Seismic Collapse-Resistant Performance of Stone Houses in Tibetan and Qiang Autonomous Prefectures of Western Sichuan
-
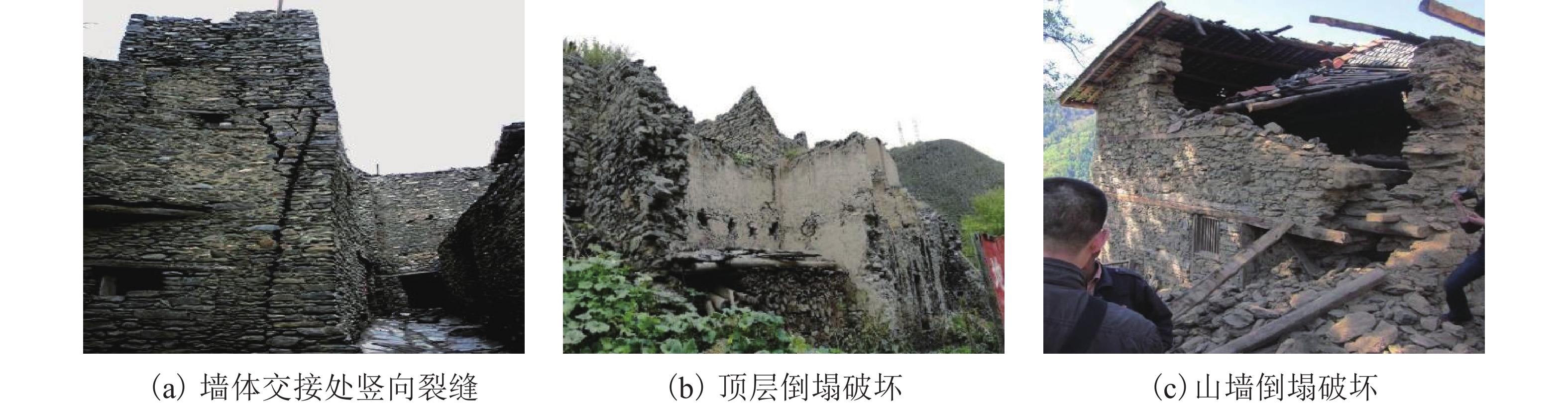
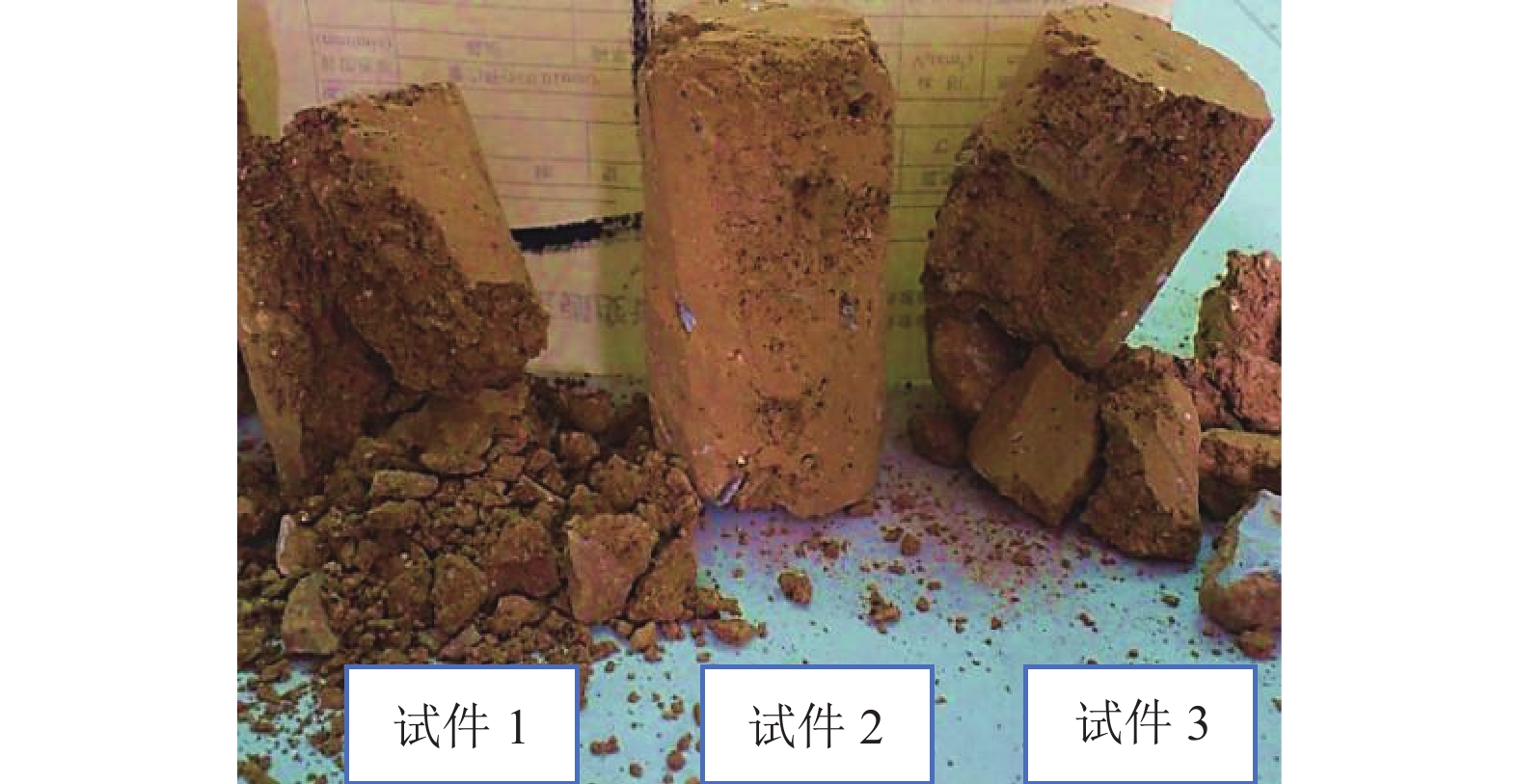
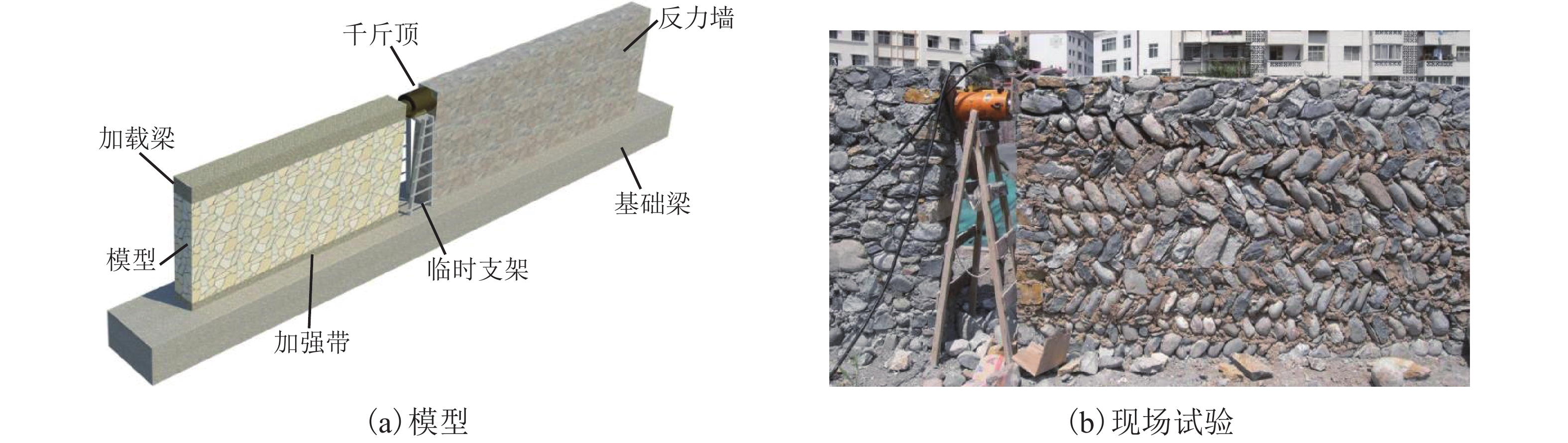
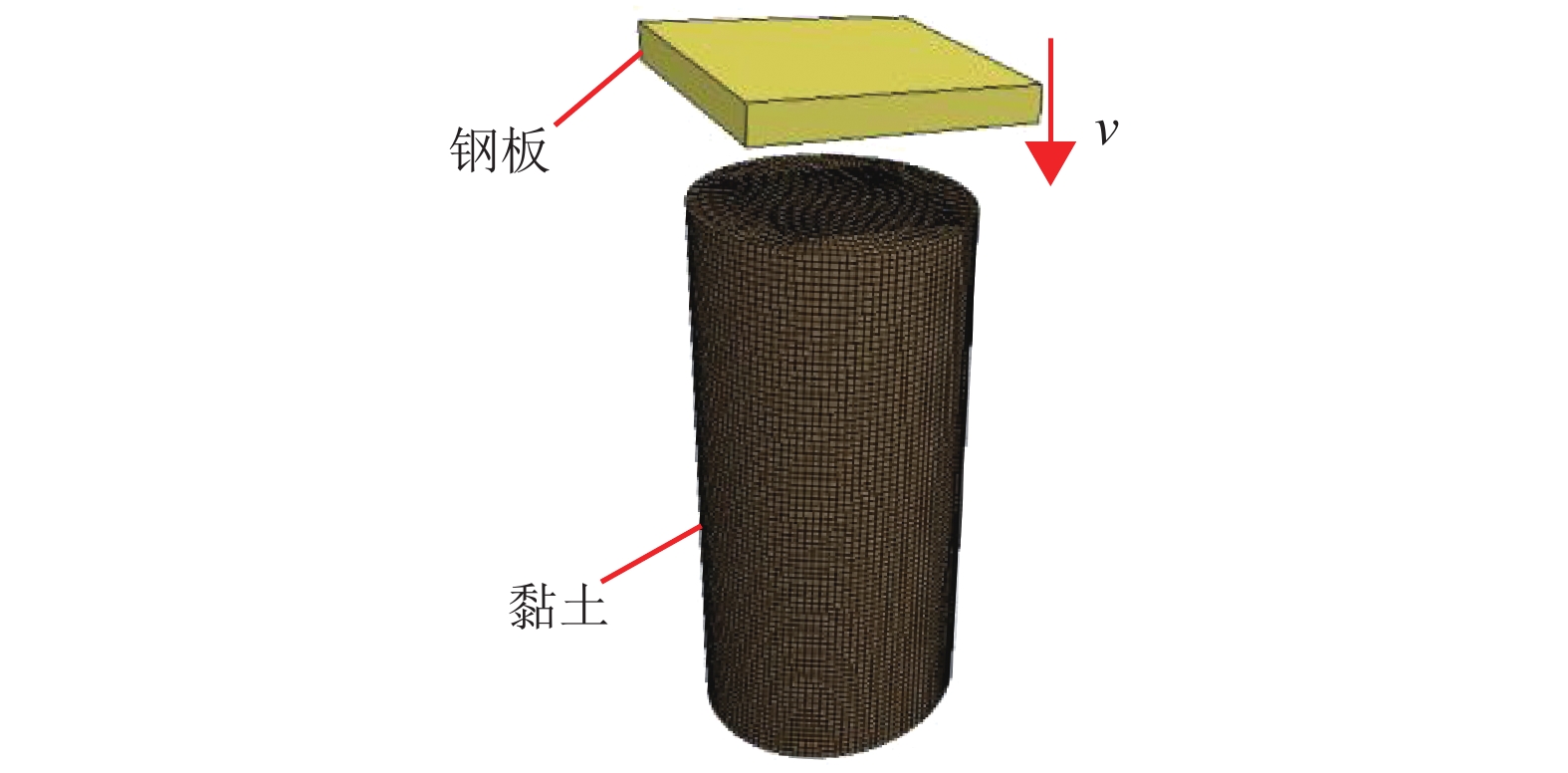
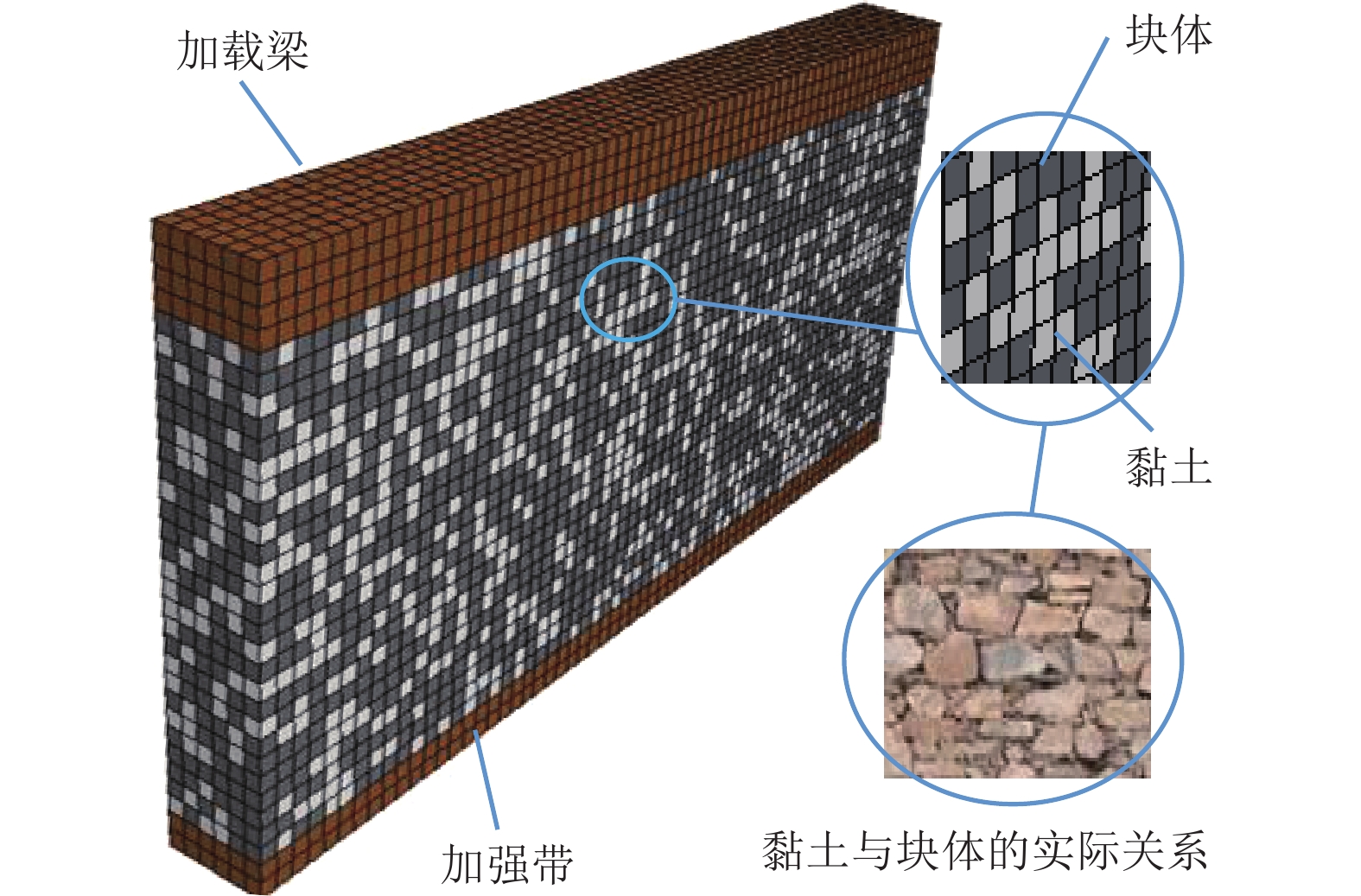
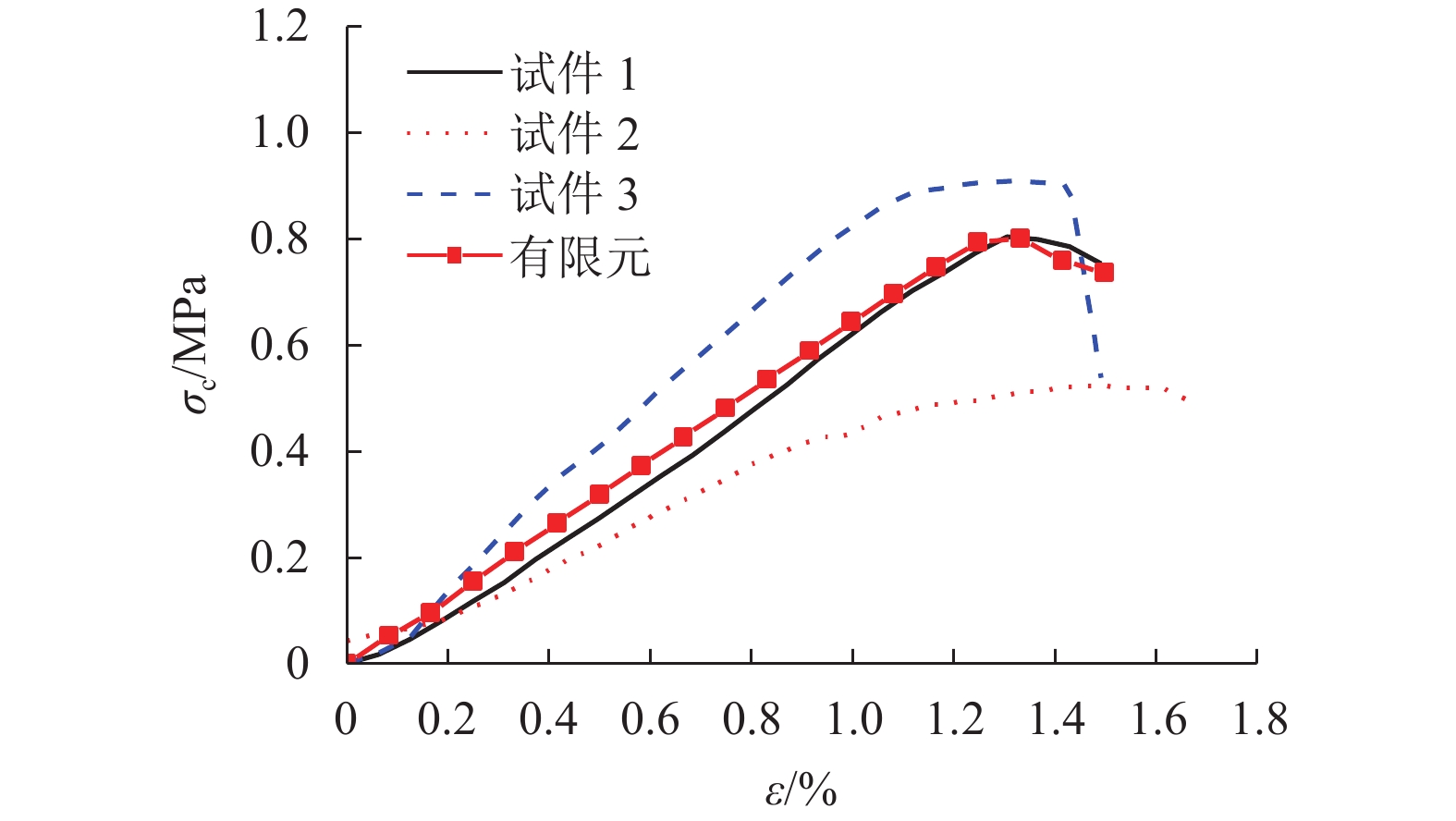
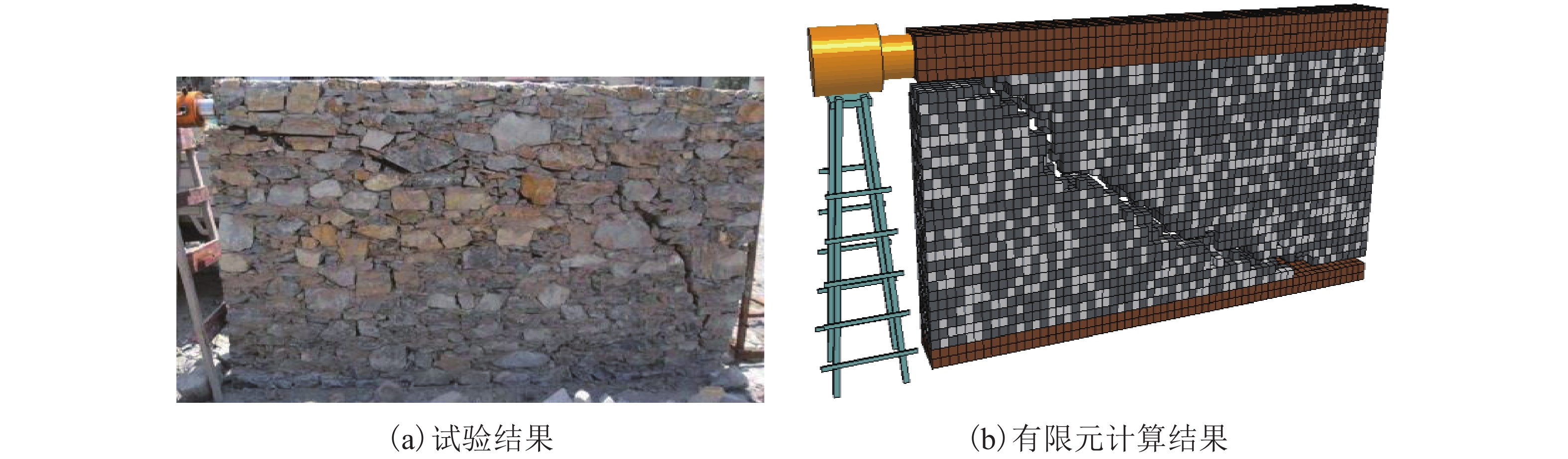
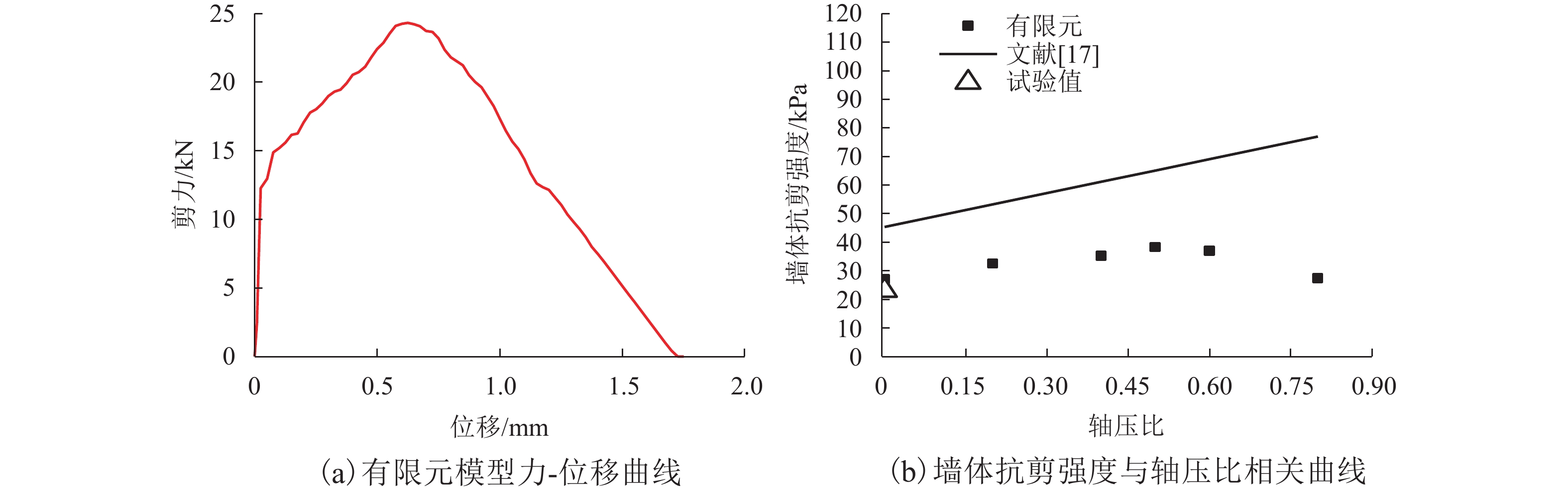
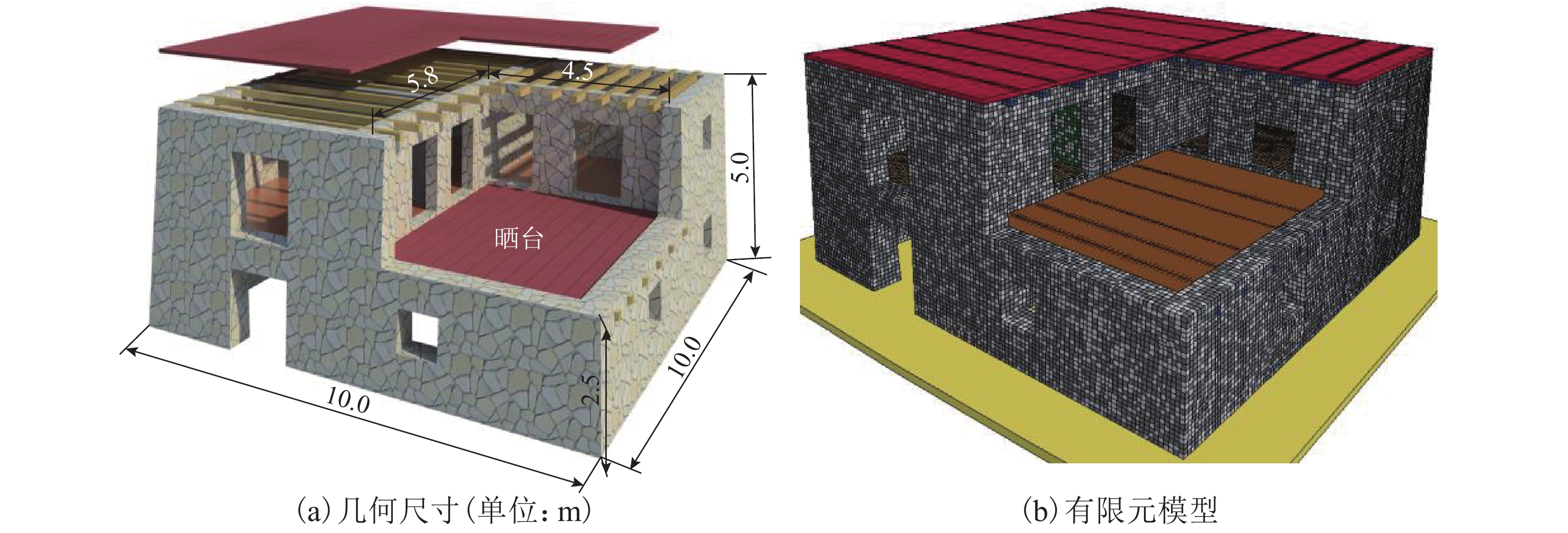
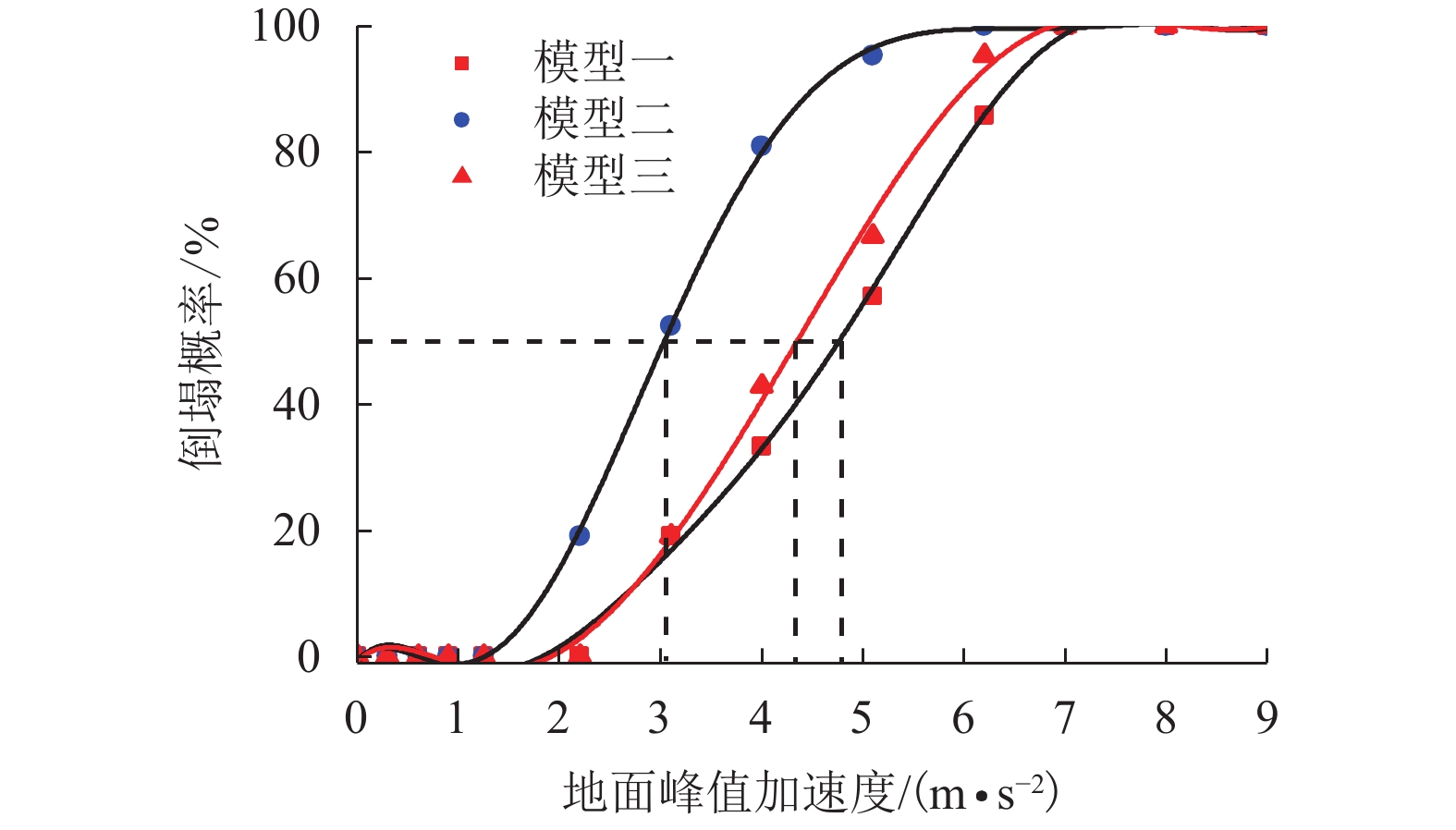
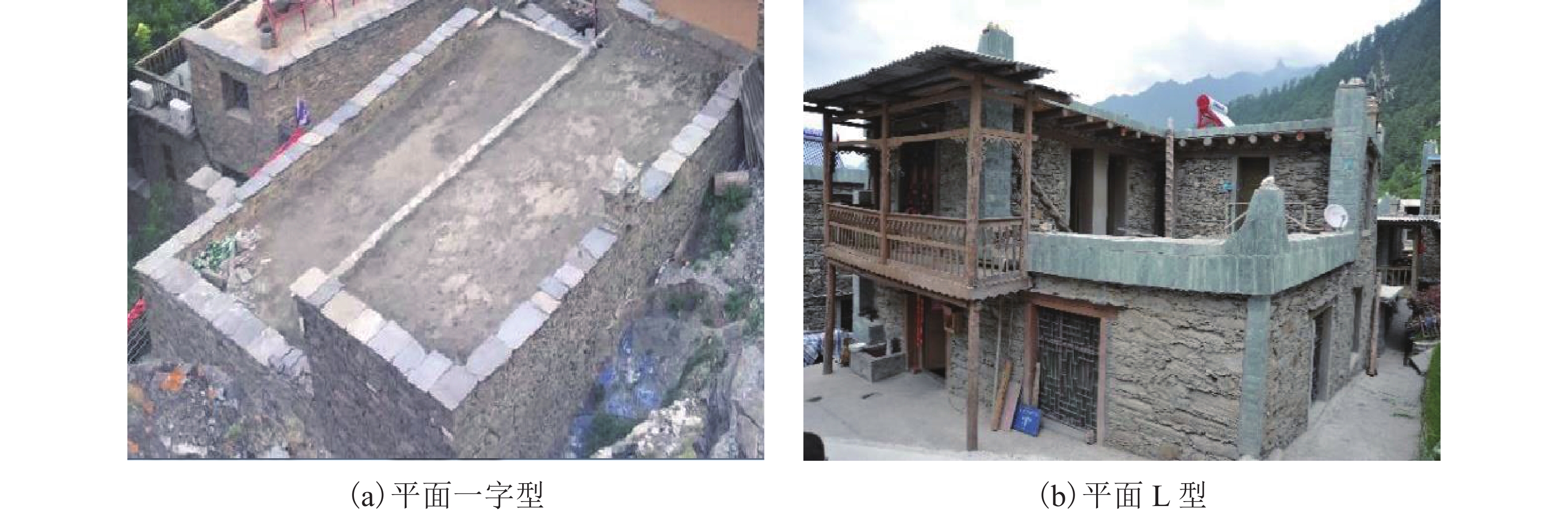
摘要: 我国川西地区的传统藏羌石砌民居具有较高的文化遗产保护价值,但在近年来的历次地震中出现了大量破坏. 结合该类房屋的砌筑材料和建筑布置特征,对其抗地震倒塌性能进行研究. 首先,开展了3组黏土试件的无侧限抗压强度试验和一个1/2缩尺黏土-石砌墙体试件的水平抗剪承载力试验,并通过显式动力数值计算手段对试验过程进行模拟;其次,针对黏土和毛石材料均采用Holmquist-Johnson-Cook (HJC)本构模型,基于随机分布离散型有限元方法,根据实际墙体中两种材料的分布比例建立相应数值模型,并通过与模型试验结果的对比验证,明确了数值计算中的关键参数;在此基础上,对一典型二层平面L型缩进式民居结构进行动力时程分析计算,通过与实际震害情况的对比分析了其地震破坏机制,再现了地震倒塌全过程,并开展了结构的抗地震倒塌易损性分析,研究了不同晒台缩进面积的影响. 研究结果表明,在罕遇烈度下,平面L型缩进式结构中晒台面积比例由30%增加至45%时,结构倒塌概率增大16.7%,抗倒塌储备系数下降9%,对易损性曲线影响并不显著;但当晒台面积比例减小至15%时,二层墙体开洞率增大18%,导致结构的地震倒塌概率增加143%.
-
关键词:
- 砌体结构 /
- 民居碉房 /
- 随机分布离散型有限元模型 /
- 抗震性能 /
- 易损性分析
Abstract: Traditional stone houses in the Tibetan and Qiang autonomous prefectures of Western Sichuan, deserve preservation as indicators of cultural heritage; however many of them have been damaged during earthquakes in recent years. Based on the characteristics of masonry materials and architectural layout, seismic collapse-resistant performance of stone houses was investigated. Unconfined compression tests on three clay specimens and lateral shear tests on a half-scaled clay-brick rubble masonry wall specimen were conducted and also modeled via an explicit dynamic numerical approach. The Holmquist–Johnson–Cook (HJC) constitutive model was applied to the clay and rubble, and a randomly-distributed discrete finite element model was built to show the proportion between clay and brick rubble. Through the comparison of experimental and numerical results, the numerical model was verified and key parameters were calibrated. According to above work, a structural model of a typical two-storey residential stone house with an L-shaped indented platform was built, and its dynamic time-history analysis was conducted. By comparing the calculated seismic damage modes with its real seismic damage, the collapse mechanism was analyzed and the collapse process was simulated. Moreover, the structural fragility of seismic collapse was studied based on the influence of the indented area of the platform. The results indicate that, under rare seismic intensity, when the indented area is increased from 30% to 45%, the probability of structural collapse increases by 16.7%, and the collapse margin ratio decreases by 9%, which has little effect on the fragility curve. However, when the indented area is reduced to 15%, the failure rate of walls on the second floor increases by 18%, leading to the increase of 143% in the probability of structural collapse. -
表 1 HJC本构模型参数
Table 1. Key parameters of HJC constitutive model
参数 黏土 毛石 参数 黏土 毛石 ρ/(kg•m–3) 1 750 2 800 Smax 7 20 G/MPa 71.4 1 357 Pcrush/MPa 1.19 81.5 A 0.79 0.55 μcrush/× 10–3 3.57 12.9 B 1.6 1.23 PLock/GPa 2 2 C/× 10–3 7 9.7 μLock/× 10–1 1.74 1.74 N 0.61 0.89 D1/× 10–2 4.87 4 f’c/MPa 0.99 67.92 D2 1 1 T/MPa 0.042 2 K1/MPa 85 39 ε0/× 10–6 1 1 K2/MPa –171 –223 εf,min 0.01 0.01 K3/MPa 208 550 -
林建华,王全凤,施养杭. 石砌体结构抗震性能及其模糊抗震可靠度的研究[J]. 土木工程学报,1998,31(6): 40-48.LIN Jianhua, WANG Quanfeng, SHI Yyanghang. Study on the seismic behaviour and fuzzy earthquake-resistant reliability of stone masonry structures[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 1998, 31(6): 40-48. 张淑娴. 粗料石砌体房屋振动台试验研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2015 陶毅,古金本,信任,等. CFRP网格加固震损多层砌体开洞墙体的抗震性能研究[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 网络优先出版. (2018-05-22)[2018-08-01]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.U.20180522.2227.006.htmlTAO Yi, GU Jinben, XIN Ren, et al. Seismic performance of multi-storey masonry wall with opening repaired using CFRP grid[J/OL]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, Network Priority Publishing. (2018-05-22) [2018-08-01]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.U.20180522.2227.006.html 徐学书,喇明英. 羌族传统建筑抗震技术及其传承研究[J]. 西南民族大学学报(人文社科版),2009(2): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3926.2009.02.003 孙建刚,崔利富,王振,等. 藏族民居砌体材料物理力学性能试验研究[J]. 大连民族学院学报,2015,17(1): 61-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-315X.2015.01.016SUN Jiangang, CUI Lifu, WANG Zheng, et al. Experiment research of stone masonry materials physical mechanic property of Tibetan folk house[J]. Journal of Dalian Nationalities University, 2015, 17(1): 61-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-315X.2015.01.016 杨惠晴. 藏族民居抗震性能数值仿真分析——以木堆藏寨194号为例[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2014 刘伟兵,崔利富,孙建刚,等. 藏族民居石砌体基本力学性能试验与数值仿真[J]. 大连民族学院学报,2015,17(3): 252-256. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-315X.2015.03.015LIU Weibing, CUI Lifu, SUN Jiangang, et al. Tests and numerical simulation of basic mechanical properties of Tibetan dwellings stone masonry[J]. Journal of Dalian Nationalities University, 2015, 17(3): 252-256. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-315X.2015.03.015 张先进. 汶川大地震对藏、羌村寨聚落的破坏与恢复思考[C]//中国民族建筑研究会学术年会暨第二届民族建筑(文物)保护与发展高峰论坛. 北京: 中国民族建筑研究会, 2008: 171-174 中华人民共和国水利部. 土工试验方法标准: GB/T 50123—1999[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 1999 苗吉军,顾祥林,张伟平,等. 地震作用下砌体结构倒塌反应的数值模拟计算分析[J]. 土木工程学报,2005,38(9): 45-49. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2005.09.008MIAO Jijun, Gu Xianglin, Zhang Weiping, et al. Numerical simulation analysis for the collapse response of masonry structures under erthquakes[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2005, 38(9): 45-49. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2005.09.008 许浒,李勇志,雷敏,等. 群落生土建筑的抗地震倒塌加固措施[J]. 工程抗震与加固改造,2017,39(1): 135-142.XU Hu, LI Yongzhi, LEI Min, et al. A strengthening measure for seismic collapse resistance of the residential[J]. Earthquake Resistant Engineering And Retrofitting, 2017, 39(1): 135-142. 李耀. 混凝土HJC动态本构模型的研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2016 陕西省建筑科学研究院. 建筑砂浆基本性能试验方法标准: JGJ/T 70—2009[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1999 方秦,孔祥振,吴昊,等. 岩石Holmquist-Johnson-Cook模型参数的确定方法[J]. 工程力学,2014,31(3): 197-204.FANG Qin, KONG Xiangzhen, WU Hao, et al. Determination of Holmquist-Johnson-Cook constitutive model parameters of rock[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 31(3): 197-204. 于文. 新疆喀什生土石房屋模型振动台试验研[D]. 北京: 中国建筑科学研究院, 2007 甄昊. 阿坝州生土石砌体结构在地震作用下的抗倒塌分析[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016 工程地质手册编写委员会, 工程地质手册[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1992: 214-216 施景勋,卢志红,林建华,等. 对石墙抗震性能的研究和设计取值的建议[J]. 华侨大学学报(自然科学版),1993,14(2): 197-198.SHI Jingxun, LU Zhihong, LIN Jianhua, et al. Syudy on the antiseismic behavior of stone wall and proposal of the short-cut process in its design[J]. Journal of Huaqiao University (Natural Science), 1993, 14(2): 197-198. 余卓群. 四川藏寨传统住宅述略[C]//中国民族聚居区建筑文化遗产国际研讨会论文集. 成都: [出版者不详], 2010: 119-123 朱荣张. 马尔康直波藏寨民居建筑研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2012 孙玉红,聂立武,韩古月,等. 地震作用下建筑结构倒塌失效准则分析[J]. 中外建筑,2011,35(18): 199-201.SUN Yuhong, NIE Liwu, HAN Guyue, et al. Analysis on the rules of architecture structure tumble invalidation earthquake function[J]. Chinese and Overseas Architecture, 2011, 35(18): 199-201. 焦双健,冯启民,付长文,等. 钢筋混凝土框架结构地震破坏的计算机模拟方法[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,2002,22(2): 54-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1301.2002.02.009JIAO Shuangjian, FENG Qimin, FU Changwen, et al. Simulation method for earthquake damage to RC frames[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2002, 22(2): 54-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1301.2002.02.009 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑抗震设计规范: GB50011—2010[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2010 FEMA. NEHRP guidelines for seismic rehabilitation of builidings[R]. FEMA Report 273. Washington D. C.: Federal Emergency Management Agency, 1997: 2-10, 2-13 李吉,刘如山,越潇. 结构抗震破坏准则研究综述[J]. 世界地震工程,2015,31(1): 262-263.LI Ji, LIU Rushan, YUE Xiao. Research summary of seismic failure criteria for structures[J]. World Earthquake Engineering, 2015, 31(1): 262-263. 许浒, 余志祥, 康翔杰, 等. 多层砌体结构在地震中倒塌全过程数值模拟[J]. 建筑结构, 2012, 42(增刊1): 223-224XU Hu, YU Zhixiang, KANG Xiangjie, et al. Numerical simulation on collapse process of multistory masonry structure in earthquake[J]. Building Structure, 2012, 42 (S1): 223-224 Applied Technology Council. Quantification of building seismic performance factors: FEMA P695[R]. Washington D. C., Federal Emergency Management Agency, 2009. 陆新征,叶列平. 基于IDA分析的结构抗地震倒塌能力研究[J]. 工程抗震与加固改造,2010,32(1): 13-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8412.2010.01.003LU Xinzheng, YE Lieping. Study on the sesmic collapse resistance of structural system[J]. Earthquake Resistant Engineering and Retrofitting, 2010, 32(1): 13-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8412.2010.01.003 施炜,叶列平,陆新征,等. 不同抗震设防RC框架结构抗倒塌能力的研究[J]. 工程力学,2011,28(3): 42-43.SHI Wei, YE Lieping, LU Xinzheng, et al. Study on collapse-resistant capacity of RC frames with different sesmic fortification levels[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2011, 28(3): 42-43. -





 下载:
下载: