Influences of Foreign Object Damage on Fatigue Strength of 25CrMo4 Axle Alloy Steel
-
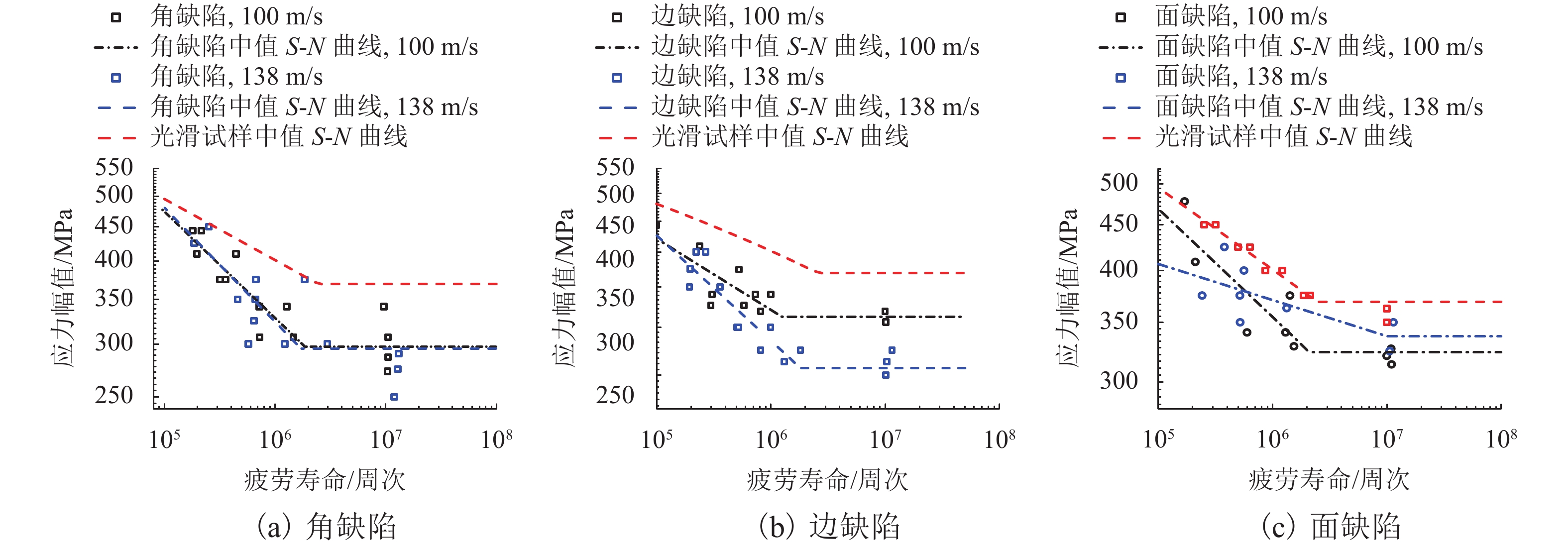
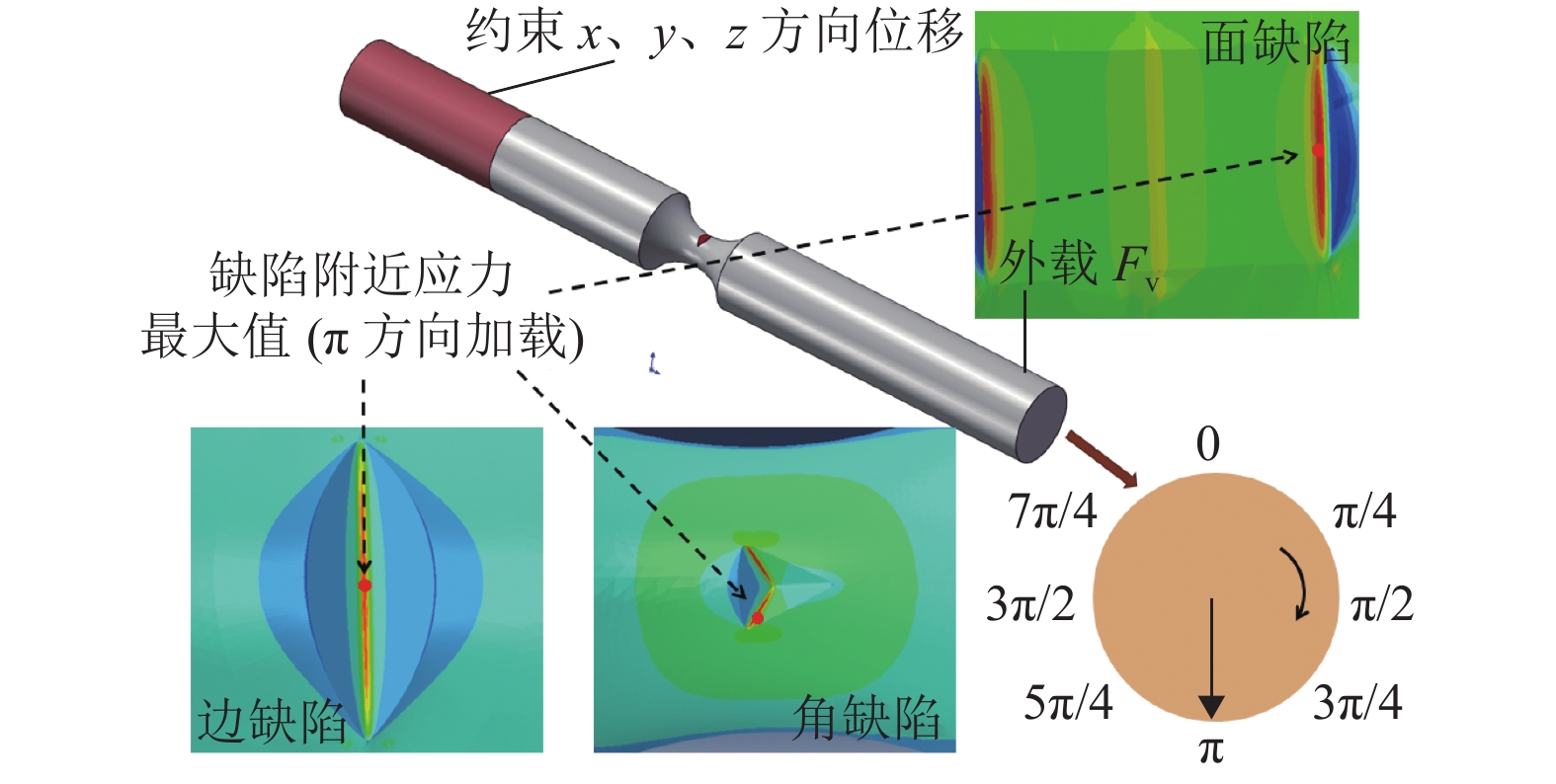
摘要: 为研究外物损伤(FOD)与25CrMo4钢疲劳性能的关联,采用空气炮装置开展高铁车轴钢试样的FOD模拟试验. 首先于试样表面预制FOD缺陷;其次,通过旋转弯曲疲劳试验获得光滑试样和含FOD试样的应力-疲劳寿命(S-N)曲线;同时,基于有限元方法估算不同缺陷试样的应力集中系数,结合Peterson公式预测疲劳缺口系数(FNC)和疲劳极限. 研究结果表明:FOD车轴钢试样的疲劳性能明显低于光滑试样,冲击速度越高,疲劳性能越低;其中边缺陷的疲劳缺口系数最大为1.52,面缺陷最小,约为1.14,但疲劳寿命分散性较大;与试验结果相比,仿真模拟和理论计算可获得更低(偏于保守)的疲劳强度估算值.
-
关键词:
- 外物损伤 /
- 铁路车轴 /
- 疲劳极限 /
- Peterson公式 /
- 疲劳裂纹萌生
Abstract: To study the correlation between the foreign object damage (FOD) and the fatigue strengh of alloy steel 25CrMo4, the simulated test for FOD of high speed railway axle steel specimens was carried out by a compressed-gas gun device. Firstly, the FOD defects were simulated on railway axle steel specimen surfaces. Secondly, the fatiuge S-N curves of smooth and FOD specimens were obtained from rotating bending fatigue tests. Furthermore, the stress concentration factor was evaluated for different types of defects by elastic finite element method (FEM). The fatigue limit and fatigue notch coefficient (FNC) of FOD specimens were calculated based on Peterson formula. The results show that the fatigue performance of FOD specimens is considerably lower than that of smoothed ones, the higher the impact velocity, the lower the fatigue performance. The FNC of edge defect specimens is the largest (about 1.52) while the smallest (about 1.14) for plane defect specimens, thus leading to a larger dispersion in lifetime. Compared with the experiments, theoretical evaluation and FEM method can obtain relatively conservative results in fatigue strength.-
Key words:
- foreign object damage /
- railway axles /
- fatigue limit /
- Peterson formula /
- fatigue crack initiation
-
表 1 外物GCr15钢的力学性能
Table 1. Mechanical properties of GCr15 steel
材质 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 密度/(kg•m−3) 硬度 /HRC GCr15 219 0.3 7 830 61~65 表 2 冲击缺陷的辨识与表征
Table 2. Identification and characterization of impact defects
类型 v /(m•s−1) d /mm A /mm2 r /mm 角缺陷 138 0.46 0.23 0.06 100 0.44 0.21 边缺陷 138 0.30 0.31 0.03 100 0.23 0.21 面缺陷 138 0.18 0.12 0.05 100 0.17 0.11 表 3 缺陷处的Kt、q和Kf
Table 3. Kt、q、Kf of defect
类型 Kt q Kf 角缺陷 2.91 0.24 1.45 边缺陷 4.61 0.14 1.52 面缺陷 1.65 0.22 1.14 表 4 冲击速度138 m/s下疲劳极限估计值
Table 4. Estimated fatigue limit at 138 m/s
MPa 缺陷类型 估算值 试验值 角缺陷 254 296 边缺陷 243 257 面缺陷 322 338 -
许祥胜,赵振华,陈伟. 外物损伤对TC4钛合金的高周疲劳强度的影响[J]. 航空发动机,2017,43(3): 88-92.XU Xiangsheng, ZHAO Zhenhua, CHEN Wei. The influences of foreign object damage on the high cycle fatigue behavior of titanium alloy TC4[J]. Aeroengine, 2017, 43(3): 88-92. PETERS J O, RITCHIE R O. Foreign-object damage and high-cycle fatigue:role of microstructure in Ti-6Al-4V[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2001, 23(1): 413-421. NOWELL D, DUO P, STEWART I F. Prediction of fatigue performance in gas turbine blades after foreign object damage[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2003, 25(9/10/11): 963-969. 罗荣梅. 叶片外物冲击损伤及其对疲劳寿命的影响[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2006. 包珍强,胡绪腾,宋迎东. 不同冲击角度外物损伤对TC4钛合金高循环疲劳强度的影响[J]. 航空动力学报,2015,30(9): 2226-2233.BAO Zhenqiang, HU Xuteng, SONG Yingdong. Effect of foreign object damage at different impact angles on high cycle fatigue strength of TC4 titanium alloys[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2015, 30(9): 2226-2233. 李东霖,何卫锋,游熙,等. 激光冲击强化提高外物打伤TC4钛合金疲劳强度的试验研究[J]. 中国激光,2016,43(7): 116-124.LI Donglin, HE Weifeng, YOU Xi, et al. Experimental research on improving fatigue strength of wounded TC4 titanium alloy by laser shock peening[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2016, 43(7): 116-124. ZERBST U, BERETTA S, KOHLER G, et al. Safe life and damage tolerance aspects of railway axles-a review[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2013, 98(1): 214-271. WU S C, LIU Y X, LI C H, et al. On the fatigue performance and residual life of intercity railway axles with inside axle boxes[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2018, 197: 176-191. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.04.046 WANG Yanling, WANG Xishu, WU Shengchuan, et al. High-cycle microscopic severe corrosion fatigue behavior and life prediction of 25CrMo steel used in railway axles[J]. Metals, 2017, 7(4): 134-136. doi: 10.3390/met7040134 MURAKAMI Y. Metal fatigue: effects of small defects and nonmetallic inclusions[M]. Tokyo: Elsevier, 2002: 5-8. PETERSON R E, PLUNKETT R. Stress concentration factor[J]. Naval Engineers Journal, 2010, 67(3): 697-708. PETERS J O, BOYCE B L, Chen X. On the appli-cation of the Kitagawa-Takahashi diagram to foreign-object damage and high-cycle fatigue[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2002, 69(13): 1425-1446. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7944(01)00152-7 -




 下载:
下载: