Influence of Phosphorus Control on Coupling System ofWinery Wastewater and Microalgae Cultivation
-
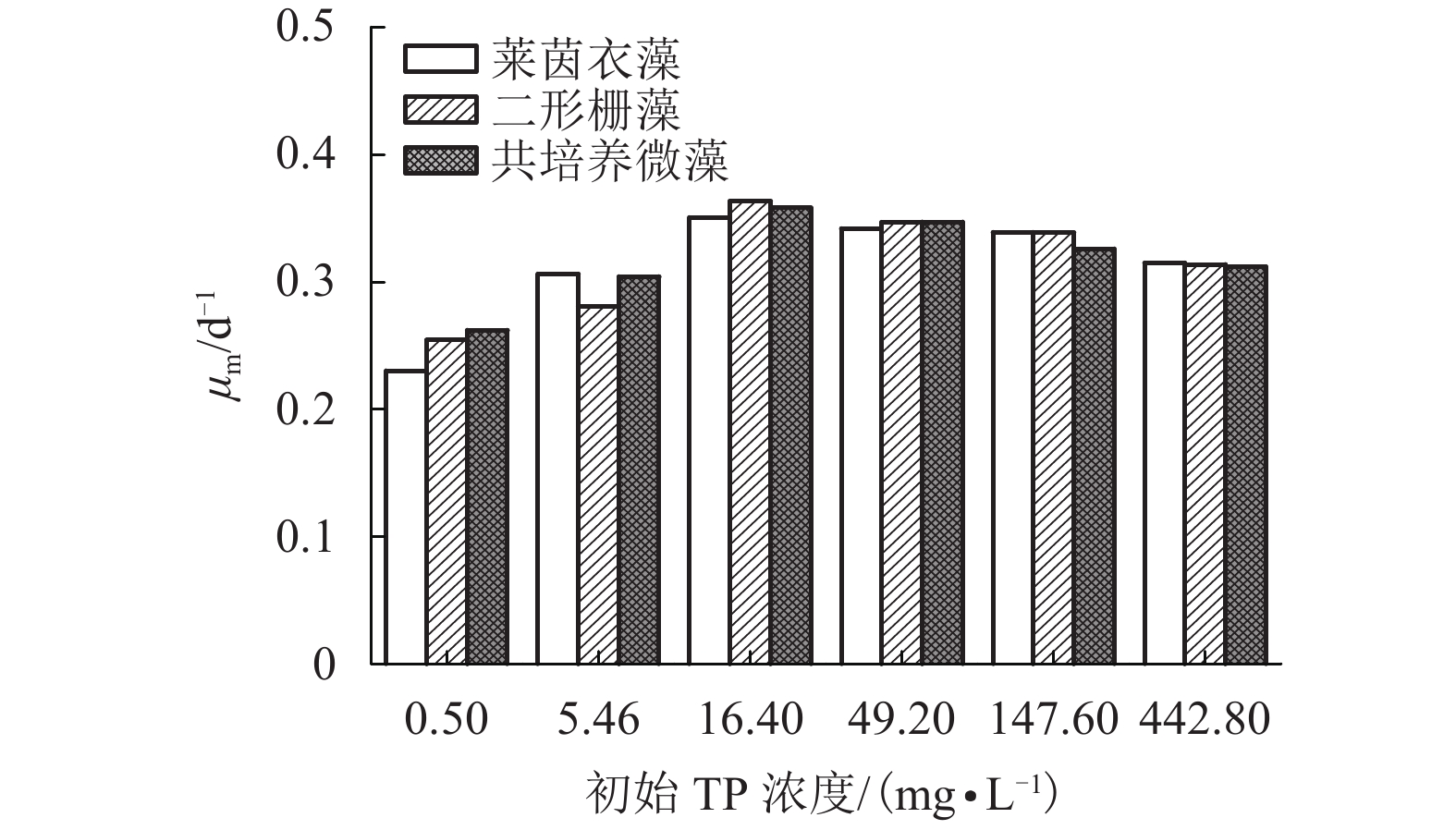
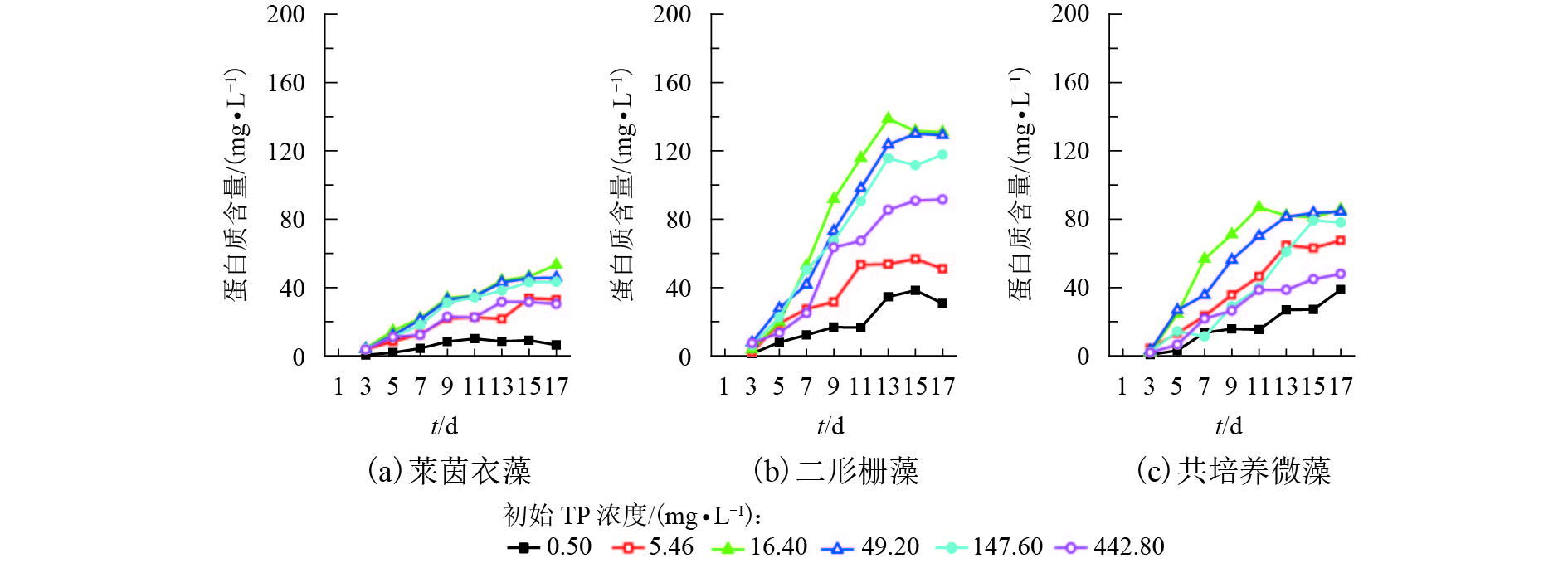
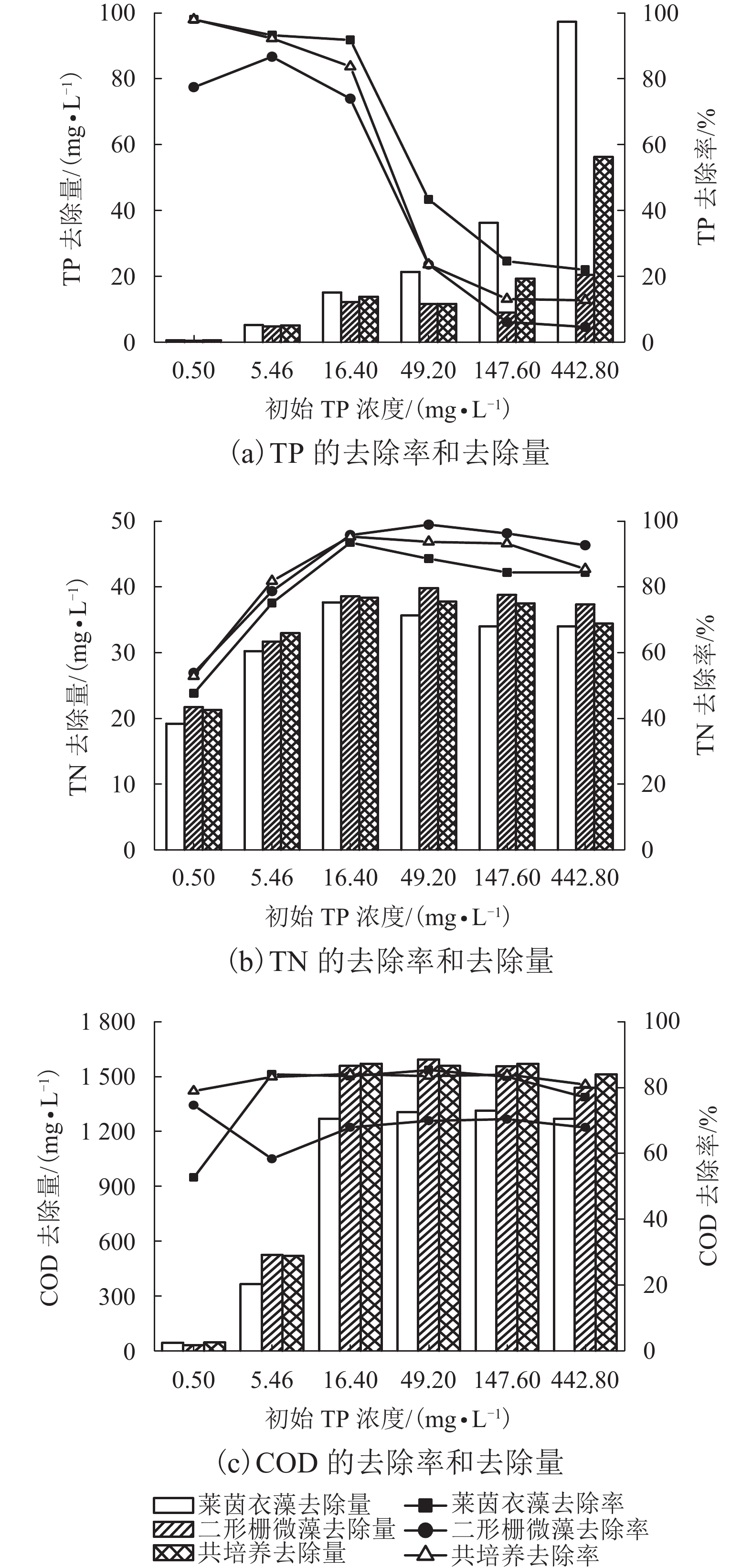
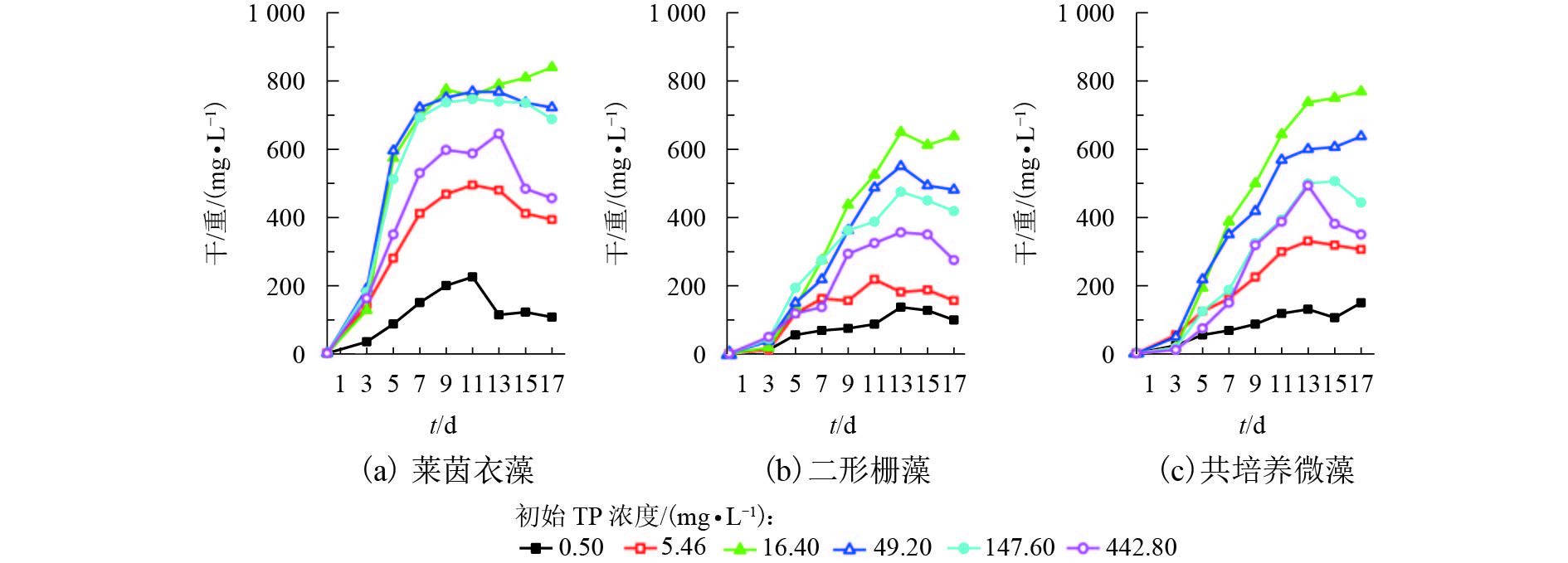
摘要: 为考察酿酒废水-微藻培育耦合体系的最适磷营养条件,对莱茵衣藻、二形栅藻在单一培养和共培养条件下的生长状况进行了观察,并剖析了对酿酒废水中营养盐的吸收去除效率. 采用控制变量法对酿酒废水总磷浓度进行调控,研究了不同磷浓度对微藻的干重、比生长速率、蛋白质含量,以及对总氮(total nitrogen,TN)、总磷(total phosphorus,TP)、化学需氧量(chemical oxygen demand,COD)去除量和去除效率的影响. 研究结果表明:莱茵衣藻对磷需求总体上大于二形栅藻对磷需求,当初始总磷浓度为16.40 mg/L,初始氮磷比为2.45时,莱茵衣藻最终生物量达到839.50 mg/L,藻蛋白含量达到53.37 mg/L,对TN、TP、COD的去除率分别为93.48%、91.75%、67.90%;二形栅藻生物量最高达到650.00 mg/L,藻蛋白含量达到131.04 mg/L,对TN、TP、COD的去除率分别为95.76%、73.93%、83.43%;而两种藻在共培养条件下,其生长曲线处于单一培养两种微藻下的生长曲线之间,TP、TN的去除率分别为83.66%、95.24%,COD的去除规律与二形栅藻类似. 研究发现酿酒废水-微藻培育耦合体系,无论是单一还是共培养体系,酿酒废水总体均能达到地表水环境质量标准(GB3838—2002)的Ⅳ类水总磷要求.Abstract: To investigate the optimum phosphorous condition for the coupling system of winery wastewater and microalgae cultivation, changes in growth of Chlamydoomonas reinhardtii and Scenedesmus dimorphus were observed under single culture and co-culture conditions, and the absorption and removal efficiency of nutrients were determined in the wastewater. The effect of different phosphorus concentrations on the dry weight, specific growth rate, protein content, and the removal amount and removal rate of total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) were studied by the control variable method. The results showed that the demand of Chlamydoomonas reinhardtii for phosphorus was greater than that of Scenedesmus dimorphus. When the initial total phosphorus concentration was 16.40 mg/L and the initial nitrogen to phosphorus ratio was 2.45, as for Chlamydoomonas reinhardtii, the final biomass reached 839.50 mg/L, the algal protein content reached 53.37 mg/L, and the removal rates of TN, TP and COD were 93.48%, 91.75%, 67.90%, respectively; as for Scenedesmus dimorphus, the final biomass reached 650.00 mg/L, the algal protein content reached 131.04 mg/L, and the removal rates of TN, TP and COD were 95.76%, 73.93%, 83.43%, respectively. Under co-culture conditions, the growth curves of the two microalgae were between their growth curves under single culture conditions, the removal rates of TP and TN were 83.66% and 95.24%, respectively, and the removal of COD was similar to that of Scenedesmus dimorphus. It was also found that through the winery wastewater-microalgae cultivation coupling system, whether it is single or co-culture condition, the wastewater can meet the total phosphorus requirements of class Ⅳ water quality specified in the Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water(GB3838—2002).
-
Key words:
- winery wastewater /
- phosphorus control /
- Chlamydoomonas reinhardtii /
- Scenedesmus dimorphus /
- removal
-
表 1 酿酒废水成分组成
Table 1. Composition of winery wastewater
指标 出厂水 预处理后 稀释2倍:50%,V/V pH值 4.87 6.92 6.98 COD/(mg•L–1) 4 037.00 3 890.00 1 867.50 TN/(mg•L–1) 87.76 84.80 40.25 TP/(mg•L–1) 35.41 34.90 16.40 -
杨婷,任春英,李娟,等. 城市生活污水中富油微藻的筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报,2015,17(3): 144-151.YANG Ting, REN Chunying, LI Juan, et al. Isolation and screening of oleaginous microalage from municipal wastewater[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015, 17(3): 144-151. 杨从发. 木薯酒精废糟培养小球藻工艺及灵芝生物转化小球藻的研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2009 胡洪营,李鑫,杨佳. 基于微藻细胞培养的水质深度净化与高价值生物质生产耦合技术[J]. 生态环境学报,2009,18(3): 1122-1127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2009.03.059HU Hongying, LI Xin, YANG Jia. Coupling of wastewater deep purification and high quality biomass production based on microalgae cultivation[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2009, 18(3): 1122-1127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2009.03.059 王小莉,王建涛,袁小强,等. 微藻生物柴油的国内外研究现状与展望[J]. 科技广场,2012,12: 139-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4792.2012.02.036 黄学平,李凤,蔡志文,等. 养猪废水污染防治及资源化培养微藻探索[J]. 南昌工程学院学报,2013,32(4): 42-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4869.2013.04.009HUANG Xueping, LI Feng, CAI Zhiwen, et al. Research on prevention of pig-breeding wastewater pollution and cultivation of microalgae as resources[J]. Journal of Nanchang Institute of Technology, 2013, 32(4): 42-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4869.2013.04.009 高政权,孟春晓. 微藻与水环境修复[J]. 环境科学与技术,2008,31(03): 30-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.03.009GAO Zhengquan, MENG Chunxiao. Microalgae and rehabilitation of water environment[J]. Environmental Sciences and Technology, 2008, 31(03): 30-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.03.009 文世勇,赵冬至,赵玲,等. 赤潮藻类的氮磷比耐受性响应模型[J]. 大连海事大学学报,2009,35(1): 118-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7031.2009.01.032WEN Shiyong, ZHAO Dongzhi, ZHAO Ling, et al. Tolerance response model of N/P ratios for red tide algae[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2009, 35(1): 118-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7031.2009.01.032 邵瑜. 微藻对养猪废水氮磷的资源化利用研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016 WANG Ping, YU Jiang, QIN Yuanqin, et al. The influence of nutrients on the growth of bio-energy microalgae Chlammydomonas reinhardtii[J]. Journal of Biobased Materials and Bioenergy, 2016, 10: 229-233. doi: 10.1166/jbmb.2016.1600 WANG Yizheng, YU Jiang, WANG, Ping, et al. Response of energy microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii to nitrogen and phosphorus stress[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 10: 1-9. 李昌灵,杨海麟,李宇佶,等. 不同培养模式对微藻Chlorella vugaris代谢与蛋白质组分的影响[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2014,33(1): 56-62.LI Changling, YANG Hailin, LI Yuji, et al. Effect of culture models on metabolism and protein components of microalgae Chlorella vulgaris[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2014, 33(1): 56-62. 顾林娣,高敏敏. 螺旋藻粉中蛋白质等几种成分的提取方法比较[J]. 植物生理学通讯,1998,34(3): 210-212. 金送笛,李永函,倪彩虹,等. 菹草(Potamogeton crispus )对水中氮、磷的吸收及若干影响因素[J]. 生态学报,1994,14(2): 168-173. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.1994.02.019JIN Songdi, LI Yonghan, NI Caihong, et al. Uptake by Potamogeton crispus of nitrogen and phosphorus from water and some affecting factors[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1994, 14(2): 168-173. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.1994.02.019 JOHN E H, FLYNN K J. Growth dynamics and toxicity of Alexandrium fundyense (Dinophyceae):the effect of changing N:P supply ratios on internal toxin and nutrient levels[J]. European Journal of Phycology, 2000, 35(1): 11-23. -




 下载:
下载: