Recognition Method for Multi-scale Sparse Power Quality Disturbance
-
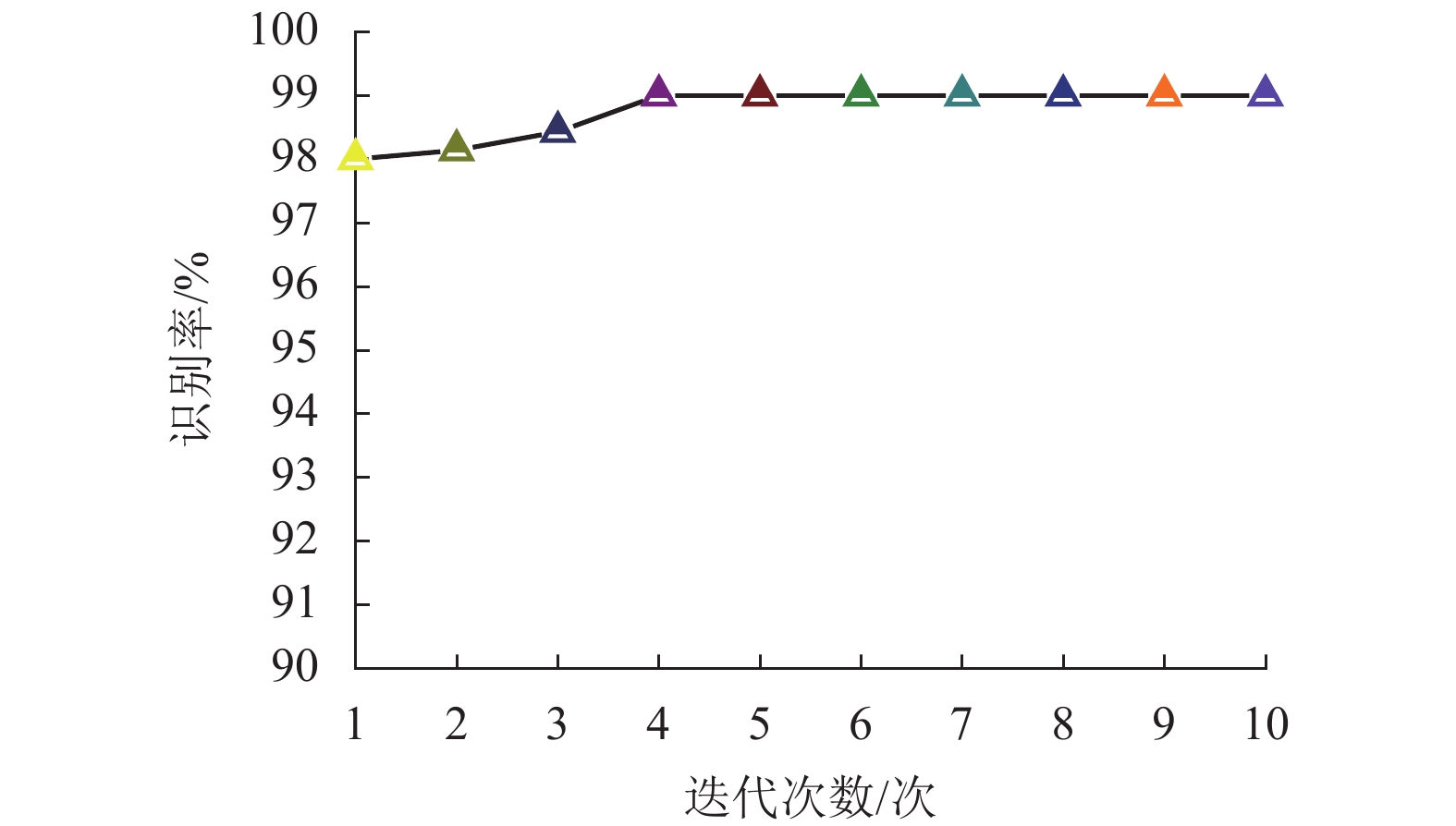
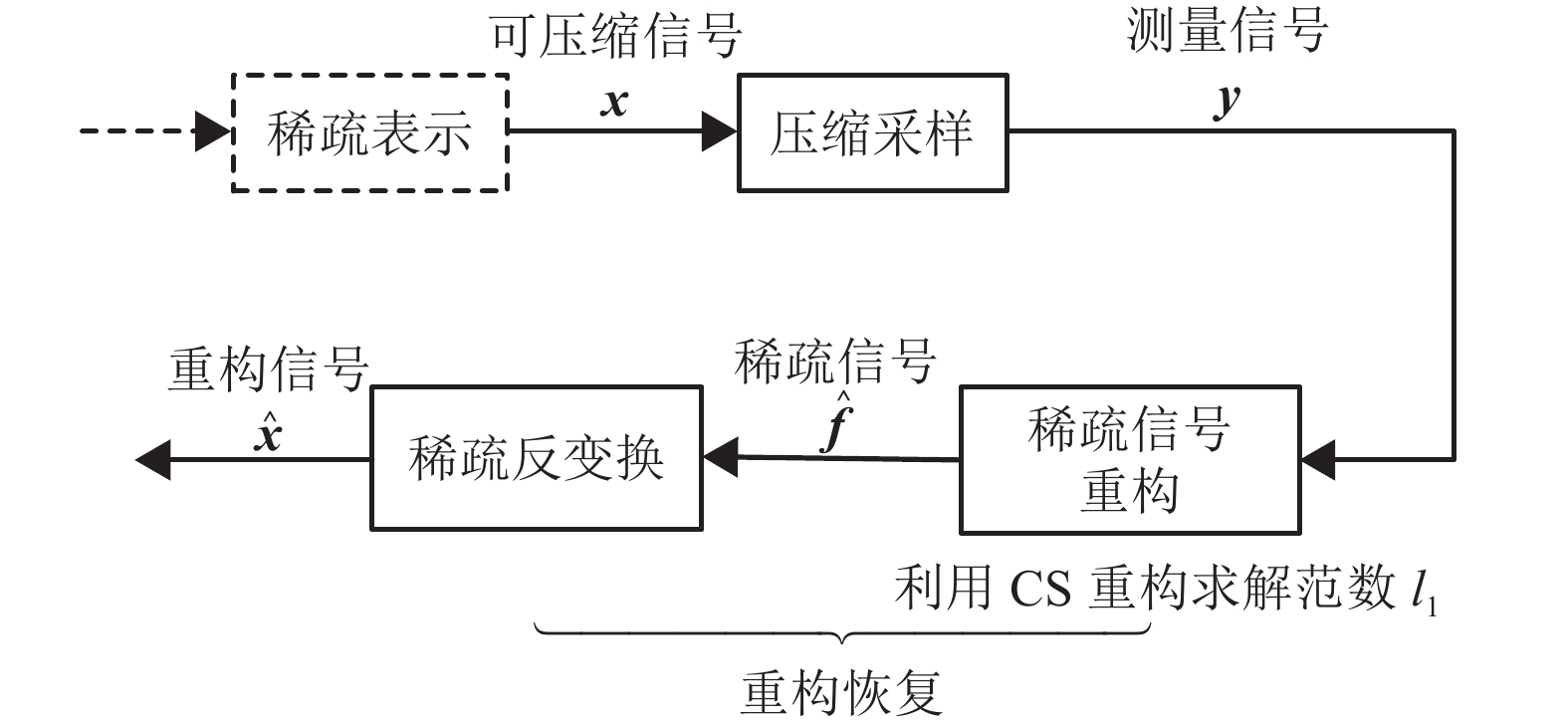
摘要: 针对传统电能质量扰动识别中存在数据量大、扰动特征依赖主观选择的问题,提出一种多尺度稀疏电能质量扰动深度识别方法. 首先,构建电能质量的多尺度稀疏模型,通过对扰动信号平稳小波多尺度变换获得扰动的低高频信息;然后,对其压缩采样获得降维的测量数据,并在此基础之上,应用正交匹配追踪算法求取各层稀疏系数组成稀疏向量,将稀疏向量输入深度置信网络,实现扰动的智能识别;同时,为进一步提高网络识别的准确性,采用交叉熵算法完成对网络隐含层数、学习率等参数寻优;最后,为验证所述方法的有效性,针对几类典型的单一扰动和复合扰动信号进行大量仿真试验. 结果表明:在理想环境和噪声环境下,针对七类典型单一扰动,平均识别率达到99.0%和96.71%以上;针对13类多重扰动,平均识别到达97.69%和94.62%以上.Abstract: In the traditional power quality disturbance recognition, there is a large amount of data and disturbance characteristics are dependent on subjective selection. To deal with these problems, a recognition method for multi-scale sparse power quality disturbance is proposed. Firstly, a multi-scale sparse model for power quality signal is constructed. Through the stationary wavelet transform (SWT) for the disturbance signal, its low and high frequency information is obtained. Then by compressed sampling for the disturbance signal, the dimension reduction data are obtained. Further, sparse coefficients calculated by orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP) algorithm constitute a sparse vector, which is directly inputted into the deep belief network to achieve intelligent disturbance classification. Meanwhile, to improve the recognition rate, cross-entropy algorithm is applied to find the optimal parameters such as the number of hidden layers and learning rate. Finally, in order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, a large number of simulation tests were performed for several typical single disturbances and mixed disturbances. The simulation results demonstrate that in the ideal environment the averaged recognition rate of this method for seven typical single disturbances and thirteen mixed disturbances is 99.0% and 97.69% respectively, and in noisy environment at least 96.71% and 94.62% respectively, which shows that the proposed method has a desirable performance in disturbance identification.
-
表 1 电能质量扰动信号数学模型
Table 1. Power quality mathematical model
信号类型 公式表达 参数范围 电压暂降 $f(t) = \left\{{\begin{array}{*{2}{l} }\!\!\!\!{\sin (2{\text{π} } ft),\:}\;\;\;\;{t \in \left[ {0,{t_1} } \right] \cup \left[ { {t_2},T} \right]}\\\!\!\!\!{a\sin (2{\text{π} } ft),}\;\;\;\;{t \in \left[ { {t_1},{t_2} } \right]}\end{array} } \right.$ $ \begin{array}{*{20}{c} }0.2 < a < 0.8\\0.01 < {t_2} - {t_1} < 1.05\end{array}$ 电压暂升 $f(t) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l} }\!\!\!\!{\sin (2{\text{π} } ft),\:}\;\;\;\;{t \in \left[ {0,{t_1} } \right] \cup \left[ { {t_2},T} \right]}\\\!\!\!\!{a\sin (2{\text{π} } ft),}\;\;\;\;{t \in \left[ { {t_1},{t_2} } \right]}\end{array} } \right.$ $\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {1.2 < a < 1.8} \\ {0.01 < {t_2} - {t_1} < 1.05} \end{array}$ 电压中断 $f(t) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l} }\!\!\!\!{\sin (2{\text{π} } ft),}\;\;\;\;{t \in \left[ {0,{t_1} } \right] \cup \left[ { {t_2},T} \right]}\\\!\!\!\!{a\sin (2{\text{π} } ft),}\;\;\;\;{t \in \left[ { {t_1},{t_2} } \right]}\end{array} } \right.$ $\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {0.00 < a < 0.1} \\ {0.01 < {t_2} - {t_1} < 1.05} \end{array}$ 短时谐波 $f(t) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}\!\!\!\!{\sin (2{\text{π}} ft),\:}\;\;\;\;{t \in \left[ {0,{t_1}} \right] \cup \left[ {{t_2},T} \right]}\\\!\!\!\!{\displaystyle \sum\limits_{i = 1,3,5,7} {{a_i}\sin (2{\text{π}} ift)} ,\:}\;\;\;\;{t \in \left[ {{t_1},{t_2}} \right]}\end{array}} \right.$ $\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {0.05 < {a_i} < 0.3} \\ {0.01 < {t_2} - {t_1} < 1.05} \end{array}$ 暂态振荡 $f(t) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l} }\!\!\!\!{\sin (2{\text{π} } ft),\:}\;\;\;\;{t \in [0,{t_1}] \cup [{t_2},0.16]\:}\\\!\!\!\!{\sin (2{\text{π} } ft) + a\sin (2n{\text{π} } ft){ {\rm{e} }^{ - mt} } }\;\;\;\;{t \in [{t_1},{t_2}]}\end{array} } \right.$ $\begin{gathered} 0 < a < 8 \\ 0 < {t_2} - {t_1} < 0.5 \\ \end{gathered} $ 电压脉冲 $f(t) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l} }\!\!\!\!{\sin (2{\text{π} } ft),}\;\;\;\;{t \in [0,{t_1}] \cup [{t_2},0.16]\:}\\\!\!\!\!{a\sin (2{\text{π} } ft),}\;\;\;\;{t \in [{t_1},{t_2}]}\end{array} } \right.$ $\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {2 < a} \\ {0 < {t_2} - {t_1} < 0.01} \end{array}$ 电压波动 $f(t) = [1 + a \sin (2n{\text{π}} ft)] \sin (2{\text{π}} ft)$ $\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {0.1 < a < 0.3} \\ {0.000\;5 < {t_2} - {t_1} < 0.000\;6} \end{array}$ 正常电压 $f(t) = \sin (2{\text{π}} ft)$ − 注:a 为各扰动的幅值分量;t 为总时长;t1 和 t2 为扰动起止时刻. 表 2 单一扰动深度识别结果
Table 2. Recognition results of single disturbance
% 信号类型 SNR 20 dB 30 dB 40 dB 无噪声 电压暂降 95(97) 97(97) 96(97) 98(98) 电压中断 98(98) 98(98) 98(100) 98(100) 短时谐波 95(96) 97(98) 97(98) 97(99) 电压暂升 97(95) 100(99) 100(99) 99(99) 脉冲暂态 98(96) 98(100) 100(97) 100(100) 短时振荡 97(100) 100(100) 100(100) 100(100) 电压闪变 98(96) 99(100) 100(100) 100(100) 平均 96.71(96.43) 98.43(98.57) 98.71(98.86) 99.00(99.43) 注:括号中为传统方法识别率. 表 3 多重扰动深度识别结果
Table 3. Recognition results for mixed disturbance
% 扰动类型 SNR 20 dB 30 dB 40 dB 无噪声 中断 & 谐波 98(96) 97(97) 97(91) 98(98) 暂升 & 谐波 91(94) 91(94) 93(93) 95(95) 暂降 & 短时振荡 98(100) 100(100) 100(99) 100(100) 脉冲 & 谐波 89(65) 97(69) 97(80) 97(82) 短时振荡 & 谐波 89(89) 89(96) 92(93) 95(95) 闪变 & 谐波 92(91) 91(93) 93(95) 94(93) 短时振荡 & 脉冲 98(100) 99(100) 100(100) 100(100) 闪变 & 脉冲 97(92) 98(100) 100(100) 99(100) 闪变 & 短时振荡 92(98) 99(100) 98(100) 100(100) 谐波 & 短时振荡 & 脉冲 97(98) 100(96) 100(99) 100(99) 谐波 & 脉冲 & 闪变 93(93) 93(94) 94(94) 94(93) 短时振荡 & 脉冲 & 闪变 96(97) 99(99) 99(100) 98(100) 暂降 & 短时振荡 & 脉冲 & 闪变 100(100) 100(100) 100(100) 100(100) 平均 94.62(93.31) 96.46(95.23) 97.15(95.69) 97.69(96.54) 注:括号中为传统方法识别率. 表 4 参数寻优结果
Table 4. Parameter optimization results
扰动类型 隐含层单元数/个 隐含层单元数/个 学习率 正则化参数 识别率/% 单一扰动 203 142 0.050 0 0.035 7 99.0 多重扰动 103 102 0.001 1 0.005 3 97.6 表 5 不同方法的用时对比
Table 5. Recognition time comparison of different methods
方法 1 000 次网络训练耗时/s 识别总耗时/s 传统方法 1 132.8 1 765.8 本文方法 895.4 1 464.7 -
杨洪耕,肖先勇,刘俊勇. 电能质量问题的研究和技术进展(一)——电能质量一般概念[J]. 电力自动化设备,2003,23(10): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6047.2003.10.001YANG Honggeng, XIAO Xianyong, LIU Junyong. Issues and technology assessment on power quality part1:general concepts on power quality[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2003, 23(10): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6047.2003.10.001 董伟杰,白晓民,朱宁辉,等. 间歇式电源并网环境下电能质量问题研究[J]. 电网技术,2013,37(5): 1265-1271.DONG Weijie, BAI Xiaomin, ZHU Ninghui, et al. Discussion on the power quality under grid-connection of intermittent power sources[J]. Power System Technology, 2013, 37(5): 1265-1271. 朱玲,刘志刚,胡巧琳,等. 基于CWD谱峭度的暂态电能质量扰动识别[J]. 电力自动化设备,2014,34(2): 125-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6047.2014.02.022ZHU Ling, LIU Zhigang, HU Qiaolin, et al. Recognition of transient power quality disturbances based on CWD spectral kurtosis[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2014, 34(2): 125-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6047.2014.02.022 黄建明,瞿合祚,李晓明. 基于短时傅里叶变换及其谱峭度的电能质量混合扰动分类[J]. 电网技术,2016,40(10): 3184-3191.HUANG Jianming, QU Hezuo, LI Xiaoming, et al. Classification for hybrid power quality disturbance based on STFT and its spectral kurtosis[J]. Power System Technology, 2016, 40(10): 3184-3191. 吴兆刚,李唐兵,姚建刚,等. 基于小波和改进神经树的电能质量扰动分类[J]. 电力系统保护与控制,2014,42(24): 86-92. doi: 10.7667/j.issn.1674-3415.2014.24.014WU Zhaogang, LI Tangbing, YAO Jiangang, et al. Power quality disturbance classification based on a wavelet and improved neural tree[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2014, 42(24): 86-92. doi: 10.7667/j.issn.1674-3415.2014.24.014 占勇,程浩忠,丁屹峰,等. 基于S变换的电能质量扰动支持向量机分类识别[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2005,25(4): 51-56. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2005.04.010ZHAN Yong, CHENG Haozhong, DING Yifeng, et al. S-transform-based classification of power quality disturbance signals by support vector machines[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2005, 25(4): 51-56. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2005.04.010 姚建刚,郭知非,陈锦攀,等. 基于小波和BP神经网络的电能扰动分类新方法[J]. 电网技术,2012,36(5): 139-144.YAO Jiangang, GUO Zhifei, CHEN Jinpan, et al. New approach to recognize power quality disturbances based on wavelet transform and BP neural network[J]. Power System Technology, 2012, 36(5): 139-144. 朱云芳,戴朝华,陈维荣,等. 压缩感知理论及其电能质量应用与展望[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报,2015,27(1): 80-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2015.01.015ZHU Yunfang, DAI Chaohua, CHEN Weirong, et al. Present status and prospect on compressed sensing in power systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2015, 27(1): 80-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2015.01.015 杨烁,曹思扬,戴朝华,等. 电能质量扰动信号时频原子分解的进化匹配追踪算法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制,2015,43(16): 79-86. doi: 10.7667/j.issn.1674-3415.2015.16.012YANG Suo, CAO Siyang, DAI Chaohua, et al. Evolutionary matching pursuit based time-frequency atom decomposition for power quality disturbance signals[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2015, 43(16): 79-86. doi: 10.7667/j.issn.1674-3415.2015.16.012 闫敬文, 刘蕾, 屈小波. 压缩感知及应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2015: 21-35. 曹思扬,戴朝华,朱云芳,等. 一种新的电能质量扰动信号压缩感知识别方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制,2017,45(3): 7-12.CAO Siyang, DAI Chaohua, ZHU Yunfang, et al. A novel compressed sensing-based recognition method for power quality disturbance signals[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2017, 45(3): 7-12. 沈跃,刘国海,刘慧. 随机降维映射稀疏表示的电能质量扰动多分类研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2011,32(6): 1371-1376.SHEN Yue, LIU Guohai, LIU Hui. Study on classification method of power quality disturbances based on random dimensionality reduction projection and sparse representation[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2011, 32(6): 1371-1376. 朱乔木,党杰,陈金富,等. 基于深度置信网络的电力系统暂态稳定评估方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2018,38(3): 735-743.ZHU Qiaomu, DANG Jie, CHEN Jinfu, et al. A method for power system transient stability assessment based on deep belief networks[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(3): 735-743. SHAO H, JIANG H, ZHANG H, et al. Rolling bearing fault feature learning using improved convolutional deep belief network with compressed sensing[J]. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2018, 100: 743-765. MA Jian, ZHANG Jun, XIAO Luxin, et al. Classification of power quality disturbances via deep learning[J]. IETE Technical Review, 2018, 34: 408-415. BARANIUK R G. Compressive sensing(Lecture Notes)[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2007, 24(4): 118-121. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.4286571 CANDES E J, WAKIN M B. An introduction to compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 21-30. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.914731 张春霞,姬楠楠,王冠伟. 受限波尔兹曼机[J]. 工程数学学报,2015,32(2): 159-173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3085.2015.02.001ZHANG Chunxia, JI Nannan, WANG Guangwei. Restricted Boltzmann machines[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 2015, 32(2): 159-173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3085.2015.02.001 孙劲光,蒋金叶,孟祥福,等. 一种数值属性的深度置信网络分类方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用,2014,50(2): 112-115. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1308-0377SUN Jinguang, JIANG Jinye, MENG Xiangfu, et al. DBN classification algorithm for numerical attribute[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2014, 50(2): 112-115. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1308-0377 孔祥玉,郑锋,鄂志君,等. 基于深度信念网络的短期负荷预测方法[J]. 电力系统自动化,2018,42(5): 133-139. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20170826002KONG Xiangyu, ZHENG Feng, E Zhijun, et al. Short-term load forecasting based on deep belief network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42(5): 133-139. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20170826002 李郝林,郭德宝,姜晨,等. 基于改进交叉熵算法的伺服电机参数优化设计[J]. 计算机应用研究,2014,31(5): 1433-1436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2014.05.035LI Haolin, GUO Debao, JIANG Chen, et al. Optimal of servo motor parameters using improved cross entropy method[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2014, 31(5): 1433-1436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2014.05.035 -




 下载:
下载: