Hierarchical Energy Management for Electric-Hydrogen Island Direct Current Micro-grid
-
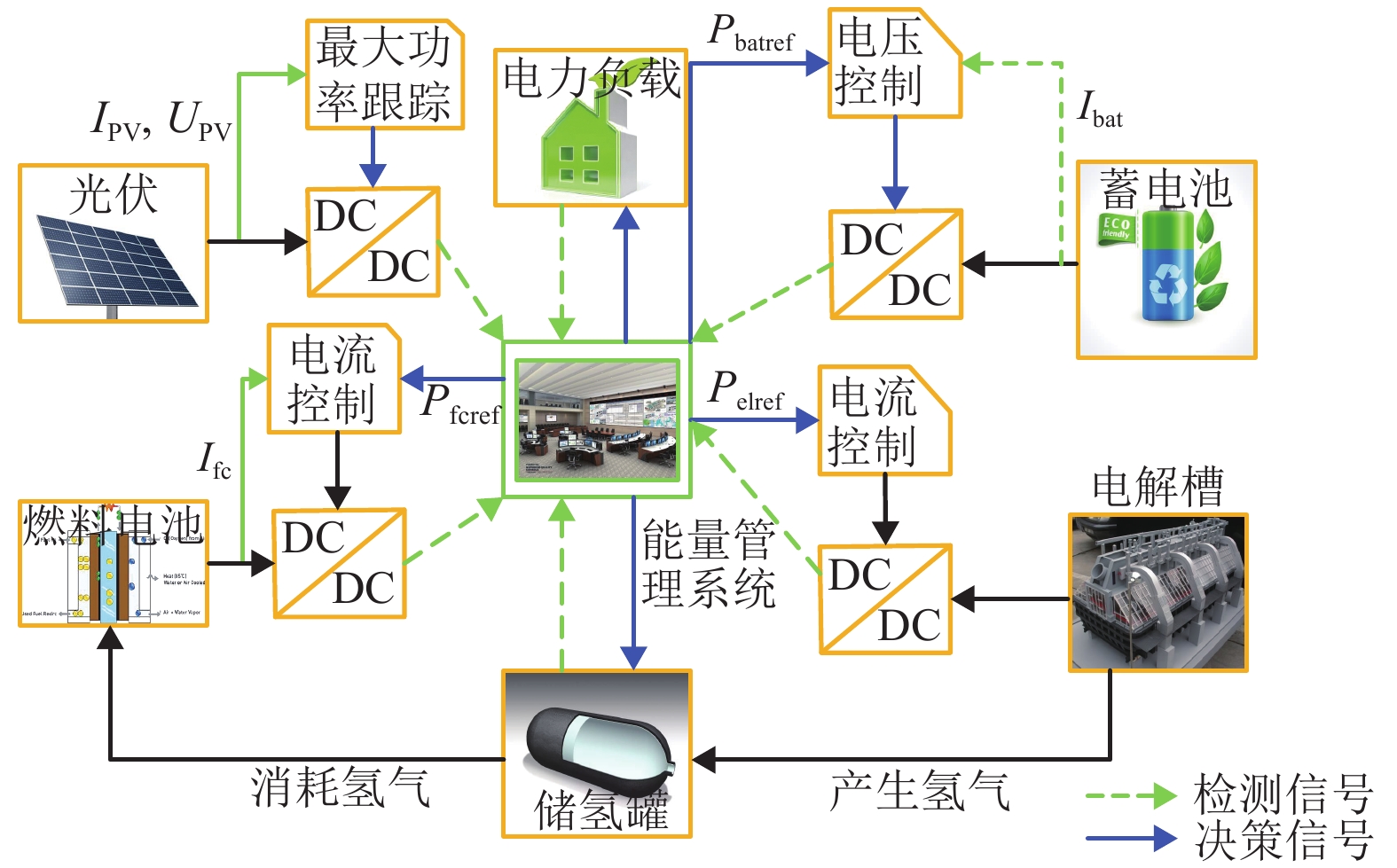
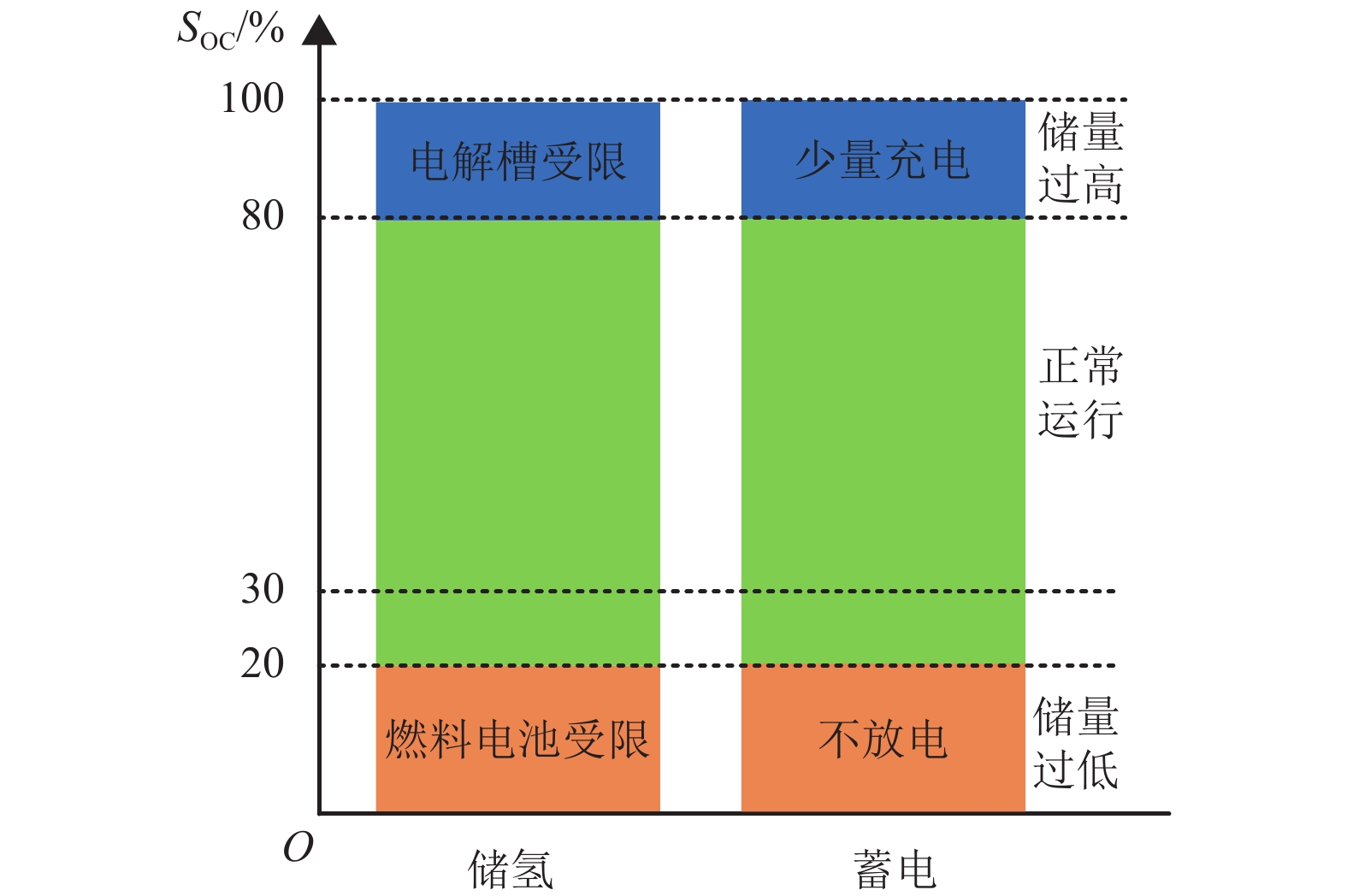
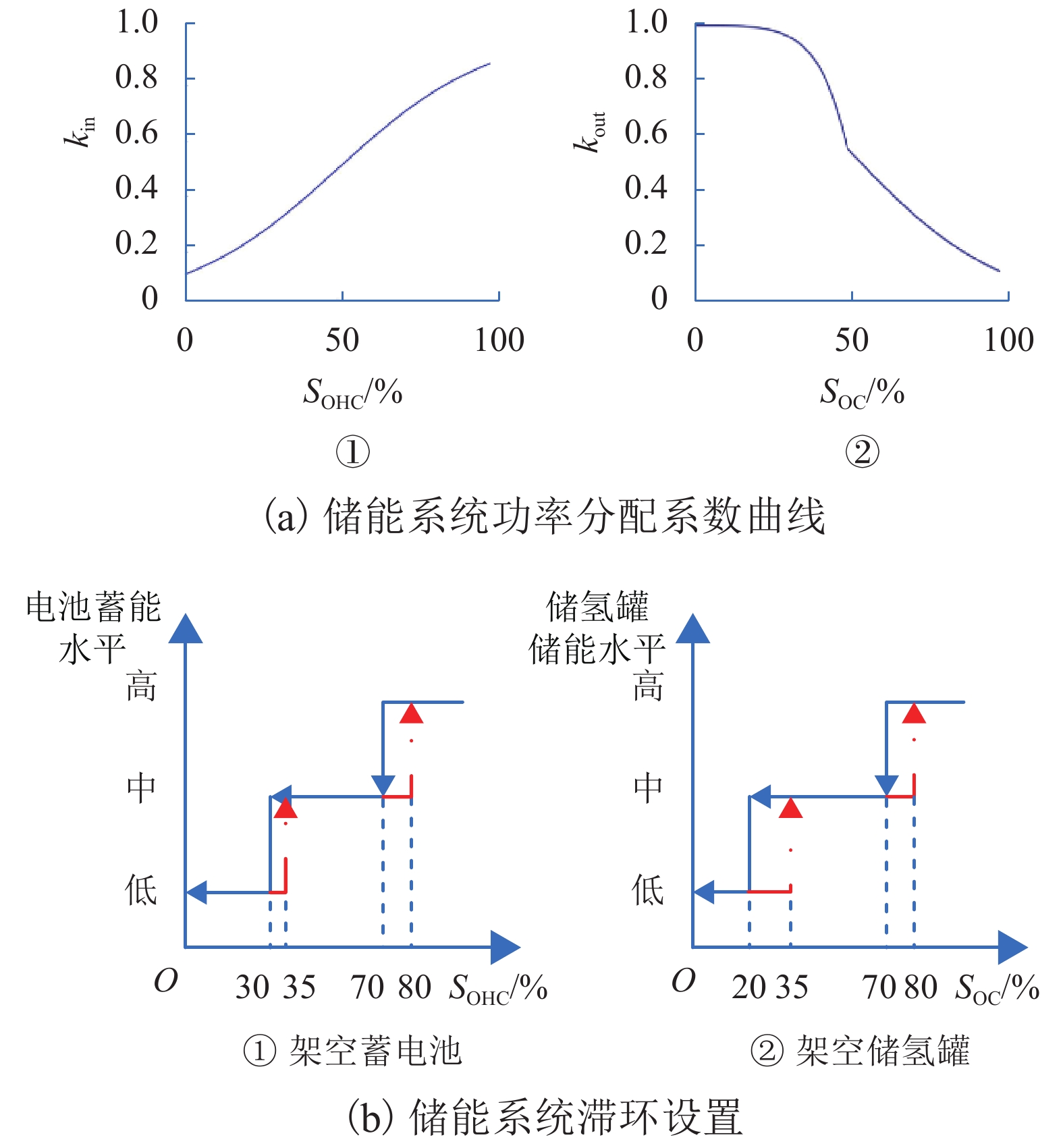
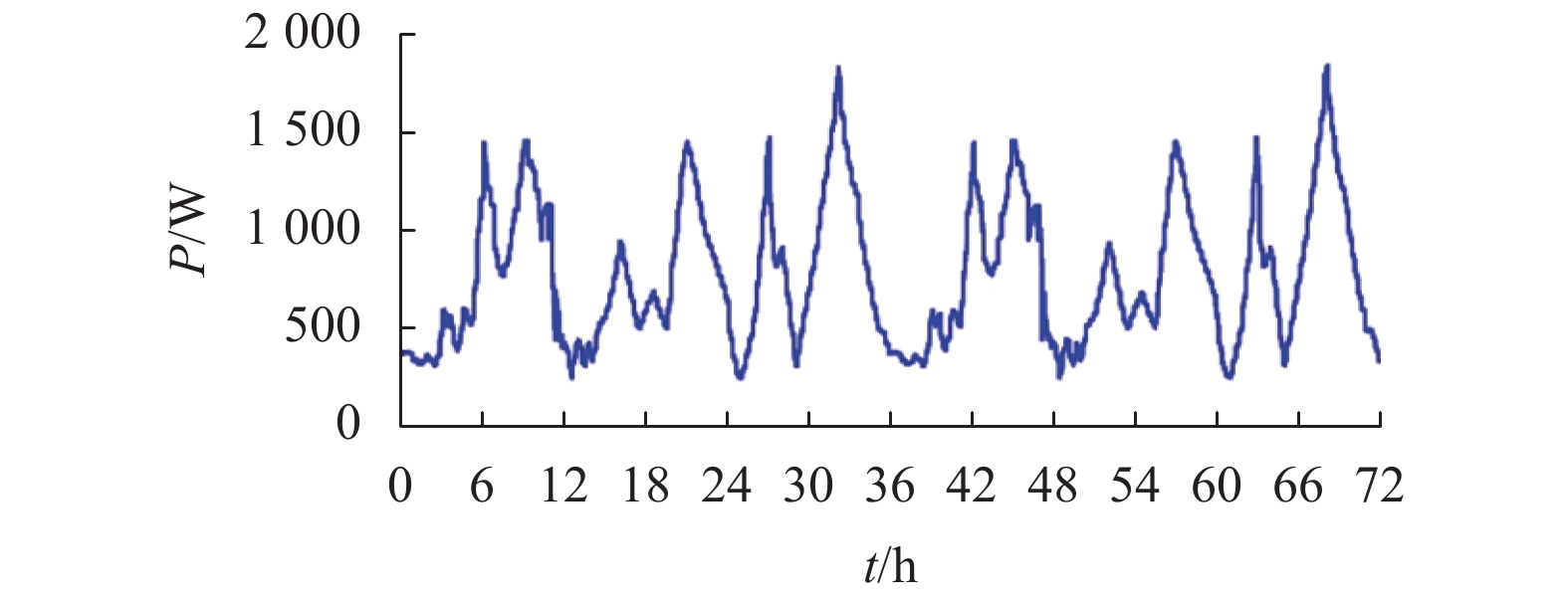
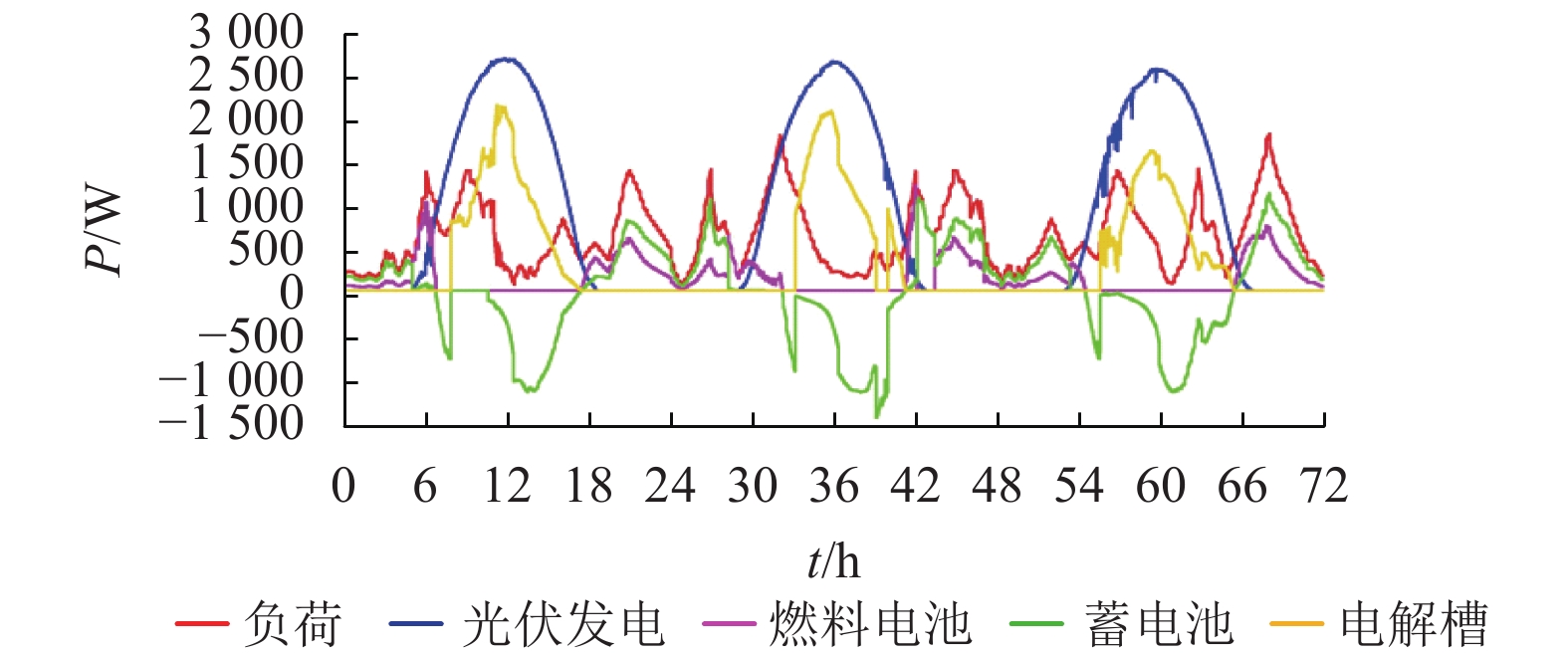
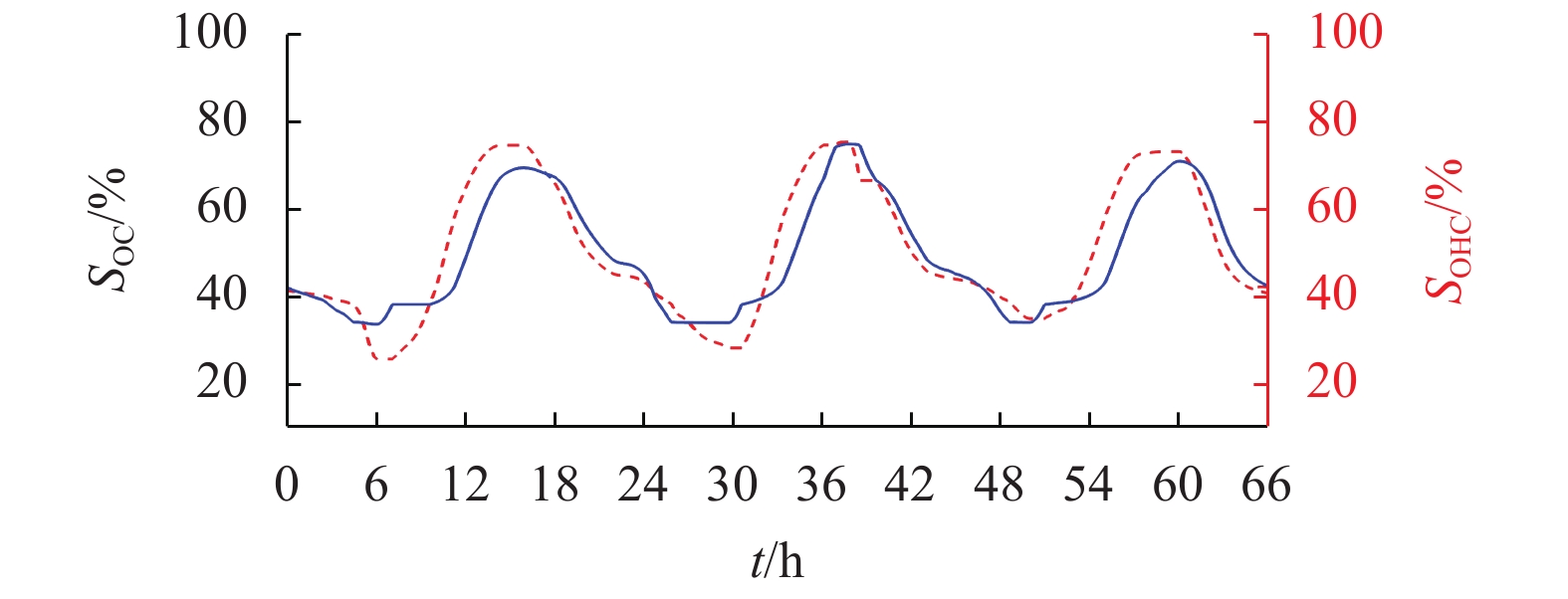
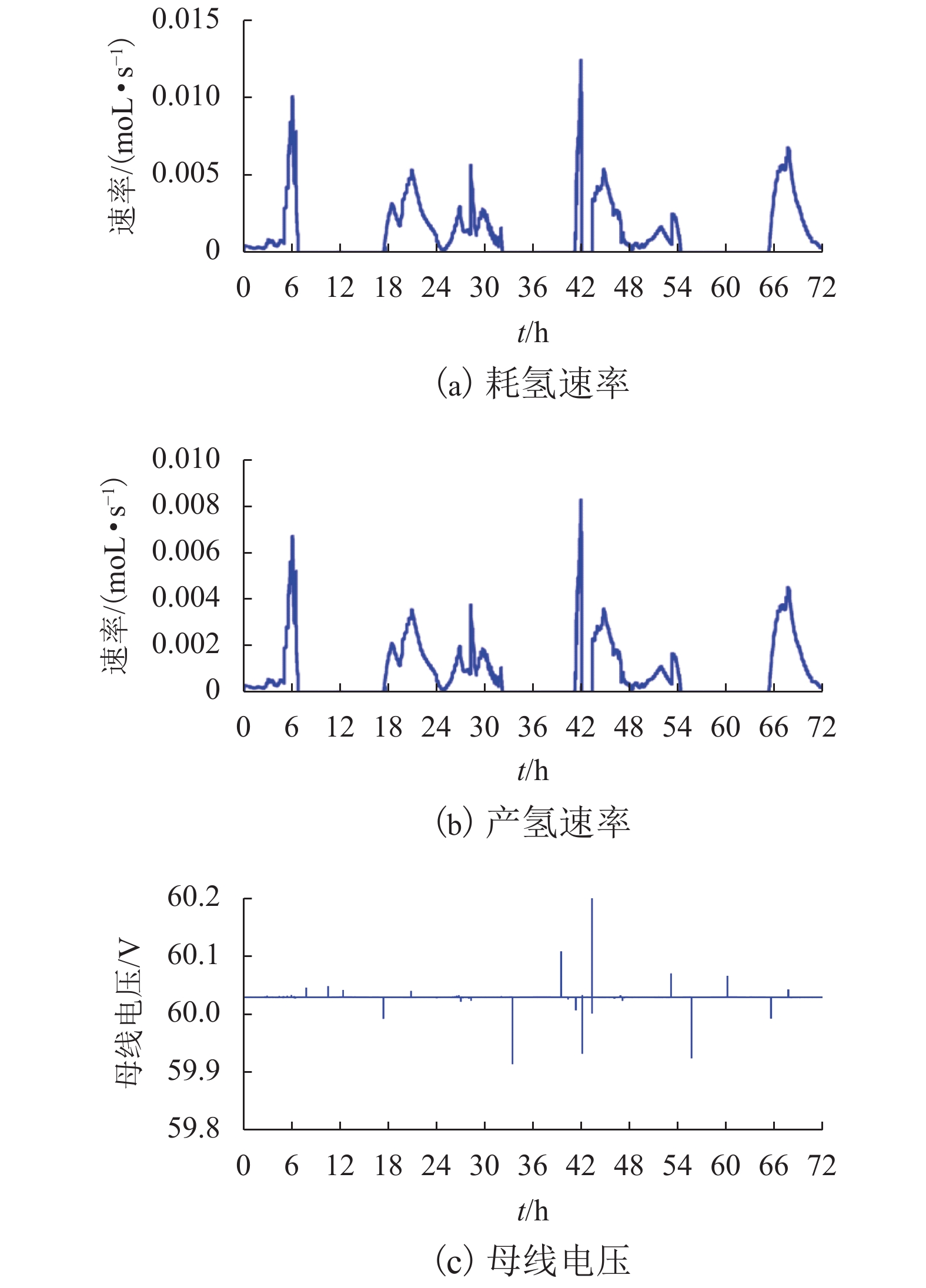
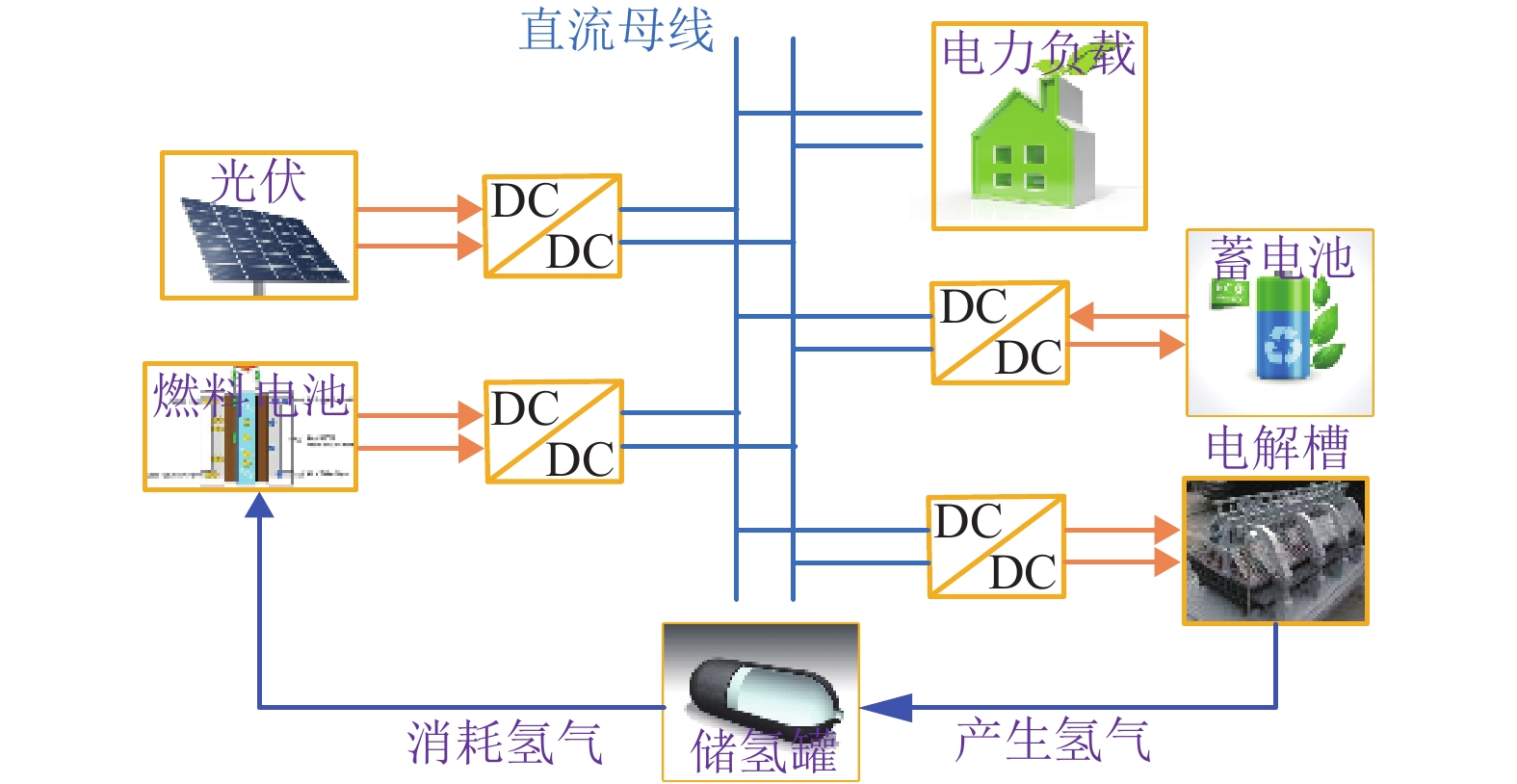
摘要: 为了实现电-氢混合储能微电网的控制与运行,提出一种该类孤岛直流微电网的全天候能量管理方法,在满足负载需求功率、控制母线电压的基础上,将微网多余电能向化学能及氢能转化,且将储存的能量通过燃料电池及蓄电池适时运用于微网功率缺额的情况;通过对各电源、负载设备DC/DC变换器控制以及管理层的协调控制,实现了该系统的能量管理;基于MATLAB/Simulink软件平台,验证了该文能量管理方法的有效性. 研究结果表明:电-氢微电网在运行过程中母线电压波动幅度小于0.33%,远小于5.00%的运行要求;锂电池等效荷电状态及储氢罐等效荷电状态初末值变化幅度分别为4.0%和0.2%,储能系统运行稳定;该能量管理方法能够在保持电-氢系统稳定运行的前提下,无需外界提供额外能量即可确保该系统的全天候正常运行.Abstract: In order to realize the control and operation of the electric-hydrogen hybrid energy storage micro-grid, an all-weather energy management method for the kind of island direct current (DC) micro-grid was proposed. The energy management method based on meeting the power demand of the load and controlling the bus voltage, and the method aimed to converse the surplus power from the micro-grid to chemical energy and hydrogen energy and released the energy timely through fuel cells and batteries. By the control of the coordination of the management layer and the DC/DC converter of the power and loading equipment, the energy management was realized. The effectiveness of the energy management method was verified based on the Matlab/Simulink software platform. The results show that the fluctuation of bus voltage is less than 0.33% which is far below the operation requirement of 5.00%, and the differences between the initial and final value of state of charge and state of hydrogen charge is 4.0% and 0.2%, respectively, the storage system operates stably. The energy management method can ensure the stability of the energy storage system and keep all-weather running without additional energy.
-
Key words:
- direct current micro-grid /
- energy management /
- hydrogen storage /
- electric storage /
- fuel cell
-
表 1 微源参数
Table 1. Parameters of micro sources
微源 参数 数值 锂电池 容量/(A•h) 300 SOC 初值/% 40 最大功率/W ± 1 500 储氢罐 体积/L 18 最大压强/MPa 35 SOHC 初值/% 39.0 电解槽 最大功率/W 2 500 燃料电池 最大功率/W 1 260 输出电压/V 24 -
REZAEI M, MOHSENI M. A predictive control based on neural network for dynamic model of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Journal of Fuel Cell Science and Technology, 2013, 10(3): 035001. AGBOSSOU K, KOLHE M, HAMELIN J, et al. Performance of a stand-alone renewable energy system based on energy storage as hydrogen[J]. IEEE Trans Energy Convers, 2004, 19(3): 633-640. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2004.827719 MEHRPOOYA M. Dynamic modeling of a hybrid Photovoltaic system with hydrogen/air PEM fuel cell[J]. Iranica Journal of Energy & Environment, 2013, 4(2): 4-9. UZUNOGLU M, ONAR O C, ALAM M S. Modeling,control and simulation of a PV/FC/UC based hybrid power generation system for stand-alone applications[J]. Renew Energy, 2009, 34(3): 9-20. KRAA O, GHODBANE H, SAADI R, et al. Energy management of fuel cell/supercapacitor hybrid source based on linear and sliding mode control[J]. Energy Procedia, 2015, 74(12): 58-64. REKIOUA D, BENSMAIL S, BETTAR N. Development of hybrid photovoltaic-fuel cell system for stand-alone application[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(3): 4-11. 张计科,王生铁. 独立运行风光互补发电系统能量优化管理协调控制策略[J]. 太阳能学报,2017,38(10): 2894-2903.ZHANG Jike, WANG Shengtie. Coordinated control strategy with energy optimum management of stand-alone wind/pv hybrid generation system[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2017, 38(10): 2894-2903. HAN Ying, CHEN Weirong, LI Qi. Energy management strategy based on multiple operating states for a photovoltaic/fuel cell/energy storage DC microgrid[J]. Energies, 2017, 136(10): 1-15. 蔡国伟,孔令国,彭龙,等. 基于氢储能的主动型光伏发电系统建模与控制[J]. 太阳能学报,2016,37(10): 2451-2459. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0096.2016.10.001CAI Guowei, KONG Lingguo, PENG Long, et al. Modeling and control of active PV generation system based on hydrogrn storage[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2016, 37(10): 2451-2459. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0096.2016.10.001 王天宏,李奇,陈维荣. 负载均流的自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(5): 1020-1028. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.05.025WANG Tianhong, LI Qi, CHENG Weirong. Adaptive virtual impedance droop control method in load sharing[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(5): 1020-1028. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.05.025 IPSAKIS D, VOUTETAKIS S, PANOS S, et al. Power management strategies for a stand-alone power system using renewable energy sources and hydrogen storage[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(16): 7081-7095. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.06.051 LAJNEF T, ABID S, AMMOUS A. Modeling,control,and simulation of a solar hydrogen/fuel cell hybrid energy system for grid-connected applications[J]. Advances in Power Electronics, 2013(4): 1-9. NASRI S, SLAMA B S, ADNANE C. Power management strategy for hybrid autonomous power system using hydrogen storage[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(2): 857-865. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.11.085 NASRI S, SLAMA B S, YAHYAOUI I, et al. Autonomous hybrid system and coordinated intelligent management approach in power system operation and control using hydrogen storage[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(15): 9511-9523. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.01.098 MARCHENKO O V, SOLOMIN S V. Modeling of hydrogen and electrical energy storages in wind/PV energy system on the Lake Baikal coast[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(15): 9361-9370. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.02.076 李奇,杨寒卿,韩莹,等. 光伏并网发电系统参数协调优化方法研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(5): 894-901. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.011LI Qi, YANG Hanqing, HAN Ying, et al. Method of parameter coordination optimization for grid-connected photovoltaic system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5): 894-901. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.011 KHAN M J, IQBAL M T. Dynamic modeling and simulation of a small wind-fuel cell hybrid energy system[J]. Renewable Energy, 2005, 30(3): 421-439. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2004.05.013 HAN Ying, LI Qi, WANG Tianhong, et al. Multisource coordination energy management strategy based on SOC consensus for a PEMFC-battery-supercapacitor hybrid tramway[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(1): 296-305. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2747135 MARUF-UL-KARIM M, IQBAL M T. Dynamic modeling and simulation of alkaline type electrolyzers[C]//Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2009: 711-715. -




 下载:
下载: