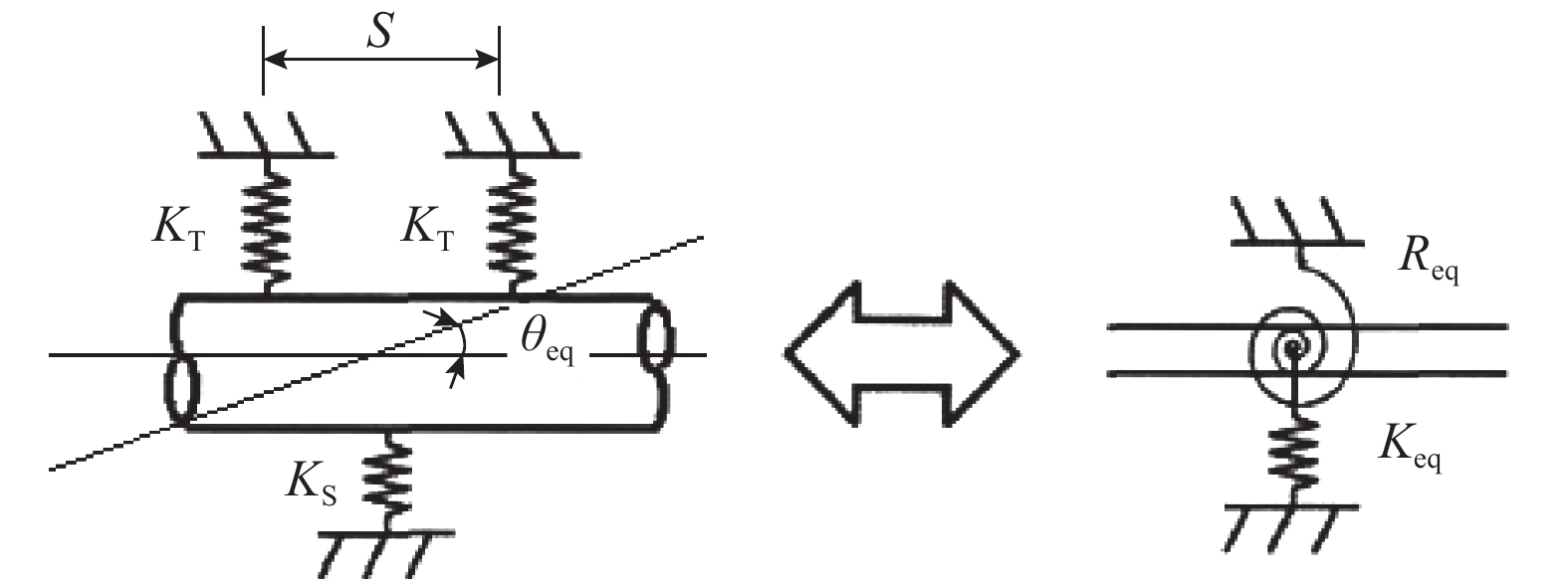
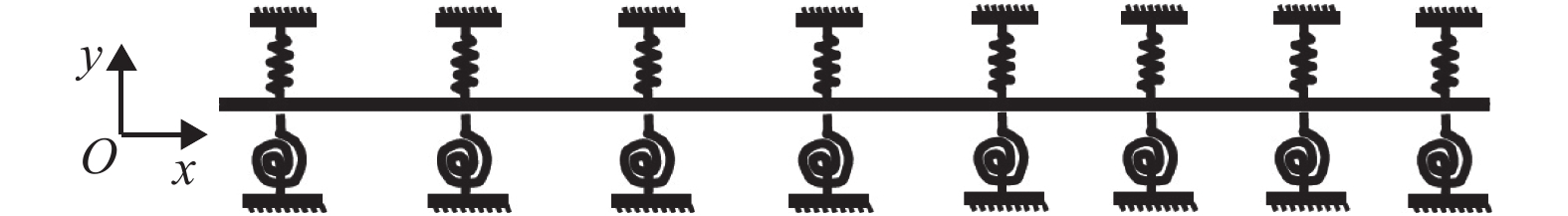
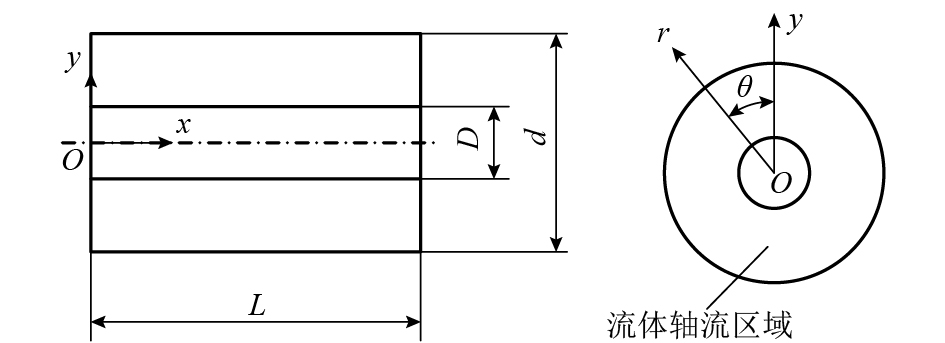
Free Vibration Characteristics of Multi-constrained Fuel Rod
-
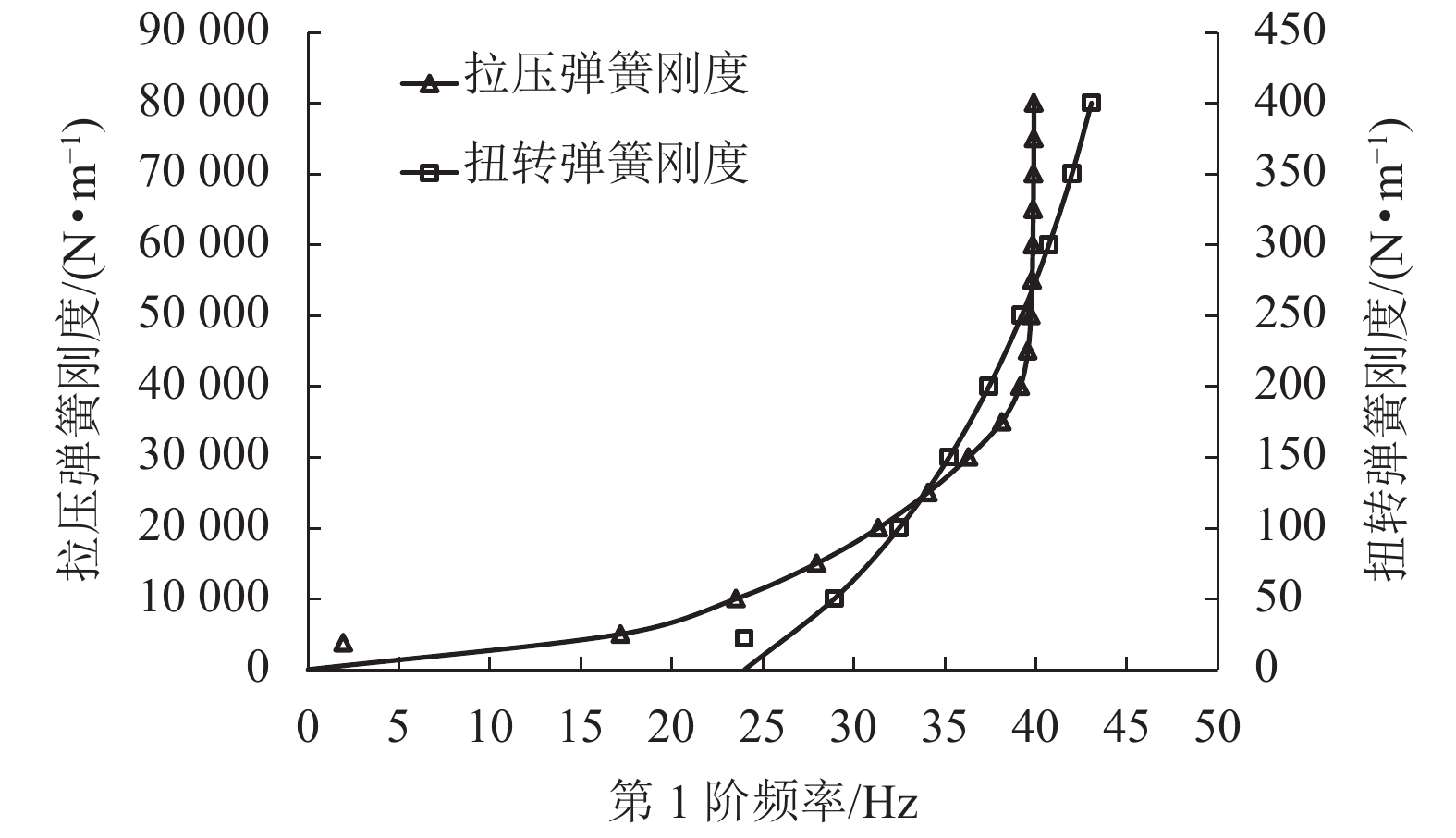
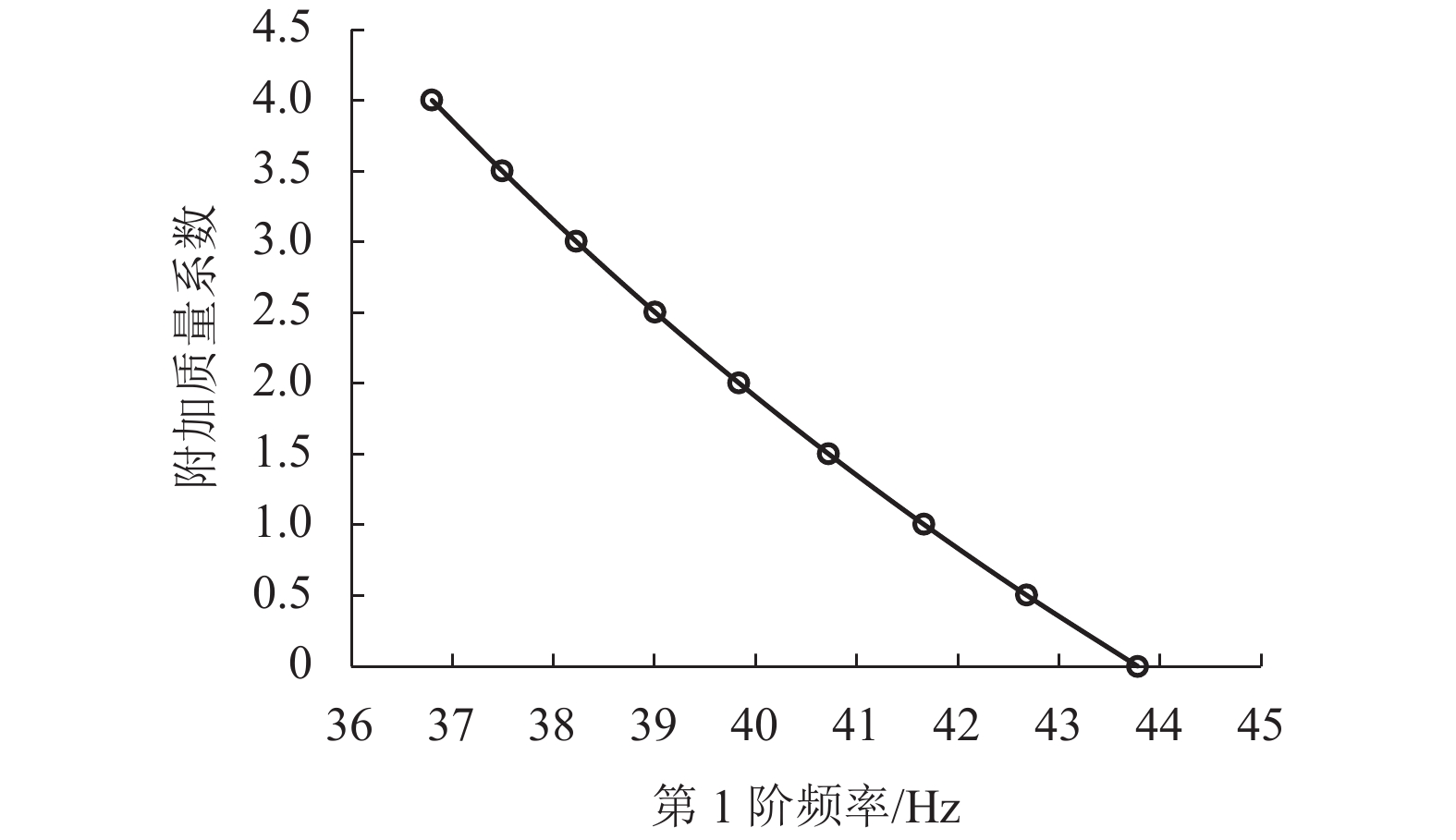
摘要: 为开发用于核燃料设计的流致振动计算程序,基于梁理论和势流理论,建立了多约束燃料棒振动问题理论分析方法. 首先通过多跨连续梁理论,得到了多约束燃料棒在空气中振动控制方程和干模态下总体刚度矩阵和质量矩阵;然后通过势流理论,考虑了流体轴流和边界条件的影响,给出了湿模态下附加质量矩阵;最后以压水堆燃料棒为例,得到了燃料棒在干模态和湿模态下自由振动固有频率和振型的理论分析结果,并研究了弹簧刚度和附加质量系数对振动固有频率的影响. 研究结果表明:通过理论分析方法所得计算结果与有限元软件ANSYS计算结果相一致;燃料棒在堆芯中结构为棒束形式,且周围为高速流动流体,振动频率及振型受到流体轴流和周边相邻燃料棒的边界效应影响,但由于多约束作用,流体轴流和边界效应仅影响了振动固有频率,而对振型基本没有影响;拉压和扭转弹簧刚度越大,燃料棒振动频率越高,增加扭转弹簧刚度可使第1阶固有频率增加79.1%,附加质量系数越高,燃料棒振动频率越低,可使第1阶固有频率降低18.2%,通过优化刚度方法可得到理想的振动特性,为格架设计提供参考.Abstract: In order to develop flow-induced vibration calculation program for nuclear fuel design, a theoretical method for analyzing multi-constrained fuel rod vibration is established based on beam theory and potential flow theory. Firstly, the vibration control equations in air and the overall stiffness matrix and mass matrix in dry modal are obtained through the multi-span continuous beam theory. Then the additional mass matrix in the wet modal is presented by considering the effect of axial flow and boundary conditions through the potential flow theory. Finally, Finally, the pressurized water reactor (PWR) fuel rod is used as an example. The theoretical analysis results about its natural frequencies and modes are obtained and the effects of spring stiffness and added mass coefficient on the natural frequency are explored. The results show that the theoretical analysis results are consistent with those calculated by the ANSYS. As the fuel rods are in bundle in the core and are surrounded by high-speed flow, its vibration frequency and mode are affected by axial fluid flow and rod boundary, but due to multi-constraints the vibration mode is seldom affected. The larger the tension and torsion spring stiffness, the higher the vibration frequencies of the fuel rod. The first natural frequency can be increased by 79.1% with the torsion spring increasing. The higher the additional mass coefficient, the lower the vibration frequencies of the fuel rod. The first natural frequency can be reduced by 18.2% as the additional mass coefficient increases. The ideal vibration characteristics can be obtained by optimizing the stiffness, which provides reference for the design of the grid.
-
Key words:
- multi-constrained /
- fuel rod /
- additional mass /
- dry modal /
- wet modal
-
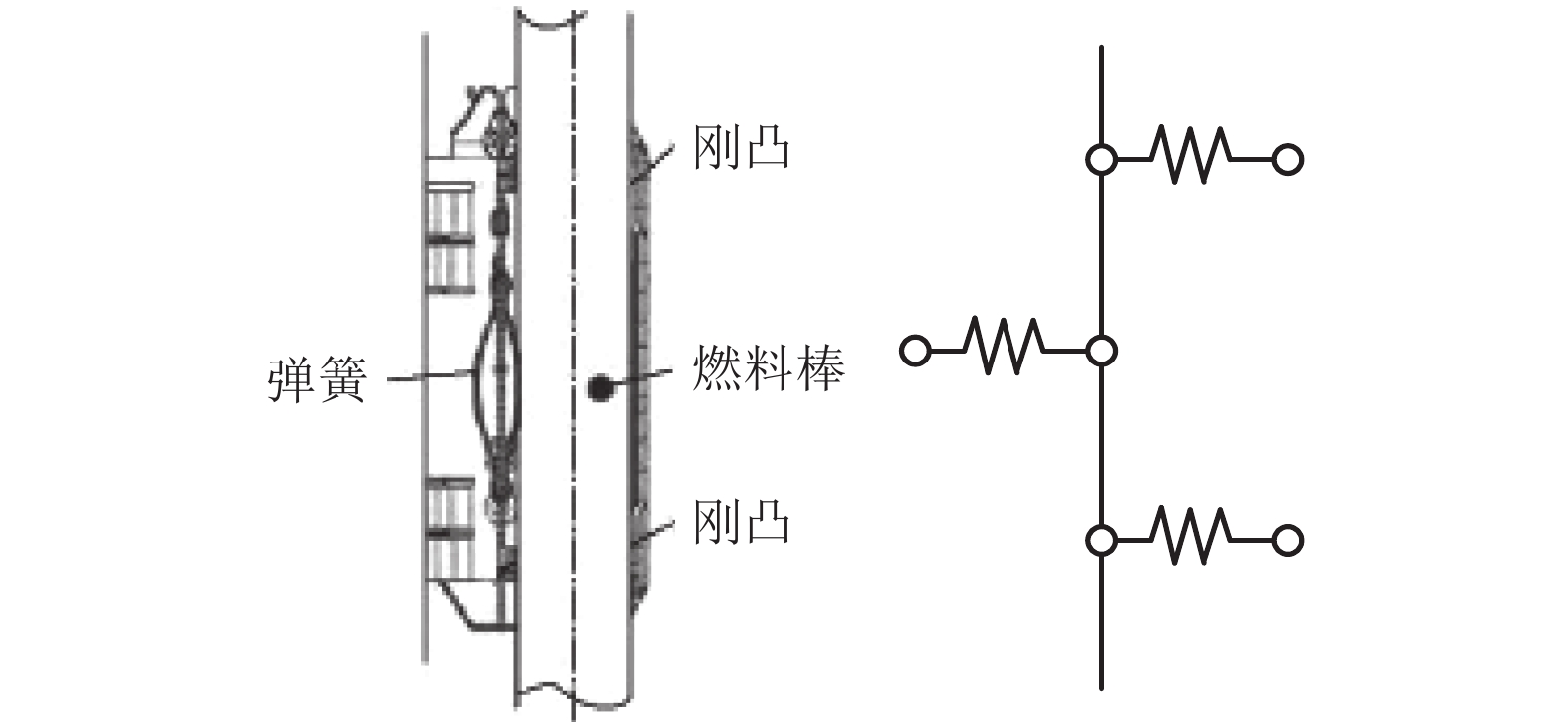
表 1 燃料棒结构设计参数
Table 1. Design parameters of the fuel rod structure
格架
数目/个燃料棒包壳
外径/m燃料棒包壳
内径/m芯块
直径/m燃料棒
长度/m两端跨
长度/m中间7跨
长度/m相邻燃料棒
中心间距/m8 0.009 5 0.083 6 0.008 192 3.86 0.18 0.50 0.013 表 2 材料性能和流体特性参数
Table 2. Parameters of material properties and fluid characteristics
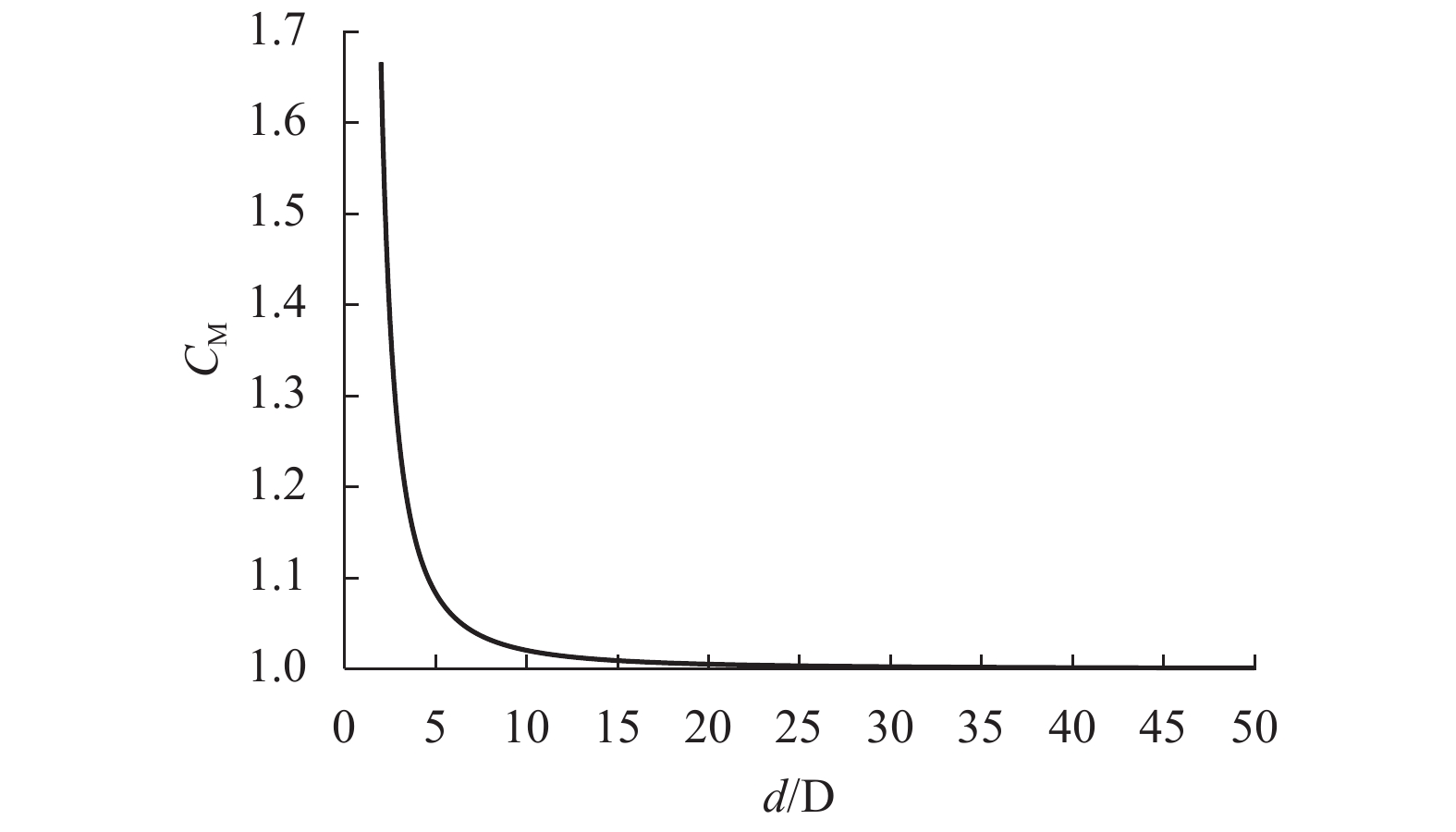
包壳弹性模量/Mpa 包壳密度/(kg•m−3) 芯块密度/(kg•m−3) 拉压弹簧刚度/(N•m−1) 扭转弹簧刚度/(N•m−1) 流体密度/(kg•m−3) 流体中声速/(m•s−1) 91 000 6 560 10 970 6.3 × 104 2.7 × 102 1 000 1 500 表 3 不同比值时附加质量系数
Table 3. Additional mass coefficients for various ratios
d/D a 0.000 1 0.001 0 0.010 0 0.100 0 1.02 50.504 95 50.505 00 50.510 10 51.025 38 1.06 17.181 23 17.181 25 17.183 05 17.365 19 1.10 10.523 81 10.523 82 10.524 97 10.640 67 1.20 5.545 45 5.545 46 5.546 12 5.612 38 1.40 3.083 33 3.083 34 3.083 75 3.126 09 1.65 2.161 10 2.161 11 2.161 44 2.195 41 1.80 1.892 86 1.892 86 1.893 17 1.924 96 2.00 1.666 67 1.666 67 1.666 96 1.697 15 6.00 1.057 14 1.057 15 1.057 46 1.092 65 10.00 1.020 20 1.020 21 1.020 56 1.068 07 100.00 1.000 20 1.000 21 1.000 89 1.022 37 表 4 燃料棒在空气及流体中自由振动频率
Table 4. Vibration frequency of fuel rod in air and fluid
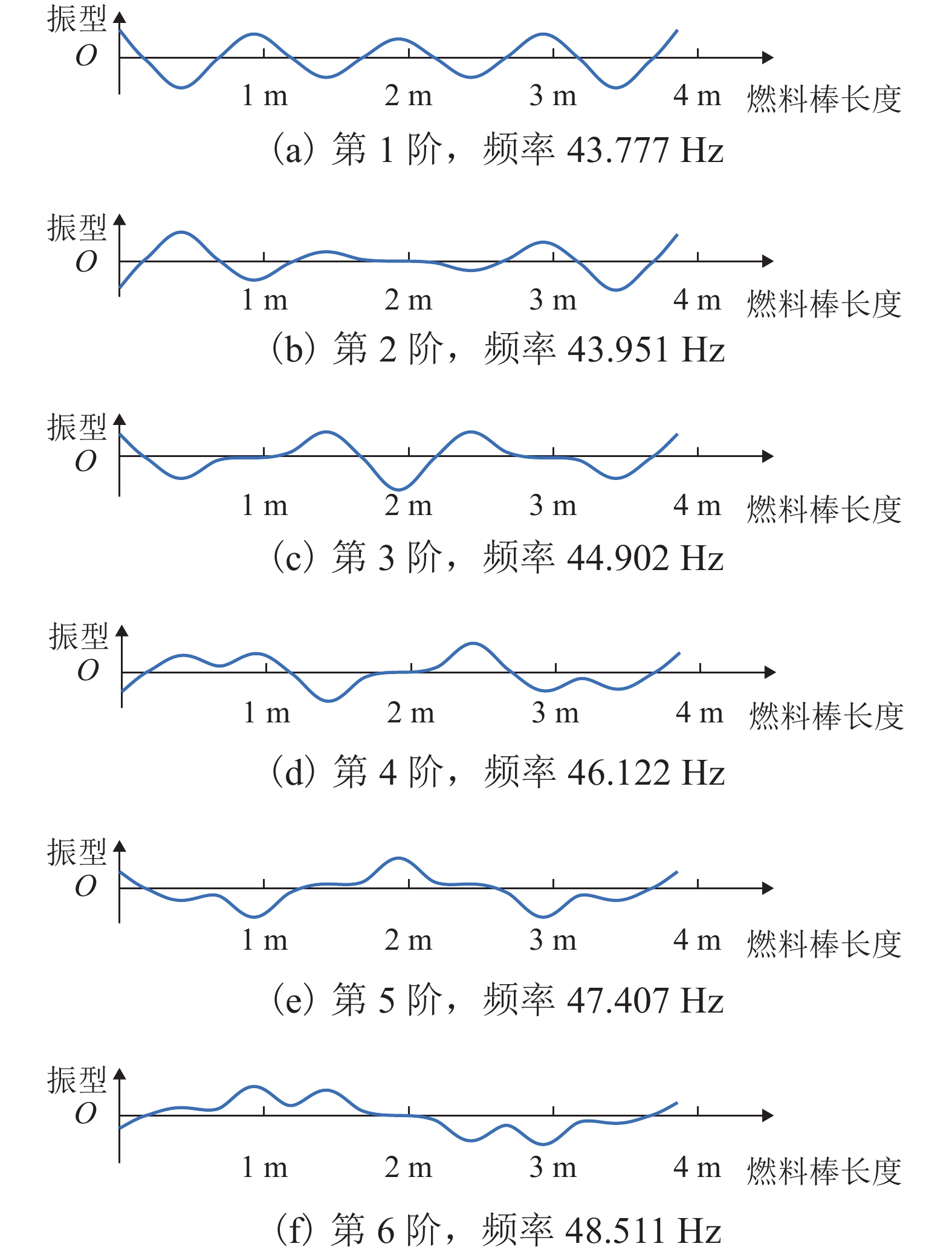
阶数 空气中
振动频率/HzANSYS
计算值/Hz流体中
振动频率/HzANSYS
计算值/Hz1 43.777 43.679 39.853 39.764 2 43.951 43.852 40.011 39.921 3 44.902 44.794 40.877 40.779 4 46.122 46.005 41.988 41.881 5 47.407 47.280 43.157 43.042 6 48.511 48.377 44.162 44.040 7 49.252 49.113 44.836 44.710 8 54.562 54.420 49.671 49.542 9 54.562 54.420 49.671 49.542 10 94.218 94.028 87.827 85.599 -
孙汗虹, 程平东, 缪鸿兴, 等. 第三代核电技术AP1000[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2010: 80-81. 蒋莉,王建立,孙成海,等. 有界域轴向流动棒束流致振动附加质量力模型[J]. 原子能科学技术,1999,33(5): 431-435.JIANG Li, WANG Jianli, SUN Chenghai, et al. Mathematical models for fluid inertial forces added on the rod bundle vibrating in the bounded axial flow[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 1999, 33(5): 431-435. KIM K T. The study on grid-to-rod fretting wear models for PWR fuel[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2009, 239(12): 2820-2824. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2009.08.018 姚起杭,姚军. 工程结构的振动疲劳问题[J]. 应用力学,2006,23(1): 12-15.YAO Qihang, YAO Jun. Vibration fatigue in engineering structures[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2006, 23(1): 12-15. 鲁丽. 非线性板状结构流固耦合复杂响应研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2006. KIM H K, LEE Y H, LEE K H. On the geometry of the fuel rod supports concerning a fretting wear failure[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2008, 238: 3321-3330. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2008.08.010 CHRISTO M A, LU Ru, BAKOSI J, et al. Fuel rod vibration and grid-to-rod fretting in pressuried water reactor[J]. Computer Physics, 2016, 322: 142-161. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2016.06.042 黄恒,刘彤,周跃民. 压水堆燃料棒在轴向流作用下的随机振动响应研究[J]. 原子能科学技术,2015,49(3): 468-472. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2014.youxian.0006HUANG Heng, LIU Tong, ZHOU Yuemin. Random response analysis of PWR fuel rod effect on axial flow[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2015, 49(3): 468-472. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2014.youxian.0006 刘延柱, 陈立群, 陈文良. 振动力学[M]. 2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2011: 183-188. CHEN S S. Vibrations of a row of circular cylinders in a liquid[J]. Journal of Engineering for Industry, 1975, 97(4): 1212-1218. doi: 10.1115/1.3438730 柳瑞锋,黄嵘,周相荣,等. 船体低阶湿模态计算方法对比研究[J]. 船舶工程,2014,36(4): 25-28.LIU Ruifeng, HUANG Rong, ZHOU Xiangrong, et al. Contrast study on calculation method for lower order wet mode of ship hull[J]. Ship Engineering, 2014, 36(4): 25-28. CHEN S S, WAMBSGANSS M W. Parallel-flow-induced vibration of fuel rods[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1972, 18: 253-278. doi: 10.1016/0029-5493(72)90144-6 郭长青. 输流管道与轴向流中板状结构的流致振动与稳定性[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2010. 温正, 陈文良. MATLAB应用教程[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016: 371-375. -




 下载:
下载: