Mechanism and Kinetic Analysis on Degradation of Atrazine by UV/PS
-
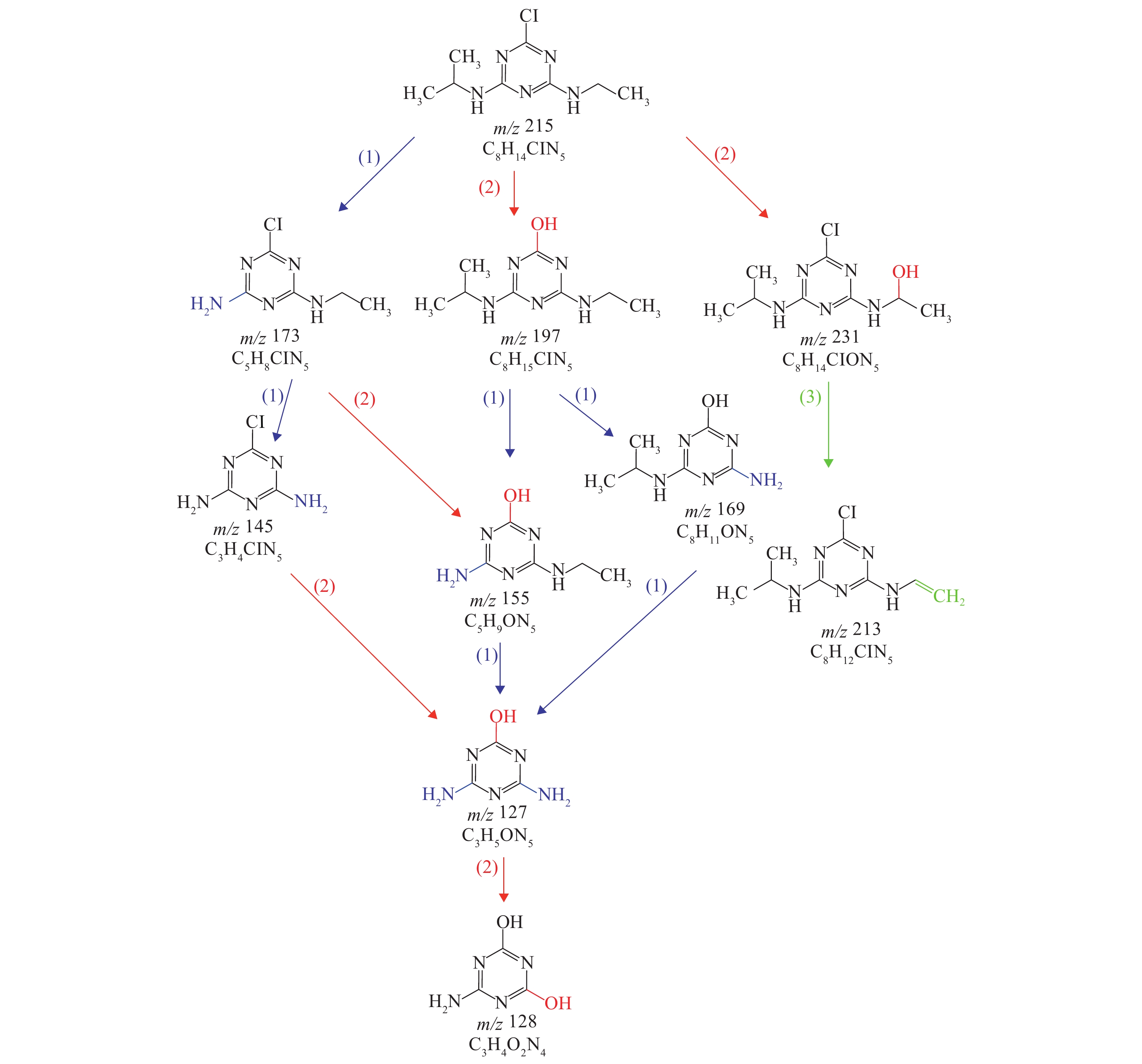
摘要: 为了解决阿特拉津(atrazine,ATZ)对水体污染问题,采用紫外/过二硫酸盐 (ultraviolet/peroxodisulfate,UV/PS) 降解水体中的ATZ,考察了不同pH值、UV强度、PS浓度、温度条件下UV/PS对ATZ的降解效果,同时对其降解机理、降解动力学及降解路径进行了探讨. 机理分析表明,UV可使ATZ发生光解,UV/PS能快速降解水体中ATZ,中性偏碱性条件下UV/PS体系中同时存在SO4−• 和 •OH. 动力学分析表明,不同温度、pH值、PS浓度、UV强度条件下UV/PS降解ATZ动力学符合准一级反应动力学. 降解路径分析表明,ATZ主要通过脱氯、加羟基、脱乙基、脱异丙基等方式被降解,几种降解方式并不孤立,但三嗪环并未开环降解. 试验结果表明,反应体系温度为25 ℃,PS浓度为70 μmol/L,UV强度为50 mW/cm2,反应体系初始pH为5.8,反应时间为20 min时,UV/PS体系对2.5 μmol/L ATZ的降解率可达91.03%.Abstract: In order to deal with water pollution caused by atrazine (ATZ), the effects, mechanism, kinetics and pathway of ATZ degradation by ultraviolet/peroxodisulfate (UV/PS) were explored in terms of pH, UV intensity, PS concentration and temperature. The analysis of degradation mechanism indicates that UV could be photolyzed by UV and rapidly degraded by UV/PS in water. SO4−• and •OH coexisted in UV/PS system under neutral and weakly alkaline conditions. Kinetic analysis show that UV/PS degradation of ATZ fitted to quasi first-order reaction kinetics with differing temperature, pH, PS concentration and UV intensity. Degradation pathway analysis suggest that the main degradation pathways of ATZ were dechlorination, hydroxylation, deethylation and deisopropyl, all of which were correlated; yet the triazine ring was notoxidized and opened. The results show that the degradation rate of 2.5 μmol/L ATZ by UV/PS system was 91.03% when the system temperature, PS concentration, UV intensity, initial pH value and response time was 25 ℃, 70 μmol/L, 50 mW/cm2, 5.8 and 20 min, respectively.
-
Key words:
- ultraviolet /
- peroxodisulfate /
- free radicals /
- atrazine /
- degradation mechanism /
- kinetics /
- degradation pathway
-
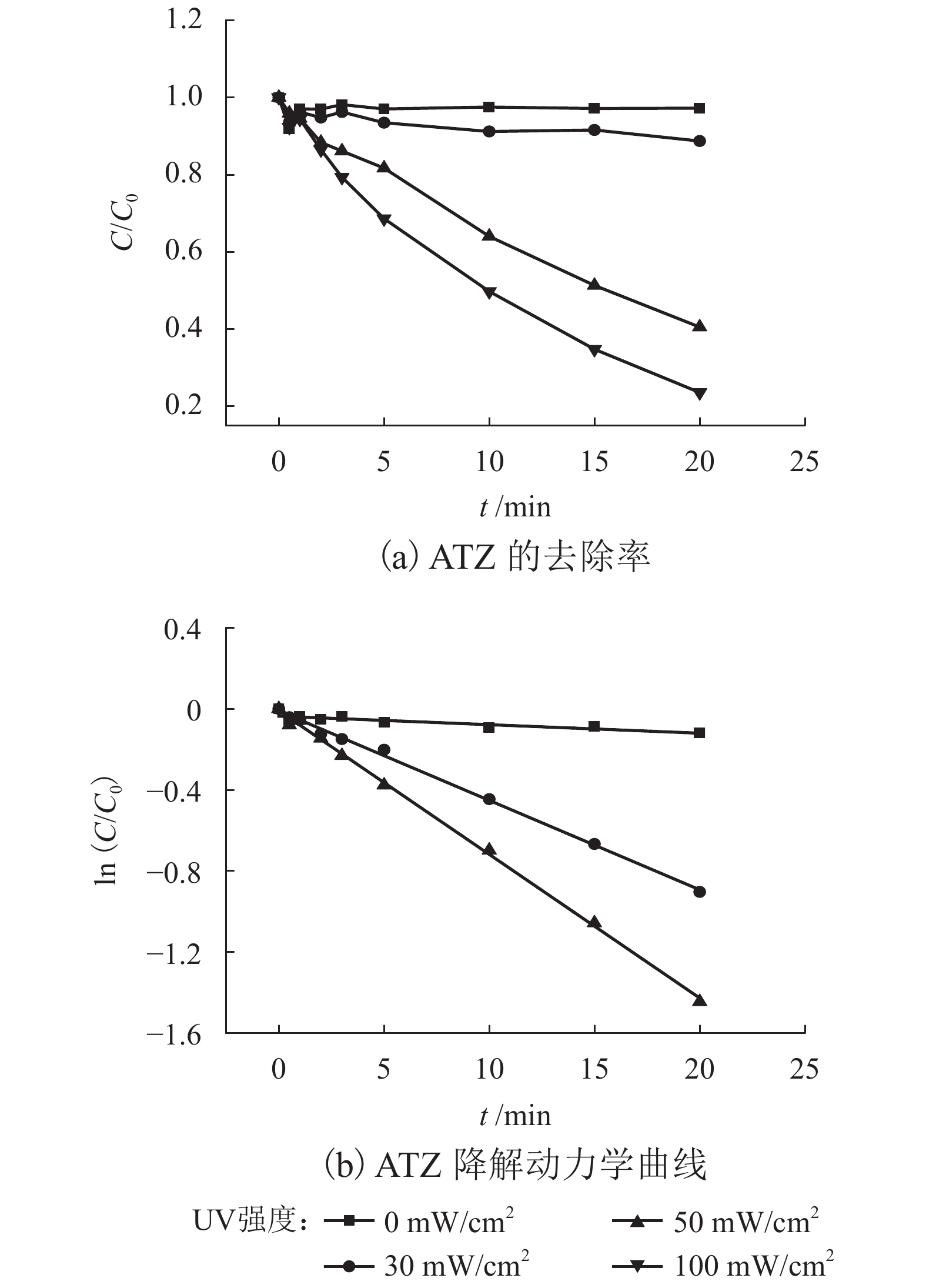
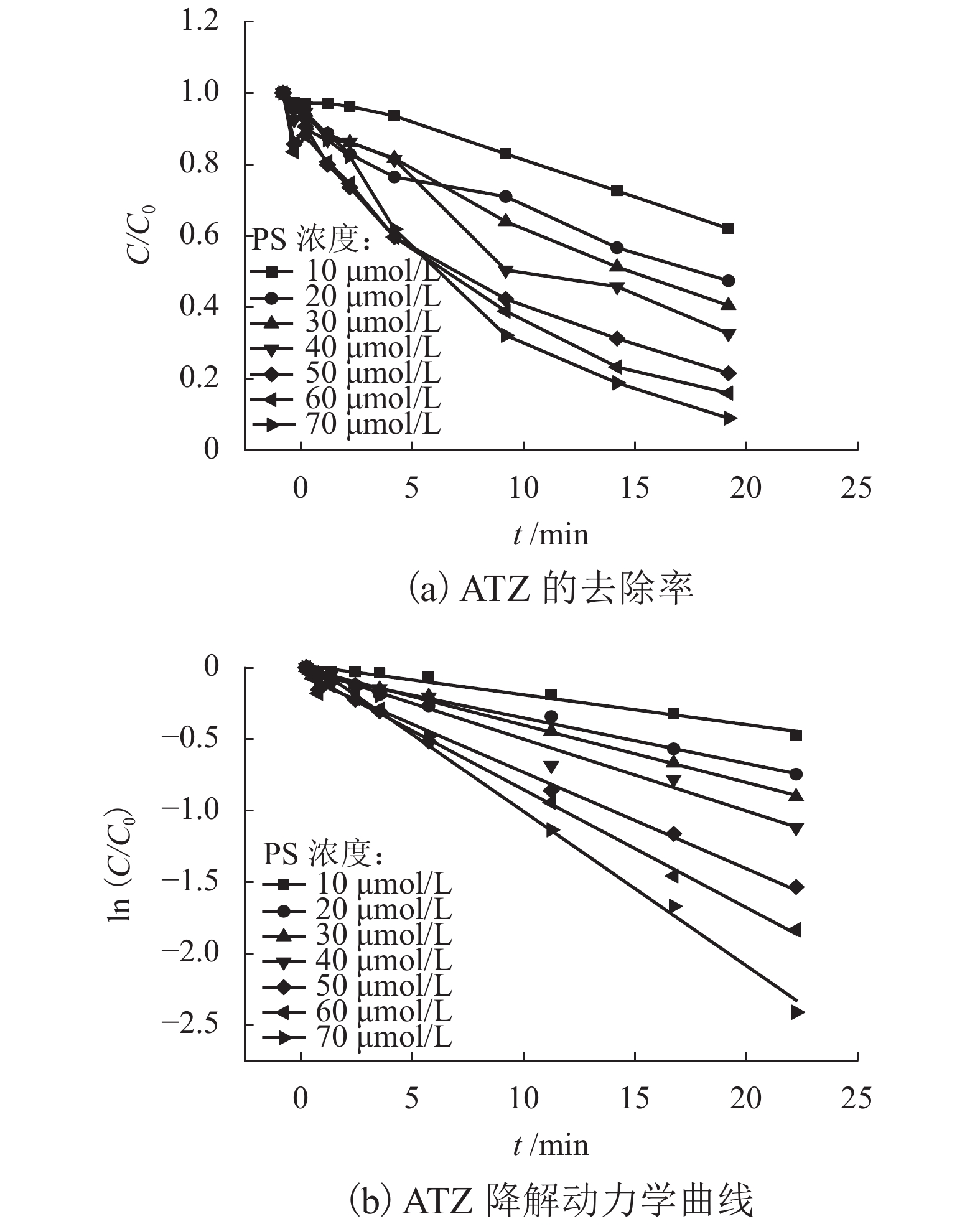
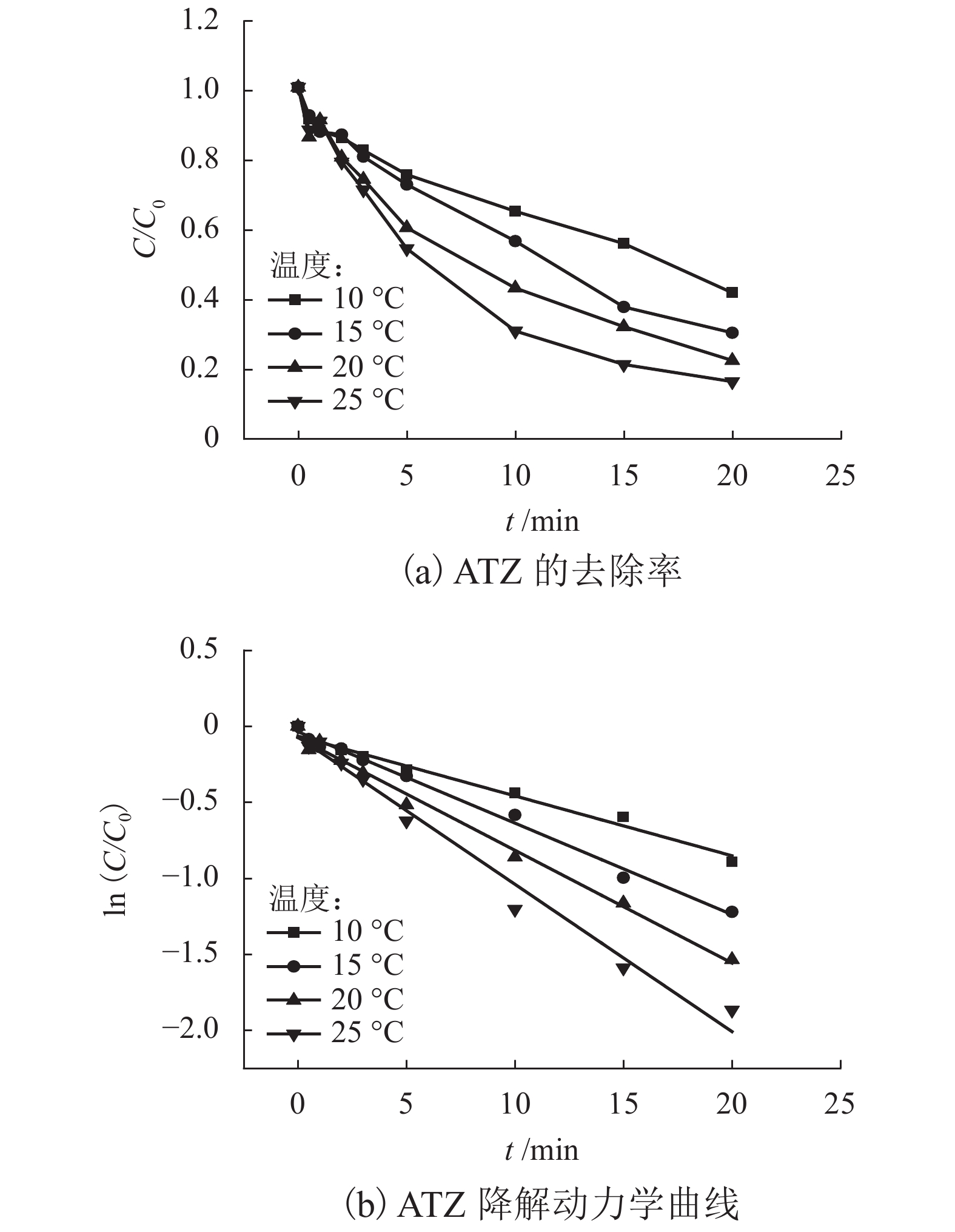
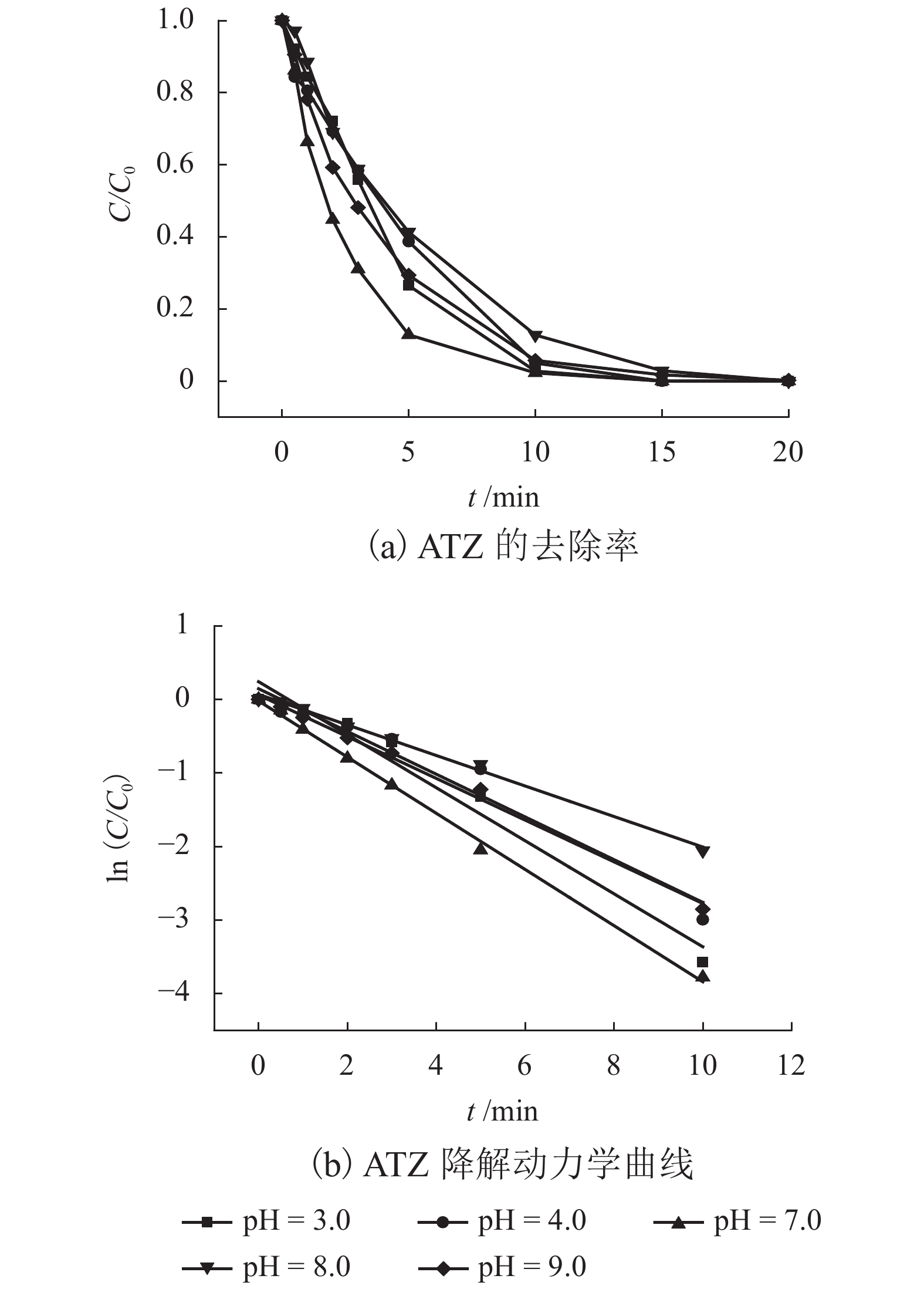
表 1 不同反应条件下UV/PS降解ATZ反应动力学拟合参数
Table 1. Fitted kinetics parameters of UV/PS degradation ATZ in different reaction conditions
反应条件 速率常数/min−1 R2 动力学方程 pH 3.0 0.360 6 0.972 3 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.360\;6t + 0.240\;6$ 4.0 0.290 6 0.956 8 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.290\;6t + 0.144\;5$ 7.0 0.381 9 0.997 9 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.381\;9t - 0.021\;6$ 8.0 0.270 5 0.995 0 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.207\;5t + 0.067\;1$ 9.0 0.283 6 0.994 6 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.283\;6t + 0.059\;5$ UV强度/(mW•cm−2) 30 0.004 9 0.912 2 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.004\;9t - 0.026\;6$ 50 0.044 1 0.997 7 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.044\;1t - 0.010\;8$ 100 0.070 9 0.998 5 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.070\;9t - 0.009\;8$ PS浓度/(μmol•L−1) 10 0.022 9 0.977 7 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.022\;9t + 0.013\;2$ 20 0.035 0 0.982 7 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.035\;0t - 0.041\;3$ 30 0.044 1 0.997 7 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.044\;1t - 0.010\;8$ 40 0.055 3 0.978 3 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.055\;3t - 0.009\;8$ 50 0.074 2 0.992 0 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.074\;2t - 0.074\;4$ 60 0.092 2 0.989 9 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.092\;2t - 0.058\;4$ 70 0.116 9 0.984 5 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.116\;9t + 0.057\;1$ 温度/℃ 10 0.032 4 0.971 5 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.032\;4t - 0.082\;9$ 15 0.053 8 0.987 7 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.053\;8t - 0.055\;8$ 20 0.074 2 0.992 0 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.074\;2t - 0.074\;4$ 25 0.122 8 0.992 2 $\ln \left( {C/{C_0}} \right) = - 0.122\;8t - 0.011\;1$ -
李清波,黄国宏,王颜红,等. 阿特拉津生态风险及其检测和修复技术研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报,2002,13(5): 625-628. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2002.05.026LI Qingbo, HUANG Guohong, WANG Yanhong, et al. Advances of studies on ecological risk of herbicide atrazine and its determination and remediation[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 13(5): 625-628. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2002.05.026 孟顺龙,胡庚东,瞿建宏,等. 阿特拉津在水环境中的残留及其毒理效应研究进展[J]. 环境污染与防治,2009,31(6): 64-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2009.06.018MENG Shunlong, HU Gengdong, QU Jianhong, et al. Research progress on atrazine residue in water environment and its toxicological effects[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2009, 31(6): 64-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2009.06.018 JONES T W, KEMP W M, STEVNSON J C, et al. Degradation of atrazine in Estuarine water/sediment systems and soils[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1982, 11(4): 632-638. COMBER S D. Abiotic persistence of atrazine and simazine in water[J]. Pest Management Science, 2015, 55(7): 696-702. LI Hongyuan, MA Hong, TAO Bo. Ecological risk assessment of atrazine and control strategy[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2006, 37(4): 552-556. 任晋,蒋可,周怀东. 官厅水库水中阿特拉津残留的分析及污染来源[J]. 环境科学,2002,23(1): 126-128. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2002.01.028REN Jin, JIANG Ke, ZHOU Huaidong. The concentration and source of atrazine residue in water of Guanting reservoir[J]. Environmental Science, 2002, 23(1): 126-128. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2002.01.028 杨敏娜,周芳,孙成,等. 长江江苏段有毒有机污染物的残留特征及来源分析[J]. 环境化学,2006,25(3): 375-376. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2006.03.030YANG Minna, ZHOU Fang, SUN Cheng, et al. Residual characteristics and source analysis of toxic organic pollutants in Jiangsu section of Yangtze River[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2006, 25(3): 375-376. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2006.03.030 严登华,何岩,王浩. 东辽河流域地表水体中atrazine的环境特征[J]. 环境科学,2005,26(3): 53-54.YAN Denghua, HE Yan, WANG Hao. Environmental characteristics of the atrazine in the waters in East Liaohe River basin[J]. Environmental Science, 2005, 26(3): 53-54. 中华人民共和国卫生部. 中国国家标准化管理委员会.生活饮用水卫生标准: GB 5749—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006. WALKER B S, KRAMER A G, LASSITER C S. Atrazine affects craniofacial chondrogenesis and axial skeleton mineralization in zebrafish (Danio rerio)[J]. Toxicology & Industrial Health, 2018, 34(5): 329-338. HAYES T B, COLLINS A, LEE M, et al. Hermaphroditic,demasculinized frogs after exposure to the herbicide atrazine at low ecologically relevant doses[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(8): 5476-5480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.082121499 LIN Jia, LI Huixin, QIN Lei, et al. A novel mechanism underlies atrazine toxicity in quails (Coturnix Coturnix coturnix):triggering ionic disorder via disruption of ATPases[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(51): 83880-83892. SANDERSON J T, SEINEN W, GIESY J P, et al. 2-Chloro-s-triazine herbicides induce aromatase (CYP19) activity in H295R human adrenocortical carcinoma cells:a novel mechanism for estrogenicity[J]. Toxicological Sciences, 2000, 54(1): 121-127. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/54.1.121 JI Yuefei, DONG Changxun, KONG Deyang, et al. Heat-activated persulfate oxidation of atrazine:implications for remediation of groundwater contaminated by herbicides[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 263: 45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.10.097 GU Xiaogang, LU Shuguang, QIU Zhaofu, et al. Comparison of photodegradation performance of 1,1,1-Trichloroethane in aqueous solution with the addition of H2O2 or S2O82− oxidants[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51: 7196-7204. LUCA A D, HE X, DIONYSIOU D D, et al. Effects of bromide on the degradation of organic contaminants with UV and Fe2+ activated persulfate[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 318: 206-213. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.066 KHAN J A, HE X, SHAH N S, et al. Kinetic and mechanism investigation on the photochemical degradation of atrazine with activated H2O2,S2O82- and HSO5-[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 252: 393-403. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.04.104 SIMONIN J P. On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 300: 254-263. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.079 HORI H, MURAYAMA M, INOUE N, et al. Efficient mineralization of hydroperfluorocarboxylic acids with persulfate in hot water[J]. Catalysis Today, 2010, 151(1/2): 131-136. WALDEMER R H, TRATNYEK P G, JOHNSON R L, et al. Oxidation of chlorinated ethenes by heat-activated persulfate:kinetics and products[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(3): 1010-1015. ANIPSITAKIS G P, DIONYSIOU D D. Radical Generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(13): 3705-3712. BUXTON G V, GREENSTOCK C L, HELMAN W P, et al. Critical review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons,hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals (HO•/•O-)in aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Physical & Chemical Reference Data, 2009, 17(2): 513-886. 康宏亮. 零价铝/锌降解水中阿特拉津及其机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中师范大学, 2016. CHEN Cheng, YANG Shaogui, GUO Yaping, et al. Photolytic destruction of endocrine disruptor atrazine in aqueous solution under UV irradiation: products and pathways[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 172(2): 675-684. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.050 -




 下载:
下载: