Evaluation Method of Seat Comfort for High-Speed Trains Based on Seat Ergonomic Parameters
-
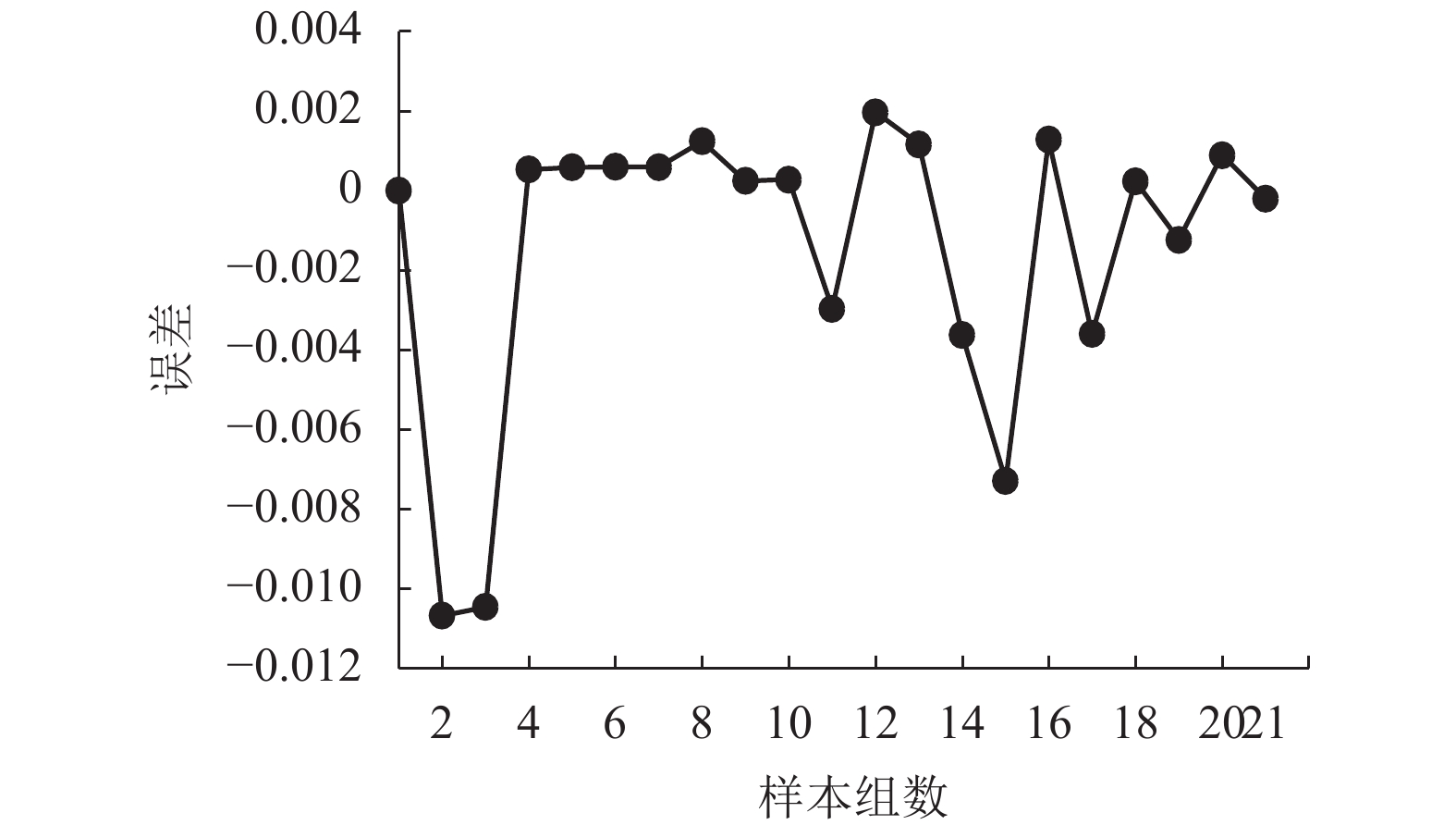
摘要: 为了降低高速列车舒适度调查的成本,避免进行大量的问卷调查和统计分析,对高速列车座椅静态舒适度评价方法进行了研究. 首先,通过确定高速列车座椅舒适度评价指标和指标权重,获得座椅舒适度计算方法;其次,利用BP神经网络构建以高速列车座椅8项人机几何参数为输入、以座椅舒适度评价为输出的座椅静态舒适度评价模型;最后,进行实例研究,对构建的神经网络评价模型进行训练和验证,并对神经网络进行权值和阈值的提取,构建神经网络的数学表达公式. 研究结果表明:当神经网络为1个隐含层、13个节点时,训练达到误差均值2.13 × 10−3、均方误差6.091 × 10−6的理想效果,且不存在过拟合现象;利用CHR2的一、二等座椅人机几何参数测量数据及对应舒适度评价对该网络进行验证,验证显示一等座的神经网络预测值跟实际评价值误差为3.07%,二等座评价误差为1.42%,该网络模型预测精度较高,且优于多元回归模型预测的结果.Abstract: To reduce the cost in the comfort evaluation of high-speed trains and avoid strenuous questionnaire investigation and statistical analysis, the static comfort evaluation method of high speed train seats is studied. Firstly, the seat comfort calculation method is derived by determining the comfort evaluation index and index weight for high-speed train seats. Secondly, the BP neural network is used to construct a static seat comfort evaluation model, which takes the 8 ergonomic parameters of the high-speed train seat as the input and the seat comfort evaluation as the output. Finally, a case study is carried out to train and verify the constructed neural network evaluation model, and the weights and thresholds of the neural network are extracted to construct a mathematical expression of the neural network. The results show that when the neural network has one hidden layer and 13 nodes, the training achieves the desirable results with the mean error of 2.13×10−3 and mean square error of 6.091×10−6, and there is no over fitting. The network is verified by the real ergonomic data of the first-class and second-class seats in CHR2 and the corresponding comfort evaluations. The error of first-class seats between the predicted value of neural network and the actual one is 3.07%, and the error of second-class seats is 1.42%, demonstrating that the network model has high prediction accuracy and is superior to the multiple regression model.
-
Key words:
- high-speed train /
- seat comfort /
- neural network /
- evaluation model
-
表 1 座椅舒适度评价方法及特点
Table 1. Methods and characteristics of seat comfort evaluation
名称 手段 文献 相关研究 特点 主观评价法 量表法 [4] 提出采用 11 种描述的
10 点量表评价座椅舒适度样本数量多;样本选择影响结果;量表及问卷设计影响结果 问卷法 [5] 建立汽车座椅不舒适性问卷,
归纳 20 个影响舒适性因素客观评价法 坐姿分析 [6] 表明受试者主观不适感的增加,其坐姿的
变换频率和运动频率也随之增大耗时少;被试样本需求少;
可靠性高体压分布 [7] 提出最舒适的姿势对应的座椅压力分布
是椎间盘的压力最低,且通过理想的
压力分布来确定座椅的形状肌电测试 [8] 研究体位和坐姿的肌电变化,提出
改善使用者的舒适性和安全性必须
减少姿势肌肉的生物力学负荷主客观相结合 多元回归 [9] 建立主观评价与体压分布之间的数学模型 具有预测功能;预测效果跟样本数量、样本质量相关 神经网络 [10] 构建神经网络预测模型,输入界面压力、
3 个人体尺寸、座椅美观评价等指标,
输出变量为综合舒适性指数[11] 构建以 8 个座椅压力分布参数和 2 个
人体参数为输入的模糊神经网络模型,
评价带有主观性的座椅舒适性[12] 应用人工神经网络技术,以座椅各部分
特征为输入变量,建立了汽车座椅
舒适度的人工智能评价系统向量回归 [13] 提出以 14 个压力分布指标和 3 个人体
变量为输入,舒适度为输出的支持向量
回归的预测座椅主观舒适度方法表 2 座椅人机几何参数舒适度权重
Table 2. Comfort weights of seat ergonomic parameters
座高 座深 座宽 靠背高 靠背宽 容膝距 靠背倾角 座间距 0.257 0.089 0.093 0.076 0.059 0.273 0.096 0.057 表 3 不同隐含层下不同节点数网络训练误差均值、均方误差
Table 3. Mean error and mean square error of network training with different hidden layers and numbers of nodes
节点数 1个隐含层 2个隐含层 误差均值/ × 10−3 均方误差/ × 10−5 误差均值/ × 10−3 均方误差/ × 10−5 5 4.635 5.969 4.340 2.715 6 4.210 6.492 4.804 10.001 7 2.954 1.516 4.520 2.937 8 3.586 2.286 5.907 6.177 9 3.489 1.686 2.660 0.992 10 3.710 2.521 4.390 3.118 11 3.460 2.102 8.090 14.641 12 3.407 2.797 3.650 2.208 13 2.130 0.609 3.841 1.857 14 3.397 2.180 6.660 11.361 15 6.420 11.073 4.330 11.073 表 4 BP神经网络验证结果
Table 4. Verification results of BP neural network
项目 一等座结果 二等座结果 实际评分 5.456 5.096 验证输出值 5.289 5.024 绝对误差 −0.167 −0.072 相对误差百分比/% 3.07 1.42 回归分析误差/% 9.11 19.96 -
彭波. 铁道客车乘坐舒适性建模、仿真与虚拟试验研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010. 张卫华,王伯铭. 中国高速列车的创新发展[J]. 机车电传动,2010(1): 8-12.ZHANG Weihua, WANG Boming. Innovation and development of high-speed railway in China[J]. Electric Drive for Locomotives, 2010(1): 8-12. 陈祥. 高速铁路客车乘坐舒适度综合评价模型研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2010. SHACKEL B, CHIDSEY K D, SHIPLEY P. The assessment of chair comfort[J]. Ergonomics, 1969, 12(2): 269-306. doi: 10.1080/00140136908931053 SMITH D R, ANDREWS D M, WAWROW P T. Development and evaluation of the automotive seating discomfort questionnaire (ASDQ)[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2006, 36(2): 141-149. doi: 10.1016/j.ergon.2005.09.005 SAMMONDS G M, FRAY M, MANSFIELD N J. Effect of long term driving on driver discomfort and its relationship with seat fidgets and movements (SFMs)[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2017, 58: 119-127. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2016.05.009 ZENK R, FRANZ M, BUBB H, et al. Technical note:spine loading in automotive seating[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2012, 43(2): 290-295. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2011.06.004 BERTOLACCINI G D S, NAKAJIMA R K, PASCHOARELLI L C, et al. The influence of seat height,trunk inclination and hip posture on the activity of the superior trapezius and longissimus[J]. Journal of Physical Therapy Science, 2016, 28(5): 1602-1606. doi: 10.1589/jpts.28.1602 KOYANO M, KIMISHIMA T, NAKAYAMA K. Quantification of static seating comfort of motorcycle seats[J]. JSAE Review, 2003, 24(1): 99-104. doi: 10.1016/S0389-4304(02)00251-5 KOLICH M. Predicting automobile seat comfort using a neural network[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2004, 33(4): 285-293. doi: 10.1016/j.ergon.2003.10.004 李培松,马佳,杨海霞,等. 运用模糊神经网络的汽车座椅舒适性评价[J]. 工业工程,2010,13(1): 97-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5429.2010.01.019LI Peisong, MA Jia, YANG Haixia, et al. Comfort evaluation of automobile seats by using fuzzy neural networks[J]. Industrial Engineering Journal, 2010, 13(1): 97-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5429.2010.01.019 马佳,柯艺杰,苏强,等. 汽车座椅舒适度人工智能评价方法研究[J]. 机械科学与技术,2011,30(3): 419-422.MA Jia, KE Yijie, SU Qiang, et al. An automobile seat comfort evaluating method based on artificial intelligence[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2011, 30(3): 419-422. 孙守迁,吴群,吴剑锋,等. 一种基于支持向量回归的驾驶座椅舒适度评价方法[J]. 中国机械工程,2008(11): 1326-1330. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2008.11.015SUN Shouqian, WU Qun, WU Jianfeng, et al. An evolution method of driving seat comfort based on support vector regression[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2008(11): 1326-1330. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2008.11.015 蒲骄子,李延来,刘宗鑫. 基于文本挖掘与神经网络的高速列车意象造型设计[J]. 机械设计,2017(9): 101-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-509X.2017.09.025PU Jiaozi, LI Yanlai, LIU Zongxin. Image modeling design of high-speed train based on text mining and neural network[J]. Journal of Machine Design, 2017(9): 101-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-509X.2017.09.025 马佳,范智声,李飞飞,等. 基于人工神经网络的汽车座椅舒适度评价模型[J]. 工业工程,2008(5): 106-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5429.2008.05.020MA Jia, FAN Zhisheng, LI Feifei, et al. Evaluation of automobile seat comfort based on artificial neural networks[J]. Industrial Engineering Journal, 2008(5): 106-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5429.2008.05.020 祝燕萍,方鸽飞. 基于动态自适应神经网络和人体舒适度的短期负荷预测[J]. 电力系统保护与控制,2012,40(1): 56-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3415.2012.01.010ZHU Yanping, FANG Gefei. Short-term load forecasting based on dynamic adaptive artificial neural network and human body amenity indicator[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2012, 40(1): 56-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3415.2012.01.010 徐明,夏群生. 体压分布的指标[J]. 中国机械工程,1997,8(1): 65-68. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.1997.01.022XU Ming, XIA Qunsheng. The index of body pressure distribution[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 1997, 8(1): 65-68. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.1997.01.022 曹志伟,李娟. 轨道车辆座椅舒适度评价方法及研究展望[J]. 包装工程,2017(2): 21-25.CAO Zhiwei, LI Juan. Evaluation methods and research prospects for rail vehicle seating comfort[J]. Packaging Engineering, 2017(2): 21-25. 苏晓峰. 我国中高速旅客列车座椅设计模式探讨[J]. 铁道车辆,1999(12): 25-26.SU Xiaofeng. Discussion on seat design mode of medium and high speed passenger trains in China[J]. Rolling Stock, 1999(12): 25-26. 霍笑,孙文磊,陶庆,等. 基于坐姿分析的座椅舒适度测试与评价[J]. 工程设计学报,2017(3): 286-294. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1006-754X.2017.03.007HUO Xiao, SUN Wenlei, TAO Qing, et al. Seat comfort test and evaluation based on sitting posture analyses[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Design, 2017(3): 286-294. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1006-754X.2017.03.007 李娟. 高速列车乘客座椅" 人-椅”接触面的舒服度设计研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2014. -





 下载:
下载: