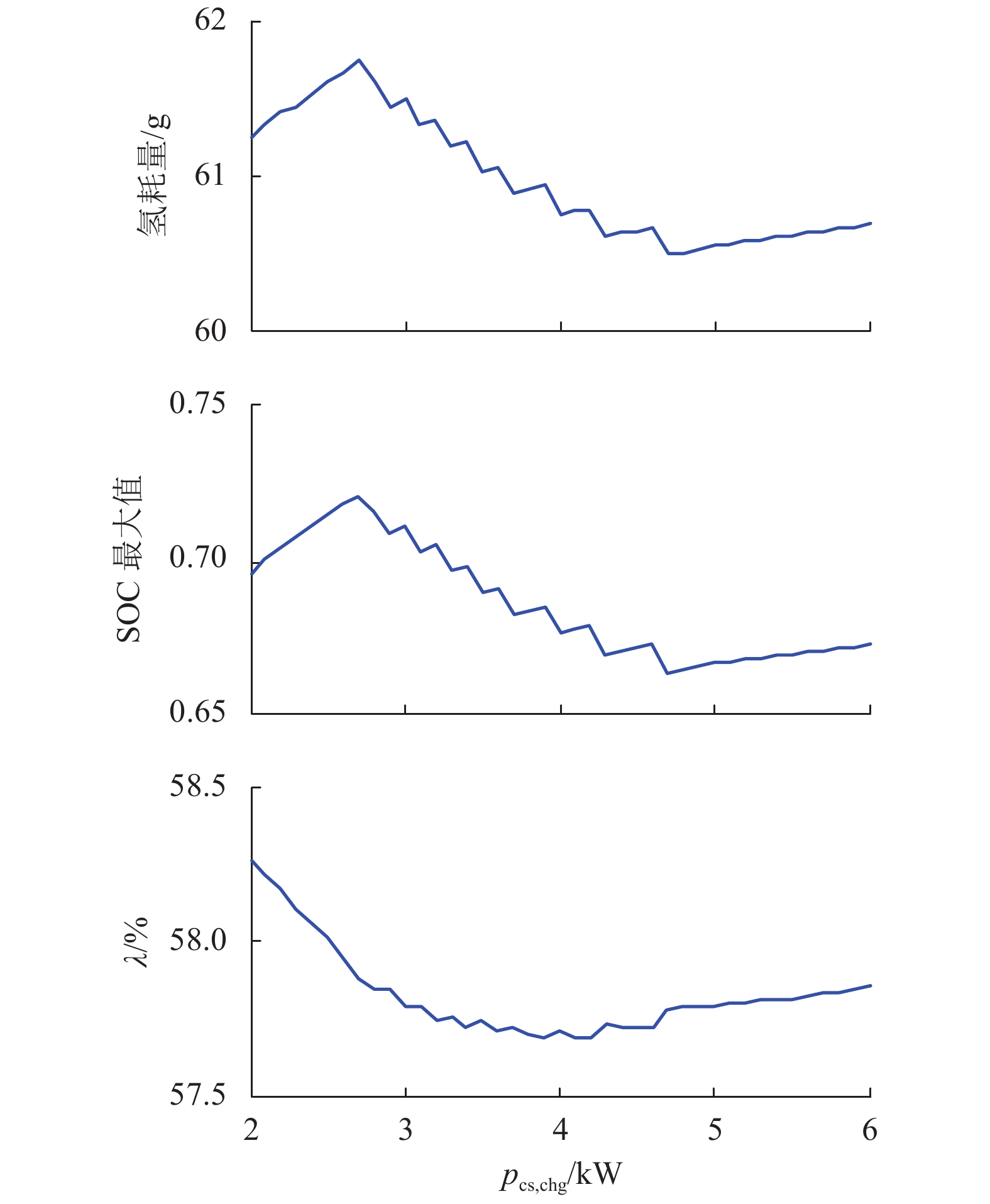
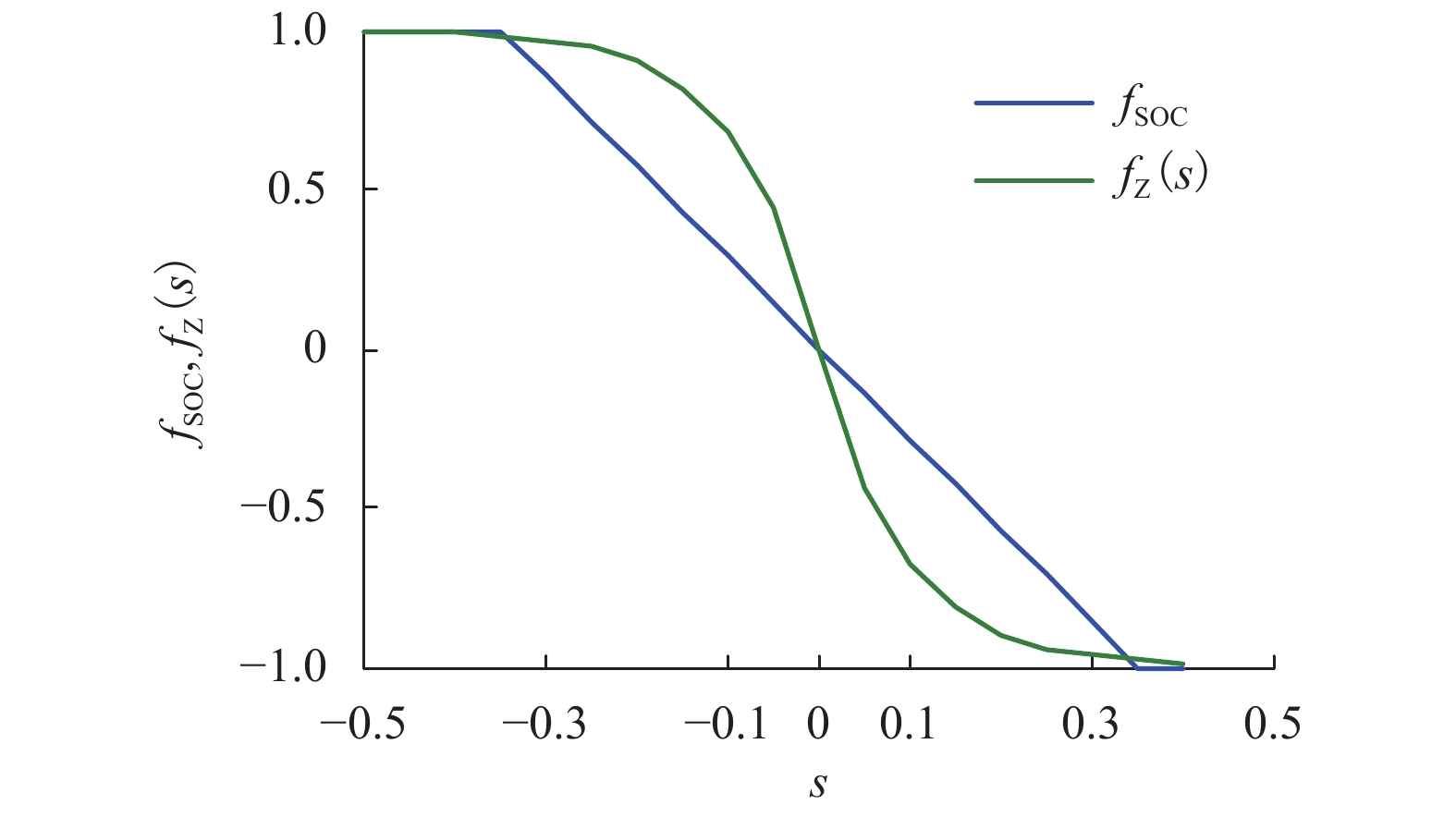
摘要: 为了提高燃料电池混合动力系统的经济性,基于燃料电池氢耗量和功率波动率,对功率跟随能量管理策略中参数和荷电状态(SOC)调节方式进行了分析,并定义了燃料电池的功率波动率;基于仿真软件ADVISOR中建立的燃料电池/超级电容混合动力系统模型,计算了不同的超级电容SOC限值和充电功率参数时的燃料氢耗量和波动率;设计了两种SOC调节方法,即Z曲线法和比例积分(PI)调节法,比较了不同SOC调节方法下的氢耗量和波动率. 研究结果表明:若SOC的下限增大,致使氢耗量和波动率增加,SOC下限为0.5时的氢耗量比0.25时增加7.10%,波动率增加3.85%;若SOC的上限增大,燃料电池波动率减小,0.95时的波动率比0.75时减小3.51%;充电功率参数在一定范围改变,能够减小燃料电池氢耗量和波动率;SOC调节方式中,当SOC初始值在 [0.28,0.52] 区间,PI调节法的波动率最优;当SOC初始值在 [0.75,0.90],Z曲线法的波动率最优.
-
关键词:
- 燃料电池 /
- 超级电容 /
- 功率跟随 /
- 荷电状态(SOC)调节 /
- 功率波动率
Abstract: In order to improve the economical efficiency of the fuel cell hybrid system, the parameters and the adjustment method of state of charge (SOC) in the power following energy management strategy were analyzed, based on the fuel cell hydrogen consumption and the power fluctuation rate. The power fluctuation rate of the fuel cell was defined. Based on the fuel cell-supercapacitor hybrid system model established in the simulation software ADVISOR, the hydrogen consumption and the fluctuation rate were estimated under different SOC limits and charging power parameters. The two methods to adjust SOC , namely the Z-curve and the proportional integral (PI) adjustment , were designed. The hydrogen consumption and the fluctuation rate were compared in the different methods.The results show that the more the lower limit of SOC increases, the more the hydrogen consumption and the fluctuation rate are produced. The hydrogen consumption with the lower limit of SOC 0.5 is more 7.10% than one with 0.25, and its fluctuation rate increases by 3.85%. When the upper limit of SOC increases from 0.75 to 0.95, the fluctuation rate decreases by 3.51%. The change of charging power parameter in a certain range produces a lower hydrogen consumption and a lower fluctuation rate. Among SOC regulation modes, the hydrogen consumption of the PI regulation method are optimal with initial SOC value in the interval [0.28, 0.52], and so is Z-curve method in the interval [0.75, 0.90].-
Key words:
- fuel cell /
- super-capacitor /
- power tracking /
- state of charge (SOC) regulation /
- power fluctuation rate
-
表 1 控制参数
Table 1. Control parameters
参数 取值 参数 取值 SOC,lo 0.25 SOC,hi 0.95 pcs,min/kW 3 pcs,max/kW 19 kcs,rise/(kW•s−1) 0.8 kcs,fall/(kW•s−1) −1.2 pcs,chg/kW 4 SOC0 0.25 表 2 不同SOC,lo时的SOC和氢耗量
Table 2. SOC and hydrogen consumption at different SOC,lo
SOC,lo 氢耗量/g SOC 最大值 SOC 最小值 SOC 的均值 功率均值/kW 方差/
kW波动率/% 0.25 60.73 0.67 0.23 0.50 9.645 5.57 57.70 0.30 61.60 0.72 0.25 0.53 9.781 5.58 57.10 0.40 63.82 0.81 0.25 0.58 10.120 5.65 55.82 0.45 64.32 0.85 0.25 0.60 10.200 5.64 55.29 0.5 65.06 0.88 0.25 0.63 10.300 5.72 55.56 表 3 3种SOC调节方式下氢耗量与燃料电池功率
Table 3. Hydrogen consumption under three adjust methods of SOC
方法 氢耗量/g 均值/kW 方差/kW 波动率λ/% 线性法 60.73 9.645 5.566 57.72 Z 曲线法 61.23 9.701 5.713 58.93 PI 调节法 60.96 9.692 5.519 56.94 -
DAUD W R W, ROSLI R E, MAJLAN E H, et al. PEM fuel cell system control:a review[J]. Renewable Energy, 2017, 113: 620-638. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2017.06.027 陈维荣,钱清泉,李奇. 燃料电池混合动力列车的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2009,44(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.01.001CHEN Weirong, QIAN Qingquan, LI Qi. Investigation status and development trend of hybrid power train based on fuel cell[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2009, 44(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.01.001 陈维荣,张国瑞,孟翔,等. 燃料电池混合动力有轨电车动力性分析与设计[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.01.001CHEN Weirong, ZHANG Guorui, MENG Xiang, et al. Dynamic performance analysis and design of fuel cell hybrid locomotive[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.01.001 PALADINI V, DONATEO T, DE RISI A, et al. Super-capacitors fuel-cell hybrid electric vehicle optimization and control strategy development[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2007, 48(11): 3001-3008. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2007.07.014 DI WU, WILLIAMSON S S. Status review of power control strategies for fuel cell based hybrid electric vehicles[C]//IEEE Canada Electrical Power Conference. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2007: 218-223. TORREGLOSA J P, JURADO F, GARCIA P, et al. Hybrid fuel cell and battery tramway control based on an equivalent consumption minimization strategy[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2011, 19(10): 1182-1194. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2011.06.008 LI C, LIU G. Optimal fuzzy power control and management of fuel cell/battery hybrid vehicles[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 192(2): 525-533. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.03.007 FERNANDEZ L M, GARCIA P, GARCIA C A, et al. Comparison of control schemes for a fuel cell hybrid tramway integrating two dc/dc converters[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(11): 5731-5744. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.02.132 RODATZ P, PAGANELLI G, SCIARRETTA A, et al. Optimal power management of an experimental fuel cell/supercapacitor-powered hybrid vehicle[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2005, 13(1): 41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2003.12.016 WU C, CHEN J, XU C, et al. Real-Time adaptive control of a fuel cell/battery hybrid power system with guaranteed stability[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2017, 25(4): 1394-1405. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2016.2611558 PAYMAN A, PIERFEDERICI S, MEIBODY-TAB-AR F, et al. An adapted control strategy to minimize DC-Bus capacitors of a parallel fuel cell/ultracapacitor hybrid system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2011, 26(12): 3843-3852. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2009.2030683 TORREGLOSA J P, GARCIA P, FERNANDEZ L M, et al. Predictive control for the energy management of a fuel-cell-battery-supercapacitor tramway[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2014, 10(1): 276-285. doi: 10.1109/TII.2013.2245140 LI Q, WANG T, DAI C, et al. Power Management Strategy based on Adaptive Droop Control for a fuel cell-battery-supercapacitor hybrid tramway[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(7): 5658-5670. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2715178 LIU J, ZHAO Y, GENG B, et al. Adaptive second order sliding mode control of a fuel cell hybrid system for electric vehicle applications[J]. Mathematical Probl-ems in Engineering, 2015, 2015(8): 1-14. 陈维荣,刘嘉蔚,郭爱,等. 14.4 kW PEMFC电堆单体电压均衡性实验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(3): 429-438. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.03.001CHEN Weirong, LIU Jiawei, GUO Ai, et al. Experi-mental study on voltage uniformity of 14.4 kW PEMFC stack single cell[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(3): 429-438. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.03.001 LARMINIE J, DICKS A. Fuel cell systems explained [M]. Second Edition. [S.l.]: West Sussex John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2003: 34. 赵坤. 城轨交通车载超级电容储能系统能量管理及容量配置研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2013. -





 下载:
下载: