Study on Leachate Recirculation Volume of Aerobic Bioreactor Landfills
-
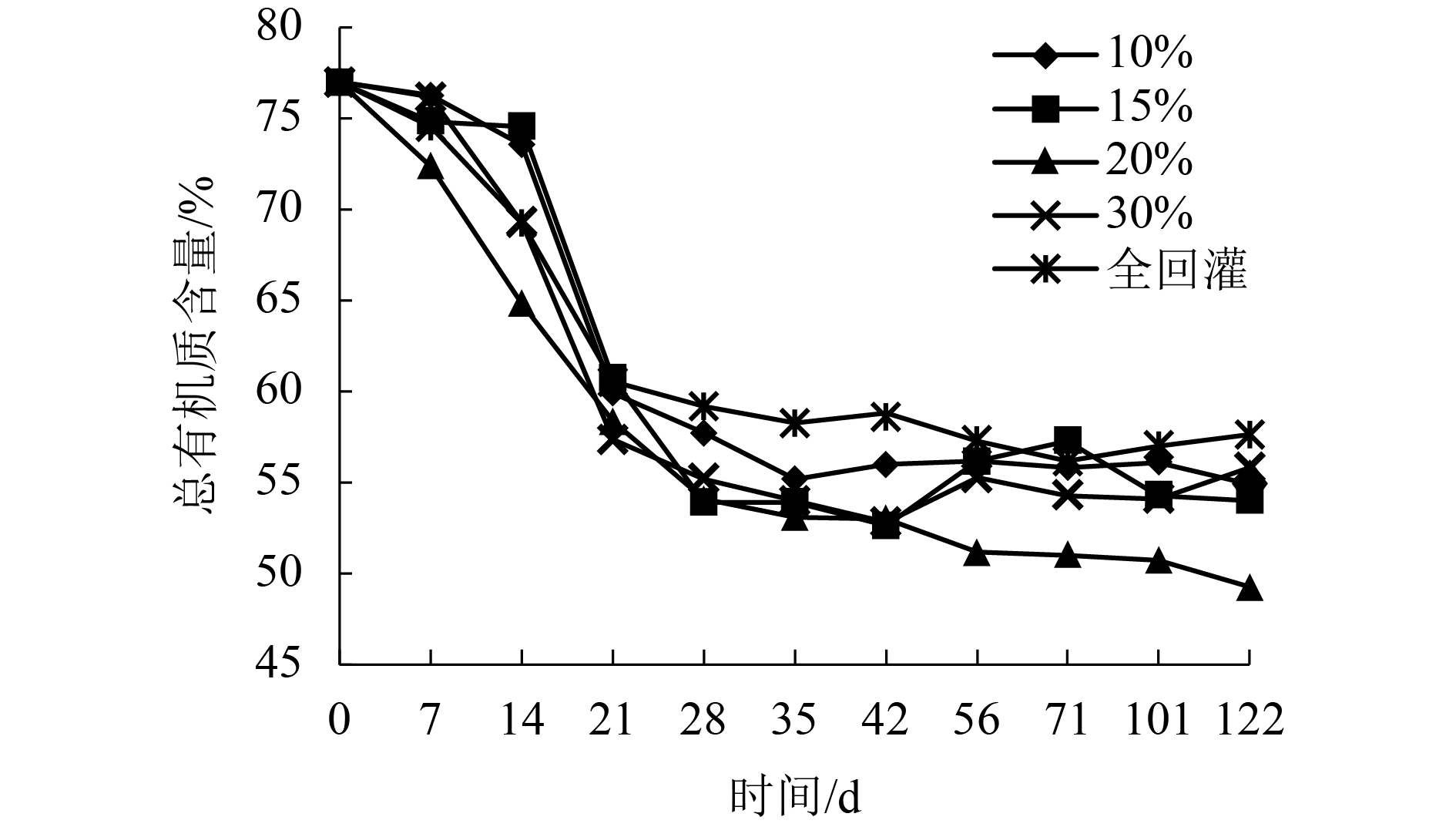
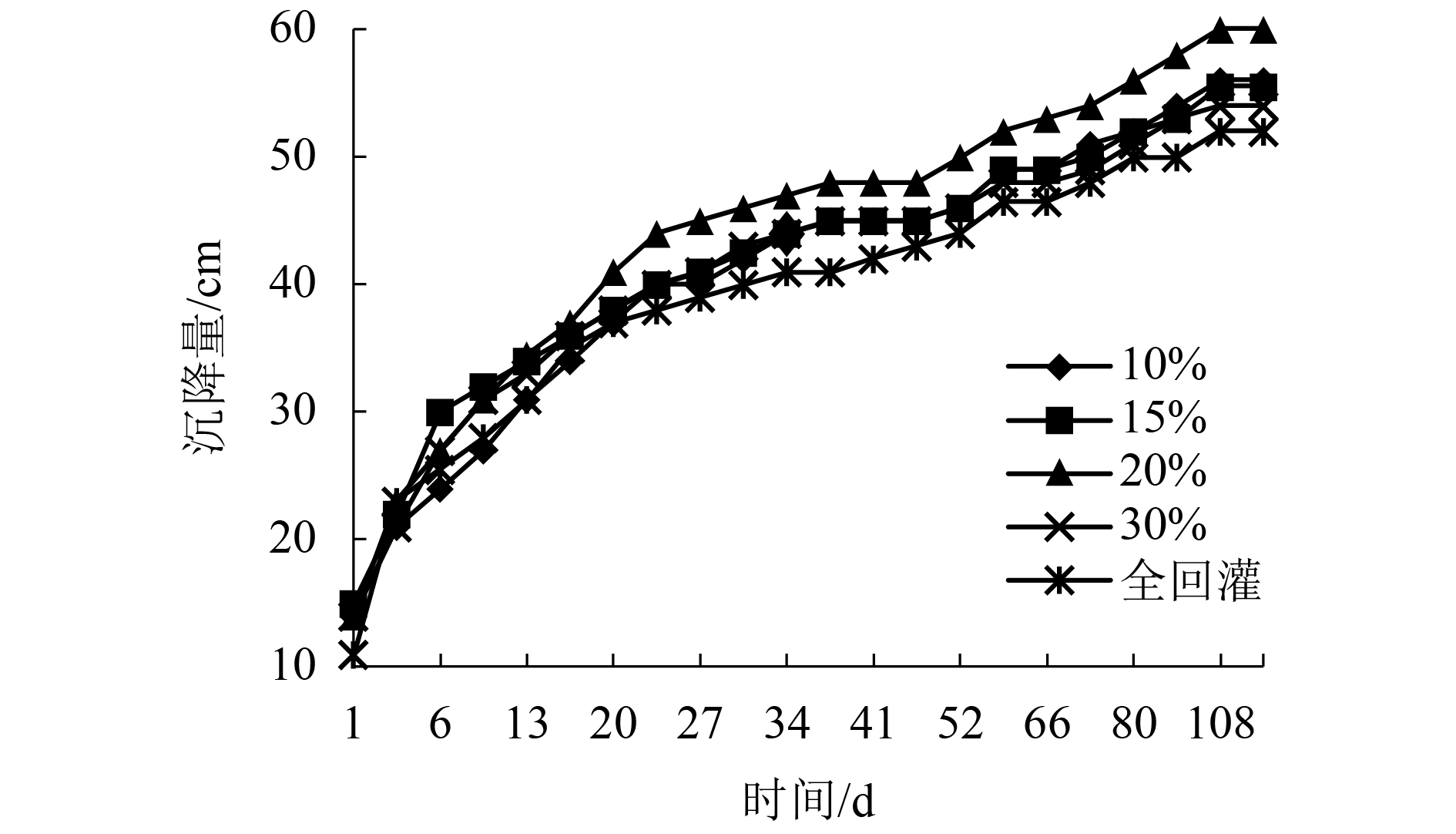
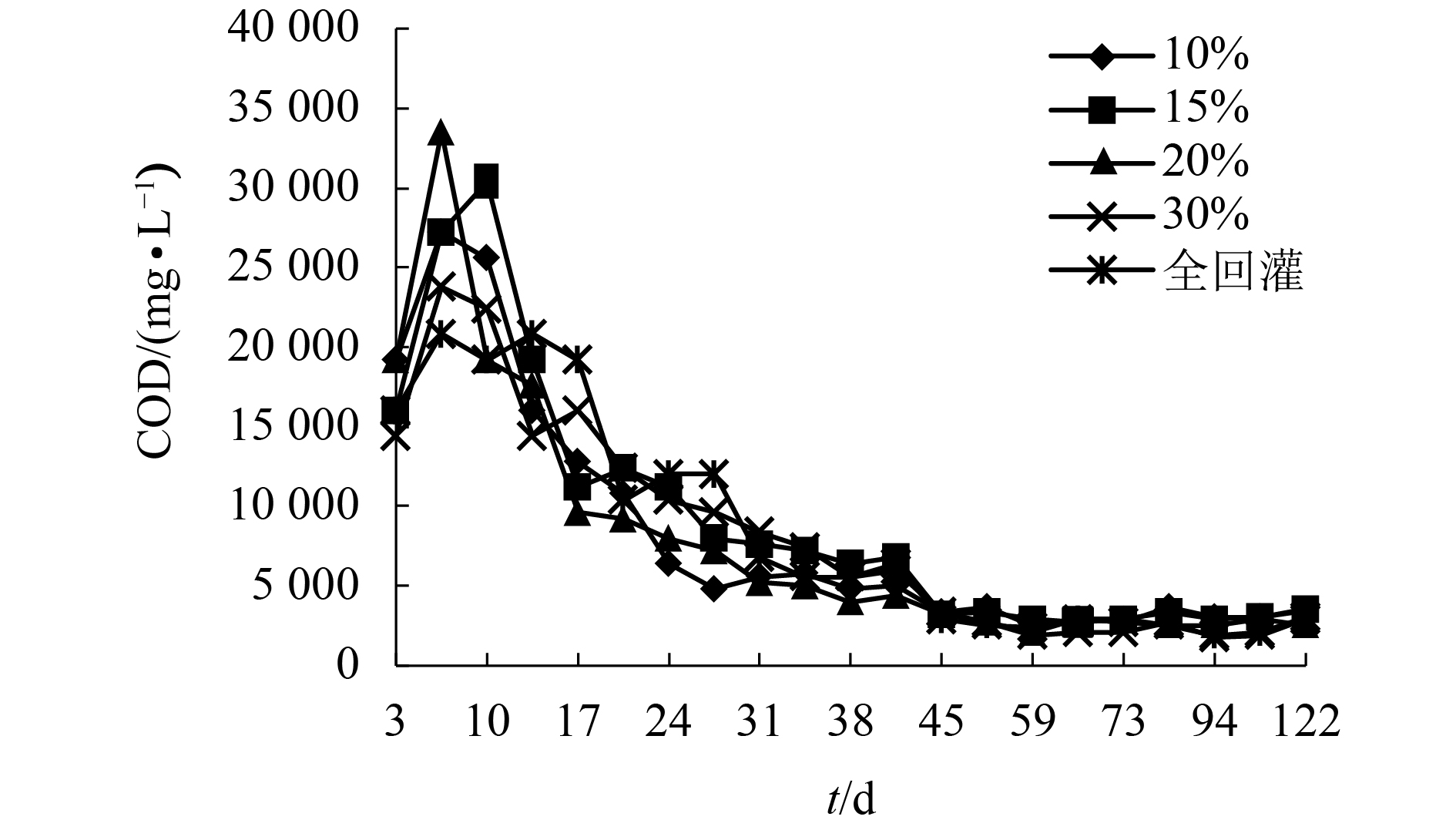
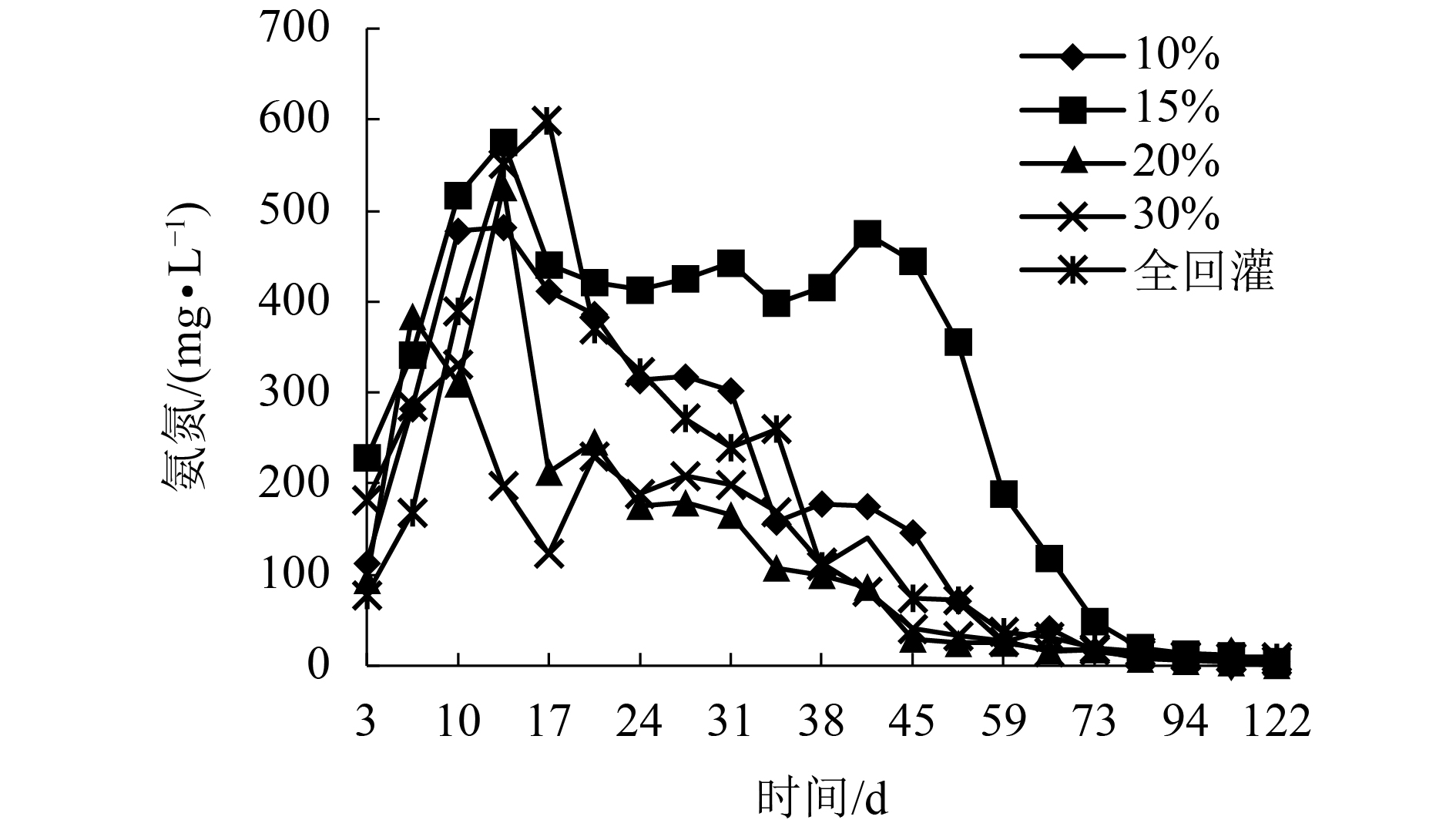
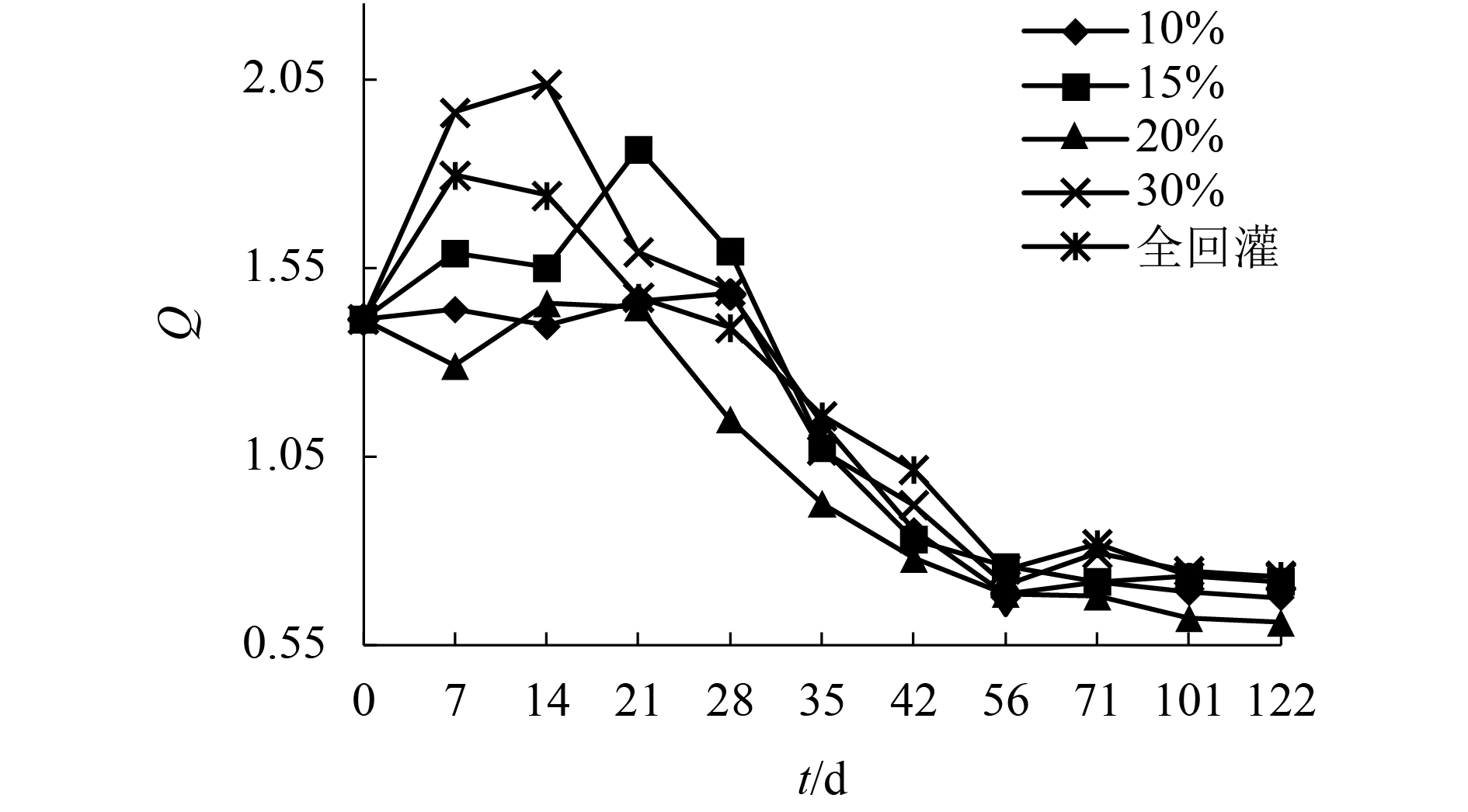
摘要: 为了研究渗滤液回灌量对好氧填埋场稳定化进程的影响,通过模拟实验,探讨了不同回灌量时,好氧填埋场固相垃圾与渗滤液特性的变化趋势,填埋周期为122 d. 结果表明,不同的渗滤液回灌下各反应器中填埋垃圾的含水率始终保持在70%左右;填埋过程中,回灌量为20%的反应器填埋垃圾中总有机质含量、(半纤维素 + 纤维素)/木质素比(Q)值与沉降量变化速度最快,至填埋结束时,总有机质含量与Q值较其他反应器低8.9%~14.6%和9.9%~16.9%,沉降量较其他反应器提高了6.6%~13.3%;在20%回灌量下,整个填埋周期填埋场所产渗滤液中的还原性有机物的量较10%、15%、30%和全回灌分别低9.8%、12.5%、17.8%和14.9%,氨氮在52 d,即降至25 mg/L,达到GB 16889—2008所规定的垃圾填埋场渗滤液氨氮排放浓度值,较其他反应器提前7~21 d.Abstract: To study the influence of leachate recirculation on the stabilization process of aerobic landfills, an experiment was conducted to assess the variation trend of solid waste and leachate characteristics in an aerobic landfill with different recirculation rates. The landfill period was 122 days. Results showed that the water content of landfill refuse in each reactor remained at about 70% under different leachate recirculation rates. The total organic carbon content, (hemicellulose + cellulose)/lignin ratio(Q), and sedimentation of landfill refuse with 20% recirculation changed fastest in the landfill process. At the end of the landfill period, the mass content and Q of landfill leachate were 8.9%–14.6% and 9.9%–16.9% lower, respectively, than that of other reactors, and the sedimentation was 6.6%–13.3% higher than that of other reactors. The amount of reductive organic matter in the leachate during the whole process with the recirculation volume as 20% was 9.8%, 12.5%, 17.8%, and 14.9% lower than that of 10%, 15%, 30%, and full recirculation, respectively, and the ammonia nitrogen was reduced to 25 mg/L, which met the concentration of ammonia nitrogen discharge in landfill leachate of GB 16889—2008, in 52 d, which was 7–21 d earlier than the other reactors.
-
Key words:
- aerobic landfill /
- recirculation volume /
- stabilization /
- biodegradation /
- leachate
-
表 1 各反应器编号与运行参数
Table 1. Code of simulated landfill bioreactor
垃圾重量/kg 压实密度/(kg•m–3) 曝气频率 回灌量/% 35.0 635 1∶3 10 35.0 635 1∶3 15 35.0 635 1∶3 20 35.0 635 1∶3 30 35.0 635 1∶3 100(全回灌) -
HOORNWEG D, BHADA-TATA P, KENNEDY C. Environment:waste production must peak this century[J]. Nature, 2013, 502: 615-617 doi: 10.1038/502615a SLEZAK R, KRZYSTEK L, LEDAKOWICZ S. Degradation of municipal solid waste in simulated landfill bioreactors under aerobic conditions[J]. Waste Management, 2015, 43: 293-299 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2015.06.017 MORELLO L, RAGA R, CRISTINA L M, et al. The S.An.A.®;concept:semi-aerobic,anaerobic,aerated bioreactor landfill[J]. Waste Management, 2017, 67: 193-202 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.05.006 SUN Yingjie, WANG Yanan, SUN Xiaojie, et al. Production characteristics of N2O during stabilization of municipal solid waste in an intermittent aerated semi-aerobic bioreactor landfill[J]. Waste Management, 2013, 33(12): 2729-2736 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2013.08.013 韩智勇,刘丹,李启彬. 厌氧-准好氧联合型生物反应器填埋场产气规律的研究[J]. 环境科学,2012,33(6): 2118-2124HAN Zhiyong, LIU Dan, LI Qibin. Aerogenesis evolution of the anaerobic-semiaerobic bioreactor landfill[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(6): 2118-2124 邱忠平,江海涛,王倩,等. 加速填埋场稳定化进程复合菌系的构建[J]. 中国环境科学,2012,32(3): 492-498 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.03.017QIU Zhongping, JIANG Haitao, WANG Qian, et al. Construction of a multifunctional microbial community for accelerating the stabilization of landfill[J]. China Environmental Science, 2012, 32(3): 492-498 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.03.017 GE Sai, LIU Lei, XUE Qiang, et al. Effects of exogenous aerobic bacteria on methane production and biodegradation of municipal solid waste in bioreactors[J]. Waste Management, 2016, 55: 93-98 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2015.11.024 HETTIARATCHI J P A, JAYASINGHE P A, BARTHOLAMEUZ E. M.Waste degradation and gas production with enzymatic enhancement in anaerobic and aerobic landfill bioreactors short communication[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 159: 433-436 doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.026 邱忠平. 生物强化技术加速填埋场稳定化进程实验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2012,47(3): 533-537 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2012.03.028QIU Zhongping. Experimental study on acceleration of landfill stabilization process using bioaugmentation technology[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2012, 47(3): 533-537 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2012.03.028 SUNA E A, ONAY T, YENIGUN O. Comparison of aerobic and anaerobic degradation of municipal solid waste in bioreactor landfills[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99(13): 5418-5426 doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2007.11.008 HECHAM O, SOHRAB R. The mathematical model of the conversion of a landfill operation from anaerobic to aerobic[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2017, 50: 53-67 doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2017.05.020 ÖNCÜ G,REISER M,KRANERT M. Aerobic in situ stabilization of landfill konstanz dorfweiher:leachate quality after 1 year of operation[J]. Waste Management,2012,32(12): 2374-2384 SANG N N, SODA S, INOUE D, et al. Effects of intermittent and continuous aeration on accelerative stabilization and microbial population dynamics in landfill bioreactors[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2009, 108(4): 336-343 doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2009.04.019 CLÉMENT R, OXARANGO L, DESCLOITRES M. Contribution of 3-D time-lapse ERT to the study of leachate recirculation in a landfill[J]. Waste Management, 2011, 31(3): 457-467 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2010.09.005 WHITE J K, BEAVEN R P, POWRIE W, et al. Leachate recirculation in a landfill:some insights obtained from the development of a simple 1-D model[J]. Waste Management, 2011, 31(6): 1210-1221 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2010.10.022 邱忠平, 刘洋, 刘源月, 等. 好氧生物反应器填埋场快速稳定的关键技术: 中国, 201510111362.2[P], 2015-03-13 水与废水监测分析方法编委会. 水与废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2003: 38, 210-213 周效志,桑树勋,程云环,等. 城市生活垃圾可生物降解有机质成分的测定[J]. 环境监测管理与技术,2007,19(2): 30-34 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2007.02.009ZHOU Xiaozhi, SANG Shuxun, CHENG Yunhuan, et al. The method for determination of biodegradable organic substances in domestic garbage[J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2007, 19(2): 30-34 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2007.02.009 唐建,邱忠平,海维燕,等. 城市生活垃圾中纤维素含量测定方法优化[J]. 环境工程学报,2011,5(11): 2615-2618TANG Jian, QIU Zhongping, HAI Weiyan, et al. Optimization of determination conditions for cellulose content of municipal solid waste[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2011, 5(11): 2615-2618 蒋建国,张唱,黄云峰,等. 垃圾填埋场稳定化评价参数的中试实验研究[J]. 中国环境科学,2008(1): 58-62 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2008.01.013JIANG Jianguo, ZHANG Chang, HUANG Yunfeng, et al. Pilot experiment on evaluation parameters of landfill stabilization process[J]. China Environmental Science, 2008(1): 58-62 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2008.01.013 邱忠平,刘洋,连红民,等. 温度对好氧生物反应器填埋场稳定化进程的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2013,48(3): 574-579QIU Zhongping, LIAN Hongmin, LIU Yang, et al. Effect of temperature on stabilizing process of aerobic bioreactor landfill[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013, 48(3): 574-579 -




 下载:
下载: