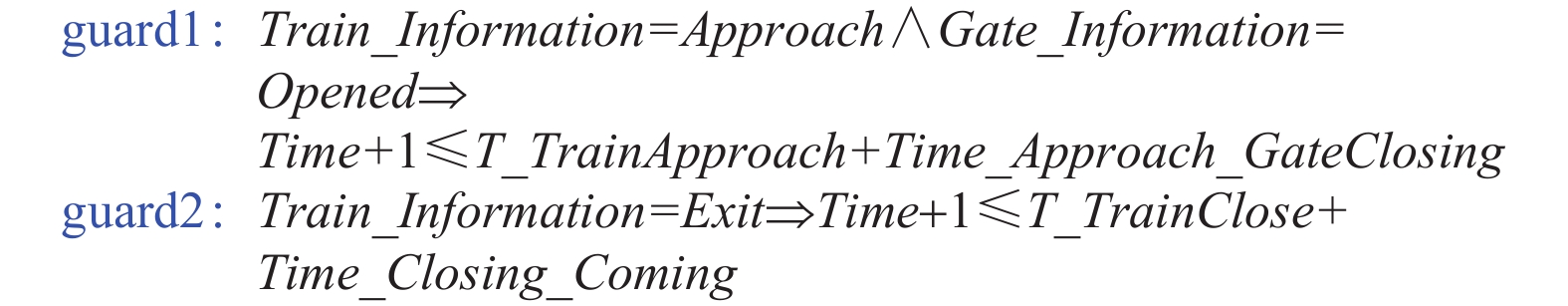Modeling and Verification of Control System Specification for Railway Level Crossings Based on Formal Method
-
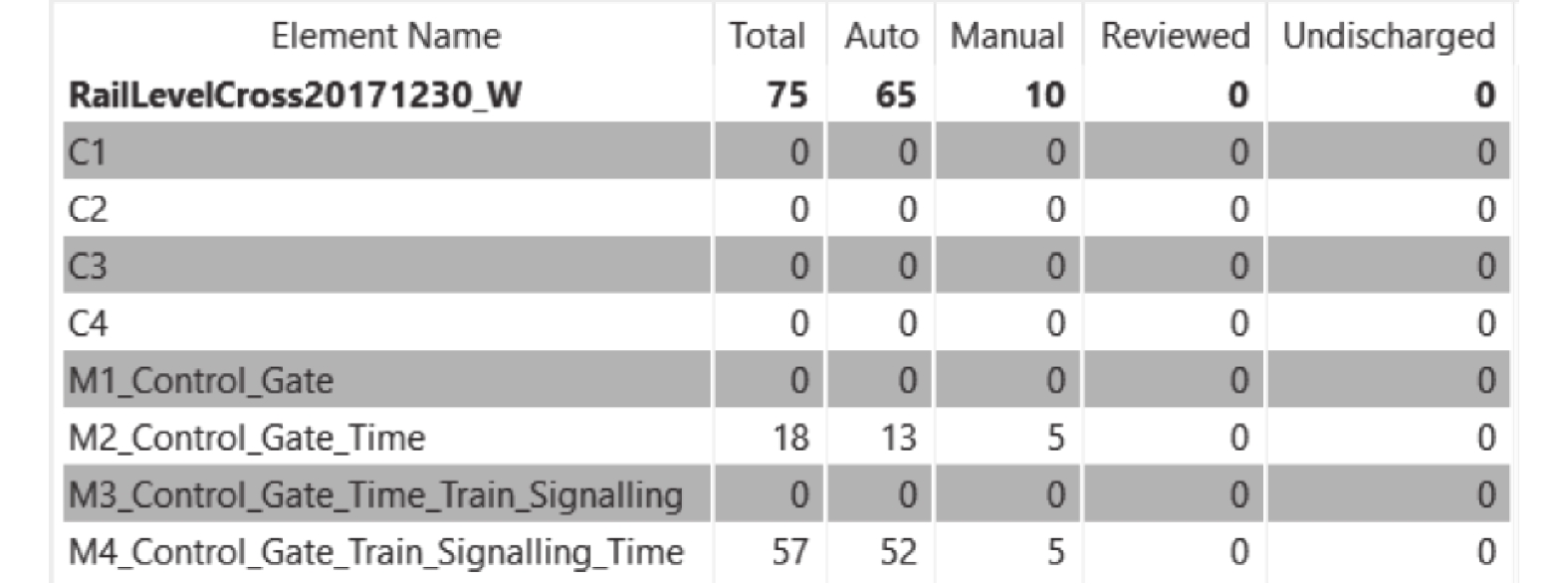
摘要: 为了增强铁路道口控制系统设计的可靠性,使用一种形式化方法对该系统进行建模与验证. 基于道口管理规范,在分析系统各类属性与事件流程的基础上,使用UML图方法并结合精化策略建立了系统各层的Event-B语言模型. 通过对不变式的证明义务进行证明,验证了系统设计中的安全、时间特性,检查出了需求规范分析中的缺陷,提出了增强系统稳健性的改进方案,修正了系统的设计原型. 最后,通过不变式冲突与死锁检验进一步确认了模型的正确性. 研究表明文中方法提高了形式化建模过程的准确性与层次性,且确认得出目前规范中存在列车驶入道口时不能确保道口出清的缺陷,证实了使用本文形式化流程可以验证道口控制系统的需求规范并形成可靠的设计原型,从而可提高铁路道口的安全性.Abstract: To improve the reliability of the control system design for the railway level crossings, a formal method is used to model and verify this system. By analyzing the management standards of the railway crossingss, the requirement properties and event processes were obtained; moreover, a multilayer Event-B model was established by using the UML diagram method and refinement policy. After theorem proving of the proof obligations generated by the invariants, the design properties of safety and time were verified; meanwhile the defect of requirement specifications were detected, with an improved event flow being proposed to enhance the robustness, thereof the system prototype was revised as well. Finally, by checking the invariant violations and deadlock, the model was validated on its correctness. The proposed method helps to improve the accuracy and hierarchy of the formal modeling process. In addition, the research result indicates that a defect exists in the current specification, i.e. the clearance of the crossings cannot be guaranteed when the train enters the level crossings. It’s concluded that the formal process presented in this paper can be used to verify the requirement specification of the railway crossings control system, so as to help developing a reliable prototype that can greatly improve the safety of the railway level crossings.
-
表 1 模型精化过程
Table 1. Refinement processes of the model
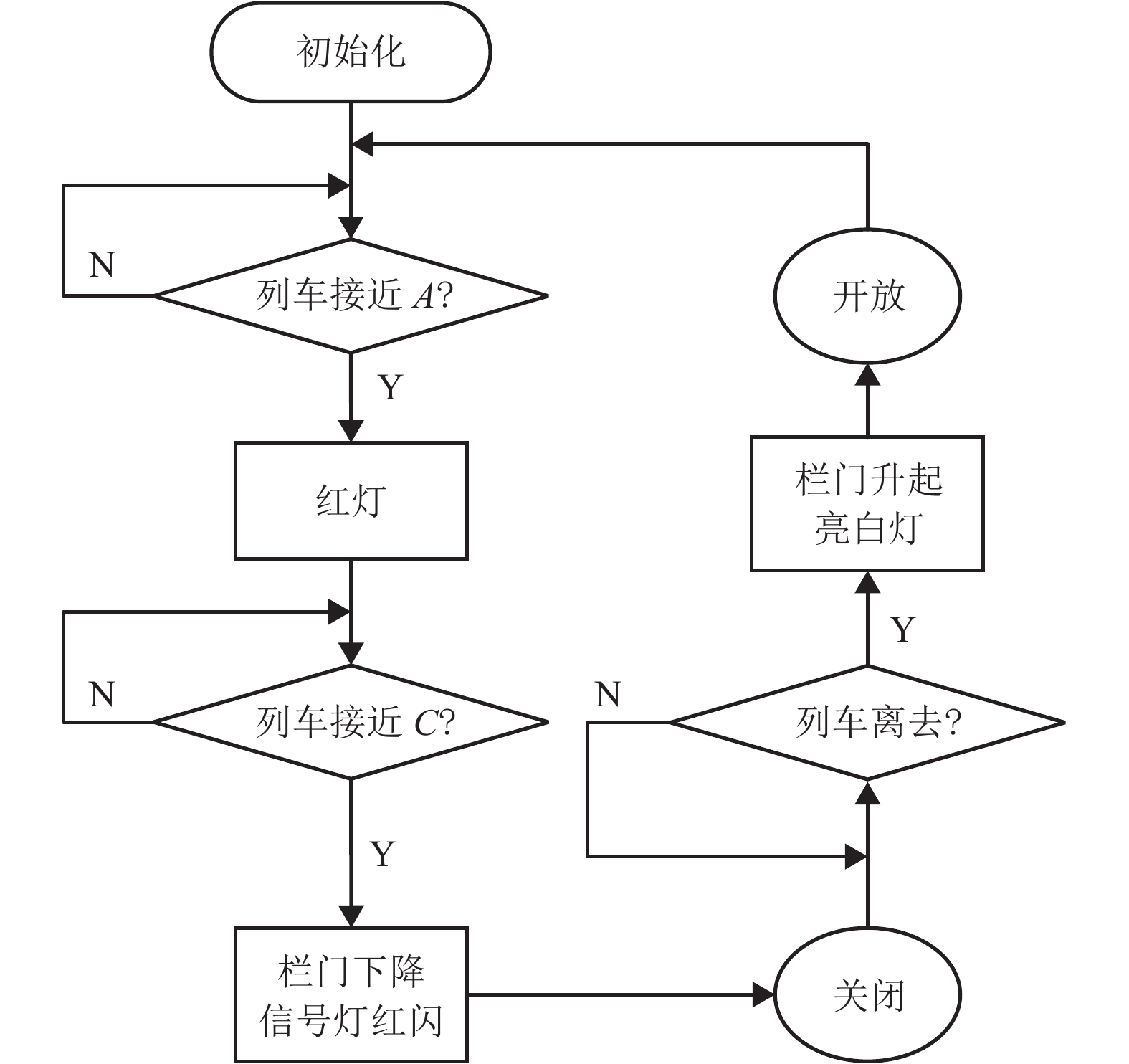
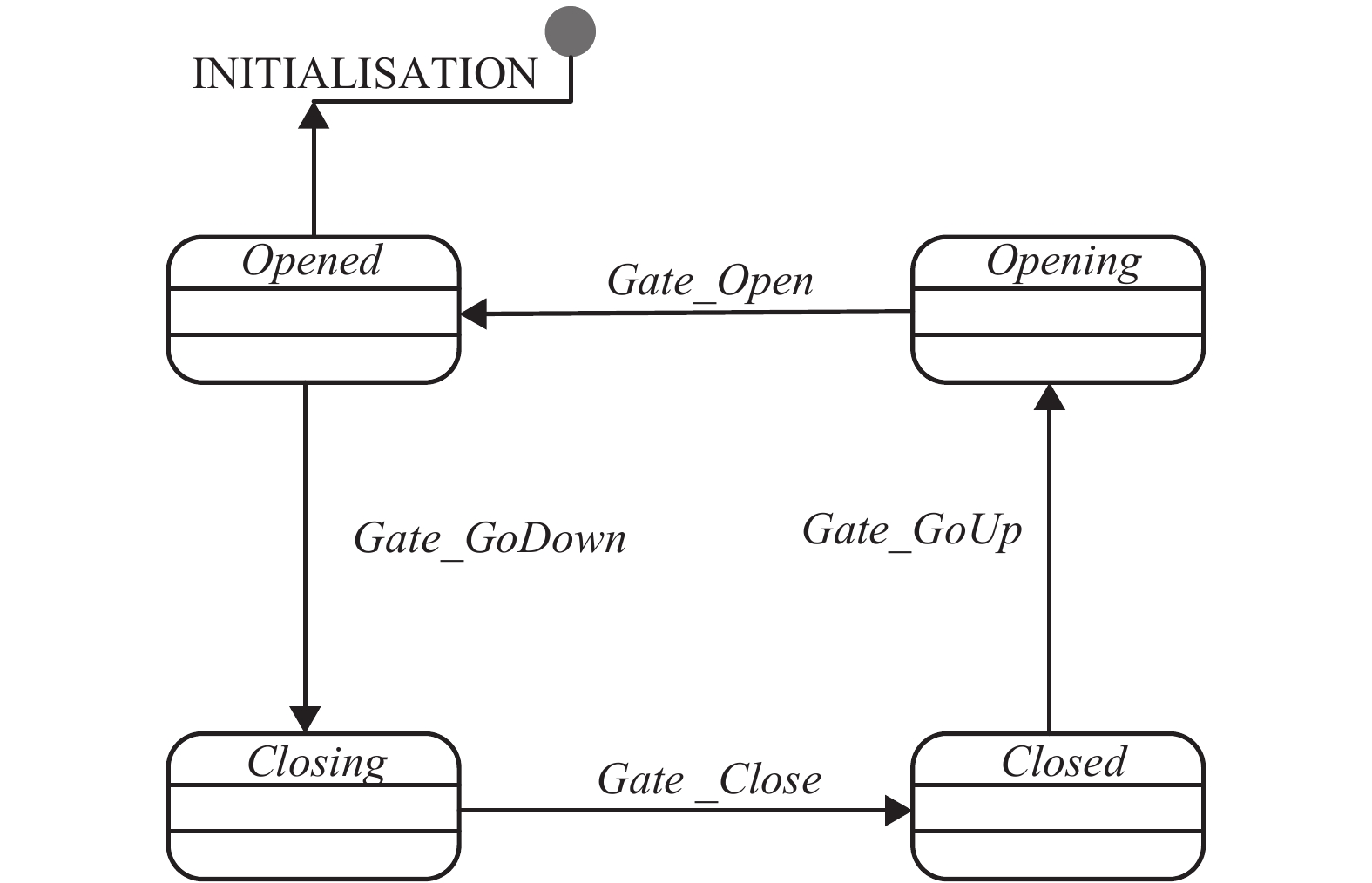
精化层级 引入对象 第1层 引入栏门、控制器对象,建立栏门开启与关闭的过程事件. 第2层 引入时间对象,建立系统时钟,完善栏门接收控制器命令后开启与关闭过程的时间要求. 第3层 引入列车、信号灯对象,增加列车接近、列车逼近、列车离去道口事件与信号灯转换事件,完善道口系统执行过程. 第4层 引入列车接近、逼近计时,完善控制器的时间约束. -
国家安全生产监管管理总局. 铁路运输行业基本情况[R/OL]. (2014-06-17)[2018-01-04]. http://www.chinasafety.gov.cn/newpage/Contents/Channel_21500/2014/0617/236238/content_236238.htm European Union Agency for Railways. Railway safety performance in the european union[R/OL]. (2016-09-13)[2018-01-04]. http://www.era.europa.eu/Document-Register/Documents/Railway%20Safety%20Performance%202016%20final%20E.pdf Eurostat. Rail accident fatalities in the EU[R/OL]. (2017-02-10)[2018-01-04]. http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Rail_accident_fatalities_in_the_EU#Further_Eurostat_information 贾明涛,王海星,肖贵平. 铁路道口安全影响因素分析及对策[J]. 安全与环境学报,2006,6(6): 123-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2006.06.033JIA Mingtao, WANG Haixing, XIAO Guiping. Safety analysis on highway-railway crossings[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2006, 6(6): 123-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2006.06.033 GHAZEL M, EL-KOURSI E M. Two-half-barrier level crossings versus four-half-barrier level crossings:a comparative risk analysis study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2014, 15(3): 1123-1133. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2013.2294874 MEKKI A, GHAZEL M, TOGUYENI A. Validation of a new functional design of automatic protection systems at level crossings with model-checking techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2012, 13(2): 714-723. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2011.2178238 SALMANE H, KHOUDOUR L, RUICHEK Y. A video-analysis-based railway-road safety system for detecting Hazard situations at level crossings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(2): 596-609. LARSEN P G, LARSEN P G, BICARREGUI J, et al. Formal methods:practice and experience[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2009, 41(4): 1-40. CENELEC. IEC61508: Functional safety of electrical/electronic/programmable electronic safety-reared systems[S/OL]. European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization. [2018-01-04]. https://webstore.iec.ch/preview/info_iec61508-0%7Bed1.0%7Db.pdf SUN J, SUN S, LI K, et al. Efficient algorithm for traffic engineering in cloud-of-things and edge computing[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2018, 69(7): 610-627. LEFFINGWELL D, WIDRIG D. Managing software requirements: a use case approach[M]. New Jersey: Addison-Wesley, 2003: 10-40 国家铁路局. 铁路站内道口信号设备技术条件: GB10493—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018: 3-5 中国铁路总公司. 铁路道口管理办法: 铁总运[2013]121号[S/OL]. 北京: [s.n.], 2013: 10-19. [2018-01-04]. https://wenku.baidu.com/view/fe0322d649649b6648d74789.html ABRIAL J R. Modeling in Event-B: system and software engineering[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2010: 217-219 BUTLER M. Reasoned modelling with Event-B[C]//Engineering Trustworthy Software Systems, SETSS 2016. Cham: Springer, 2016: 51-109 WANG K. Rail level crossing DATA[CP/OL]. [2018-5-21]. https://github.com/abidefei/RailLevelCrossing_EventB ZHU C, BUTLER M, CIRSTEA C. Refinement of timing constraints for concurrent tasks with scheduling[C]//International Conference on Abstract State Machines, Alloy, B, TLA, VDM, and Z. Cham: Springer, 2018: 219-233 -




 下载:
下载: