Operating Environment and Pollutant Distribution in Xiang’an Undersea Tunnel
-
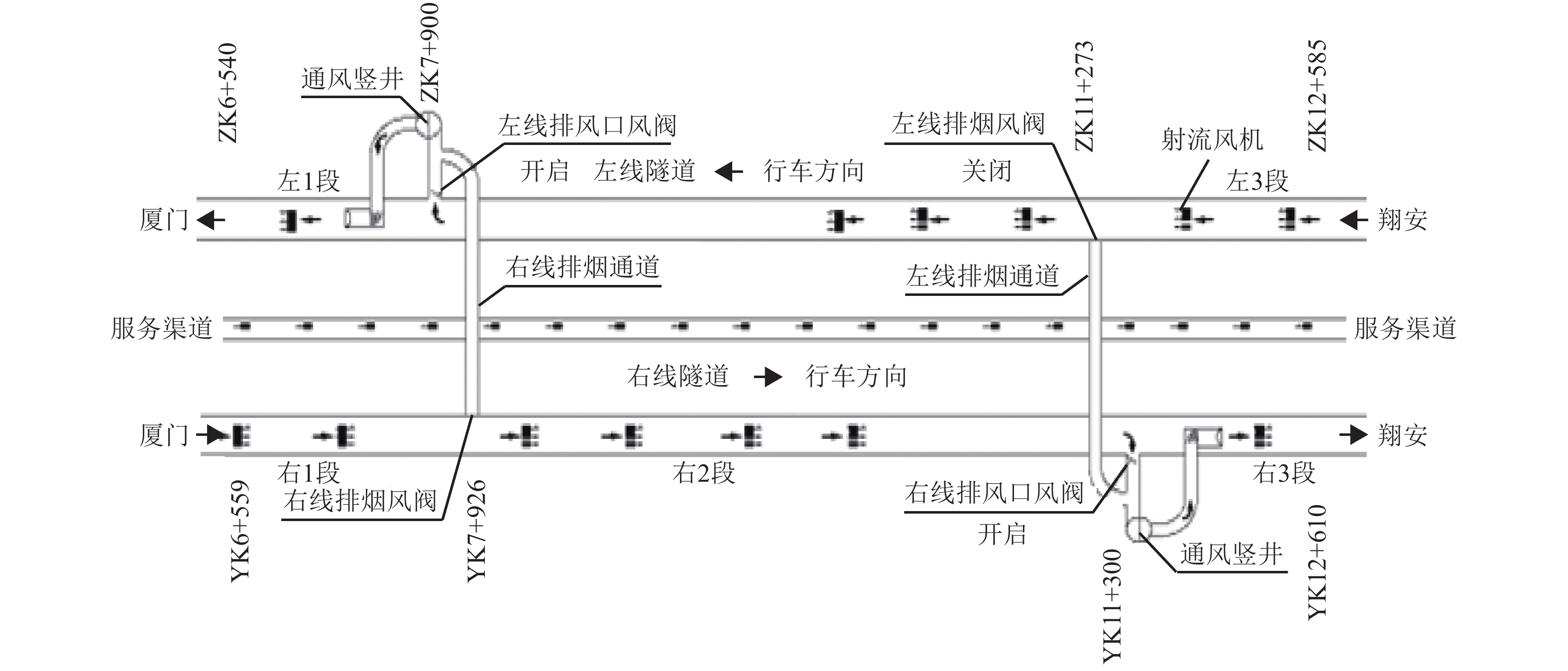
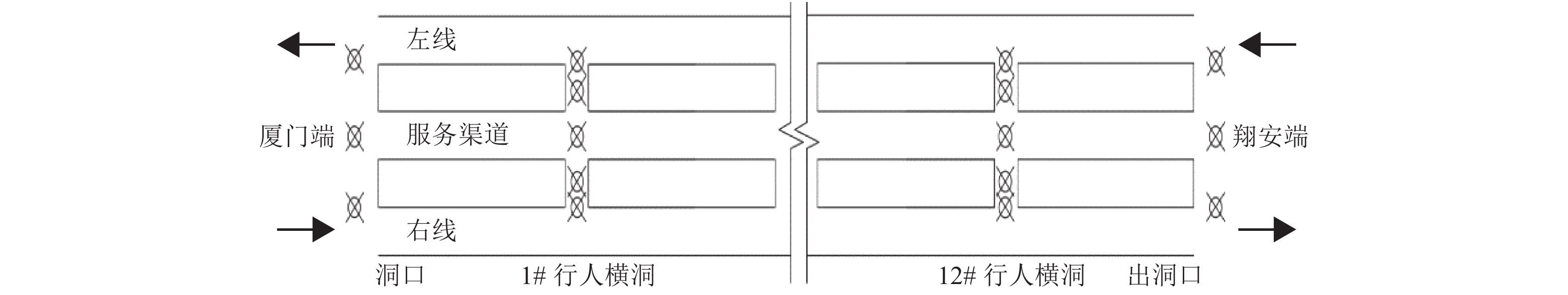
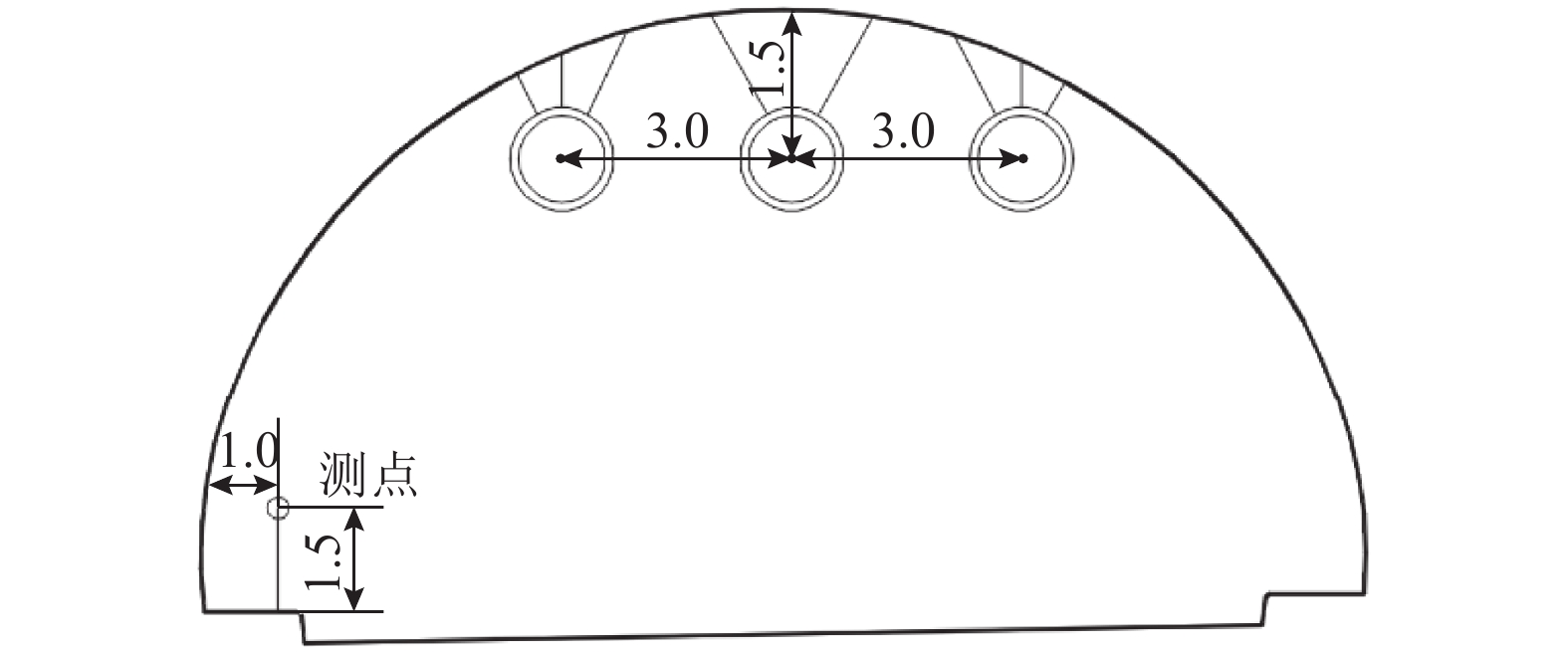
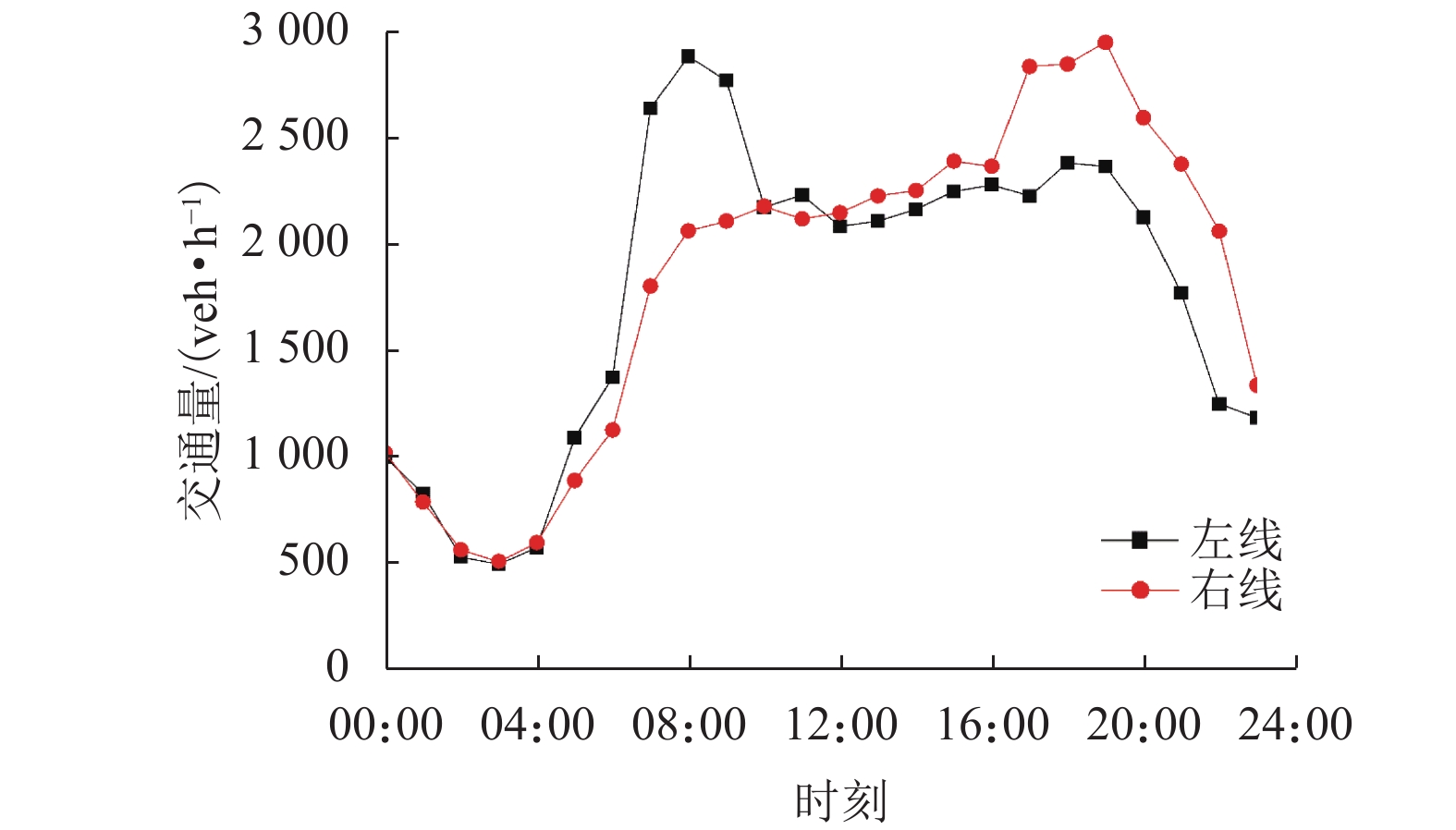
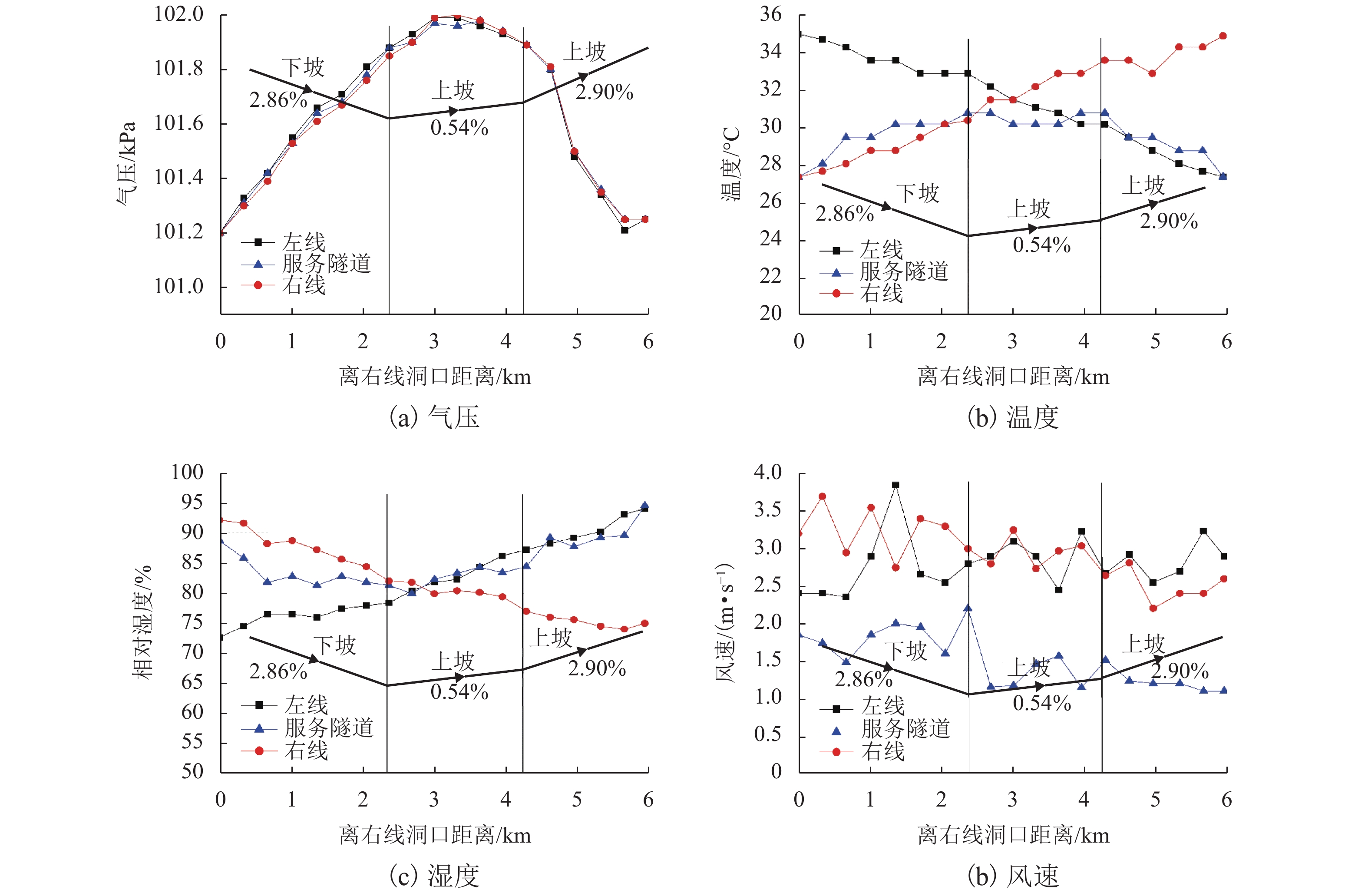
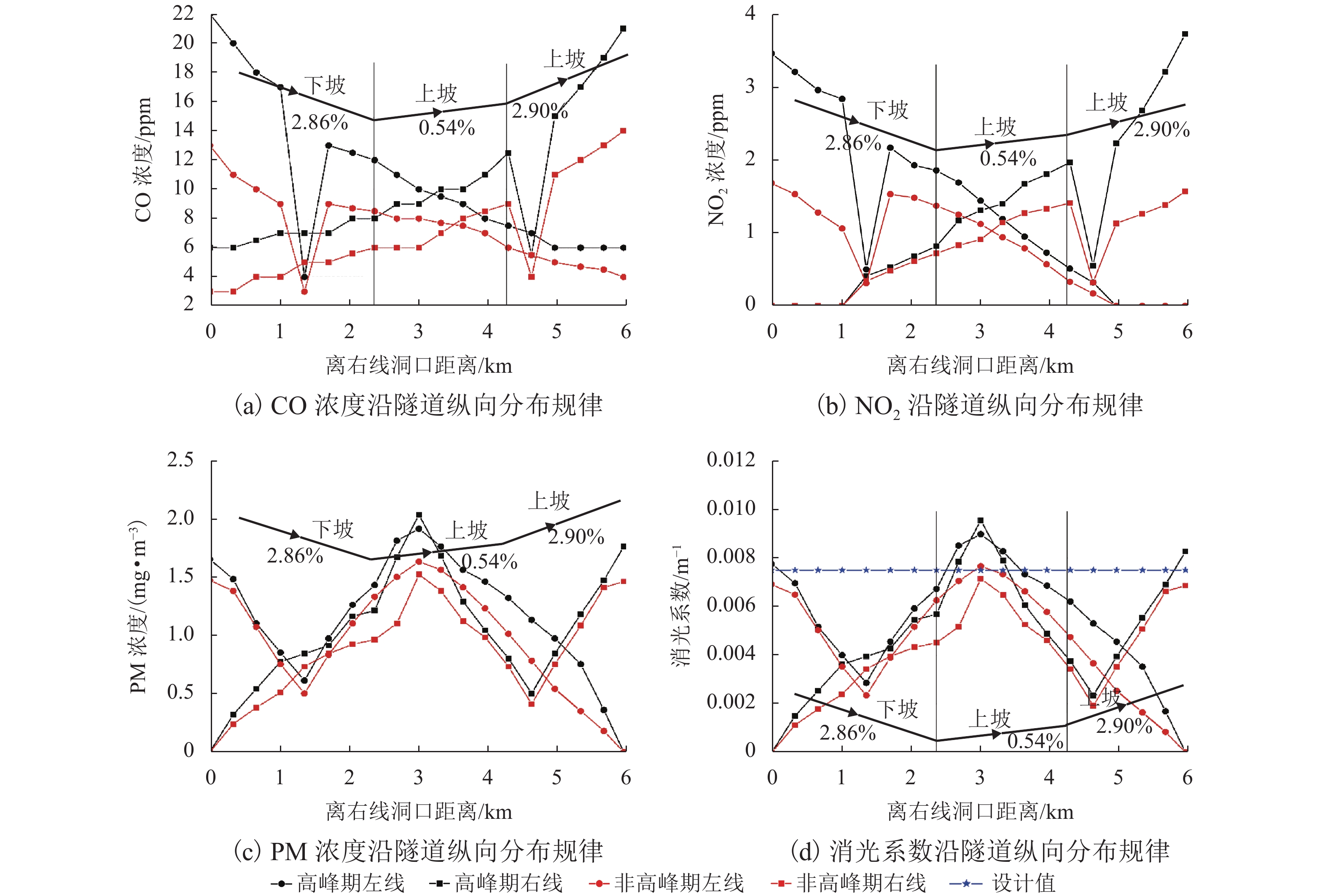
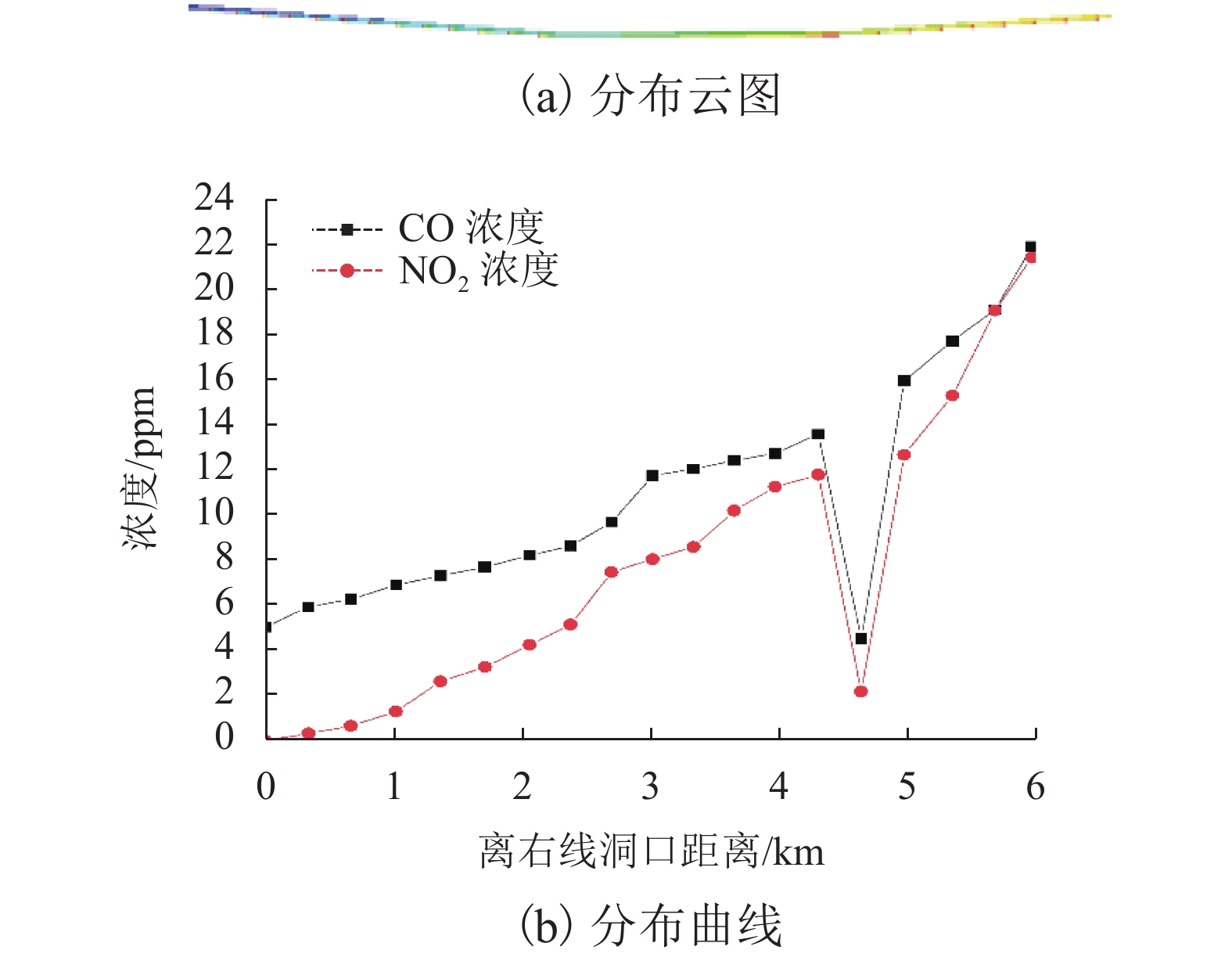
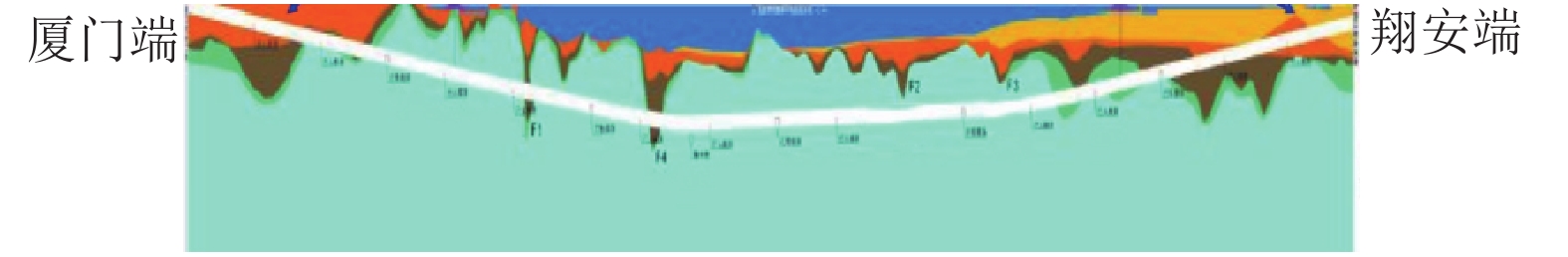
摘要: 为了明确城市海底公路隧道内环境参数和污染物的分布规律,针对厦门翔安海底隧道运营通风效果进行了现场测试,获取了交通高峰期和非高峰期两个时段隧道内气压、温湿度、风速、CO、NO2和PM浓度的分布规律,结合一维扩散理论和Fluent组分输运模型研究了海底公路隧道内环境参数和污染物随交通流的分布规律. 研究结果表明:(1) 交通高峰期时段,温度沿车流方向逐渐升高,出口处达到最高温度36 ℃;湿度沿车流方向逐渐降低,入口处最大湿度为94%;CO、NO2和PM浓度随车流方向逐渐升高,在出口处达到最大,最大浓度分别为21.00 ppm、3.73 ppm和1.76 mg/m3,V型坡坡底处PM浓度也较高(2.03 mg/m3);根据烟尘质量浓度与消光系数的转换公式得到出口处和V型坡坡底处的消光系数分别为0.008 3 m−1和0.009 5 m−1,NO2和PM浓度超过了规范值.(2) 非交通高峰期NO2最大浓度为1.68 ppm,出口处和V型坡坡底处的消光系数分别为0.006 9 m−1和0.007 7 m−1,出口处NO2浓度和坡底处消光系数超过了规范值.Abstract: In order to clarify the distribution of environmental parameters and pollutants in the urban undersea road tunnel, a field test was carried out for the ventilation effect of Xiamen Xiang'an undersea tunnel. The atmosphere pressure, temperature and humidity, air speed, CO, NO2, and PM concentration in the tunnel were tested during the peak and off-peak periods. Combined with the one-dimensional diffusion theory and the Fluent component transport model, the distribution of environmental parameters and pollutants along the traffic volume in the undersea road tunnel was studied. The results show that: (1) during the rush hours, the temperature increases gradually along the direction of traffic flow and reaches to 36℃ at the outlet. The humidity decreases gradually along the direction of traffic flow and reaches to 94% at the inlet. The CO, NO2, and PM concentrations increase gradually with the direction of traffic flow and reach to maximum at the outlet, the maximum concentrations were 21.00 ppm, 3.73 ppm and 1.76 mg/m3, respectively. The PM concentration at the bottom of the V-shaped slope reaches to 2.03 mg/m3. According to the conversion formula of particulate matter concentration and extinction coefficient, the extinction coefficients at the outlet and the bottom of the V-shaped slope are 0.008 3 m−1 and 0.009 5 m−1 , respectively. The NO2 and PM concentrations exceed the threshold value. (2) The maximum concentration of NO2 during off-peak hours is 1.68 ppm, and the extinction coefficients at the outlet and the bottom of the V-shaped slope are 0.006 9 m−1 and 0.007 7 m−1 , respectively. The NO2 concentration at the outlet and the extinction coefficient at the bottom of the slope exceed the threshold value.
-
Key words:
- undersea road tunnel /
- ventilation design /
- field testing /
- pollutant distribution /
- V-shaped slope
-
表 1 不同隧道污染物浓度测试结果比较
Table 1. Comparison of pollutant concentrations measured in different tunnels
隧道名称 地区 长度/m 交通量/
(veh•h−1)轻型车
占比/%平均车速/
(km•h−1)出口浓度 CO/ppm NO2/ppm PM/(mg•m−3) 狮子山隧道 香港 1 295 2 300 43~58 6.5 0.33 雪山隧道 台湾 12 900 1 400 89.1 80 12.0~39.0 1.20~3.10 0.148~0.178 Janio Quardros隧道 圣保罗 850 1 500~2 000 85.0 72 6.7 ± 1.8 0.20 0.123 ± 0.031 Rodoanel隧道 圣保罗 1 150 3 000 70.0 83 6.3 ± 1.5 1.15 0.245 ± 0.059 东延安路隧道 上海 2 261 2 700 95.0 20~40 17.4 营盘路隧道 长沙 2 510 1 700~2 600 98.4 30 20.3 1.65 翔安海底隧道 厦门 6 050 2 000~2 952 77.0 40~60 13.0~22.0 1.57~3.73 1.47~1.65 表 2 设计限值标准
Table 2. Design threshold criteria values
标准名称 地区 CO/
ppmNO2/
ppmPM/
(mg•m−3)PIARC 2012 国际 70 1 1.489 公路隧道通风
设计细则中国 100 必要时考虑 1.596 -
孙钧. 海底隧道工程设计施工若干关键技术的商榷[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2006,25(8): 1513-1521. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.08.001SUN Jun. Discussion on some key technical issues for design and construction of undersea tunnels[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(8): 1513-1521. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.08.001 王梦恕. 水下交通隧道发展现状与技术难题——兼论“台湾海峡海底铁路隧道建设方案”[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(11): 2161-2172. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.11.001WANG Mengshu. Current developments and technical issues of underwater traffic tunnel—discussion on construction scheme of Taiwan strait undersea railway tunnel[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(11): 2161-2172. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.11.001 祝兵,关宝树,郑道坊. 公路长隧道纵向通风的数值模拟[J]. 西南交通大学学报,1999,34(2): 133-137.ZHU Bing, Guan Baoshu, ZHENG Daofang. Numerical simulation of longitudinal ventilation of long highway tunnels[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 1999, 34(2): 133-137. WANG F, WANG M, HE S, et al. Computational study of effects of traffic force on the ventilation in highway curved tunnels[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2011, 26(3): 481-489. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2011.01.003 EFTEKHARIAN E, DASTAN A, ABOUALI O, et al. A numerical investigation into the performance of two types of jet fans in ventilation of an urban tunnel under traffic jam condition[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2014, 44: 56-67. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2014.07.005 SAMBOLEK M. Model testing of road tunnel ventilation in normal traffic conditions[J]. Engineering Structures, 2004, 26(12): 1705-1711. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2004.06.001 谢永利. 秦岭终南山特长公路隧道通风技术研究报告[R]. 西安: 长安大学, 2005. 王书涛. 港珠澳海底隧道通风物理模型试验研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2010. 曾艳华,李永林,何川,等. 隧道通风网络及调节[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2003,38(2): 183-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2003.02.015ZENG Yanhua, LI Yonglin, HE Chuan, et al. Tunnel ventilation network and regulation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2003, 38(2): 183-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2003.02.015 KROL M, KROL A, KOPER P, et al. Full scale measurements of the operation of fire ventilation in a road tunnel[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2017, 70: 204-213. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2017.07.016 金文良,谢永利,李宁军,等. 新七道梁公路隧道运营通风效果测试及分析[J]. 现代隧道技术,2006(1): 41-45,51.JIN Wenliang, XIE Yongli, LI Ningjun, et al. Analysis and analysis of ventilation effect of new seven road tunnels[J]. Modern Tunneling, 2006(1): 41-45,51. 刘宏,王晓雯,陈建忠. 中梁山公路隧道通风效果测试分析[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版),2010,29(4): 529-532.LIU Hong, WANG Xiaowen, CHEN Jianzhong. Test and analysis of ventilation effect in Zhongliangshan highway tunnel[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 29(4): 529-532. LEVONI P, ANGELI D, STALIO E, et al. Fluid-dynamic characterisation of the Mont Blanc tunnel by multi-point airflow measurements[J]. Tunneling and Underground Space Technology, 2015, 48: 110-122. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2015.03.006 王亚琼,谢永利,张素磊,等. 氮氧化物对隧道需风量影响研究[J]. 公路交通科技,2010,27(10): 89-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2010.10.016WANG Yaqiong, XIE Yongli, ZHANG Sulei, et al. Study on the influence of nitrogen oxides on the air volume of tunnels[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation, 2010, 27(10): 89-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2010.10.016 DENG Y, CHEN C, LI Q, et al. Measurements of real-world vehicle CO and NOx fleet average emissions in urban tunnels of two cities in China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2015, 122: 417-426. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.08.036 陈丹,胡明华,张洪海,等. 考虑周期性波动因素的中长期空中交通流量预测[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(3): 562-568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.03.028CHEN Dan, HU Minghua, ZHANG Honghai, et al. A medium- and long-term air traffic flow forecast considering periodic fluctuation factors[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(3): 562-568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.03.028 中华人民共和国行业推荐性标准. 公路隧道通风设计细则: JTG/T D70/2-02—2014 [S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2014 PIARC World Road Association. Road tunnels: vehicle emissions and air demand for ventilation[R]. [S.l.]: 2012 PIARC Technical Committee on Road Tunnels, 2012. CHEN P H, LAI J H, LIN C T. Application of fuzzy control to a road tunnel ventilation system[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 1998, 100(1/2/3): 9-28. 何川,李祖伟,方勇,等. 公路隧道通风系统的前馈式智能模糊控制[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2005,40(5): 575-579. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2005.05.002HE Chuan, LI Zuwei, FANG Yong, et al. Feedforward intelligent fuzzy control of highway tunnel ventilation system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2005, 40(5): 575-579. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2005.05.002 BHAUTMAGE U, GOKHALE S. Effects of moving-vehicle wakes on pollutant dispersion inside a highway road tunnel[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 218: 783-793. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.002 CHUNG C Y, CHUNG P L. A numerical and experimental study of pollutant dispersion in a traffic tunnel[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2007, 130(1/2/3): 289-299. -




 下载:
下载: