Evolutionary Game Model of Traffic Violations among Taxi Drivers
-
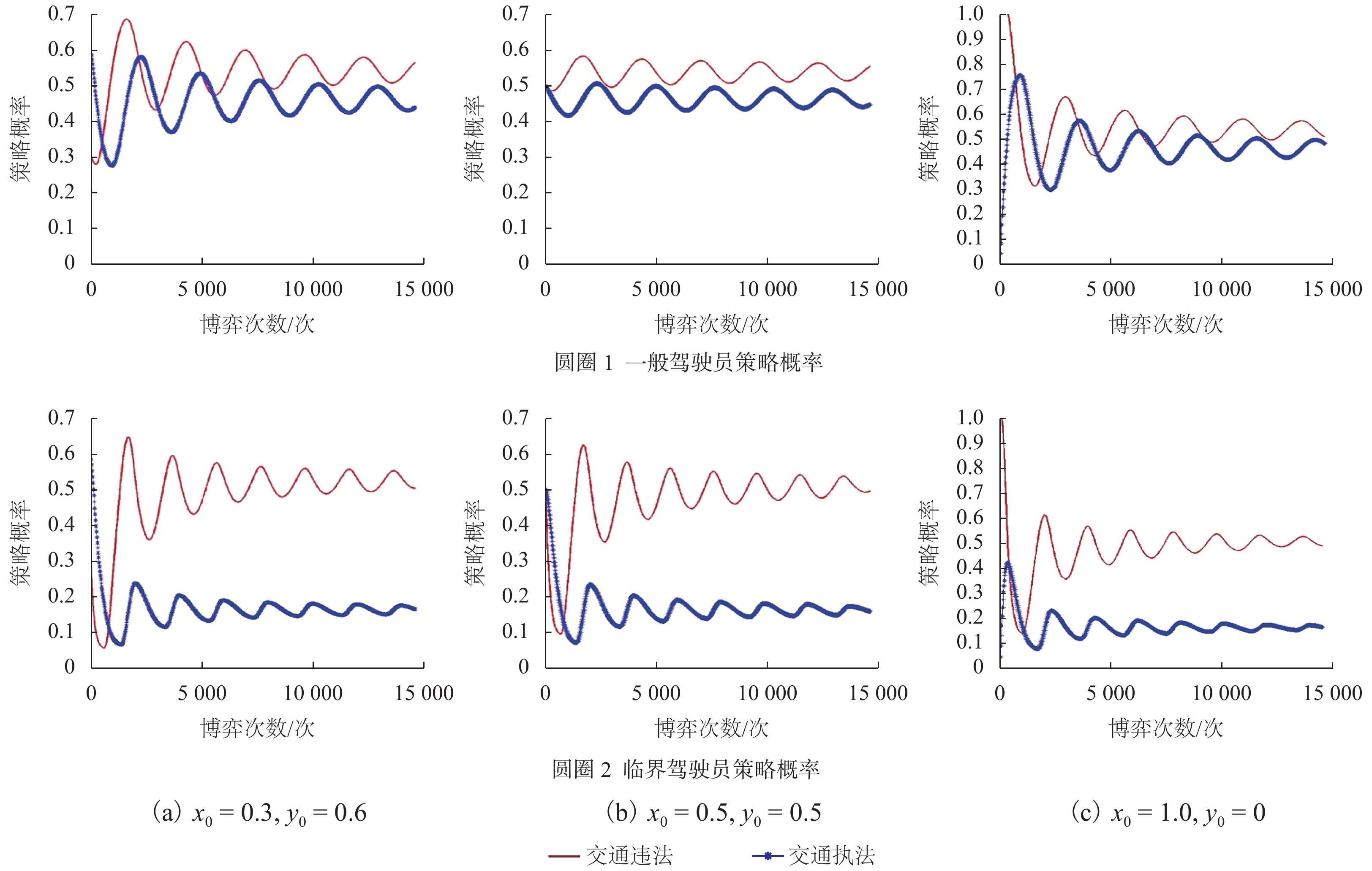
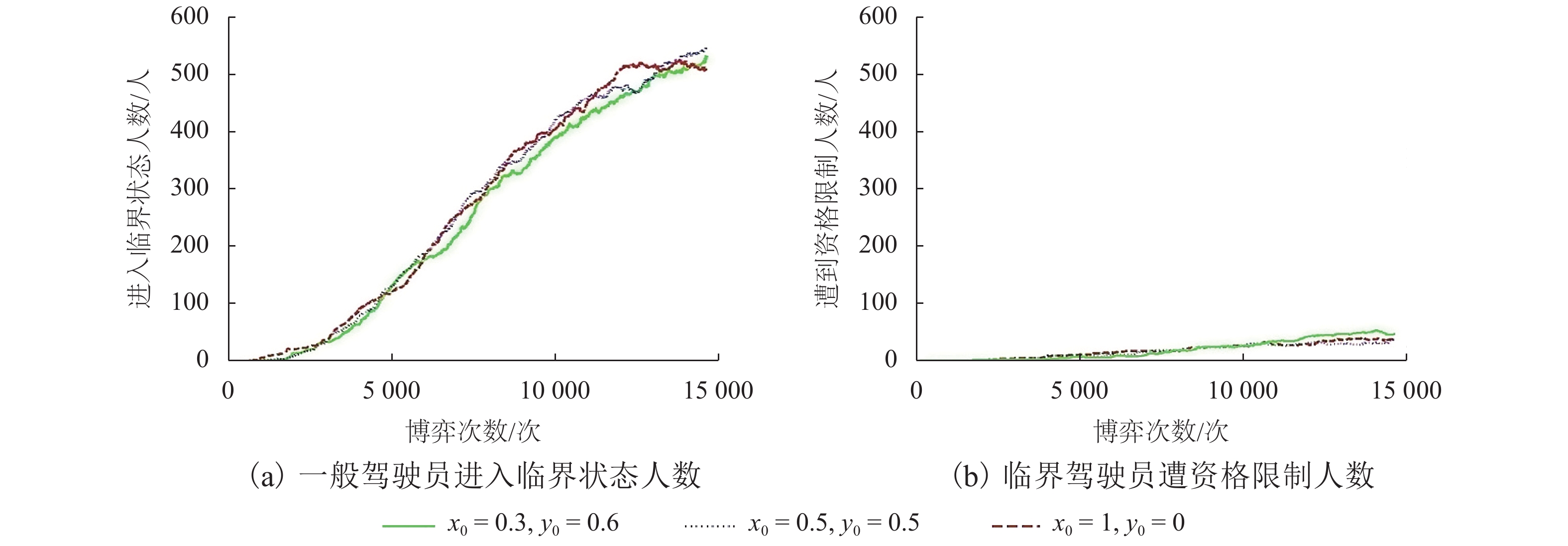
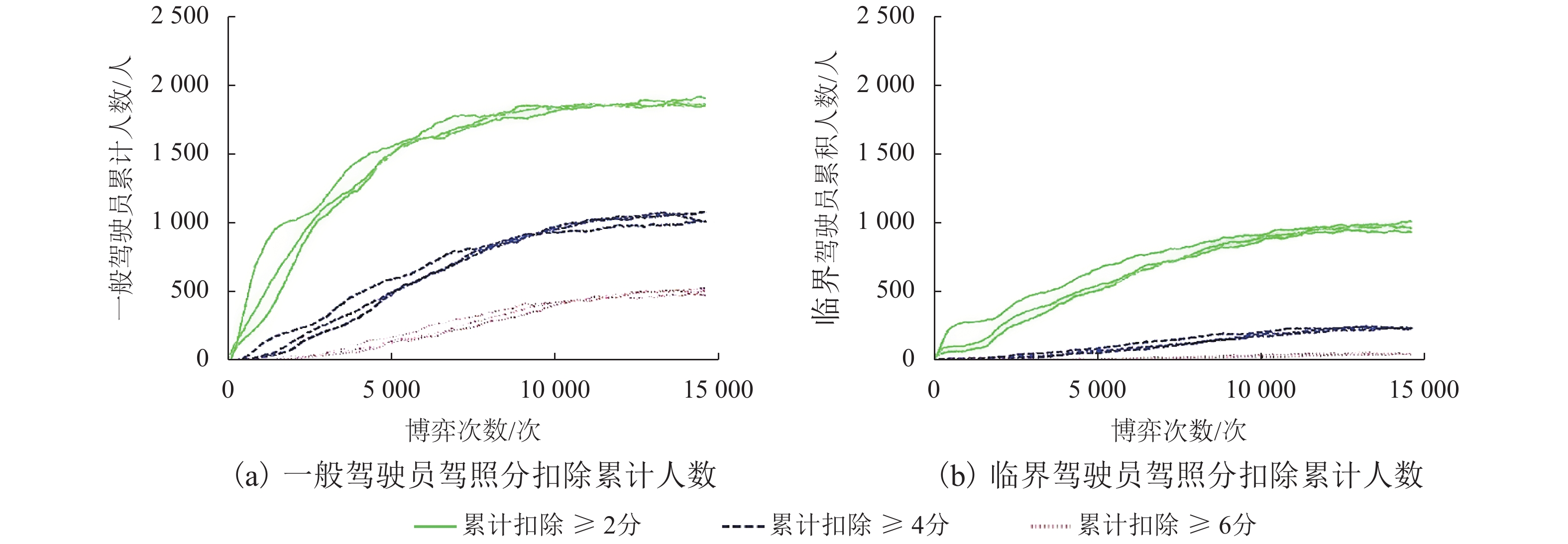
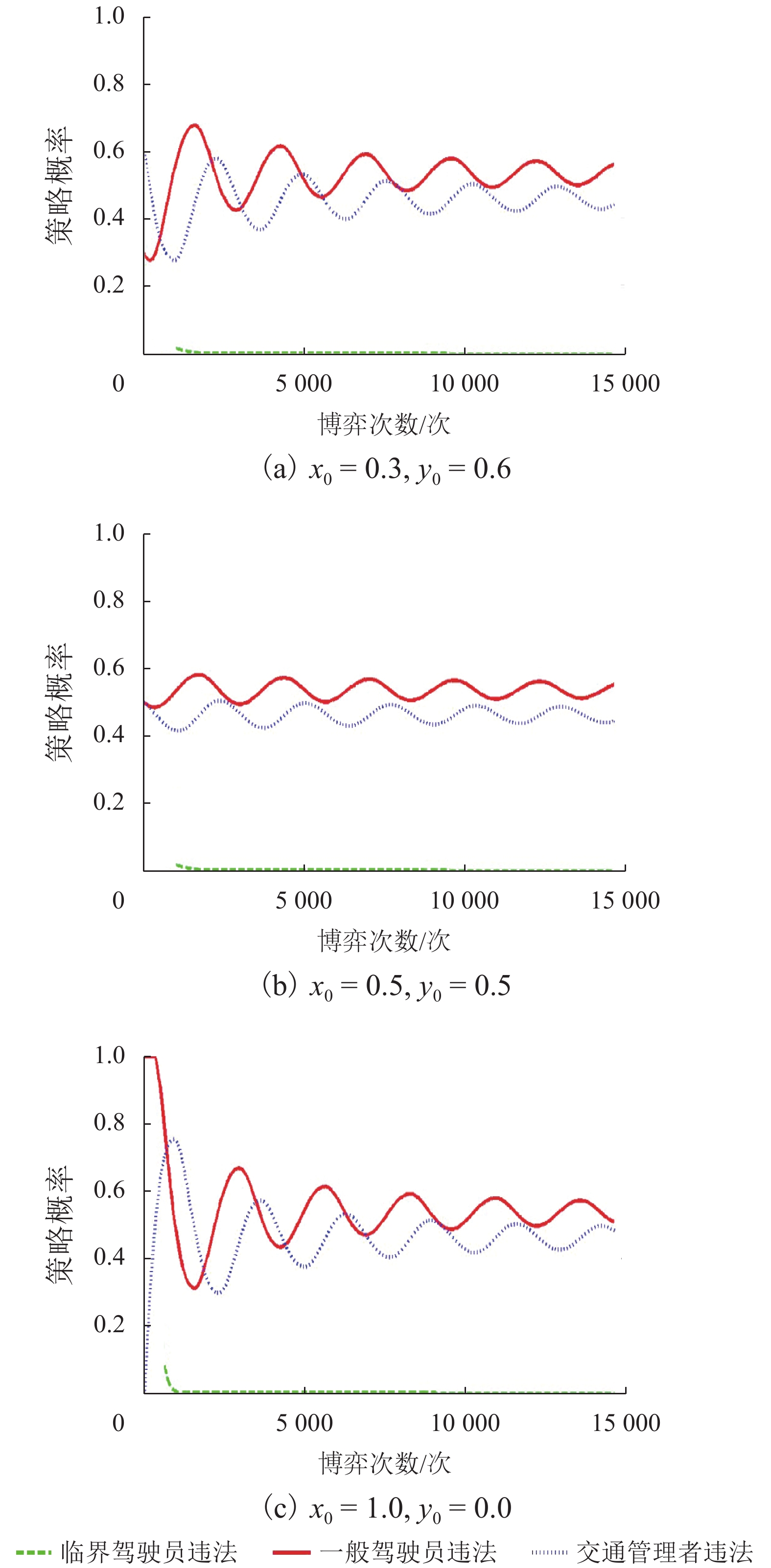
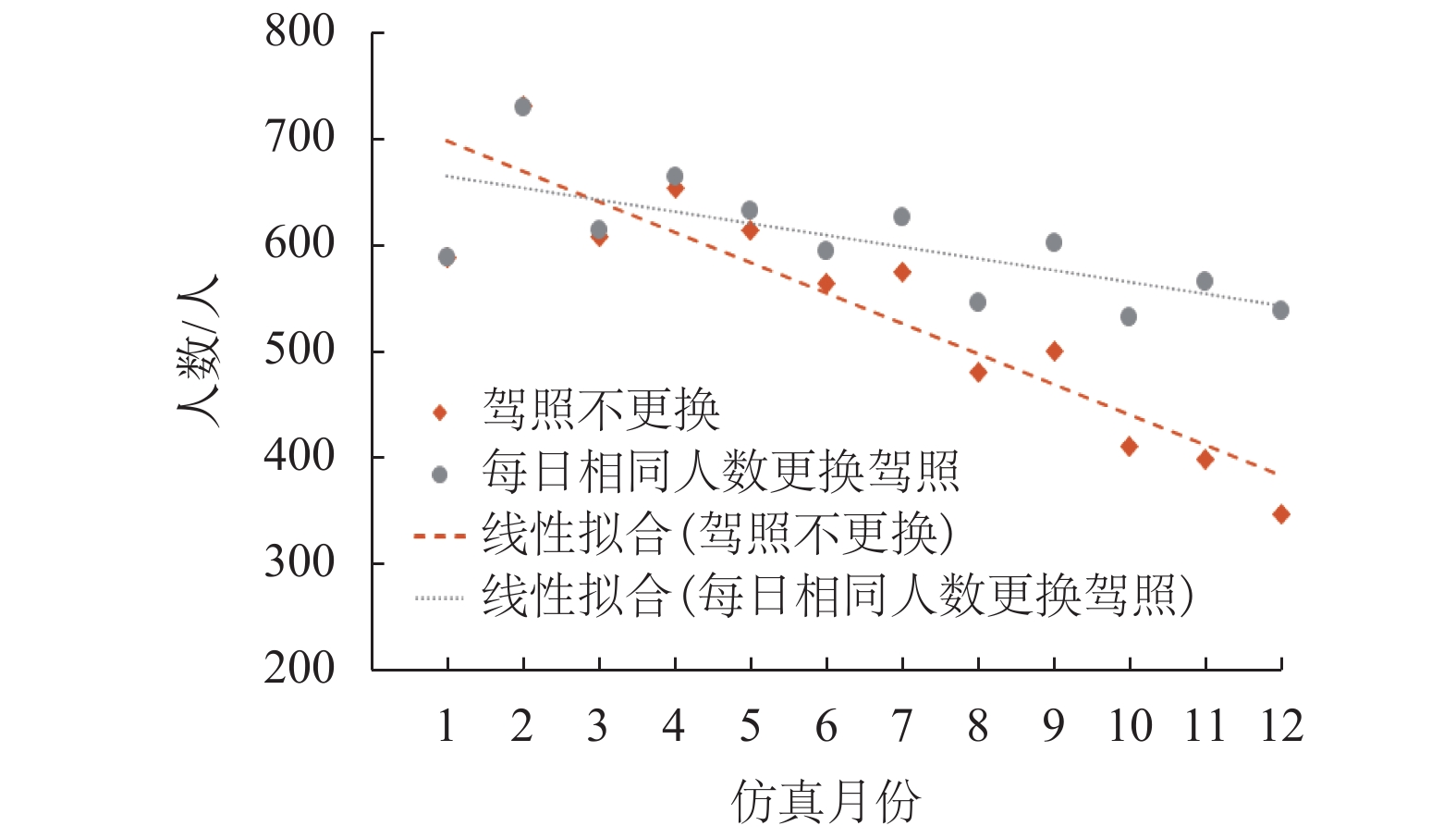
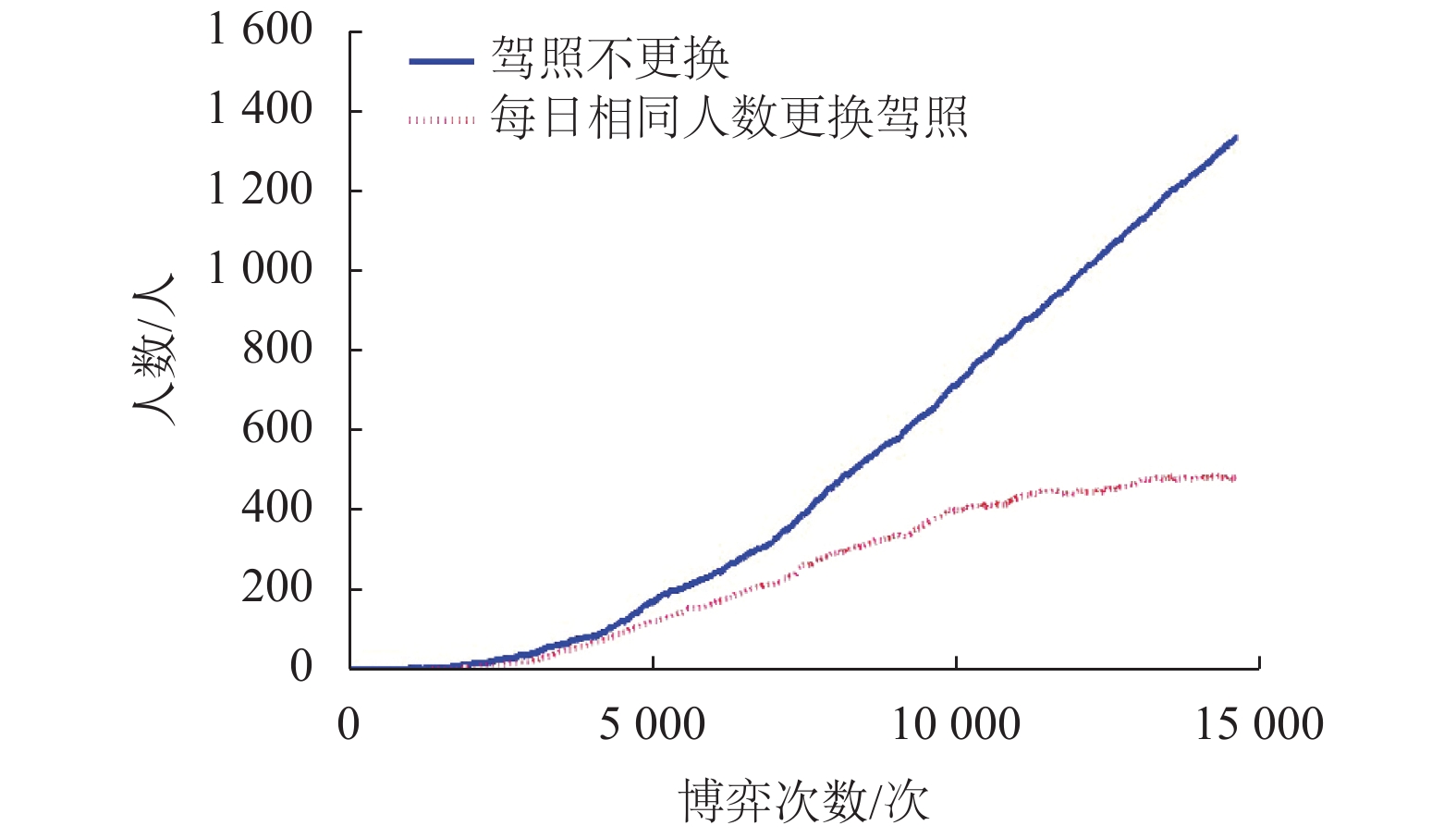
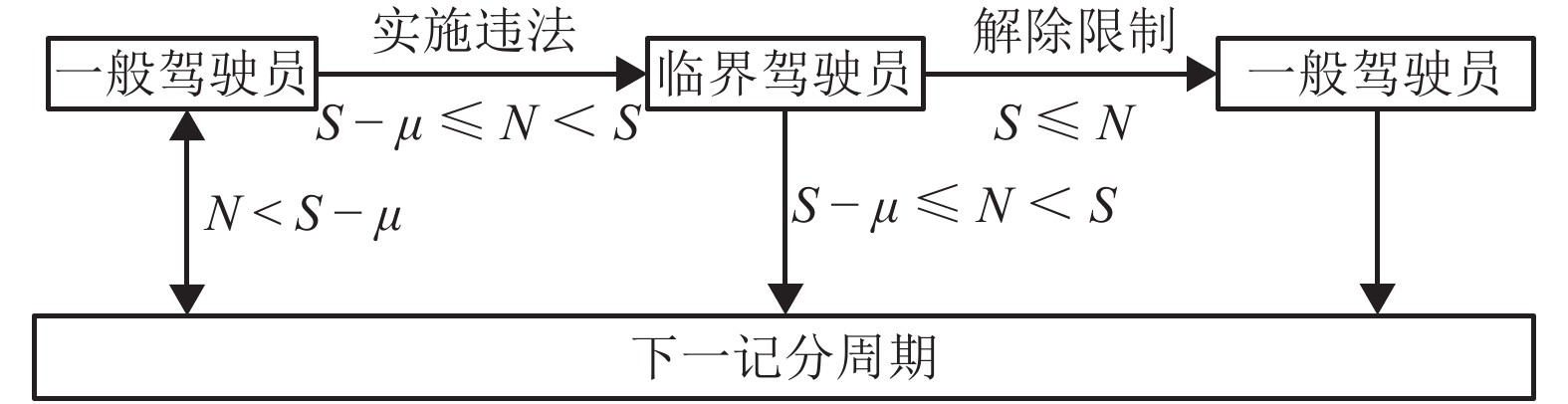
摘要: 为研究违法成本对出租车驾驶员实施违法行为的影响,根据驾照管理方式,对交通违法成本构成及其累积过程进行研究. 通过设置警戒分数线,将出租车驾驶员分为一般和临界两个状态,构建了不同执法策略条件下,出租车驾驶员与交通执法者间的演化博弈模型,并采用仿真手段模拟不同执法及驾照管理条件下,出租车驾驶员的违法策略变化情况. 研究结果显示:执法水平和驾照分扣除程度直接影响违法成本,并决定双方的演化均衡;交通管理者对临界驾驶员采取低于一般驾驶员约30%的执法概率即可达到类似执法效果,临界驾驶员执法成本更低;相同执法水平下,临界驾驶员违法概率低于一般驾驶员;记分周期(1 a)内,每天相同人数更换驾照时,遭交通处罚的一般驾驶员人数相比不更换驾照条件多约10%,且随时间推移人数持续增加. 相关改善措施可考虑调整执法策略或改变驾照更新制度,促使出租车驾驶员驾照资格从一般转入临界状态,有助于遏制其交通违法行为,降低交通执法成本.Abstract: In order to investigate the mechanism of violation costs on taxi drivers’ traffic violation behavior, the composition and cumulation of traffic violation costs over time are explored with a demerit point system. To be specific, the taxi driver’s license status were classified into two categories by setting warning score, i.e., ordinary driver and critical driver. An evolutionary game model was introduced to analyze the strategies adopted by taxi drivers and traffic policemen. Simulations were conducted to reveal the evolutionary outcomes of violation strategies under different enforcement and license management conditions. The results show that the violation costs, which impact the strategy equilibrium, is predominately determined by the level of law enforcement and deducted penalty points; for the numerical example, the administrative costsfor critical drivers are lower than those of the ordinary ones, revealing that police could use about 30% lower enforcement possibility to obtain the similar effectiveness; the violation probability of critical drivers is far lower as opposed to that of the ordinary drivers under the same enforcement; If there is equal number of drivers who daily reset their licenses, they would have 10% penalties than that of the driver whose licenses never reset in one cycle (1 a). Moreover, the penalty difference become much remarkable with time. The results demonstrate that turning the taxi driver’s license qualification from ordinary into critical state through adjustable enforcement strategy will help to constrain the traffic violations and reduce the enforcement costs.
-
Key words:
- taxicabs /
- game theory /
- costs /
- taxi driver /
- traffic violation /
- evolutionary game model /
- demerit point system
-
表 1 抽样调查结果
Table 1. Questionnaire Results
统计结果 日工作时间/h 月净收入/元 公司是否会二次罚款 1 a 内可接受罚金/元 1 a 内可接受累积扣分/分 最大值 14 6 500 1 3 000 12 最小值 7 2 000 0 100 1 均值 11.19 4 244 0.33 468 6.02 注:“公司是否会二次罚款”中的“1”表示会二次处罚,“0”表示不会二次处罚. 表 2 出租车驾驶员与交通执法者博弈矩阵
Table 2. Game matrix of taxi dirvers and traffic enforcement men
驾驶员 策略 交通执法者 执法 不执法 一般驾驶员 违法 $\left(\left(B - {C_{\rm{O}}} - r{C_{\rm{T}}} - r{C_{\rm{E}}} - r{C_{\rm{A}}}\right)\right)$,$\left. r{C_{\rm{E}}} - A - I\right)$ $\left(B - {C_{\rm{O}}}\right.$,$\left. - I\right)$ 不违法 $(0$,$ - A)$ $(0$,$0)$ 临界驾驶员 违法 $( B - {C_{\rm{O}}} - r{C_{\rm{T}}} - r{C_{\rm{E}}} - r\alpha {C_{\rm{Q}}} - r\alpha {C_{\rm{C}}} - r{C_{\rm{A}}}$,$r{C_{\rm{E}}}{\rm{ + }}r\alpha {C_{\rm{Q}}} - A - I)$ $(B - {C_{\rm{O}}}$,$ - I)$ 不违法 $(0$,$ - A)$ $(0$,$0)$ -
SANI S R H, TABIBI Z, FADARDI J S, et al. Aggression,emotional self-regulation,attentional bias,and cognitive inhibition predict risky driving behavior[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2017, 109: 78-88. KIM D, SUL J. Analysis of pedestrian accidents based on the in-vehicle real accident videos[C]//Proceedings of 23rd International Technical Conference on the Enhanced Safety of Vehicles (ESV). Seoul: Korea Transport Institute, 2013: 1-12. WANG Y LI L, PRATO C G. The relation between working conditions,aberrant driving behaviour and crash propensity among taxi drivers in China[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2018, 126: 17-24. DALZIEL J R, JOB R F S. Motor vehicle accidents,fatigue and optimism bias in taxi drivers[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 1997, 29(4): 489-494. TSENG C M. Operating styles,working time and daily driving distance in relation to a taxi driver’s speeding offenses in Taiwan[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2013, 52: 1-8. ELIAS W, BlANK-GOMEL A, HABIB-MATAR C, et al. Who are the traffic offenders among ethnic groups and why?[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2016, 91: 64-71. ZHANG G, YAU K K W, CHEN Guanghan. Risk factors associated with traffic violations and accident severity in China[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2013, 59: 18-25. JING S, LI T, LI X, et al. A survey of taxi drivers’ aberrant driving behavior in Beijing[J]. Journal of Transportation Safety & Security, 2013, 6(1): 34-43. BURNS P, WILDE J S. Risk taking in male taxi drivers:relationships among personality,observational data and driver records[J]. Personality and Individual Differences, 1995, 18(2): 267-278. doi: 10.1016/0191-8869(94)00150-Q MANI K, MUN S W, HAYATI K. Speeding among taxi drivers in Selangor,Malaysia[J]. Injury Prevention, 2011, 16: A14. HUANG Y, SUN J, TANG J. Taxi driver speeding:who,when,where and how? a comparative study between Shanghai and New York City[J]. Traffic Injury Prevention, 2017, 19(3): 311-316. CHENG A S K, TING K H, LIU K P, et al. Impulsivity and risky decision making among taxi drivers in Hong Kong:an event-related potential study[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2015, 95: 387-394. YEH M S, TSENG C M, LIU H H, et al. The factors of female taxi drivers’ speeding offenses in Taiwan[J]. Transportation Research Part F:Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2015, 32: 35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.trf.2015.04.005 BIDASCA L, TOWNSEND E. Making taxis safer: managing road risks for taxi drivers, their passengers and other road users[R]. Brussels: European Transport Safety Council, 2016. HUANG Y, SUN J, L. ZHANG L. Effects of congestion on drivers’ speed choice:assessing the mediating role of state aggressiveness based on taxi floating car data[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2018, 117: 318-327. CASTELLA J, PEREZ J. Sensitivity to punishment and sensitivity to reward and traffic violations[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2004, 36: 947-952. LAM T L. Environmental factors associated with crash-related mortality and injury among taxi drivers in New South Wales,Australia[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2004, 36(5): 905-908. WU J, YAN X, RADWAN E. Discrepancy analysis of driving performance of taxi drivers and non-professional drivers for red-light running violation and crash avoidance at intersections[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2016, 91: 1-9. ROSENBLOOM T, SHAHAR A. Differences between taxi and nonprofessional male drivers in attitudes towards traffic-violation penalties[J]. Transportation Research Part F:Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2007, 10(5): 428-435. doi: 10.1016/j.trf.2007.04.002 COOK P J. Reviewed work:the economics of crime:an introduction to rational crime analysis by Harold Winter[J]. Journal of Economic Literature, 2009, 47(3): 804-806. BECKER G S. Crime and punishment:an economic approach[J]. Journal of Political Economy, 1968, 76(2): 169-217. doi: 10.1086/259394 郭东. 理性犯罪决策——成本收益模型[J]. 广西社会科学,2007,8: 84-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6917.2007.01.023 中华人民共和国公安部. 机动车驾驶证申领和使用规定[EB/OL]. (2016-01-29)[2018-06-15]. https://baike.baidu.com/item/机动车驾驶证申领和使用规定/4379120?fr=aladdin SMITH M J. The stability of a dynamic model of traffic assignment —an application of a method of Lyapunov[J]. Transportation Science, 1984, 18(3): 245-252. doi: 10.1287/trsc.18.3.245 -




 下载:
下载: